The Impact of Bioinformatics Pipelines on Microbiota Studies: Does the Analytical “Microscope” Affect the Biological Interpretation?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.3. Comparison of Bacterial Diversity, Richness and Composition and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
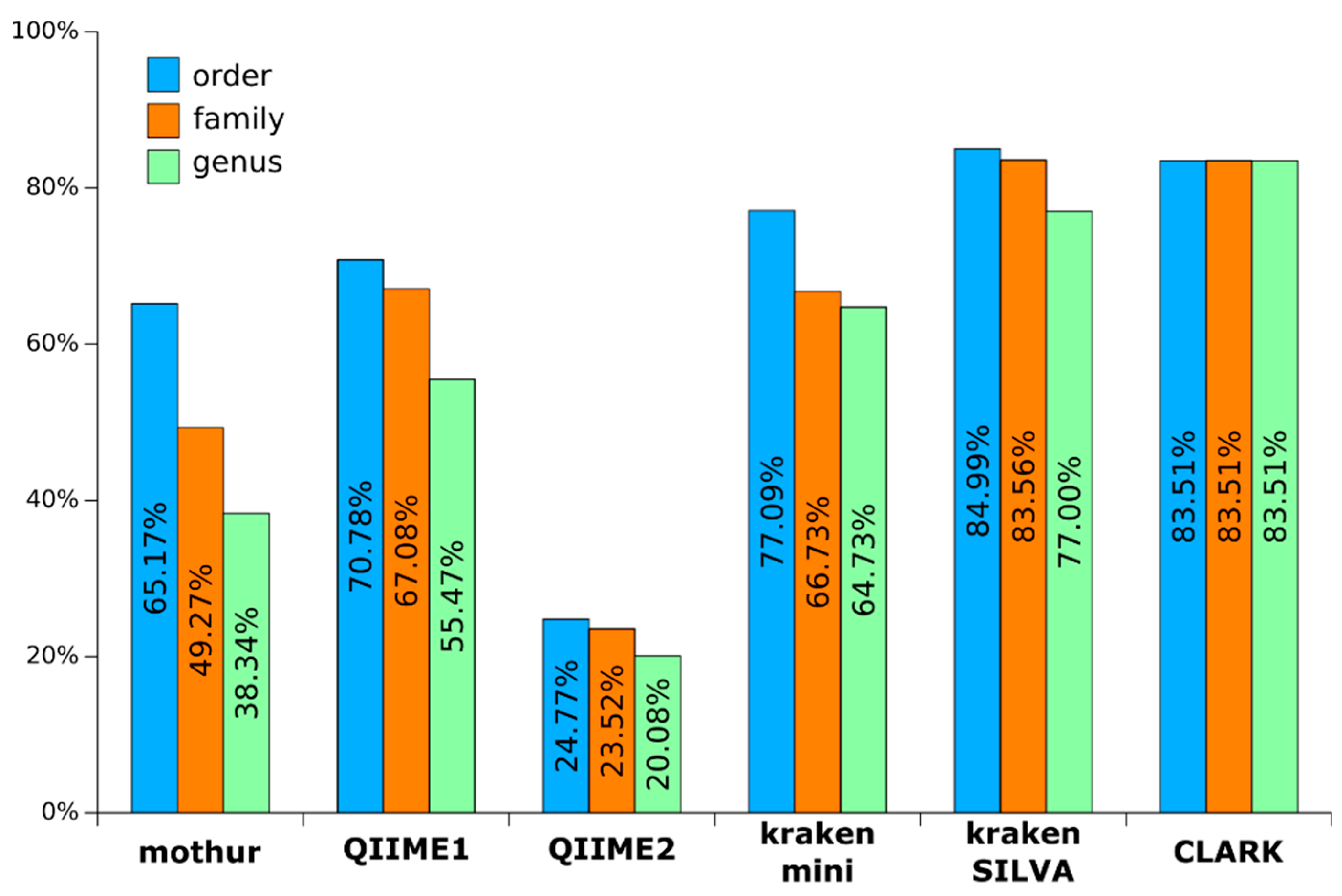
3.1. Richness/Diversity
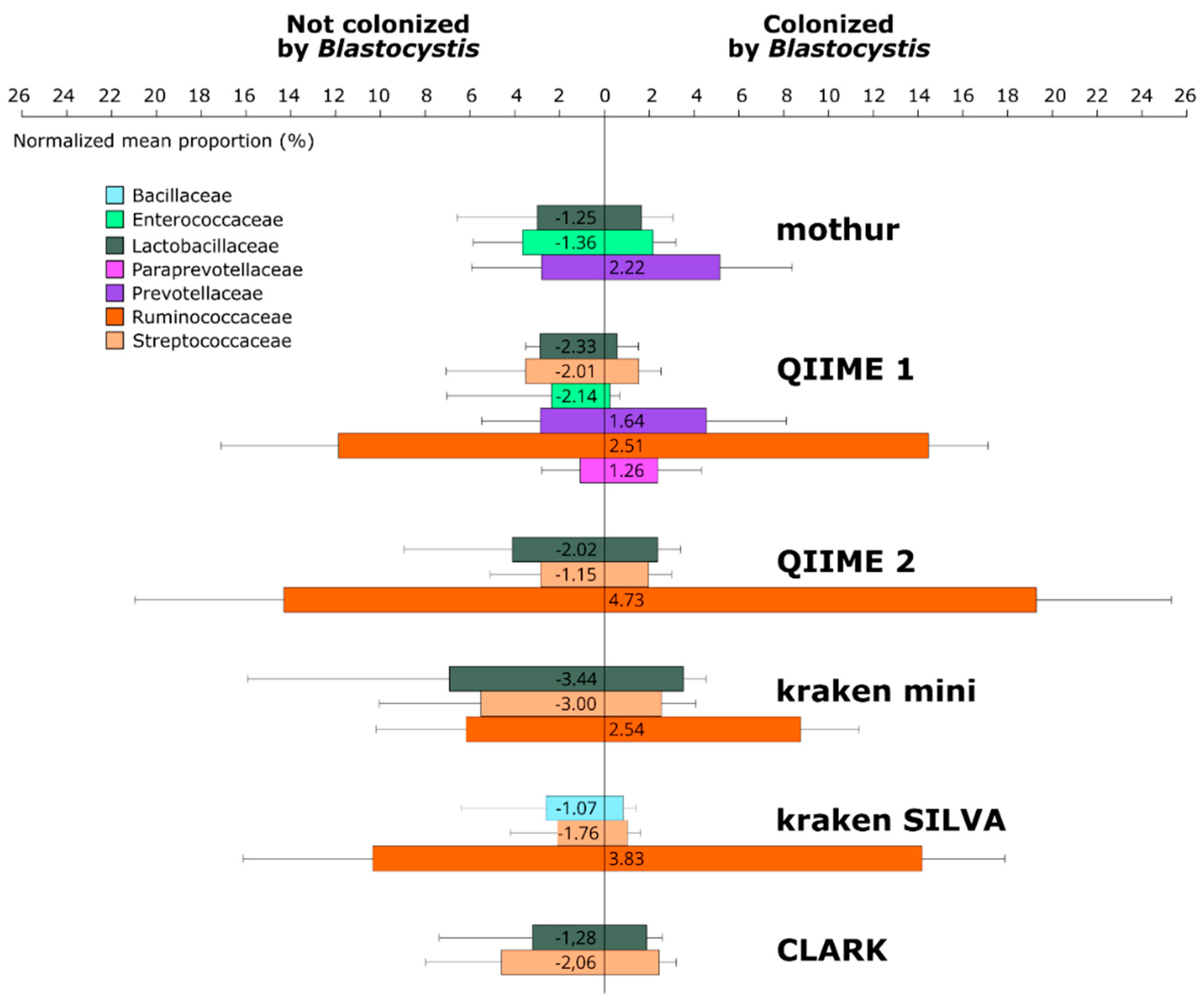
3.2. Composition
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pollock, J.; Glendinning, L.; Wisedchanwet, T.; Watson, M. The Madness of Microbiome: Attempting To Find Consensus “Best Practice” for 16S Microbiome Studies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.; Abu-Ali, G.; Vogtmann, E.; Fodor, A.A.; Ren, B.; Amir, A.; Schwager, E.; Crabtree, J.; Ma, S.; Abnet, C.C.; et al. Assessment of variation in microbial community amplicon sequencing by the Microbiome Quality Control (MBQC) project consortium. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, J.P.; Edwards, D.J.; Harwich, M.D.; Rivera, M.C.; Fettweis, J.M.; Serrano, M.G.; Reris, R.A.; Sheth, N.U.; Huang, B.; Girerd, P.; et al. The truth about metagenomics: Quantifying and counteracting bias in 16S rRNA studies. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserstein, R.L.; Lazar, N.A. The ASA’s Statement on p -Values: Context, Process, and Purpose. Am. Stat. 2016, 70, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, R. Scientific method: Statistical errors. Nature 2014, 506, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegwald, L.; Touzet, H.; Lemoine, Y.; Hot, D.; Audebert, C.; Caboche, S. Assessment of Common and Emerging Bioinformatics Pipelines for Targeted Metagenomics. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirmer, M.; Ijaz, U.Z.; D’Amore, R.; Hall, N.; Sloan, W.T.; Quince, C. Insight into biases and sequencing errors for amplicon sequencing with the Illumina MiSeq platform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, A.; McDonald, D.; Navas-Molina, J.A.; Kopylova, E.; Morton, J.T.; Zech Xu, Z.; Kightley, E.P.; Thompson, L.R.; Hyde, E.R.; Gonzalez, A.; et al. Deblur Rapidly Resolves Single-Nucleotide Community Sequence Patterns. MSystems 2017, 