Whole-Genome Analysis of Bacillus paranthracis Qf-1 Isolated from Mink (Neogale vison)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Bacterial Isolation
2.3. Morphological Observation of Pathogenic Bacteria
2.4. Characterization of the Pathogenic Bacterial Strain Under the Biolog Gen III Microtest System
2.5. Amplification and Sequencing of the 16S rRNA Gene and Construction of a Phylogenetic Tree
2.6. Genome Sequencing and Analysis of Average Nucleotide Identity (ANI)
2.7. Comparative Genomic Analysis
2.8. Mouse Lethality Assay
3. Results
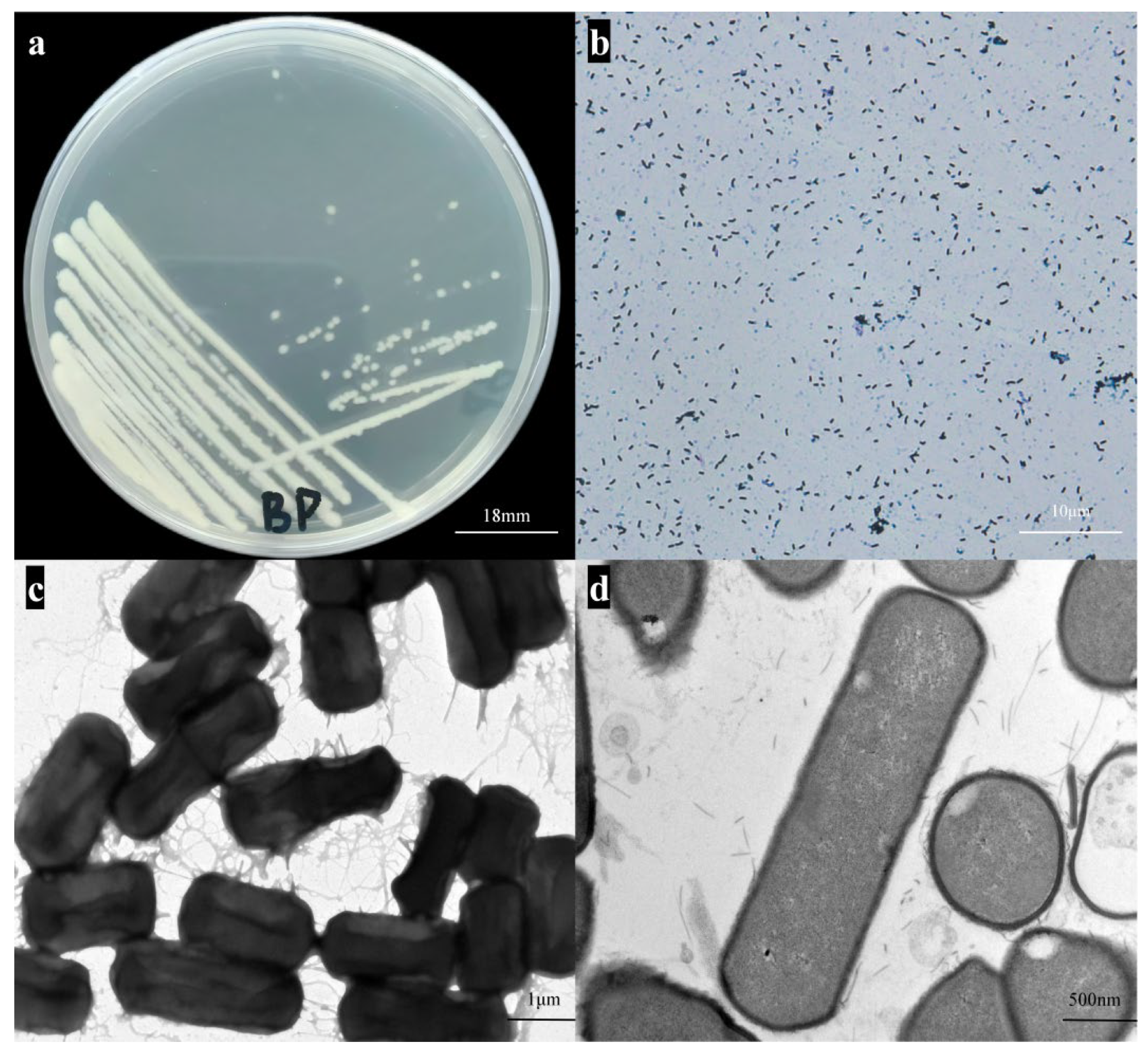
3.1. Morphological and Staining Characteristics Observation and Growth Properties Study of Strain BpQf-1
3.2. Biochemical Characterization of BpQf-1 Using Biolog Gen III Microtest System
3.3. Molecular Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis
3.4. Genomic Features of Strain BpQf-1
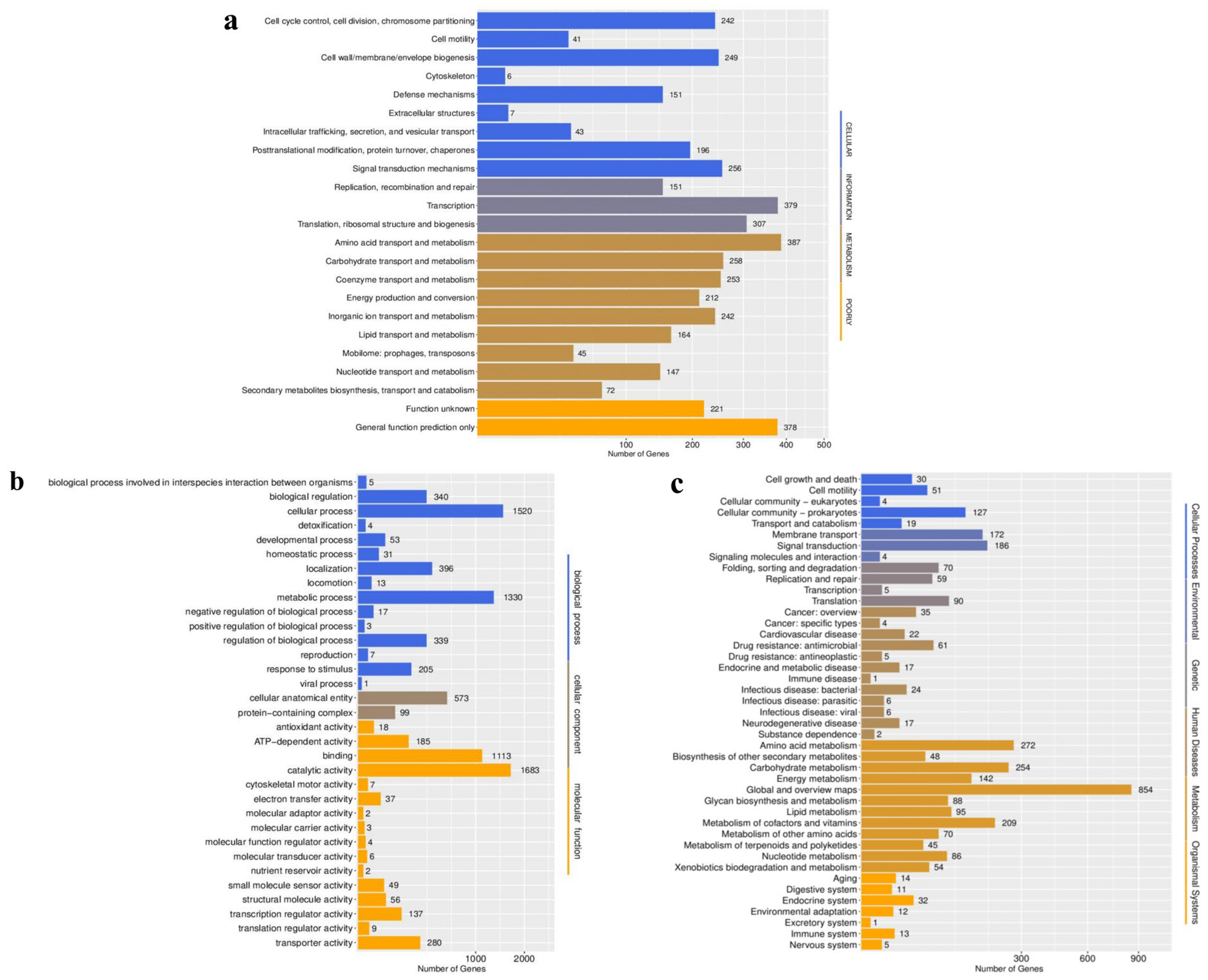
3.5. Functional Annotation of Strain BpQf-1
3.6. Analysis of Virulence Factors and Antibiotic Resistance Genes of BpQf-1
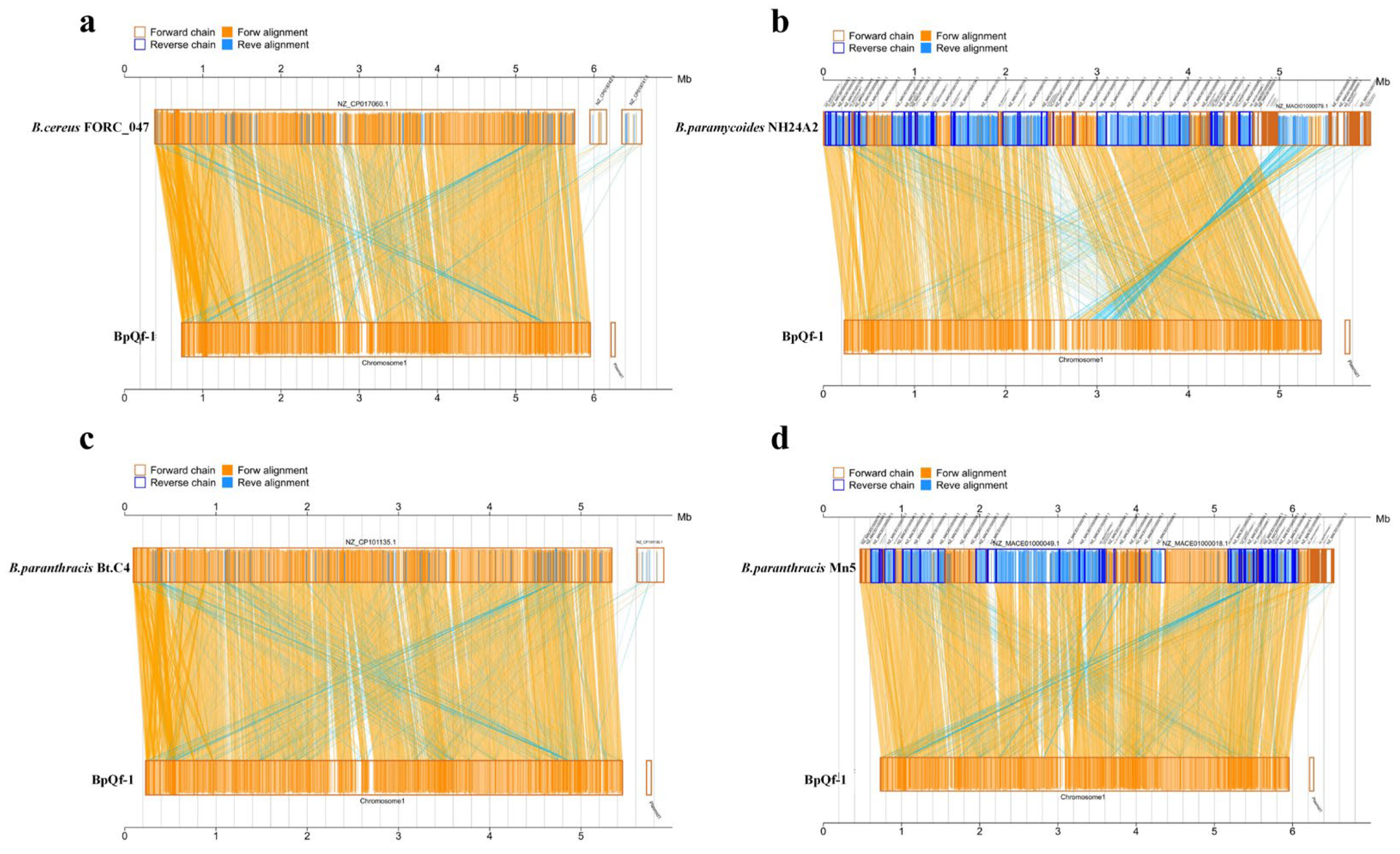
3.7. Collinearity Analysis
3.8. Core Genome and Pan Genome Analysis
3.9. Pathological Analysis to Explore Strain Pathogenicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, J.; Nituch, L.A.; Bowman, J.; Beauclerc, K.B.; Schulte-Hostedde, A.I. Mink Farms Predict Aleutian Disease Exposure in Wild American Mink. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissinger, J.A.; Gregory, B.R.B.; Clarkson, C.; Libera, N.; Eickmeyer, D.C.; Kimpe, L.E.; Kurek, J.; Smol, J.P.; Blais, J.M. Tracking pollution from fur farms using forensic paleolimnology. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 335, 122307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, L.; Li, J.; Fang, B.; Huang, X. Molecular epidemiology, antimicrobial susceptibility, and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis genotyping of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from mink. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 82, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, N.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.-S.; Shao, X.-Q.; Zhang, S.-Q.; Wang, F.-X.; Tan, B.; Tian, F.-L.; Cheng, S.-P.; Wen, Y.-J. Detection and Characterization of Avastrovirus Associated with Diarrhea Isolated from Minks in China. Food Environ. Virol. 