Abstract
Sea urchin aquaculture has experienced remarkable growth in recent years. However, this growth has been accompanied by increased disease prevalence. Notably, spotting disease has particularly severe impacts. In this study, we isolated the pathogen HZ-3-2 from 10 sea urchins with spotting disease, and it was identified as Vibrio splendidus through morphological observations, 16S rDNA sequencing, and whole-genome sequencing. Subsequently, experimental infection confirmed that V. splendidus (HZ-3-2) is the causative agent of spotting disease in this outbreak. The drug sensitivity confirmed the presence of drug resistance genes, such as CPR, QNRS5, and rsmA, which were identified in the genome. The tests indicated that V. splendidus was sensitive to various antibiotics, including fluoroquinolones and florfenicol. Finally, we used the transcriptome to explore the molecular response of the diseased sea urchin. Compared to the control group, a group of sea urchins immersed in a pathogen suspension with a concentration of 107 CFU/mL (group M) resulted in 439 annotated differentially expressed genes. KEGG pathway analysis indicated significant activation of cholesterol metabolism and starch and sucrose metabolism in the S. intermedius. This study highlights the genes NPC1, AMY2A, and MGAM as critical regulators of energy metabolism, and cholesterol synthesis in infected sea urchins. These findings confirm V. splendidus as the bacterium responsible for spotting disease and provide valuable insights into the intestinal molecular response of S. intermedius to infection.
1. Introduction
The global aquaculture industry has proliferated during the last decades, particularly with the increased use of high-density farming techniques. This expansion has led to disease outbreaks in aquaculture animals, displaying explosive and cyclical epidemic patterns [1]. Bacterial diseases occur frequently and pose important challenges to the growth of the global sea urchin aquaculture [2,3]. In China, sea urchin production reached 470.6 tons in 2023, covering an aquaculture area of 16,800 hectares [4]. Among these, Strongylocentrotus intermedius is a primary farmed species in northern China. Currently, its annual production exceeds 200 tons [5] and yields at least 18 million freshly metamorphosed juveniles, which can be used to initiate a culture annually [5]. Sea urchins are also eaten or farmed in Norway [6], the United States [7,8], and Russia [9,10]. The rational development and utilisation of sea urchin resources positively protect the marine ecological balance [11]. However, with the development of aquaculture, outbreaks of spotting disease have become more frequent. This impacts the development of China’s sea urchin aquaculture [12].
The clinical signs of spotting disease include the appearance of red or purplish-red spots or patches on the test of sea urchins, ulceration and tissue damage at the site of infection, and spine shedding. Eventually, the sea urchin’s internal contents, such as gonadal tissue leak due to test fragmentation, ultimately resulting in the sea urchin’s death [12,13]. During the summers of 2002 and 2003, large-scale mortalities of S. intermedius farmed along the coast of Dalian occurred due to outbreaks of spotting disease, resulting in substantial economic losses for local aquaculture farmers. The identification of pathogens was a prerequisite for the prevention and control of aquatic diseases. Previous studies have identified that the pathogens responsible for causing spotting disease are mainly Vibrio sp. [12,14], Flexibacter sp. [15], and Enacibaculum sp. [16]. In 2005, an outbreak of spotting disease caused by other species of Vibrio was reported [17]. However, it is unclear which Vibrio species caused the disease in 2005. This undoubtedly poses a severe challenge to using immunological methods for preventing and controlling “spotting disease” in sea urchin aquaculture. Therefore, it is crucial to isolate and identify new bacteria associated with spotting disease.
In aquaculture, various methods for disease prevention and control have been identified. For instance, probiotics such as Clostridium butyricum [17] and Bacillus [18] were added during the farming process to enhance animal immunity [19]. Alternatively, chemical methods such as sodium hypochlorite and ozone were used for disinfection [20]. These measures aimed to reduce the occurrence of diseases during the farming process, thereby improving the survival rate of aquatic animals. However, in the actual production processes of aquaculture, the use of antibiotics to address bacterial diseases remains one of the most cost-effective and efficient methods [21]. Conducting drug sensitivity tests on an isolated bacterium is essential for identifying effective antibiotics. Therefore, recommending appropriate antibiotics based on relevant aquaculture medication standards is constructive for preventing and controlling the spotting disease of sea urchins.
Gene expression analysis serves as a link between genetic material and traits, and it can be regulated by changes in the external environment to adapt to environmental variations [22]. Transcriptome sequencing remains one of the effective methods for studying gene regulatory expression and analyzing biological processes at the molecular level [23,24]. In recent years, transcriptomics has been applied to study the immune response mechanisms of S. intermedius in response to the infection of Vibrio harveyi [1], as well as to elucidate the role of phagocytosis as the primary immune response in sea urchins [25]. These experiments primarily focused on the molecular response of the coelomic fluid of sea urchins to the pathogen. As an organ in aquatic animals, the intestine also has certain immune functions [26]. However, it remains unknown whether the intestine of sea urchins possesses similar immune functions and molecular response changes. In summary, this study employed transcriptome sequencing to investigate the molecular response mechanisms of the intestine in S. intermedius following spotting disease infection, aiming to provide reasonable hypotheses and insights.
In this study, we isolated and identified the pathogen (HZ-3-2) of spotting disease. Following this, we assess the drug sensitivity of the HZ-3-2 strain and analyze the molecular response of S. intermedius following infection with HZ-3-2. This study provides theoretical references for preventing and controlling the spotting disease of S. intermedius.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Animals
The sea urchins (S. intermedius) used in this experiment were 1–1.5 years old and cultivated at an aquaculture facility in Lvshun, Dalian, China. We randomly selected 100 healthy sea urchins with a mean test diameter of 40.27 ± 4.53 mm, test height of 20.63 ± 2.9 mm, and body weight of 25.98 ± 6.55 g. They were transported to the Key Laboratory of Mariculture & Stock Enhancement in North China’s Sea, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Dalian Ocean University, on 1 March 2024. The temperature was increased by 0.5 °C per day until it reached a constant value of 22 ± 0.5 °C, and the water temperature was maintained until the end of the experiment. They were kept in 60 L plastic seawater tanks for 14 days. During the acclimation period, water was replaced at approximately 50% daily, and the sea urchins were fed with kelp Laminaria japonica at 5% of their body weight per day. After acclimation, the healthy sea urchins were randomly divided into five groups of 15 individuals each and placed in 60 L plastic tanks in preparation for the subsequent experiments.
