Microbiological Insights into the Stress-Alleviating Property of an Endophytic Bacillus altitudinis WR10 in Wheat under Low-Phosphorus and High-Salinity Stresses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents, Media, and Growth Conditions
2.2. Germination Test of Wheat Seeds under Salinity Stress
2.3. Growth Test of Wheat Seedlings Under Low-Phosphorus Stress
2.4. Growth Test of B. altitudinis WR10 under Different Conditions
2.5. Biochemical Analysis of B. altitudinis WR10
2.6. Enzymatic Analysis of B. altitudinis WR10 and Potential Genes
2.7. Morphological Analysis and Biofilm Formation of B. altitudinis WR10
2.8. Phytase Activity Assays under Different Levels Phosphorus
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. B. altitudinis WR10 Alleviates Abiotic Stresses under Either High Saline or Low Phosphorus
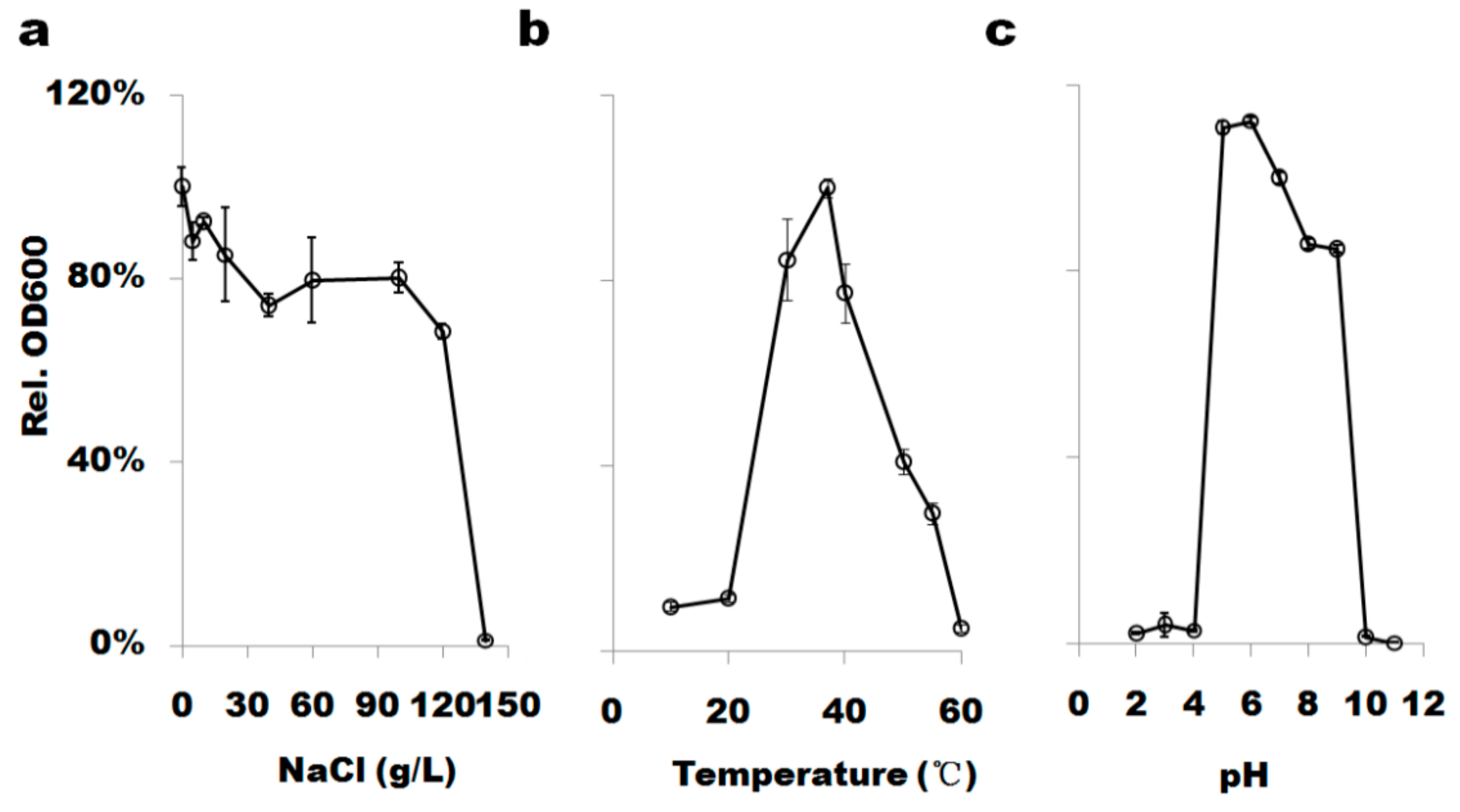
3.2. B. altitudinis WR10 Resists High Saline and Grows under Different Conditions
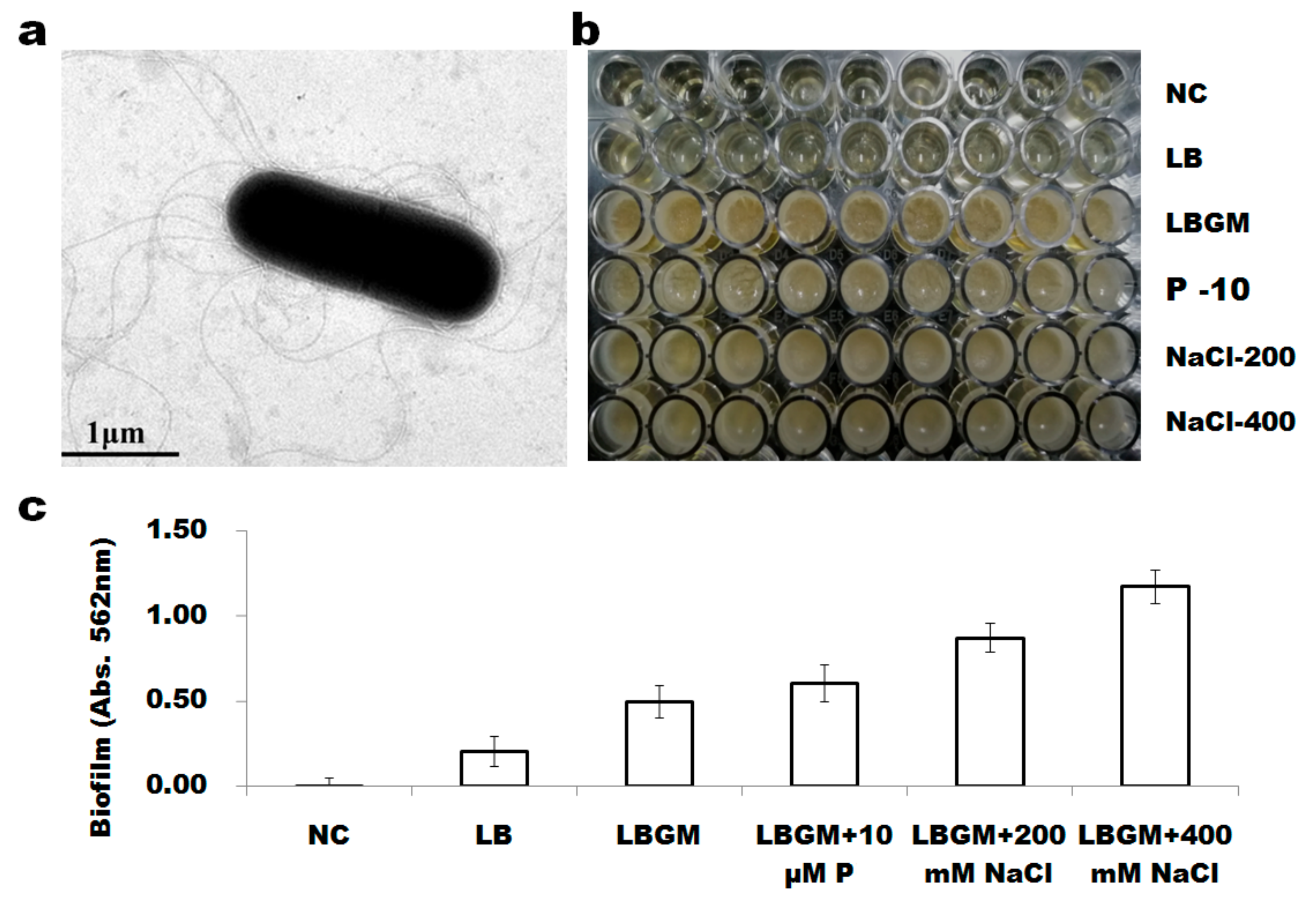
3.3. B. altitudinis WR10 Forms Flagella and Produces Biofilm
3.4. B. Altitudinis WR10 Ferments a Versatile of Plant-Derived Substrates
3.5. B. altitudinis WR10 Produces Many Stress-Alleviating Enzymes
3.6. B. altitudinis WR10 Degrades Insoluble Phosphate and Produces Phytases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robin, A.H.; Matthew, C.; Uddin, M.J.; Bayazid, K.N. Salinity-induced reduction in root surface area and changes in major root and shoot traits at the phytomer level in wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 3719–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irshad, U.; Yergeau, E. Bacterial subspecies variation and nematode grazing change P dynamics in the wheat rhizosphere. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, E.A. Seed priming to alleviate salinity stress in germinating seeds. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 192, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wen, S.; Zhang, C.; Rustgi, S.; von Wettstein, D.; Liu, B. Evolution of physiological responses to salt stress in hexaploid wheat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11882–11887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, M.N.; Mostofa, M.G.; Akter, M.M.; Srivastava, A.K.; Sayed, M.A.; Hasan, M.S.; Tran, L.P. Impact of salt-induced toxicity on growth and yield-potential of local wheat cultivars: Oxidative stress and ion toxicity are among the major determinants of salt-tolerant capacity. Chemosphere 2017, 187, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, V.V.; Kalagudi, G.M. Enhancing plant phosphorus use efficiency for sustainable cropping. Biotechnol. Adv. 2005, 23, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, W.; Deng, Y.; Chen, X.P.; Xu, X.F.; Chen, R.Y.; Lv, Y.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Zhao, X.; He, X.; Li, B.; et al. Characterization of root response to phosphorus supply from morphology to gene analysis in field-grown wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Teng, W.; Tong, Y.P.; Chen, X.P.; Zou, C.Q. Phosphorus efficiency mechanisms of two wheat cultivars as affected by a range of phosphorus levels in the field. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1614. [Google Scholar]