2014, 6, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Li, L.; Du, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Luo, Y.; Che, J.; Lu, J.; Liu, H.; Hu, G.; et al. The identification, typing, and antimicrobial susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from mink with hemorrhagic pneumonia. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 170, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, X.; Xue, Y. Drug Resistance and Genetic Relatedness of Escherichia coli from Mink in Northeast China. Pak. Vet. J. 2023, 43, 824–827. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Shang, Y.; Guo, S.; Diao, F.; Yu, J.; Wei, X.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, S.; Xie, Z. Serotype and virulence genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from mink and its pathogenesis in mice and mink. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, H.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Shang, Y.; Wei, Q.; Sha, W.; Qi, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H. Identification and Pathogenicity Analysis of Huaxiibacter chinensis Qf-1 in Mink (Neogale vison). Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.S.; Du, Y.; Wu, J.Q.; Tian, F.L.; Yu, X.J.; Wang, J.B. Vaccine resistant pseudorabies virus causes mink infection in China. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehling-Schulz, M.; Lereclus, D.; Koehler, T.M. The Bacillus cereus Group: Bacillus Species with Pathogenic Potential. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Du, J.; Lai, Q.; Zeng, R.; Ye, D.; Xu, J.; Shao, Z. Proposal of nine novel species of the Bacillus cereus group. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 2499–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, M.J.; Anzick, S.L.; Feldmann, F.; Martens, C.A.; Drake, S.K.; Feldmann, H.; Massaquoi, M.; Chertow, D.S.; Munster, V.J. Bacillus paranthracis Isolate from Blood of Fatal Ebola Virus Disease Case. Pathogens 2020, 9, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skóra, M.; Zając, M.; Kwit, R.; Skarżyńska, M.; Pasim, P.; Mikos-Wojewoda, E.; Bomba, A.; Giza, A.; Chesneau, O.; Hendriksen, R.S.; et al. Draft Genome Sequences of Six Isolates of the Bacillus cereus Group Isolated from Pet Reptiles. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2022, 11, e0038522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xie, H.; Liu, L.; Du, L.; Yin, F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, G.; Zhang, X.; Sun, D.; et al. A rare waterborne outbreak of Bacillus paranthracis in Shandong province, China, 2020: Epidemiologic survey, genomic insights, and virulence characteristics. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2348498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, L.P. Genomic and pathogenicity of a Bacillus paranthracis isolated from book page surface. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 92, 104867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukharin, O.V.; Perunova, N.B.; Andryuschenko, S.V.; Ivanova, E.V.; Bondarenko, T.A.; Chainikova, I.N.; Rasko, D. Genome Sequence Announcement of Bacillus paranthracis Strain ICIS-279, Isolated from Human Intestine. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, L.M.; Wiedmann, M.; Mukherjee, M.; Nicholas, D.C.; Mingle, L.A.; Dumas, N.B.; Cole, J.A.; Kovac, J. Characterization of Emetic and Diarrheal Bacillus cereus Strains From a 2016 Foodborne Outbreak Using Whole-Genome Sequencing: Addressing the Microbiological, Epidemiological, and Bioinformatic Challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Yao, H.; Ji, L.; Dong, F.; Xu, D.; Yan, W. Epidemiological and genomic characterization of a rare foodborne outbreak caused by Bacillus paranthracis in Huzhou, China, 2024. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2025, 439, 111265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsuki, H.; Zhang, T.; Yahiro, K.; Toyomoto, T.; Sawa, T. Non-canonical inflammasome activation analysis in a mouse model of Citrobacter rodentium infection. STAR Protoc. 2022, 3, 101741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, M.; Gałązka, A.; Tyśkiewicz, R.; Jaroszuk-Ściseł, J. Endophytic Bacteria Potentially Promote Plant Growth by Synthesizing Different Metabolites and their Phenotypic/Physiological Profiles in the Biolog GEN III MicroPlate(TM) Test. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, A.Y.Z.; Bekhet, G. First isolation and characterization of the pathogenic Aeromonas veronii bv. veronii associated with ulcerative syndrome in the indigenous Pelophylax ridibundus of Al-Ahsaa, Saudi Arabia. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 117, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, J.L.; Jukes, T.H. Non-Darwinian evolution. Science 1969, 164, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindgreen, S. AdapterRemoval: Easy cleaning of next-generation sequencing reads. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Yuan, J.; He, G.