2.2. Strain Isolation and Identification
The isolation method was performed as described [3]. We selected 10 sea urchins showing apparent red spots, which were raised in the laboratory at Dalian Ocean University. The sea urchins were rinsed with UV-sterilised seawater. The peristomal membrane of diseased S. intermedius was cut open using sterile scissors. We used a pipette to aspirate 100 μL of body cavity fluid and streaked it onto 2% NaCl Nutrient Agar (NA) plates for isolation. The colonies were cultured at 28 °C for 24 h, and their colony morphology was observed. Colonies with consistent morphology were selected and streaked for further isolation and identification. This procedure was repeated 3–4 times until a pure culture of the dominant strain was obtained. The identified strain was preserved in glycerol and stored at −80 °C for further use.
The identified strains were submitted to Biotechnology Bioengineering (Shanghai) Ltd. (Shanghai, China) for sequencing analysis. The bacterial genomic DNA was extracted using a bacterial genomic DNA extraction kit (Tiangen, Beijing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Two universal bacteria primers [27] for the 16S rDNA gene were synthesized by Biotechnology Bioengineering (Shanghai) Ltd. (Table S1). The quantitative qRT-PCR reaction mixture consisted of a total volume of 20 µL, comprising 2 µL of cDNA template, 10 µL of 2× SYBR Green Master Mix (TaKaRa, Shiga, Japan), 0.8 µL of each primer, and 6.4 µL of PCR-grade water. The PCR conditions were set as follows: initial denaturation at 94 °C for 5 min, denaturation at 94 °C for 45 s, annealing at 55 °C for 45 s, extension at 72 °C for 90 s, followed by 30 cycles, and final extension at 72 °C for 10 min. Finally, the obtained sequences were subjected to homology searches using GenBank, and a phylogenetic tree was built based on previous studies [28].
2.3. Drug Sensitivity Test of Isolated Strains
The antibiotic resistance and susceptibility of the target strain (HZ-3-2) to 18 commonly used antibiotics were determined using the Kirby–Bauer disc diffusion method. A 100 µL aliquot of bacterial suspension (The concentration is 107 CFU/mL) culture was evenly spread on 2% NaCl NA. After the bacterial suspension was fully absorbed, the plate was divided into four quadrants and a circular antibiotic disc was placed in each quadrant. The plate was then incubated at 28 °C for 24 h. The diameter of the inhibitory zone was measured by using vernier calipers. Finally, we determine the sensitivity of the isolated strains to various antibiotics, in accordance with the specified sensitivity ranges.
2.4. Experimental Infection on V. splendidus
The experimental infection method was performed as described previously [1]. The isolated bacterial suspension was cultured on agar plates containing 2% NaCl and incubated at 27 °C for 24 h in a biochemical incubator. Single colonies were then selected and inoculated into a 2% NaCl NA liquid medium. The culture was incubated overnight at 27 °C in a shaking incubator, followed by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 10 min. After centrifugation, the supernatant was discarded. Later, a 1000 μL aliquot of sterilized seawater was added to the centrifuge tube, and the pellet was transferred into it. The cell concentration was determined using a hemocytometer. Three bacterial suspensions were prepared at concentrations of 103 CFU/mL, 105 CFU/mL, and 107 CFU/mL.
Five groups of sea urchins were selected, four of which were wounded by scraping 1.5 cm2 of spines. Three of the scraping spine groups were randomly selected and immersed in 3 L of bacterial suspension at concentrations of 103 CFU/mL, 105 CFU/mL, and 107 CFU/mL for a duration of two hours, respectively. To prevent oxygen depletion in the small water volume, the infection procedure was repeated every two hours over three cycles, totalling six hours of infection. Sea urchins that were immersed in a bacterial suspension with a concentration of 107 CFU/m were designated group M. The remaining group of sea urchins was immersed directly in seawater to serve as the control group (designated as group C). Additionally, the group that did not undergo spine scraping was directly immersed in a bacterial suspension at 107 CFU/mL. After completing the above procedures, the sea urchins were transferred to a water tank, and daily observations along with clinical signs were documented. The test was conducted over seven days.
After the experimental infection, we dissected the sea urchins that survived in the bacterial suspension at 107 CFU/mL. We used three samples, each composed of two randomly selected pieces of intestine, for transcriptome sequencing, which comprised three pooled replicates (n = 3).
2.5. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Analysis
DNA was extracted using MagPure Bacterial DNA Kit (D6361-02, Magen, Foshan, China). The concentration of DNA was determined using the Qubit 4.0 (Thermo, Waltham, MA, USA, Q33226). And the integrity of the DNA was evaluated through 1% agarose gel electrophoresis.
The whole genome DNA was randomly fragmented to an average size of 200–400 bp. The fragments were obtained through end-repair, 3′ adenylation, adapter ligation, and PCR amplification. After purification with magnetic beads, the Qubit 4.0 fluorometer was used to validate the library, while the library length was evaluated using 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. The qualified libraries were sequenced using the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform at Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China). Following the sequencing process, raw reads were filtered utilizing Trimmomatic (v0.36) to eliminate adaptors and low-quality reads, resulting in the clean reads. Genome assembly was conducted employing SPAdes (v3.15), and Gapfiller (v1.11) was used for the purpose of filling gaps. We used Pilon (v3.5.0) to improve the accuracy of draft genomes by correcting base errors and filling gaps. Gene prediction was performed using Prokka (v1.1). Tandemly repeated DNA motifs were identified with TRF (v4.09). Finally, we utilized Circos software (v0.66) to create circular genome maps.
2.6. Genome Functional Annotation
Gene predictions and annotations were generated using Prokka (Version 1.10) and the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) non-redundant protein (NR) database [29]. Subsequently, Cluster of Orthologous Groups (COG) [30], Gene Ontology (GO) [31], and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) [32] were used to predict gene functions. The Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database (CARD) [33] was consulted to predict which were the virulence genes and antibiotic resistance genes.
2.7. Libraries Construction and High-Throughput Sequencing
Total RNA was extracted from the tissues using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol [34]. Subsequently, total RNA was assessed for quality and quantity using an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The sample standards were OD260/280 ≥ 1.8.
