Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus aureus is a major zoonotic and foodborne pathogen with substantial One Health implications, yet its prevalence, resistance, and virulence potential within the aquaculture sector in Nigeria remains poorly characterized. Objectives: To supplement existing information, this current study investigated the prevalence, clonal distribution, antimicrobial resistance, and virulence gene profiles of S. aureus isolates from fish, fish water, and occupationally exposed fish handlers in Anambra State, Southeast Nigeria. Methods: A total of 607 samples—comprising 465 surface swabs from raw and processed fish, 36 fish water samples, and 106 nasal swabs from fish handlers—were processed using selective culture, biochemical tests, antimicrobial susceptibility testing, DNA microarray analysis, spa typing, and SCCmec typing. Results: S. aureus was recovered from 16.5% (100/607) of the samples. Fourteen (14%) isolates were methicillin-resistant (MRSA), harboring mecA and SCCmec types IV and V, with a combined MRSA prevalence of 2.3%. Multidrug resistance was observed in 52.2% of isolates (mean Multiple Antimicrobial Resistance index: 0.23), with 19 resistance genes spanning nine antimicrobial classes—including heavy metal and biocide resistance. Twenty-eight spa types across 13 clonal complexes (CCs) were identified, with CC1, CC5, and CC8 predominating. The detection of shared spa types between fish and handlers indicates potential cross-contamination. Detected virulence genes included those for accessory gene regulators (agrI-IV), Pantone–Valentine leucocidin (lukFS-PV), toxic shock syndrome (tsst-1), hemolysins (hla, hlb, hld/hlIII, hlgA), biofilm formation (icaA, icaD), immune evasion (chp, scn, sak), enterotoxins (sea, seb, sec, sed, egc, and others), exfoliative toxins (etA, etB), epidermal cells differentiation (edinA, edinB), and capsular types (cap5, cap8). Conclusions: This study reveals that the aquaculture sector in Southeast Nigeria serves as a significant reservoir of genetically diverse, multidrug-resistant S. aureus strains with robust virulence profiles. These findings highlight the necessity of integrated One Health surveillance and targeted interventions addressing antimicrobial use and hygiene practices within aquatic food systems.
1. Introduction
Staphylococcus aureus is a highly adaptable bacterium that colonizes the skin and mucous membranes of humans and animals. It can cause a wide range of infections, including skin and soft tissue infections, septicemia, food poisoning, and bone and joint diseases. Its pathogenicity is driven by an array of virulence factors regulated by global systems such as the accessory gene regulator (agr) and staphylococcal accessory regulator (sar) [1]. These systems control the expression of structural and secreted virulence factors—including biofilms, hemolysins, Panton–Valentine leukocidin (PVL), exfoliative toxins, epidermal cell differentiation inhibitors (EDINs), and toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1)—that facilitate colonization, immune evasion, and host tissue damage [1,2]. Foodborne S. aureus is among major causes of staphylococcal food poisoning (SFP), characterized by abdominal cramps, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever. This condition results from ingestion of preformed, heat-stable enterotoxins that act as superantigens that disrupt the immune homeostasis by bypassing antigen presentation, triggering excessive cytokine production and impairing adaptive immune responses [3]. Toxigenic S. aureus strains may enter the food chain through contamination by infected or colonized food handlers, respiratory secretions, or unsanitary processing environments [4]. Although SFP is typically self-limiting, it can cause severe illnesses requiring hospitalization. However, its true incidence is often underestimated due to misdiagnosis, underreporting, or its sporadic occurrence [3,4]. In Nigeria, as in many other developing countries, inadequate food safety regulations, poor sanitation, and improper food storage practices contribute to elevated rates of S. aureus food contamination and bacterial proliferation [5,6]. SFP contributes to both direct and indirect economic losses, with disproportionately severe impacts in low- and middle-income countries [5]. While the economic burden of SFP appear underestimated at US$57,670 annually, the global economic impact of foodborne diseases projects to reach approximately US$95.2 billion per year, driven predominantly by healthcare expenditures and legal/reputational consequences as well as productivity losses [5,7].
Importantly, the clinical impact of S. aureus is compounded by its capacity to acquire antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs), including those conferring resistance to last-line agents such as methicillin and vancomycin. For instance, those of methicillin resistance, encoded by the mecA or mecC genes within the staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec), renders the organism resistant to virtually all β-lactam antibiotics. SCCmec types I–XV can also harbor genes for resistance to other antimicrobials and heavy metals, further complicating treatment. Both methicillin-resistant (MRSA) and methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) strains are frequently multidrug-resistant (MDR), representing a serious global health challenge. Between 2019 and 2021, S. aureus contributed to an estimated one million of the 127 million deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance globally [8,9,10]. In response, the World Health Organization (WHO) has classified S. aureus as a priority pathogen for surveillance and control within the One Health framework [11]. The organism’s ability to form biofilms exacerbates treatment difficulty, shielding it from antibiotics and host defenses [1,12]. Molecular tools such as DNA microarrays enable high-resolution genotyping of S. aureus via spa typing, multi-locus sequence typing (MLST), SCCmec classification, agr typing, and detection of virulence and resistance genes. These methods help characterize transmission dynamics across healthcare, community, and animal settings. Based on genotypic features, MRSA strains are categorized into healthcare-associated (HA-MRSA), community-associated (CA-MRSA), or livestock-associated (LA-MRSA) lineages. LA-MRSA, commonly of clonal complex (CC) 398, has been found in both animal products and community settings. SCCmec types I–III are primarily linked with HA-MRSA, while types IV and V are associated with CA-MRSA [13]. The agr system—a quorum-sensing regulator comprising RNAII (agrB, agrD, agrC, agrA) and RNAIII transcripts—controls biofilm formation and toxin expression. Four agr types (I–IV) are known, with distinct virulence patterns associated with each [14].
While studies from Egypt [15], South Africa [16], Asia [13,17,18], and Europe [19,20,21] have profiled S. aureus from fish and aquatic environments, the data specific to Nigeria appear limited. More so, most local (food) safety/epidemiological related studies in Nigeria have largely focused on human, animal, and animal-derived food samples [6], with minimal molecular characterization of isolates specific to fish and related environments [22]. Although fish are not natural hosts for staphylococci, contamination can occur via polluted water, human contact, or poor hygiene during handling and processing [4,23]. This situation is particularly applicable to Nigeria, where the unregulated antimicrobial use in aquaculture and widespread water pollution from industrial and agricultural sources [24,25], foster the selection and spread of resistant pathogens. In addition, fish remains a dietary staple in Nigeria, contributing to about 40% of the national protein intake, with per capita consumption estimated at 13.3 kg/year [26]. Traditional preservation methods such as smoking and oven-drying, often carried out under suboptimal hygienic conditions, increase the risk of S. aureus contamination and SFP. As the consumption of raw or undercooked fish [13] continues to emerge, this risk would further exacerbate. Occupational exposure in aquaculture settings combined with the use of fishpond effluents for irrigation [25] facilitates the environmental spread of S. aureus to humans, food crops, and wider ecosystem. Indeed, understanding the association between S. aureus antimicrobial resistance patterns, clonal lineages, and virulence gene profiles is essential for designing targeted public health interventions and informing empirical therapy. Therefore, to supplement existing information, this current study aimed to investigate the prevalence, molecular characteristics (including clonal structure, resistance determinants, and virulence profiles), and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of S. aureus isolates from raw farmed and captured African catfish (Clarias spp.), fish water (fishpond, fish processing and river water), and occupationally exposed fish handlers in Anambra State, Southeast Nigeria.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Schematic Overview of the Experimental Program
The schematic representation of the experimental program (Figure 1) illustrates the principal stages of this study, beginning with the sampling of African catfish, pond water, and fish handlers/owners, and extending through bacterial isolation, identification, and subsequent analytical characterization. This research was specifically designed to investigate the prevalence, clonal distribution, antimicrobial resistance, and virulence gene profiles of Staphylococcus aureus isolates derived from fish, aquaculture water, and occupationally exposed handlers in Anambra State, Southeast Nigeria. The selected sampling sites were considered representative of the region, and all sampling procedures were conducted in accordance with ethical guidelines and good laboratory practices established by the Department of Veterinary Public Health and Preventive Medicine, University of Nigeria, Nsukka. Furthermore, all chemicals employed in this study were of analytical grade and sourced from certified suppliers.
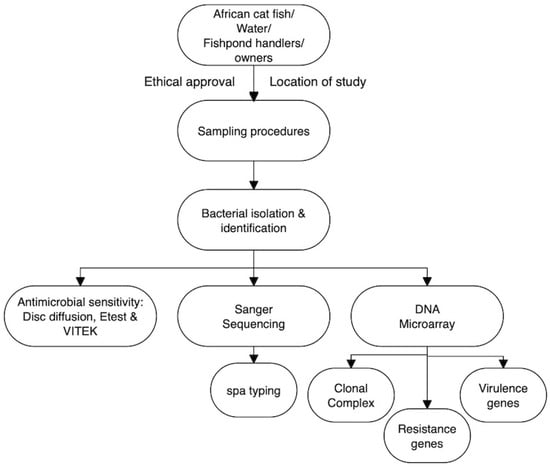
Figure 1.
The schematic overview of the experimental program showing the major stages of this current work, from the targeted African catfish, water from the fishponds, and the handlers/owners (of those fishponds), through sampling procedures, to the bacterial isolation, identification, and subsequent analytical/characterization. Etest and VITEK = ETEST® &VITEK brand associated with bioMérieux; spa typing = Staphylococcal Protein A (spa) Typing (Figure drawn using Flowchart Designer 5 Software Version 1.2.25, Apple Inc., California, USA).
