Effects of Transgenic Insect-Resistant Maize HGK60 on Rhizosphere Soil Bacterial Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Research Area
2.2. Test Materials and Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Full-Length Sequencing of 16S rDNA Amplification
2.5. Statistical Analysis of Diversity and Structure of Bacterial Communities
2.6. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
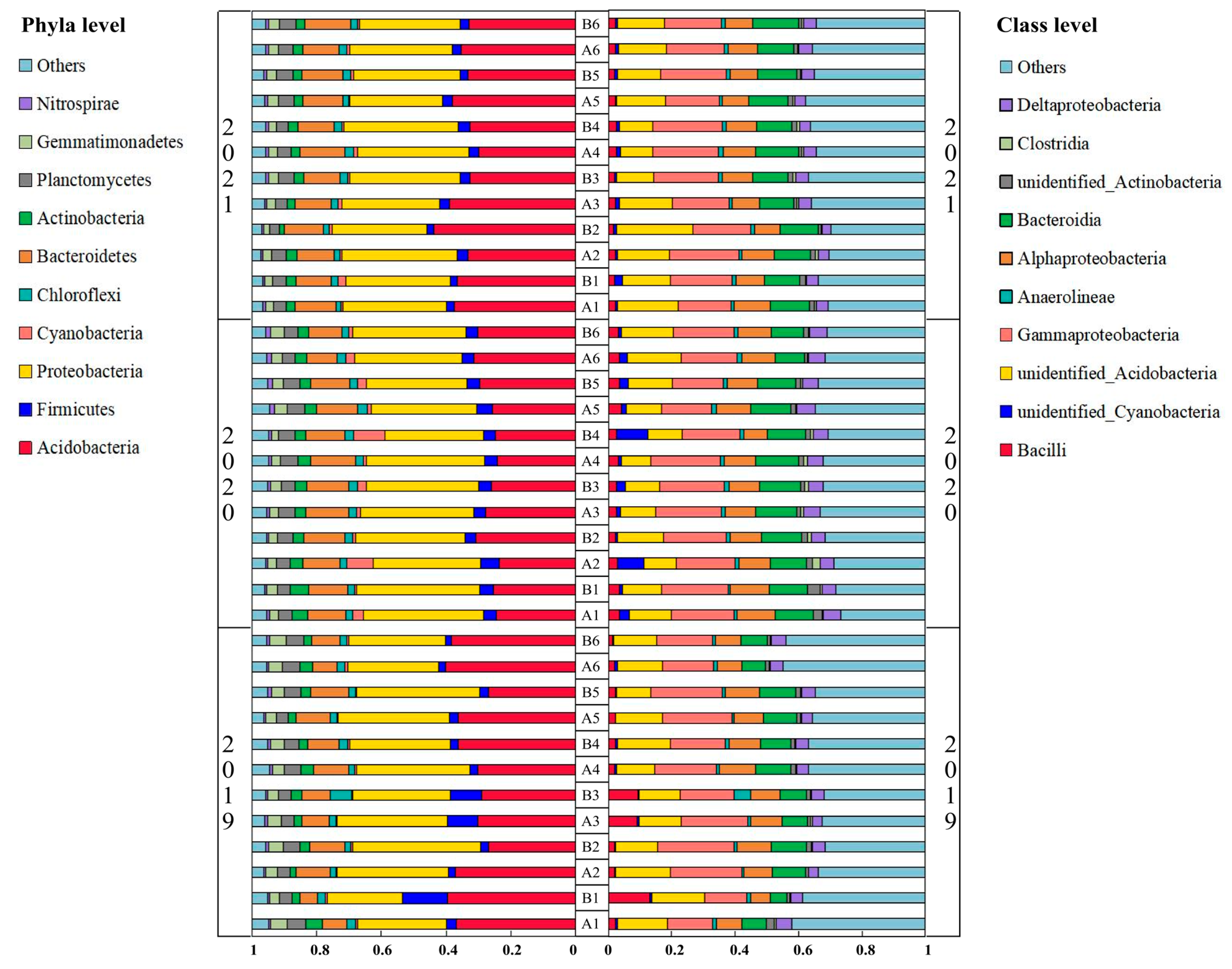
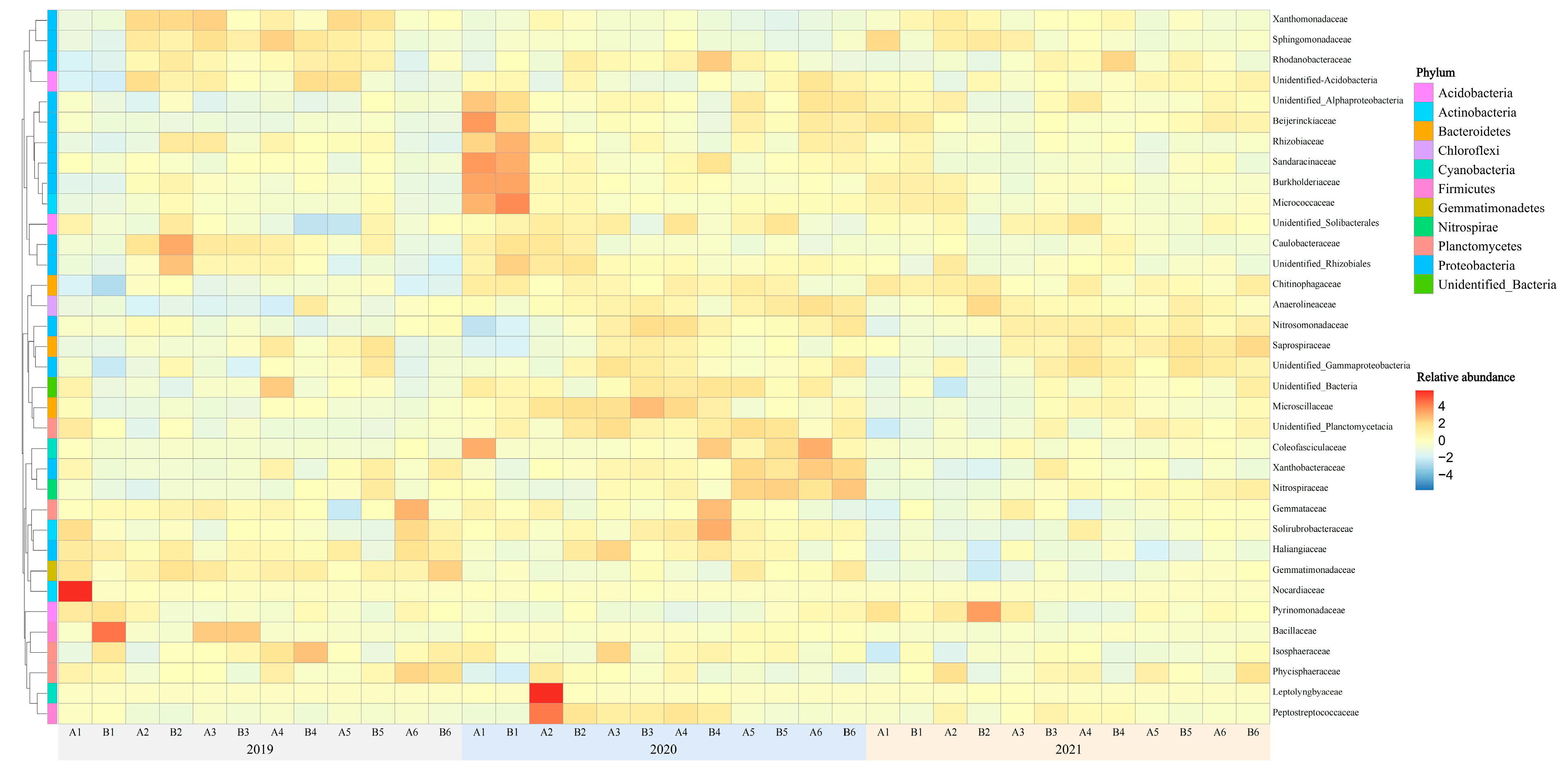
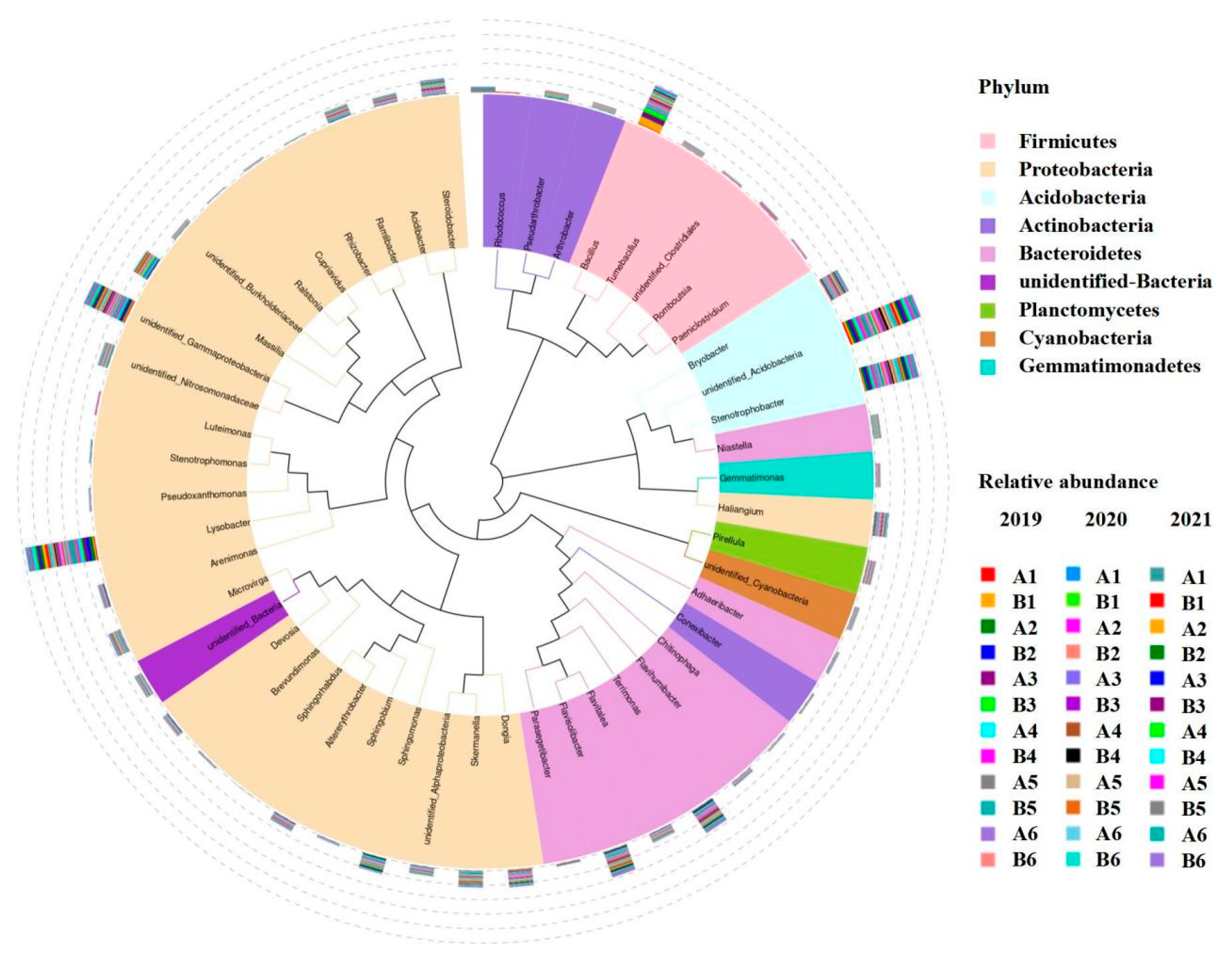
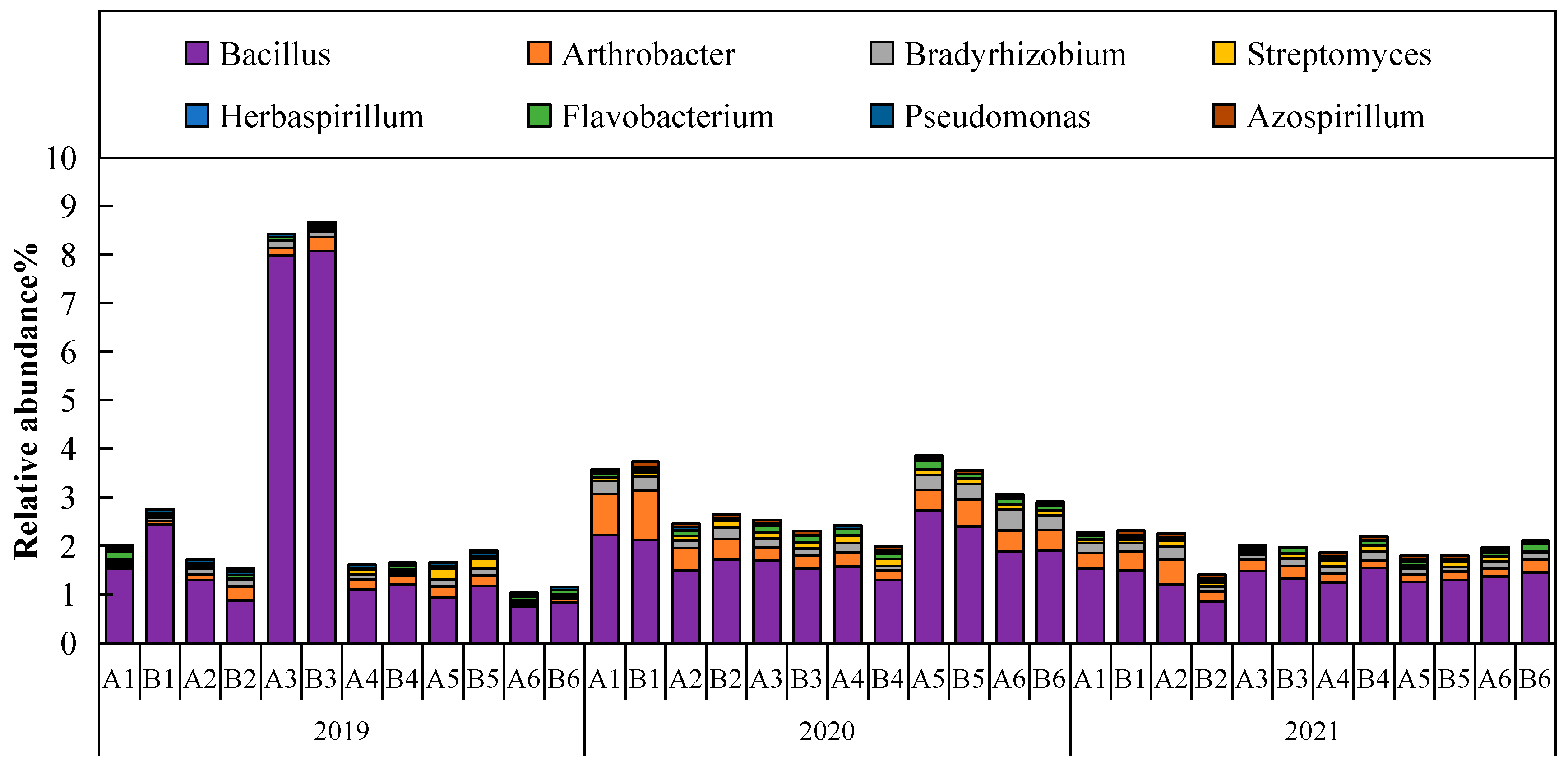
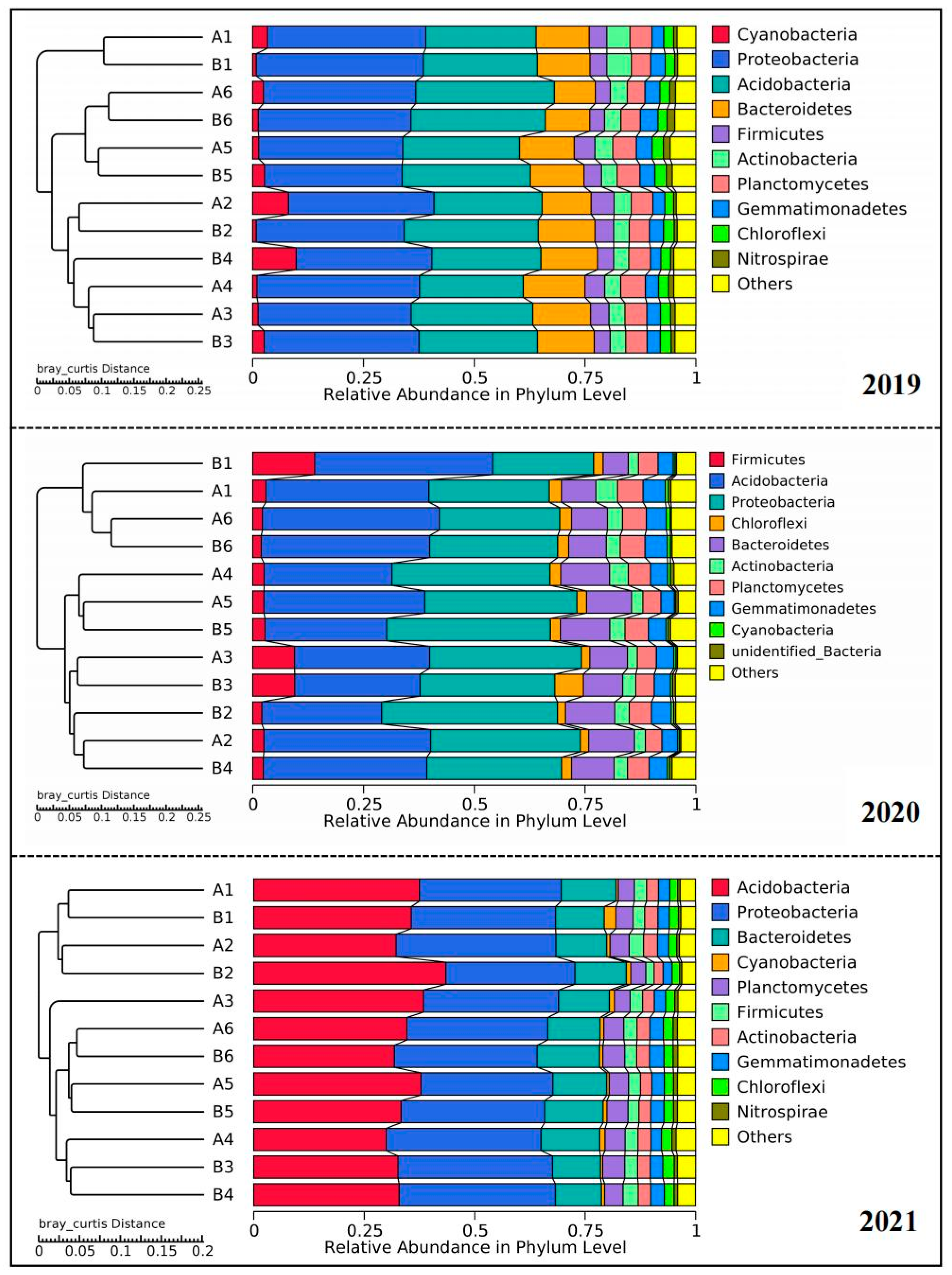
3.1. Relative Abundance of Rhizosphere Soil Bacterial Species
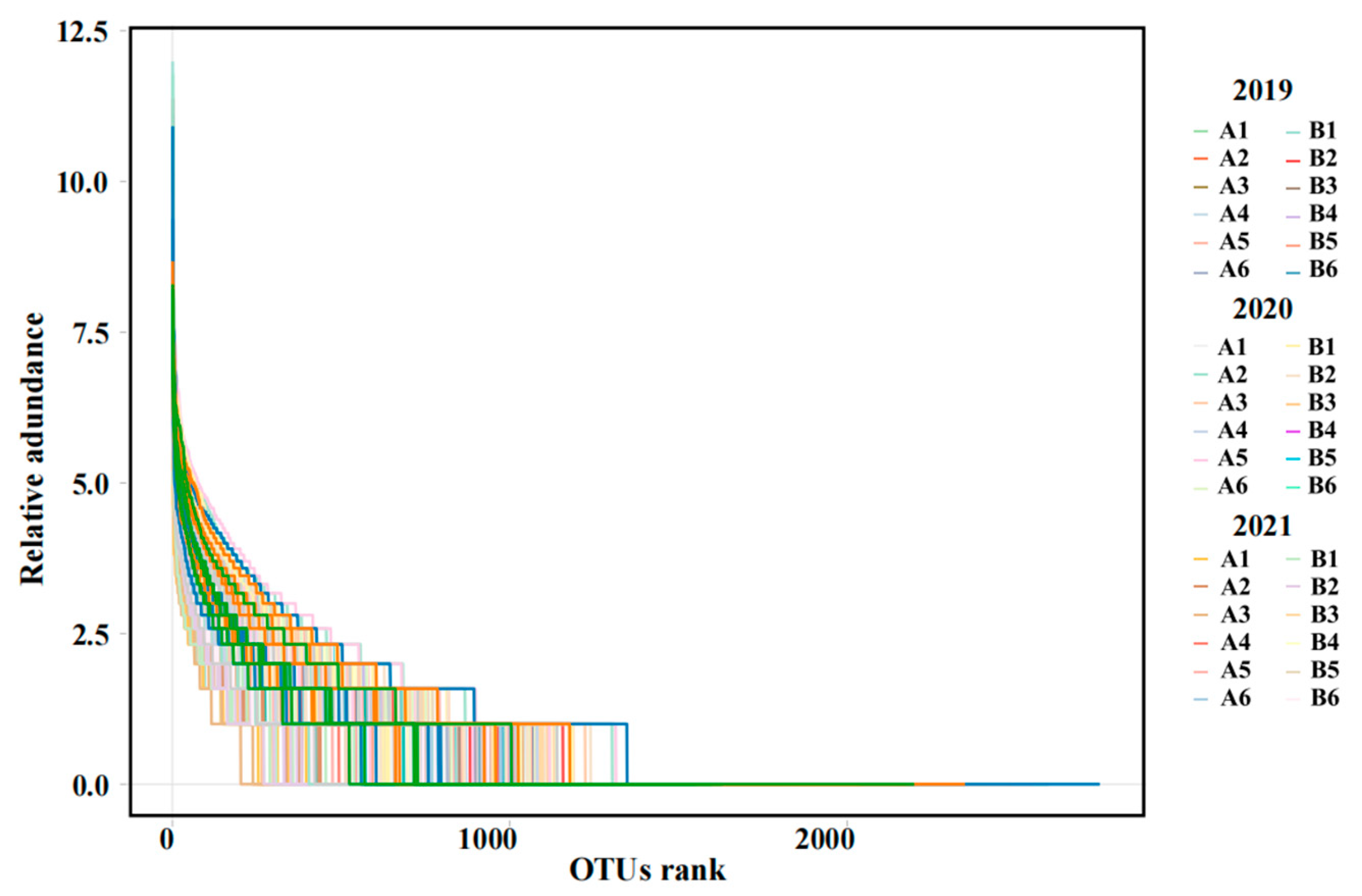
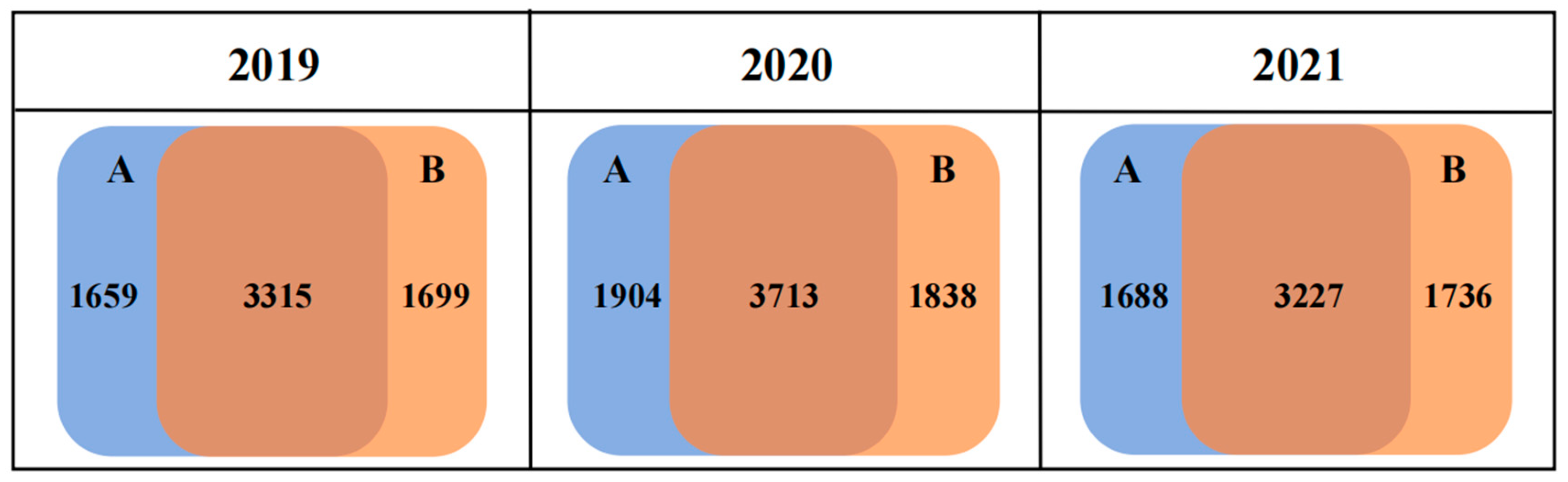
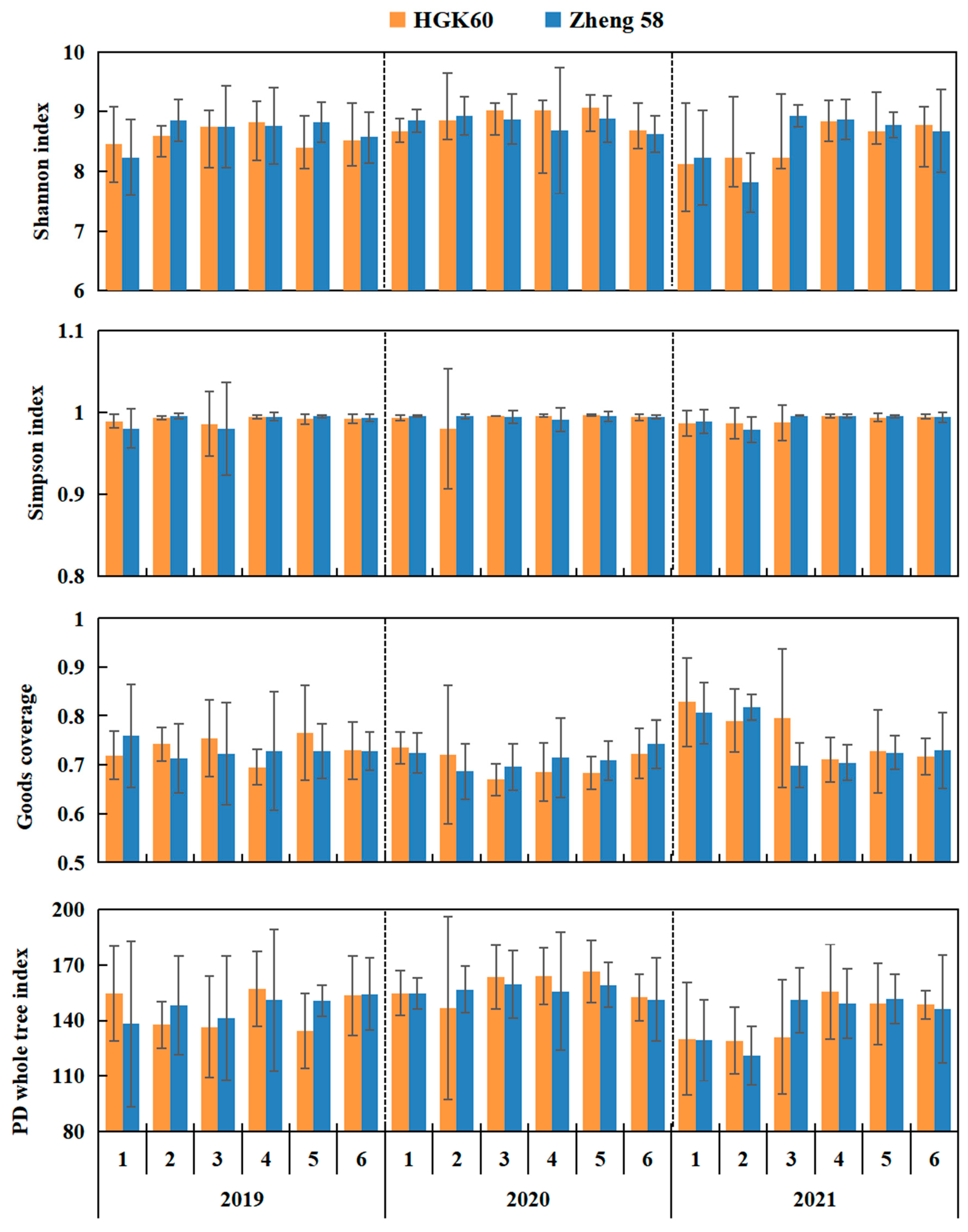
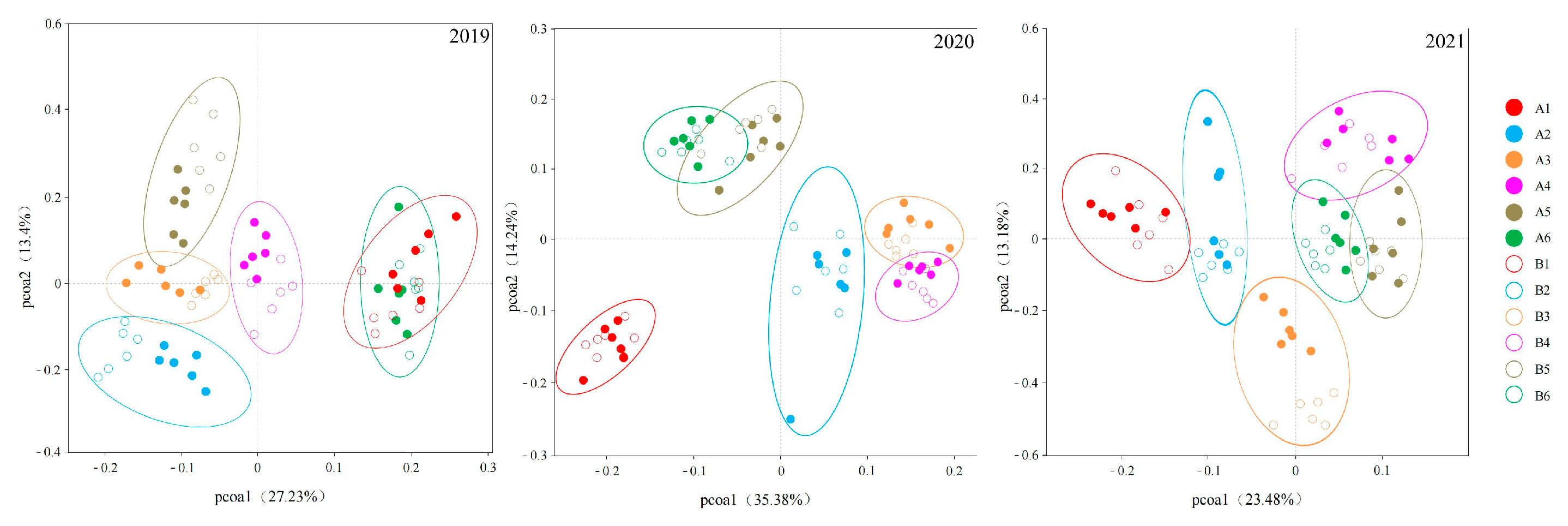
3.2. Diversity and Structure of Bacterial Communities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramankutty, N.; Mehrabi, Z.; Waha, K.; Jarvis, L.; Kremen, C.; Herrero, M.; Rieseberg, L.H. Trends in global agricultural land use: Implications for environmental health and food security. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 789–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catacora-Vargas, G.; Binimelis, R.; Myhr, A.I.; Wynne, B. Socio-economic research on genetically modified crops: A study of the literature. Agric. Hum. Values 2018, 35, 489–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.A.; Ellsworth, P.C.; Faria, J.C.; Head, G.P.; Owen, M.D.K.; Pilcher, C.D.; Shelton, A.M.; Meissle, M. Genetically engineered crops: Importance of diversified integrated pest management for agricultural sustainability. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; Gambhir, G.; Dass, A.; Tripathi, A.K.; Singh, A.; Jha, A.K.; Yadava, P.; Choudhary, M.; Rakshit, S. Genetically modified crops: Current status and future prospects. Planta 2020, 251, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Lui, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Tang, Q. Global Genetically Modified Crop Industrialization Trends in 2022. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2023, 25, 6–16. [Google Scholar]
- Berendsen, R.L.; Pieterse, C.M.; Bakker, P.A. The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.K.U.; Zhou, X.G.; Wu, F.Z. The role of root exudates, CMNs, and VOCs in plant–plant interaction. J. Plant Interact. 2019, 14, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.C.; Chang, Y.Y.; Hussain, M.; Lu, B.; Pei, D. Soil chemical and microbiological properties are changed by long-term chemical fertilizers that limit ecosystem functioning. Microorganisms 2020, 28, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Leach, J.E.; Tringe, S.G.; Sa, T.; Singh, B.K. Plant–microbiome interactions: From community assembly to plant health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, C.M.; Farag, M.A.; Hu, C.H.; Reddy, M.S. Bacterial volatiles promote growth in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4927–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yao, S.; Joachim, V.; Wang, J. Analysis of Antibacterial Substances Produced by Bacillus subtilis B2 Strain. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2003, 19, 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Kloepper, J.W.; Ryu, C.M.; Zhang, S. Induced systemic resistance and promotion of plant growth by Bacillus spp. Phytopathology 2008, 94, 1259–1266. Phytopathology 2008, 94, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.H.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhang, N.; Shen, Q.R.; Zhang, R.F. Contribution of indole-3-acetic acid in the plant growth promotion by the rhizospheric strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2015, 51, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuklinsky-Sobral, J.; Araújo, W.L.; Mendes, R.; Geraldi, I.O.; Pizzirani-Kleiner, A.A.; Azevedo, J.L. Isolation and characterization of soybean-associated bacteria and their potential for plant growth promotion. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, P.N.; Jha, D.K. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): Emergence in agriculture. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 1327–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thokchom, E.; Kalita, M.C.; Talukdar, N.C. Isolation, screening, characterization, and selection of superior rhizobacterial strains as bioinoculants for seedling emergence and growth promotion of Mandarin orange (Citrus reticulata Blanco). Can. J. Microbiol. 2014, 60, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haiyambo, D.H.; Chimwamurombe, P.M.; Reinhold-Hurek, B. Isolation and screening of rhizosphere bacteria from grasses in east Kavango Region of Namibia for plant growth promoting characteristics. Curr. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, D.; Flores, S.; Stotzky, G. Bt Toxin is released in root exudates from 12 transgenic corn hybrids representing three transformation events. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, H.; Ullah, M.; Ahmed, M.Z. Allelopathic assessment for the environmental biosafety of the transgenic oilseed rape lines harboring the antifungal synthetic chitinase (NiC) gene. Pak. J. Bot. 2019, 51, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Li, Y.C.; Shi, J.L.; Yu, Z.B.; Pan, A.H.; Tang, X.M.; Ming, F. Impact of transgenic Cry1Ac+ CpTI cotton on diversity and dynamics of rhizosphere bacterial community of different root environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Chen, G.M.; Liu, F.X.; Bu, C.P.; Liu, L.; Zhao, X.X. Effects of transgenic glufosinate-tolerant rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) and the associated herbicide application on rhizospheric bacterial communities. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 106, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfora, L.; Sbrana, C.; Avio, L.; Felici, B.; Scatà, M.C.; Neri, U.; Benedetti, A. Risk management tools and the case study Brassica napus: Evaluating possible effects of genetically modified plants on soil microbial diversity. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.L.; Yang, M.K.; Du, M.H.; Zhong, Z.Z.; Lu, Y.T.; Wang, G.H.; Hua, X.M.; Fazal, A.; Mu, C.H.; Yan, S.F.; et al. Enrichments/derichments of root-associated bacteria related to plant growth and nutrition caused by the growth of an EPSPS-transgenic maize line in the field. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.J.; Feng, M.C.; Xiao, L.J.; Song, X.Y.; Ding, G.W.; Yang, W.D. Persistence of Cry1Ac protein from transgenic Bt cotton cultivation and residue returning in fields and its effect on functional diversity of soil microbial communities. Pedosphere 2019, 29, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Han, J.; Xue, K. Progress in the environmental monitoring of transgenic plants. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 2490–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Lang, Z.H.; Zhang, J.; He, K.L.; Zhu, L.; Huang, D.F. Acquisition of insect-resistant transgenic maize harboring a truncated cry1Ah gene via Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, L.C.R.S.; Peixoto, R.S.; Cury, J.C.; Sul, W.J.; Pellizari, W.H.; Tiedje, J.; Rosado, A.S. Bacterial diversity in rhizosphere soil from Antarctic vascular plants of Admiralty Bay, maritime Antarctica. ISME J. 2010, 4, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Sarkar, B.; Owens, G.; Thakur, J.K.; Manna, M.C.; Niazi, N.K.; Jayaraman, S.; Patra, A.K. Impact of genetically modified crops on rhizosphere microorganisms and processes: A review focusing on Bt cotton. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 148, 103492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Dubey, S.K. Current trends in Bt crops and their fate on associated microbial community dynamics: A review. Protoplasma 2016, 253, 663–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zeng, Q.; Yan, F.M.; Xu, H.G.; Xu, C.R. Effects of transgenic plants on soil microorganisms. Plant Soil 2005, 271, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, F. Assessing effects of transgenic crops on soil microbial communities. In Green Gene Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 207–234. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, B.; Guan, X.; Tao, J. Impact of Transgenic Insect-Resistant Maize HGK60 with Cry1AhGene on Biodiversity in the Fields. Res. Environ. Sci. 2021, 34, 964–975. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, B.; Xu, W.; Cao, W.; Fang, Z.; Liu, D.; He, Z.; Han, Z. Effect of Transgenic Bt Cotton on Biodiversity of Soil Microbial Community. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2011, 27, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Badri, D.V.; Vivanco, J.M. Regulation and function of root exudates. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 32, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, M.I.; Hussain, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, M.; Liu, X. Successive soybean-monoculture cropping assembles rhizosphere microbial communities for the soil suppression of soybean cyst nematode. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fiw222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.X.; Tian, Q.; Rahman, M.K.; Wu, F.Z. Effect of anti-fungal compound phytosphingosine in wheat root exudates on the rhizosphere soil microbial community of watermelon. Plant Soil 2020, 456, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filion, M. Do transgenic plants affect rhizobacteria populations? Microb. Biotechnol. 2008, 1, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.S.; Geng, L.L.; Wang, M.L.; Shao, G.X.; Liu, Y.F.; Shu, C.L.; Zhang, J. No adverse effects of transgenic maize on population dynamics of endophytic Bacillus subtilis strain B916-gfp. Microbiol. Open 2016, 6, e00404. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.; Wu, F.C.; Dong, J.Y.; Wang, B.F.; Song, X.Y. No impact of transgenic cry1Ie maize on the diversity, abundance and composition of soil fauna in a 2-year field trial. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazal, A.; Wen, Z.L.; Lu, Y.T.; Hua, X.M.; Yang, M.K.; Yin, T.M.; Han, H.W.; Lin, H.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Lu, G.H.; et al. Assembly and shifts of the bacterial rhizobiome of field grown transgenic maize line carrying mcry1ab and mcry2Ab genes at different developmental stages. Plant Growth Regul. Int. J. Nat. Synth. Regul. 