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. SOAPdenovo2: An empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. Gigascience 2012, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coil, D.; Jospin, G.; Darling, A.E. A5-miseq: An updated pipeline to assemble microbial genomes from Illumina MiSeq data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, M.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Y.; Pevzner, P.A. Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.; Rainey, F.A. Integrating genomics into the taxonomy and systematics of the Bacteria and Archaea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galperin, M.Y.; Wolf, Y.I.; Makarova, K.S.; Vera Alvarez, R.; Landsman, D.; Koonin, E.V. COG database update: Focus on microbial diversity, model organisms, and widespread pathogens. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D274–D281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D457–D462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, D.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Jin, Q. VFDB 2016: Hierarchical and refined dataset for big data analysis—10 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D694–D697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, B.P.; Raphenya, A.R.; Lau, T.T.Y.; Tsang, K.K.; Bouchard, M.; Edalatmand, A.; Huynh, W.; Nguyen, A.V.; Cheng, A.A.; Liu, S.; et al. CARD 2020: Antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D517–D525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Phillippy, A.; Delcher, A.L.; Smoot, M.; Shumway, M.; Antonescu, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Versatile and open software for comparing large genomes. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sornchuer, P.; Saninjuk, K.; Amonyingcharoen, S.; Ruangtong, J.; Thongsepee, N.; Martviset, P.; Chantree, P.; Sangpairoj, K. Whole Genome Sequencing Reveals Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes of Both Pathogenic and Non-Pathogenic B. cereus Group Isolates from Foodstuffs in Thailand. Antibiot. 2024, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senesi, S.; Ghelardi, E. Production, Secretion and Biological Activity of Bacillus cereus Enterotoxins. Toxins 2010, 2, 1690–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottone, E.J. Bacillus cereus, a Volatile Human Pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 382–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasko, D.; Altherr, M.; Han, C.; Ravel, J. Genomics of the group of organisms. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 303–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Süzük Yıldız, S.; Polat, A.; Yalçın, S.; Ölmez, M.E.; Darçın, T.; Özdel, K.; Mumcuoğlu, İ.; Dal, T. Can Bacillus paranthracis cause bacteremia in a T-ALL patient? WGS-based diagnosis. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2025, 19, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garufi, G.; Butler, E.; Missiakas, D. ESAT-6-Like Protein Secretion in Bacillus anthracis. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 7004–7011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfleger, B.F.; Kim, Y.; Nusca, T.D.; Maltseva, N.; Lee, J.Y.; Rath, C.M.; Scaglione, J.B.; Janes, B.K.; Anderson, E.C.; Bergman, N.H.; et al. Structural and functional analysis of AsbF: Origin of the stealth 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid subunit for petrobactin biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17133–17138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najimi, M.; Lemos, M.L.; Osorio, C.R. Identification of siderophore biosynthesis genes essential for growth of Aeromonas salmonicida under iron limitation conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusca, T.D.; Kim, Y.; Maltseva, N.; Lee, J.Y.; Eschenfeldt, W.; Stols, L.; Schofield, M.M.; Scaglione, J.B.; Dixon, S.D.; Oves-Costales, D.; et al. Functional and Structural Analysis of the Siderophore Synthetase AsbB through Reconstitution of the Petrobactin Biosynthetic Pathway from Bacillus anthracis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 16058–16072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusca, T.D. Detailed Analysis of Biosynthetic Components for the Virulence-Associated Siderophore Petrobactin from Bacillus anthracis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kajfasz, J.K.; Martinez, A.R.; Rivera-Ramos, I.; Abranches, J.; Koo, H.; Quivey, R.G.; Lemos, J.A. Role of Clp Proteins in Expression of Virulence Properties of Streptococcus mutans. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 2060–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Foulston, L.; Chai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Losick, R. Alternative modes of biofilm formation by plant—Associated Bacillus cereus. MicrobiologyOpen 2015, 4, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Huang, T.; Huang, Z.; Powell, C.A.; Guan, X. Expression and characterization of inhA gene from Bacillus thuringiensis 8010. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 23, 1621–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandvalet, C.; Gominet, M.; Lereclus, D. Identification of genes involved in the activation of the Bacillus thuringiensis inhA metalloprotease gene at the onset of sporulation. Microbiology 2001, 147, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Positive Reaction with the Following Substrate/Test | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dextrin | d-Galacturonic Acid | Acetic Acid |