2.2. Ethical Approval
This study received ethical clearance from the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Nigeria (Protocol No. FVM-UNN-IACUC-2019–0143, approved 5 January 2019) and the Ethics Committee of Chukwuemeka Odimegwu Ojukwu University Teaching Hospital, Awka (Protocol No. COOUTH/CMAC/ETH.C/VOL.1/FN:04/243, approved 15 May 2019). The study was conducted in accordance with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki (2024) [27]. Prior to sample collection, both verbal and written informed consent were obtained from all fishpond owners and fish handlers who participated in the study.
2.3. Sampling
A cross-sectional study was conducted between October 2019 and February 2020 across three Local Government Areas (LGAs), each representing one senatorial zone of Anambra State, Nigeria (Figure 1). The LGAs were selected based on the presence of fish farms, markets, and processing facilities. In each LGA, one major town—Awka, Nnewi, and Onitsha—was selected based on its notable involvement in African catfish (ACF; Clarias spp.) farming and oven-drying, and one fish farm was chosen from each town. Additionally, two fishing communities, Ose and Otuocha, where only smoking is used for fish preservation, were included (Figure 2). Weekly visits were made to these towns, during which a total of 465 ACF were randomly sampled. These included 246 freshly captured fish—64 farmed fish, 138 smoked captured fish, and 17 oven-dried farmed fish. Additionally, 36 water samples were collected, which included 24 from rivers and 12 from fishponds. A total of 106 occupationally exposed individuals involved in fish processing (70 using smoking and 36 using oven-drying were also randomly selected for sampling after obtaining written informed consent. About 5 cm2 area of the skin and freshly cut surfaces in raw fish and processed fish samples were swabbed using sterile swabs. Water samples were aseptically collected by immersing autoclaved 100 mL wide-mouth bottles with screw caps directly into the water (fish-holding [river and fishpond] and fish-processing waters) using gloved hands. Nasal swabs were obtained from each of the 76 fish handlers using sterile swabs. All fish and human samples represented approximately 5% and 50%, respectively, of the total individuals and fish available during the study period. Samples were transported on ice to the Microbiology Laboratory, Department of Veterinary Public Health and Preventive Medicine, University of Nigeria, and processed either immediately or within 24 h of collection for the isolation of Staphylococcus aureus. Importantly, all sampling procedures adhered to good laboratory practices prescribed by the Department of Veterinary Public Health and Preventive Medicine, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Nigeria.
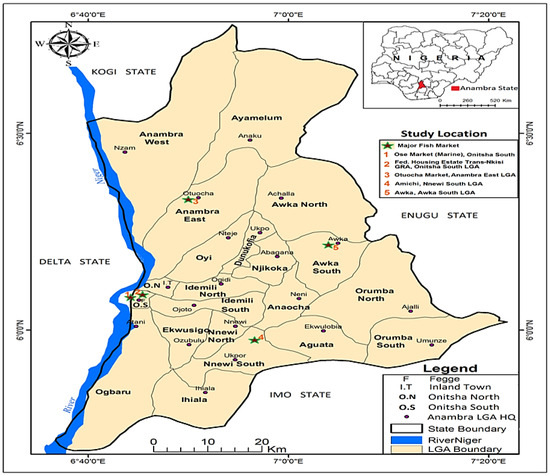
Figure 2.
Map of Anambra State, Nigeria showing Local Government Areas and fishing communities (star 1–5) where fish, fish waters, and fish handlers were sampled.
2.4. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
Swab samples were selectively enriched in 5 mL nutrient broth (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) supplemented with 6.5% NaCl and incubated aerobically at 35 ± 2 °C for 24 h. Following incubation, a loopful of the enriched culture was streaked onto Baird-Parker Agar (BPA) (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) containing egg yolk tellurite (EYT) and incubated in ambient air at 35 ± 2 °C for 48 h. Water samples (100 mL) were filtered through 0.45 µm membranes, which were placed directly on BPA and similarly incubated. Presumptive S. aureus colonies (black, shiny colonies with clear halos, with or without opaque zones) were sub-cultured on BPA with EYT for purification. Purified colonies were subjected to Gram staining and tested using catalase, slide and tube coagulase, and S. aureus-specific latex agglutination (Pastorex Staph-plus, Bio-Rad, Marnes-la-Coquette, France). Hemolysis was assessed on 5% sheep blood agar incubated aerobically at 35 ± 2 °C for 24 h. Isolates phenotypically identified as S. aureus were further confirmed and characterized using DNA microarray analysis capable of detecting 330 genetic determinants. For emphasis, the DNA microarray analysis was conducted at the Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, Safat, Kuwait.
2.5. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of S. aureus isolates was conducted using the disk diffusion method, following the guidelines of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI M100-ED35:2025) [28]. This method was selected because S. aureus is not covered under the aquatic-specific CLSI VET03/VET04 standards [29,30]. A total of 16 antimicrobial agents representing 11 different classes were tested using antibiotic-impregnated disks (Oxoid, Hampshire, UK): β-lactams—penicillin (10 units) and cefoxitin (30 μg), aminoglycosides—gentamicin (10 μg), fluoroquinolones—ciprofloxacin (5 μg), macrolides—erythromycin (15 μg), lincosamides—clindamycin (2 μg), lipoglycopeptides—teicoplanin (30 μg), phenicols—chloramphenicol (30 μg), tetracyclines—tetracycline (10 μg), ansamycins—rifampicin (5 μg), folate pathway inhibitors—trimethoprim (5 μg), and monoxycarbolic acid—mupirocin (200 μg). In addition, amikacin (30 μg, aminoglycoside) and fusidic acid (10 μg; fusidanes steroidal antibiotic), and tigecycline (glycylcycline class) were, respectively, tested using the disk diffusion and minimum inhibition concentration (MIC) methods as per the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST v.15, 2025) guidelines [31]. Isolates were adjusted to a 0.5 McFarland turbidity standard (approximately 1.5 × 108 colony-forming unit (CFU)/mL) and uniformly spread onto Mueller–Hinton agar plates (Oxoid, Hampshire, UK). Antibiotic disks were applied within 15 min of inoculation, ensuring a minimum spacing of 24 mm (center to center). All plates were incubated aerobically at 35 ± 2 °C: minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) for cefoxitin, vancomycin (glycopeptides class), and teicoplanin were determined using ETEST® strips (bioMérieux, Marcy l’Étoile, France) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions and the results interpreted as per the CLSI guidelines [28]. Inducible clindamycin resistance was assessed by the D-test [28]. Briefly, a 0.5 McFarland suspension of each isolate was spread onto Mueller–Hinton agar, and erythromycin (15 μg) and clindamycin (2 μg) disks were placed 15–26 mm apart within 15 min. Plates were incubated at 35 ± 2 °C for 18–24 h. The appearance of a D-shaped zone of inhibition adjacent to the erythromycin disk indicated inducible clindamycin resistance. Alternatively, hazy growth around the clindamycin disk, in the absence of a D-zone, was interpreted as resistance [28]. Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 was used as a quality control strain for disk diffusion testing while S. aureus ATCC 29213 was used as control for MIC determination. The multiple antibiotic resistance index (MARI) was calculated for each isolate using the formula a/b, where a is the number of antibiotics to which the isolate was resistant, and b is the total number of antibiotics tested. Isolates resistant to three or more antimicrobial classes were classified as multidrug-resistant (MDR) [32].
2.6. Molecular Typing of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates
2.6.1. Extraction of Genomic DNA for Amplification
S. aureus genomic DNA was obtained from a 24 h-old culture on 5% Columbia blood agar (Oxoid, Hampshire, UK). A prelysis step was conducted as previously described [33]. Thereafter, the DNA was extracted using the DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s protocol
2.6.2. Staphylococcal Protein A (spa) Typing and DNA Microarray Analysis
spa typing was performed by sequencing the hyper-variable region of the protein A gene (spa) following a previously described method [34,35]. The DNA microarray analysis was used to assess the presence of antimicrobial resistance genes and to assign the isolates to clonal complexes (CCs) using the S. aureus Genotyping Kit 2.0 system microarray-based assay (Abbott Rapid Diagnostics GmbH, Jena, Germany). The DNA microarray was performed as described by Monecke et al. [36,37].
2.7. Statistical Analysis
The frequencies of occurrence of S. aureus, spa types, clonal complexes, SCCmec types, resistance and virulence genes, and phenotypic resistance of the isolates to antimicrobial agents were entered into Microsoft Excel version 2010 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, USA) and subjected to descriptive statistics to determine their percentages. Associations between categorical variables were assessed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 31, applying two-tailed Fisher’s exact tests for independence in 2 × 2 contingency tables. Statistical significance was determined at a threshold of p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus
Out of 607 samples comprising fish (n = 465), fish waters (n = 36), and nasal swabs from fish handlers (n = 106), 100 non-duplicate S. aureus isolates were recovered, resulting in an overall prevalence of 16.5% (100/607) (Table 1). Prevalence rates by source were 15.5% in fish, 5.6% in water, and 24.5% in fish handlers. No statistically significant association (p > 0.05) was observed between isolation rates and sample type.

Table 1.
Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus in fish, fish waters, and fish handlers.
Of the 100 isolates, 14 (14%) were resistant to cefoxitin and were classified as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), yielding an overall MRSA prevalence of 2.3% (14/607) (Table 1). The source-specific MRSA prevalence was 2.4% in fish and 2.8% in fish handlers; none was detected in fish water. The remaining 86 isolates were methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA), corresponding to a 24% prevalence.
3.2. spa Typing and Distribution of Clonal Complex (CC) of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates
The 100 S. aureus isolates were assigned to 28 distinct spa types, with t948 (n = 16; 16%) and t311 (n = 12; 12%) being the most prevalent, collectively accounting for 28% of all isolates (Table 2). Other notable spa types included t355 (8%) and t091 (7%). Six isolates (6%) were typed as t094 and t5911, while five (5%) were typed as t002 and t3040. Four isolates (4%) belonged to t189, and three each to t174, t315, t044, and t1814. Two isolates (2%) each were identified as t064, t1476, t6675, and t605, while one isolate (1%) each belonged to t084, t934, t1931, t6275, t1299, t4690, t2723, t2049, t1400, t5227, and t693.