Library preparation was performed using the Optimal Dual-mode mRNA Library Prep Kit (BGI, Shenzhen, China). A defined amount of RNA was denatured at an appropriate temperature to disrupt its secondary structure, and the mRNA was subsequently enriched using oligo (dT)- attached magnetic beads. RNA was fragmented using fragmentation reagents after incubating at an appropriate temperature for a specified period.
First-strand cDNA was generated using random hexamer-primed reverse transcription, followed by second-strand cDNA synthesis. The synthesized double-strand cDNA is subject to an end-repair reaction. After the end-repair of the cDNA, a single ‘A’ nucleotide was added to the 3′ ends of the blunt fragments through an A-tailing reaction. Subsequently, an adaptor-ligation reaction system was configured to ligate adaptors to the cDNA, and the library products were amplified PCR and subjected to quality assessment.
Next, the single-stranded library products were generated through denaturation. A circularisation reaction system was established to create the single-stranded cyclized DNA products. Any uncyclised single-stranded linear DNA molecules were digested. The final single-stranded circularised library was amplified using phi29 and rolling circle amplification (RCA) to produce DNA nanoballs (DNBs), each containing more than 300 copies of the initial single-stranded circularised library molecule. The DNBs are loaded into the patterned nanoarray, and PE 100/150 base reads are generated on the G400/T7/T10 platform (BGI-Shenzhen, Shenzhen, China).
2.8. Transcriptome Assembly and Annotation
The raw data was filtered with SOAPnuke (v1.6.5) [35] by removing reads containing adapters (adapter trimming). Clean reads were obtained and stored in FASTQ format. The clean data were mapped to the reference genome by HISAT (v2.2.1) [36]. The clean data were mapped to the assembled unique gene by Bowtie2 (v2.4.5) [37].
The expression level of genes was calculated by RSEM (v1.3.1) [38]. Transcripts were reconstructed using StringTie (v2.2.1) [39], and cuffmerge was employed to integrate the assembled transcripts. Cuffcompare was employed to compare the integrated transcripts with a reference annotation. Transcripts with class code types u, i, o, and j were selected as novel transcripts. The protein-coding potential of the novel transcripts was predicted using CPC (v0.1). Gene annotation was performed using public databases (e.g., KEGG, GO).
Differential gene analysis was conducted between groups using DEGSeq. (Bioconductor version v3.20), with a fold change ≥ 2 and an Adjusted p-value ≤ 0.001. PoissonDis was used for between-sample differential gene analysis, with a fold change of ≥2 and a false discovery rate (FDR) of ≤0.001. DEGs were functionally classified according to KEGG annotation results and official classification. KEGG enrichment analysis was performed using the phyper function in R software (v4.4.3). With Q-value ≤ 0.05 as the threshold, candidate genes that met this condition were defined as being significantly enriched.
2.9. Real-Time Fluorescent PCR (qRT-PCR) Gene Validation
To validate the RNA-seq results, six DEGs were selected for qRT-PCR (Table S2). Total RNA was extracted, and reverse transcription was performed as described previously [40]. The relative quantities of the target genes were calculated using β-actin from S. intermedius as an endogenous control gene. The qRT-PCR was performed using the LightCycler96 real-time system (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). The reactions were carried out according to the manufacturer’s instructions for FastStart Essential DNA Green Master (Roche, Switzerland). PCR primers were designed and synthesized by Sangon Biotechnology (Shanghai, China). The quantitative qRT-PCR reaction mixture consisted of a total volume of 20 µL, comprising 2 µL of cDNA template, 10 µL of 2 × SYBR Green Master Mix (TaKaRa, Tokyo, Japan), 0.8 µL of each primer, and 6.4 µL of PCR-grade water. The thermal cycling conditions were set: an initial denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, followed by 45 cycles. Annealing and elongation phases were conducted at 95 °C for 5 s and 60 °C for 32 s. Three independent biological replicates and three technical replicates were performed for each group. Melt curve analysis of the amplification products confirmed the presence of a single PCR product at the end of the PCR reaction. The relative expression levels of target genes were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCT method described previously [41].
3. Results
3.1. Pathogenic Bacterium of Sea Urchin Spotting Disease
In order to determine the strain of HZ-3-2, which was isolated from the outbreak of diseased S. intermedius, we conducted morphological observations, 16S rDNA, and whole-genome sequencing analysis. After 24 h of isolation and culturing, yellow, round colonies with smooth surfaces and regular edges were observed.
PCR amplification of 16S rDNA resulted in a 1210-bp fragment. We first sequenced the PCR fragment and then performed a homology search using GenBank. Based on the results, the strain was identified as V. splendidus with 99% similarity and an e-value of 0.0. Comparison results and PCR pictures can be found in Supplement S1 and Figure S1. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using Mega 5.0 software. V. splendidus and other Vibrio 16S rDNA sequences were selected from GenBank. The 16S rDNA phylogenetic tree results showed that HZ-3-2 and V. splendidus (GenBank accession No. MN945355.1) were clustered into one branch (Figure 1). The results of the Average Nucleotide Identity (ANI) analysis indicated that strain HZ-3-2 shares a 97.48% identity with V. splendidus S 27 09 GCA 029890915.1 (Figure 2 and Table S3). Therefore, based on the above results, it was preliminarily concluded that the HZ-3-2 was V. splendidus, and the identification result is at the species level.
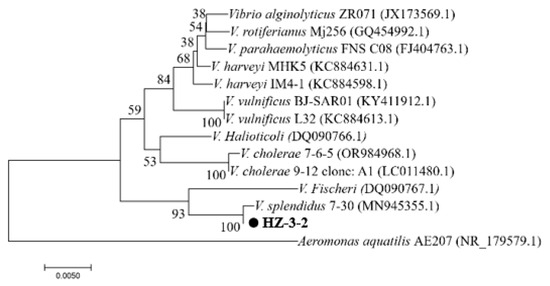
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree of Vibrio spp. based on the 16S rDNA gene sequence. Note: Numbers in parentheses represent the sequences’ accession numbers in GenBank.
