Driving Effects of Large-Scale Sand Mining Activities on Bacterial Communities in Subtropical River Sediments—A Case Study of the Jialing River
Abstract
1. Introduction
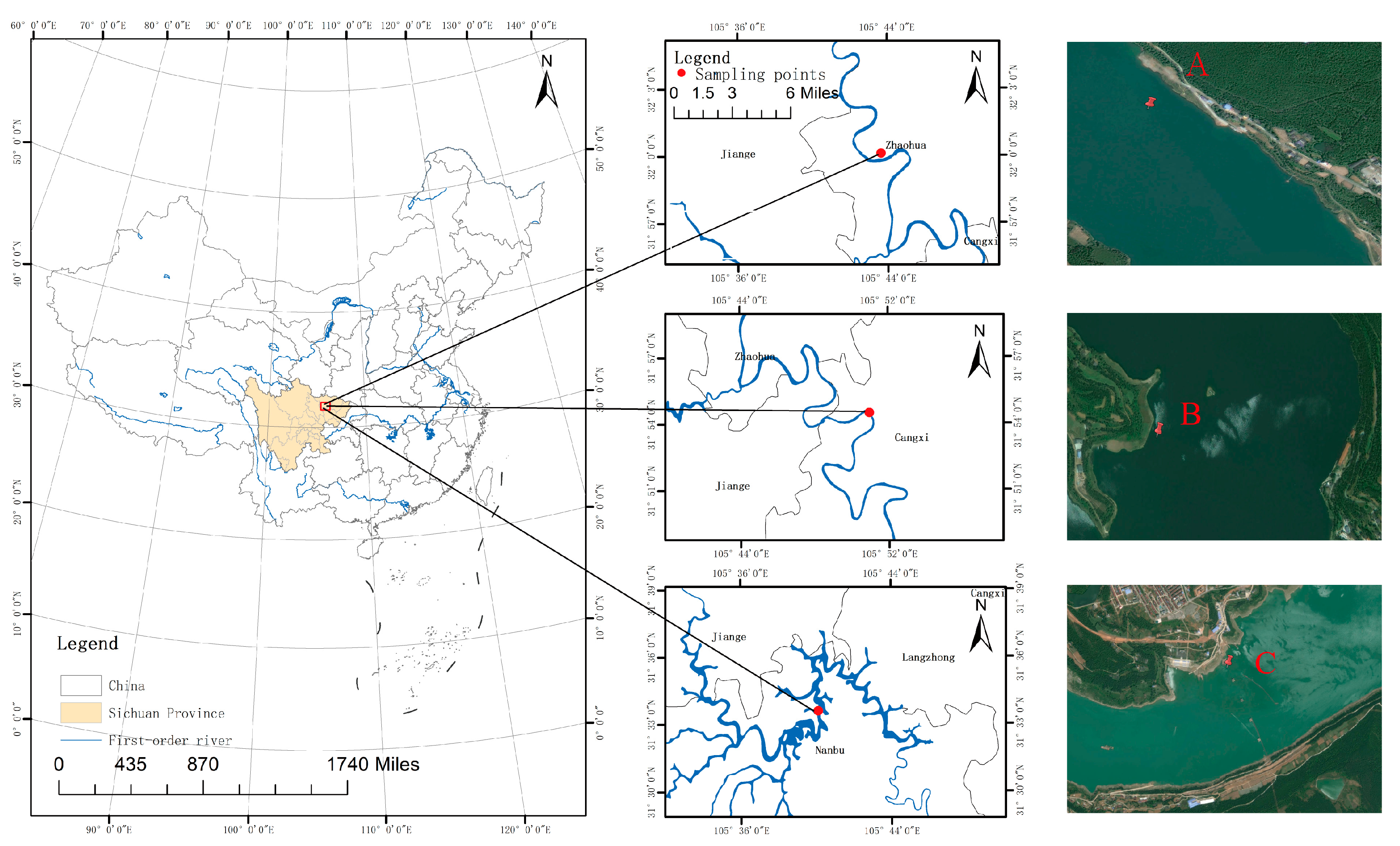
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
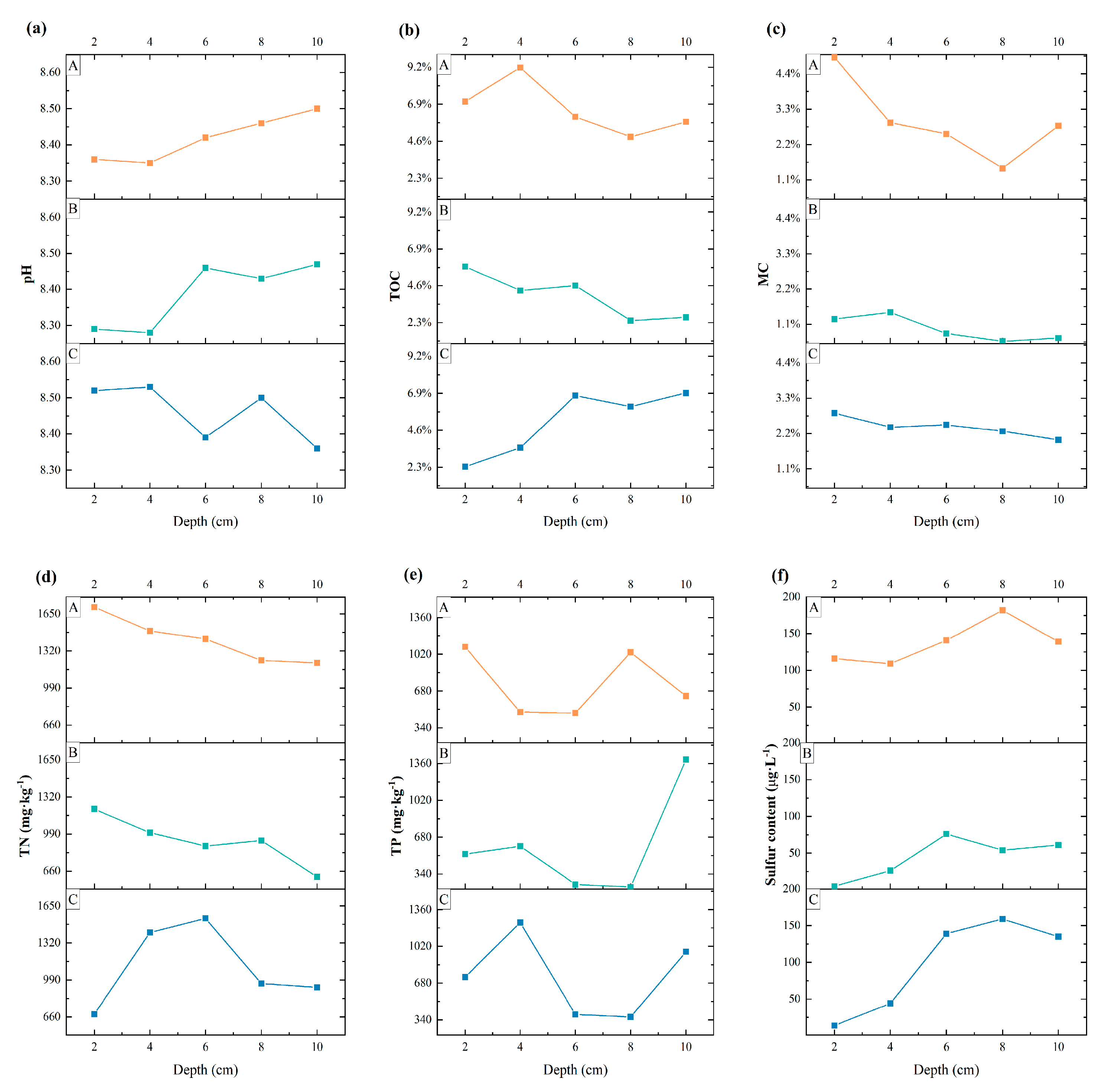
3.1. Physical and Chemical Properties of the Sediments at Each Sampling Point
3.2. Bacterial Community Structure and Differences
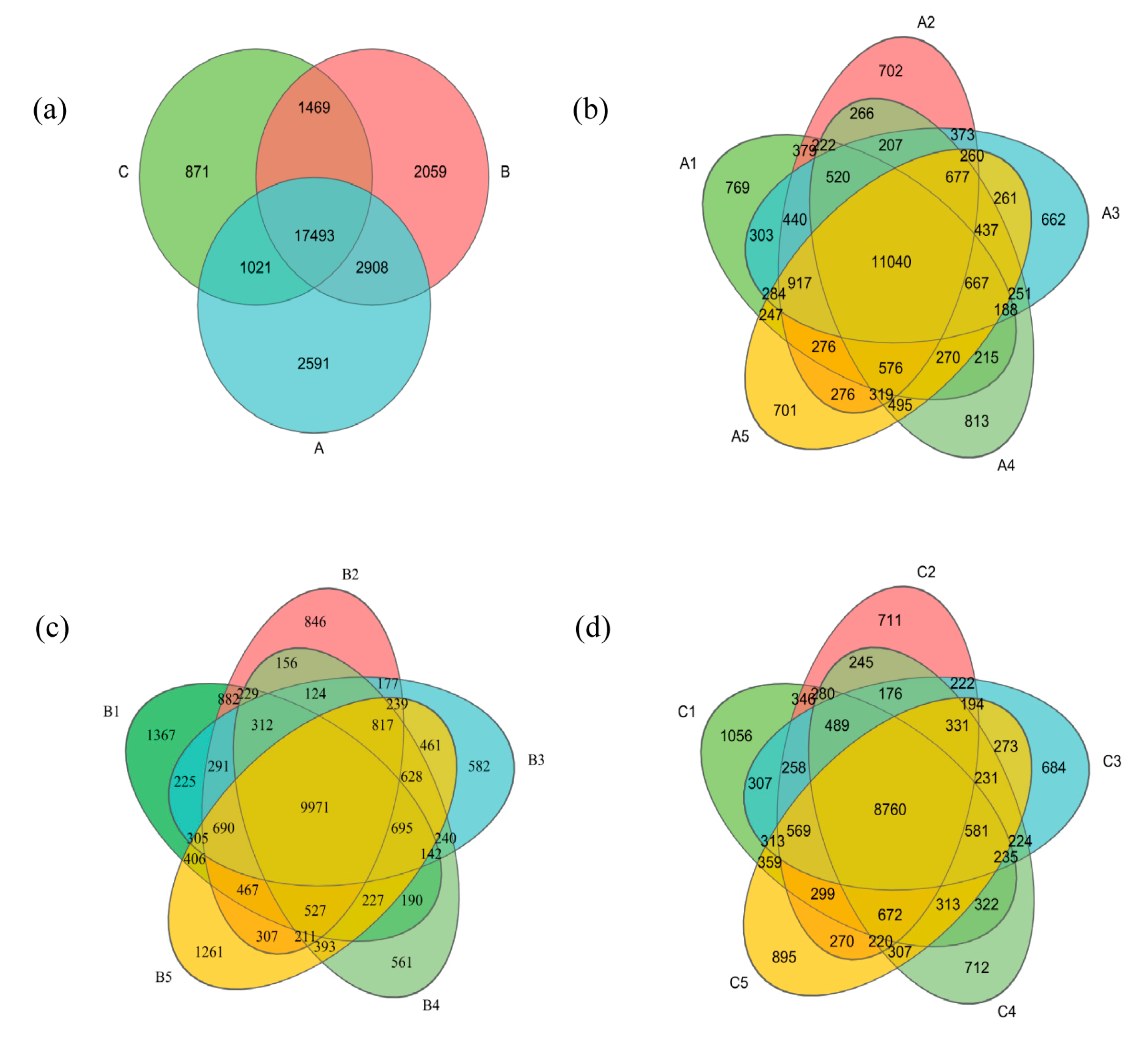
3.2.1. Bacterial OTU Number
3.2.2. Alpha Diversity of the Bacterial Community
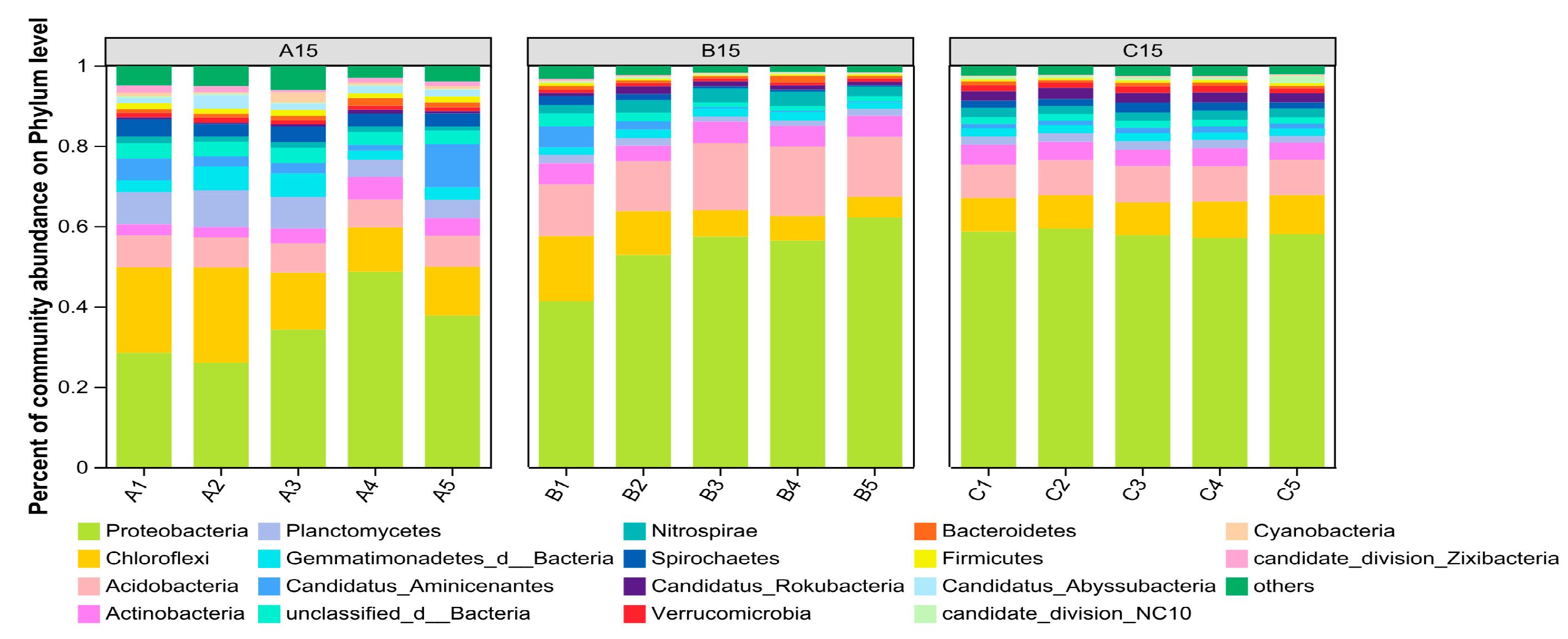
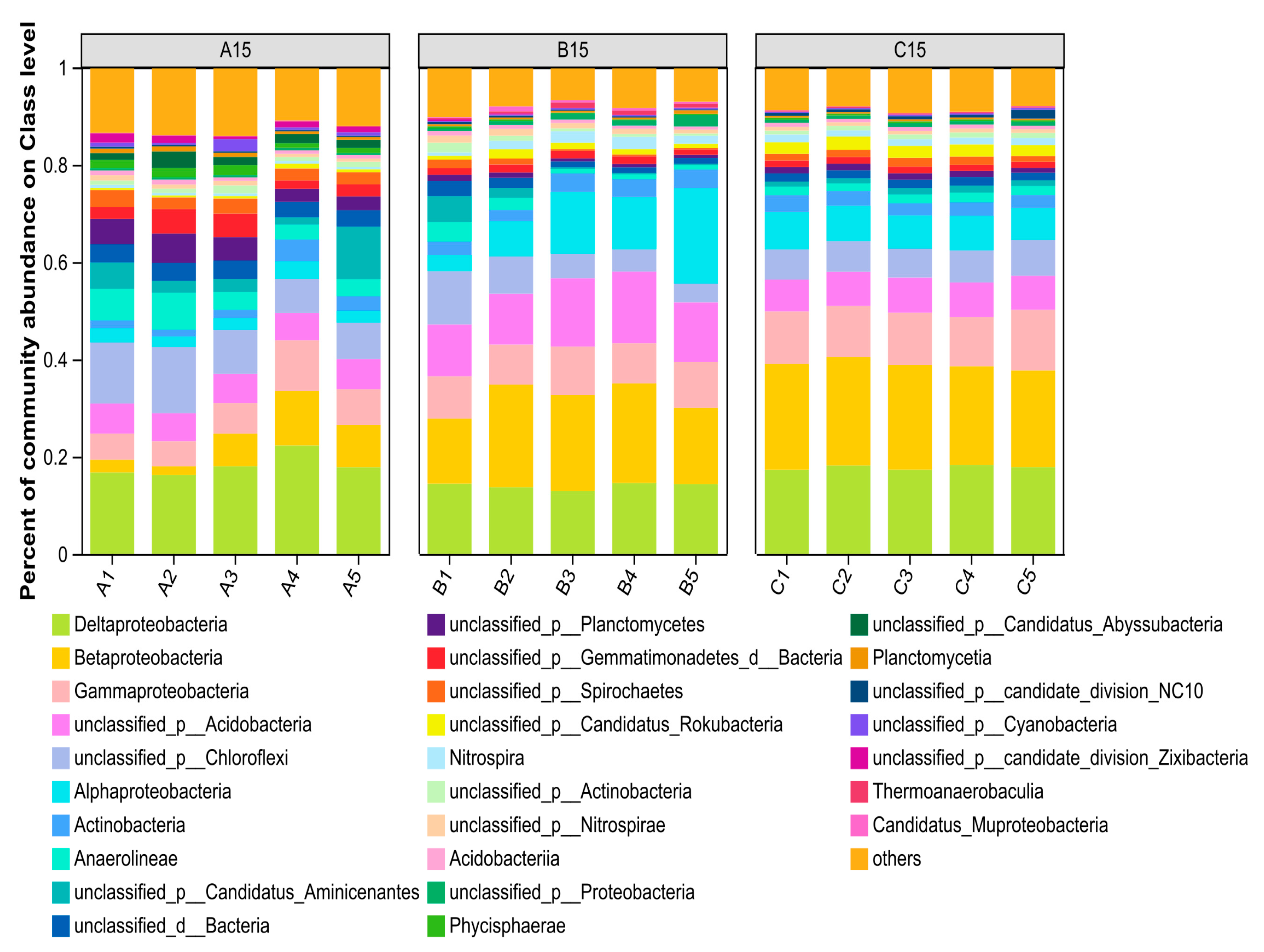
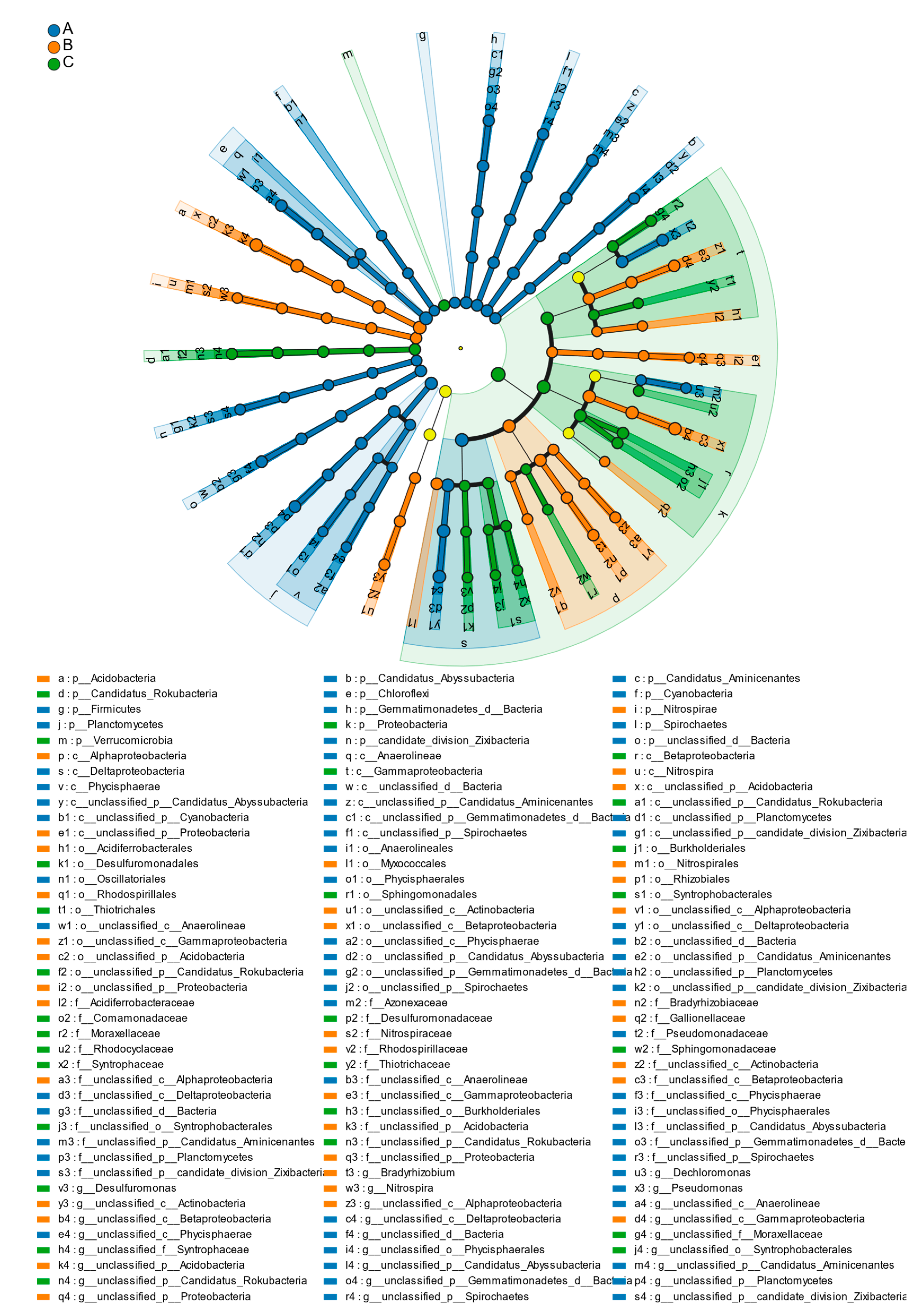
3.2.3. Analysis of Bacterial Community Species Composition and Community Structure
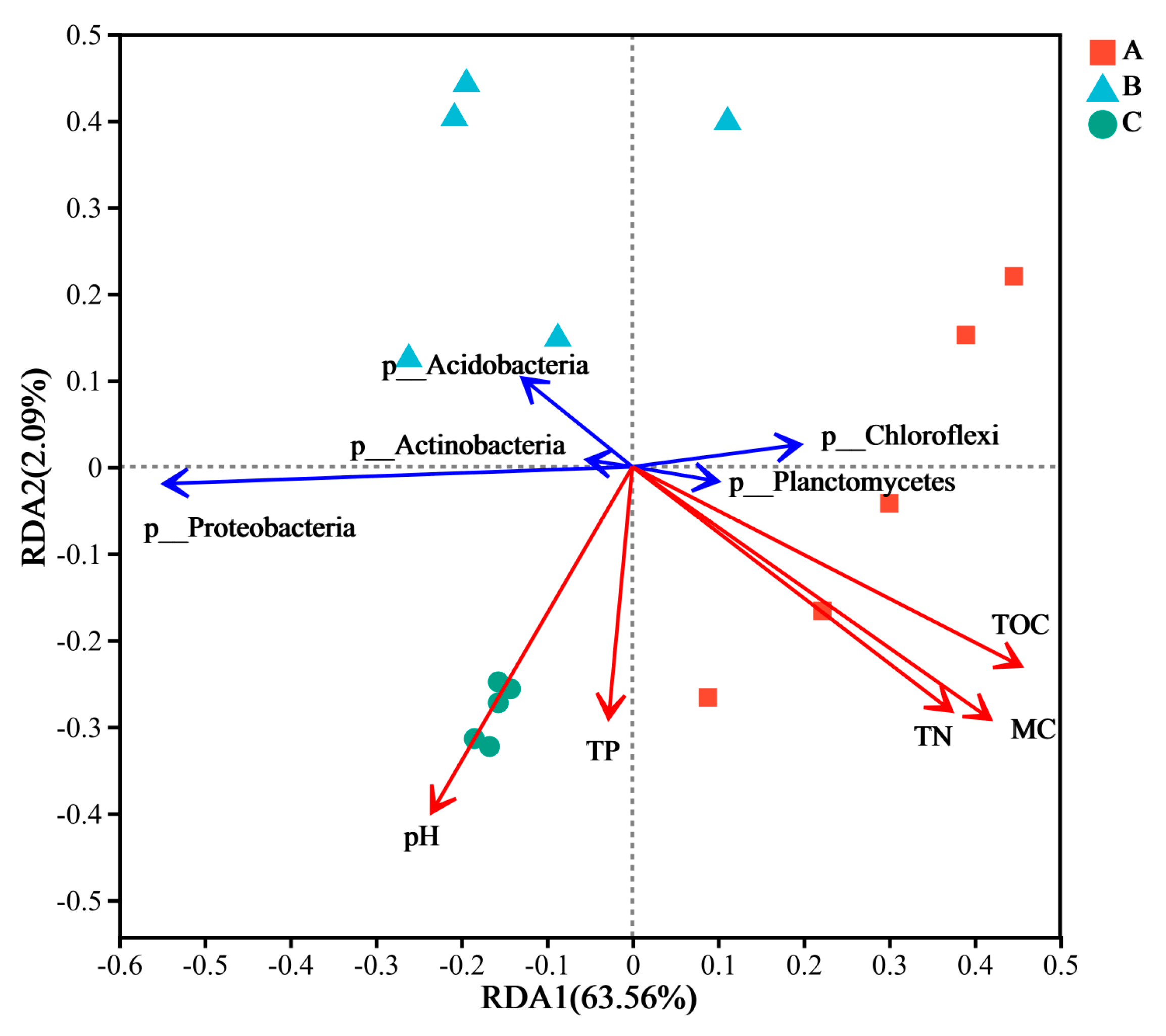
3.3. Correlations Between Bacterial Community Structure and Environmental Factors
3.4. Functional Diversity of Sediment Bacterial Communities
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Differences in the Diversity of Sediment Bacterial Communities in Different Sand Mining Environments
4.2. Functional Analysis of Sediment Bacteria in Different Sand Mining Environments
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.L.; Zhou, W.Q.; Pickett, S.T.A.; Yu, W.J.; Li, W.F. A multiscale analysis of urbanization effects on ecosystem services supply in an urban megaregion. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasare, L.I.; Opoku, S.A.; Amponsah, A.; Tom, D.D.; Asante, W.J.; Baatuuwie, B.N. Effect of sand mining on riparian landcover transformation in Dallung-Kukou catchment of the White Volta basin, Ghana. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentier, E.S.; Cammeraat, L.H. The environmental impacts of river sand mining. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, L.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, F.B.; Xu, F.; Zhang, T. The impact of river sand mining on remobilization of lead and cadmium in sediments—A case study of the Jialing River. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 246, 114144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdevari, S.; Fazli Allah Abadi, A. A model based on the evolutionary game theory for implementing green mining principles in riverine sand and gravel resources. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 428, 139501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyan, L.; Wang, Y.C. Dynamics of sediment transport in the Yangtze River and their key drivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 862, 160688. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.L.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, J.F. Quantifying the hydrodynamic impacts of cumulative sand mining on a large river-connected floodplain lake: Poyang Lake. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castello, L.; Macedo, M.N. Large-scale degradation of Amazonian freshWater environment. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 990–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruel, C.R.; Park, E.; Switzer, A.D.; Kumar, S.; Ho, H.L.; Kantoush, S.; Van Binh, D.; Feng, L. New systematically measured sand mining budget for the Mekong Delta reveals rising trends and significant volume underestimations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 108, 102736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, S.A.; Ganie, D.H.; Teeli, J.I.; Bhat, S.U. A policy approach for sustainable governance of sand mining activities in NW Kashmir Himalayas. Extract. Ind. Soc. 2023, 13, 101204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türetken, P.S.Ç. Environment variables, composition and metabolic characteristics of culturable sediment bacteria isolated around Gökçeada Island, Aegean Sea, Turkey. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 42, 101613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, N.; Kim, K.; Kang, H.J.; Park, R.S.; Lee, J.H. Exploring the Impacts of Anthropogenic Disturbance on Seawater and Sediment Microbial Communities in Korean Coastal Waters Using Metagenomics Analysis. Int. J. Environ. 2017, 14, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, K.R.; Chatterjee, N.; Dolui, G. Consequences of sand mining on water quality and instream biota in alluvial stream: A case-specific study in South Bengal River, India. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 5, 1815–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.L.; Xue, W.J.; Zeng, G.M.; Wan, J.; Chen, G.M.; Huang, C.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, M.; Xu, P. Immobilization of Cd in river sediments by sodium alginate modified nanoscale zero-valent iron: Impact on enzyme activities and microbial community diversity. Water Res. 2016, 106, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeppl, R.E.; Fryirs, K.A.; Tunnicliffe, J.; Brierley, G. Managing sediment (dis)connectivity in fluvial systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.S.; Braz, B.F.; Sanjad, P.; Cruz, A.C.R.; Crapez, M.A.C.; Neumann, R.; Santelli, R.E.; Keim Santos, C.N. Role of indigenous microorganisms and organics in the release of iron and trace elements from sediments impacted by iron mine tailings from failed Fundão dam. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, Q.; Dou, Q.; Lan, S.; Peng, Y.; Yang, J. The molecular characteristics of dissolved organic matter in urbanized river sediments and their environmental impact under the action of microorganisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.P.; Zhang, S.K.; Zhang, L.Y.; Li, X.G.; Wang, F.; Li, G.W.; Li, J.X.; Li, W. In-situ remediation of sediment by calcium nitrate combined with composite microorganisms under low-DO regulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, L.J.; Xu, F.; Chen, X.Y.; Du, L. Evaluation of the environment risk, fractions and mobilization of nickel (Ni) in sediments of the Jialing River by sediment quality guidelines, sequential extraction and Chelex-AgI gel DGT probe. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 118, 104634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, W.; An, W.; Hou, J.; Hou, X.; Tang, C.; Gan, Z. Temporal and spatial evolutionary trends of regional extreme precipitation under different emission scenarios: Case study of the Jialing River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 129156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.L.; Li, C.A.; Kuiper, K.F.; Zhang, Z.J.; Gao, J.H.; Wijbrans, J.R. Human impact on erosion patterns and sediment transport in the Yangtze River. Glob. Planet Change 2016, 143, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.W.; Wang, D.Y.; Miao, W.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, P.; Li, D.X. Characteristics of runoff and sediment load during flood events in the Upper Yangtze River, China. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, D.F.; Lu, J.Y.; Yao, S.M.; Yan, X.; Jin, Z.W.; Liu, L.; Lu, X.X. Distinguishing the multiple controls on the decreased sediment flux in the Jialing River basin of the Yangtze River, Southwestern China. Catena 2020, 193, 104593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Leung, P.M.; Cook, P.L.M.; Wong, W.W.; Hutchinson, T.; Eate, V.; Chris Greening, C. Hydrodynamic disturbance controls microbial community assembly and biogeochemical processes in coastal sediments. ISME J. 2022, 16, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.E.G.; Das, A.; Nath, B.N.; Faria, D.G.; Bharathi, P.A.L. Mixed response in bacterial and biochemical variables to simulated sand mining in placer-rich beach sediments, Ratnagiri, West coast of India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 2677–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Tang, L.; Luan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.X.; Guo, C.H. Effect of triticale (Triticale hexaploide L.) growth on the bacterial community and petroleum hydrocarbon degradation in petroleum-contaminated saline-alkali soil. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 9143–9151. [Google Scholar]