2, e00191-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audebert, C.; Even, G.; Cian, A.; Blastocystis Investigation Group; Loywick, A.; Merlin, S.; Viscogliosi, E.; Chabé, M.; El Safadi, D.; Certad, G.; et al. Colonization with the enteric protozoa Blastocystis is associated with increased diversity of human gut bacterial microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollister, E.B.; Gao, C.; Versalovic, J. Compositional and functional features of the gastrointestinal microbiome and their effects on human health. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegwald, L.; Audebert, C.; Even, G.; Viscogliosi, E.; Caboche, S.; Chabé, M. Targeted metagenomic sequencing data of human gut microbiota associated with Blastocystis colonization. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, D.E.; Salzberg, S.L. Kraken: Ultrafast metagenomic sequence classification using exact alignments. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ounit, R.; Wanamaker, S.; Close, T.J.; Lonardi, S. CLARK: Fast and accurate classification of metagenomic and genomic sequences using discriminative k-mers. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcoxon, F. Individual Comparisons by Ranking Methods. Biom. Bull. 1945, 1, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.R.; Nagarajan, N.; Pop, M. Statistical Methods for Detecting Differentially Abundant Features in Clinical Metagenomic Samples. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Chatelier, E.; Nielsen, T.; Qin, J.; Prifti, E.; Hildebrand, F.; Falony, G.; Almeida, M.; Arumugam, M.; Batto, J.-M.; Kennedy, S.; et al. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature 2013, 500, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosca, A.; Leclerc, M.; Hugot, J.P. Gut microbiota diversity and human diseases: Should we reintroduce key predators in our ecosystem? Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, H.B.; Whitney, D.R. On a Test of Whether one of Two Random Variables is Stochastically Larger than the Other. Ann. Math. Stat. 1947, 18, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddle, A.; Stewart, L.; Blanchard, J.; Leschine, S. Untangling the genetic basis of fibrolytic specialization by lachnospiraceae and ruminococcaceae in diverse gut communities. Diversity 2013, 5, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manichanh, C.; Borruel, N.; Casellas, F.; Guarner, F. The gut microbiota in IBD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyra, A.; Lahtine, S. Dysbiosis of the Intestinal Microbiota in IBS. Curr. Concepts Colon. Disord. 