Abstract
Proteus mirabilis is a major uropathogen with growing concern over its presence in animal products and the associated zoonotic transmission risks. As a gut commensal in both humans and animals, it is increasingly detected in wild, farm, and companion animals, as well as in animal-derived foods and related environments. This review summarizes current evidence on its distribution across these sources and explores potential transmission routes to humans. Special attention is given to reported genomic similarities and shared antibiotic resistance patterns between animal and human isolates. The role of P. mirabilis in exacerbating intestinal inflammation further highlights its relevance beyond urinary infections. By revealing the epidemiology, pathogenic traits, and resistance profiles of animal-associated isolates, this review underscores the zoonotic potential of P. mirabilis and emphasizes the need for enhanced surveillance and research from a One Health perspective.
1. Introduction
Proteus mirabilis, a Gram-negative facultative anaerobic bacterium, belongs to the genus Proteus within the family Morganellaceae. Traditionally classified in the Enterobacteriaceae family, the taxonomy of P. mirabilis was reassessed with advancements in genomic analysis, leading to its reclassification under Morganellaceae by Adeolu et al. in 2016 based on phylogenetic studies [1]. As of 9 December 2024, the LPSN database lists P. mirabilis as a formally recognized species within this family, alongside other species such as Proteus vulgaris, Proteus cibi, and Proteus faecis (https://lpsn.dsmz.de/genus/proteus, 15 May 2025). The genus Proteus includes ten officially named species, with additional unnamed genomic species (genotypes 4, 5, and 6) [2,3].
Morphologically, P. mirabilis displays remarkable features, with a cell size ranging from 1.0 to 3.0 µm in length and 0.4 to 0.8 µm in width. The bacterium is polymorphic, appearing as short rods, spheres, and filaments, and lacks both a capsule and spore structure [4,5]. It is motile due to the presence of flagella and exhibits a characteristic swarming behavior on agar surfaces. This strong motility leads to the formation of concentric rings and visible demarcation lines, known as Dienes’ lines, which are used for strain differentiation [6,7]. The bacterium also possesses pili, enabling adhesion to epithelial cells of plants and fungi [8]. P. mirabilis is a major uropathogen, contributing to more than 40% of catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) cases [9,10,11,12]. Its virulence factors, including urease, flagella, pili, hemolysins, and metalloproteases, play crucial roles in its ability to colonize the host, damage tissues, and evade immune responses [13,14]. Although typically a commensal in the intestinal tract, recent studies have linked P. mirabilis to inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn’s disease [15]. It has been shown to exacerbate colitis by disrupting the intestinal mucus barrier and modulating host immune responses [16].
Although the epidemiology and pathogenicity of P. mirabilis have been widely studied, its significance as a zoonotic pathogen remains poorly documented. This review summarizes current findings on the distribution of P. mirabilis in wildlife, farm animals, companion animals, and associated environments and products. We also aim to elucidate the potential transmission routes of this zoonotic pathogen between humans and animals, with a focus on reported genomic similarities and shared antibiotic resistance patterns. By highlighting the zoonotic risks associated with P. mirabilis, this review seeks to provide a basis for future research on its pathogenic mechanisms and its impact on human and animal health.
2. The Detection of P. mirabilis in Animals
As a commensal bacterium in the gastrointestinal tract of both humans and animals, P. mirabilis is widely distributed across diverse animal species, including wildlife, farm animals, and companion animals. This broad host range suggests potential transmission routes between domestic and wild environments, as well as between animals and humans. As shown in Table 1, the frequent isolation of P. mirabilis from various animal sources underscores its widespread presence.
Wildlife has been identified as a significant reservoir for P. mirabilis, with the bacterium isolated from a wide range of species and their environments, underscoring its zoonotic potential. As shown in Table 1, in undisturbed environments, 17 P. mirabilis was isolated from 23 Egyptian vulture chicks in the Canary Islands, a single strain from 37 migratory bird feces at Dianchi Lake, China as well as one isolate was found in a fruit bat in Indonesia’s Gunung Halimun Salak National Park [17,18,19]. For wild mammals, two out of 110 wild boars (2.2%) from 19 rural and urban areas of northern Tunisia were isolated P. mirabilis [20]. From wildlife in a national park in Gabon, 7 isolates were from gorillas, mandrills, and African buffaloes [21]. Raptors in Catalonia, Spain, including Eurasian goshawks and barn owls, also carried this bacterium [22]. Notably, it was recovered from a juvenile sea lion in Uruguay (20%, 1/5) [23], indicating its presence in marine mammals. Beyond vertebrate hosts, ectoparasites may play a role in transmission. Ergunay et al. detected P. mirabilis in 48.5% (17/35) of ticks collected from various wild mammals (e.g., rhinos, giraffes, lions) and domestic cattle in Kenya [24].
In wildlife held in controlled environments such as zoos or farms, P. mirabilis has also been successfully isolated. Liu et al. used multiplex PCR to detect P. mirabilis in 100 fecal samples from giant pandas in Sichuan, China, with a detection rate of 30% (35/100) [25]. In the same facility, P. mirabilis was identified in kidney, liver, and urine samples from 3 out of 32 deceased red pandas, yielding an isolation rate of 9.4% [26]. Lv et al. isolated 53 P. mirabilis strains from farmed foxes, raccoons, and minks, as well as from their surrounding environments. Specifically, 12 isolates came from fox feces, 15 from raccoon feces, 12 from minks (feces, carcasses, throats, and anal swabs), and 14 from the feeding environment (soil and surfaces) [27]. Under controlled laboratory conditions, Yu et al. detected P. mirabilis in 9.5% of diarrheal rhesus macaques (7/74) and 30% of ferrets (4/12) [28]. In tree shrews, which are an emerging model in biomedical research, P. mirabilis was the most frequently isolated species with 34 isolates came from fecal samples [29].

Table 1.
Isolation of Proteus mirabilis from animals and animal-derived foods.
Table 1.
Isolation of Proteus mirabilis from animals and animal-derived foods.