- Olanrewaju, O.S.; Glick, B.R.; Babalola, O.O. Mechanisms of action of plant growth promoting bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numan, M.; Bashir, S.; Khan, Y.; Mumtaz, R.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Khan, A.L.; Khan, A.; Al-Harrasi, A. Plant growth promoting bacteria as an alternative strategy for salt tolerance in plants: A review. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 209, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyota, K. Bacillus-related spore formers: Attractive agents for plant growth promotion. Microbes Environ. 2015, 30, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.; Prasad, V.; Chauhan, P.S.; Lata, C. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens confers tolerance to various abiotic stresses and modulates plant response to phytohormones through osmoprotection and gene expression regulation in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.J.; Yoo, S.J.; Hong, J.K.; Weon, H.Y.; Song, J.; Sang, M.K. Effect of Bacillus aryabhattai H26–2 and B. siamensis H30–3 on growth promotion and alleviation of heat and drought stresses in Chinese cabbage. Plant Pathol. J. 2019, 35, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.J.; Weon, H.Y.; Song, J.; Sang, M.K. Induced tolerance to salinity stress by halotolerant bacteria Bacillus aryabhattai H19–1 and B. mesonae H20–5 in tomato plants. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoyo, G.; Moreno-Hagelsieb, G.; Orozco-Mosqueda, M.C.; Glick, B.R. Plant growth-promoting bacterial endophytes. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 183, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Liu, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, K.D.; Yu, D.S.; Wang, J.; Hu, L.Z.; Chen, L.; Li, C.W. IAA producing Bacillus altitudinis alleviates iron stress in Triticum aestivum L. seedling by both bioleaching of iron and up-regulation of genes encoding ferritins. Plant Soil. 2017, 419, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaji, S.; Chaturvedi, P.; Suresh, K.; Reddy, G.S.; Dutt, C.B.; Wainwright, M.; Narlikar, J.V.; Bhargava, P.M. Bacillus aerius sp. nov., Bacillus aerophilus sp. nov., Bacillus stratosphericus sp. nov. and Bacillus altitudinis sp. nov., isolated from cryogenic tubes used for collecting air samples from high altitudes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Yadav, A.N.; Khannam, K.S.; Kumar, S.; Saxena, A.K.; Suman, A. Molecular diversity and multifarious plant growth promoting attributes of Bacilli associated with wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) rhizosphere from six diverse agro-ecological zones of India. J. Basic Microbiol. 2016, 56, 44–58. [Google Scholar]
- Orhan, F. Alleviation of salt stress by halotolerant and halophilic plant growth-promoting bacteria in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Ashraf, M. Growth stage-based modulation in physiological and biochemical attributes of two genetically diverse wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars grown in salinized hydroponic culture. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 6227–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, W. The photometric determination of phosphorus in fertilizers using the phosphovanado-molybdate complex. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2010, 1, 172–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, D.M.; Glick, B.R. Methods for isolating and characterizing acc deaminase-containing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Physiol. Plant 2003, 118, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; He, X.; Brancaccio, V.F.; Yuan, J.; Riedel, C.U. Bifidobacteria exhibit LuxS-dependent autoinducer 2 activity and biofilm formation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Yu, Y.; Gozzi, K.