2012, 261–276. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, T.A.N.; Lawley, T.D. Emerging insights on intestinal dysbiosis during bacterial infections. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2014, 17, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Sun, Y. ESPRIT-Tree: Hierarchical clustering analysis of millions of 16S rRNA pyrosequences in quasilinear computational time. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, S.E.; Bäumler, A.J. Why related bacterial species bloom simultaneously in the gut: Principles underlying the “like will to like” concept. Cell. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siegwald, L.; Caboche, S.; Even, G.; Viscogliosi, E.; Audebert, C.; Chabé, M. The Impact of Bioinformatics Pipelines on Microbiota Studies: Does the Analytical “Microscope” Affect the Biological Interpretation? Microorganisms 2019, 7, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7100393
Siegwald L, Caboche S, Even G, Viscogliosi E, Audebert C, Chabé M. The Impact of Bioinformatics Pipelines on Microbiota Studies: Does the Analytical “Microscope” Affect the Biological Interpretation? Microorganisms. 2019; 7(10):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7100393
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiegwald, Léa, Ségolène Caboche, Gaël Even, Eric Viscogliosi, Christophe Audebert, and Magali Chabé. 2019. "The Impact of Bioinformatics Pipelines on Microbiota Studies: Does the Analytical “Microscope” Affect the Biological Interpretation?" Microorganisms 7, no. 10: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7100393
APA StyleSiegwald, L., Caboche, S., Even, G., Viscogliosi, E., Audebert, C., & Chabé, M. (2019). The Impact of Bioinformatics Pipelines on Microbiota Studies: Does the Analytical “Microscope” Affect the Biological Interpretation? Microorganisms, 7(10), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7100393






