Anti-QS Strategies Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Virulence Mechanisms of P. aeruginosa
2.1. Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance in P. aeruginosa
2.2. QS and Virulence Regulation in P. aeruginosa
2.3. Motility Mechanisms and Host Colonization in P. aeruginosa
2.4. Toxins and Enzymes Involved in Tissue Damage
2.5. Immune Evasion Strategies
2.6. Antibiotic Resistance
3. Inhibitors of QS in P. aeruginosa
3.1. Plant-Derived Natural Inhibitors of QS
3.2. Nanoparticles as Inhibitors of QS
3.3. Enzymes, Peptides, and Proteins as Inhibitors of QS
3.4. Synthetic and Derived Molecular Inhibitors
3.5. Microorganisms Producing QSIs
3.6. Other Inhibitors
3.7. Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats-Based Inhibition of QS
3.8. Comparative Analysis of QS Inhibitor Classes
4. Molecular Mechanisms of Plant-Derived Compounds That Antagonize QS Receptors
4.1. Competitive Inhibition of LasR Through Ligand Mimicry
4.2. Dual Targeting of QS Receptors and Synthases
4.3. Multi-Receptor Antagonism Across QS Hierarchies
4.4. Enzymatic Interference with AHL Synthesis
4.5. Transcriptional Repression of QS Regulatory Genes
5. Mechanisms of Resistance to QSI in P. aeruginosa
5.1. Mutations in QS Regulatory Genes
5.2. Overproduction of QS Signal Molecules
5.3. Activation of Alternative QS Pathways
5.4. Efflux Pump Overexpression
5.5. Catabolic Degradation of QSIs
5.6. Biofilm-Mediated Resistance
5.7. Compensatory Activation of Virulence Pathways
5.8. Structural Modifications of Autoinducers
5.9. Environmental Modulation of QS Hierarchy
5.10. Mutations Enhancing Autoinducer Affinity
6. Challenges and Limitations of QSIs
6.1. High Required Concentrations
6.2. Cytotoxicity and Host Cell Damage
6.3. Resistance Risks
6.4. Pharmacokinetic and Formulation Challenges
6.5. Specificity and Off-Target Effects
6.6. Ecological and Safety Concerns
6.7. Mechanistic Ambiguity
6.8. Partial Efficacy and Strain Dependency
6.9. Lack of In Vivo Validation
6.10. Translational and Economic Barriers
7. Future Perspectives
7.1. Structural Optimization and Multi-Target Inhibitor Design
7.1.1. Chemical Modifications for Enhanced Bioavailability and Target Affinity
7.1.2. Computational-Driven Design of Hybrid Inhibitors
7.1.3. Synthetic Biology and Efflux Pump Evasion Strategies
7.2. Synergistic Therapies and Combinatorial Approaches
7.3. Engineered Biological Systems and Nanotechnology
7.3.1. Nanotechnology-Driven Delivery Platforms
7.3.2. Inhalable and Topical Formulations
7.4. Translational Challenges and Ecological Integration
7.4.1. Preclinical Validation: Bridging the Gap Between Bench and Bedside
7.4.2. Standardization and Reproducibility
7.4.3. Ecological and Evolutionary Considerations
7.4.4. Regulatory and Commercialization Hurdles
7.4.5. Future Directions: Toward Sustainable Anti-Infective Strategies
7.5. Mechanistic Insights and Resistance Management
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kerr, K.G.; Snelling, A.M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Formidable and Ever-Present Adversary. J. Hosp. Infect. 2009, 73, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Z.; Raudonis, R.; Glick, B.R.; Lin, T.-J.; Cheng, Z. Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanisms and Alternative Therapeutic Strategies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strateva, T.; Mitov, I. Contribution of an Arsenal of Virulence Factors to Pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Ann Microbiol 2011, 61, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, J.P.; Pesci, E.C.; Iglewski, B.H. Roles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Las and Rhl Quorum-Sensing Systems in Control of Elastase and Rhamnolipid Biosynthesis Genes. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 5756–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thi, M.T.T.; Wibowo, D.; Rehm, B.H.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, M.A.; Gupta, K.; Mandal, M. Microbial Biofilm: Formation, Architecture, Antibiotic Resistance, and Control Strategies. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mohler, J.; Mahajan, S.D.; Schwartz, S.A.; Bruggemann, L.; Aalinkeel, R. Microbial Biofilm: A Review on Formation, Infection, Antibiotic Resistance, Control Measures, and Innovative Treatment. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidar, A.; Muazzam, A.; Nadeem, A.; Atique, R.; Saeed, H.A.; Naveed, A.; Sharif, J.; Perveen, A.; Fatima, H.R.; Samad, A. Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbe 2024, 3, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jia, T.; Yang, L. Targeting Anti-Virulence Factor Strategies of Bacterial Pathogens. Biosaf. Health 2025, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruwa, C.E.; Chellan, T.; S’thebe, N.W.; Dweba, Y.; Sabiu, S. ESKAPE Pathogens and Associated Quorum Sensing Systems: New Targets for Novel Antimicrobials Development. Health Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Li, M.; Yi, G.; Liao, L.; Cheng, Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, M. Screening Strategies for Quorum Sensing Inhibitors in Combating Bacterial Infections. J. Pharm. Anal. 2022, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truchado, P.; Larrosa, M.; Castro-Ibáñez, I.; Allende, A. Plant Food Extracts and Phytochemicals: Their Role as Quorum Sensing Inhibitors. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 43, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Bhattacharya, D.; Lahiri, D.; Nag, M.; Dey, A.; Ray, S. Gold and Silver Nanoparticles as Potent Quorum Quenchers: A Critical Review. BioNanoScience 2024, 15, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cruz, J.C.; Huelgas-Méndez, D.; Jiménez-Zúñiga, J.S.; Rebollar-Juárez, X.; Hernández-Garnica, M.; Fernández-Presas, A.M.; Husain, F.M.; Alenazy, R.; Alqasmi, M.; Albalawi, T.; et al. Myriad Applications of Bacteriophages beyond Phage Therapy. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodenak-Kladniew, B.; Scioli Montoto, S.; Sbaraglini, M.L.; Di Ianni, M.; Ruiz, M.E.; Talevi, A.; Alvarez, V.A.; Durán, N.; Castro, G.R.; Islan, G.A. Hybrid Ofloxacin/Eugenol Co-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles with Enhanced and Targetable Antimicrobial Properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, B.; Lu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Sun, J.; Wei, B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Quorum Sensing Inhibitors from Marine Microorganisms and Their Synthetic Derivatives. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-W.; Guo, C.; Xuan, C.-G.; Gu, J.-W.; Cui, Z.-N.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, L.-Q. High-Throughput, Quantitative Screening of Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors Based on a Bacterial Biosensor. ACS Chem. Biol. 2023, 18, 2544–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy-Pérez, E.; Herrera-Gabriel, J.P.; Olvera-Navarro, E.; Ugalde-Tecillo, L.; García-Cortés, L.R.; Moreno-Noguez, M.; Martínez-Gregorio, H.; Vaca-Paniagua, F.; Paniagua-Contreras, G.L. Molecular Properties of Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Causing Clinically Critical Infections. Pathogens 2024, 13, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendra, E.; Fernández-Muñoz, A.; Zamorano, L.; Oliver, A.; Horcajada, J.P.; Juan, C.; Gómez-Zorrilla, S. Impact of Multidrug Resistance on the Virulence and Fitness of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Microbiological and Clinical Perspective. Infection 2024, 52, 1235–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.W.; Floyd, R.V.; Fothergill, J.L. The Contribution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence Factors and Host Factors in the Establishment of Urinary Tract Infections. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364, fnx124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zezzi do Valle Gomes, M.; Nitschke, M. Evaluation of Rhamnolipid and Surfactin to Reduce the Adhesion and Remove Biofilms of Individual and Mixed Cultures of Food Pathogenic Bacteria. Food Control 2012, 25, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N. Cystic Fibrosis and the Clinical Biofilm Revolution A Survey of the Danish CF Center’s Contribution. Biofilm 2025, 9, 100246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N. Understanding Bacterial Biofilms in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis: Current and Innovative Approaches to Potential Therapies. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2002, 1, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuon, F.F.; Dantas, L.R.; Suss, P.H.; Tasca Ribeiro, V.S. Pathogenesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm: A Review. Pathogens 2022, 11, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behzadi, P.; Baráth, Z.; Gajdács, M. It’s Not Easy Being Green: A Narrative Review on the Microbiology, Virulence and Therapeutic Prospects of Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kievit, T.R. Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.-C.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Neu, T.R.; Nielsen, P.H.; Seviour, T.; Stoodley, P.; Wingender, J.; Wuertz, S. The Biofilm Matrix: Multitasking in a Shared Space. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciofu, O.; Rojo-Molinero, E.; Macià, M.D.; Oliver, A. Antibiotic Treatment of Biofilm Infections. APMIS 2017, 125, 304–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, M.; Alghetaa, H.; Mohammed, A.; Abdulla, O.A.; Wisniewski, P.J.; Singh, N.; Nagarkatti, P.; Nagarkatti, M. The Endocannabinoid Anandamide Attenuates Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Downregulating miRNA That Target Inflammatory Pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 644281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Jiménez, A.; Llamas, M.A.; Marcos-Torres, F.J. Transcriptional Regulators Controlling Virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.J.; Kuzel, T.M.; Shafikhani, S.H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Infections, Animal Modeling, and Therapeutics. Cells 2023, 12, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretsch, A.M.; Morgan, G.L.; Acken, K.A.; Barr, S.A.; Li, B. Pseudomonas Virulence Factor Pathway Synthesizes Autoinducers That Regulate the Secretome of a Pathogen. ACS Chem. Biol. 2021, 16, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.; Yao, C.; Ding, Y.; Hu, H.; Qian, G.; He, M.; Deng, X. The Transcriptional Regulators of Virulence for Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Therapeutic Opportunity and Preventive Potential of Its Clinical Infections. Genes. Dis. 2023, 10, 2049–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelaziz, A.A.; Kamer, A.M.A.; Al-Monofy, K.B.; Al-Madboly, L.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa’s Greenish-Blue Pigment Pyocyanin: Its Production and Biological Activities. Microb. Cell Factories 2023, 22, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zou, Y.; She, P.; Wu, Y. Composition, Function, and Regulation of T6SS in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 172, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, R.D.; Decho, A.W. Flexibility and Adaptability of Quorum Sensing in Nature. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, G.A.; Kolter, R. Flagellar and Twitching Motility Are Necessary for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Development. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 30, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, A.C.; Waters, V.J. Microbiology of Cystic Fibrosis Airway Disease. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 40, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Zarza, V.M.; Mangwani-Mordani, S.; Martínez-Maldonado, A.; Álvarez-Hernández, D.; Solano-Gálvez, S.G.; Vázquez-López, R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Pathogenicity and antimicrobial resistance in urinary tract infection. Rev. Chil. Infectologia 2019, 36, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, C.K.; Whitfield, G.B.; Brun, Y.V. Type IV Pili: Dynamic Bacterial Nanomachines. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 46, fuab053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazmierczak, B.I.; Schniederberend, M.; Jain, R. Cross-Regulation of Pseudomonas Motility Systems: The Intimate Relationship between Flagella, Pili and Virulence. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2015, 28, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, T.H. Pathogen Recognition and Inflammatory Signaling in Innate Immune Defenses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 240–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, R.E.; Isberg, R.R.; Portnoy, D.A. Patterns of Pathogenesis: Discrimination of Pathogenic and Non-Pathogenic Microbes by the Innate Immune System. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 6, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metelkina, O.; Konstantinović, J.; Klein, A.; Shafiei, R.; Fares, M.; Alhayek, A.; Yahiaoui, S.; Elgaher, W.A.M.; Haupenthal, J.; Titz, A.; et al. Dual Inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence Factors LecA and LasB. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 13333–13342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folkesson, A.; Jelsbak, L.; Yang, L.; Johansen, H.K.; Ciofu, O.; Høiby, N.; Molin, S. Adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the Cystic Fibrosis Airway: An Evolutionary Perspective. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, D.; Kollef, M. The Epidemiology and Pathogenesis and Treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections: An Update. Drugs 2021, 81, 2117–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagener, B.M.; Hu, R.; Wu, S.; Pittet, J.-F.; Ding, Q.; Che, P. The Role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence Factors in Cytoskeletal Dysregulation and Lung Barrier Dysfunction. Toxins 2021, 13, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, J.T.; Sun, J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa ExoS and ExoT. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 152, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulkes, D.M.; McLean, K.; Haneef, A.S.; Fernig, D.G.; Winstanley, C.; Berry, N.; Kaye, S.B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Toxin ExoU as a Therapeutic Target in the Treatment of Bacterial Infections. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Jia, P.; Yu, W.; Chu, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q. The Epidemiology and Virulence of Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in China. Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyy, A.; Mechold, U.; Renault, L.; Ladant, D. ExoY, an Actin-Activated Nucleotidyl Cyclase Toxin from P. aeruginosa: A Minireview. Toxicon 2018, 149, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wretlind, B.; Pavlovskis, O.R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Elastase and Its Role in Pseudomonas Infections. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1983, 5, S998–S1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everett, M.J.; Davies, D.T. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Elastase (LasB) as a Therapeutic Target. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 2108–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galdino, A.C.M.; Branquinha, M.H.; Santos, A.L.S.; Viganor, L. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Its Arsenal of Proteases: Weapons to Battle the Host. In Pathophysiological Aspects of Proteases; Chakraborti, S., Dhalla, N.S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 381–397. ISBN 978-981-10-6141-7. [Google Scholar]
- West, S.E.H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Exotoxin A: Structure/Function, Production, and Intoxication of Eukaryotic Cells. In Bacterial Protein Toxins; Aktories, K., Just, I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 67–89. ISBN 978-3-662-05971-5. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, Y.-H.; Xu, J.-F. How Does Pseudomonas aeruginosa Affect the Progression of Bronchiectasis? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soberón-Chávez, G.; González-Valdez, A.; Soto-Aceves, M.P.; Cocotl-Yañez, M. Rhamnolipids Produced by Pseudomonas: From Molecular Genetics to the Market. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 14, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, R.M.; Soberón-Chávez, G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Rhamnolipids: Biosynthesis and Potential Applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 54, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, Q.; Job, V.; Maillard, A.P.; Imbert, L.; Teulon, J.-M.; Favier, A.; Pellequer, J.-L.; Huber, P.; Attrée, I.; Dessen, A. Exolysin (ExlA) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa Punctures Holes into Target Membranes Using a Molten Globule Domain. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 4466–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboud, E.; Basso, P.; Maillard, A.P.; Huber, P.; Attrée, I. Exolysin Shapes the Virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clonal Outliers. Toxins 2017, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, T.S.; Parker, D.; Prince, A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Host Immune Evasion. In Pseudomonas: Volume 7: New Aspects of Pseudomonas Biology; Ramos, J.-L., Goldberg, J.B., Filloux, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 3–23. ISBN 978-94-017-9555-5. [Google Scholar]