Table 2.
Distribution of spa types and clonal complexes of S. aureus from fish, fish waters, and fish handlers.
DNA microarray analysis grouped the isolates into 13 clonal complexes (CCs) (Table 2), with the majority belonging to CC1 (n = 21), CC5 (n = 19), and CC152 (n = 11). CC1 was detected in isolates from fish and fishpond water, whereas isolates representing other CCs (CC5, CC6, CC7, CC15, CC45, CC152, CC80, CC88, CC361, and CC188) were obtained from fish and fish handlers (Figure 3). Of the 72 isolates from fish, 23 spa types and 13 CCs were identified, while the 26 isolates from fish handlers comprised 13 spa types and 10 CCs. Only four spa types associated with three CCs were linked to MRSA isolates. These were t091-CC7 (n = 7), t064-CC8 (n = 2), and t1476-CC8 (n = 2) from fish, and t1814-CC88 from a fish handler. Of the 13 CCs, only CC88 included both MRSA and MSSA spa types. Notably, none of the spa types were shared between MRSA and MSSA isolates.
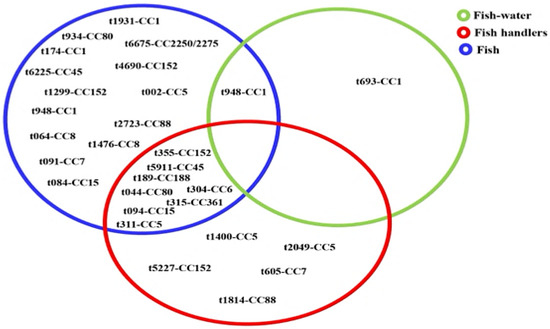
Figure 3.
Distribution of 28 spa-clonal complexes of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from fish, fish waters, and fish handlers.
3.3. Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates
The antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of the 100 S. aureus isolates against 16 antimicrobial agents are summarized in Table 3. Resistance to penicillin was the most common (85%), followed by resistance to trimethoprim (69%), amikacin (51%), tetracycline (47%), clindamycin (34%), and erythromycin (32%). The lowest resistance rates were observed for gentamicin (23%), cefoxitin (14%), ciprofloxacin (11%), and chloramphenicol (6%). Overall, 92% of the isolates exhibited resistance to at least one antimicrobial agent. Statistically significant associations (p < 0.05) were observed between isolate type and resistance to cefoxitin, gentamicin, amikacin, erythromycin, clindamycin, chloramphenicol, tetracycline, trimethoprim, and ciprofloxacin (Table 3). Methicillin resistance (cefoxitin resistance) was detected in 14 isolates, which belonged to clonal complexes CC7 (n = 7), CC8 (n = 4), and CC88 (n = 3). None of the isolates exhibited resistance to tigecycline, rifampicin, mupirocin, fusidic acid, vancomycin, teicoplanin, and linezolid.

Table 3.
Antimicrobial susceptibility profile of Staphylococcus aureus from fish, fish waters, and fish handlers.
Among the 100 isolates, 8% were susceptible to all tested antibiotics. Resistance to one, two, three, four, six, seven, eight, and nine antimicrobial agents was observed in 12%, 32%, 14%, 3%, 3%, 15%, 7%, and 6% of isolates, respectively (Table 4) with the most common pattern being resistance to penicillin and trimethoprim (PEN-TRI, n = 16). Of the 92 resistant isolates, 49 (53.2%) demonstrated multiple drug resistance (defined as resistance to at least three antimicrobial classes). The predominant multiple drug resistance pattern among isolates from fish was PEN-GEN-AMK-ERY-CLI-TET-TRI (n = 13), while PEN-TRI (n = 6) predominated among those from fish handlers. Two distinct multiple drug resistance patterns were demonstrated by the isolates from fish water.

Table 4.
Antimicrobial resistance patterns and antimicrobial resistance indices of Staphylococcus aureus from fish, fish handlers, and fish waters.
Overall, 52.2% (48/92) of the resistant isolates were classified as multidrug-resistant (MDR) (Table 4). The multidrug resistance prevalence among isolates from fish, fish handlers, and fish waters was 47.8% (33/69), 38.1% (8/21), and 100% (2/2), respectively (Table 4). The mean Multiple Antibiotic Resistance Index (MARI) across all isolates was 0.23 (range: 0.06–0.56). MRSA isolates exhibited the highest MARI values, ranging from 0.44 to 0.56. Notably, only isolates belonging to CC188 did not exhibit multidrug resistance (defined as resistance to at least one agent in three or more antibiotic classes).
3.4. Antimicrobial Resistance Genotypes of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates
A total of 19 antimicrobial resistance genes were identified among the 100 S. aureus isolates (Table 5). The mecA gene, associated with methicillin resistance, was detected in all 14 cefoxitin-resistant isolates. These mecA-positive isolates carried SCCmec types IV (n = 3) and V (n = 11). The efflux pump gene sdrM was the most frequently detected (98%), followed by β-lactamase-encoding genes blaZ, blaI, and blaR, present in 81% of the isolates. Resistance genes for chloramphenicol (cat, encoding chloramphenicol acetyltransferase) and trimethoprim (dfrS1, encoding dihydrofolate reductase) were found in 6% and 4% of the isolates, respectively. Tetracycline resistance genes, tet(K) (28%) and tet(M) (4%), occurred in 28% and 4% of the isolates, respectively. Aminoglycoside resistance genes were detected at varying frequencies: aphA3 (11%), aadD (3%), and the bifunctional aacA-aphD (23%) encoding aminoglycoside phosphotransferase gene, aminoglycoside adenyltransferase, and aminoglycoside acetyltransferase–phosphotransferase enzymes, respectively. Macrolide resistance genes included the erythromycin ribosome methylase genes, erm(B) (18%), and erm(C) (13%), as well as the macrolide efflux gene, msr(A) (2%). In contrast, Inu(A), a lincosamide nucleotidyltransferase gene, was found in 8% of the isolates.

Table 5.
Frequency of antimicrobial resistance genes in Staphylococcus aureus isolates from fish, fish waters, and fish handlers.
The phenotypic resistance profiles generally aligned with the genotypic findings. However, a macrolide–lincosamide-susceptible CC152-MSSA-t355 isolated from fish harbored both erm(C) and InuA, and a tetracycline-susceptible CC152-MSSA-t355 isolate carried tet(K). Genes conferring resistance to streptothricin, sat (encoding streptothricin acetyltransferase, 16%), and quaternary ammonium compounds (qacC, 5%), although not phenotypically assessed, were also detected. Notably, the prevalence of blaZ, blaI, blaR, aacA-aphD, aphA3, erm(C), cat, sat, tet(K), and dfrS1 were significantly higher (p < 0.05) among MRSA compared to MSSA isolates (Table 5).
3.5. Prevalence of Virulence-Associated Genes in Staphylococcus aureus Isolates
3.5.1. Regulatory Genes
All 100 S. aureus isolates carried the regulatory genes sarA, saeS, and vraS (Table 6). Among the accessory gene regulator (agr) types, agrI was the most prevalent (43%), followed by agrIV (31%), agrIII (28%), and agrII (26%). The carriage of agrI was significantly higher (p = 0.007) in MRSA isolates (78.6%) compared to MSSA (37.2%) (Table 6). Similarly, agrIV was more frequently (p = 0.031) detected in MRSA (57.1%) than in MSSA (27.1%), while agrII was identified exclusively (p = 0.01816) in MSSA isolates (30.2%). All isolates belonging to CC45 and CC152 were positive for agrI, while CC1 and CC88 isolates were positive for agrIII. CC5, CC15, and CC80 isolates were positive for agrII (Figure 4). Isolates of CC6, CC7, CC8, CC152, CC188, and CC361 were positive for agrI. All CC2250 isolates were negative for all agr types (Figure 4).

Table 6.
Prevalence of regulatory and virulence-associated genes in Staphylococcus aureus isolates from fish, fish waters, and fish handlers.
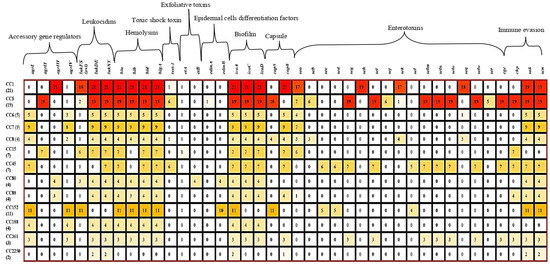
Figure 4.
Tricolor scale depicting the association among Staphylococcus aureus virulence genes, agr types, and clonal complex. CC: clonal complex, agr: accessory gene regulator, pvl: Pantone–Valentine leucocidin, luk: Leucocidin, hl: Haemolysin, et: exfoliative toxin, edin: epidermal cells differentiation inhibitors, ica: intracellular capsular adhesion, se: Staphylococcus enterotoxin, sak: Staphylokinase, chp: chemotaxis inhibitory protein, scn: Staphylococcal complement inhibitor.
3.5.2. Virulence Genes
All isolates harbored at least two of the tested virulence-associated genes (Figure 4). The Pantone–Valentine leukocidin gene (lukFS-PV) was detected in 40% of the isolates, with a significantly higher (p = 0.00063) prevalence in MSSA (46.5%) compared to none in MRSA. Other leukocidin genes, lukD/E and lukX/Y, were detected in 84% and 88% of isolates, respectively (Table 6). The lukFS-PV gene was most common in CC152 (100%), CC1 (85.7%), CC15 (85.7%), and CC80 (75%), but was rare in CC5 (10.5%). All isolates carried lukD/E (except those of CC45 and CC152) and lukXY (absent in CC152) (Figure 4).
