Investigation on Antibiotic-Resistance, Biofilm Formation and Virulence Factors in Multi Drug Resistant and Non Multi Drug Resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Molecular Typing
2.4. Determination of Antibiotic-Resistance Profile
2.4.1. Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion Method
2.4.2. Amplification of Antibiotic-Resistance Genes (ARg)
2.5. Biofilm Analysis
2.5.1. Identification of Biofilm-Forming Strains
2.5.2. Amplification of Biofilm-Associated Genes and Agr-Typing
2.6. Virulence Factors Carriage
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Identification of S. pseudintermedius, MLST, and SCCmec Typing
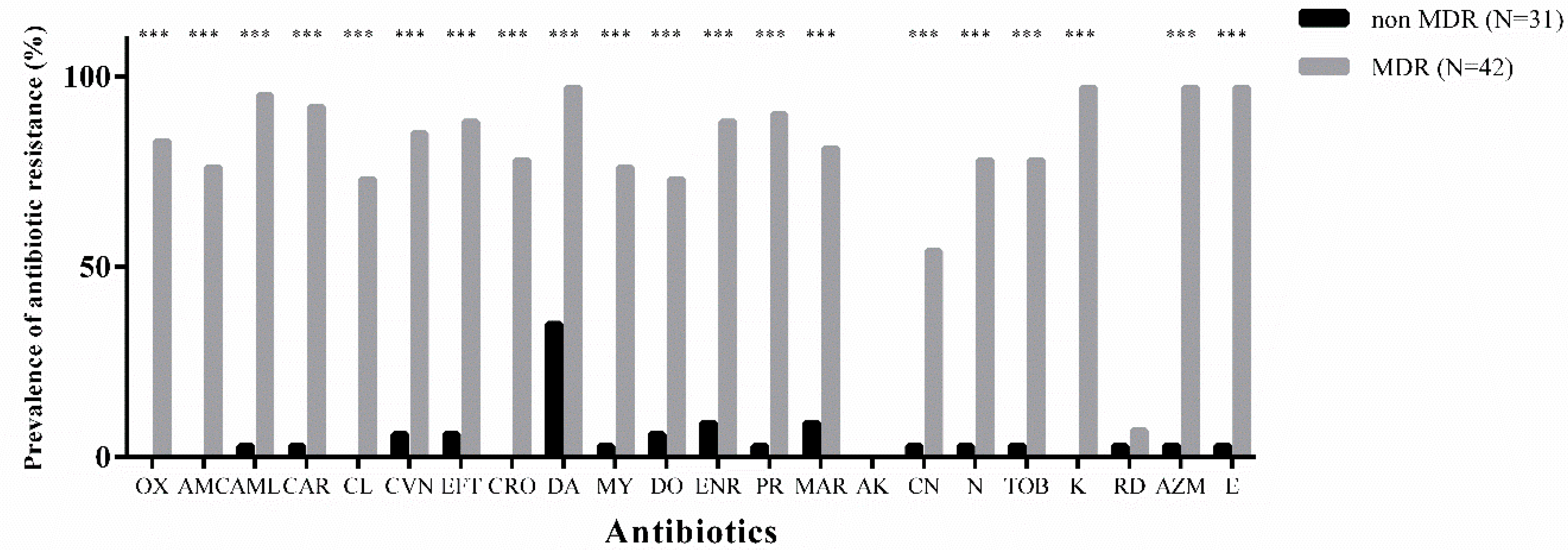
3.2. Overall Antibiotic-Resistance
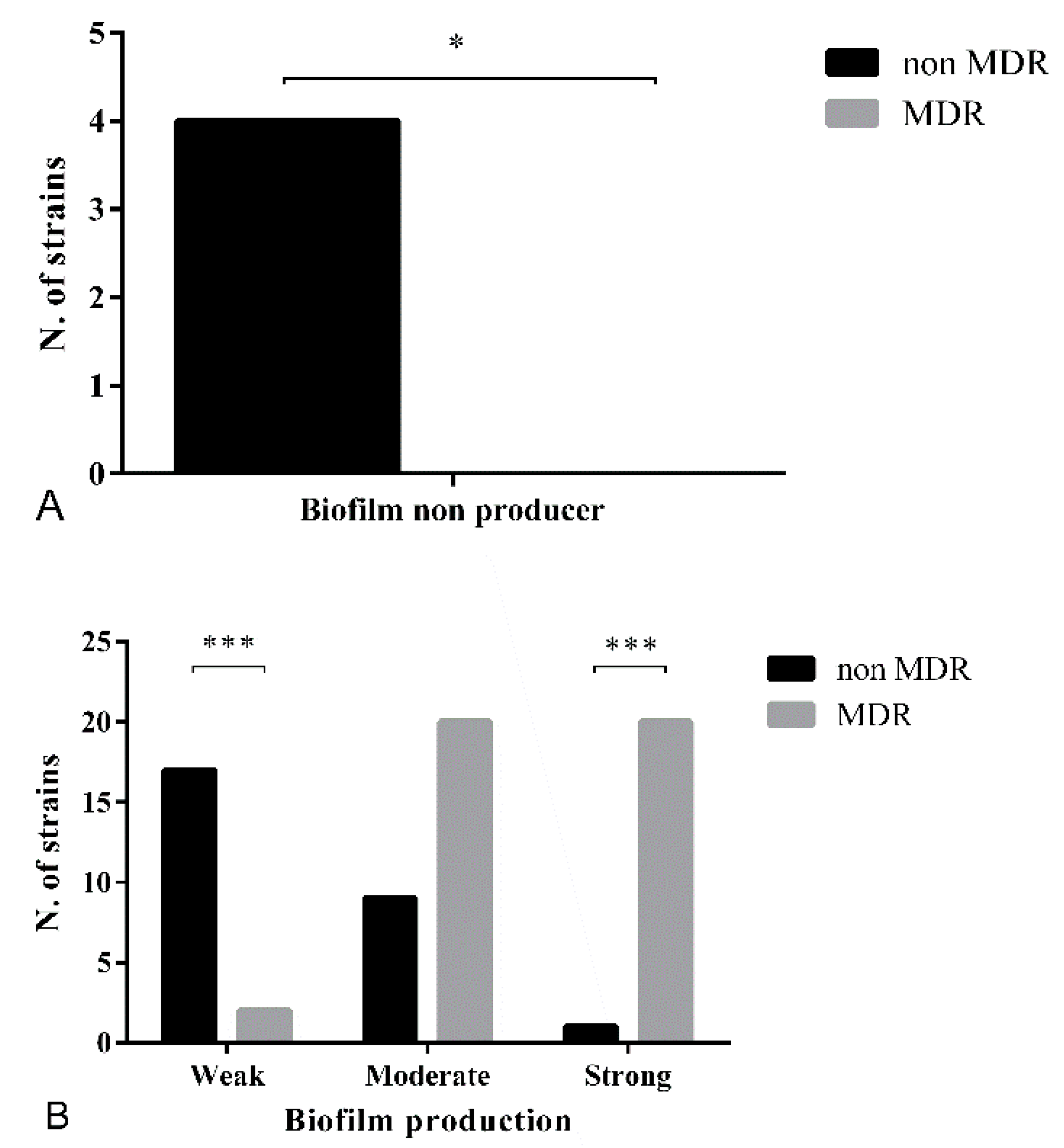
3.3. Biofilm Formation Assay
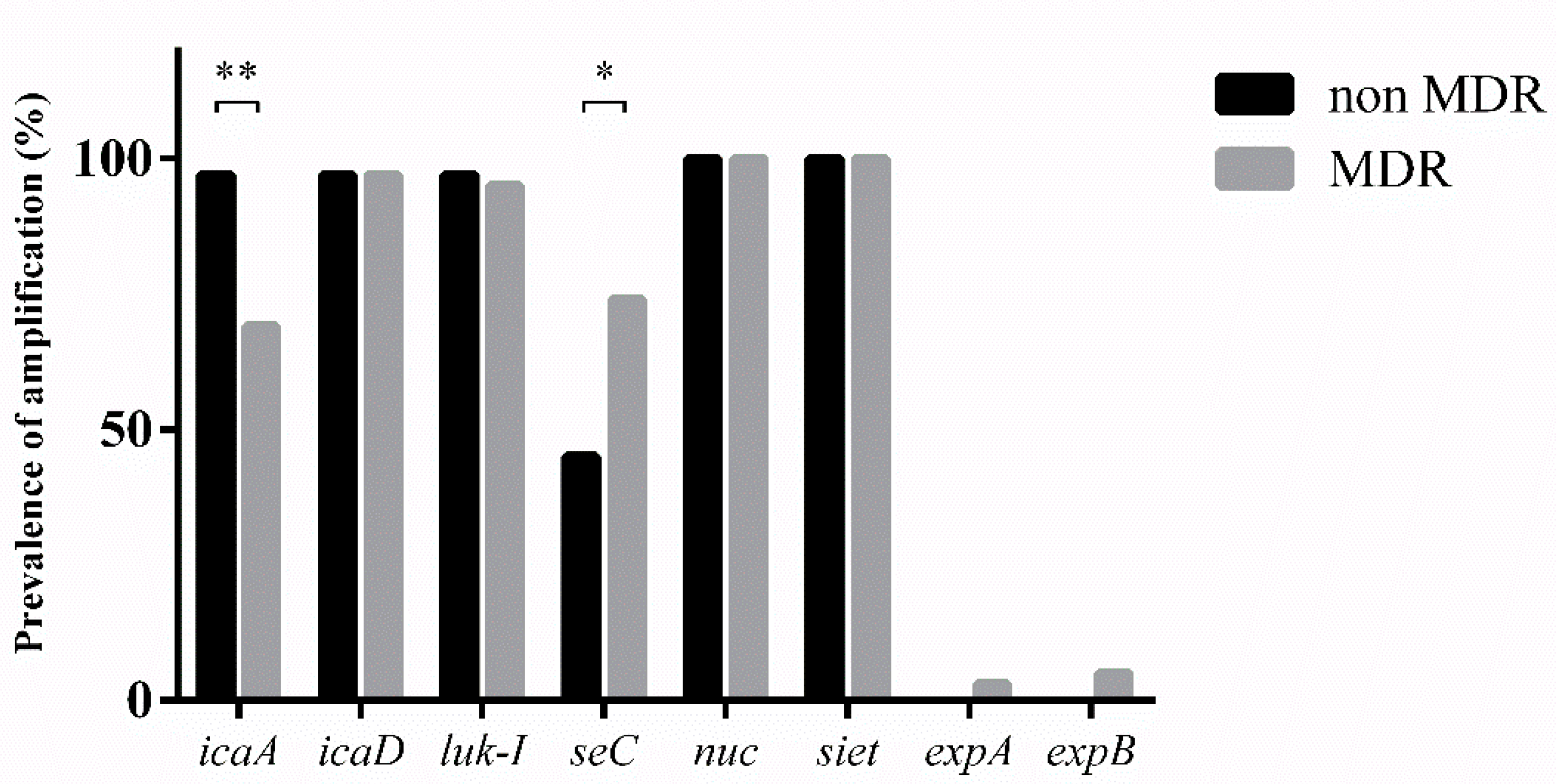
3.4. Virulence Factors
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Devriese, L.A.; Vancanneyt, M.; Baele, M.; Vaneechoutte, M.; De Graef, E.; Snauwaert, C.; Haesebrouck, F. Staphylococcus pseudintermedius sp. nov., a coagulase-positive species from animals. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1569–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoovels, L.; Vankeerberghen, A.; Boel, A.; Van Vaerenbergh, K.; De Beenhouwer, H. First case of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius infection in a human. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 4609–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannoehr, J.; Franco, A.; Iurescia, M.; Battisti, A.; Fitzgerald, J.R. Molecular diagnostic identification of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardabassi, L.; Loeber, M.E.; Jacobson, A. Transmission of multiple antimicrobial-resistant Staphylococcus intermedius between dogs affected by deep pyoderma and their owners. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 98, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannoehr, J.; Guardabassi, L. Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in the dog: Taxonomy, diagnostics, ecology, epidemiology and pathogenicity. Vet. Dermatol. 2012, 23, 253-e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, S.J.; Rosenkrantz, W.S.; Sanchez, S. Bacterial contamination of commercial ear cleaners following routine home use. Vet. Dermatol. 