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.H.; Chai, Y. Genome-wide investigation of biofilm formation in Bacillus cereus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e00561-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Yue, Z.; Yang, X.; Hao, X.; Song, M.; Li, L.; Chen, C.; Chu, C.; Li, C. Efficient phytase secretion and phytate degradation by recombinant Bifidobacterium longum JCM 1217. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temel, A.; Gozukirmizi, N. Physiological and molecular changes in barley and wheat under salinity. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 2950–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, R.; Anwar, K.; Das, P.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Pareek, A. Overview of methods for assessing salinity and drought tolerance of transgenic wheat lines. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1679, 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Silini, A.; Silini-Cherif, H.; Ghoul, M. Effect of Azotobacter vinelandii and compatible solutes on germination wheat seeds and root concentrations of sodium and potassium under salt stress. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 15, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, T.; Mirzaeiheydari, M.; Maleki, A.; Bazgir, M. Effect of native growth promoting bacteria and commercial biofertilizers on growth and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and barley (Hordeum vulgare) under salinity stress conditions. Cell. Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand) 2019, 65, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorty, A.M.; Meena, K.K.; Choudhary, K.; Bitla, U.M.; Minhas, P.S.; Krishnani, K.K. Effect of plant growth promoting bacteria associated with halophytic weed (Psoralea corylifolia L) on germination and seedling growth of wheat under saline conditions. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 180, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaukat, K.; Affrasayab, S.; Hasnain, S. Growth responses of Triticum aestivum to plant growth promoting rhizobacteria used as a biofertilizer. Res. J. Microbiol. 2006, 1, 330–338. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, K.; Liu, X.D.; Xie, Q.; He, Z.H. Two faces of one seed: Hormonal regulation of dormancy and germination. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaih, S.; Guedira, M.; Paulsen, G.M. Relationship of indole acetic acid and tryptophan to dormancy and preharvest sprouting of wheat. Funct. Plant Biol. 2003, 30, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S.G.; Jung, J.H.; Woo, J.C.; Park, C.M. Integration of auxin and salt signals by the NAC transcription factor NTM2 during seed germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gan, Y.; Xu, B. Mechanisms of the IAA and ACC-deaminase producing strain of Trichoderma longibrachiatum T6 in enhancing wheat seedling tolerance to NaCl stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, P.; Inostroza, N.; Acuña, J.; Mora, M.M.; Crowley, D.E.; Jorquera, M.A. Formulation of bacterial consortia from avocado (Persea americana Mill.) and their effect on growth, biomass and superoxide dismutase activity of wheat seedlings under salt stress. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 102, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Jha, P.N. A halotolerant bacterium Bacillus licheniformis HSW-16 augments induced systemic tolerance to salt stress in wheat plant (Triticum aestivum). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1890. [Google Scholar]
