Fugacium Spliced Leader Genes Identified from Stranded RNA-Seq Datasets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genomic and Transcriptomic Data
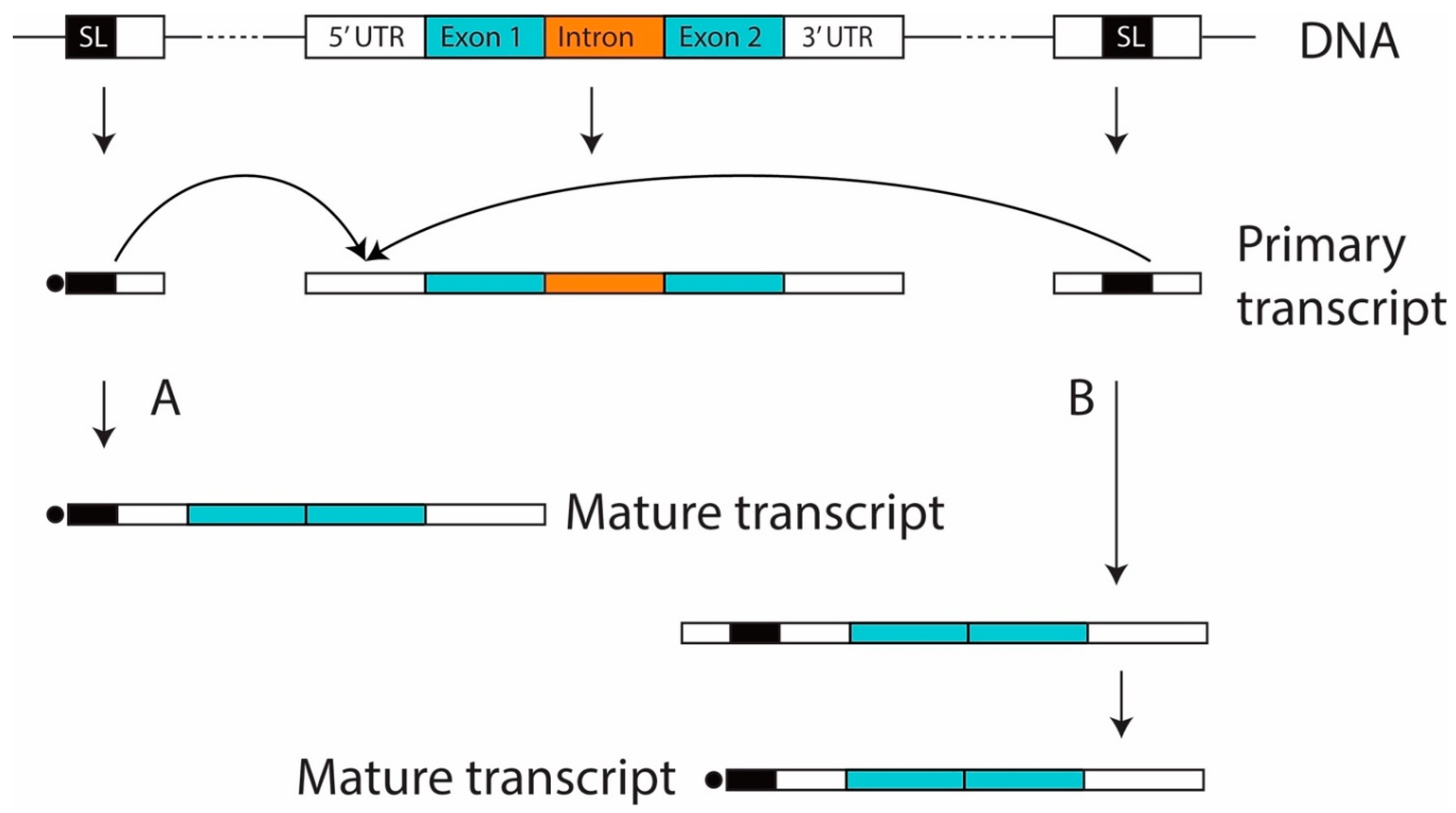
2.2. Clustering and Assembly of SL-Containing Reads
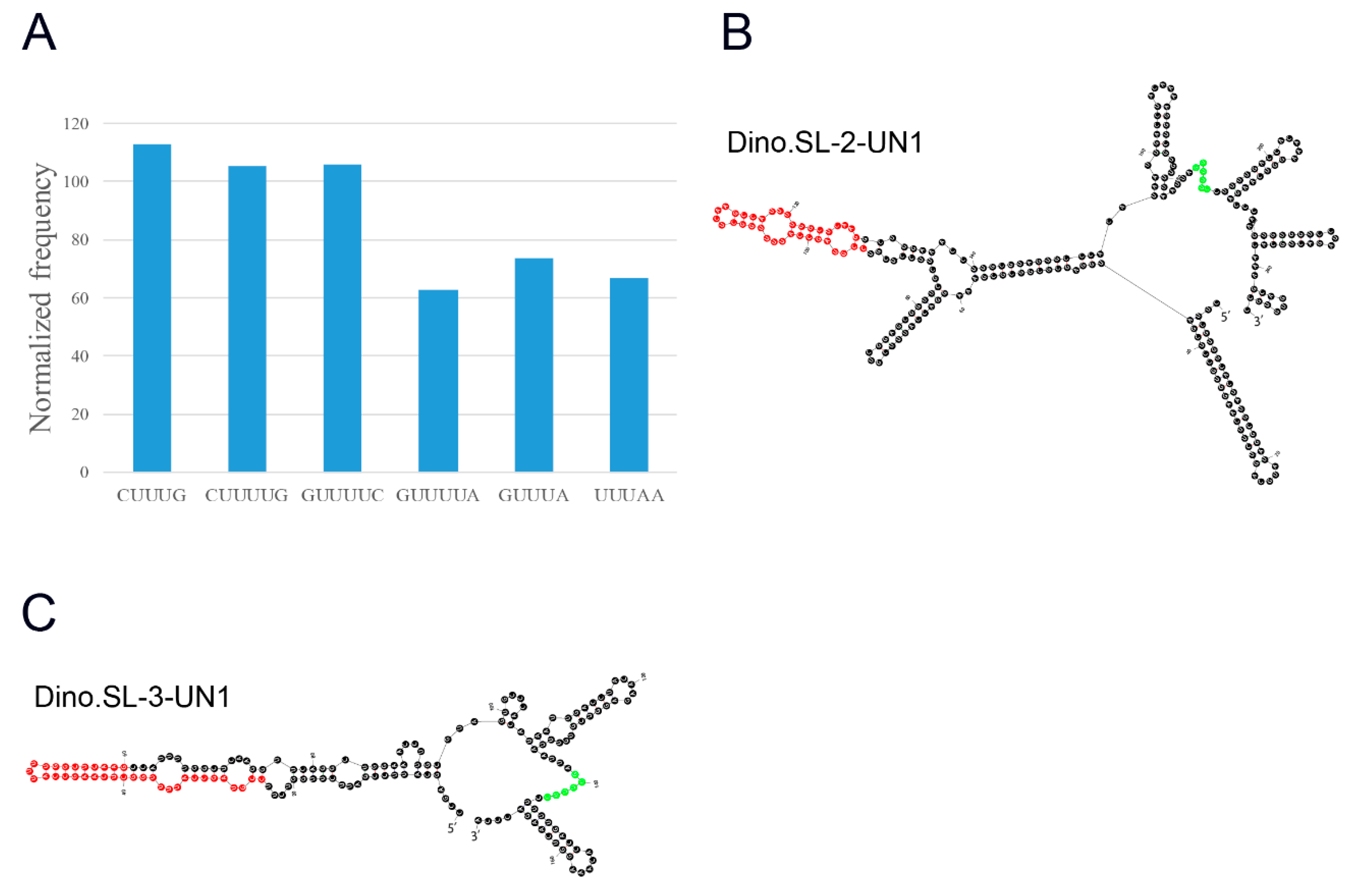
2.3. Identification of Sm-Protein Binding Sites and Structural Analysis of SL Genes
3. Results
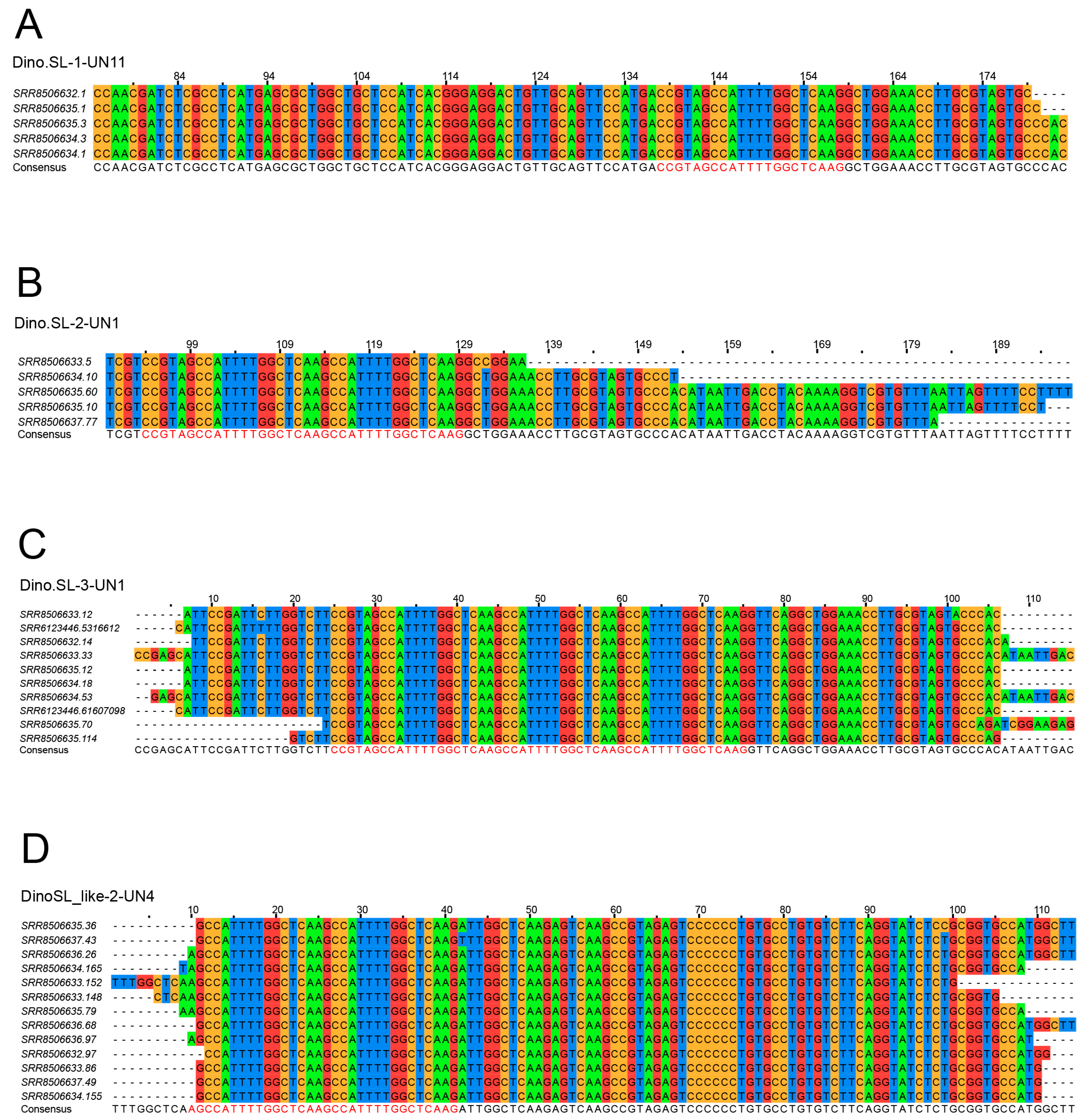
3.1. Searches for SL-Containing Reads
3.2. Tandem-SL Genes
3.3. Introns in SL Genes
3.4. SL-like Genes
4. Discussion
4.1. The Lengths of SL Genes in F. kawagutii Are Longer
4.2. The Fate of the Upstream Sequences
4.3. Novel Sm-Protein Binding Sites
4.4. SL-like Genes in F. kawagutii
4.5. Tandem-SL Genes in F. kawagutii
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, S. Genomic understanding of dinoflagellates. Res. Microbiol. 2011, 162, 551–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Hou, Y.; Miranda, L.; Campbell, D.A.; Sturm, N.R.; Gaasterland, T.; Lin, S. Spliced leader RNA trans-splicing in dinoflagellates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4618–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastings, K.E. SL trans-splicing: Easy come or easy go? Trends Genet. 2005, 21, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, J.; Dewar, K.; Wasserscheid, J.; Wiley, G.B.; Macmil, S.L.; Roe, B.A.; Zeller, R.W.; Satou, Y.; Hastings, K.E. High-throughput sequence analysis of Ciona intestinalis SL trans-spliced mRNAs: Alternative expression modes and gene function correlates. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, D.; Gunasekera, K.; Mani, J.; Osteras, M.; Farinelli, L.; Baerlocher, L.; Roditi, I.; Ochsenreiter, T. Spliced leader trapping reveals widespread alternative splicing patterns in the highly dynamic transcriptome of Trypanosoma brucei. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitar, M.; Boroni, M.; Macedo, A.M.; Machado, C.R.; Franco, G.R. The spliced leader trans-splicing mechanism in different organisms: Molecular details and possible biological roles. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Campbell, D.A.; Sturm, N.R.; Lin, S. Dinoflagellate spliced leader RNA genes display a variety of sequences and genomic arrangements. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1757–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Gill, J.; Lin, S. Proof that dinoflagellate spliced leader (DinoSL) is a useful hook for fishing dinoflagellate transcripts from mixed microbial samples: Symbiodinium kawagutii as a case study. Protist 2013, 164, 510–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slamovits, C.H.; Keeling, P.J. Widespread recycling of processed cDNAs in dinoflagellates. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, R550–R552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeckisch, N.; Yang, I.; Wohlrab, S.; Glöckner, G.; Kroymann, J.; Vogel, H.; Cembella, A.; John, U. Comparative genomic and transcriptomic characterization of the toxigenic marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.; Lai, H.; Malik, S.B.; Saldarriaga, J.F.; Keeling, P.J.; Slamovits, C.H. Analysis of EST data of the marine protist Oxyrrhis marina, an emerging model for alveolate biology and evolution. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.; Morse, D.; Song, Y.; Fu, Y.; Lin, X.; Wang, W.; Cheng, S.; Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Lin, S. Comparative genomics reveals two major bouts of gene retroposition coinciding with crucial periods of Symbiodinium evolution. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 2037–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoguchi, E.; Shinzato, C.; Kawashima, T.; Gyoja, F.; Mungpakdee, S.; Koyanagi, R.; Takeuchi, T.; Hisata, K.; Tanaka, M.; Fujiwara, M. Draft assembly of the Symbiodinium minutum nuclear genome reveals dinoflagellate gene structure. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Cheng, S.; Song, B.; Zhong, X.; Lin, X.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ji, Z. The Symbiodinium kawagutii genome illuminates dinoflagellate gene expression and coral symbiosis. Science 2015, 350, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranda, M.; Li, Y.; Liew, Y.J.; Baumgarten, S.; Simakov, O.; Wilson, M.C.; Piel, J.; Ashoor, H.; Bougouffa, S.; Bajic, V.B. Genomes of coral dinoflagellate symbionts highlight evolutionary adaptations conducive to a symbiotic lifestyle. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Stephens, T.G.; González-Pech, R.A.; Beltran, V.H.; Lapeyre, B.; Bongaerts, P.; Cooke, I.; Aranda, M.; Bourne, D.G.; Forêt, S. Symbiodinium genomes reveal adaptive evolution of functions related to coral-dinoflagellate symbiosis. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, J.Z.; Yassour, M.; Adiconis, X.; Nusbaum, C.; Thompson, D.A.; Friedman, N.; Gnirke, A.; Regev, A. Comprehensive comparative analysis of strand-specific RNA sequencing methods. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaJeunesse, T.C.; Parkinson, J.E.; Gabrielson, P.W.; Jeong, H.J.; Reimer, J.D.; Voolstra, C.R.; Santos, S.R. Systematic Revision of Symbiodiniaceae Highlights the Antiquity and Diversity of Coral Endosymbionts. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 2570–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mendoza, A.; Bonnet, A.; Vargas-Landin, D.B.; Ji, N.; Hong, F.; Yang, F.; Li, L.; Hori, K.; Pflueger, J.; Buckberry, S. Recurrent acquisition of cytosine methyltransferases into eukaryotic retrotransposons. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhao, L.; Gao, J.; Fei, Z. iAssembler: A package for de novo assembly of Roche-454/Sanger transcriptome sequences. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Chen, S.; Chen, W. Dinoflagellates, a unique lineage for retrogene research. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouchkina-Stantcheva, N.N.; Tunnacliffe, A. Spliced leader RNA–mediated trans-splicing in PHYLUM ROTIFERA. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1482–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stover, N.A.; Steele, R.E. Trans-spliced leader addition to mRNAs in a cnidarian. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5693–5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberghe, A.E.; Meedel, T.H.; Hastings, K.E. mRNA 5′-leader trans-splicing in the chordates. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Zaheri, B.; Liu, M.; Sahu, S.K.; Liu, H.; Chen, W.; Song, B.; Morse, D. Fugacium Spliced Leader Genes Identified from Stranded RNA-Seq Datasets. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7060171
Song Y, Zaheri B, Liu M, Sahu SK, Liu H, Chen W, Song B, Morse D. Fugacium Spliced Leader Genes Identified from Stranded RNA-Seq Datasets. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(6):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7060171
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yue, Bahareh Zaheri, Min Liu, Sunil Kumar Sahu, Huan Liu, Wenbin Chen, Bo Song, and David Morse. 2019. "Fugacium Spliced Leader Genes Identified from Stranded RNA-Seq Datasets" Microorganisms 7, no. 6: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7060171
APA StyleSong, Y., Zaheri, B., Liu, M., Sahu, S. K., Liu, H., Chen, W., Song, B., & Morse, D. (2019). Fugacium Spliced Leader Genes Identified from Stranded RNA-Seq Datasets. Microorganisms, 7(6), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7060171





