Mutations in the Ferric Uptake Regulator Gene (fur) Suppress the Bacitracin Sensitivity of a Helicobacter pylori fapH Deletion Mutant
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. PCR Methods
2.3. Construction of H. pylori B128 Δfur Mutants
2.4. Motility Assay in Soft Agar Medium
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.6. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Analysis
3. Results
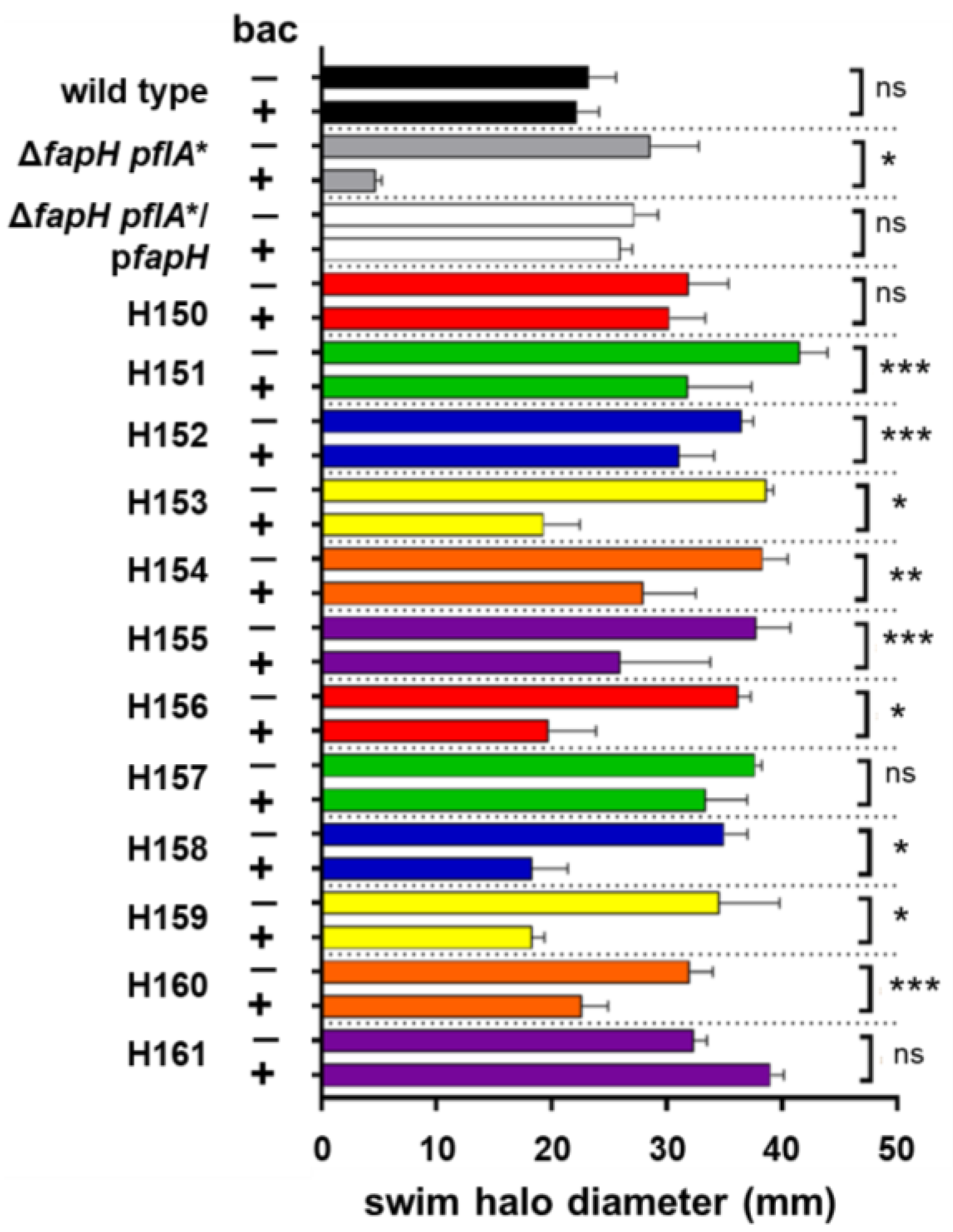
3.1. Bacitracin-Resistant Isolates of the ΔfapH pflA* Mutant Have Mutations in fur and hp0771
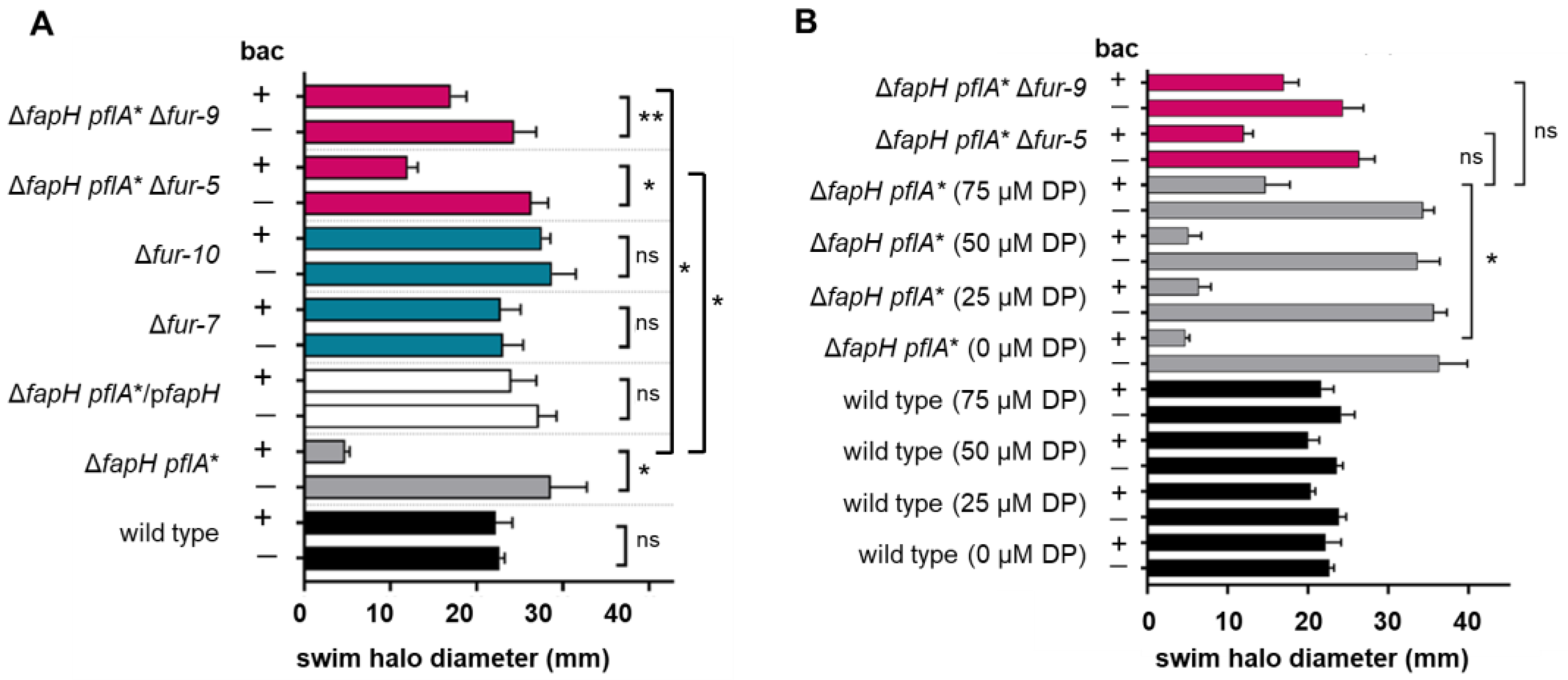
3.2. Deletion of Fur Suppresses the Bacitracin Sensitivity of the ΔfapH pflA* Mutant
3.3. Depletion of Ferrous Iron Suppresses the Bacitracin Sensitivity of the ΔfapH pflA* Mutant
3.4. H. pylori B128 ΔfapH Isolates That Have a Loss-of-Function Mutation in the LPS Biosynthetic Pathway Gene lpxF Display Resistance to Bacitracin
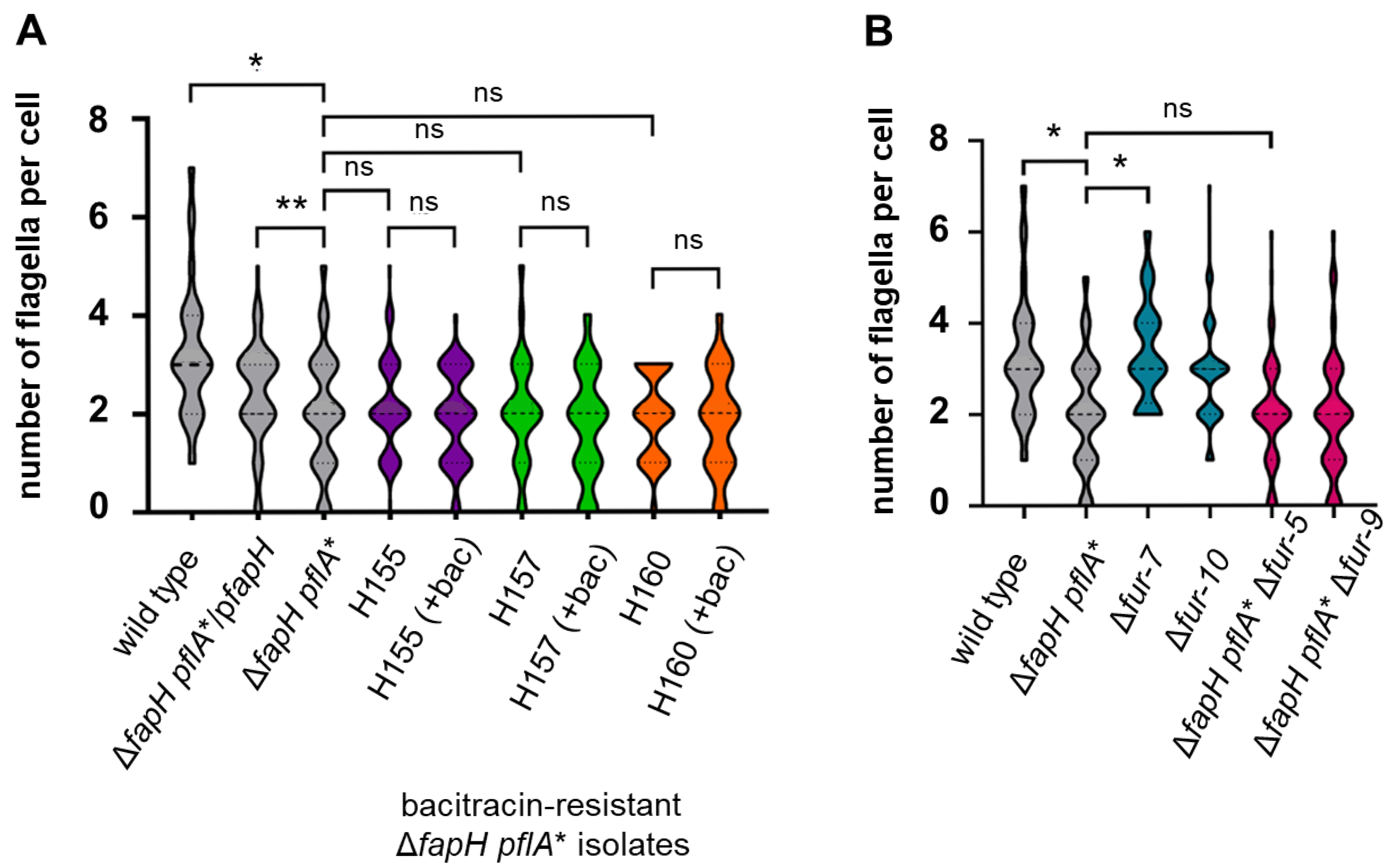
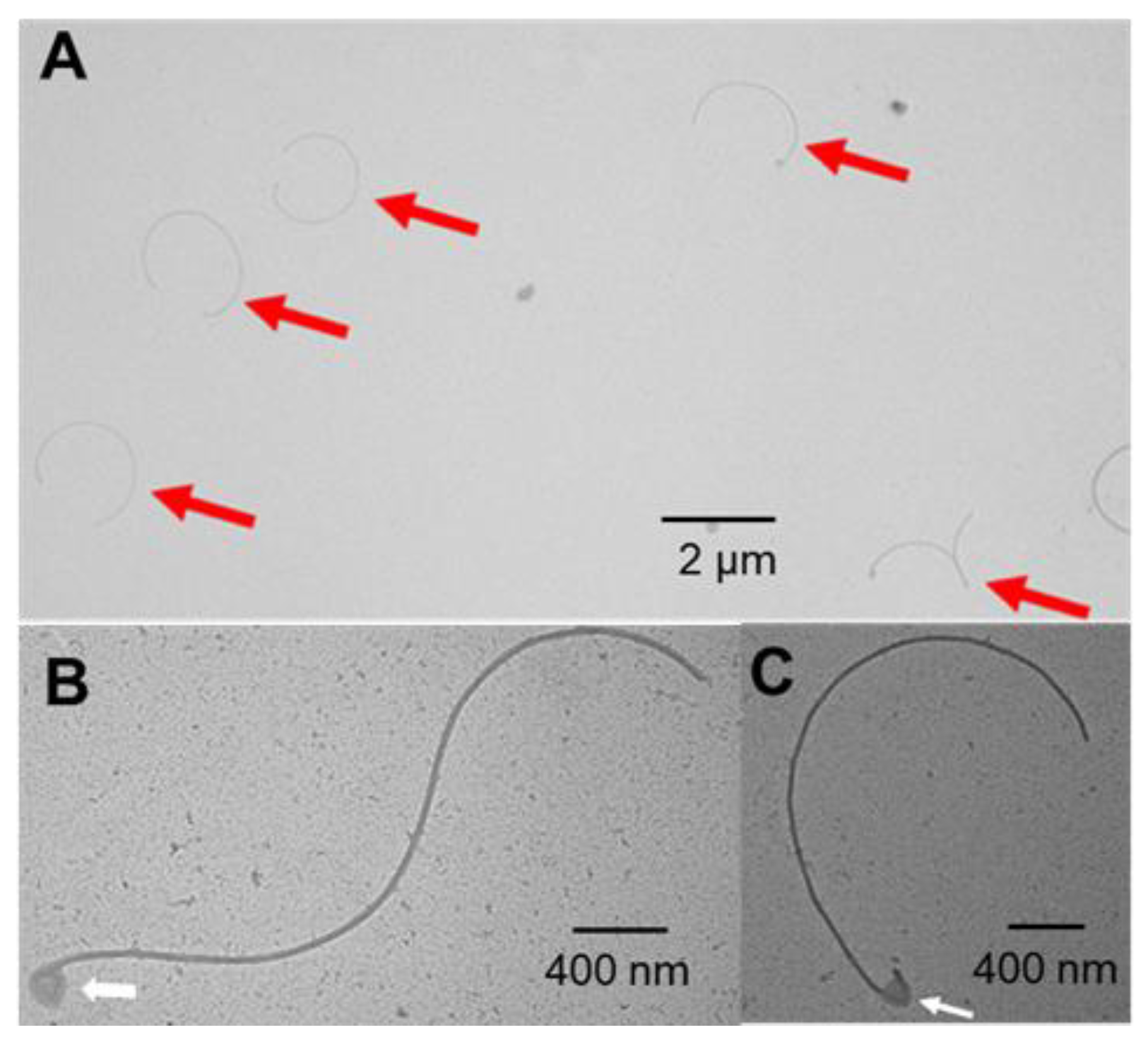
3.5. Cells of the ΔfapH pflA* Mutant Possess Fewer Flagella When Cultured in Soft Agar Medium
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OM | Outer membrane |
| OMV | Outer membrane vesicle |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| TSA-HS | Tryptic soy agar supplemented with horse serum |
| gDNA | Genomic DNA |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| LB | Lysogeny broth |
| SNP | Single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| TM | Transmembrane |
| bac | Bacitracin |
| DP | 2,2′-dipyridyl |
| pmxB | Polymyxin B |
References
- Hooi, J.K.Y.; Lai, W.Y.; Ng, W.K.; Suen, M.M.Y.; Underwood, F.E.; Tanyingoh, D.; Malfertheiner, P.; Graham, D.Y.; Wong, V.W.S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; et al. Global prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atherton, J.C.; Blaser, M.J. Coadaptation of Helicobacter pylori and humans: Ancient history, modern implications. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2475–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cover, T.L.; Blaser, M.J. Helicobacter pylori and gastroduodenal disease. Annu. Rev. Med. 1992, 43, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuipers, E.J. Helicobacter pylori and the risk and management of associated diseases: Gastritis, ulcer disease, atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 11 (Suppl. 1), 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Camargo, M.C.; El-Omar, E.; Liou, J.M.; Peek, R.; Schulz, C.; Smith, S.I.; Suerbaum, S. Helicobacter pylori infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, K.A.; Morgan, D.R.; Krakowka, S. Motility as a factor in the colonisation of gnotobiotic piglets by Helicobacter pylori. J. Med. Microbiol. 