Pharmacologic Inhibition of Erythrocyte Ferroportin Expression Exacerbates Plasmodium Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. Plasmodium yoelii (P. yoelii) Infection and Parasitemia Quantification
2.3. Administration of VIT-2763
2.4. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Reticulocytes
2.5. Serum Collection
2.6. Preparation of Red Blood Cell (RBC) Ghosts
2.7. Hematological Analyses
2.8. Estimation of Serum Iron
2.9. Tissue Iron Estimation
2.10. Measurement of Liver Injury Markers
2.11. Serum ELISA
2.12. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.13. Immunoblot Analysis for RBC Ferroportin
2.14. Histological Analysis of Liver and Spleen Sections
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
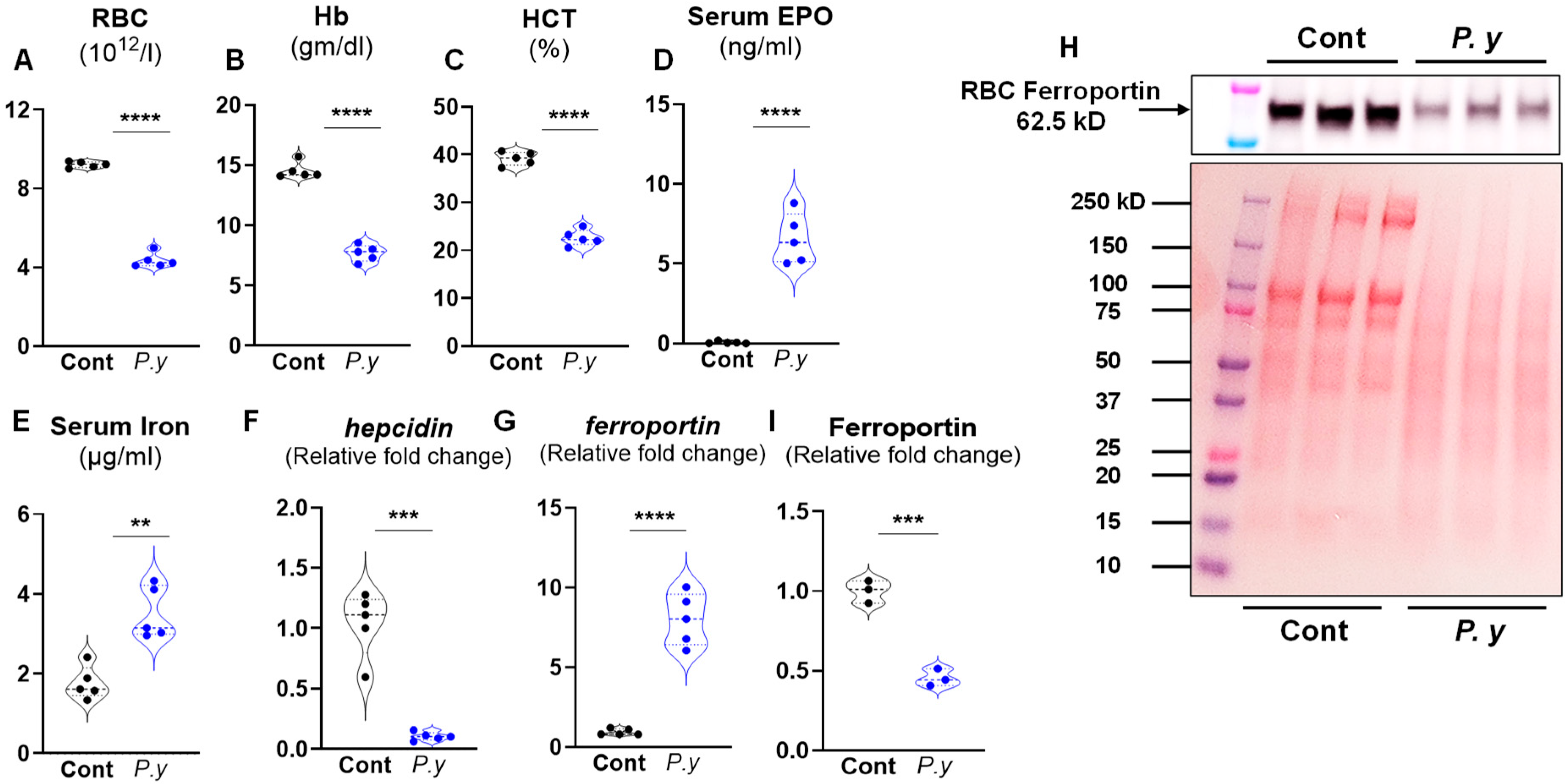
3.1. P. yoelii Infection Suppressed Hepatic Hepcidin Expression and Increased Ferroportin (Fpn) Expression
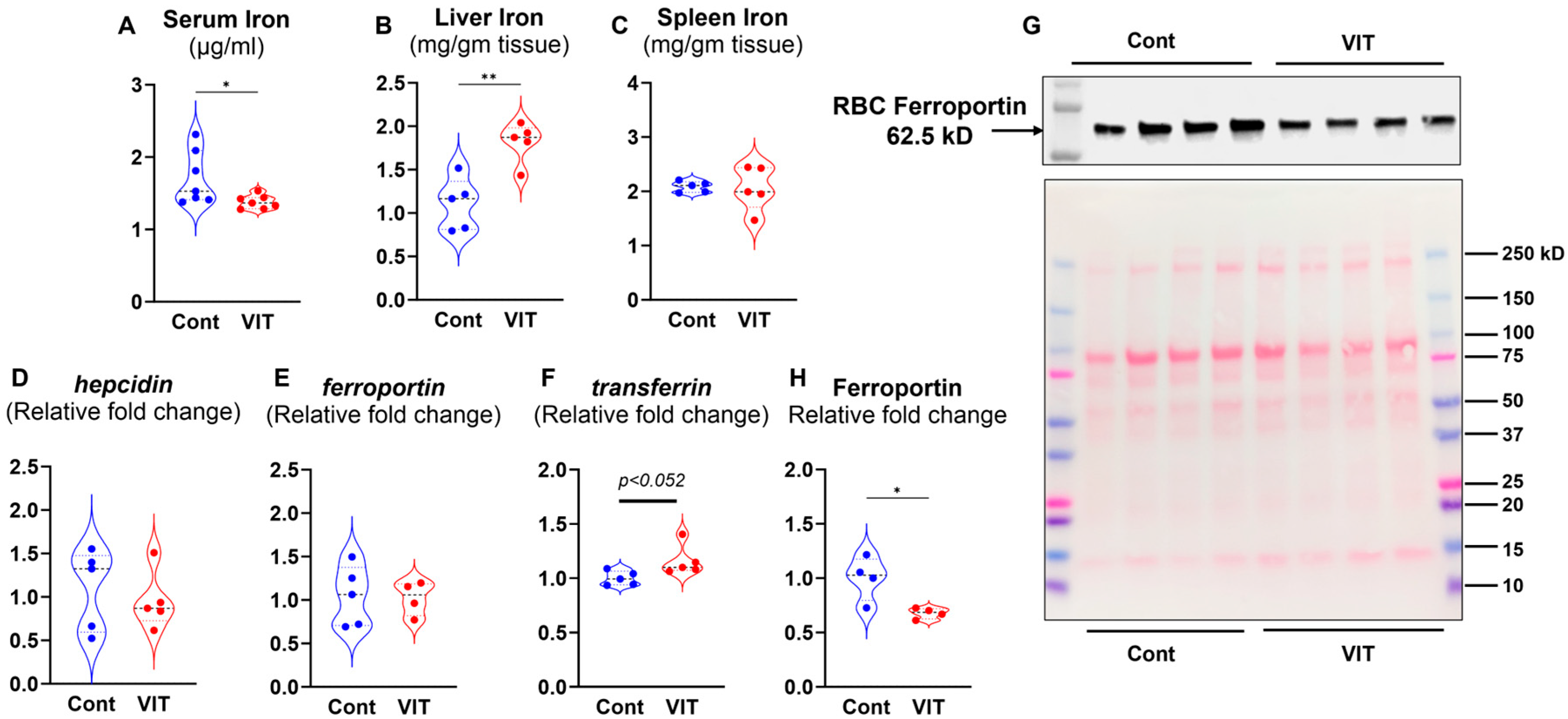
3.2. Inhibition of FPN by VIT Lowers the Circulating Iron and Enhances Liver Iron Storage
3.3. Inhibition of FPN Aggravates the P. yoelii Infection
3.4. VIT-Treated P. yoelii Infected Mice Showed Heightened Inflammatory Responses
3.5. VIT-Treated P. yoelii Infected Mice Showed Increased Hepatic Injury and Inflammation
3.6. VIT Treatment Increased Hepatic Fpn Expression and Suppressed RBC-FPN in P. yoelii-Infected Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate transaminase |
| CBC | Complete blood count |
| EPO | Erythropoietin |
| FPN | Ferroportin |
| Hb | Hemoglobin |
| HCT | Hematocrit |
| i.p. | Intra-peritoneally |
| IRE | Iron-response element |
| Lcn2 | Lipocalin 2 |
| MCH | Mean corpuscular hemoglobin |
| MCHC | Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration |
| MCV | Mean corpuscular volume |
| p.i. | Post-infection |
| P. yoelii | Plasmodium yoelii |
| RBC | Red blood cell |
| RBC-FPN | Red blood cell Ferroportin |
| SAA | Serum amyloid A |
| TBA | Total bile acids |
| VIT | VIT-2763 |
| WBC | White blood cell |
References
- Andrade, M.V.; Noronha, K.; Diniz, B.P.C.; Guedes, G.; Carvalho, L.R.; Silva, V.A.; Calazans, J.A.; Santos, A.S.; Silva, D.N.; Castro, M.C. The economic burden of malaria: A systematic review. Malar. J. 2022, 21, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, A.; Battle, K.E.; Meagher, N.; Howes, R.E.; Dini, S.; Gething, P.W.; Simpson, J.A.; Price, R.N.; Lubell, Y. Global economic costs due to vivax malaria and the potential impact of its radical cure: A modelling study. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thellier, M.; Gemegah, A.A.J.; Tantaoui, I. Global Fight against Malaria: Goals and Achievements 1900–2022. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyakeriga, A.M.; Troye-Blomberg, M.; Dorfman, J.R.; Alexander, N.D.; Back, R.; Kortok, M.; Chemtai, A.K.; Marsh, K.; Williams, T.N. Iron deficiency and malaria among children living on the coast of Kenya. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 190, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, F.A.; Calis, J.C.; van Hensbroek, M.B.; Phiri, K.; Geskus, R.B.; Brabin, B.J.; Leenstra, T. Iron status predicts malaria risk in Malawian preschool children. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spottiswoode, N.; Duffy, P.E.; Drakesmith, H. Iron, anemia and hepcidin in malaria. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.T.; Lamb, T.J.; Deroost, K.; Opdenakker, G.; Van den Steen, P.E. Hemozoin in Malarial Complications: More Questions Than Answers. Trends Parasitol. 2021, 37, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyberghein, A.; Deroost, K.; Schwarzer, E.; Arese, P.; Van den Steen, P.E. Immunopathological effects of malaria pigment or hemozoin and other crystals. Biofactors 2014, 40, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazawal, S.; Black, R.E.; Ramsan, M.; Chwaya, H.M.; Stoltzfus, R.J.; Dutta, A.; Dhingra, U.; Kabole, I.; Deb, S.; Othman, M.K.; et al. Effects of routine prophylactic supplementation with iron and folic acid on admission to hospital and mortality in preschool children in a high malaria transmission setting: Community-based, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2006, 367, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, A.M.; Ghattas, H.; Doherty, C.; Cox, S.E. Iron metabolism and malaria. Food Nutr. Bull. 2007, 28, S524–S539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.L.; Wu, J.; Shah, B.N.; Greutelaers, K.C.; Ghosh, M.C.; Ollivierre, H.; Su, X.Z.; Thuma, P.E.; Bedu-Addo, G.; Mockenhaupt, F.P.; et al. Erythrocytic ferroportin reduces intracellular iron accumulation, hemolysis, and malaria risk. Science 2018, 359, 1520–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, J.; Kotov, V.; Votborg-Novel, L.; Ntalla, C.; Geffken, M.; Peine, S.; Portugal, S.; Strauss, J. Iron transport pathways in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum revealed by RNA-sequencing. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1480076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muriuki, J.M.; Mentzer, A.J.; Band, G.; Gilchrist, J.J.; Carstensen, T.; Lule, S.A.; Goheen, M.M.; Joof, F.; Kimita, W.; Mogire, R.; et al. The ferroportin Q248H mutation protects from anemia, but not malaria or bacteremia. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw0109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalleda, N.; Flace, A.; Altermatt, P.; Ingoglia, G.; Doucerain, C.; Nyffenegger, N.; Durrenberger, F.; Manolova, V. Ferroportin inhibitor vamifeport ameliorates ineffective erythropoiesis in a mouse model of β-thalassemia with blood transfusions. Haematologica 2023, 108, 2703–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyffenegger, N.; Zennadi, R.; Kalleda, N.; Flace, A.; Ingoglia, G.; Buzzi, R.M.; Doucerain, C.; Buehler, P.W.; Schaer, D.J.; Durrenberger, F.; et al. The oral ferroportin inhibitor vamifeport improves hemodynamics in a mouse model of sickle cell disease. Blood 2022, 140, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, J.; Taher, A.; Viprakasit, V.; Kattamis, A.; Coates, T.D.; Garbowski, M.; Durrenberger, F.; Manolova, V.; Richard, F.; Cappellini, M.D. Oral ferroportin inhibitor vamifeport for improving iron homeostasis and erythropoiesis in β-thalassemia: Current evidence and future clinical development. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2021, 14, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyffenegger, N.; Flace, A.; Doucerain, C.; Durrenberger, F.; Manolova, V. The Oral Ferroportin Inhibitor VIT-2763 Improves Erythropoiesis without Interfering with Iron Chelation Therapy in a Mouse Model of β-Thalassemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolova, V.; Nyffenegger, N.; Flace, A.; Altermatt, P.; Varol, A.; Doucerain, C.; Sundstrom, H.; Durrenberger, F. Oral ferroportin inhibitor ameliorates ineffective erythropoiesis in a model of β-thalassemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 130, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, F.; van Lier, J.J.; Roubert, B.; Haboubi, T.; Gohring, U.M.; Durrenberger, F. Oral ferroportin inhibitor VIT-2763: First-in-human, phase 1 study in healthy volunteers. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, T.; Tadakuma, T.; Rodriguez, A. Plasmodium yoelii yoelii 17XNL constitutively expressing GFP throughout the life cycle. Exp. Parasitol. 2007, 115, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.J.; Ekholm, J.E. The preparation of red cell ghosts (membranes). Methods Enzymol. 1974, 31, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrance, J.D.; Bothwell, T.H. A simple technique for measuring storage iron concentrations in formalinised liver samples. S. Afr. J. Med. Sci. 1968, 33, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Masaratana, P.; Patel, N.; Latunde-Dada, G.O.; Vaulont, S.; Simpson, R.J.; McKie, A.T. Regulation of iron metabolism in Hamp (−/−) mice in response to iron-deficient diet. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyoumi, S.; Abitbol, M.; Andrieu, V.; Henin, D.; Robert, E.; Schmitt, C.; Gouya, L.; de Verneuil, H.; Deybach, J.C.; Montagutelli, X.; et al. Increased plasma transferrin, altered body iron distribution, and microcytic hypochromic anemia in ferrochelatase-deficient mice. Blood 2007, 109, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, C.T.; McKakpo, U.S.; Quakyi, I.A.; Bosompem, K.M.; Addison, E.A.; Sun, K.; Sullivan, D.; Semba, R.D. Relationship of hepcidin with parasitemia and anemia among patients with uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Ghana. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mast, Q.; Nadjm, B.; Reyburn, H.; Kemna, E.H.; Amos, B.; Laarakkers, C.M.; Silalye, S.; Verhoef, H.; Sauerwein, R.W.; Swinkels, D.W.; et al. Assessment of urinary concentrations of hepcidin provides novel insight into disturbances in iron homeostasis during malarial infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mast, Q.; Syafruddin, D.; Keijmel, S.; Riekerink, T.O.; Deky, O.; Asih, P.B.; Swinkels, D.W.; van der Ven, A.J. Increased serum hepcidin and alterations in blood iron parameters associated with asymptomatic P. falciparum and P. vivax malaria. Haematologica 2010, 95, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Z.; He, Y.X.; Yang, C.J.; Zhou, W.; Zou, C.G. Hepcidin is regulated during blood-stage malaria and plays a protective role in malaria infection. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 6410–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.; Ghosh, K. Pathogenesis of anemia in malaria: A concise review. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, K.; Mohandas, N. Malaria, erythrocytic infection, and anemia. Hematol.-Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2009, 1, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zheng, X.; Berzins, K.; Chaudhuri, A. Cytokine dysregulation associated with malarial anemia in Plasmodium yoelii infected mice. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2013, 5, 235–245. [Google Scholar]
- Dumarchey, A.; Lavazec, C.; Verdier, F. Erythropoiesis and Malaria, a Multifaceted Interplay. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchard, G.D.; Radloff, P.; Philipps, J.; Nkeyi, M.; Knobloch, J.; Kremsner, P.G. Increased erythropoietin production in children with severe malarial anemia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1995, 53, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgmann, H.; Looareesuwan, S.; Kapiotis, S.; Viravan, C.; Vanijanonta, S.; Hollenstein, U.; Wiesinger, E.; Presterl, E.; Winkler, S.; Graninger, W. Serum levels of erythropoietin in acute Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1996, 54, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misugi, Y. Comparative studies on human plasma insulin by stereoisomer galactose loading (author’s transl). Nihon Naibunpi Gakkai Zasshi 1977, 53, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, Y.W.; Russell, B.; Malleret, B.; Renia, L. Erythrocyte tropism of malarial parasites: The reticulocyte appeal. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1022828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, A.; Suri, V.; Singh, V. Malarial hepatopathy. J. Postgrad. Med. 2006, 52, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Anand, A.C.; Puri, P. Jaundice in malaria. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 20, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Kaushik, R.; Kaushik, R.M. Malarial hepatopathy: Clinical profile and association with other malarial complications. Acta Trop. 2016, 159, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahati, Y.L.; Delanghe, J.; Balaluka, G.B.; Vandepoele, K.; Cirhuza, J.C.; Kishabongo, A.S.; Philippe, J. Ferroportin Q248H mutation was not found to be protective against malaria and anemia in children under 5 years living in South Kivu/Democratic Republic of Congo, an endemic area of Plasmodium infection. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.L.; Ghosh, M.C.; Ollivierre, H.; Li, Y.; Rouault, T.A. Ferroportin deficiency in erythroid cells causes serum iron deficiency and promotes hemolysis due to oxidative stress. Blood 2018, 132, 2078–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, Y.Z. Cellular Iron Metabolism and Regulation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1173, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.M.; Kaplan, J. Ferroportin-mediated iron transport: Expression and regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leipuviene, R.; Theil, E.C. The family of iron responsive RNA structures regulated by changes in cellular iron and oxygen. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 2945–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latour, C.; Wlodarczyk, M.F.; Jung, G.; Gineste, A.; Blanchard, N.; Ganz, T.; Roth, M.P.; Coppin, H.; Kautz, L. Erythroferrone contributes to hepcidin repression in a mouse model of malarial anemia. Haematologica 2017, 102, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casals-Pascual, C.; Huang, H.; Lakhal-Littleton, S.; Thezenas, M.L.; Kai, O.; Newton, C.R.; Roberts, D.J. Hepcidin demonstrates a biphasic association with anemia in acute Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1695–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegboro, A.G.; Afolabi, I.S. Molecular mechanisms of mitochondria-mediated ferroptosis: A potential target for antimalarial interventions. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1374735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, A.; Amos, A.; Samson, B.W. The Link between Malaria and Ferroptosis—A Review. Covenant J. Phys. Life Sci. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzer, E.; Arese, P.; Skorokhod, O.A. Role of the lipoperoxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal in the pathogenesis of severe malaria anemia and malaria immunodepression. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 638416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skorokhod, O.; Barrera, V.; Mandili, G.; Costanza, F.; Valente, E.; Ulliers, D.; Schwarzer, E. Malaria Pigment Hemozoin Impairs GM-CSF Receptor Expression and Function by 4-Hydroxynonenal. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skorokhod, O.A.; Caione, L.; Marrocco, T.; Migliardi, G.; Barrera, V.; Arese, P.; Piacibello, W.; Schwarzer, E. Inhibition of erythropoiesis in malaria anemia: Role of hemozoin and hemozoin-generated 4-hydroxynonenal. Blood 2010, 116, 4328–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thawani, N.; Tam, M.; Bellemare, M.J.; Bohle, D.S.; Olivier, M.; de Souza, J.B.; Stevenson, M.M. Plasmodium products contribute to severe malarial anemia by inhibiting erythropoietin-induced proliferation of erythroid precursors. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugenin, E.A.; Martiney, J.A.; Berman, J.W. The malaria toxin hemozoin induces apoptosis in human neurons and astrocytes: Potential role in the pathogenesis of cerebral malaria. Brain Res. 2019, 1720, 146317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nekhai, S.; Xu, M.; Foster, A.; Kasvosve, I.; Diaz, S.; Machado, R.F.; Castro, O.L.; Kato, G.J.; Taylor, J.G., VI; Gordeuk, V.R. Reduced sensitivity of the ferroportin Q248H mutant to physiological concentrations of hepcidin. Haematologica 2013, 98, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H.; Shen, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Fang, X.; Duan, L.; et al. Hepatic transferrin plays a role in systemic iron homeostasis and liver ferroptosis. Blood 2020, 136, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeydabadinejad, S.; Theis, B.F.; Park, J.S.; Gohara, A.F.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Yeoh, B.S.; Saha, P. Pharmacologic Inhibition of Erythrocyte Ferroportin Expression Exacerbates Plasmodium Infection. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081859
Zeydabadinejad S, Theis BF, Park JS, Gohara AF, Vijay-Kumar M, Yeoh BS, Saha P. Pharmacologic Inhibition of Erythrocyte Ferroportin Expression Exacerbates Plasmodium Infection. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081859
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeydabadinejad, Sareh, Benjamin Frederick Theis, Jun Sung Park, Amira F. Gohara, Matam Vijay-Kumar, Beng San Yeoh, and Piu Saha. 2025. "Pharmacologic Inhibition of Erythrocyte Ferroportin Expression Exacerbates Plasmodium Infection" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081859
APA StyleZeydabadinejad, S., Theis, B. F., Park, J. S., Gohara, A. F., Vijay-Kumar, M., Yeoh, B. S., & Saha, P. (2025). Pharmacologic Inhibition of Erythrocyte Ferroportin Expression Exacerbates Plasmodium Infection. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081859