2011, 22, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, S.V.; Bryan, L.K.; Hillhouse, A.E.; Cohen, N.D.; Lawhon, S.D. Characterization of agr Groups of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius Isolates from Dogs in Texas. mSphere 2019, 4, e00033-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starlander, G.; Börjesson, S.; Grönlund-Andersson, U.; Tellgren-Roth, C.; Melhus, Å. Cluster of Infections Caused by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in Humans in a Tertiary Hospital. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 3118–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somayaji, R.; Priyantha, M.A.R.; Rubin, J.E.; Church, D. Human infections due to Staphylococcus pseudintermedius, an emerging zoonosis of canine origin: Report of 24 cases. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 85, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börjesson, S.; Gómez-Sanz, E.; Ekström, K.; Torres, C.; Grönlund, U. Staphylococcus pseudintermedius can be misdiagnosed as Staphylococcus aureus in humans with dog bite wounds. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanetti, V.; Bietta, A.; Pascucci, L.; Marenzoni, M.L.; Coletti, M.; Franciosini, M.P.; Passmonti, F.; Casagrandde, P.P. Investigation of the antibiotic resistance and biofilm formation of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius strains isolated from canine pyoderma. Vet. Ital. 2017, 53, 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Arciola, C.R.; Campoccia, D.; Gamberini, S.; Donati, M.E.; Pirini, V.; Visai, L.; Speziale, P.; Montanaro, L. Antibiotic resistance in exopolysaccharide-forming Staphylococcus epidermidis clinical isolates from orthopaedic implant infections. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6530–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, A.; Rosenstein, R.; Nerz, C.; Götz, F. Differential gene expression profiling of Staphylococcus aureus cultivated under biofilm and planktonic conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2663–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proietti, P.C.; Stefanetti, V.; Hyatt, D.R.; Marenzoni, M.L.; Capomaccio, S.; Coletti, M.; Bietta, A.; Franciosini, M.P.; Passmonti, F. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of canine pyoderma isolates of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius for biofilm formation. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 945–951. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Walker, M.; Rousseau, J.; Weese, J.S. Characterization of the biofilm forming ability of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius from dogs. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gara, J.P. Ica and beyond: Biofilm mechanisms and regulation in Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 270, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Singh, D.V. Biofilm formation by ica-negative ocular isolates of staphylococcus haemolyticus. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, S.; Wai, S.N.; Ziebuhr, W. Spontaneous switch to PIA-independent biofilm formation in an ica-positive Staphylococcus epidermidis isolate. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 297, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Tsubakishita, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Sakusabe, A.; Ohtsuka, M.; Hirotaki, S.; Kawakami, T.; Fukata, T.; Hiramatsu, K. Multiplex-PCR method for species identification of coagulase-positive staphylococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adwan, K. Fast DNA isolation and PCR protocols for detection of methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Folia Microbiol. 2014, 59, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solyman, S.M.; Black, C.C.; Duim, B.; Perreten, V.; Duijkeren, E.V.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Eberlein, L.C.; Sadeghi, L.N.; Videla, R. Multilocus Sequence Typing for Characterization of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannoehr, J.; Zakour, N.L.B.; Waller, A.S.; Guardabassi, L.; Thoday, K.L.; Van Den Broek, A.H.; Fitzgerald, J.R. Population genetic structure of the Staphylococcus intermedius group: Insights into agr diversification and the emergence of methicillin-resistant strains. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 8685–8692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlec, K.; Schwarz, S.; Perreten, V.; Grönlund Andersson, U.; Finn, M.; Greko, C.; Moodley, A.; Kania, S.A.; Frank, L.A.; Bemis, D.A. Molecular analysis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius of feline origin from different European countries and North America. J. Antimicrob Chemother. 2010, 65, 1826–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreten, V.; Kadlec, K.; Schwarz, S.; Andersson, U.G.; Finn, M.; Greko, C.; Moodley, A.; Kania, S.A.; Frank, L.A.; Bemis, D.A. Clonal spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in Europe and North America: An international multicentre study. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.H.; Chae, M.J.; Yoon, J.W.