1992, 37, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottemann, K.M.; Lowenthal, A.C. Helicobacter pylori uses motility for initial colonization and to attain robust infection. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 1984–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geis, G.; Suerbaum, S.; Forsthoff, B.; Leying, H.; Opferkuch, W. Ultrastructure and biochemical studies of the flagellar sheath of Helicobacter pylori. J. Med. Microbiol. 1993, 38, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Carroll, B.L.; Zhao, X.; Charon, N.W.; Norris, S.J.; Motaleb, M.A.; Li, C.; Liu, J. Molecular mechanism for rotational switching of the bacterial flagellar motor. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deme, J.C.; Johnson, S.; Vickery, O.; Aron, A.; Monkhouse, H.; Griffiths, T.; James, R.H.; Berks, B.C.; Coulton, J.W.; Stansfeld, P.J.; et al. Structures of the stator complex that drives rotation of the bacterial flagellum. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, S.; Okada, Y.; Takada, S. Theoretical insights into rotary mechanism of MotAB in the bacterial flagellar motor. Biophys. J. 2024, 123, 3587–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiveri, M.; Roa-Eguiara, A.; Kuhne, C.; Wadhwa, N.; Hu, H.; Berg, H.C.; Erhardt, M.; Taylor, N.M.I. Structure and function of stator units of the bacterial flagellar motor. Cell 2020, 183, 244–257.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, Y.; Kojima, S.; Kato, H.; Nishioka, N.; Kawagishi, I.; Homma, M. Putative channel components for the fast-rotating sodium-driven flagellar motor of a marine bacterium. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 5104–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Homma, M. Functional reconstitution of the Na(+)-driven polar flagellar motor component of Vibrio alginolyticus. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 5718–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Fong, Y.H.; Deme, J.C.; Furlong, E.J.; Kuhlen, L.; Lea, S.M. Symmetry mismatch in the MS-ring of the bacterial flagellar rotor explains the structural coordination of secretion and rotation. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Chang, S.; Wu, H.; Wang, T.; Liang, H.; Gao, H.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Structural basis of assembly and torque transmission of the bacterial flagellar motor. Cell 2021, 184, 2665–2679 e2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, N.R.; Sosinsky, G.E.; Thomas, D.; DeRosier, D.J. Isolation, characterization and structure of bacterial flagellar motors containing the switch complex. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 235, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowenthal, A.C.; Hill, M.; Sycuro, L.K.; Mehmood, K.; Salama, N.R.; Ottemann, K.M. Functional analysis of the Helicobacter pylori flagellar switch proteins. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 7147–7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Furlong, E.J.; Deme, J.C.; Nord, A.L.; Caesar, J.J.E.; Chevance, F.F.V.; Berry, R.M.; Hughes, K.T.; Lea, S.M. Molecular structure of the intact bacterial flagellar basal body. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Makino, F.; Miyata, T.; Minamino, T.; Kato, T.; Namba, K. Structure of the molecular bushing of the bacterial flagellar motor. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Kato, T.; Namba, K. Specific arrangement of alpha-helical coiled coils in the core domain of the bacterial flagellar hook for the universal joint function. Structure 2009, 17, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samatey, F.A.; Matsunami, H.; Imada, K.; Nagashima, S.; Shaikh, T.R.; Thomas, D.R.; Chen, J.Z.; Derosier, D.J.; Kitao, A.; Namba, K. Structure of the bacterial flagellar hook and implication for the molecular universal joint mechanism. Nature 2004, 431, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macnab, R.M. How bacteria assemble flagella. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 57, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeby, M.; Ribardo, D.A.; Brennan, C.A.; Ruby, E.G.; Jensen, G.J.; Hendrixson, D.R. Diverse high-torque bacterial flagellar motors assemble wider stator rings using a conserved protein scaffold. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1917–E1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botting, J.M.; Tachiyama, S.; Gibson, K.H.; Liu, J.; Starai, V.J.; Hoover, T.R. FlgV forms a flagellar motor ring that is required for optimal motility of Helicobacter pylori. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0287514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tachiyama, S.; Zhou, X.; Mathias, R.A.; Bonny, S.Q.; Khan, M.F.; Xin, Y.; Roujeinikova, A.; Liu, J.; Ottemann, K.M. Bacterial flagella hijack type IV pili proteins to control motility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2317452121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Lin, W.T.; Zhu, S.; Franco, A.T.; Liu, J. Imaging the motility and chemotaxis machineries in Helicobacter pylori by cryo-electron tomography. J. Bacteriol. 