| Category | Host | Region (Year) | Isolation Rate | Virulence Gene | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wildlife | Egyptian vulture | Spain (2022) | 17 isolates # | NA | [17] |
| Migratory Birds | China (2024) | 2.70% (1/37) | NA | [18] | |
| Fruit bat | Indonesia (2021) | 50% (1/2) | NA | [19] | |
| Wild boar | Tunisia (2021) | 2% (2/110) | NA | [20] | |
| Western lowland gorilla | Gabon (2021) | 3 isolates # | NA | [21] | |
| Mandrill | Gabon (2021) | 2 isolates # | NA | [21] | |
| African buffalo | Gabon (2021) | 2 isolates # | NA | [21] | |
| Eurasian goshawk | Spain (2019) | 1 isolate # | NA | [22] | |
| Barn owl | Spain (2019) | 1 isolate # | NA | [22] | |
| South American sea lion | Uruguay (2022) | 20% (1/5) | NA | [23] | |
| Tick from wildlife | Kenya (2022) | 48.5% (17/35) | NA | [24] | |
| Panda | China (2023) | 30% (30/100) | NA | [25] | |
| Red panda | China (2022) | 9.38% (3/32) | NA | [26] | |
| Fox | China (2022) | 12 isolates # | ureC, zapA, pmfA, atfA, mrpA, atfC, hmpA, rsmA, rsbA, ucaA | [27] | |
| Raccoon | China (2022) | 15 isolates # | ureC, zapA, pmfA, atfA, mrpA, atfC, hmpA, rsmA, rsbA, ucaA | [27] | |
| Ferrets | China (2015) | 30% (4/12) | NA | [28] | |
| Mink | China (2020, 2022) | 24.53% (13/53), 12 isolates # | ureC, zapA, pmfA, atfA, mrpA, atfC, hmpA, rsmA, rsbA, ucaA, FliL | [27,30] | |
| Rhesus Monkeys | China (2015) | 9.5% (7/74) | NA | [28] | |
| Tree shrews | China (2020) | 34 isolates # | NA | [29] | |
| Farm animals | Pig | China (2021, 2022), Rome (2021), India (2021) | 5.55% (30/541)–21.43% (21/98) | ureC, hpmA, zapA, pmfA, rsbA, ucaA, mrpA, atfA, ireA, ptA | [31,32,33,34] |
| Broiler | China (2020, 2022), India (2021), South Africa (2024) | 5.4% (26/480)–22.5% (18/80) | ureC, rsmA, hmpA, FliL, ireA, ptA, zapA, ucaA, pmfA, atfA, mrpA, hlyA, hpmA | [30,31,35,36] | |
| Duck | Egypt (2021) | 14.6% (35/240) | atpD, ureC, rsbA, zapA | [37] | |
| Cattle | China (2020), India (2021) | 23.26% (20/86)–33.33% (20/60) | ureC, zapA, rsmA, hmpA, mrpA, atfA, pmfA, FliL, ucaA | [30,31] | |
| Sheep | India (2021) | 31.91% (15/47) | NA | [31] | |
| Companion animals | Dog | China (2020, 2022, 2023), Egypt (2022), UK (2021), Thailand (2019), Europe (2016), Portugal (2018, 2021) | 11.0% (48/437)–44.4% (8/18) | ureC, FliL, ireA, zapA, ptA, hpmA, hpmB, pmfA, rsbA, mrpA, ucaA, rsmA, atfA | [30,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46] |
| Cat | UK (2021), Thailand (2020), Europe (2017), Portugal (2019, 2022) | 0–2.2% (4/171) | hmpA/hmpB, mrpA, pmfA, ucaA | [38,40,41,42,45] | |
| Pet turtle | South Korea (2018) | 28.8% (15/52) | ureC, rsbA, zapA, mrpA | [47] | |
| Animal-derived foods | Pork | China (2022, 2023), Brazil (2021), India (2021) | 14.38% (23/160)–65.61% (149/227) | mrpA, pmfA, ucaA, atfA, hpmA, zapA, ptA, ireA | [31,48,49,50] |
| Beef | Brazil (2021), India (2021) | 27.8% (100/360)–30.90% (17/55) | mrpA, pmfA, ucaA, atfA, hpmA, zapA, ptA, ireA | [31,48] | |
| Mutton | India (2021) | 25.51% (25/98) | NA | [31] | |
| Chicken | China (2022, 2023), Belgium (2020), Brazil (2021), India (2021), Egypt (2023) | 1.51% (1/66)–100% (200/200) | mrpA, pmfA, ucaA, atfA, hpmA, zapA, ptA, ireA | [31,48,49,50,51,52] | |
| Duck meat | China (2023) | 67.9% (84/124) | NA | [50] | |
| Milk/Dairy Products | India (2021), Egypt (2023) | 3.45% (2/58)–22.11% (21/95) | NA | [31,51] | |
| Other source | Aquatic products | China (2022) | 7.61% (7/92) | NA | [49] |
| Vegetables | China (2023) | 62.5% (5/8) | hpmA, mrpA, ptA, ireA, zapA, pmfA, atfA | [53] |
# Number of isolates reported; sample size not provided, so isolation rate could not be calculated.
Farm animals are significant reservoirs of P. mirabilis, raising concerns for both animal health and food safety (Table 1). Chinnam et al. reported a 15.95% (26/163) isolation rate from pig rectal swabs in Andhra Pradesh, India [31], while Qu et al. found 5.55% (30/541) in pigs from Zhejiang, China, with Jinhua showing the highest rate at 8.91% [32]. In Italy, P. mirabilis was also found in boar semen, negatively affecting sperm motility [33]. Beyond pigs, the bacterium was isolated from healthy chickens (21.36%, 47/220), cattle (33.33%, 20/60), and sheep (31.91%, 15/47) in Andhra Pradesh [31]. In China, broilers showed a 7.07% (50/707) isolation rate [35], while South African farms reported 5.4% (26/480) from chicken manure [36].
However, the association of P. mirabilis with disease in farm animals raises significant concern. In Guangxi, China, Ge et al. reported a 21.42% (21/98) isolation rate from fecal and tissue samples of diseased pigs, highlighting its potential pathogenic role [34]. Similarly, Sun et al. found isolation rates of 22.5% (18/80) in diarrheal poultry and 23.26% (20/86) in cattle in northeastern China, suggesting P. mirabilis may worsen animal health [30]. In Egypt, Algammal et al. detected the bacterium in 14.6% (35/240) of ducks, both healthy and diseased, indicating its diverse impact on animal health [37].
Companion animals, due to their close contact with humans, represent a potential source of zoonotic pathogens like P. mirabilis (Table 1). This bacterium has been increasingly detected in pets, highlighting its epidemiological importance. Marques et al. reported isolation from both humans (12.5%, 3/24) and dogs (44.4%, 8/18) in households, with no detection in cats [38]. Liu et al. found P. mirabilis in 31.12% (75/241) of fecal samples from household and stray dogs in Sichuan, China, with higher prevalence in stray dogs (36.17%) than household dogs (27.89%) [39]. Exotic pets also carry the bacterium; Pathirana et al. isolated it from 28.8% (15/52) of pet turtles in South Korea [47].
P. mirabilis is implicated in urinary tract infections (UTIs) in companion animals. Fonseca et al. found it in 22.7% (145/637) of canine urine samples but only 2.2% (4/171) in cats in the UK [40]. Similarly, Moyaert et al. reported rates of 11.0% in dogs and 1.1% in cats across Europe [41]. In Thailand, Amphaiphan et al. detected Proteus spp. in 13.6% of dog and 16.7% of cat urine samples [42]. Beyond UTIs, P. mirabilis was isolated from 19.35% (12/62) of dogs with diarrhea in China [43], and Sui et al. found it in dogs co-infected with canine parvovirus (47.37%) and distemper (10%) [44].
3. Detection of P. mirabilis in Animal-Derived Foods
Animal-derived foods have become a major focus of public health concern due to their contamination with P. mirabilis. The prevalence of P. mirabilis in animal products varies significantly across different countries and regions, reflecting differences in hygiene practices and environmental conditions (as shown in Table 1). In Andhra Pradesh, India, beef samples exhibited the highest contamination rate at 32.73% (17/55), while chicken and pork samples showed relatively lower detection rates of 19.49% (38/195) and 14.38% (23/160), respectively [31]. In Londrina-PR regions, Brazil, chicken meat displayed the contamination rate of chicken meat was the highest at 100% (200/200), that of beef was much lower at 27.8% (100/360) [48]. In Al Qalyubia Governorate, Egypt, chicken and milk samples had contamination rates of 1.51% (1/66) and 3.45% (2/58) [51]. In Ghent, Belgium, Yu et al. reported P. mirabilis in 36.25% (29/80) broiler carcasses [52], while Liu et al. reported a much higher contamination rate of 66% (66/100) in fresh chicken at Hebei, China [54]. A study by Ma et al. in wet market in Chengdu, China, isolated 89 strains of P. mirabilis from 347 samples of chicken, pork, and aquatic products, with an overall contamination rate of 25.65% (89/347). Among these, chicken showed the highest rate at 54.39% (62/114), followed by pork 14.18% (20/141) and aquatic products 7.61% (7/92) [49]. Lan et al. found P. mirabilis in 490 of 579 fresh meat samples (84.63%) from five wet markets in Zhongshan, China, with chicken 78.95% (180/228), duck 67.90% (84/124), and pork 65.61% (149/227) being the most contaminated [50]. These findings indicate that poor hygiene at poultry and meat stalls may result in significant contamination and cross-contamination, particularly affecting poultry meat. Flies associated with animal-derived food also appear to serve as potential vectors of transmission. Zaher et al. detected P. mirabilis from flies collected on pig carcasses [55].