Nearly all isolates (98%) harbored hemolysin-encoding genes (hla, hld/hlIII, and hlgA), except for CC2250 (Figure 4). The hlb gene was the least frequent, present in 83% of all isolates, but was absent in CC15 and CC45 isolates (Table 6; Figure 4). Exfoliative toxin genes were rare. The etA was detected in 14.3% of CC15 isolates, and etB was detected in all CC8 isolates (Figure 4). These genes occurred exclusively in MSSA, accounting for 5% of the total isolates (Table 6). Moreover, genes encoding epidermal cell differentiation inhibitors were detected in 14% of isolates: edinA was found in one CC5 isolate (5.2%), while edinB was present in all CC80 and 90.9% of CC152 isolates. The TSST-1 gene, encoding toxic shock syndrome toxin, was identified in 14% of isolates, including 7.1% of MRSA and 15.1% of MSSA (Table 6). Its carriage was strongly associated with CC45 (85.7%), followed by CC5 (31.6%), CC8 (25%), and CC1 (4.8%) (Figure 4).
Classical enterotoxin genes were found at the following frequencies: sea (45%), seb (9%), sec (11%), and sed (6%). The sea gene was common in CC15 (85.7%), CC1 (81%), CC8 (75%), CC5 (36.8%), and CC88 (25%) (Table 3). seb was primarily associated with CC8 (75%), sec with CC45 (85.7%), and sed with both CC45 (85.7%) and CC152 (45.5%) (Figure 4). Other enterotoxin genes (sek, seq) were found in 22% of the isolates but showed no significant difference (p > 0.05) between MRSA and MSSA. Several non-classical enterotoxin genes occurred exclusively in MSSA, including seg (6%), seh (19%), sei (29%), sej (6%), sel (9%), selm (29%), seln (29%), selo (29%), ser (5%), and selu (29%) (Table 6). The prevalence of sei, selm, seln, selo, and selu was significantly higher (p = 0.00889) in MSSA compared to MRSA. These genes were mostly associated with CC5, CC45, and CC361, which were the only lineages carrying the enterotoxin gene cluster (egc) (Figure 4).
Immune evasion genes were detected as follows: chp (40%), sak (87%), and scn (94%) (Table 6). All MRSA isolates carried sak and scn, while chp was present in 21.4% of MRSA and 43.0% of MSSA isolates. CC188 isolates lacked all immune evasion genes; chp was absent in CC1, while sak and scn were absent in CC5 and CC45 isolates (Figure 4). Moreover, biofilm-associated genes (icaA, icaC, icaD) were prevalent across isolates. Both MRSA and MSSA showed 100% prevalence for icaA, while icaC and icaD were found in 87% and 98% of isolates, respectively (Figure 4). These genes were absent in isolates of CC152 and CC2250. Capsule-encoding genes cap5 and cap8 were detected in 33% and 65% of isolates, respectively (Table 6). cap5 gene was found in over 90% of CC5 and CC8 isolates, while cap8 was present in all isolates of CC1, CC6, CC7, CC8, CC15, CC45, CC88, CC152, and CC361 (Figure 4). No statistically significant association (p > 0.05) was found between agr type, source of isolation, and presence of virulent gene.
4. Discussion
This current study investigated the genetic diversity and antimicrobial resistance of S. aureus in aquaculture-associated environments (fish, fish handlers, and fish waters) within a local Nigerian fishery sector, through the One Health standpoint. The overall prevalence of S. aureus (16.5%) indicates a moderate yet concerning level of contamination. As S. aureus is not conventionally associated with aquatic environments, this finding implicates both fish and handlers as potential reservoirs and vectors, thereby underscoring their role in the human–animal–environment transmission cycle. The higher prevalence in fish (15.5%) and handlers (24.5%) compared to water (5.6%) likely reflects the post-harvest contamination, stemming from poor hygiene practices such as reuse of unwashed tools, inadequate hand hygiene, and lack of use of personal protective equipment. Although Staphylococcus aureus is not typically waterborne, its detection in fishpond water suggests anthropogenic contamination—potentially from farm runoff, human handling, or other environmental exposures. This raises environmental health concerns, as S. aureus can persist in aquatic environments and may enter the food chain through crops irrigated with fishpond effluents [38]. Compared to global reports from Iran [4], Egypt [15], Japan [39], Greece [21], and India [40], where S. aureus prevalence ranged from 0.4% to 27.83%, our findings fall within international trends. However, they are lower than the 52.1% and 57% reported in China [13] and Abuja Nigeria [41], respectively. The 24.5% carriage rate among (fish) handlers is particularly concerning, highlighting their critical role as conduits for pathogens’ introduction into aquatic ecosystems and potential dissemination along the food chain.
Moreover, the DNA genotyping in this current study revealed a substantial genetic diversity among the 100 S. aureus isolates, comprising 28 spa types distributed across 13 clonal complexes (CCs). This observation likely reflects the combined influence of multiple sources of contamination (humans, environment, and fish), selective pressures exerted by antimicrobial agents within the aquatic ecosystem that potentially stimulates the emergence of diverse lineages, and inadequate biosecurity measures that facilitate cross-contamination. These findings highlight the dynamic One Health interface inherent in aquaculture and underscore the potential of the Nigerian aquaculture sector to serve as a reservoir and dissemination pathway for diverse S. aureus lineages, some of which may carry zoonotic significance. The highest diversity was found in fish (23 spa types from 13 CCs) and handlers (13 spa types from 10 CCs). Most of these CCs, including CC1, CC8, CC15, CC5, and CC152, have been previously reported in food animals and human clinical isolates in Nigeria [42,43,44,45,46,47,48], and in both animal and human hosts globally [48,49,50,51,52,53,54], supporting their zoonotic potential. Notably, CC80 and CC88, which are well-documented in human and food animal infections in Nigeria [42,44], were also detected in this study, underscoring the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental reservoirs.
Further, there were several CCs associated with multiple spa types, for example, CC15 (t094, t084), CC8 (t064, t1476), and CC5 (t311, t002, t2049, t1400) were observed in both aquatic and human-related samples (Figure 3), which would be indicative of genetic heterogeneity and multiple transmission sources [35]. The detection of t311 (CC5)—a human-associated spa type linked to infections in Nigeria [55,56], which appeared dominant in healthcare settings in Ghana [57], and associated with bloodstream infections globally [58,59,60,61,62]—potentially in both fish and handlers would suggest human-to-fish transmission. Similarly, the most prevalent clone, t948 (CC1), identified in both fish and water, has been widely reported in clinical isolates across Africa [55,57,63] and Europe [62], indicating potential reverse zoonotic transmission. Other spa types such as t690, t355, t044, and t189 have also been reported in both human and animal isolates from Nigeria and various regions [41,44,46,50,51,60,64,65,66,67,68,69]. Eight MSSA spa-CC combinations, including t311-CC5, t355-CC152, and t044-CC80, appear as shared between fish and handlers, indicative of probable cross-contamination during handling or shared environmental sources [6]. Given that many of these lineages are primarily human-associated, their detection in aquaculture environments raises concern about the spillover of antimicrobial-resistant strains from humans to fish and the wider ecosystem.
Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) was identified in both fish and handlers, albeit at a relatively low prevalence (2.3%). Nonetheless, the detection of mecA-positive strains, CC7-MRSA-V, CC8-MRSA-V, and CC88-MRSA-IV in distinct hosts suggests independent acquisition events and underscores the public health threat posed by aquaculture-related MRSA. These findings are consistent with previous reports of MRSA in food animals and humans in Nigeria [70,71]. The observed prevalence exceeds the 1% reported in fish/fish handlers in Borno State, Nigeria [22], but is lower than values from fish in Poland (29.5%) [72], Brazil (30%) [73], and India (50%) [40]. This study revealed epidemic and multidrug-resistant MRSA lineages such as ST7-MRSA-V-t091 (WA-MRSA-131), CC8-MRSA-V (t064, t1476), and CC88-MRSA-IV-t1814 (the WA-MRSA-2 lineage called ‘African clone’) in fish and fish handlers. These clones have been implicated in human infections across Nigeria and globally [44,45,47,74,75,76,77], underscoring their zoonotic and environmental adaptability. The dual detection of MRSA and MSSA variants of CC88 (t1814 and t2723, respectively) suggests genomic flexibility and selective pressure for SCCmec acquisition, likely driven by antimicrobial use. This aligns with earlier reports that CC88-MRSA is more prevalent than CC88-MSSA in Nigerian food animals [42]. The ST8-MRSA-V lineage, observed as multiple spa types (t064, t1814, t1417), further illustrates the widespread distribution of high-risk clones. This lineage has been reported in clinical samples from Nigeria [45,78], Sao Tome and Principe [79], hospital environments in Armenia [80], and poultry from southwestern Nigeria [71], highlighting its ability to adapt across hosts and environments.
Possibly, the situation of antimicrobial resistance appears widespread among the isolates of this current study. Specifically, the penicillin resistance (85%) was correlated with a high prevalence of β-lactamase-encoding genes blaZ, blaI, and blaR, possibly due to antibiotic misuse in both the aquaculture and human sectors in Nigeria [81,82]. Resistance to erythromycin (33%) and inducible clindamycin (32%) was linked to erm(B), erm(C), Inu(A), and msr(A), some of which appeared to be unexpressed (like the lincosamide-susceptible CC152-MSSA-t355 isolated from fish harbored both ermC and InuA), which would be suggestive of possible silent reservoirs. Tetracycline resistance (43%), predominantly mediated by tet(K), also likely emanated from its overuse in the human healthcare domain and aquaculture [80]. Notably, tet(K) was detected in a phenotypically susceptible isolate, suggesting the potential for cryptic resistance. Aminoglycoside resistance (14–47%) and low-level chloramphenicol resistance (6%) were linked to genes encoding known modifying enzymes (aphA3, aadD, and the bifunctional aacA-aphD encoding aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, aminoglycoside adenyltransferase and aminoglycoside acetyltransferase–phosphotransferase, and cat encoding chloramphenicol acetyltransferase, respectively). In contrast, resistance to trimethoprim in most isolates were found to occur in the absence of dfrS1, implicating other determinants, such as dfrG, which appears not included in the microarray panel. Of particular concern is the detection of the fosfomycin resistance gene fosB in CC5, CC8, and CC15. Fosfomycin is a last-resort treatment for MDR S. aureus, and its resistance in aquaculture suggests either environmental contamination or antibiotic misuse.