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, S.Y.; Yoo, J.H.; Park, H.M. Antibiotic resistance and molecular characterization of ophthalmic Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolates from dogs. J. Vet. Sci. 2014, 15, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strommenger, B.; Kettlitz, C.; Werner, G. Multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of nine clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4089–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shopsin, B.; Mathema, B.; Alcabes, P.; Said-Salim, B.; Lina, G.; Matsuka, A. Prevalence of agr specificity groups among Staphylococcus aureus strains colonizing children and their guardians. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futagawa-Saito, K.; Sugiyama, T.; Karube, S.; Sakurai, N.; Ba-Thein, W.; Fukuyasu, T. Prevalence and characterization of leukotoxin-producing Staphylococcus intermedius in isolates from dogs and pigeons. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 5324–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.W.; Lee, G.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, C.; Yoo, J.H.; Park, H.M. Prevalence of genes for enterotoxins, toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 and exfoliative toxin among clinical isolates of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius from canine origin. Vet. Dermatol. 2010, 21, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautz, S.; Kanbar, T.; Alber, J.; Lämmler, C.; Weiss, R.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; Zschock, M. Dissemination of the gene encoding exfoliative toxin of Staphylococcus intermedius among strains isolated from dogs during routine microbiological diagnostics. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2006, 53, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futagawa-Saito, K.; Makino, S.; Sunaga, F.; Kato, Y.; Sakurai-Komada, N.; Ba-Thein, W.; Fukuyasu, T. Identification of first exfoliative toxin in Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 301, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyori, K.; Hisatsune, J.; Kawakami, T.; Shibata, S.; Murayama, N.; Ide, K.; Nagata, M.; Fukata, T.; Iwasaki, T.; Oshima, K. Identification of a novel Staphylococcus pseudintermedius exfoliative toxin gene and its prevalence in isolates from canines with pyoderma and healthy dogs. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 312, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Zubeir, I.E.M.; Kanbar, T.; Alber, J.; Lämmler, C.; Akineden, Ö.; Weiss, R.; Zschock, M. Phenotypic and genotypic characteristics of methicillin/oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus intermedius isolated from clinical specimens during routine veterinary microbiological examinations. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 121, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanovic, S.; Vukovic, D.; Dakic, I.; Savic, B.; Svabic-Vlahovic, M. A modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 40, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanović, S.; Vuković, D.; Hola, V.; Di Bonaventura, G.; Djukić, S.; Cirković, I.; Ruzicka, F. Quantification of biofilm in microtiter plates: Overview of testing conditions and practical recommendations for assessment of biofilm production by staphylococci. Apmis 2007, 115, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchior, M.B.; Van Osch, M.H.J.; Graat, R.M.; Van Duijkeren, E.; Mevius, D.J.; Nielen, M.; Gaastra, W.; Fink-Gremme, J. Biofilm formation and genotyping of Staphylococcus aureus bovine mastitis isolates: Evidence for lack of penicillin-resistance in Agr-type II strains. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 137, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmieciak, W.; Szewczyk, E.M. Are zoonotic Staphylococcus pseudintermedius strains a growing threat for humans? Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 2018, 63, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somayaji, R.; Rubin, J.E.; Priyantha, M.A.; Church, D. Exploring Staphylococcus pseudintermedius: An emerging zoonotic pathogen? Future Microbiol. 2016, 11, 1371–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyaert, H.; de Jong, A.; Simjee, S.; Rose, M.; Youala, M.; Garch, F.E.; Vila, T.; Klein, U.; Rzewuska, M.; Morrissey, I. Survey of antimicrobial susceptibility of bacterial pathogens isolated from dogs and cats with respiratory tract infections in Europe: ComPath results. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damborg, P.; Moodley, A.; Aalbæk, B.; Ventrella, G.; dos Santos, T.P.; Guardabassi, L. High genotypic diversity among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolated from canine infections in Denmark. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bergot, M.; Martins-Simoes, P.; Kilian, H.; Châtre, P.; Worthing, K.A.; Norris, J.M.; Madec, J.-Y.; Laurent, F.; Haenni, M. Evolution of the Population Structure of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in France. Front. Microbil. 2018, 9, 3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, T.P.; Damborg, P.; Moodley, A.; Guardabassi, L. Systematic review on global epidemiology of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus pseudintermedius: Inference of population structure from multilocus sequence typing data. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinsky, J.L.; Nadimpalli, M.; Wing, S.; Hall, D.; Baron, D.; Price, L.B.; Larsen, J.; Stegger, M.; Stewart, J.; Heaney, C.D. Livestock-Associated Methicillin and Multidrug Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Is Present among Industrial, Not Antibiotic-Free Livestock Operation Workers in North Carolina. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Genes | Sequence (5’-3’) | Amplicon Size (bp) | PCR Conditions | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic-resistance genes | mecA | F | AAAATCGATGGTAAAGGTTGGC | 532 | 95 °C × 4 min, 30 × (95 °C × 1 min, 58 °C × 1 min, 72 °C × 1 min) 72 °C × 7 min, 4 °C | [25] |
| R | AGTTCTGCAGTACCGGATTTGC | |||||
| blaZ | F | TGACCACTTTTATCAGCAACC | 750 | |||
| R | GCCATTTCAACACCTTCTTTC | |||||
| tetK | F | GTAGCGACAATAGGTAATAGT | 360 | 94 °C × 3 min, 30 × (94 °C × 30 s, 55 °C × 30 s, 72 °C × 30 s) 72 °C × 7 min, 4 °C | [26] | |
| R | GTAGTGACAATAAACCTCCTA | |||||
| tetM | F | AGTGGAGCGATTACAGAA | 158 | |||
| R | CATATGTCCTGGCGTGTCTA | |||||
| aacA-aphD | F | TAATCCAAGAGCAATAAGGGC | 227 | |||
| R | GCCACACTATCATAACCACTA | |||||
| Biofilm genes | icaA | F | ACTGTTTCGGGGACAAGCAT | 134 | 94 °C × 3 min, 35 × (94 °C × 15 s, 60 °C × 20 s, 72 °C × 20 s) 72 °C × 7 min, 4 °C | [14] |
| R | ATTGAGGCTGTAGGGCGTTG | |||||
| icaD | F | CGTTAATGCCTTCTTTCTTATTGCG | 166 | 94 °C × 3 min, 35 × (94 °C × 15 s, 56 °C × 20 s, 72 °C × 20 s) 72 °C × 7 min, 4 °C | ||
| R | ATTAGCGCACATTCGGTGTT | |||||
| Quorum-sensing genes | pan-agr | F | ATGCACATGGTGCACATGC | 94 °C × 3 min, 35 × (94 °C × 15 s, 56 °C × 20 s, 72 °C × 20 s) 72 °C × 7 min, 4 °C | [27] | |
| agrI | R | GTCACAAGTACTATAAGCTGCGAT | ||||
| agrII | R | GTATTACTAATTGAAAAGTGCCATAGC | ||||
| agrIII | R | CTGTTGAAAAAGTCAACTAAAAGCTC | ||||
| agrIV | R | CGATAATGCCGTAATACCCG | ||||
| Virulence factors | luk-F | F | CCTGTCTATGCCGCTAATCCA | 572 | 94 °C × 3 min, 35 × (94 °C × 1 min, 57 °C × 1 min, 72 °C × 1 min) 72 °C × 7 min, 4 °C | [28] |
| R | AGGTCATGGAAGCTATCTCGA | |||||
| luk-S | F | TGTAAGCAGCAGAAAATGGGG | 503 | |||
| R | GCCCGATAGGACTTCTTACAA | |||||
| seC | F | GGCGGCAATATTGGCGCTCG | 271 | 95 °C × 2 min, 30 × (95 °C × 1 min, 55 °C × 1 min, 72 °C × 2 min) 72 °C × 5 min, 4 °C | [29] | |
| R | TTACTGTCAATGCTCTGACC | |||||
| nuc | F | TRGGCAGTAGGATTCGTTAA | 926 | 95 °C × 2 min, 30 × (95 °C × 30 s, 52 °C × 30 s, 72 °C × 30 s) 72 °C × 2 min, 4 °C | [19] | |
| R | CTTTTGTGCTYCMTTTTGG | |||||
| siet | F | ATGGAAAATTTAGCGGCATCTGG | 359 | 94 °C × 3 min, 30 × (94 °C × 30 s, 56 °C × 30 s, 72 °C × 1 min) 72 °C × 5 min, 4 °C | [30] | |
| R | CCATTACTTTTCGCTTGTTGTGC | |||||
