An AI-Designed Antibody-Engineered Probiotic Therapy Targeting Urease to Combat Helicobacter pylori Infection in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Molecular Dynamics Analysis and Evolutionary Design of Single-Domain Antibodies
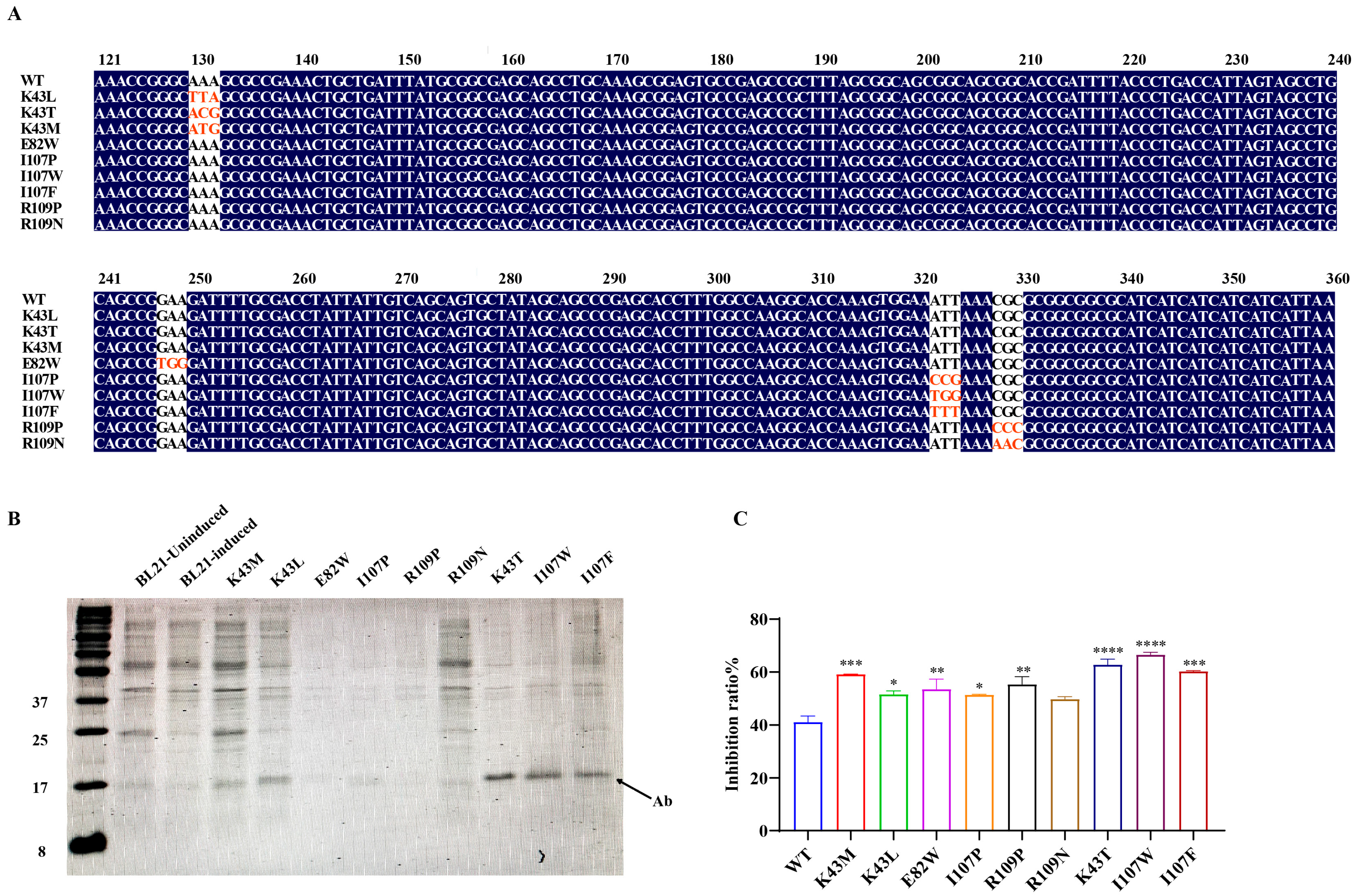
2.2. Single-Point Mutation and Vector Construction
2.3. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
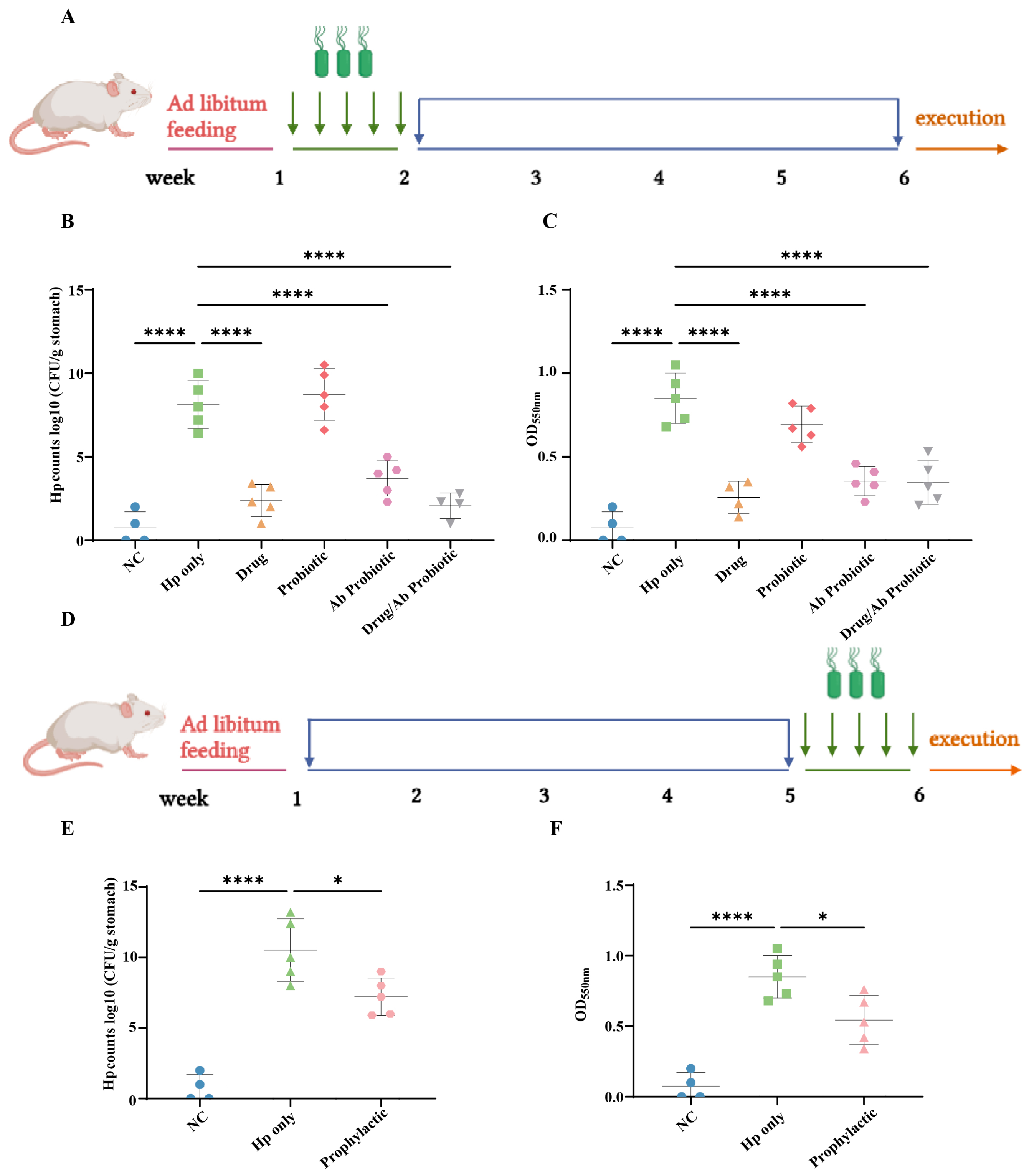
2.4. Animal Models
2.5. Detection of Hp Colonization in the Stomach
2.6. ELISA Detection of Inflammatory Cytokines
2.7. 16S rDNA High-Throughput Sequencing of Gut Microbiota
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
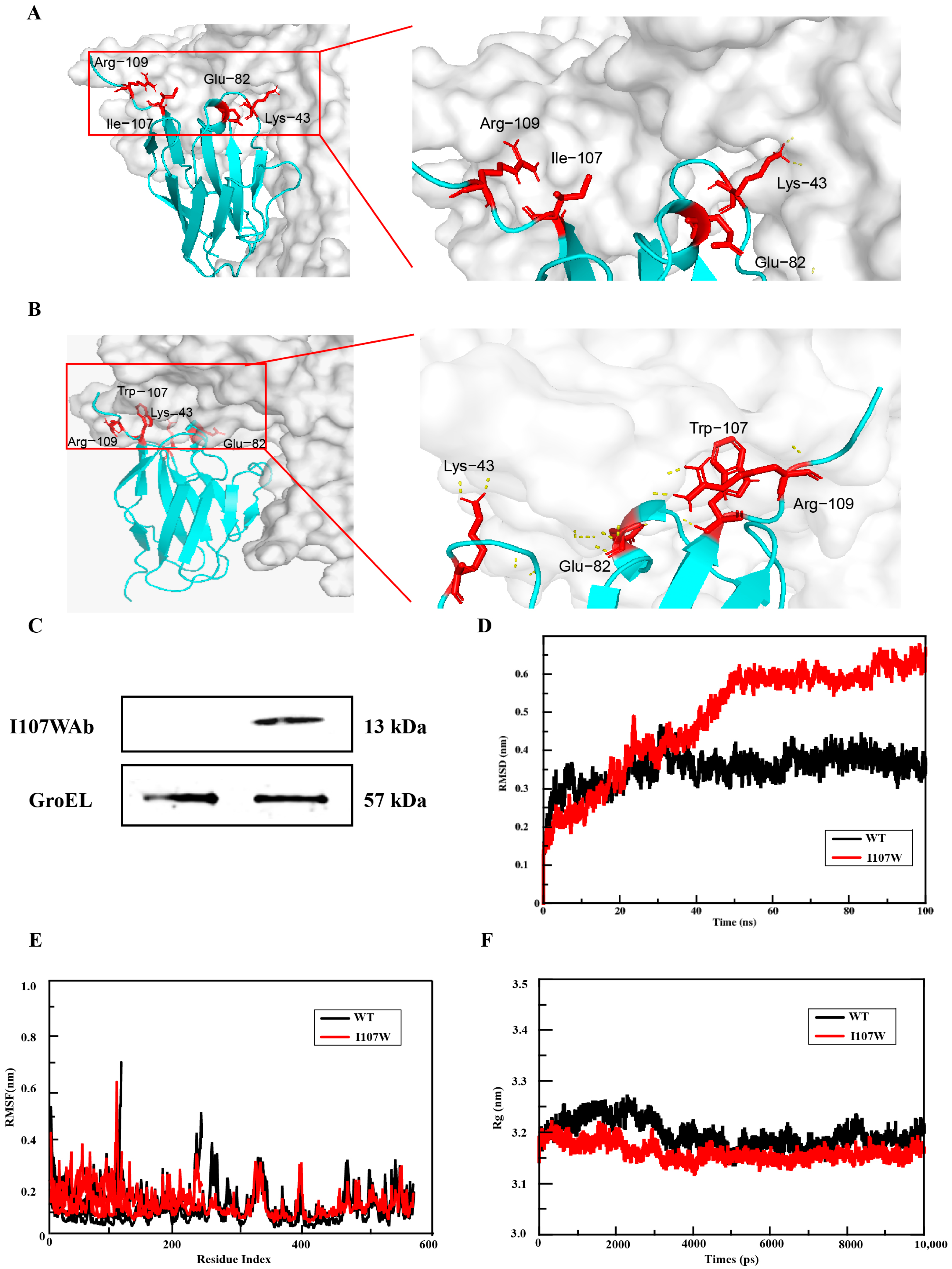
3.1. Identification of Affinity-Enhancing Sites and Mutant Screening via Structural Prediction and Computational Optimization
3.2. Engineering E. coli Nissle 1917 for High-Activity Expression of the Single-Domain Antibody Mutant (Ab-I107W)
3.3. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Results of Mutants
3.4. Engineered Probiotics Suppress Hp Colonization In Vivo
3.5. Engineered Probiotics Regulate the Expression of Inflammatory Factors That Alleviate Hp Infection
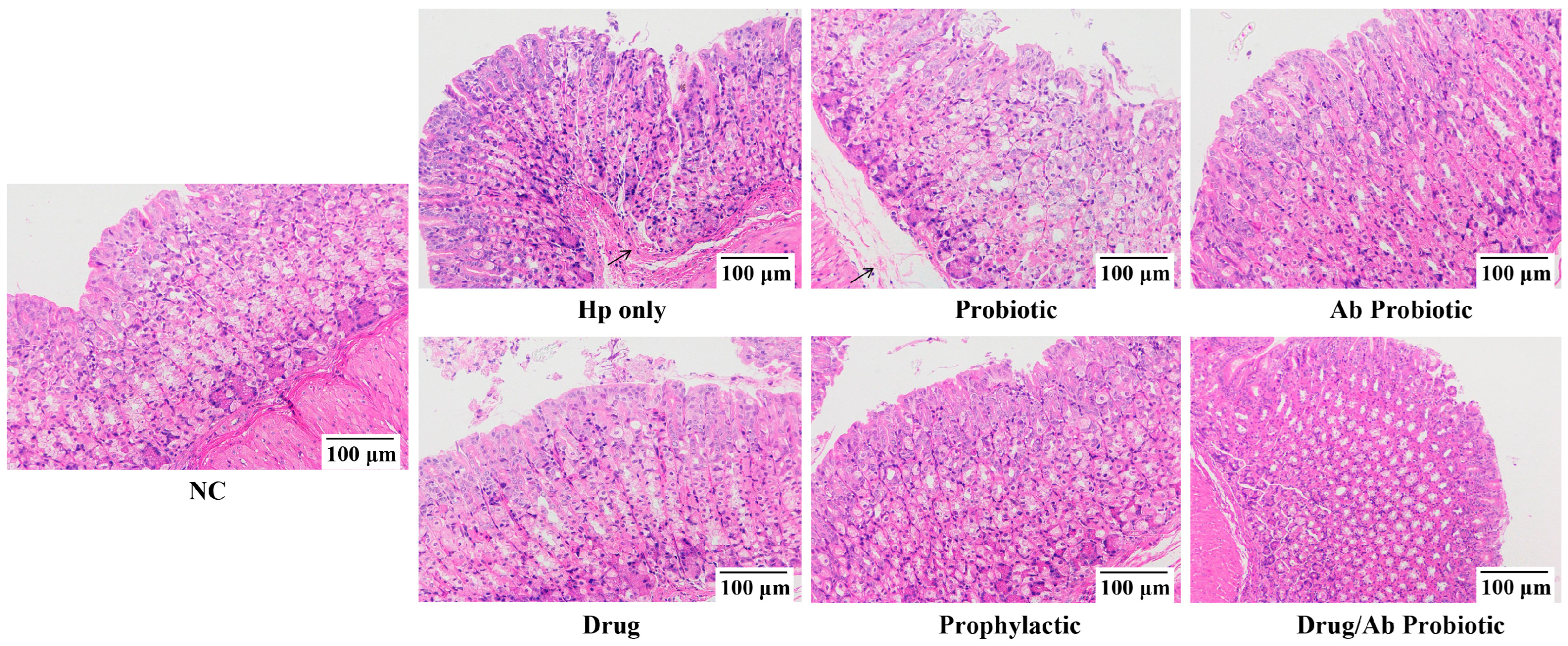
3.6. Engineered Probiotics Overinhibited Neutrophil Infiltration and Gastric Mucosal Structural Repair to Reduce Pathological Damage to Gastric Tissue Caused by Hp Infection
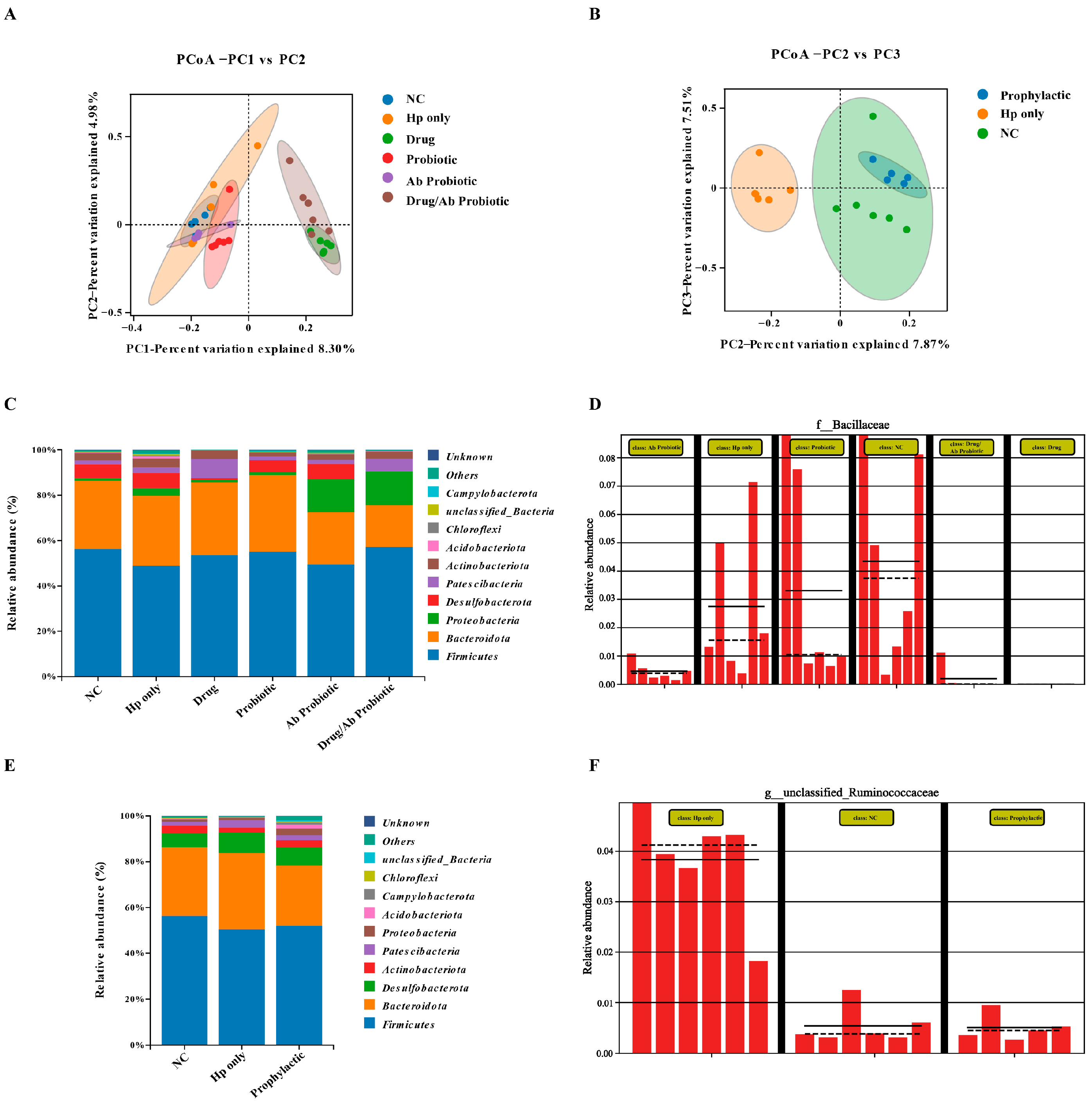
3.7. Engineered Probiotics Antagonize Hp Infection and Antibiotic Damage by Maintaining Gut Microbiota Diversity and Structural Remodeling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Hp | Helicobacter pylori |
| EcN | Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 |
| NC | Negative control |
| UreB | Urease subunit B |
| IARC | International Agency for Research on Cancer |
| NMDS | Non-metric multidimensional scaling |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
References