2017, 199, e00695-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosinke, K.; Tachiyama, S.; Mrasek, J.; Liu, J.; Hoover, T.R. A Helicobacter pylori flagellar motor accessory is needed to maintain the barrier function of the outer membrane during flagellar rotation. PLoS Pathog. 2025, 21, e1012860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachiyama, S.; Chan, K.L.; Liu, X.; Hathroubi, S.; Peterson, B.; Khan, M.F.; Ottemann, K.M.; Liu, J.; Roujeinikova, A. The flagellar motor protein FliL forms a scaffold of circumferentially positioned rings required for stator activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2118401119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachiyama, S.; Rosinke, K.; Khan, M.F.; Zhou, X.; Xin, Y.; Botting, J.M.; Yue, J.; Roujeinikova, A.; Hoover, T.R.; Liu, J. FlgY, PflA, and PflB form a spoke-ring network in the high-torque flagellar motor of Helicobacter pylori. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2421632122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, B.L.; Liu, J. Structural conservation and adaptation of the bacterial flagella motor. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaban, B.; Coleman, I.; Beeby, M. Evolution of higher torque in Campylobacter-type bacterial flagellar motors. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manson, M.D. Dynamic motors for bacterial flagella. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11151–11152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aschtgen, M.S.; Lynch, J.B.; Koch, E.; Schwartzman, J.; McFall-Ngai, M.; Ruby, E. Rotation of Vibrio fischeri flagella produces outer membrane vesicles that induce host development. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 2156–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, C.A.; Hunt, J.R.; Kremer, N.; Krasity, B.C.; Apicella, M.A.; McFall-Ngai, M.J.; Ruby, E.G. A model symbiosis reveals a role for sheathed-flagellum rotation in the release of immunogenic lipopolysaccharide. eLife 2014, 3, e01579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silhavy, T.J.; Kahne, D.; Walker, S. The bacterial cell envelope. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielli, A.; Roncarati, D.; Delany, I.; Chiarini, V.; Rappuoli, R.; Scarlato, V. In vivo dissection of the Helicobacter pylori Fur regulatory circuit by genome-wide location analysis. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 4654–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delany, I.; Spohn, G.; Rappuoli, R.; Scarlato, V. The Fur repressor controls transcription of iron-activated and -repressed genes in Helicobacter pylori. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 42, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pich, O.Q.; Carpenter, B.M.; Gilbreath, J.J.; Merrell, D.S. Detailed analysis of Helicobacter pylori Fur-regulated promoters reveals a Fur box core sequence and novel Fur-regulated genes. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 84, 921–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, T.W.; Giles, D.K.; Wolf, L.N.; Ecobichon, C.; Boneca, I.G.; Trent, M.S. Helicobacter pylori versus the host: Remodeling of the bacterial outer membrane is required for survival in the gastric mucosa. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stead, C.M.; Beasley, A.; Cotter, R.J.; Trent, M.S. Deciphering the unusual acylation pattern of Helicobacter pylori lipid A. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 7012–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copass, M.; Grandi, G.; Rappuoli, R. Introduction of unmarked mutations in the Helicobacter pylori vacA gene with a sucrose sensitivity marker. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 1949–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deatherage, D.E.; Barrick, J.E. Identification of mutations in laboratory-evolved microbes from next-generation sequencing data using breseq. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1151, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbreath, J.J.; Pich, O.Q.; Benoit, S.L.; Besold, A.N.; Cha, J.H.; Maier, R.J.; Michel, S.L.; Maynard, E.L.; Merrell, D.S. Random and site-specific mutagenesis of the Helicobacter pylori ferric uptake regulator provides insight into Fur structure-function relationships. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 89, 304–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, B.M.; Gancz, H.; Benoit, S.L.; Evans, S.; Olsen, C.H.; Michel, S.L.; Maier, R.J.; Merrell, D.S. Mutagenesis of conserved amino acids of Helicobacter pylori fur reveals residues important for function. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5037–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bzymek, M.; Lovett, S.T. Instability of repetitive DNA sequences: The role of replication in multiple mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8319–8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontenot, C.R.; Tasnim, H.; Valdes, K.A.; Popescu, C.V.; Ding, H. Ferric uptake regulator (Fur) reversibly binds a [2Fe-2S] cluster to sense intracellular iron homeostasis in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 