| d-Maltose | l-Galactonic Acid Lactone | Formic Acid |
| d-Trehalose | d-Gluconic Acid | pH 6 |
| β-Methyl-d-Glucoside | d-Glucuronic Acid | 1% NaCl |
| N-Acetyl-d-Glucosamine | Glucuronamide | 4% NaCl |
| d-Fructose 1 | d-Saccharic Acid | 8% NaCl |
| Glycerol | Methyl Pyruvate | 1% Sodium Lactate |
| d-Glucose-6-PO4 | d-Lactic Acid Methyl Ester | d-Serine |
| d-Fructose-6-PO4 | l-Lactic Acid | Guanidine HCl |
| d-Serine | l-Malic Acid | Lithium Chloride |
| Gelatin | Bromo-Succinic Acid | Potassium Tellurite |
| l-Arginine | Tween 40 | Aztreonam |
| l-Aspartic Acid | β-Hydroxy-d, l-Butyric Acid | Sodium Butyrate |
| l-Glutamic Acid | Acetoacetic Acid | |
| l-Serine | Propionic Acid | |
| Weak Positive Reaction with the Following Substrate/Test | ||
| N-Acetyl-β-D Mannosamine | L-Alanine | Citric Acid |
| D-Fucose | L-Histidine | α-Keto-Glutaric Acid |
| Inosine | Mucic Acid | D-Malic Acid |
| Negative Reaction with the Following Substrate/Test | ||
| D-Cellobiose 1 | L-Fucose | pH 5 |
| Gentiobiose | L-Rhamnose | Fusidic Acid |
| Sucrose | D-Sorbitol | Troleandomycin |
| D-Turanose 1 | D-Mannitol | Rifamycin SV |
| Stachyose | D-Arabitol | Minocycline |
| D-Raffinose | myo-Inositol | Lincomycin |
| α-D-Lactose | D-Aspartic Acid | Niaproof 4 |
| D-Melibiose | Glycyl-L-Proline | Vancomycin |
| D-Salicin | L-Pyroglutamic Acid | Tetrazolium Violet |
| N-Acetyl-D-Galactosamine | Pectin | Tetrazolium Blue |
| D-Cellobiose | L-Fucose | pH 5 |
| N-Acetyl-Neuraminic Acid | Quinic Acid | Nalidixic Acid |
| α-D-Glucose | p-Hydroxy-Phenylacetic Acid | Sodium Bromate |
| D-Mannose 1 | γ-Amino-Butryric Acid | |
| D-Galactosea 1 | α-Hydroxy Butyric Acid | |
| 3-Methyl Glucose | α-Keto-Butyric Acid | |
| Characteristic | Genome | Characteristic | Gnome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw data (Mb) | 1310 | CRISPRs | 7 |
| Total reads | 8,738,130 | VFDB | 286 |
| Clean data (Mb) | 1261 | CARD | 4 |
| Genome size (bp) | 5,276,703 | T3SS | 593 |
| GC content (%) | 36.13 | Coding gene annotated | 5334 |
| Gene total size (bp) | 4,409,133 | Coding gene assigned to COG | 3822 |
| rRNA | 42 | Coding gene assigned to KEGG | 2971 |
| tRNA | 105 | Coding gene assigned to GO | 2923 |