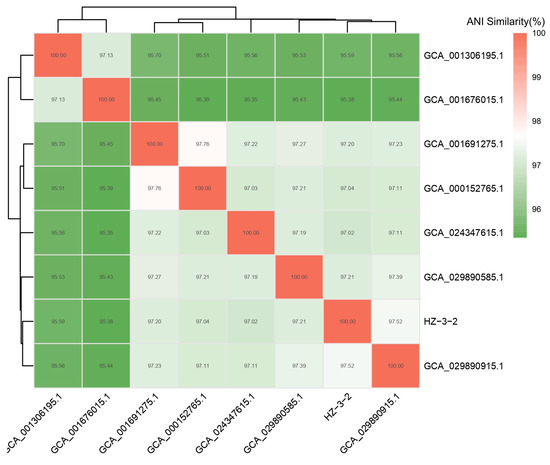
Figure 2.
Average nucleotide identity distance heat map.
3.2. Results of Experimental Infection on V. splendidus
We infected healthy urchins with HZ-3-2 to confirm that it was the pathogen responsible for spotting disease. Before the formal experiments, we conducted pre-experiments to determine that sea urchins died at a bacterial concentration of 105 CFU/mL. The results showed that in all experimental groups, sea urchins displayed distinct red spots, a clinical sign of infection (Figure 3). During the experiment, the mortality rate increased with higher bacterial concentrations. In group M, with a bacterial concentration of 105 CFU/mL, the average mortality rate reached 20% within 7 d. When the bacterial concentration was 107 CFU/mL, the average mortality rate in group M was 66.7% (Table S4). The above analysis showed that V. splendidus is the pathogenic bacterium of spotting disease.

Figure 3.
Signs of spotting disease in sea urchin. Note: The red arrows show signs of spotting disease.
3.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing Analysis of HZ-3-2
3.3.1. Genome Assembly
Regarding the assembled genomic data, we used the Circos (v0.66) software to create a circular genome map, which included GC content, sequencing depth, Gene element content, and COG category. The results showed that the genome size was 2,814,132 bp, with a GC content of 44.13%, and a 100% coverage (Figure 4).
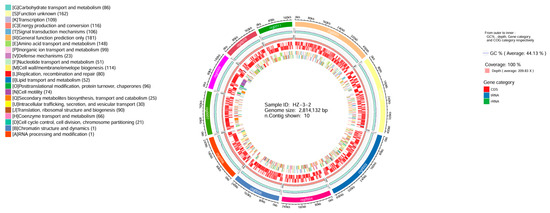
Figure 4.
Genome circos diagram. Note: From the inside out, they are GC content, sequencing depth, gene element display, and COG function display, respectively.
3.3.2. NR Database Annotation
We used the NR database annotation to reveal that Vibrio accounted for 84.72% of the organisms showing sequence homology with the HZ-3-2 strain. Among them, V. splendidus accounted for 62.94% and others accounted for 15.28% (Figure 5).
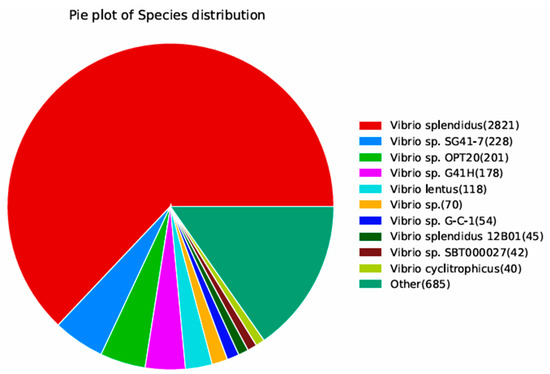
Figure 5.
Species distribution map of the results of sequence alignment using the NR database.
3.3.3. Database Annotation
In the CARD database annotation analysis, we discovered that the HZ-3-2 strain contained CRP, rsmA, tet(35), ugd, catB9, and other resistance genes. These resistance genes produce resistance to fluoroquinolone antibiotics, macrolide antibiotics, penicillin, peptide antibiotics, phenicol antibiotics, etc. (Table S5).
The results of the COG, GO, and KEGG analyses of HZ-3-2 are presented in Figures S2, S3, and S4, respectively.
3.4. Results of Drug Susceptibility Testing of V. splendidus
To determine the susceptibility of V. splendidus to antibiotics, we chose cultured bacterial suspension for drug sensitivity testing. We analyzed the results based on drug sensitivity testing and the inhibition zone interpretation standard of the disk diffusion method. The results show that the V. splendidus strain is sensitive to several antibiotics, including cephalosporins (ceftazidime), tetracyclines (doxycycline), fluoroquinolones (enoxacin, levofloxacin, norfloxacin, and ciprofloxacin), sulfonamides (trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole), aminoglycosides (gentamicin and streptomycin), polymyxin, and florfenicol. In addition, the V. splendidus strain showed intermediate sensitivity to other antibiotics, such as penicillin, Rifampin, Chloramphenicol, and erythromycin. Furthermore, the V. splendidus strain was resistant to vancomycin, Ofloxacin, and Tetracycline (Table 1).

Table 1.
Drug sensitivity test result of HZ-3-2.
3.5. Transcriptome Analysis of Sea Urchins Infected with V. splendidus in Different Ways
3.5.1. Transcriptomic Data Quality Control Information
In this study, to investigate the molecular responses of sea urchins to infection with V. splendidus, we selected the intestines of sea urchins for transcriptome sequencing. And three biological replicates were set up for each group. The results yielded 202.56 million raw reads. After quality assessment, 199.05 million clean reads and 59.71 Gb of clean bases were obtained. The proportion of bases with a quality score ≥ Q20 and ≥Q30 (Ratio of bases with mass values > 20 and 30) for each sample exceeded 98% and 94%, respectively. The clean read rate was greater than 97%, demonstrating the high quality of the reads (Table S6).
3.5.2. Statistical Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
We compared DEGs between the S. intermedius infected by different methods. Genes were selected using the thresholds |log2fc| ≥ 2 and p < 0.05, and the gene expression changes were visualized using a volcano plot. The comparison between groups M and C revealed 439 DEGs, with 245 genes upregulated and 194 genes downregulated (Figure 6).
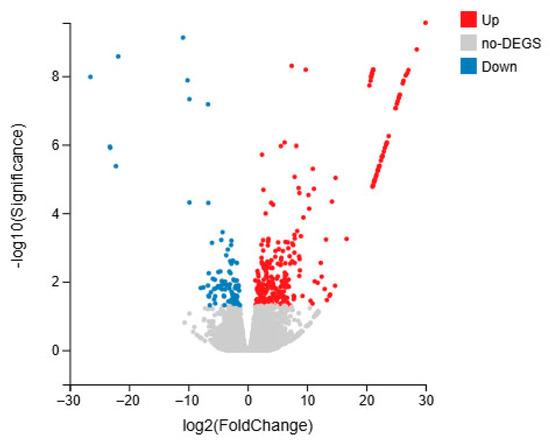
Figure 6.