The widespread presence of the sdrM efflux gene (98%) and the biocide resistance gene qacC (5%) further reflects environmental exposure to selective pressures from disinfectants and heavy metals used in fish farming, which raises important concerns about the co-selection of resistance. Preliminary phenotypic assays (disk diffusion screening) corroborate this, with high resistance to cadmium, mercury, and ethidium bromide. These findings have significant One Health ramifications, as resistant strains from aquaculture can spread into the broader environment and community through water, food, or direct human contact. Most resistance genes (except tet(M), msr(A), and aadD) were found in isolates carrying SCCmec types IV and V. The resistance genes are likely mediated by plasmids (such as pT181) or other mobile elements [43,83,84], facilitating their dissemination. The high rate of multidrug resistance (52.2%), with 90.2% of resistant isolates exhibiting resistance to two or more antimicrobial classes and mean MARI values exceeding 0.2 (0.23), underscores exposure to high-risk environments. MDR was particularly high in fish water (100%) and fish (47.8%) as well as in fish handlers (38.1%), reinforcing the notion that aquaculture practices in Nigeria may serve as hotbeds for antimicrobial resistance. Encouragingly, all isolates remained susceptible to critical ‘Reserve’ antibiotics like tigecycline, mupirocin, and vancomycin. Nonetheless, the detection of resistance to commonly used antimicrobials in all clonal complexes except CC88 is concerning. The dissemination of diverse S. aureus clones from aquaculture into the human population may compromise treatment efficacy and establish persistent reservoirs of resistance genes across ecosystems.
In this current study, the detection of universal regulators sarA, saeS, and vraS genes in all Staphylococcus aureus isolates underscores their conserved nature and critical role as global regulators across both MRSA and MSSA strains. These genes, encoding staphylococcal accessory regulator A, the sensor histidine kinase SaeS, and the sensor histidine kinase VraS, respectively, are key modulators of virulence gene expression, particularly those regulated by the agr quorum-sensing system [1]. Their ubiquitous presence across various strain types highlights their fundamental importance in regulating virulence. Given their role in biofilm formation, immune evasion, severe clinical manifestations such as sepsis, osteomyelitis, and necrotizing pneumonia [1,12], their presence represents a significant One Health concern.
Further, the detection of four distinct agr types with varying distributions between MRSA and MSSA isolates suggests that strain-specific regulatory mechanisms drive virulence. The agr locus, a central quorum-sensing regulator, facilitates biofilm dispersion, promotes intracellular survival, enhances dissemination through phagocytes, and induces the production of virulence factors such as proteases, hemolysins, and superantigens [2,85]. The significantly higher prevalence of agrI and agrIV among MRSA strains implies that carriage of multiple agr alleles may enhance the ability of these strains to acquire multidrug resistance determinants, consistent with the elevated resistance gene burden and high multiple antibiotic resistance (MAR) indices observed in MRSA. Interestingly, agrII was exclusively detected in MSSA isolates belonging to clonal complexes (CCs) 5, 15, and 80, suggesting lineage-specific regulatory adaptation. The detection of agrIII in both MRSA and MSSA (e.g., CC1, CC88, and CC7) indicates its broader distribution and potential involvement in the acquisition of resistance. The diversity of agr alleles among genetically distinct strains raises public health concerns, as agr regulation plays a central role in community-associated MRSA and MSSA infections [85]. Moreover, the potential for these lineages to share a common evolutionary origin can be reflected by the observation that strains within the same agr group often exhibit similar biological behavior and close genetic relatedness [86]. The lack of a significant association between agr types and virulence gene carriage, particularly in this current study, suggests that agr polymorphisms may influence phenotypic behavior such as resistance or persistence more than the mere presence of virulence genes, in line with previous findings [87]. The agr-deficiency observed in CC2250, along with reduced toxin production, suggests an atypical regulatory profile that may promote persistence rather than acute virulence. Dysfunction of the agr system has been associated with increased biofilm formation, impaired autolysis, and immune evasion, which together contribute to chronic infection and therapeutic failure [2]. The detection of agr-deficient strains in this study carries significant public health implications, as such strains have been linked to endocarditis, osteomyelitis, bacteremia, and increased mortality [85].
Of particular concern is the high detection rate (40%) of the Pantone–Valentine leucocidin gene (lukFS-PV) among MSSA isolates exclusively. This indicates that a substantial proportion of S. aureus strains circulating in the fishery sector may harbor this potent leukotoxin. PVL (Panton–Valentine leucocidin) is a bicomponent pore-forming toxin that contributes to leukocyte lysis and tissue necrosis, and is implicated in community-associated infections, including skin and soft tissue infections and necrotizing pneumonia [13]. The detection of PVL in MSSA from this sector represents a significant zoonotic risk to individuals who handle or consume contaminated fish. Comparative studies have reported varying prevalence of the PVL gene in MSSA from aquatic environments—100% in Egypt and 2% in India [15,40], and 18% detection rate in MRSA in South Africa [16], while a 50.4% detection rate was observed in aquatic products in China [13]. In Nigeria, the PVL gene has been previously reported in MRSA isolates from humans and food animals [42,88]. The significant association of PVL with MSSA in this study, especially among CC152, CC1, CC15, and CC80, reinforces the known link between PVL and community-associated lineages. These lineages have been implicated in human infections and are increasingly reported in community settings [1,85,89]. The widespread detection of other leucocidin genes, including lukDE and lukXY, further supports the strong cytolytic potential of the isolates. The near-universal presence of lukD, lukE, lukX, and lukY suggests their conservation and potential role in immune evasion and pathogenesis [90].
The high prevalence of hla, hld/hlIII, and hlgA (98%) underscores their conserved role in S. aureus virulence and immune evasion. Their absence only in CC2250 indicates universal distribution across CCs, suggesting evolutionary conservation. In contrast, the hlb gene, encoding β-hemolysin, was detected in only 83% of isolates and was absent in CC5, CC15, CC45, and CC80—human-adapted lineages previously associated with hlb disruption due to bacteriophage integration [90]. This lineage-specific absence likely reflects niche adaptation, as these CCs are often associated with colonization rather than invasive disease. The hla gene encodes α-hemolysin, which disrupts epithelial barriers, induces necrosis, and contributes to systemic infection, including sepsis and food poisoning outbreaks [13,85]. The hld/hlIII gene encodes δ-hemolysin, a component of the RNAIII regulatory system linked to the agr locus, known to lyse various host cells [90]. hlb, encoding β-hemolysin (a sphingomyelinase and non-pore-forming toxin), is implicated in inflammatory skin infections due to its activity as an epidermal growth factor receptor agonist [91]. hlgA encodes γ-hemolysin, a bicomponent leukocidin critical for survival in blood and implicated in serious infections such as bacteremia, septic arthritis, and toxic shock syndrome [90]. While workers like Rong et al. [13] reported hla and hlb detection rates of 89.4% and 6.7%, respectively, others like Sivaraman et al. [40] observed 0.78% for hla and 0% for hlb. Specific to Nigeria, Shittu et al. [40] detected all hemolysin genes in isolates from food animals.
Exfoliative toxin genes were detected in only 5% of MSSA isolates (CC15 and CC8), suggesting clonal restriction and vertical gene transmission [1]. Although uncommon in this setting, the presence of these serine proteases, which cause epidermal cell dissociation in staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome and bullous impetigo, is of clinical concern [92]. The detection of edinA and edinB in 14% of isolates—particularly the high prevalence of edinB in CC80 and CC152—indicates the emergence of virulent lineages within the aquatic food chain. EDINs disrupt epidermal cell development and have been implicated in pneumonia, bacteremia, and diabetic foot ulcers [93], warranting inclusion of these markers in AMR surveillance to monitor zoonotic risk. The 14% prevalence of TSST-1 among diverse isolates from fish and handlers suggests the potential for menstrual and non-menstrual toxic shock syndrome. TSST-1, a pyrogenic toxin superantigen, induces systemic inflammation via T-cell [93,94]. Its presence in fish and handlers raises public health concerns, especially for female handlers, even though foodborne toxic shock syndrome has not been confirmed. Global reports corroborate this: 3.9% prevalence in Iran [4], 12.5% in Egypt [15], 2.7% in China [13], and 6.25% in India [40]. In Nigeria, TSST-1 has been detected in S. aureus from ready-to-eat seafood [88].
Classical staphylococcal enterotoxins (SEA-SED), which are heat-stable superantigens associated with food poisoning [4], were detected in 4–45% of the isolates. This is particularly concerning given the increase in consumption of inadequately cooked smoked and roasted fish in Nigeria. sea, detected in 45% of isolates, was the most prevalent, consistent with global reports of SEA as the predominant enterotoxin in foodborne outbreaks [3]. Similar prevalences were recorded in fish sectors in Iran, Egypt, and South Africa [4,15,16] and in fishery products from China, India, and Spain [19,95,96]. The carriage of classical enterotoxin genes across multiple CCs suggests horizontal transmission, possibly via plasmids [3]. However, the exclusive presence of enterotoxin genes such as seg, seh, sei, sej, sek, sel, selm, seln, selo, seq, ser, and selu in MSSA isolates suggests a broader enterotoxin diversity within this group. The enterotoxin gene cluster (egc), containing several of these genes, was found only in CC5, CC45, and CC361, implying genomic island localization. Co-occurrence of selm, seln, selo, and selu in the same lineages suggest possible co-mobilization via pathogenicity islands [3].