- Deng, R.; Zheng, H.; Cai, H.; Li, M.; Shi, Y.; Ding, S. Effects of Helicobacter pylori on tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy responses. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 923477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieye, Y.; Nguer, C.M.; Thiam, F.; Diouara, A.A.M.; Fall, C. Recombinant Helicobacter pylori Vaccine Delivery Vehicle: A Promising Tool to Treat Infections and Combat Antimicrobial Resistance. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelli, M.; Franza, L.; Cianci, R.; Pignataro, G.; Merra, G.; Piccioni, A.; Ojetti, V.; Gasbarrini, A.; Franceschi, F. The Interplay between Helicobacter pylori and Gut Microbiota in Non-Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Special Focus on Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zheng, H.; Qiu, M.; Hao, S.; Liu, X.; Zhu, X.; Cai, X.; Huang, Y. Helicobacter pylori infection and risk of cardiovascular disease. Helicobacter 2023, 28, e12967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Z.; Huang, H.; Chen, L.; Shang, Y.; Huang, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Xie, X.; Chen, M.; Wu, L.; et al. Development of a High-Resolution Melting Method for the Detection of Clarithromycin-Resistant Helicobacter pylori in the Gastric Microbiome. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nista, E.C.; Pellegrino, A.; Giuli, L.; Candelli, M.; Schepis, T.; De Lucia, S.S.; Ojetti, V.; Franceschi, F.; Gasbarrini, A. Clinical Implications of Helicobacter pylori Antibiotic Resistance in Italy: A Review of the Literature. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.; Dutta, K.; Kumar, V. Artificial intelligence techniques for prediction of drug synergy in malignant diseases: Past, present, and future. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 144, 105334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, B.; Liu, F.; Xu, S.; Li, P.; Chen, Y. An Updated Review on Developing Small Molecule Kinase Inhibitors Using Computer-Aided Drug Design Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijit, A.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Chen, Y.; Xue, W. Mapping synthetic binding proteins epitopes on diverse protein targets by protein structure prediction and protein-protein docking. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 163, 107183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wodak, S.J.; Vajda, S.; Lensink, M.F.; Kozakov, D.; Bates, P.A. Critical Assessment of Methods for Predicting the 3D Structure of Proteins and Protein Complexes. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2023, 52, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Guo, F.; Wang, E.; Tang, J. ComDock: A novel approach for protein-protein docking with an efficient fusing strategy. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 167, 107660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangpheak, K.; Waraho-Zhmayev, D.; Haonoo, K.; Torpaiboon, S.; Teacharsripaiboon, T.; Rungrotmongkol, T.; Poo-Arporn, R.P. Investigation of interactions between binding residues and solubility of grafted humanized anti-VEGF IgG antibodies expressed as full-length format in the cytoplasm of a novel engineered E. coli SHuffle strain. RSC. Adv. 2021, 11, 6035–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baryshnikova, N.V.; Ilina, A.S.; Ermolenko, E.I.; Uspenskiy, Y.P.; Suvorov, A.N. Probiotics and autoprobiotics for treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. World J. Clin. Cases 2023, 11, 4740–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossotti, M.A.; Bélanger, K.; Henry, K.A.; Tanha, J. Immunogenicity and humanization of single-domain antibodies. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 4304–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakharian, F.; Sadeghi, A.; Pouresmaeili, F.; Soleimani, N.; Yadegar, A. Anti-inflammatory effects of extracellular vesicles and cell-free supernatant derived from Lactobacillus crispatus strain RIGLD-1 on Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammatory response in gastric epithelial cells in vitro. Folia Microbiol. 2024, 69, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhu, M.; He, Y.; Wang, T.; Tian, D.; Shu, J. The impacts of probiotics in eradication therapy of Helicobacter pylori. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Peng, X.