DEG expression changes in S. intermedius of immersed infection (group M vs. C).
3.5.3. KEGG Pathway Classification Analysis
In the KEGG pathway classification analysis, the genes involved in KEGG metabolic pathways were categorized into five branches: cellular processes, environmental information processing, genetic information processing, metabolism, and organismal systems. Further classification and statistical analysis were conducted within each branch. The cellular processes category primarily involves transport, catabolism, and cellular community-eukaryotes. In the classification of environmental information processing, enrichment was predominantly in signal transduction. In the genetic information processing category, group M was primarily classified under replication and repair. In the organismal systems category, the digestive, endocrine, and immune systems were the most enriched (Figure 7).
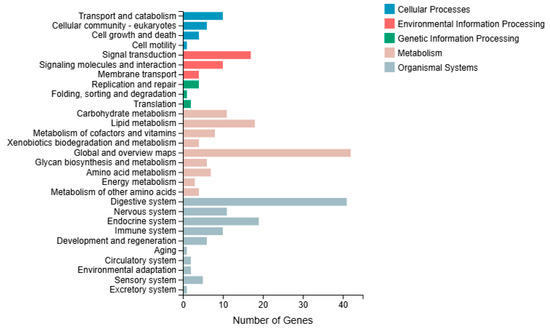
Figure 7.
KEGG classification analysis in the immersed infection of S. intermedius (group M vs. C).
3.5.4. KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
The top 20 most significantly correlated pathways were selected for KEGG enrichment analysis, with 158 DEGs enriched in group M. Compared to group C, group M was primarily enriched in cholesterol metabolism and starch and sucrose metabolism (Figure 8).
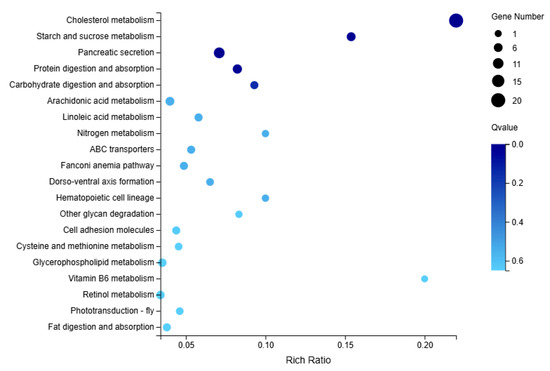
Figure 8.
KEGG enrichment analysis in the immersed infection of S. intermedius (group M vs. C).
3.6. Transcriptome Quality Analysis Based on qRT-PCR Verification
In order to determine the accuracy of the DEGs identified in the RNA-seq expression analysis, we selected 6 DEGs from the mRNA library for verification. These genes may be involved in sea urchins’ energy metabolism, immunity, and cholesterol secretion. The qRT-PCR results were significantly correlated with the RNA-seq results (p < 0.05). We find that qRT-PCR and RNA-seq show the same trend. Therefore, it was confirmed that the transcriptome data of the S. intermedius used in this study are reliable (Figure 9).
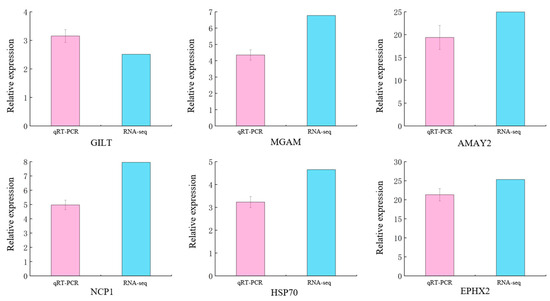
Figure 9.
Verification of DEGs using qRT-PCR in immersed infected ways of S. intermedius. Note: The type of error bars is mean ± SD.
4. Discussion
4.1. V. splendidus Is the Pathogen of S. intermedius Spotting Disease
With the expansion of the sea urchin aquaculture industry, bacterial infections remain a major challenge, and spotting disease is one of the most severe threats [3]. The 16S rDNA gene sequence is the most widely employed genetic marker for bacterial taxonomy [42]. However, due to the exceptionally high similarity of 16S rDNA gene sequences among Vibrio species, the precision of species-level identification is constrained [43]. Therefore, we performed 16S rDNA and whole-genome sequencing of the isolated bacterial strain, confirming its identification as V. splendidus at the species level. The experimental results indicated that clinical signs of artificially infected S. intermedius were similar to those of naturally infected sea urchins, and the strains isolated from the diseased sea urchins were the same type. In this experiment, S. intermedius suffering from spotting disease exhibited red spots on the body wall, spine loss, reduced vitality, and a noticeable decline in tube foot adhesion, which is similar to findings of previous research [25,44]. V. splendidus is a Gram-negative bacterium belonging to the family Vibrionaceae, genus Vibrio, and is widely distributed in marine environments [45]. Different strains of V. splendidus have been linked to the mortality of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) [46], turbot larvae (Scophthalmus maximus) [45], and oysters (Crassostrea gigas) [47]. They are also associated with ulcerative syndrome in sea cucumbers (Apostichopus japonicus) [48], which seriously threatens the aquaculture industry’s growth.
Infections in marine systems are usually characterized by complex interactions among multiple microbial species, some of which may be pathogenic, while others are opportunistic [49,50]. Previous studies have found that spotting disease can be caused by several bacteria [12,14,15,16]. However, the underlying mechanism of infections related to the spotting disease remains unknown and requires further study.
4.2. Spotting Disease Prevention and Treatment Recommendations
This study utilised varying concentrations of V. splendidus to infect S. intermedius, finding that higher bacterial concentrations led to a gradual increase in sea urchin mortality. These results are consistent with prior research findings [44]. In immersed experiments, the disease did not occur without damage to the body surface. Therefore, we suggest that damage to the body surface of sea urchins may be an important factor in causing spotting disease. In sea urchin aquaculture, controlling stocking density (the current consensus is 33.7 g/m2 to 2.7 kg/m2 [51,52]) is essential to reduce test damage that may allow sea urchins to avoid V. splendidus infection. At the same time, we can reduce the rate of disease and deaths by using segregation methods in sea urchin aquaculture [53,54].