- Huszczynski, S.M.; Lam, J.S.; Khursigara, C.M. The Role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lipopolysaccharide in Bacterial Pathogenesis and Physiology. Pathogens 2019, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawa, T.; Shimizu, M.; Moriyama, K.; Wiener-Kronish, J.P. Association between Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type III Secretion, Antibiotic Resistance, and Clinical Outcome: A Review. Crit. Care 2014, 18, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, A.; Chakrabarty, A.M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms: Role of the Alginate Exopolysaccharide. J. Ind. Microbiol. 1995, 15, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyczak, J.B.; Cannon, C.L.; Pier, G.B. Establishment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection: Lessons from a Versatile Opportunist1. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolar, S.L.; Liu, G.Y. RAS and ROS—A Story of Pseudomonas Survival. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 551–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xu, B.; Wang, M. Scavenging of Reactive Oxygen Species Effectively Reduces Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms through Disrupting Policing. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minagawa, S.; Inami, H.; Kato, T.; Sawada, S.; Yasuki, T.; Miyairi, S.; Horikawa, M.; Okuda, J.; Gotoh, N. RND Type Efflux Pump System MexAB-OprM of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Selects Bacterial Languages, 3-Oxo-Acyl-Homoserine Lactones, for Cell-to-Cell Communication. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriquez, T.; Falciani, C. Extracellular Vesicles of Pseudomonas: Friends and Foes. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, P.; Basso, P.; Reboud, E.; Attrée, I. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Renews Its Virulence Factors. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2016, 8, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustyniak, D.; Olszak, T.; Drulis-Kawa, Z. Outer Membrane Vesicles (OMVs) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Provide Passive Resistance but Not Sensitization to LPS-Specific Phages. Viruses 2022, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, S.; Hayes, D.; Wozniak, D.J. Cystic Fibrosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: The Host-Microbe Interface. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00138-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy, H.; Charron-Mazenod, L.; Lewenza, S. Extracellular DNA Chelates Cations and Induces Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisinger, E.; Isberg, R.R. Interplay Between Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence During Disease Promoted by Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, S9–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Chauhan, K.; Singh, G.; Chaudhary, S.; Rathore, J.S. Decoding Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Embracing Innovative Therapies beyond Conventional Antibiotics. Microbe 2025, 6, 100233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, A.B.; Carrara, J.A.; Barroso, C.D.N.; Tuon, F.F.; Faoro, H. Role of Efflux Pumps on Antimicrobial Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pechère, J.-C.; Köhler, T. Patterns and Modes of β-Lactam Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 1999, 5, S15–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, J.; Grosso, F.; Peixe, L. Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa—Mechanisms, Epidemiology and Evolution. Drug Resist. Updat. 2019, 44, 100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, A.X.; Herman, C. Horizontal Gene Transfer and beyond: The Delivery of Biological Matter by Bacterial Membrane Vesicles to Host and Bacterial Cells. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2024, 81, 102525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Urretavizcaya, B.; Vilaplana, L.; Marco, M.-P. Strategies for Quorum Sensing Inhibition as a Tool for Controlling Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 64, 107323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duplantier, M.; Lohou, E.; Sonnet, P. Quorum Sensing Inhibitors to Quench P. aeruginosa Pathogenicity. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.-L.; Sam, C.-K.; Yin, W.-F.; Tan, L.Y.; Krishnan, T.; Chong, Y.M.; Chan, K.-G. Plant-Derived Natural Products as Sources of Anti-Quorum Sensing Compounds. Sensors 2013, 13, 6217–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Celik, I.; Khan, H.M.; Shahid, M.; Shahzad, A.; Kumar, S.; Ahmed, B. Antibiofilm and Anti-Quorum Sensing Activity of Psidium guajava L. Leaf Extract: In Vitro and In Silico Approach. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0295524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, Ş.; Gökalsın, B.; Şenkardeş, İ.; Doğan, A.; Sesal, N.C. Anti-Quorum Sensing and Anti-Biofilm Activities of Hypericum perforatum Extracts against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 235, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önem, E.; Sarısu, H.C.; Özaydın, A.G.; Muhammed, M.T.; Ak, A. Phytochemical Profile, Antimicrobial, and Anti-Quorum Sensing Properties of Fruit Stalks of Prunus avium L. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 73, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaralleh, H. Chemical Composition and Quorum Sensing Inhibitory Effect of Nepeta curviflora Methanolic Extract against ESBL Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Pharmacopunct. 2023, 26, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, I.; Abbas, H.A.; Ashour, M.L.; Yasri, A.; El-Shazly, A.M.; Wink, M.; Sobeh, M. Polyphenols from Salix tetrasperma Impair Virulence and Inhibit Quorum Sensing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules 2020, 25, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, K.; Ramanathan, T. Musa acuminata and Its Bioactive Metabolite 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Mitigates Quorum Sensing (Las and Rhl) Mediated Biofilm and Virulence Production of Nosocomial Pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa In Vitro. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 246, 112242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalifar, H.; Samadi, N.; Nowroozi, J.; Dezfulian, M.; Fazeli, M.R. Down-Regulatory Effects of Green Coffee Extract on Las I and Las R Virulence-Associated Genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 27, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Núñez, J.L.; Pérez-López, M.; Espinosa, N.; Campos-Hernández, N.; García-Contreras, R.; Díaz-Guerrero, M.; Cortes-López, H.; Vázquez-Sánchez, M.; Quezada, H.; Martínez-Vázquez, M.; et al. Anti-Virulence Properties of Plant Species: Correlation between In Vitro Activity and Efficacy in a Murine Model of Bacterial Infection. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Křížkovská, B.; Hoang, L.; Brdová, D.; Klementová, K.; Szemerédi, N.; Loučková, A.; Kronusová, O.; Spengler, G.; Kaštánek, P.; Hajšlová, J.; et al. Modulation of the Bacterial Virulence and Resistance by Well-Known European Medicinal Herbs. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 312, 116484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Yin, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Wang, T.; Ren, G. Antimicrobial Activities of Asian Ginseng, American Ginseng, and Notoginseng. Phytother Res. 2020, 34, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Singh, S.P.; Manhar, A.K.; Saikia, D.; Namsa, N.D.; Konwar, B.K.; Mandal, M. Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm and Virulence by Active Fraction of Syzygium cumini (L.) Skeels Leaf Extract: In-Vitro and In Silico Studies. Indian J. Microbiol. 2019, 59, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alreshidi, M.; Noumi, E.; Bouslama, L.; Ceylan, O.; Veettil, V.N.; Adnan, M.; Danciu, C.; Elkahoui, S.; Badraoui, R.; Al-Motair, K.A.; et al. Phytochemical Screening, Antibacterial, Antifungal, Antiviral, Cytotoxic, and Anti-Quorum-Sensing Properties of Teucrium polium L. Aerial Parts Methanolic Extract. Plants 2020, 9, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanović, M.; Morić, I.; Nikolić, B.; Pavić, A.; Svirčev, E.; Šenerović, L.; Mitić-Ćulafić, D. Anti-Virulence Potential and In Vivo Toxicity of Persicaria maculosa and Bistorta officinalis Extracts. Molecules 2020, 25, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, F.; Hadi, N.; Bazargani, A. Evaluation of Quorum-Sensing Inhibitory Effects of Extracts of Three Traditional Medicine Plants with Known Antibacterial Properties. New Microbes New Infect 2020, 38, 100769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miari, M.; Rasheed, S.S.; Haidar Ahmad, N.; Itani, D.; Abou Fayad, A.; Matar, G.M. Natural Products and Polysorbates: Potential Inhibitors of Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2020, 14, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Xu, H.; Huang, T.; Liu, G.; Cao, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Yao, X. Fuzheng Touxie Jiedu Huayu Decoction Inhibits the MexAB-OprM Efflux Pump and Quorum Sensing-Mediated Biofilm Formation in Difficult-to-Treat Multidrug Resistance Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 332, 118365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruparel, F.J.; Shah, S.K.; Patel, J.H.; Thakkar, N.R.; Gajera, G.N.; Kothari, V.O. Network Analysis for Identifying Potential Anti-Virulence Targets from Whole Transcriptome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus Exposed to Certain Anti-Pathogenic Polyherbal Formulations. Drug Target Insights 2023, 17, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, C.; Patel, P.; Palep, H.; Kothari, V. Validation of the Anti-Infective Potential of a Polyherbal “Panchvalkal” Preparation, and Elucidation of the Molecular Basis Underlining Its Efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shravani, V.; Girija, A.S.; Krishnan, M.; Babu, S. Anti-Quorum Sensing Activity of Boerhavia diffusa against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Bioinformation 2023, 19, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Seenivasan, B.; Li, R.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ravichandran, V.; Zhong, L.; Li, A. Exploring Daidzein Dimethyl Ether from Albizzia lebbeck as a Novel Quorum Sensing Inhibitor against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Insights from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2025, 156, 108168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnamte, S.; Parasuraman, P.; Ranganathan, S.; Ampasala, D.R.; Reddy, D.; Kumavath, R.N.; Suchiang, K.; Mohanty, S.K.; Busi, S. Mosloflavone Attenuates the Quorum Sensing Controlled Virulence Phenotypes and Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1: In Vitro, In Vivo and In Silico Approach. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 131, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Feng, Y.; Han, X.; Cai, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, C.; Shen, L. Inhibition of Virulence Factors and Biofilm Formation by Wogonin Attenuates Pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 via Targeting Pqs Quorum-Sensing System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.P.R.R.; Boopathi, S.; Priya, P.S.; Pasupuleti, M.; Pachaiappan, R.; Almutairi, B.O.; Arokiyaraj, S.; Arockiaraj, J. Luteolin, a Promising Quorum Quencher Mitigates Virulence Factors Production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa—In Vitro and In Vivoapproach. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 180, 106123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Cheng, Y. Antibiofilm Activity of Allicin and Quercetin in Treating Biofilm-Associated Orthopaedics Infection. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, S.K.; Panda, A.K.; Mishra, R.; Mahanty, A.; Bisht, S.S. Structure Based Virtual Screening and Molecular Dynamics of Natural Anti-Biofilm Compounds against SagS Response Regulator/Sensor Kinase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 6011–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghannay, S.; Aouadi, K.; Kadri, A.; Snoussi, M. GC-MS Profiling, Vibriocidal, Antioxidant, Antibiofilm, and Anti-Quorum Sensing Properties of Carum carvi L. Essential Oil: In Vitro and In Silico Approaches. Plants 2022, 11, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, D.; Huang, X.; Yang, H.; Qiu, Z.; Zou, L.; Liang, Q.; Shi, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, S.; et al. Study on Antibacterial and Quorum-Sensing Inhibition Activities of Cinnamomum camphora Leaf Essential Oil. Molecules 2019, 24, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S’thebe, N.W.; Aribisala, J.O.; Sabiu, S. Cheminformatics Bioprospection of Sunflower Seeds’ Oils against Quorum Sensing System of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wira Septama, A.; Arvia Chiara, M.; Turnip, G.; Nur