| expA | F | GTKTTAATTGGWAAAAATACA | 413 | 94 °C × 3 min, 30 × (94 °C × 1 min, 42 °C × 1 min, 72 °C × 1 min) 72 °C × 4 min, 4°C | [31] | |
| R | ATNCCWGAKCCTGAATTWCC | |||||
| expB | F | GGGCATGCACATATGATGAAGCC | 820 | 95 °C × 3 min, 30 × (95 °C × 1 min, 53 °C × 1 min, 72 °C × 1 min) 72 °C × 4 min, 4 °C | [32] | |
| R | CCAGATCTATCTTCTGATTCAGC |
| MLST | SCCmec Types | No. of Isolates (%) |
|---|---|---|
| ST 71 | II-III | 24 (68.5%) |
| ST 258 | IV | 9 (25.7%) |
| ST 106 | IV | 2 (5.7%) |
| Genes | not MDR Strains | MDR Strains | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic-resistance genes | mecA | 0 | 35/42 (83%) | <0.0001 |
| blaZ | 7/31 (23%) | 42/42 (100%) | <0.0001 | |
| tetK | 2/31 (6.4%) | 13/42 (31%) | 0.0171 | |
| tetM | 0 | 22/42 (50%) | <0.0001 | |
| aacA-aphD | 5/31 (16.6%) | 32/42 (76%) | <0.0001 | |
| Biofilm genes | icaA | 30/31 (97%) | 29/42 (69%) | 0.0026 |
| icaD | 30/31 (97%) | 41/42 (97%) | >0.05 | |
| Virulence factors | luk-I | 30/31 (97%) | 40/42 (95%) | >0.05 |
| seC | 14/31 (45%) | 31/42 (74%) | 0.016 | |
| nuc | 31/31 (100%) | 42/42 (100%) | >0.05 | |
| siet | 31/31 (100%) | 42/42 (100%) | >0.05 | |
| expA | 0 | 3/42 (7%) | >0.05 | |
| expB | 0 | 5/42 (12%) | >0.05 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meroni, G.; Soares Filipe, J.F.; Drago, L.; Martino, P.A. Investigation on Antibiotic-Resistance, Biofilm Formation and Virulence Factors in Multi Drug Resistant and Non Multi Drug Resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120702
Meroni G, Soares Filipe JF, Drago L, Martino PA. Investigation on Antibiotic-Resistance, Biofilm Formation and Virulence Factors in Multi Drug Resistant and Non Multi Drug Resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(12):702. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120702
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeroni, Gabriele, Joel F. Soares Filipe, Lorenzo Drago, and Piera A. Martino. 2019. "Investigation on Antibiotic-Resistance, Biofilm Formation and Virulence Factors in Multi Drug Resistant and Non Multi Drug Resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius" Microorganisms 7, no. 12: 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120702
APA StyleMeroni, G., Soares Filipe, J. F., Drago, L., & Martino, P. A. (2019). Investigation on Antibiotic-Resistance, Biofilm Formation and Virulence Factors in Multi Drug Resistant and Non Multi Drug Resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. Microorganisms, 7(12), 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120702