Immune evasion cluster (IEC) genes—scn (94%), chp (60%), and sak (40%)—were moderately to highly prevalent, reflecting a likely human origin, as these genes are typically phage-encoded and human-specific [97]. Nonetheless, some lineages lacked these genes entirely: CC188 had none, chp was absent in CC1, and sak/scn were absent in CC5 and CC45. Their presence or absence reflects phage-mediated acquisition or loss and may indicate host-specific transmission dynamics [97]. Biofilm-associated genes were widely distributed, with icaA (100%), icaC (87%), and icaD (98%) being particularly prevalent in CC1, CC5, and CC361, indicating a strong biofilm-forming capacity across isolates. Biofilm formation enhances antimicrobial tolerance, persistence, and immune evasion, often contributing to treatment failure even in MSSA infections [98]. The universal presence of icaA highlights the conserved role of intercellular adhesion in early biofilm development [99]. The icaADBC operon encodes enzymes critical for polysaccharide intercellular adhesin (PIA) synthesis and export [98,100]. Absence of icaC and icaD in CC152 and CC2250 suggests lineage-specific biofilm deficiencies, which seem consistent with previous findings that show CC152 as a poor biofilm producer as well as CC2250 being able to rely on alternative pathogenic mechanisms [65]. Capsule genes also show differential distribution with cap8 (65%) being more prevalent than cap5 (33%), consistent with global dominance of serotype 8 in both community-/hospital-associated strains [100]. While those of cap5 appear limited to fewer lineages, those of cap8 are broadly distributed across CC1, CC6, CC7, CC8, CC15, CC45, CC88, CC152, and CC361. Capsules enhance S. aureus virulence by suppressing phagocytosis, promoting intracellular survival, and supporting biofilm formation [100].
5. Conclusions
Raw and processed farmed or captured African catfish sold for human consumption in Anambra State, Southeast Nigeria, are potential reservoirs of diverse, virulent, multidrug-resistant (MDR), and methicillin-resistant S. aureus clones. These isolates form distinct molecular clusters and carry a broad arsenal of virulence and immune evasion genes. The local fish sector—often overlooked in zoonotic risk evaluations—may contribute to the environmental dissemination of human-adapted S. aureus strains via contaminated water, biofilm formation, or cross-contamination during handling and processing. This presents a significant One Health concern, particularly for individuals in direct contact with these fish, including farmers, processors, fishermen, animal health workers, vendors, and consumers. The findings underscore the urgent need for targeted surveillance, strict biosecurity measures, prudent antimicrobial use, and molecular monitoring in aquaculture systems to limit the emergence and spread of MDR S. aureus. Routine screening and coordinated One Health interventions are crucial for mitigating the zoonotic and public health risks associated with these resistant pathogens.
Public health initiatives should emphasize antimicrobial stewardship, hygiene practices at both pre- and post-harvest stages, and responsible antibiotic use in both human and aquaculture settings. This study represents the first comprehensive genetic characterization of S. aureus from fish and the fishery sector in West Africa. A limitation of this current study would be the relatively small number of fish water samples and nasal swabs from fish handlers, which might likely restrict the ability to draw firm conclusions about the low prevalence of S. aureus and MRSA observed in these sources. Additionally, phenotypic assessment of virulence—particularly biofilm production—was not performed. This is critical, as the presence of the ica operon does not always correlate with expression, which may be influenced by environmental factors, genetic background, or the functionality of the agr system. Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) would have provided deeper insight into the genetic context of resistance and virulence genes, elucidating the mechanisms of acquisition, regulation, and transmission.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, U.C.O. and O.J.O.-K.; methodology, U.C.O., O.J.O.-K., E.E.U. (Ejike Ekene Ugwuijem) and E.E.U. (Edet Ekpenyong Udo); software, U.C.O., C.F.I., A.C.M., C.F.O., I.O.N., O.U., S.C.O. and G.O.E.; validation, O.J.O.-K., C.O.R.O., U.C.O., S.C.O., A.J.O., O.C.N., N.H.I.-E., A.C.M., C.O.A., L.O.M.-A., E.V.E., I.R.O., C.F.O., G.O.E. and C.O.R.O.; formal analysis, U.C.O., O.J.O.-K., S.C.O., M.U.A. and C.F.O.; investigation, U.C.O., S.C.O., O.J.O.-K., E.E.U. (Ejike Ekene Ugwuijem) and E.E.U. (Edet Ekpenyong Udo); resources, U.C.O., O.J.O.-K., C.F.I., S.C.O., O.C.N., C.F.O., N.H.I.-E., A.C.M., I.O.N., C.O.A., L.O.M.-A., O.U., E.V.E., I.R.O. and C.O.R.O.; data curation, U.C.O., O.J.O.-K., S.C.O., M.U.A., I.R.O., E.E.U. (Ejike Ekene Ugwuijem) and E.E.U. (Edet Ekpenyong Udo); writing—original draft preparation, M.U.A.; writing—review and editing, U.C.O., O.J.O.-K., M.U.A., C.O.R.O. and E.E.U. (Edet Ekpenyong Udo); visualization, C.O.R.O.; supervision, O.J.O.-K., A.J.O., M.U.A. and G.O.E.; project administration, U.C.O., O.J.O.-K., E.E.U. (Ejike Ekene Ugwuijem), G.O.E. and E.E.U. (Edet Ekpenyong Udo); funding acquisition: U.C.O., O.J.O.-K., C.F.I., S.C.O., A.J.O., O.C.N., I.O.N., N.H.I.-E., A.C.M., C.O.A., L.O.M.-A., E.V.E., I.R.O., C.F.O., G.O.E., C.O.R.O. and E.E.U. (Edet Ekpenyong Udo). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study received ethical clearance from the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Nigeria (Protocol No. FVM-UNN-IACUC-2019–0143, approved 5 January 2019) and the Ethics Committee of Chukwuemeka Odimegwu Ojukwu University Teaching Hospital, Awka (Protocol No. COOUTH/CMAC/ETH.C/VOL.1/FN:04/243, approved 15 May 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Prior to sample collection, both verbal and written informed consent were obtained from all fishpond owners and fish handlers who participated in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Touaitia, R.; Mairi, A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Basher, N.S.; Idres, T.; Touati, A. Staphylococcus aureus: A Review of the Pathogenesis and Virulence Mechanisms. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.O.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.E.; Song, K.H.; Kang, C.K.; Wi, Y.M.; San-Juan, R.; López-Cortés, L.E.; Lacoma, A.; Prat, C.; et al. Dysfunctional Accessory Gene Regulator (Agr) as a Prognostic Factor in Invasive Staphylococcus aureus Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieza, M.Y.R.; Bonsaglia, E.C.R.; Rall, V.L.M.; dos Santos, M.V.; Silva, N.C.C. Staphylococcal Enterotoxins: Description and Importance in Food. Pathogens 2024, 13, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arfatahery, N.; Davoodabadi, A.; Abedimohtasab, T. Characterization of Toxin Genes and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates in Fishery Products in Iran. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, srep34216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadariya, J.; Smith, T.C.; Thapaliya, D. Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcal Food-Borne Disease: An Ongoing Challenge in Public Health. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 827965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okpala, C.O.R.; Korzeniowska, M. Understanding the relevance of quality management in agro-food product industry: From ethical considerations to assuring food hygiene quality safety standards and its associated processes. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 1879–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Oh, H.; Seo, Y.; Kang, J.; Park, E.; Yoon, Y. Risk and Socio-Economic Impact for Staphylococcus aureus Foodborne Illness by Ready-to-Eat Salad Consumption. Microb. Risk Anal. 2022, 21, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuta, K.S.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Sharara, F.; Mestrovic, T.; Gray, A.P.; Davis Weaver, N.; Wool, E.E.; Han, C.; Gershberg Hayoon, A.; et al. Global Mortality Associated with 33 Bacterial Pathogens in 2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2022, 400, 2221–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2021 Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990–2021: A systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050 Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance 1990–2021: A Systematic Analysis with Forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Jesudason, T. WHO Publishes Updated List of Bacterial Priority Pathogens. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, 100940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, G.Y.C.; Bae, J.S.; Otto, M. Pathogenicity and Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Virulence 2021, 12, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, D.; Wu, Q.; Xu, M.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S. Prevalence, Virulence Genes, Antimicrobial Susceptibility, and Genetic Diversity of Staphylococcus aureus from Retail Aquatic Products in China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Huang, Y.; Shang, W.; Yang, Y.; Peng, H.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Rao, Y.; Hu, Q.; Rao, X.; et al. Accessory Gene Regulator (Agr) Allelic Variants in Cognate Staphylococcus aureus Strain Display Similar Phenotypes. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 700894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, M.B.; Salah Eldin, D.A.; Eldin, A.I.A.Z.; Shaapan, R.M.; Ata, E.B.; Elaadli, H. Prevalence, Virulence Determinants and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes of Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Retail Market Fish and Their Handlers in Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2024, 28, 1101–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fri, J.; Njom, H.A.; Ateba, C.N.; Ndip, R.N. Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Gene Characteristics of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Isolated from Healthy Edible Marine Fish. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 9803903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidat, M.M.; Salman, A.E.B.; Lafi, S.Q. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus in Imported Fish and Correlations between Antibiotic Resistance and Enterotoxigenicity. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 1999–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, G.K.; Sivam, V.; Ganesh, B.; Elangovan, R.; Vijayan, A.; Mothadaka, M.P. Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of Multi Drug Resistant Community Associated Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Food Fish: Detection of Clonal Lineage ST 28 and Its Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Sánchez, D.; López-Cabo, M.; Saá-Ibusquiza, P.; Rodríguez-Herrera, J.J. Incidence and Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus in Fishery Products Marketed in Galicia (Northwest Spain). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 157, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Ferreira, E.; Manageiro, V.; Reis, L.; Tejedor-Junco, M.T.; Sampaio, A.; Capelo, J.L.; Caniça, M.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Distribution and Clonal Diversity of Staphylococcus aureus and Other Staphylococci in Surface Waters: Detection of ST425-T742 and ST130-T843 MecC-Positive MRSA Strains. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahim, A.; Sergelidis, D.; Kirkoudis, I.; Anagnostou, V.; Kaitsa-Tsiopoulou, E.; Kazila, P.; Papa, A. Isolation and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus spp. in Freshwater Fish and Greek Marketplaces. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2010, 19, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan Mohammed, U.; Mustapha Bala, A.; Bako Malam, M.; Zanna Barde, M. Phenotypic and Molecular Detection of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Isolated from Clarias gariepinus (Burchel, 1822) and Oreochromis niloticus (Linneaus, 1758) IN Maiduguri. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2020, 8, 365–372. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg Goldstein, R.E.; Micallef, S.A.; Gibbs, S.G.; He, X.; George, A.; Sapkota, A.; Joseph, S.W.; Sapkota, A.R. Occupational Exposure to Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus spp. among Spray Irrigation Workers Using Reclaimed Water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2014, 11, 4340–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okocha, R.C.; Olatoye, I.O.; Alabi, P.I.; Ogunnoiki, M.G.; Adedeji, O.B. Aquaculture Management Practices Associated with Antimicrobial Residues in Southwestern Nigeria. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famoofo, O.O.; Adeniyi, I.F. Impact of Effluent Discharge from a Medium-Scale Fish Farm on the Water Quality of Odo-Owa Stream near Ijebu-Ode, Ogun State, Southwest Nigeria. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EGUN, N.K.; OBOH, I.P. Potential Contribution of Captured Fishes to the Recommended Nutrient Intakes (RNIs): A Case Study of Commercial Fish Species from Ikpoba Reservoir, Edo State, Nigeria. Meas. Food 2022, 5, 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMA Declaration of Helsinki-Ethical Principles For Medical Research Involving Human Participants General Principles. Available online: https://www.wma.net/policies-post/wma-declaration-of-helsinki/ (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- CLSI M100-ED35; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 35th ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Malvern, PA, USA, 2025.