Currently, P. mirabilis has been detected in food derived from farm animals, and its epidemiology in these animals has been well-documented. Moreover, its presence in wild boar and African buffalo, which are common sources of game meat, suggests a potential route of zoonotic transmission from wildlife to humans. However, this possibility requires further investigation.
4. Genomic Similarity of P. mirabilis Between Animal and Human
High genomic similarity has been observed between P. mirabilis isolates from humans, animals, and associated products and environments (as shown in Figure 1). Notably, P. mirabilis isolates from companion animals have been shown to share high genomic similarity with human isolates, with some strain pairs originating from individuals and pets within the same household. Marques et al. collected urine samples from 76 human patients and 107 companion animals with UTIs, and subsequently constructed a phylogenetic tree based on PFGE genotyping to compare the genetic relatedness of the isolates [45]. Among 39 clusters, 17 contained both human and animal isolates, with genomic similarity ranging from 80% to 100%. One canine isolate of P. mirabilis showed 100% similarity with a human isolate, while a feline isolate shared over 90% similarity with a human strain [45]. In a separate study, Marques et al. identified a human–dog pair harboring genetically related P. mirabilis strains, exhibiting 82.5% similarity to the animal-derived clinical strain FMV4938/07, which was isolated from a dog with a urinary tract infection [38]. One fecal P. mirabilis isolate from a dog in a separate household clustered with two human community-acquired UTI isolates, showing 80.9% and 88.9% genomic similarity, respectively [38]. Wang et al. isolated P. mirabilis (CC16012 strain) from a diarrheal dog, which was closely related to the human-derived Crl143 strain from the United States [43]. Pathirana et al. found that the mrpA gene sequence of P. mirabilis from pet turtles showed 96.4% and 94.9% similarity to human isolates from UTI and respiratory infections, respectively [47]. In experimental animals, Yu et al. isolated P. mirabilis from diarrheal primate feces, showing 99.6% genomic similarity to the human UTI-associated strain HI4320 [28]. Similarly, five P. mirabilis isolates from ducks also exhibited close phylogenetic relatedness to the HI4320 strain and other reference strains from diverse sources, based on atpD gene sequencing [37].
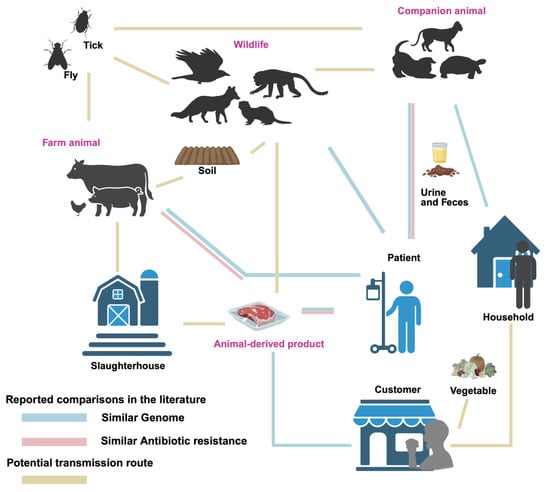
Figure 1.
Transmission routes of Proteus mirabilis between animals, products, environments, and humans. Line for similar genome: Similarity of genomes between isolates from both sources has been reported. Line for similar antibiotic resistance: Similar patterns of antibiotic resistance have been reported. Line for potential route: Potential connection between sources, but not yet studied.
Isolates from animal-derived products have shown high genomic similarity with those from human sources. Yu et al. reported that, based on PFGE analysis, the highest similarity observed between a broiler carcass isolate and a human stool isolate was 83.3%, differing by only two bands [52]. Similarly, Sanches et al. confirmed clonal relationships exclusively between chicken-derived isolates and those causing community-acquired urinary tract infections (UTI-CA), particularly within cluster C01. Notably, two strains within this cluster, one isolated from chicken meat and the other from a community-acquired urinary tract infection (UTI) patient, exhibited 100% genomic similarity as determined by PFGE [56]. Furthermore, the blaNDM-1 gene in strain JZ109 showed 100% nucleotide identity (with only a single base difference) to SGI1-1NDM, which was the first reported clinical P. mirabilis strain from China [49].
5. Pathogenicity of P. mirabilis in Humans and Animals
The pathogenicity of P. mirabilis has been reported in various tissues and organs of both humans and animals, with severe cases leading to death. One of the most notable associations of P. mirabilis is as a major pathogen in UTIs in both humans and companion animals [41,57]. Studies indicate that P. mirabilis accounts for 1–10% of all UTI cases in humans [58]. In nearly 3000 confirmed UTI cases in North America, infections caused by P. mirabilis represented 4% of all cases. Furthermore, the incidence of catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) caused by P. mirabilis is as high as 45% or more [59]. The incidence of P. mirabilis-induced UTI is significantly higher in women and the elderly population [58,59,60]. In animals, P. mirabilis has been linked to recurrent urinary stones in dogs with urinary system disorders, as evidenced by Song et al. [61]. Herout et al. also reported a high infection rate of P. mirabilis in a murine CAUTI model, further highlighting the bacterium’s role in urinary infections across species [62]. These findings highlight the role of P. mirabilis in UTIs in both humans and animals, with important implications for medical treatment and public health.
P. mirabilis has also been implicated in food poisoning incidents. Between 2016 and 2017, 3.61% of reported food poisoning cases in the Datong, China were caused by P. mirabilis, with symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and dizziness [63]. Wang et al. reported a food poisoning incident in Beijing in 2018, where P. mirabilis contamination in braised meatballs led to illness among customers, with the bacterium detected on the hands of the chef and waitstaff [64]. Furthermore, between August and December 2018, Fan et al. isolated P. mirabilis from 49 out of 486 diarrheal pediatric samples, yielding a detection rate of 10.1% [65]. Zhang et al. compared the feces and inflamed colon samples from Crohn’s disease (CD) patients and healthy individuals, finding a significant increase in the abundance of P. mirabilis in CD patients. The experimental results showed signs of colon shortening, and liver and spleen enlargement, indicating that P. mirabilis plays a critical role in inducing CD inflammation [15]. Additionally, Kitamoto et al. suggested that oral inflammation could exacerbate intestinal inflammation, and the use of proton pump inhibitors may promote the proliferation of P. mirabilis and other microbes in the intestines, thus triggering intestinal inflammation [66].