- Viscardi, S.; Ventorino, V.; Duran, P.; Maggio, A. Assessment of plant growth promoting activities and abiotic stress tolerance of Azotobacter chroococcum strains for a potential use in sustainable agriculture. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2016, 16, 848–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Marschner, P.; Cao, W.; Zuo, C.Q.; Qin, W. Influence of salinity and water content on soil microorganisms. Int. Soil Water Cons. Res. 2015, 3, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qurashi, A.W.; Sabri, A.N. Bacterial exopolysaccharide and biofilm formation stimulate chickpea growth and soil aggregation under salt stress. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2012, 11, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasim, W.A.; Gaafar, R.M.; Abou-Ali, R.M.; Omar, M.N.; Hewait, H.M. Effect of biofilm forming plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on salinity tolerance in barley. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2016, 61, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, M.; Kaushik, A.; Rani, N.; Kaushik, C.P. Effect of cyanobacterial exopolysaccharides on salt stress alleviation and seed germination. J. Environ. Biol. 2010, 31, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, M.; Hasnain, S.; Berge, O.; Mahmood, T. Inoculating wheat seedlings with exopolysaccharide-producing bacteria restricts sodium uptake and stimulates plant growth under salt stress. Biol. Fertil. Soils. 2004, 40, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, I.C.; Pérez-Alfocea, F. Microbial amelioration of crop salinity stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 636, 3415–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, N.B.; Ghosh, A. Comprehensive analysis and transcript profiling of Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa catalase gene family suggests their specific roles in development and stress responses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 123, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, S.S.; Carciofi, M.; Martens, H.J.; Hebelstrup, K.H.; Blennow, A. Starch bioengineering affects cereal grain germination and seedling establishment. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2257–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afridi, M.S.; Mahmood, T.; Salam, A.; Mukhtar, T.; Mehmood, S.; Ali, J.; Khatoon, Z.; Bibi, M.; Javed, M.T.; Sultan, T.; et al. Induction of tolerance to salinity in wheat genotypes by plant growth promoting endophytes: Involvement of ACC deaminase and antioxidant enzymes. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 139, 569–577. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Pandey, S. ACC deaminase producing bacteria with multifarious plant growth promoting traits alleviates salinity stress in French bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) plants. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbi, Z.O.; Abdelly, C.; Debez, A. Interactive effects of salinity and phosphorus availability on growth, water relations, nutritional status and photosynthetic activity of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Biol. 2011, 13, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, Y.; Xu, G.; Tian, X.; Xie, H.; Yang, X.; Cao, C.; Chen, Y. Root colonization and growth promotion of soybean, wheat and Chinese cabbage by Bacillus cereus YL6. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200181. [Google Scholar]