15454–15463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, J.P.; Rodriguez-Quinones, F.; Abdul-Tehrani, H.; Svistunenko, D.A.; Poole, R.K.; Cooper, C.E.; Andrews, S.C. Global iron-dependent gene regulation in Escherichia coli. A new mechanism for iron homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 29478–29486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orwa, J.A.; Govaerts, C.; Busson, R.; Roets, E.; Van Schepdael, A.; Hoogmartens, J. Isolation and structural characterization of polymyxin B components. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 912, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Jayol, A.; Nordmann, P. Polymyxins: Antibacterial activity, susceptibility testing, and resistance mechanisms encoded by plasmids or chromosomes. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 557–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimble, M.J.; Mlynarcik, P.; Kolar, M.; Hancock, R.E. Polymyxin: Alternative mechanisms of action and resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.A.; Chopra, I. Leakage of periplasmic proteins from Escherichia coli mediated by polymyxin B nonapeptide. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1986, 29, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, P.N. Primary sequence of the Escherichia coli fadL gene encoding an outer membrane protein required for long-chain fatty acid transport. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, K.L.; Silhavy, T.J. The Escherichia coli phospholipase PldA regulates outer membrane homeostasis via lipid signaling. mBio 2018, 9, e00379-18, Erratum in mBio 2018, 9, e00718-18. https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.00718-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hug, I.; Couturier, M.R.; Rooker, M.M.; Taylor, D.E.; Stein, M.; Feldman, M.F. Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide is synthesized via a novel pathway with an evolutionary connection to protein N-glycosylation. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Marceau, M.; Yang, T.; Liao, T.; Tang, X.; Hu, R.; Xie, Y.; Tang, H.; Tay, A.; Shi, Y.; et al. East-Asian Helicobacter pylori strains synthesize heptan-deficient lipopolysaccharide. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, F.D.; Bereswill, S.; Waidner, B.; Stoof, J.; Mader, U.; Kusters, J.G.; Kuipers, E.J.; Kist, M.; van Vliet, A.H.M.; Homuth, G. Transcriptional profiling of Helicobacter pylori Fur- and iron-regulated gene expression. Microbiology 2005, 151, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roier, S.; Zingl, F.G.; Cakar, F.; Durakovic, S.; Kohl, P.; Eichmann, T.O.; Klug, L.; Gadermaier, B.; Weinzerl, K.; Prassl, R.; et al. A novel mechanism for the biogenesis of outer membrane vesicles in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaput, C.; Ecobichon, C.; Cayet, N.; Girardin, S.E.; Werts, C.; Guadagnini, S.; Prevost, M.C.; Mengin-Lecreulx, D.; Labigne, A.; Boneca, I.G. Role of AmiA in the morphological transition of Helicobacter pylori and in immune escape. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steimle, A.; Autenrieth, I.B.; Frick, J.S. Structure and function: Lipid A modifications in commensals and pathogens. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 306, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, P.D.; Brun, Y.V. Getting in the loop: Regulation of development in Caulobacter crescentus. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 13–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, J.L.; Gao, F.Z.; Rossmann, F.M.; Nans, A.; Brenzinger, S.; Hosseini, R.; Wilson, A.; Briegel, A.; Thormann, K.M.; Rosenthal, P.B.; et al. gamma-proteobacteria eject their polar flagella under nutrient depletion, retaining flagellar motor relic structures. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Schniederberend, M.; Zhitnitsky, D.; Jain, R.; Galan, J.E.; Kazmierczak, B.I.; Liu, J. In situ structures of polar and lateral flagella revealed by cryo-electron tomography. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, e00117-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, N.; Arora, S.K.; Ramphal, R. fleN, a gene that regulates flagellar number in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, M.; Sweredoski, M.J.; Rodrigues, J.; Tocheva, E.I.; Chang, Y.W.; Ortega, D.R.; Beeby, M.; Jensen, G.J. Bacterial flagellar motor PL-ring disassembly subcomplexes are widespread and ancient. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 8941–8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Strain | Description/Relevant Genotype | a Bacitracin Resistance | Polymyxin B Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| H. pylori B128 wild type | Wild type | + | + |
| ΔfapH pflA* | ΔfapH, pflA allele encodes a variant of PflA that has altered amino acid sequence from Leu-465 to Ile-476 | − | + |
| H150 | Bacitracin-resistant isolate of ΔfapH pflA*, frameshift in fur (codon 18), frameshift in hp0771 (codon 19) | + | + |
| H151 | Bacitracin-resistant isolate of ΔfapH pflA*, frameshift in fur (codon 18), frameshift in hp0771 (codon 19) | +/− | + |
| H152 | Bacitracin-resistant isolate of ΔfapH pflA*, frameshift in fur (codon 18), frameshift in hp0771 (codon 19) | +/− | + |
| H153 | Bacitracin-resistant isolate of ΔfapH pflA*, frameshift in fur (codon 18), 27-bp deletion in hp0771 | +/− | + |