2020, 91, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y. Physicochemical properties and fungal community diversity in rhizosphere soil of transgenie glyphosate resistant Brassica napus. Chin. J. Ecol. 2024, 43, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Houlden, A.; Timms-Wilson, T.M.; Day, M.J.; Bailey, M.J. Influence of plant developmental stage on microbial community structure and activity in the rhizosphere of three field crops. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 65, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Pan, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, N.; Guan, X. Effects of Transgenic Insect-Resistant Maize HGK60 on Rhizosphere Soil Bacterial Communities. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081892
Chen Y, Yang J, Pan L, Liu M, Wang Q, Xiao N, Guan X. Effects of Transgenic Insect-Resistant Maize HGK60 on Rhizosphere Soil Bacterial Communities. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081892
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yanjun, Junyi Yang, Libo Pan, Meng Liu, Qiuming Wang, Nengwen Xiao, and Xiao Guan. 2025. "Effects of Transgenic Insect-Resistant Maize HGK60 on Rhizosphere Soil Bacterial Communities" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081892
APA StyleChen, Y., Yang, J., Pan, L., Liu, M., Wang, Q., Xiao, N., & Guan, X. (2025). Effects of Transgenic Insect-Resistant Maize HGK60 on Rhizosphere Soil Bacterial Communities. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081892