-J.; Liu, X.L.; Hu, X.-K.; Xing, D.-M. Current and future perspectives for Helicobacter pylori treatment and management: From antibiotics to probiotics. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1042070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestre, A.; Sathiya Narayanan, R.; Rivas, D.; John, J.; Abdulqader, M.A.; Khanna, T.; Chakinala, R.C.; Gupta, S. Role of Probiotics in the Management of Helicobacter pylori. Cureus 2022, 14, e26463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, L., Jr.; Rios, J.; Berice, B.; Benson, J.; Bafford, N.; Parson, K.; Halloran, D. Predictive Effect of Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Carcinoma Development: Systematic Review and Quantitative Evidence Synthesis. Medicines 2021, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Jiang, Q.; Xue, S.; Hui, W.; Kong, W.; Zhang, M.; Gao, F. Clinical characteristics of ulcerative colitis patients with different types of Helicobacter pylori infection. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0355423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ge, W.; Wang, M.; Liu, H.; Xun, L.; Xia, Y. Engineered Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 with urate oxidase and an oxygen-recycling system for hyperuricemia treatment. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2070391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangra, V.; Sharma, N.; Chhillar, A.K. Therapeutic approaches for combating Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Microbes Infect. 2022, 24, 104950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Liang, T.; Xie, X.-Q.; Feng, Z.; Meng, L. A new era of antibody discovery: An in-depth review of AI-driven approaches. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 103984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-F.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Guo, L.; Zhong, F.-L.; Luo, X.-G. Genetic engineering and molecular modification of recombinant fully humanized single-domain antibody against Helicobacter pylori UreB. J. China Pharm. Univ. 2024, 55, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janson, G.; Paiardini, A. PyMod 3: A complete suite for structural bioinformatics in PyMOL. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 1471–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Wu, Z.; Pausch, P.; Al-Shayeb, B.; Amerasekera, J.; Doudna, J.A.; Jacobsen, S.E. Genome editing in plants using the compact editor CasΦ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2216822120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Mo, F.; Xu, Z.; Xu, W.; Xu, J.; Yi, Y.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Long, Y.; Zhao, X.; et al. 16S rDNA sequencing analyzes differences in intestinal flora of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) patients and association with immune activation. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 4085–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fu, B.; Song, Z.; Wang, L.; Fu, R.; Lu, X.; Xing, J.; Lv, J.; et al. Sustained exposure to Helicobacter pylori induces immune tolerance by desensitizing TLR6. Gastric Cancer 2024, 27, 324–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.-F.; Xie, S.-A.; Zhang, S.-T. Current research on the interaction between Helicobacter pylori and macrophages. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Bella, C.; D’Elios, S.; Coletta, S.; Benagiano, M.; Azzurri, A.; Cianchi, F.; de Bernard, M.; D’Elios, M.M. Increased IL-17A Serum Levels and Gastric Th17 Cells in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Patients with Gastric Premalignant Lesions. Cancers 2023, 15, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, K.; Meng, W.; Shu, X.; Liang, D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, D. Fecal metabonomics combined with 16S rDNA sequencing to analyze the changes of gut microbiota in rats fed with different protein source diets. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 2687–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iino, C.; Shimoyama, T.; Chinda, D.; Arai, T.; Chiba, D.; Nakaji, S.; Fukuda, S. Infection of Helicobacter pylori and Atrophic Gastritis Influence Lactobacillus in Gut Microbiota in a Japanese Population. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poustforoosh, A.; Faramarz, S.; Negahdaripour, M.; Hashemipour, H. Modeling and affinity maturation of an anti-CD20 nanobody: A comprehensive in-silico investigation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, J.; Kang, G.; Hu, M.; Yuan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H. Homology Modeling-Based in Silico Affinity Maturation Improves the Affinity of a Nanobody. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, S.; Lobo, S.; Shell, M.S.; Shea, J.E. Context Dependency of Hydrophobicity in Intrinsically Disordered Proteins: Insights from a New Dewetting Free Energy-Based Hydrophobicity Scale. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2025, 129, 1904–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, C.; Zerbe, O. The role of leucine and isoleucine in tuning the hydropathy of class A GPCRs. Proteins 2024, 92, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, J.A. Proteins’ Evolution upon Point Mutations. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 14371–14376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento-Miranda, M.; Figueiredo, C. Helicobacter heilmannii sensu lato: An overview of the infection in humans. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 17779–17787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Vosmaer, G.D.; Tytgat, G.N.; Xiao, S.-D.; Ten Kate, F.J. Gastrin (G) cells and somatostatin (D) cells in patients with dyspeptic symptoms: Helicobacter pylori associated and non-associated gastritis. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 58, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Xu, H.; Shen, C.; Chen, X.; Li, C. Effects of sodium butyrate supplementation on inflammation, gut microbiota, and short-chain fatty acids in Helicobacter pylori-infected mice. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.-L.; Xu, T.-T.; Lin, Y.; Mo, Y.-S.; He, B.-Y.; Han, Y.-Y.; Li, J.-Y.; Xia, S.-H.; Zhou, Y.-N.; Liao, J.