| H154 | Bacitracin-resistant isolate of ΔfapH pflA*, missense mutation in fur (Asp135Asn), 27-bp deletion in hp0771 | +/− | + |
| H155 | Bacitracin-resistant isolate of ΔfapH pflA*, frameshift in fur (codon 18), frameshift in hp0771 (codon 19) | +/− | + |
| H156 | Bacitracin-resistant isolate of ΔfapH pflA*, missense mutation in fur (Asp135Asn), 27-bp deletion in hp0771 | +/− | + |
| H157 | Bacitracin-resistant isolate of ΔfapH pflA*, frameshift in fur (codon 18), frameshift in hp0771 (codon 19) | + | + |
| H158 | Bacitracin-resistant isolate of ΔfapH pflA*, frameshift in fur (codon 18), 27-bp deletion in hp0771 | +/− | + |
| H159 | Bacitracin-resistant isolate of ΔfapH pflA*, frameshift in fur (codon 18), frameshift in hp0771 (codon 19) | +/− | + |
| H160 | Bacitracin-resistant isolate of ΔfapH pflA*, missense mutation in fur (Asp135Asn), 27-bp deletion in hp0771 | +/− | + |
| H161 | Bacitracin-resistant isolate of ΔfapH pflA*, frameshift in fur (codon 18), frameshift in hp0771 (codon 19) | + | + |
| ΔfapH pflA* Δfur-5 | Deletion of fur in ΔfapH pflA* strain | +/− | + |
| ΔfapH pflA* Δfur-9 | Deletion of fur in ΔfapH pflA* strain | +/− | + |
| Δfur-7 | Deletion of fur in H. pylori B128 | + | + |
| Δfur-10 | Deletion of fur in H. pylori B128 | + | n.d. |
| ΔfapH-2 | Deletion of fapH in H. pylori B128, nonsense mutation in lpxF (codon 14) | + | − |
| ΔfapH-11 | Deletion of fapH in H. pylori B128, nonsense mutation in lpxF (codon 14) | + | − |
| ΔfapH-4 | Deletion of fapH in H. pylori B1218 | − | + |
| ΔfapH-9 | Deletion of fapH in H. pylori B128 | − | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosinke, K.; Hoover, T.R. Mutations in the Ferric Uptake Regulator Gene (fur) Suppress the Bacitracin Sensitivity of a Helicobacter pylori fapH Deletion Mutant. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092103
Rosinke K, Hoover TR. Mutations in the Ferric Uptake Regulator Gene (fur) Suppress the Bacitracin Sensitivity of a Helicobacter pylori fapH Deletion Mutant. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092103
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosinke, Kyle, and Timothy R. Hoover. 2025. "Mutations in the Ferric Uptake Regulator Gene (fur) Suppress the Bacitracin Sensitivity of a Helicobacter pylori fapH Deletion Mutant" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092103
APA StyleRosinke, K., & Hoover, T. R. (2025). Mutations in the Ferric Uptake Regulator Gene (fur) Suppress the Bacitracin Sensitivity of a Helicobacter pylori fapH Deletion Mutant. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092103