It is widely recognised that the reasonable use of antibiotics is an effective strategy for preventing and controlling diseases in aquatic species. [23]. The antimicrobial susceptibility assays in this study revealed that V. splendidus is sensitive to norfloxacin, ofloxacin, enrofloxacin, and florfenicol. According to the guidelines from the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China on the regulated use of antibiotics in aquaculture [55], norfloxacin, and ofloxacin [56] are prohibited in aquaculture. Therefore, florfenicol and enrofloxacin are recommended as potential treatments for spotting disease induced by V. splendidus. However, the HZ-3-2 strain is highly sensitive to fluoroquinolone antibiotics and cephalosporins. This may be related to the weakening and loss of function caused by mutations or methylation in resistance genes [57,58]. In treating spotting disease, we can isolate and identify its pathogenic bacteria at first. After that, we can perform drug testing to screen for drugs sensitive to the causative microorganisms to prevent and control the spotting disease.
4.3. Molecular Responses of Sea Urchins Infected with V. splendidus
Prior research has demonstrated that V. splendidus profoundly threatens the survival of various marine species, thus hindering the growth of the aquaculture industry [47,59]. This study confirms V. splendidus is the pathogenic bacterium of spotting disease in S. intermedius. Nevertheless, the molecular responses of S. intermedius to infection by V. splendidus remain primarily uncharacterized, posing a challenge for effective prevention and control. In this study, we used the immersion method to simulate natural conditions, strengthening the validity of the experimental findings. We found that S. intermedius mounts a complex molecular response and involving numerous DEGs following the infection of V. splendidus. This information enhances our understanding of the molecular responses of sea urchin intestines to the infection of V. splendidus.
As invertebrates, sea urchins’ immune response primarily relies on coelomic fluid phagocytes to counter invading pathogens [25,60]. The intestine is recognized as an immune organ [26]. However, the kind of immune effects it exerts and its potential role in molecular responses after V. splendidus infection in sea urchins remain unknown.
The experimental results indicate that the starch and sucrose metabolism pathway was significantly activated in group M, with AMY2A and MGAM expression being upregulated. AMY2A [61,62] and MGAM [63,64] are crucial in the metabolic processing of starch and carbohydrates. The upregulation of both genes promotes the absorption of carbohydrates. This phenomenon may indicate a correlation between the energy metabolism and bacterial infection in sea urchins.
The cholesterol metabolism pathway showed the most significant response in group M, with NPC1 expression significantly upregulated. NPC1 and NPC2 have a synergistic effect that enhances the efficiency of cholesterol binding and transport [65,66]. These findings suggest a noticeable increase in cholesterol expression within the intestine of S. intermedius after the infection of V. splendidus. Cholesterol possesses pro-inflammatory properties that promote macrophage accumulation, trigger inflammatory responses, and induce apoptosis, with excessive levels potentially affecting immune regulation [67]. That likely reflects toxic damage to the sea urchin following the bacteria’s invasion of its intestinal tissues. This discovery contributes to our understanding of the molecular response changes in S. intermedius infection with V. splendidus.
Moreover, NPC1 is an essential antigen receptor and an important component of filovirus entry into the host to initiate infection and pathogenesis [68]. Whether NPC1 also functions as a carrier or mediator for V. splendidus entry into the host is uncertain. That deserves further investigation in future studies.
5. Conclusions
This study confirmed V. splendidus as a causative agent of spotting disease in sea urchins. Based on antimicrobial susceptibility testing, florfenicol and enrofloxacin are potential treatments for V. splendidus-induced spotting disease. We used immersed methods to infect S. intermedius with V. splendidus and compared transcriptome sequencing results with the control group, ultimately identifying 439 DEGs. S. intermedius exhibits altered energy metabolism, cholesterol synthesis, and immune responses following V. splendidus infection, with starch and sucrose metabolism, and cholesterol metabolism pathways activated in the intestine. This transcriptome sequencing study provides valuable insights into the intestinal molecular response of S. intermedius to V. splendidus infection.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms13092019/s1, Figure S1. PCR photo; Figure S2. Function classification statistics of COG functional genes. Figure S3. GO function annotation classification statistics chart. Figure S4. KEGG annotation classification statistics. Table S1. List of primers used for 16S rDNA validation. Table S2. List of primers used for qRT-PCR validation. Table S3. Candidate species with the most optimal Average Nucleotide Identity comparison outcomes. Table S4. Table of immersed infection results (group M). Table S5. CARD database annotation statistics. Table S6. Quality of the Transcriptome Sequencing Data. Supplement S1. 16S result.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.L.; Methodology, S.L. and J.D.; Formal analysis, S.L., F.T., L.H. and J.S.; Investigation, S.L., F.T., Y.W., H.X., Z.Z., L.C., L.H. and J.S.; Writing—original draft, S.L.; Writing—review and editing, C.Z. and J.D.; Visualization, F.T., Y.W., H.X., Z.Z. and L.C.; Supervision, J.D.; Funding acquisition, J.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Major Agriculture Project of the Liaoning Provincial Science and Technology Department (Project No. 2023JH1/10200007, for Jun Ding), the Liaoning Province “Xingliao Talent Plan” Leading Talents Project (Project No. XLYC2202001, for Jun Ding), the Central Government Subsidy Project for Liaoning Fisheries (for Jun Ding, 2023), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program) (Project No. 32373109, for Jun Ding).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study due to sea urchins belonging to the invertebrates.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article, and all sequence data have been submitted to the NCBI Short-Read Archive (SRA) with the accession number PRJNA1202030. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| NA | Nutrient Agar |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| HGAP | Hierarchical Genome Assembly Process |
| COG | Cluster of Orthologous Groups |
| NR | non-redundant |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| CARD | Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database |
| RCA | rolling circle amplification |
| DNABs | DNA nanoballs |
| PE | Paired-end |
| DEGSeq | Differentially Expressed Genes from RNA-seq data |
| FDR | false discovery rate |
| qRT-PCR | Real-Time Fluorescent PCR |
| Q20 | Ratio of bases with mass values >20 |
| Q30 | Ratio of bases with mass values >30 |
References
- Hao, P.; Han, L.; Quan, Z.; Jin, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Gao, C.; Wang, L. Integrative mRNA-miRNA interaction analysis associated with the immune response of Strongylocentrotus intermedius to Vibrio harveyi infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 134, 108577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Zhuang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Shao, Y.; Guo, M.; Lv, Z.; Li, C.; Han, Q.; Zhang, W. Green fluorescent protein-tagged Vibrio splendidus for monitoring bacterial infection in the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Aquaculture 2020, 523, 735169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Dang, H.; Huang, Y.; Quan, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, W.; Ding, J. Vibrio coralliilyticus as an agent of red spotting disease in the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Aquac. Rep. 2019, 16, 100244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs; China Fisheries Society. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2024; Volume 978, p. 3, (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.M.; Zhao, C.; Chang, Y. Large-scale production of sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus intermedius) seed in a hatchery in China. Aquac. Int. 2019, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, P.; Siikavuopio, S.; Mortensen, A. Sea urchin aquaculture in Norway. In Echinoderm Aquaculture; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 147–173. [Google Scholar]