In animals, P. mirabilis has been associated with various cases of gastrointestinal diseases. In 2018, a bamboo rat farm in Guangdong, China reported the deaths of 400 bamboo rats due to vomiting and diarrhea, with P. mirabilis identified as the causative agent [67]. Yu et al. reported similar symptoms in 74 rhesus monkeys infected with P. mirabilis, including diarrhea and bloody stools [28]. In a rabbit farm in Henan, China, P. mirabilis (strain HN001) infection resulted in lethargy, yellow watery diarrhea, and mass fatalities, accompanied by multi-organ tissue damage [68]. In Lhasa, China, a breeding farm experienced deaths of breeding rabbits due to P. mirabilis (strain T2018) infection, presenting with diarrhea and subsequent fatality [69]. Moreover, Dong et al. identified P. mirabilis (strain 17f) as the primary pathogen responsible for diarrhea in lambs in the Hotan area of Xinjiang, China [70]. These reports underscore the significant role of P. mirabilis as a gastrointestinal pathogen in both humans and animals, with implications for public health, food safety, and animal welfare.
In addition to affecting the urinary and gastrointestinal systems, P. mirabilis has been implicated in a wide range of infections across various organs in both animals and humans. In human medicine, Mistry et al. reported the isolation of P. mirabilis from skin abscesses with an isolation rate of 21.6%, second only to methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (24.3%) [71]. In pigs, Qin et al. and Chen et al. identified P. mirabilis (GX-PM1 and GX-Y9251 strains) as a cause of respiratory symptoms such as fever and difficulty breathing. They also noted that P. mirabilis could cross the placental barrier, resulting in fetal death [72,73]. Similarly in animals, Li et al. found that P. mirabilis caused multi-organ lesions and systemic inflammation in pigs, which progressed to septicemia and death [74]. In Northern Paraná, Brazil, Sanches et al. isolated P. mirabilis strains (LBUEL-A33 and LBUEL-A34) from broiler chickens, where the bacterium induced caseous exudates and hemorrhaging in the subcutaneous tissue, leading to condemnation in poultry industry. Histopathological analysis revealed edema, congestion, and necrosis in the pectoral muscles, along with cellulitis and infiltration of inflammatory cells [75].
Furthermore, P. mirabilis has been reported to cause severe infections in other animal species. Abdollahi et al. and Ghahremani et al. were the first to document P. mirabilis-induced pyoderma and purulent pericarditis in sheep [76,77]. Sacristán et al. identified P. mirabilis as a significant causative agent of neck abscesses and bacteremia in sea lions [78]. Pattanayak et al. observed P. mirabilis-induced hemorrhaging in the glomeruli and localized necrosis with mononuclear cell infiltration in the kidneys of infected Indian carp [79].
6. Antibiotic Resistance of P. mirabilis from Animals and Animal-Derived Products
Antibiotic resistance in P. mirabilis from animals and food sources is a growing public health concern (Supplementary Table S1). In wildlife, isolates from fruit bats, wild boars, gorillas, mandrills, African buffaloes, and sea lions show intrinsic tetracycline resistance. Fruit bat isolates are susceptible to amoxicillin-clavulanate and cefoxitin but resistant to oxacillin. Sea lion isolates resist amoxicillin-clavulanate but are sensitive to cefovecin. For aminoglycosides, fruit bat isolates are amikacin-sensitive; wild boar isolates resist gentamicin; sea lion isolates resist streptomycin but remain gentamicin-sensitive. Sea lions also show resistance to doxycycline, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and azithromycin but remain susceptible to quinolones (ciprofloxacin, enrofloxacin) [19,20,21,22,23]. Wild raptors (Eurasian goshawks, barn owls) resist quinolones (ciprofloxacin, nalidixic acid), sulfonamides, and polymyxin but are aminoglycoside-sensitive [22]. Among farmed wildlife, P. mirabilis from foxes display high resistance to cefotaxime (94.4%), gentamicin (83.3%), and ampicillin (88.9%), significantly higher than raccoons and minks. Minks showed narrower resistance, remaining sensitive to cefotaxime, ceftazidime, and ofloxacin. Most isolates were imipenem-resistant (71.7%) [27].
In farmed livestock, pig isolates are multidrug-resistant (MDR), with 100% resistance to tetracyclines, ampicillin, and sulfonamides. Imipenem and kanamycin resistance reach 85.7%; gentamicin and amikacin resistance are lower (9.5%); ciprofloxacin resistance is 38.1%, fosfomycin 28.6% [34,72]. Another study found 100% pig isolates resistant to tetracyclines, chloramphenicol, and macrolides, with high ciprofloxacin resistance (76.67%) but sensitivity to meropenem. Gentamicin and amikacin resistance were 56.67% and 20%, respectively [32]. In poultry, all 50 chicken isolates in Shandong were MDR, with over 50% resistance to β-lactams (cefazolin, ceftriaxone, cefuroxime) and aminoglycosides (tobramycin, gentamicin). Resistance to ciprofloxacin, chloramphenicol, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole reached 98% [35]. Broiler isolates showed 30.7% MDR, with ciprofloxacin resistance at 61.5% and gentamicin at 38.5% [36]. Duck isolates showed 100% resistance to amoxicillin, penicillin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and doxycycline; 31.4% were extensively drug-resistant (XDR), and 8.6% pan-drug-resistant (PDR) [37]. Environmental isolates include P. mirabilis carrying blaNDM-1 from houseflies on a sheep farm [80], and multidrug-resistant strains from captured houseflies resistant to streptomycin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and amoxicillin [81].
In companion animals, 75 isolates from dogs in Chengdu showed 53.33% MDR; pet dogs had 75% MDR versus 25% in stray dogs. Pet dog isolates showed β-lactam resistance (e.g., cefotaxime 31.71%, ciprofloxacin 36.59%), while all were tetracycline-resistant (100%). Stray dog isolates remained largely susceptible [39]. This suggests that antibiotic use in pet clinics drives resistance.
From diseased animals, Portuguese companion animal isolates from UTIs showed moderate resistance to β-lactams and chloramphenicol [45]. In China, 60.22% of isolates from diarrheal animals (dogs, minks, cattle, fowl) were MDR, with 16.48% XDR. Resistance rates were high for ampicillin (59.09%), ciprofloxacin (57.39%), streptomycin (55.68%), doxycycline (63.64%), and tetracycline (55.12%) [30]. Egyptian isolates from diarrheal dogs showed 100% resistance to penicillin, amoxicillin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, with variable resistance to other β-lactams and tetracycline [46]. Fish isolates also showed MDR and XDR to eight antibiotic classes, including β-lactams and polymyxins [79].
Widespread resistance in farm animals raises public health concerns regarding food safety. MDR rates were reported as 76.5% in chicken, 46% in pork, and 6% in beef isolates; chicken strains showed the highest resistance except for chloramphenicol and florfenicol [56]. Another study of 490 strains from meat found chicken isolates had highest resistance to doxycycline (83.33%), β-lactams (82.87%), aminoglycosides (89.81%), sulfonamides (91.67%), and quinolones (54.17%), with 14.9% PDR [50]. In meat and aquatic products, 91% were MDR, with high resistance to β-lactams, quinolones, chloramphenicol, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole [49]. Interestingly, P. mirabilis from vegetables also showed multidrug resistance across β-lactams, quinolones, aminoglycosides, and tetracyclines, suggesting cross-contamination between animal and non-animal food sources [53].
In addition to genomic similarities, antibiotic resistance profiles of human- and animal-derived P. mirabilis strains also show notable similarities (see Figure 1). Marques et al. reported that P. mirabilis strains isolated from companion animals and human with UTIs in Portugal harboured common antibiotic resistance [45]. Both companion animal and human strains were sensitive to carbapenems like imipenem, meropenem, and ertapenem. Similarly, Yu et al. found higher resistance rates in poultry-derived P. mirabilis strains compared to human patient isolates for quinolones (ciprofloxacin) and penicillins (ampicillin), with poultry strains showing 48% (25/52) resistance to ciprofloxacin and 62% (32/52) resistance to ampicillin, compared to 35% (17/48) and 44% (21/48) in human isolates. Moreover, both groups exhibited two MDR profiles, suggesting the potential for cross-transmission of resistance genes [52]. These findings indicate a risk of resistance transmission between clinical and food sources.