| ncRNA | 184 | Coding gene assigned to Swiss Prot | 2592 |
| sRNA | 37 |
| Gene Name | Category | Description | Identify (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AsbD | Nutritional/Metabolic factor | petrobactin biosynthesis protein AsbD | 100 |
| EsxB | Effector delivery system | type VII secretion system protein EsxB | 100 |
| EssC | Effector delivery system | type VII secretion system protein EssC | 99.7 |
| AsbF | Nutritional/Metabolic factor | petrobactin biosynthesis 3-dehydroshikimate dehydratase AsbF | 99.6 |
| BAS_RS10600 | Effector delivery system | type VII secretion system protein | 99.3 |
| InhA | Exoenzyme | immune inhibitor A metalloprotease | 99.2 |
| EsxL | Effector delivery system | type VII secretion system protein EsxL | 97.2 |
| ClpP | Stress survival | ATP-dependent Clp protease proteolytic subunit | 78.2 |
| ClpC | Stress survival | endopeptidase Clp ATP-binding chain C | 77 |
| Gene Name | Antibiotics | Resistance Mechanism | AMR Gene Family | Identify (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCR-4.1 | peptide antibiotic | antibiotic target alteration | MCR phosphoethanolamine transferase | 100 |
| Bla2 | carbapenem; cephalosporin; penam | antibiotic inactivation | subclass B1 Bacillus anthracis Bla beta-lactamase | 95.93 |
| FosB | fosfomycin | antibiotic inactivation | fosfomycin thiol transferase | 89.86 |
| MphL | macrolide antibiotic | antibiotic inactivation | macrolide phosphotransferase (MPH) | 88.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Shang, Y.; Wei, Q.; Sha, W.; Zhang, H. Whole-Genome Analysis of Bacillus paranthracis Qf-1 Isolated from Mink (Neogale vison). Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092106
Cai H, Chen Y, Wu X, Wang X, Shang Y, Wei Q, Sha W, Zhang H. Whole-Genome Analysis of Bacillus paranthracis Qf-1 Isolated from Mink (Neogale vison). Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092106
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Haotian, Yao Chen, Xiaoyang Wu, Xibao Wang, Yongquan Shang, Qinguo Wei, Weilai Sha, and Honghai Zhang. 2025. "Whole-Genome Analysis of Bacillus paranthracis Qf-1 Isolated from Mink (Neogale vison)" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092106
APA StyleCai, H., Chen, Y., Wu, X., Wang, X., Shang, Y., Wei, Q., Sha, W., & Zhang, H. (2025). Whole-Genome Analysis of Bacillus paranthracis Qf-1 Isolated from Mink (Neogale vison). Microorganisms, 13(9), 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092106