- Rogier, T.T. An Integrated Assessment of the Red Sea Urchin (Strongylocentrotus franciscanus) Fisheries in Southern California and Washington State: Addressing Sustainability and Vulnerability in the face of Climate Change. Environmental Science, Biology. Master’s Thesis, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA, 2016. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1773/36739 (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Angwin, R.E.; Hentschel, B.T.; Anderson, T.W. Gonad enhancement of the purple sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus, collected from barren grounds and fed prepared diets and kelp. Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Aquaculture of green sea urchin in the Barents Sea: A brief review of Russian studies. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 2080–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Distribution patterns and biological aspects of Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis (Echinoidea: Echinoida) in Russian waters of the Barents Sea: Implications for commercial exploration. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2024, 34, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers-Bennett, L.; Okamoto, D. Mesocentrotus franciscanus and Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. In Developments in Aquaculture and Fisheries Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 43, pp. 593–608. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Qu, J.; Zhao, X. Pathogenic mechanism of causative Vibrio found in “red spotting” diseased sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. J. Dalian Ocean Univ. 2005, 20, 11–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Kong, Y. Biological characteristic and pathogenicity of the pathogenic vibrio on the “red spot disease” of Strongylocentrotus intermedius. J. Fish. China 2006, 30, 371–376. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; He, B.; Chang, Y.; Ding, J. Characterization of the bacterial community associated with red spotting disease of the echinoid Strongylocentroyus intermedius. Aquaculture 2020, 529, 735606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, K.; Hirano, T.; Shimizu, M.; Ezura, Y. Isolation and pathogenicity of the causative bacterium of spotting disease of sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Fish. Sci. 1997, 63, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, Y.; Tajima, K.; Ezura, Y. Resuscitation of Tenacibaculum sp., the causative bacterium of spotting disease of sea urchin Strongylocentroutus intermedius, from the viable but non-culturable state. Fish. Sci. 2004, 70, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yu, X.; Li, L.; Ye, H.; Wang, S.; Gai, C.; Xu, L. Potential effects of dietary probiotics with Chinese herb polysaccharides on the growth performance, immunity, disease resistance, and intestinal microbiota of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. World Aquac. Soc. 2021, 52, 1194–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengpipat, S.; Rukpratanporn, S.; Piyatiratitivorakul, S.; Menasaveta, P. Immunity enhancement in black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) by a probiont bacterium (Bacillus S11). Aquaculture 2000, 191, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattaraj, S.; Ganguly, A.; Mandal, A.; Das Mohapatra, P. A review of the role of probiotics for the control of viral diseases in aquaculture. Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 2513–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munang’andu, H.; Mutoloki, S.; Evensen, Ø. Prevention and control of viral diseases in aquaculture. In Aquaculture Virology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 77–93. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.; Cheng, J.; Feng, W.; Lei, M.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, Y.; Deng, G. Identification and antibiotic sensitivity of a pathogenic Aeromonas veronii from Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Genom. Appl. Biol. 2021, 40, 2047–2053. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.; Ding, B.; Han, L.; Xie, J.; Wu, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W. Gene expression patterns of sea urchins (Strongylocentrotus intermedius) exposed to different combinations of temperature and hypoxia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2022, 41, 100953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Su, Y.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Ke, Q.; Han, K.; Zheng, W. Transcriptome analysis of the Larimichthys crocea liver in response to Cryptocaryon irritans. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 48, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvaraj, S.; Yasin, I.; Karim, M.; Saad, M. Transcriptome analysis of immune response in recombinant cell vaccine expressing OmpK vaccinated juvenile seabass (lates calcarifer) head kidney against vibrio harveyi infection. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 21, 100799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Leng, X.; Jiang, H.; Liu, L.; Li, C.; Chang, Y. Transcriptome sequencing reveals phagocytosis as the main immune response in the pathogen-challenged sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 94, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.; Yamamoto, F.; Low, C.; Loh, J.; Chong, C. Gut immune system and the implications of oral-administered immunoprophylaxis in finfish aquaculture. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 773193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Hongyu, B.; Jiang, C.; Mino, S.; Meirelles, P.M.; Thompson, F.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Sawabe, T. Vibrio taketomensis sp. nov. by genome taxonomy. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 43, 126048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limin, F.; Beifang, N.; Zhengwei, Z.; Sitao, W.; Weizhong, L. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar]
- Galperin, M.Y.; Wolf, Y.I.; Makarova, K.S.; Alvarez, R.V.; Landsman, D.; Koonin, E.V. COG database update: Focus on microbial diversity, model organisms, and widespread pathogens. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D274–D281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.; Blake, J.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.; Davis, A.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.; Eppig, J.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoru, K.; Susumu, G.; Shuichi, K.; Yasushi, O.; Masahiro, H. The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D277–D280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Raphenya, A.R.; Alcock, B.; Waglechner, N.; Guo, P.; Tsang, K.K.; Lago, B.A.; Dave, B.M.; Pereira, S.; Sharma, A.N.; et al. CARD 2017: Expansion and model-centric curation of the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D566–D573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Gao, C.; Xiao, H.; Ruan, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Chang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, H.; Han, B. Feeding Behavior, Gut Microbiota, and Transcriptome Analysis Reveal Individual Growth Differences in the Sea Urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Biology 2024, 13, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shi, C.