-Z.; et al. High-dose dual therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication inducing less impact on the gut microbiota. Gut. Pathog. 2025, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidary, M.; Akrami, S.; Madanipour, T.; Shakib, N.H.; Mahdizade Ari, M.; Beig, M.; Khoshnood, S.; Ghanavati, R.; Bazdar, M. Effect of Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric cancer on gastrointestinal microbiota: A narrative review. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1495596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sang, S.; Guan, Q.; Tao, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C. Oral Administration of a Shigella 2aT32-Based Vaccine Expressing UreB-HspA Fusion Antigen with and without Parenteral rUreB-HspA Boost Confers Protection Against Helicobacter pylori in Mice Model. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 894206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, H.; Zeng, G.; Pang, B.; Wang, Q.; Wei, J. Gut microbiome-mediated mechanisms in aging-related diseases: Are probiotics ready for prime time? Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1178596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, G.; Pottakkat, B. Probiotics-A Promising Novel Therapeutic Approach in the Management of Chronic Liver Diseases. J. Med. Food 2024, 27, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Alonso, M.; Aguirre Camorlinga, A.; Messiah, S.E.; Marroquin, E. Effect of adding probiotics to an antibiotic intervention on the human gut microbial diversity and composition: A systematic review. J. Med. Microbiol. 2022, 71, 001625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, S.; Okuno, Y.; Ohta, M. Structure-Based Affinity Maturation of Antibody Based on Double-Point Mutations. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2552, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, M.; Bolender, A.L.; Ducret, A.; Fraidling, J.; Hartman, K.; Looney, C.M.; Rohr, O.; Hickling, T.P.; Kettenberger, H.; Lechmann, M.; et al. Internalization of therapeutic antibodies into dendritic cells as a risk factor for immunogenicity. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1406643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Grouping | Processing Time (Days) | Method of Handling | Animal Numbers |