Furthermore, similar antibiotic resistance patterns were observed between isolates from animals and those from animal-derived food (shown in Figure 1). Chinnam et al. found that 72 P. mirabilis strains (31.03%) from 232 animal and food sources were positive for β-lactamase production, including 60 strains confirmed to produce extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs), which were resistant to ceftazidime and cefotaxime but could be inhibited by β-lactamase inhibitors. About 42% of the sub-clusters contained strains from different hosts, indicating the potential for cross-contamination in slaughterhouse environments [31].
7. Antibiotic Resistance Genes Identified in P. mirabilis
Antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) contribute significantly to the resistance phenotypes of P. mirabilis isolates and have been identified across various animal sources and related products (see Supplementary Table S1). For β-lactam antibiotics, resistance genes blaOXA-1, blaPSE, blaTEM, blaCTX-M, blaSHV, blaIMP and blaNDM have been found in isolates from farmed wildlife (fox, raccoon, and mink) and wildlife in natural environments (fruit bat, wild boar, gorilla, mandrill, African buffalo, sea lion, Eurasian goshawk and barn owl). resistance genes blaOXA-48, blaTEM, blaTEM-1, blaSHV-28, blaSHV-12, blaCTX-M-G1, blaCMY-1, blaCMY-2, andhave been found in isolates from wild mammals [19,20,21,22,23,27]. In farm animals such as pigs, chickens, and ducks, a wider range of resistance genes was detected, including norA, acrB, blaOXA, blaTEM, blaCTX-M, blaNDM, blaDHA, and blaKPC [31,32,34,35,36,37,73]. Isolates from companion animals (dogs and cats) carried blaOXA-1, blaTEM, blaCTX-M, and blaDHA [39,45,46], while foodborne isolates harbored blaCTX-M, blaOXA, blaDHA, blaCMY-2, blaNDM, blaTEM, blaSHV, blaFOX, blaCIT, blaEBC, and bleMBL [31,49,53,56].
For quinolones antibiotics, resistance genes qnrA was detected in isolates from wild mammals [20]. Resistance genes qnrA and qnrC were detected in isolates from farm-raied wild animals [27], and additional genes such as qnrS, parC, qnrD, and oqxA were reported in farm animal isolates [32,34,35]. qnrA and qnrD were also found in isolates from companion animals [39,45,46], while only qnrD was identified in food-derived isolates [49,56]. Aminoglycosides resistance genes including aac(6′)-Ib-cr, aadA, aadB, aphA6, and aaC2 were identified in farmed wild animal isolates [27], while only aac(3)-II was identified in wild mammals [20]. Farm animals carried aac(6′)-Ib-cr, aph(3)-IIa, rmtB, aaC1, and aaC2 [32,34,35,73], while companion animals harboured aphAI-IAB, aac(3′)-IV, aac(6′)-Ib, and aadA1 [39,45,46]. In foodborne isolates, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, aph(4)-Ia, aadA1, aadA2, aac(3′)-Ia, aac(3)-IV, and aac(3)-IVa were detected [49,53,56].
Tetracycline resistance genes such as tetO, catI, tet(J), tetA (48), tetA, tetB, tet(C), and tetM were found in isolates from wildlife, farm animals, companion animals, and food sources [20,32,37,39,46,49,53,72,73]. Sulfonamide resistance genes (sul1, sul2, sul3, dfrIa) and chloramphenicol resistance genes (floR, catB3, cml, cmlA, stcM, cat, cat1, cat2) were widely present in isolates from farm animals (pigs, poultry) [32,35,37,72,73], companion animals (dogs, cats) [45,46], wild animals (foxes, raccoons, minks) [27], and food sources (chicken, pork, beef, vegetables, aquatic products) [49,53,56].
Resistance genes to macrolides, including mphE, ermB, mefA, and mrsD, were only reported in isolates from pigs and chickens [26,28]. The polymyxin resistance gene mcr-1 and glycopeptide resistance gene mecA were exclusively found in chicken-derived isolates [36]. fos and fosA3, related to fosfomycin resistance, were identified in isolates from pigs and chickens, as well as food sources such as chicken, pork, and aquatic products [32,49,56].
Lincosamide resistance genes cfr and lnu(F) were detected by Ma et al. and Li et al. in food sources including chicken, pork, aquatic products, and vegetables. The same teams also identified the tigecycline resistance gene tmexCD3-toprJ1 and the rifampin resistance gene arr-3, respectively [49,53]. In addition, the rifampin resistance gene arr-3 and the disinfectant resistance gene qacH were found in pig-derived isolates [32]. The co-occurrence of arr-3 and qacH may enhance resistance to rifampin and reduce susceptibility to common disinfectants, potentially compromising hygiene measures and increasing the risk of cross-contamination.
8. Perspectives
The emergence and spread of P. mirabilis across diverse animal hosts and food products, coupled with its multidrug resistance and virulence, underscore its growing importance as a zoonotic and foodborne pathogen. The widespread detection of clinically relevant ARGs such as blaNDM, mcr-1, and tmexCD3-toprJ1 in isolates from farm animals, companion animals, wildlife, and animal-derived food highlight the urgent need for integrated surveillance systems. Global genomic analyses have revealed the transmission of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) among humans, animal sources, and the environment, highlighting their critical role within the One Health framework [82]. Antibiotic residues and drug-resistant bacteria present in urban domestic sewage and agricultural breeding wastes can enter the habitats of wild animals through environmental media such as soil and water bodies. In wildlife (e.g., wildboar and raptors) that have close contact with urban and agricultural areas, strains carrying the blaSHV-12 gene have been isolated. This phenomenon indicates that the environmental pollution of drug resistance caused by human activities has extended to wild animal populations. Moreover, the identification of resistance genes in vectors such as houseflies and in contaminated slaughterhouse environments suggests overlooked transmission routes that warrant further investigation.
In terms of pathogenicity, P. mirabilis has been shown to cause similar pathological injuries in both animals and humans, suggesting a common bacterial pathogenic mechanism that is not host-specific. Pathogenicity can spread alongside the bacterium and its virulence genes, as horizontal transfer of these genes has been observed between isolates from captive pandas via mobile genetic elements [83]. Although numerous studies have reported the presence of virulence genes in P. mirabilis isolates from both animals and humans, comparative analyses of phylogenetic patterns and virulence at the genomic level between the two sources are still lacking. Notably, genomic studies have revealed a high degree of heterogeneity within P. mirabilis populations. Therefore, further investigation into the phylotypes of virulence and in-depth analysis of its pathogenic mechanisms is warranted to better understand its cross-host pathogenic potential.