- Dépret, T.; Virmoux, C.; Gautier, E.; Piégay, H.; Doncheva, M.; Plaisant, B.; Ghamgui, S.; Mesmin, E.; Saulnier-Copard, S.; de Milleville, L.; et al. Lowland gravel-bed river recovery through former mining reaches, the key role of sand. Geomorphology 2021, 373, 107493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, S. Gravel excavation and geomorphic evolution of the mining affected river in the upstream reach of the Yangtze River, China. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2022, 37, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgilio, A.; Raposo, J.L., Jr.; Cardoso, A.A.; Nóbrega, J.A.; Gomes, N.J.A. Determination of Total Sulfur in Agricultural Samples by High-Resolution Continuum Source Flame Molecular Absorption Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2197–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.F.; Fu, Y.; Li, S.A.; Nong, Y.K.; Feng, Q.M.; Tan, Y.L. Analysis of bacterial community in sediments of Longjiang River and its response to environmental changes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 46, 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Yu, X.; Jiang, G.P.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Wen, J.; Xia, L.; Liu, X.D.; et al. Response of bacterial ecological and functional properties to anthropogenic interventions during maturation of mine sand soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 938, 173354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Tang, X.Q.; Hu, Y.P.; Lu, S.Q.; Gu, J.J.; Sun, Y.G. Response of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Release Flux at the Sediment-Water Interface to the Drainage of Pore Water. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2023, 57, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, H.; Park, J.; Takagi, T. MetaGene: Prokaryotic gene finding from environmental genome shotgun sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 5623–5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; He, Y.; Peng, C.; Wen, X.Y.; Ye, Y.Q.; Ren, D.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, D. Dispersal of antibiotic resistance genes in an agricultural influenced multi-branch river network. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Jin, Z.W.; Guo, L.C.; Lu, J.Y.; Ren, S.; Zhou, Y.J. On the cumulative dam impact in the upper Changjiang River: Streamflow and sediment load changes. Catena 2020, 184, 104250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendixen, M.; Noorbhai, N.; Zhou, J.; Iversen, L.L.; Huang, K. Drivers and effects of construction-sand mining in Sub-Saharan Africa. Extract. Ind. Soc. 2023, 16, 101364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilaseca, F.; Chreties, C. A simple method for annual sediment transport estimation at ungauged cross-sections and its application to assess sustainable sand mining from river margins in Uruguay. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2023, 124, 104261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.B.; Chen, Z.H.; Ding, B.J.; Li, Z.K. Impact of sand mining on the carbon sequestration and nitrogen removal ability of soil in the riparian area of Lijiang River, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Tolonen, K.T.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Peng, K.; Cai, Y.; Gong, Z. Catastrophic effects of sand mining on macroinvertebrates in a large shallow lake with implications for management. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Yi, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Q. How the flow and sediment pulse influencing the distribution and functional gene composition of bacterial communities? Case study of the lower Yellow River, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, O.C.; Enrique, J.M.M.; Carolina, R.F.A.; Albert, S.C.J.; Diana, M.F.; Hascibe, P.B.L. Historical fluxes of metal and metalloids in an aquatic ecosystem affected by land-use change and mining activities in northwestern Mexico. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2023, 38, 724–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.W.; Wang, J.Z.; Wu, Y.K.T.; Ren, C.; Song, C.; Yang, J.H.; Yu, H.X.; Giesy, J.P.; Zhang, X.W. Using in situ bacterial communities to monitor contaminants in river sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.Z.; He, L.Y.; Hu, L.X.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.Y.; Zou, H.Y.; He, L.X.; Bai, H.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhao, J.L.; et al. Anthropogenic activities and seasonal properties jointly drive the assemblage of bacterial communities in subtropical river basins. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Tran, P.Q.; Kieft, K.; Karthik, K. Genome diversification in globally distributed novel marine Proteobacteria is linked to environmental adaptation. ISME J. 2020, 14, 2060–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.C.; Wang, F. Integrating high-throughput sequencing and metagenome analysis to reveal the characteristic and resistance mechanism of microbial community in metal contaminated sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 136116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Chaves, M.G.; Silva, G.G.Z.; Rossetto, R.; Edwards, R.A.; Tsai, S.M.; Navarrete, A.A. Acidobacteria Subgroups and Their Metabolic Potential for Carbon Degradation in Sugarcane Soil Amended with Vinasse and Nitrogen Fertilizers. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Guo, G.; Wu, W. Effects of muddy water irrigation with different sediment particle sizes and sediment concentrations on soil microbial communities in the Yellow River Basin of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 270, 107750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.X.; Wang, L.; Du, J.T.; Liu, Y.H.; Hu, L.; Wei, H.; Fang, J.S.; Liu, R.L. Biogeographic distribution, ecotype partitioning and controlling factors of Chloroflexi in the sediments of six hadal trenches of the Pacific Ocean. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Lou, Y.H.; Xu, M.M.; Wu, C.; Meng, J.; Shi, L.; Xia, F.; Xu, Y. Spatial distribution and influencing factors on the variation of bacterial communities in an urban river sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 115984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; He, M.; Liu, H.; Ouyang, W.; Liu, X.; Li, Q.; Lin, C.; Liu, X. Distribution heterogeneity of sediment bacterial community in the river-lake system impacted by nonferrous metal mines: Diversity, composition and co-occurrence patterns. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 338, 122715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temporetti, P.; Beamud, G.; Nichela, D.; Baffico, G.; Pedrozo, F. The effect of pH on phosphorus sorbed from sediments in a river with a natural pH gradient. Chemosphere 2019, 228, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Chen, J.H.; Wen, H.; Wan, Z.; Tang, T.Y. Emissions assessment of bulk carriers in China’s east Coast-Yangtze River maritime network based on different shipping modes. Ocean Eng. 2022, 249, 110903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Los Santos Valladares, L.; Camapaza, J.L.; Bedgregal, R.V.; Castro, L.B.; Velazquez, J.; Perera, D.H.N.; Ionescu, A.; Arvidsson, D.; Barnes, E.P.; Newton, P.J.; et al. Physical and chemical characterization of sediments from an Andean river exposed to mining and agricultural activities: The Moquegua River, Peru. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2022, 37, 780–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.Y.; Yi, Y.J.; Song, J.; Zhou, Y. Effect of water-sediment regulation operation on sediment grain size and nutrient content in the lower Yellow River. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, M.L.T.; dos Santos, F.F.; de Carvalho, K.M.; Peixoto, D.S.; Uezu, A.; Avanzi, J.C.; Serafim, M.E.; Nunes, M.R.; van Es, H.M.; Curi, N.; et al. Interactions between land use and soil type drive soil functions, highlighting water recharge potential, in the Cantareira System, Southeast of Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.A.; Martin, S.J.P.; Casermeiro, M.A.; Quintana, J.R. Soil depth and vegetation type influence ecosystem functions in urban greenspaces. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 194, 105209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, S.H.; Wang, D.H.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.S.; Zuo, R. Screening of hazardous groundwater pollutants responsible for microbial ecological consequences by integrated nontargeted analysis and high-throughput sequencing technologies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, F.; Wang, W.; Gao, R.; Fan, L.; Wang, A.; Gao, S.H. Application of high-throughput sequencing technologies and analytical tools for pathogen detection in urban water systems: Progress and future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, P.; Raghavan, R.V.; Che, O.J.; Lee, H.J.; Priya, P.V.; Dharani, G.; Kirubagaran, R. Complex bacterial communities in the deep-sea sediments of the Bay of Bengal and volcanic Barren Island in the Andaman Sea. Mar. Genom. 2017, 31, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, Y.R.; Bao, M.T. Investigation of kinetics in bioaugmentation of crude oil via high-throughput sequencing: Enzymatic activities, bacterial community composition and functions. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Zeng, X.Y.; Zheng, J.; Zou, Y.M.; Qiu, S.Y.; Dai, Y.F. AHL-mediated quorum sensing to regulate bacterial substance and energy metabolism: A review. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 262, 127102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xin, Y.; Guang, S.B.; Lin, G.F.; Zeng, L.Q.; He, S.Q.; Zheng, Y.M.; Chen, G.Y.; Zhao, Q.B. Planktonic microbial community and biological metabolism in a subtropical drinking water river-reservoir system. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 116999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sampling Point | Ace Index | Shannon Index | Simpson Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 3397 | 4.28967 | 0.041277 |
| A2 | 3380 | 4.131143 | 0.046858 |
| A3 | 3382 | 4.356504 | 0.038633 |
| A4 | 3309 | 4.457314 | 0.039228 |
| A5 | 3400 | 4.399154 | 0.039693 |
| B1 | 3268 | 4.311992 | 0.043663 |
| B2 | 3167 | 4.380076 | 0.04315 |
| B3 | 3076 | 4.311935 | 0.050867 |
| B4 | 3071 | 4.310983 | 0.053499 |
| B5 | 3255 | 4.505017 | 0.041089 |
| C1 | 3009 | 4.648298 | 0.03563 |
| C2 | 2902 | 4.511715 | 0.040251 |
| C3 | 2927 | 4.651078 | 0.034217 |
| C4 | 2944 | 4.634756 | 0.034542 |
| C5 | 2982 | 4.613699 | 0.036462 |
| Secondary Function | A | B | C | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| global and overview maps | 0.2755 ± 0.1852 b | 0.2717 ± 0.1122 b | 0.2693 ± 0.0056 c | L1 |
| carbohydrate metabolism | 0.0947 ± 0.0026 a | 0.0899 ± 0.0019 b | 0.0908 ± 0.0006 b | L1 |
| amino acid metabolism | 0.0804 ± 0.0017 b | 0.0854 ± 0.0029 a | 0.0866 ± 0.0007 a | L1 |