- Suleman, M.; Yasmin, S.; Rasul, M.; Yahya, M.; Atta, B.M.; Mirza, M.S. Phosphate solubilizing bacteria with glucose dehydrogenase gene for phosphorus uptake and beneficial effects on wheat. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezakhani, L.; Motesharezadeh, B.; Tehrani, M.M.; Etesami, H.; Mirseyed, H.H. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and silicon synergistically augment phosphorus (P) uptake by wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) plant fertilized with soluble or insoluble P source. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 173, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Substrates | Results |
|---|---|
| Control | − |
| d–glucose | ++ |
| d–fructose | ++ |
| d–mannitol | ++ |
| d–cellobiose | ++ |
| d–maltose | ++ |
| d–melibiose | ++ |
| d–trehalose | ++ |
| d–raffinose | + |
| d–turanose | + |
| Methyl–d–glucopyranoside | + |
| Inositol | + |
| Enzymes | Phenotypes | Potential Function | Reference Gene(s) Tag |
|---|---|---|---|
| catalase | + | converts hydrogen peroxide to water and keeps ROS level down | ID12_04890, ID12_09825 |
| amylase | + | hydrolyzes starch | not available |
| Alkaline phosphatase | + | hydrolyzes phosphate | ID12_09845, ID12_18380, ID12_18885 |
| (acid) phosphatase | + | hydrolyzes phosphate | ID12_02705, D12_10250, ID12_10605, D12_11490, ID12_13905, D12_13990, ID12_14990 |
| phytase | + | hydrolyzes phytate | not available |
| 1–aminocyclopropane–1–carboxylate (ACC) deaminase | + | declines stress induced ethylene | not available |
| nitroreductase | + | defenses against oxidative stress | ID12_02145, D12_04220, ID12_07940, D12_09215, ID12_14945 |
| nitrite reductase | + | reduces nitrite to NO, alleviates oxidative stress | ID12_14600, D12_14605, ID12_14610, ID12_14615 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, Z.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liang, A.; Chu, C.; Chen, C.; Sun, Z. Microbiological Insights into the Stress-Alleviating Property of an Endophytic Bacillus altitudinis WR10 in Wheat under Low-Phosphorus and High-Salinity Stresses. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7110508
Yue Z, Shen Y, Chen Y, Liang A, Chu C, Chen C, Sun Z. Microbiological Insights into the Stress-Alleviating Property of an Endophytic Bacillus altitudinis WR10 in Wheat under Low-Phosphorus and High-Salinity Stresses. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(11):508. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7110508
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Zonghao, Yihao Shen, Yanjuan Chen, Anwen Liang, Cuiwei Chu, Can Chen, and Zhongke Sun. 2019. "Microbiological Insights into the Stress-Alleviating Property of an Endophytic Bacillus altitudinis WR10 in Wheat under Low-Phosphorus and High-Salinity Stresses" Microorganisms 7, no. 11: 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7110508
APA StyleYue, Z., Shen, Y., Chen, Y., Liang, A., Chu, C., Chen, C., & Sun, Z. (2019). Microbiological Insights into the Stress-Alleviating Property of an Endophytic Bacillus altitudinis WR10 in Wheat under Low-Phosphorus and High-Salinity Stresses. Microorganisms, 7(11), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7110508