|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 28 | Physiological saline | 10 |
| Hp only | 28 | Physiological saline | 16 |
| Drug | 28 | Positive drug | 10 |
| Probiotic | 28 | Non-antibody EcN | 10 |
| Ab Probiotic | 28 | Antibody-engineered EcN | 10 |
| Drug/Ab Probiotic | 28 | Antibody-engineered EcN + Positive drug | 10 |
| Prophylactic | (Front) 28 | Engineering EcN | 10 |
| (after) 7 | 0.2 mol/L NaHCO3 + Hp |
| Mutation Site | mCMS-AB | Fold X | I-Mutant |
|---|---|---|---|
| K43L | 0.100 | −0.1298840 | −0.02 |
| K43T | 0.056 | −0.3313354 | −0.97 |
| K43M | 0.019 | −0.0915588 | −0.25 |
| E82W | 0.124 | −0.3929000 | −0.03 |
| I107P | 0.083 | −1.4463000 | −2.33 |
| I107W | 0.178 | −0.1029980 | −1.78 |
| I107F | 0.146 | −0.0543059 | −1.03 |
| R109P | 0.033 | −0.0887277 | −0.85 |
| R109N | 0.007 | −0.0101818 | −0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Hou, M.; Guo, L.; Luo, X. An AI-Designed Antibody-Engineered Probiotic Therapy Targeting Urease to Combat Helicobacter pylori Infection in Mice. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092043
Zhong F, Liu X, Wang X, Hou M, Guo L, Luo X. An AI-Designed Antibody-Engineered Probiotic Therapy Targeting Urease to Combat Helicobacter pylori Infection in Mice. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092043
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Feiliang, Xintong Liu, Xuefang Wang, Mengyu Hou, Le Guo, and Xuegang Luo. 2025. "An AI-Designed Antibody-Engineered Probiotic Therapy Targeting Urease to Combat Helicobacter pylori Infection in Mice" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092043
APA StyleZhong, F., Liu, X., Wang, X., Hou, M., Guo, L., & Luo, X. (2025). An AI-Designed Antibody-Engineered Probiotic Therapy Targeting Urease to Combat Helicobacter pylori Infection in Mice. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092043