| energy metabolism | 0.0751 ± 0.0005 b | 0.0730 ± 0.0019 a | 0.0785 ± 0.0004 c | L1 |
| metabolism of cofactors and vitamins | 0.0480 ± 0.0007 a | 0.0460 ± 0.0007 b | 0.0444 ± 0.0007 c | L1 |
| membrane transport | 0.0420 ± 0.0008 b | 0.0436 ± 0.0007 a | 0.0434 ± 0.0003 a | L3 |
| cellular community–prokaryotes | 0.0390 ± 0.0005 a | 0.0392 ± 0.0007 a | 0.0392 ± 0.0002 a | L4 |
| signal transduction | 0.0338 ± 0.0012 b | 0.0371 ± 0.0014 a | 0.0341 ± 0.0003 b | L3 |
| translation | 0.0356 ± 0.0009 a | 0.0288 ± 0.0016 c | 0.0322 ± 0.0001 b | L2 |
| nucleotide metabolism | 0.0291 ± 0.0004 a | 0.0282 ± 0.0006 b | 0.0292 ± 0.0001 a | L1 |
| replication and repair | 0.0261 ± 0.0004 a | 0.0236 ± 0.0011 b | 0.0244 ± 0.0003 b | L2 |
| lipid metabolism | 0.0229 ± 0.0002 c | 0.0245 ± 0.0005 a | 0.0236 ± 0.0003 b | L1 |
| metabolism of other amino acids | 0.0207 ± 0.0002 c | 0.0241 ± 0.0013 a | 0.0226 ± 0.0002 b | L1 |
| folding, sorting and degradation | 0.0201 ± 0.0004 b | 0.0194 ± 0.0005 c | 0.0216 ± 0.0003 a | L2 |
| xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism | 0.0157 ± 0.0008 b | 0.0206 ± 0.0021 a | 0.0198 ± 0.0041 a | L1 |
| glycan biosynthesis and metabolism | 0.0183 ± 0.0014 a | 0.0163 ± 0.0011 b | 0.0139 ± 0.0003 c | L1 |
| biosynthesis of other secondary metabolites | 0.0163 ± 0.0005 a | 0.0156 ± 0.0002 b | 0.0142 ± 0.0002 c | L1 |
| cell growth and death | 0.0145 ± 0.0004 b | 0.0149 ± 0.0001 a | 0.0150 ± 0.0002 a | L4 |
| metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides | 0.0130 ± 0.0013 a | 0.0120 ± 0.0002 a | 0.0115 ± 0.0001 b | L1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, J.; Zhang, T.; Xu, F.; Huang, M.; Zhang, F. Driving Effects of Large-Scale Sand Mining Activities on Bacterial Communities in Subtropical River Sediments—A Case Study of the Jialing River. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13091998
Xia J, Zhang T, Xu F, Huang M, Zhang F. Driving Effects of Large-Scale Sand Mining Activities on Bacterial Communities in Subtropical River Sediments—A Case Study of the Jialing River. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13091998
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Jia, Tuo Zhang, Fei Xu, Maojin Huang, and Fubin Zhang. 2025. "Driving Effects of Large-Scale Sand Mining Activities on Bacterial Communities in Subtropical River Sediments—A Case Study of the Jialing River" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13091998
APA StyleXia, J., Zhang, T., Xu, F., Huang, M., & Zhang, F. (2025). Driving Effects of Large-Scale Sand Mining Activities on Bacterial Communities in Subtropical River Sediments—A Case Study of the Jialing River. Microorganisms, 13(9), 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13091998