Moving forward, a One Health approach should be emphasized, integrating data from human, animal, food, and environmental sectors to better understand the ecology and evolution of P. mirabilis. Molecular epidemiology tools such as whole-genome sequencing, resistome and virulome profiling, and comparative genomics will be invaluable for tracking its transmission and adaptation mechanisms. In addition, studies exploring biofilm formation, quorum sensing, and host–pathogen interactions may offer new targets for intervention. As P. mirabilis continues to adapt and spread under antibiotic selective pressure, coordinated international efforts are needed to mitigate its threat to public health and food safety.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms13092060/s1, Table S1: Antibiotic resistance of Proteus mirabilis from animals and animal-derived products.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.-L.L., S.-Y.W. and Z.Y.; validation, X.-L.L., S.-Y.W. and Z.Y.; resources, X.-L.L.; data curation, X.-L.L.; writing—original draft preparation, X.-L.L., S.-Y.W. and Z.Y.; writing—review and editing, Z.Y.; visualization, X.-L.L., S.-Y.W. and Z.Y.; supervision, Z.Y.; project administration, Z.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
During the preparation of this manuscript/study, the authors used ChatGPT-4o-2024-05-13 for the purposes of improving readability and language. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| P. mirabilis | Proteus mirabilis |
| NDR | multi-drug resistant |
| XDR | extensively drug-resistant |
| PDR | pan-drug-resistant |
References
- Adeolu, M.; Alnajar, S.; Naushad, S.; Gupta, R.S. Genome-based phylogeny and taxonomy of the ‘Enterobacteriales’: Proposal for Enterobacterales ord. nov. divided into the families Enterobacteriaceae, Erwiniaceae fam. nov., Pectobacteriaceae fam. nov., Yersiniaceae fam. nov., Hafniaceae fam. nov., Morganellaceae fam. nov., and Budviciaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 5575–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Xia, N.; Suksawat, F.; Tengjaroenkul, B.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Huang, C.; Bao, Y.; Wu, Q.; et al. Prevalence and characterization of IncQ1α-mediated multi-drug resistance in Proteus mirabilis Isolated from pigs in Kunming, Yunnan, China. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1483633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr O’hara, C.; Brenner, F.W.; Miller, J.M. Classification, Identification, and Clinical Significance of Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chai, J. Research Progress on Proteus mirabilis. Chin. J. Vet. Sci. 2017, 37, 196–200. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zahng, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. Mixed Infection and Drug Sensitivity Analysis of Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis and Coccidia from Rabbits. Acta Vet. Zootech. Sin. 2024, 55, 4204–4212. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Karaynir, A.; Salih, H.; Öncü, S.; Bozdoğan, B. Characterization, genome analysis and antibiofilm efficacy of lytic Proteus phages RP6 and RP7 isolated from University hospital sewage. Virus Res. 2023, 326, 199049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienes, L. Reproductive Processes in Proteus Cultures. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1946, 63, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y. Isolation and Identification of Proteus mirabilis Producing ESBLs from Fur Animals and Analysis of Drug Resistance and Virulence Genes. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cobbley, H.K.; Evans, S.I.; Brown, H.M.F.; Eberhard, B.; Eberhard, N.; Kim, M.; Moe, H.M.; Schaeffer, D.; Sharma, R.; Thompson, D.W.; et al. Complete Genome Sequences of Six Chi-Like Bacteriophages That Infect Proteus and Klebsiella. Microbiol. Resour. Announce. 2022, 11, e01215-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.J.; Navarro, N.; Cruz, E.; Sánchez, S.; Morales, J.O.; Zunino, P.; Robino, L.; Lima, A.; Scavone, P. First report on the physicochemical and proteomic characterization of Proteus mirabilis outer membrane vesicles under urine-mimicking growth conditions: Comparative analysis with Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1493859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzewiecka, D. Significance and Roles of Proteus Spp. Bacteria in Natural Environments. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 72, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.D.; Bens, L.; Santos, A.J.D.C.; Lavigne, R.; Soares, J.; Melo, L.D.; Vallino, M.; Dias, R.S.; Drulis-Kawa, Z.; de Paula, S.O.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of the Acadevirus Members BigMira and MidiMira Infecting a Highly Pathogenic Proteus mirabilis Strain. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coker, C.; Poore, C.A.; Li, X.; Mobley, H.L.T. Pathogenesis of Proteus mirabilis Urinary Tract Infection. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Tian, Y.; Li, X. Unveiling the hidden arsenal: New insights into Proteus mirabilis virulence in UTIs. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1465460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hoedt, E.C.; Liu, Q.; Berendsen, E.; Teh, J.J.; Hamilton, A.; O’ Brien, A.W.; Ching, J.Y.L.; Wei, H.; Yang, K.; et al. Elucidation of Proteus mirabilis as a Key Bacterium in Crohn’s Disease Inflammation. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 317–330.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, P.; Qiu, K.; Liao, Y.; Chen, X.; Xuan, J.; Wang, F.; Ma, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M. Proteus mirabilis exacerbates ulcerative colitis by inhibiting mucin production. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1556953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Pérez, A.; Corbera, J.A.; González-Martín, M.; Tejedor-Junco, M.T. Antibiotic resistance patterns of bacteria isolated from Chicks of Canarian Egyptian Vultures (Neophron percnopterus majorensis): A “One Health” Problem? Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 92, 101925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, S.; Bano, S.; Xia, X.; Baloch, Z. First Report of Complete Genome Analysis of Multiple Drug Resistance Proteus mirabilis KUST-1312 Isolate from Migratory Birds in China: A Public Health Threat. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2024, 2024, 8102506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, S.; Rizal, S.; Sopha Sushadi, P.; Supriatna, N. Identification and Antibiotic Resistance Profile of Bacteria from Fruit Bat (Chironax melanocephalus). Adv. Biol. Sci. Res. 2021, 14, 478–484. [Google Scholar]
- Selmi, R.; Tayh, G.; Srairi, S.; Mamlouk, A.; Ben Chehida, F.; Lahmar, S.; Bouslama, M.; Daaloul-Jedidi, M.; Messadi, L. Prevalence, risk factors and emergence of extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing-, carbapenem- and colistin-resistant Enterobacterales isolated from wild boar (Sus scrofa) in Tunisia. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 163, 105385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguema, P.P.M.; Onanga, R.; Atome, G.R.N.; Tewa, J.J.; Mabika, A.M.; Nzambe, J.U.M.; Mbeang, J.C.O.; Essono, P.Y.B.; Bretagnolle, F.; Godreuil, S. High level of intrinsic phenotypic antimicrobial resistance in enterobacteria from terrestrial wildlife in Gabonese national parks. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257994. [Google Scholar]