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Yu, C.; Li, Z. SOAPnuke: A MapReduce acceleration-supported software for integrated quality control and preprocessing of high-throughput sequencing data. Gigascience 2018, 7, gix120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Feng, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. DEGseq: An R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Ding, J.; Wang, H.; Zuo, R.; Quan, Z.; Fan, Z.; Liu, Q.; Chang, Y. Molecular characterization and expression of SiFad1 in the sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus intermedius). Gene 2019, 705, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, H.; Denner, E.; Lubitz, W. Classification and identification of bacteria: Current approaches to an old problem. Overview of methods used in bacterial systematics. J. Biotechnol. 1996, 47, 3–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zhu, J.; Chang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Qiu, X. Phylogenetic analysis of four Vibrio strains of pathogenic bacteria based on hemolysin genes and 16S rRNA genes. In Proceedings of the 2009 3rd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Beijing, China, 11–13 June 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, G.; Jiayang, L.; Lingshu, H.; Chao, G.; Xianglei, Z.; Luo, W.; Weijie, Z.; Yaqing, C.; Jun, D. Structural Characteristics of Bacterial Flora in Coelomatic Fluid of Sea Urchin with. Chin. J. Fish. 2023, 36, 14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, R.; Macpherson, H.; Riaza, A.; Birkbeck, T. Vibrio splendidus biotype 1 as a cause of mortalities in hatchery-reared larval turbot, Scophthalmus maximus (L.). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 99, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rørbo, N.; Rønneseth, A.; Kalatzis, P.G.; Rasmussen, B.B.; Engell-Sørensen, K.; Kleppen, H.P.; Wergeland, H.I.; Gram, L.; Middelboe, M. Exploring the effect of phage therapy in preventing Vibrio anguillarum infections in cod and turbot larvae. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacoste, A.; Jalabert, F.; Malham, S.; Cueff, A.; Gelebart, F.; Cordevant, C.; Lange, M.; Poulet, S. A Vibrio splendidus strain is associated with summer mortality of juvenile oysters Crassostrea gigas in the Bay of Morlaix (North Brittany, France). Dis. Aquat. Org. 2001, 46, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Liu, H.; Lv, T.; Zhao, X.; Shao, Y.; Han, Q.; Li, C.; Zhang, W. Characteristics of the iron uptake-related process of a pathogenic Vibrio splendidus strain associated with massive mortalities of the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2018, 155, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, S.; Gardiner, M. Microbial dysbiosis: Rethinking disease in marine ecosystems. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mougin, J.; Joyce, A. Fish disease prevention via microbial dysbiosis-associated biomarkers in aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Zhang, W.; Jing, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, M.; Chang, Y. Long-term effects of stocking density on survival, growth performance and marketable production of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Aquac. Int. 2016, 24, 1323–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhan, Y.; Qi, S.; Chang, Y. Interactive effects of family and stocking density on survival and growth of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2019, 50, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Yang, M.; Chi, X.; Ding, P.; Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Zhao, C. Segregation in multi-layer culture avoids precocious puberty, improves thermal tolerance and decreases disease transmission in the juvenile sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius: A new approach to longline culture. Aquaculture 2021, 543, 736956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Huang, X.; Hu, F.; Yang, M.; Yin, D.; Tian, R.; Li, X.; Chang, Y.; Zhao, C. Transmission of black mouth disease shed light on the aquaculture management of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Announcement of the Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China (No. 560). Gaz. Minist. Agric. People’s Repub. China 2005, 40, 40. (In Chinese)
- Announcement of the Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China (No. 2292). Gaz. Minist. Agric. People’s Repub. China 2005, 49, 40. (In Chinese)
- Lei, Y.; Dan, L.; Xin-Hua, W.; Yunkun, W.; Bo, Z.; Mingyu, W.; Hai, X. Bacterial plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in aquatic environments in China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker-Austin, C.; McArthur, J.V.; Lindell, A.H.; Wright, M.S.; Tuckfield, R.C.; Gooch, J.; Warner, L.; Oliver, J.; Stepanauskas, R. Multi-site analysis reveals widespread antibiotic resistance in the marine pathogen Vibrio vulnificus. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 57, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Li, Y.; Shi, W.; Zhang, W.; Han, Q. Ajpacifastin-like is involved in the immune response of Apostichopus japonicus challenged by Vibrio splendidus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 140, 108997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Leng, X.; Gao, H.; Jiang, H.; Chang, Y. Effects of artificial challenge of black mouth disease pathogen on phagocytosis related immune parameters in sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. J. Dalian Ocean Univ. 2021, 36, 241–247. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, D.; Chen, X.; Song, H.; Xiang, L.; Yu, H.; Peng, L.; Zhu, Q. Nutritional-status dependent effects of microplastics on activity and expression of alkaline phosphatase and alpha-amylase in Brachionus rotundiformis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brayer, G.D.; Sidhu, G.; Maurus, R.; Rydberg, E.H.; Braun, C.; Wang, Y.; Nguyen, N.T.; Overall, C.M.; Withers, S.G. Subsite mapping of the human pancreatic α-amylase active site through structural, kinetic, and mutagenesis techniques. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 4778–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, B.L.; Avery, S.; Sen, P.; Swallow, D.M.; Hahn, D.; Sterchi, E. The maltase-glucoamylase gene: Common ancestry to sucrase-isomaltase with complementary starch digestion activities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Rose, D.; Lin, A.H.; Quezada-Calvillo, R.; Nichols, B.; Hamaker, B. Contribution of the individual small intestinal α-glucosidases to digestion of unusual α-linked glycemic disaccharides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6487–6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, R.E.; Wang, M.L.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Kwon, H.J.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. NPC2 facilitates bidirectional transfer of cholesterol between NPC1 and lipid bilayers, a step in cholesterol egress from lysosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15287–15292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.J.; Abi-Mosleh, L.; Wang, M.L.; Deisenhofer, J.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S.; Infante, R.E. Structure of N-terminal domain of NPC1 reveals distinct subdomains for binding and transfer of cholesterol. Cell 2009, 137, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, R.; He, C.; Asai, A.; Hellwig, M.; Henle, T.; Toda, M. The impacts of cholesterol, oxysterols, and cholesterol lowering dietary compounds on the immune system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Fatemi, S.; Ghaheri, M.; Rezvani, A.; Khezri, D.; Natami, M.; Yasamineh, S.; Gholizadeh, O.; Bahmanyar, Z. An overview of the role of Niemann-pick C1 (NPC1) in viral infections and inhibition of viral infections through NPC1 inhibitor. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).