- CLSI. 2020a; Methods for Antimicrobial Broth Dilution and Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Testing of Bacteria Isolated from Aquatic Animals. CLSI Guideline VET03, 2nd ed. Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020.
- CLSI. 2020b; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Bacteria Isolated from Aquatic Animals. CLSI Guideline VET04, 3rd ed. Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020.
- EUCAST. The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 15.0. 2024. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Haqan, A.; Boswihi, S.S.; Pathan, S.; Udo, E.E. Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Determinants in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated Mainly from Preterm Neonates. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmsen, D.; Claus, H.; Witte, W.; Rothgänger, J.; Claus, H.; Turnwald, D.; Vogel, U. Typing of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a University Hospital Setting by Using Novel Software for Spa Repeat Determination and Database Management. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5442–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswihi, S.S.; Udo, E.E.; Al-Sweih, N. Shifts in the Clonal Distribution of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Kuwait Hospitals: 1992–2010. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monecke, S.; Coombs, G.; Shore, A.C.; Coleman, D.C.; Akpaka, P.; Borg, M.; Chow, H.; Ip, M.; Jatzwauk, L.; Jonas, D.; et al. A Field Guide to Pandemic, Epidemic and Sporadic Clones of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monecke, S.; Berger-Bächi, B.; Coombs, G.; Holmes, A.; Kay, I.; Kearns, A.; Linde, H.J.; O’Brien, F.; Slickers, P.; Ehricht, R. Comparative Genomics and DNA Array-Based Genotyping of Pandemic Staphylococcus aureus Strains Encoding Panton-Valentine Leukocidin. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszewska, M.; Dabrowska, A.; Murray, G.G.R.; Kett, S.M.; Vick, A.J.A.; Banister, S.C.; Pantoja Munoz, L.; Cunningham, P.; Welch, J.J.; Holmes, M.A.; et al. Absence of Staphylococcus aureus in Wild Populations of Fish Supports a Spillover Hypothesis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0485822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, E.; Yoshida, N.; Kawano, J.; Shimizu, A.; Igimi, S. Isolation of Staphylococcus aureus from Raw Fish in Relation to Culture Methods. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2011, 73, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaraman, G.K.; Gupta, S.S.; Visnuvinayagam, S.; Muthulakshmi, T.; Elangovan, R.; Perumal, V.; Balasubramanium, G.; Lodha, T.; Yadav, A. Prevalence of S. Aureus and/or MRSA from Seafood Products from Indian Seafood Products. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matouke, M.M.; Nour, K. Characterization of Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Gills and Gastro-Intestinal Tracts of Catfish (Clarias gariepinus), and Water Samples from Jabi Lake, Abuja, Nigeria. Afr. J. Clin. Exp. Microbiol. 2019, 20, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okorie-Kanu, O.J.; Anyanwu, M.U.; Ezenduka, E.V.; Mgbeahuruike, A.C.; Thapaliya, D.; Gerbig, G.; Ugwuijem, E.E.; Okorie-Kanu, C.O.; Agbowo, P.; Olorunleke, S.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology, Genetic Diversity and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Chicken and Pig Carcasses, and Carcass Handlers. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shittu, A.O.; Adesoji, T.; Udo, E.E. DNA Microarray Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus from Nigeria and South Africa. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0237124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebremedhin, B.; Olugbosi, M.O.; Raji, A.M.; Layer, F.; Bakare, R.A.; König, B.; König, W. Emergence of a Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strain with a Unique Resistance Profile in Southwest Nigeria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 2975–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obasuyi, O.; McClure, J.; Oronsaye, F.E.; Akerele, J.O.; Conly, J.; Zhang, K. Molecular Characterization and Pathogenicity of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Benin-City, Nigeria. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momoh, A.H.; Kwaga, J.K.P.; Bello, M.; Sackey, A.K.B.; Larsen, A.R. Antibiotic Resistance and Molecular Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Backyard-Raised Pigs and Pig Workers. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2018, 50, 1565–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaumburg, F.; Alabi, A.S.; Peters, G.; Becker, K. New Epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus Infection in Africa. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffing, U.; Alabi, A.; Kazimoto, T.; Vubil, D.C.; Akulenko, R.; Abdulla, S.; Alonso, P.; Bischoff, M.; Germann, A.; Grobusch, M.P.; et al. Community-Associated Staphylococcus aureus from Sub-Saharan Africa and Germany: A Cross-Sectional Geographic Correlation Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaiyapuri, M.; Joseph, T.C.; Rao, B.M.; Lalitha, K.V.; Prasad, M.M. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Seafood: Prevalence, Laboratory Detection, Clonal Nature, and Control in Seafood Chain. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 3341–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires-de-Sousa, M. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus among Animals: Current Overview. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.U.; Chua, K.H.; Chew, C.H.; Yeo, C.C.; Abdullah, F.H.; Othman, N.; Kee, B.P.; Puah, S.M. Spa Diversity of Methicillin-Resistant and -Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in Clinical Strains from Malaysia: A High Prevalence of Invasive European Spa-Type T032. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Sun, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Cai, T.; Yuan, X.; Gao, Y.; He, D.; Liu, J.; Yuan, L.; et al. Prevalence, Resistance Pattern, and Molecular Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Healthy Animals and Sick Populations in Henan Province, China. Gut Pathog. 2018, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkhoo, E.; Udo, E.E.; Boswihi, S.S.; Monecke, S.; Mueller, E.; Ehricht, R. The Dissemination and Molecular Characterization of Clonal Complex 361 (CC361) Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Kuwait Hospitals. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 658772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, Q.; Dai, Y.; Shang, J.; Li, M. Molecular Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus Causing Bovine Mastitis between 2014 and 2015. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shittu, A.O.; Okon, K.; Adesida, S.; Oyedara, O.; Witte, W.; Strommenger, B.; Layer, F.; Nübel, U. Antibiotic Resistance and Molecular Epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus in Nigeria. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, A.; Ojemhen, O.; Umejiburu, U.; Ogunleye, A.; Blanc, D.S.; Basset, P. High Genetic Diversity of Staphylococcus aureus in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Southwest Nigeria. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 77, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egyir, B.; Guardabassi, L.; Sørum, M.; Nielsen, S.S.; Kolekang, A.; Frimpong, E.; Addo, K.K.; Newman, M.J.; Larsen, A.R. Molecular Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Clinical Staphylococcus aureus from Healthcare Institutions in Ghana. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilczyszyn, W.M.; Sabat, A.J.; Akkerboom, V.; Szkarlat, A.; Klepacka, J.; Sowa-Sierant, I.; Wasik, B.; Kosecka-Strojek, M.; Buda, A.; Miedzobrodzki, J.; et al. Clonal Structure and Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Strains from Invasive Infections in Paediatric Patients from South Poland: Association between Age, Spa Types, Clonal Complexes, and Genetic Markers. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, H.; Yu, F.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Wang, H. Molecular Epidemiology and Antibiotic Resistance Profiles of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strains in a Tertiary Hospital in China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, C.H.; de Lourdes Ribeiro de Souza da Cunha, M.; Bonesso, M.F.; Da Cunha, F.P.; Barbosa, A.N.; Fortaleza, C.M.C.B. Systemic CA-MRSA Infection Following Trauma during Soccer Match in Inner Brazil: Clinical and Molecular Characterization. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 76, 372–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Huang, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Lei, T.; Chen, M.; Ding, Y.; Xue, L. Prevalence and Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Retail Vegetables in China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, H.; Aanensen, D.M.; Van Den Wijngaard, C.C.; Spratt, B.G.; Harmsen, D.; Friedrich, A.W.; Sabat, A.J.; Muilwijk, J.; Monen, J.; Tami, A.; et al. Geographic Distribution of Staphylococcus aureus Causing Invasive Infections in Europe: A Molecular-Epidemiological Analysis. PLoS Med. 2010, 7, e1000215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, C.; Seck, A.; Richard, V.; Ndour, M.; Sembene, M.; Laurent, F.; Breurec, S. Epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus in Pigs and Farmers in the Largest Farm in Dakar, Senegal. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 962–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nulens, E.; Stobberingh, E.E.; Van Desse, H.; Sebastian, S.; Van Tiel, F.H.; Beisser, P.S.; Deurenberg, R.H. Molecular Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Isolates Collected in a Dutch University Hospital between 1999 and 2006. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 2438–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, S.; Rhod Larsen, A.; Martins Simões, P.; Laurent, F.; Johannesen, T.B.; Lilje, B.; Tristan, A.; Schaumburg, F.; Egyir, B.; Cirkovic, I.; et al. Evolution and Population Dynamics of Clonal Complex 152 Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. mSphere 2020, 5, e00226-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, K.A.S.; Abdulkareem, Z.H.; Alzaalan, A.R.; Yaqoob, A.K. Spa Typing of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Clinical Specimens from Outpatients in Iraq. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2021, 70, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udo, E.E.; Al-Lawati, B.A.H.; Al-Muharmi, Z.; Thukral, S.S. Genotyping of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the Sultan Qaboos University Hospital, Oman Reveals the Dominance of Panton-Valentine Leucocidin-Negative ST6-IV/T304 Clone. New Microbes New Infect. 2014, 2, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hakimi Alni, R.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Mahmoodi, P. Molecular Typing of Staphylococcus aureus of Different Origins Based on the Polymorphism of the Spa Gene: Characterization of a Novel Spa Type. 3Biotech 2018, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fang, F.; Zhao, J.; Lou, N.; Li, C.; Huang, T.; Li, Y. Molecular Characteristics and Virulence Gene Profiles of Staphylococcus aureus Causing Bloodstream Infection. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 22, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odetokun, I.A.; Maurischat, S.; Adetunji, V.O.; Fetsch, A. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Municipal Abattoirs in Nigeria: Showing Highly Similar Clones and Possible Transmission from Slaughter Animals to Humans. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2022, 19, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogundipe, F.O.; Ojo, O.E.; Feßler, A.T.; Hanke, D.; Awoyomi, O.J.; Ojo, D.A.; Akintokun, A.K.; Schwarz, S.; Maurischat, S. Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Human, Chicken and Environmental Samples within Live Bird Markets in Three Nigerian Cities. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukułowicz, A.; Steinka, I.; Siwek, A. Presence of Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Fish and Seafood Originating from Points of Sale in the Tri-City Area (Poland). J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 1911–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, A.; Niederhauser, I.; Johler, S. Virulence and Resistance Gene Profiles of Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Ready-to-Eat Foods. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombs, G.W.; Pearson, J.C.; O’Brien, F.G.; Murray, R.J.; Grubb, W.B.; Christiansen, K.J. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clones, Western Australia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupieux, C.; Mouton, W.; André, C.; Vandenesch, F.; Bes, M.; Tristan, A.; Laurent, F. Performance of the Revised Version of an Immunochromatographic Assay for Detection of MecA- and MecC-Mediated Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01346-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.; Kim, C.K.; Conceição, T.; Aires-De-Sousa, M.; De Lencastre, H.; Tomasz, A. Heterogeneous Oxacillin-Resistant Phenotypes and Production of PBP2A by Oxacillin-Susceptible/MecA-Positive MRSA Strains from Africa. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 2804–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayeni, F.A.; Ruppitsch, W.; Allerberger, F. Molecular Characterization of Clonal Lineage and Staphylococcal Toxin Genes from S. aureus in Southern Nigeria. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shittu, A.; Oyedara, O.; Abegunrin, F.; Okon, K.; Raji, A.; Taiwo, S.; Ogunsola, F.; Onyedibe, K.; Elisha, G. Characterization of Methicillin-Susceptible and -Resistant Staphylococci in the Clinical Setting: A Multicentre Study in Nigeria. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conceição, T.; Aires-de-sousa, M.; Füzi, M.; Tóth, Á.; Pászti, J.; Ungvári, E.; Van Leeuwen, W.B.; Van Belkum, A.; Grundmann, H.; De Lencastre, H. Replacement of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clones in Hungary over Time: A 10-Year Surveillance Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mkrtchyan, H.V.; Xu, Z.; Yacoub, M.; Ter-Stepanyan, M.M.; Karapetyan, H.D.; Kearns, A.M.; Cutler, R.R.; Pichon, B.; Hambardzumyan, A.D. Detection of Diverse Genotypes of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Hospital Personnel and the Environment in Armenia. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2017, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Adelowo, O.O.; Okunlola, I. Field Assessment of Antibiotic Use in Fish Farms in Southwestern Nigeria. Rev. D’elevage Et. De. Med. Vet. Des. Pays Trop. 2019, 72, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oloso, N.O.; Fagbo, S.; Garbati, M.; Olonitola, S.O.; Awosanya, E.J.; Aworh, M.K.; Adamu, H.; Odetokun, I.A.; Fasina, F.O. Antimicrobial Resistance in Food Animals and the Environment in Nigeria: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Koizumi, A.; Saito, M.; Muramatsu, Y.; Tamura, Y. Detection of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Pseudintermedius ST169 and Novel ST354 SCCmec II-III Isolates Related to the Worldwide ST71 Clone. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côrtes, M.F.; Botelho, A.M.N.; Almeida, L.G.P.; Souza, R.C.; Cunha, O.d.L.; Nicolás, M.F.; Vasconcelos, A.T.R.; Figueiredo, A.M.S. Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from ST1 Lineage Harboring a New SCCmec IV Subtype (SCCmec IVm) Containing the TetK Gene. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 2583–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Ito, T.; Tamai, M.; Nakagawa, S.; Nakamura, Y. The Role of Staphylococcus aureus Quorum Sensing in Cutaneous and Systemic Infections. Inflamm. Regen. 2024, 44, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgueiro, V.; Manageiro, V.; Bandarra, N.M.; Ferreira, E.; Clemente, L.; Caniça, M. Genetic Relatedness and Diversity of Staphylococcus aureus from Different Reservoirs: Humans and Animals of Livestock, Poultry, Zoo, and Aquaculture. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saedi, S.; Derakhshan, S.; Ghaderi, E. Antibiotic Resistance and Typing of Agr Locus in Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Clinical Samples in Sanandaj, Western Iran. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beshiru, A.; Igbinosa, I.H.; Igbinosa, E.O. Characterization of Enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus from Ready-to-Eat Seafood (RTES). LWT 2021, 135, 110042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monecke, S.; Akpaka, P.E.; Smith, M.R.; Unakal, C.G.; Thoms Rodriguez, C.A.; Ashraph, K.; Müller, E.; Braun, S.D.; Diezel, C.; Reinicke, M.; et al. Clonal Complexes Distribution of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Clinical Samples from the Caribbean Islands. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divyakolu, S.; Chikkala, R.; Ratnakar, K.S.; Sritharan, V. Hemolysins of Staphylococcus aureus—An Update on Their Biology, Role in Pathogenesis and as Targets for Anti-Virulence Therapy. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2019, 9, 80–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Guan, Z.; Liu, C.; Huang, M.; Li, J.; Feng, J.; Shen, B.; Yang, G. Staphylococcus aureus β-Hemolysin Causes Skin Inflammation by Acting as an Agonist of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0222723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanishi, I.; Nicolas, A.; Caetano, A.C.B.; de Paula Castro, T.L.; Tartaglia, N.R.; Mariutti, R.; Guédon, E.; Even, S.; Berkova, N.; Arni, R.K.; et al. Exfoliative Toxin E, a New Staphylococcus aureus Virulence Factor with Host-Specific Activity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad-Mansour, N.; Loubet, P.; Pouget, C.; Dunyach-Remy, C.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.P.; Molle, V. Staphylococcus aureus Toxins: An Update on Their Pathogenic Properties and Potential Treatments. Toxins 2021, 13, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufresne, K.; Al, K.F.; Craig, H.C.; Coleman, C.E.M.; Kasper, K.J.; Burton, J.P.; McCormick, J.K. TSST-1 Promotes Colonization of Staphylococcus aureus within the Vaginal Tract by Activation of CD8+ T Cells. Infect. Immun. 2025, 93, e0043924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.S.; Sanjeev, S. Prevalence of Enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus in Fishery Products and Fish Processing Factory Workers. Food Control 2007, 18, 1565–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.S.; Lupindu, A.M.; Mdegela, R.H.; Mmoch, A.J. Occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus in Fresh Indian Mackerel Fish. Tanzan. Vet. J. 2020, 37, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohmer, C.; Wolz, C. The Role of Hlb-Converting Bacteriophages in Staphylococcus aureus Host Adaption. Microb. Physiol. 2021, 31, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beenken, K.E.; Smeltzer, M.S. Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm-Associated Infections: Have We Found a Clinically Relevant Target? Microorganisms 2025, 13, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulrahim, U.; Kachallah, M.; Rabiu, M.; Usman, N.A.; Adeshina, G.O.; Olayinka, B.O. Molecular Detection of Biofilm-Producing Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from National Orthopaedic Hospital Dala, Kano State, Nigeria. Open J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.; Timofeyeva, Y.; Jamrozy, D.; Rojas, E.; Hao, L.; Silmon de Monerri, N.C.; Hawkins, J.; Singh, G.; Cai, B.; Liberator, P.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology and Expression of Capsular Polysaccharides in Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates in the United States. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0208356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).