- Darwich, L.; Vidal, A.; Seminati, C.; Albamonte, A.; Casado, A.; López, F.; Molina-López, R.A.; Migura-Garcia, L. High prevalence and diversity of extended-spectrum β-Lactamase and emergence of OXA-48 producing Enterobacterales in wildlife in Catalonia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliopulos, N.; Alsina, L.; Diana, L.; Brandl, S. Multiple antibiotic resistance in Enterobacteriaceae isolated from a Sea Lion (Otaria flavescens) specimen from Isla de Lobos, Uruguay: A case report. Braz. J. Anim. Environ. Res. 2022, 5, 3477–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergunay, K.; Mutinda, M.; Bourke, B.; Justi, S.A.; Caicedo-Quiroga, L.; Kamau, J.; Mutura, S.; Akunda, I.K.; Cook, E.; Gakuya, F.; et al. Metagenomic Investigation of Ticks from Kenyan Wildlife Reveals Diverse Microbial Pathogens and New Country Pathogen Records. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 932224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zheng, W.; Huang, H.; Liu, S.; Yang, M.; Yan, X.; Li, Y.; Yue, C.; Hou, R.; Zhang, D. Establishment and application of multiplex PCR detection method for Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli from giant panda. Chin. J. Prev. Vet. Med. 2023, 45, 598–603. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Su, X.; Yue, C.; E.Ayala, J.; Yan, X.; Hou, R.; Li, L.; Xie, Y.; et al. Mortality analysis of captive red panda cubs within Chengdu, China. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Hao, G.; Cao, Y.; Cui, L.; Wang, G.; Sun, S. Detection of Carbapenem Resistance of Proteus mirabilis Strains Isolated from Foxes, Raccoons and Minks in China. Biology 2022, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; He, Z.; Huang, F. Multidrug-Resistant Proteus mirabilis Isolated from Newly Weaned Infant Rhesus Monkeys and Ferrets. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2015, 8, e16822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Wang, W.; Tong, P.; Liu, C.; Jia, J.; Lu, C.; Han, Y.; Sun, X.; Kuang, D.; Li, N.; et al. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Proteus Spp. Isolated from Tree Shrews Indicated Unexpectedly High Genetic Diversity. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wen, S.; Zhao, L.; Xia, Q.; Pan, Y.; Liu, H.; Wei, C.; Chen, H.; Ge, J.; Wang, H. Association among biofilm formation, virulence gene expression, and antibiotic resistance in Proteus mirabilis isolates from diarrhetic animals in Northeast China. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnam, B.K.; Nelapati, S.; Tumati, S.R.; Bobbadi, S.; Peddada, V.C.; Bodempudi, B. Detection of β-Lactamase-Producing Proteus mirabilis Strains of Animal Origin in Andhra Pradesh, India and Their Genetic Diversity. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 1374–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Zhou, J.; Huang, H.; Wang, W.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, B.; Liu, H.; Xu, C.; Xiao, X. Genomic Investigation of Proteus mirabilis Isolates Recovered from Pig Farms in Zhejiang Province, China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 952982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costinar, L.; Herman, V.; Pitoiu, E.; Iancu, I.; Degi, J.; Hulea, A.; Pascu, C. Boar Semen Contamination: Identification of Gram-Negative Bacteria and antibiotic Resistance Profile. Animals 2022, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Ma, D.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Yuan, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X. Isolation, Identification and Biological Characteristics of Proteus mirabilis of Swine. China Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2021, 48, 1804–1815. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Peng, C.; Zhang, G.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, F. Prevalence and characteristics of multidrug-resistant Proteus mirabilis from broiler farms in Shandong Province, China. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramatla, T.; Ramaili, T.; Lekota, K.; Mileng, K.; Ndou, R.; Mphuthi, M.; Khasapane, N.; Syakalima, M.; Thekisoe, O. Antibiotic resistance and virulence profiles of Proteus mirabilis isolated from broiler chickens at abattoir in South Africa. Vet. Med. Sci. 2024, 10, e1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algammal, A.M.; Hashem, H.R.; Alfifi, K.J.; Hetta, H.F.; Sheraba, N.S.; Ramadan, H.; El-Tarabili, R.M. atpD gene sequencing, multidrug resistance traits, virulence-determinants, and antibiotic resistance genes of emerging XDR and MDR-Proteus mirabilis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.; Belas, A.; Menezes, J.; da Silva, J.M.; Cavaco-Silva, P.; Trigueiro, G.; Gama, L.T.; Pomba, C. Human and Companion Animal Proteus mirabilis Sharing. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 13, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Dong, Z.; Ai, S.; Chen, S.; Dong, M.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhong, Z.; Ma, X.; et al. Virulence-related factors and antibiotic resistance in Proteus mirabilis isolated from domestic and stray dogs. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1141418. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, J.D.; Mavrides, D.E.; Graham, P.A.; McHugh, T.D. Results of urinary bacterial cultures and antibiotic susceptibility testing of dogs and cats in the UK. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 62, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyaert, H.; Morrissey, I.; De Jong, A.; El Garch, F.; Klein, U.; Ludwig, C.; Thiry, J.; Youala, M. Antibiotic Susceptibility Monitoring of Bacterial Pathogens Isolated from Urinary Tract Infections in Dogs and Cats across Europe: ComPath Results. Microb. Drug Resist. 2017, 23, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amphaiphan, C.; Yano, T.; Som-in, M.; Kungwong, P.; Wongsawan, K.; Pusoonthornthum, R.; Salman, M.D.; Tangtrongsup, S. Antibiotic drug resistance profile of isolated bacteria in dogs and cats with urologic problems at Chiang Mai University Veterinary Teaching Hospital, Thailand (2012–2016). Zoonoses Public Health 2021, 68, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Kong, L.; Dong, W.; Liu, S.; Gao, Y.; Ma, H.; Luan, W. Isolation identification and biological characteristics of Proteus mirabilis of canine. Heilongjiang Anim. Sci. Vet. Med. 2020, 68, 72–76+154. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, Z. Isolation, Identification and Drug Susceptibility of Proteus mirabilis Isolates from Dogs in Weifang City. Chin. J. Anim. Infect. Dis. 2022, 30, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, C.; Belas, A.; Aboim, C.; Trigueiro, G.; Cavaco-Silva, P.; Gama, L.T.; Pomba, C. Clonal relatedness of Proteus mirabilis strains causing urinary tract infections in companion animals and humans. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 228, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Tarabili, R.M.; Ahmed, E.M.; Alharbi, N.K.; Alharbi, M.A.; AlRokban, A.H.; Naguib, D.; Alhag, S.K.; El Feky, T.M.; Ahmed, A.E.; Mahmoud, A.E. Prevalence, antibiotic profile, virulence determinants, ESBLs, and non-β-lactam encoding genes of MDR Proteus Spp. isolated from infected dogs. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 952689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirana, H.N.K.S.; De Silva, B.C.J.; Wimalasena, S.H.M.P.; Hossain, S.; Heo, G.J. Comparison of virulence genes in Proteus species Isolated from human and pet turtle. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 19, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Sanches, M.S.; Rodrigues da Silva, C.; Silva, L.C.; Montini, V.H.; Lopes Barboza, M.G.; Migliorini Guidone, G.H.; Dias de Oliva, B.H.; Nishio, E.K.; Faccin Galhardi, L.C.; Vespero, E.C.; et al. Proteus mirabilis from community-acquired urinary tract infections (UTI-CA) shares genetic similarity and virulence factors with isolates from chicken, beef and pork meat. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 158, 105098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.Q.; Han, Y.Y.; Zhou, L.; Peng, W.Q.; Mao, L.Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, T.J.; Wang, H.N.; Lei, C.W. Contamination of Proteus mirabilis harbouring various clinically important antibiotic resistance genes in retail meat and aquatic products from food markets in China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1086800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.; Hu, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, C.; Bi, S. Prevalence and Antibiotics Resistance of Proteus mirabilis in Raw Meat. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2023, 44, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Edris, S.N.; Hamad, A.; Awad, D.A.B.; Sabeq, I.I. Prevalence, antibiotic resistance patterns, and biofilm formation ability of Enterobacterales recovered from food of animal origin in Egypt. Vet. World 2023, 16, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Joossens, M.; Van den Abeele, A.M.; Kerkhof, P.J.; Houf, K. Isolation, characterization and antibiotic resistance of Proteus mirabilis from Belgian broiler carcasses at retail and human stool. Food Microbiol. 2021, 96, 103724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.A.; Guo, C.H.; Yang, T.Y.; Li, F.Y.; Song, F.J.; Liu, B.T. Whole-Genome Analysis of blaNDM-Bearing Proteus mirabilis Isolates and mcr-1-Positive Escherichia coli Isolates Carrying blaNDM from the Same Fresh Vegetables in China. Foods 2023, 12, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Liu, N.; Liu, Y.; Du, J. Quantitative PCR Detection and Drug Resistance Analysis of Proteus mirabilis in Fresh Chicken meat. Agri. Prod. Process 2022, 24, 63–67+71. [Google Scholar]
- Zaher, A.H.; Kabadaia, M.M.; Hammad, K.M.; Mekky, A.E.; Salem, S.S. Forensic flies as carries of pathogenic bacteria associated with a pig carcass in Egypt. Al-Azhar Bull. Sci. 2023, 34, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, M.S.; Silva, L.C.; da Silva, C.R.; Montini, V.H.; Oliva, B.H.D.d.; Guidone, G.H.M.; Nogueira, M.C.L.; Menck-Costa, M.F.; Kobayashi, R.K.T.; Vespero, E.C.; et al. Prevalence of antibiotic Resistance and Clonal Relationship in ESBL/AmpC-Producing Proteus mirabilis Isolated from Meat Products and Community-Acquired Urinary Tract Infection (UTI-CA) in Southern Brazil. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, T.; Linhares, I.; Ferreira, R.; Neves, J.; Almeida, A. Frequency and Antibiotic Resistance of Bacteria Implicated in Community Urinary Tract Infections in North Aveiro between 2011 and 2014. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, J.N.; Pearson, M.M. Proteus mirabilis and Urinary Tract Infections. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, 383–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakkour, M.; Hammoud, Z.; Farhat, S.; El Roz, A.; Ezzeddine, Z.; Ghssein, G. Overview of Proteus mirabilis pathogenicity and virulence. Insights into the role of metals. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1383618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiz, T.A.; Alghamdi, G.S.; Alkudmani, Z.S.; Alyami, A.S.; Almazyed, A.; Alhumaidan, O.S.; Mubaraki, M.A.; Alotaibi, F.E. Multidrug-Resistant Proteus mirabilis Infections and Clinical Outcome at Tertiary Hospital in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Infect. Drug Resist. 2024, 17, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Ruan, H.; Yang, H.; Mu, H.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ge, Y.; Zheng, J. Study on identification, biological characteristic of Proteus mirabilis isolated from canine and its ability to induced calculus formation. Heilongjiang Anim. Sci. Vet. Med. 2021, 68, 80–84, 163. [Google Scholar]
- Herout, R.; Khoddami, S.; Moskalev, I.; Reicherz, A.; Chew, B.H.; Armbruster, C.E.; Lange, D. Role of Bacterial Surface Components in the Pathogenicity of Proteus mirabilis in a Murine Model of Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection. Pathogens 2023, 12, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Shi, X.; Bai, F.; He, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Lin, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, Q.; et al. Characterization of a Novel Diarrheagenic Strain of Proteus mirabilis Associated with Food Poisoning in China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yu, J.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Song, H. An outbreak of Proteus mirabilis food poisoning associated with eating stewed pork balls in brown sauce, Beijing. Food Control. 2010, 21, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Ni, K. Etiological characteristics and clinical features analysis of 486 pediatric diarrhea cases caused by Proteus mirabilis. Chin. J. Rural Med. Pharm. 2021, 28, 52–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto, S.; Nagao-Kitamoto, H.; Jiao, Y.; Gillilland, M.G.; Hayashi, A.; Imai, J.; Sugihara, K.; Miyoshi, M.; Brazil, J.C.; Kuffa, P.; et al. The Intermucosal Connection between the Mouth and Gut in Commensal Pathobiont-Driven Colitis. Cell 2020, 182, 447–462.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Zhai, S.; Lv, Y.; Wen, X.; Wu, G.; Huo, W.; Tu, D.; Wei, W.; Jia, C.; Zhou, X. Isolation, Identification and Drug Resistance of Proteus mirabilis from Bamboo Rats. Chin. J. Anim. Infect. Dis. 2021, 29, 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Wei, L.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y. Isolation, identification and pathogenicity analysis of Proteus mirabilis from rabbits. Chin. J. Prev. Vet. Med. 2024, 46, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Jin, H.; Hou, S.; Feng, J. Isolation, Identification and Drug Resistance Analysis of Rabbit Proteus mirabilis. China Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2019, 46, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.; Yang, G.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Hr, J.; Tao, D. Isolation and identification of Proteus mirabilis from diarrhea lamb in Xinjiang and its pathogenicity in mice. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2022, 54, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Mistry, R.D.; Scott, H.F.; Alpern, E.R.; Zaoutis, T.E. Prevalence of Proteus mirabilis in Skin Abscesses of the Axilla. J. Pediatr. 2010, 156, 850–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; He, C.; Li, C.; Zeng, W.; Ma, L.; Liu, J.; Bai, A.; Yang, L.; Wu, J. Isolation, and identification and biological-charactistics of swine-sourced Proteus mirabils producing AmpC enzyme. Chin. J. Anim. Infect. Dis. 2023, 31, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Ma, L.; Qin, S.; Chen, Y.; Song, R.; Sun, Q.; Qin, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, F.; Wu, J. Isolation, identification and biological characteristics of swine-sourced Proteus mirabilis producing AmpC enzyme. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2023, 55, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Wang, B.; Shu, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, T.; Tang, D.; Wu, X. Isolation and identification of swine-sourced Proteus mirabilis, and detection of its drug resistance and virulence genes. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2021, 53, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Sanches, M.S.; Baptista, A.A.S.; de Souza, M.; Menck-Costa, M.F.; Justino, L.; Nishio, E.K.; Oba, A.; Bracarense, A.P.F.R.L.; Rocha, S.P.D. Proteus mirabilis causing cellulitis in broiler chickens. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2020, 51, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, M.; Javan, A.J.; Shokrpoor, S.; Beidokhtinezhad, M.; Tamai, I.A. Pyoderma caused by Proteus mirabilis in sheep. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 2562–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najd Ghahremani, A.; Abdollahi, M.; Shokrpoor, S.; Ashrafi Tamai, I. Pericarditis caused by Proteus mirabilis in sheep. Vet. Med. Sci. 2023, 9, 1737–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacristán, C.; Costa-Silva, S.; Reisfeld, L.; Navas-Suárez, P.E.; Ewbank, A.C.; Duarte-Benvenuto, A.; Coelho Couto de Azevedo Fernandes, N.; Albergaria Ressio, R.; Antonelli, M.; Rocha Lorenço, J.; et al. Novel alphaherpesvirus in a wild South American sea lion (Otaria byronia) with pulmonary tuberculosis. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 2489–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattanayak, S.; Kumar, P.R.; Sahoo, M.K.; Paul, A.; Sahoo, P.K. First field-based Evidence of association of Proteus mirabilis causing large scale mortality in Indian major carp farming. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Chen, G.; Dong, N. Isolation of four carbapenem-resistant gram-negative species from a single fly. Anim. Dis. 2024, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odetoyin, B.; Adeola, B.; Olaniran, O. Frequency and antibiotic Resistance Patterns of Bacterial Species Isolated from the Body Surface of the Housefly (Musca Domestica) in Akure, Ondo State, Nigeria. J. Arthropod Borne Dis. 2020, 14, 88–96. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Zhu, D.; Zhao, X.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Q.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Proteus Mirabilis: Unraveling Global Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance Dissemination—Emerging Challenges for Public Health and Biosecurity. Environ. Int. 2025, 199, 109487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Wu, R.; Xin, J.; Yang, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhong, Z.; Fu, H. Proteus mirabilis from Captive Giant Pandas and Red Pandas Carries Diverse Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Virulence Genes Associated with Mobile Genetic Elements. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).