Tasfiyati, A.; Triana Dewi, R.; Anggrainy Sianipar, E.; Jaisi, A. Essential Oil of Zingiber cassumunar Roxb. and Zingiber officinale Rosc.: A Comparative Study on Chemical Constituents, Antibacterial Activity, Biofilm Formation, and Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing System. Chem. Biodivers 2023, 20, e202201205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, S.; Shi, K.; Mei, J.; Ying, G.; Wu, S. Screening and Isolation of Quorum Sensing Inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Phellodendron amurense Extracts Using Bio-Affinity Chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2024, 47, e2400222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Dastidar, D.G.; Paul, P.; Dutta, S.; Basu, D.; Sharma, S.R.; Basu, S.; Sarker, R.K.; Sen, A.; Sarkar, A.; et al. Inhibition of Biofilm Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Caffeine: A Potential Approach for Sustainable Management of Biofilm. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, A.; Mukherjee, S.K.; Barik, S.; Hossain, S.T. Antimicrobial Activity of Trigonelline Hydrochloride Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Its Quorum-Sensing Regulated Molecular Mechanisms on Biofilm Formation and Virulence. ACS Infect. Dis. 2024, 10, 746–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wu, L.; Su, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, L.; Xia, Z.; Huang, H.; Wang, W.; Fang, J.; Gu, Z.; et al. Inhibitory Effects of Compounds from Plumula nelumbinis on Biofilm and Quorum Sensing Against P. aeruginosa. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, N.E.-A.; Bashir, S.I.; Rabei, N.H.; Saber, W.I.A. Innovative Biosynthesis, Artificial Intelligence-Based Optimization, and Characterization of Chitosan Nanoparticles by Streptomyces Microflavus and Their Inhibitory Potential against Pectobacterium Carotovorum. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Ma, X.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, D.; Ning, W.; Xiao, W.; Mao, Q.; Bai, Z.; Mao, R.; Cheng, J.; et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine Monomer Bakuchiol Attenuates the Pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa via Targeting PqsR. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 26, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Rodriguez, M.R.; Bernal-Mercado, A.T.; Gutierrez-Pacheco, M.M.; Vazquez-Armenta, F.J.; Hernandez-Mendoza, A.; Gonzalez-Aguilar, G.A.; Martinez-Tellez, M.A.; Nazzaro, F.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F. Virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Exposed to Carvacrol: Alterations of the Quorum Sensing at Enzymatic and Gene Levels. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 13, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, S.; Singh, V.; Nag, S.; Roy, D.N. Carvacrol, a Monoterpenoid, Binds Quorum Sensing Proteins (LasI and LasR) and Swarming Motility Protein BswR of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Resulting in Loss of Pathogenicity: An In Silico Approach. Can. J. Microbiol. 2025, 71, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastry, R.P.; Kanekar, S.; Pandial, A.S.; Rekha, P.D. Isoeugenol Suppresses Multiple Quorum Sensing Regulated Phenotypes and Biofilm Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wen, F.; Yang, X.; Gou, S.; Chu, Y.; Zhao, K. Isovanillin Decreases the Virulence Regulated by the Quorum Sensing System of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 196, 107010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Hao, S.; Zhao, L.; Shi, F.; Ye, G.; Zou, Y.; Song, X.; Li, L.; Yin, Z.; He, X.; et al. Paeonol Attenuates Quorum-Sensing Regulated Virulence and Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 692474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, N.; Chan, S.Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Chua, S.L. Vanillin Inhibits PqsR-Mediated Virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 6496–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, K.E.; Akhter, S.; Rodriguez, B.; Townsend, K.A.; Smith, N.; Smith, B.; Wambua, A.; Craddock, V.; Abisado-Duque, R.G.; Santa, E.E.; et al. Characterization of Natural Product Inhibitors of Quorum Sensing Reveals Competitive Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa RhlR by Ortho-Vanillin. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0068124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, A.; Chu, W. Phillyrin Is an Effective Inhibitor of Quorum Sensing with Potential as an Anti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection Therapy. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anju, V.T.; Busi, S.; Ranganathan, S.; Ampasala, D.R.; Kumar, S.; Suchiang, K.; Kumavath, R.; Dyavaiah, M. Sesamin and Sesamolin Rescues Caenorhabditis elegans from Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection through the Attenuation of Quorum Sensing Regulated Virulence Factors. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 155, 104912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfaky, M.A.; Elbaramawi, S.S.; Eissa, A.G.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Ali, M.A.M.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Drug Repositioning: Doxazosin Attenuates the Virulence Factors and Biofilm Formation in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 3763–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, E.M.F.; de Almeida, F.A.; Pinto, U.M. Exploring the Antivirulence Potential of Phenolic Compounds to Inhibit Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2025, 41, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalgudi, R.; Tamimi, R.; Kyazze, G.; Keshavarz, T. Effect of Quorum Quenchers on Virulence Factors Production and Quorum Sensing Signalling Pathway of Non-Mucoid, Mucoid, and Heavily Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ji, P.-C.; Qi, Y.-H.; Chen, S.-J.; Wang, C.-Y.; Yang, Y.-J.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Zhou, J.-W. Inactivation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms by Thymoquinone in Combination with Nisin. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1029412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rabia, M.W.; Asfour, H.Z.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Abdulaal, W.H.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Abbas, H.A.; Salem, I.M.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Nazeih, S.I. Thymoquinone Is a Natural Antibiofilm and Pathogenicity Attenuating Agent in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1382289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, X.; Ran, Q.; Gan, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Chu, Y.; Zhao, K. Discovery of Psoralen as a Quorum Sensing Inhibitor Suppresses Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasthuri, T.; Barath, S.; Nandhakumar, M.; Karutha Pandian, S. Proteomic Profiling Spotlights the Molecular Targets and the Impact of the Natural Antivirulent Umbelliferone on Stress Response, Virulence Factors, and the Quorum Sensing Network of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 998540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, S.-Y.; Hu, J.-Y.; Chen, Q.-X.; Jiao, S.-M.; Xiao, H.-C.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, J.; Zhao, J.-F.; Zhou, H.-B.; et al. Novel Coumarin Derivatives Inhibit the Quorum Sensing System and Iron Homeostasis as Antibacterial Synergists against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 14735–14754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chu, W.; Ye, C.; Gaeta, B.; Tao, H.; Wang, M.; Qiu, Z. Chlorogenic Acid Attenuates Virulence Factors and Pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Regulating Quorum Sensing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naga, N.G.; Zaki, A.A.; El-Badan, D.E.; Rateb, H.S.; Ghanem, K.M.; Shaaban, M.I. Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing by Methyl Gallate from Mangifera Indica. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nortje, N.Q.; Aribisala, J.O.; Pillay, C.; Sabiu, S. Molecular Modelling and Experimental Validation of Mangiferin and Its Related Compounds as Quorum Sensing Modulators of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch. Microbiol. 2025, 207, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmassry, M.M.; Bisht, K.; Colmer-Hamood, J.A.; Wakeman, C.A.; San Francisco, M.J.; Hamood, A.N. Malonate Utilization by Pseudomonas aeruginosa Affects Quorum-Sensing and Virulence and Leads to Formation of Mineralized Biofilm-like Structures. Mol. Microbiol. 2021, 116, 516–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, P.; Oliveira, J.; Fernandes, I.; Araújo, P.; Pereira, A.R.; Gameiro, P.; Bessa, L.J. Pyranoanthocyanins Interfering with the Quorum Sensing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampathkumar, S.J.; Srivastava, P.; Ramachandran, S.; Sivashanmugam, K.; Gothandam, K.M. Lutein: A Potential Antibiofilm and Antiquorum Sensing Molecule from Green Microalga Chlorella Pyrenoidosa. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 135, 103658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Nan, M.; Cai, X.; Qiao, B.; Chen, L.; Shen, L. Sennoside A Inhibits Quorum Sensing System to Attenuate Its Regulated Virulence and Pathogenicity via Targeting LasR in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1042214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-Q.; Feng, X.-C.; Shi, H.-T.; Wang, Y.-M.; Jiang, C.-Y.; Xiao, Z.-J.; Xu, Y.-J.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Ren, N.-Q. Biofilm Inhibition Based on Controlling the Transmembrane Transport and Extracellular Accumulation of Quorum Sensing Signals. Environ. Res. 2023, 221, 115218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bhasme, P.; Reddy, D.S.; Liu, D.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, T.; Zheng, Y.; Kumar, A.; Yu, H.; Ma, L.Z. Dual Functions: A Coumarin–Chalcone Conjugate Inhibits Cyclic-Di-GMP and Quorum-Sensing Signaling to Reduce Biofilm Formation and Virulence of Pathogens. mLife 2023, 2, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppiah, V.; Thirunanasambandham, R.; Thangaraj, G. Anti-Quorum Sensing and Antibiofilm Potential of 1,8-Cineole Derived from Musa Paradisiaca against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strain PAO1. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamfu, A.N.; Ceylan, O.; Cârâc, G.; Talla, E.; Dinica, R.M. Antibiofilm and Anti-Quorum Sensing Potential of Cycloartane-Type Triterpene Acids from Cameroonian Grassland Propolis: Phenolic Profile and Antioxidant Activity of Crude Extract. Molecules 2022, 27, 4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, M.; Misra, T.K.; Roy, D.N. In Vitro Anti-Biofilm Activity of 14-Deoxy-11,12-Didehydroandrographolide from Andrographis Paniculata against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2020, 51, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Wu, H.; Li, J.-J.; Wang, B.; Jia, A.-Q. Two Cinnamoyl Hydroxamates as Potential Quorum Sensing Inhibitors against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1424038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-S.; He, Z.; Shi, Y.; Guan, M.; Zhao, D.-S.; Zhu, D.; Xiong, L.-T.; Li, Y.; Deng, X.; Cui, Z.-N. Structure-Based Discovery of Symmetric Disulfides from Garlic Extract as Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing Inhibitors. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2024, 72, 20299–20307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, Q.; Chen, L.; Duan, K. Virulence-Inhibiting Herbal Compound Falcarindiol Significantly Reduced Mortality in Mice Infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qais, F.A.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, I. Nanoparticles as Quorum Sensing Inhibitor: Prospects and Limitations. In Biotechnological Applications of Quorum Sensing Inhibitors; Kalia, V.C., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 227–244. ISBN 978-981-10-9026-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ilk, S.; Tan, G.; Emül, E.; Sağlam, N. Investigation the Potential Use of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Propolis Extract as N-Acyl-Homoserine Lactone-Mediated Quorum Sensing Systems Inhibitor. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 50, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreres, G.; Ivanova, K.; Torrent-Burgués, J.; Tzanov, T. Multimodal Silver-Chitosan-Acylase Nanoparticles Inhibit Bacterial Growth and Biofilm Formation by Gram-Negative Pseudomonas aeruginosa Bacterium. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 646, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadelkareem, A.M.; Al-Shammari, E.; Elkhalifa, A.O.; Adnan, M.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Patel, M.; Khan, M.I.; Mehmood, K.; Ashfaq, F.; Badraoui, R.; et al. Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Eruca sativa Miller Leaf Extract Exhibits Antibacterial, Antioxidant, Anti-Quorum-Sensing, Antibiofilm, and Anti-Metastatic Activities. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, X.; Liao, S.; Jiang, C.; Wang, L.; Tang, Y.; Wu, G.; Dai, G.; Chen, L. Quantitative Proteomics Reveals the Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles against Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 3109–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, E.K.; Yamada, A.Y.; de Araujo, L.A.; Anversa, L.; Garcia, D.d.O.; de Souza, R.L.B.; Martins, H.M.; Kobayashi, R.K.T.; Nakazato, G. Subinhibitory Concentrations of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles Affect Motility and Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 656984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour-Khezri, E.; Moqadami, A.; Barzegar, A.; Mahdavi, M.; Skurnik, M.; Zarrini, G. Bacteriophages and Green Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Combination Are Efficient against Biofilm Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Viruses 2024, 16, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Husain, F.M.; Zia, Q.; Ahmad, E.; Jamal, A.; Alaidarous, M.; Banawas, S.; Alam, M.M.; Alshehri, B.A.; Jameel, M.; et al. Anti-Quorum Sensing and Anti-Biofilm Activity of Zinc Oxide Nanospikes. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 32203–32215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prateeksha; Rao, C.V.; Das, A.K.; Barik, S.K.; Singh, B.N. ZnO/Curcumin Nanocomposites for Enhanced Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence via LasR-RhlR Quorum Sensing Systems. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 3399–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanak, K.R.; Dass, R.S.; Pan, A. Anti-Quorum Sensing Potential of Selenium Nanoparticles against LasI/R, RhlI/R, and PQS/MvfR in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Molecular Docking Approach. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1203672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gómez, B.; Arregui, L.; Serrano, S.; Santos, A.; Pérez-Corona, T.; Madrid, Y. Selenium and Tellurium-Based Nanoparticles as Interfering Factors in Quorum Sensing-Regulated Processes: Violacein Production and Bacterial Biofilm Formation. Metallomics 2019, 11, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.Y.; Aly, U.F.; Abd El-Baky, R.M.; Waly, N.G.F.M. Effect of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on the Expression of Efflux Pump and Quorum-Sensing Genes in MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarif, M.; Jegel, O.; Gazanis, A.; Hartmann, J.; Plana-Ruiz, S.; Hilgert, J.; Frerichs, H.; Viel, M.; Panthöfer, M.; Kolb, U.; et al. High-Throughput Synthesis of CeO2 Nanoparticles for Transparent Nanocomposites Repelling Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.B.; Rayyif, S.M.I.; Curutiu, C.; Birca, A.C.; Oprea, O.-C.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Ditu, L.-M.; Gheorghe, I.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Mihaescu, G.; et al. Eugenol-Functionalized Magnetite Nanoparticles Modulate Virulence and Persistence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Strains. Molecules 2021, 26, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hu, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zheng, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, T. From Quorum Sensing Inhibition to Antimicrobial Defense: The Dual Role of Eugenol-Gold Nanoparticles against Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2025, 247, 114415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltayb, E.K.; Alqahtani, F.Y.; Alkahtani, H.M.; Alsarra, I.A.; Alfaraj, R.; Aleanizy, F.S. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing Virulence of Biofilm and Pyocyanin by mBTL-Loaded Calcium Alginate Nanoparticles. Polymers 2022, 14, 3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, S.; Akalin, R.B.; Çevikbaş, H.; Berisha, A.; Oral, A.; Boşgelmez-Tinaz, G. Zeolite 4A as a Jammer of Bacterial Communication in Chromobacterium violaceum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Future Microbiol. 2022, 17, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, F.M.; Ansari, A.A.; Khan, A.; Ahmad, N.; Albadri, A.; Albalawi, T.H. Mitigation of Acyl-Homoserine Lactone (AHL) Based Bacterial Quorum Sensing, Virulence Functions, and Biofilm Formation by Yttrium Oxide Core/Shell Nanospheres: Novel Approach to Combat Drug Resistance. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Rajwade, J.; Paknikar, K.M. Transcriptome Analysis of Silver Nanoparticles Treated Staphylococcus aureus Reveals Potential Targets for Biofilm Inhibition. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 175, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarvizhi, K.; Ramyadevi, D.; Vedha Hari, B.N.; Sarveswari, H.B.; Solomon, A.P.; Fang, H.; Luo, R.H.; Zheng, Y.T. Mercuric-Sulphide Based Metallopharmaceutical Formulation as an Alternative Therapeutic to Combat Viral and Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) Bacterial Infections. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Hill, P.; Liu, J.; Qian, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, S. Marine-Source Quorum Quenching Enzyme YtnP to Improve Hygiene Quality in Dental Units. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Jácome, L.E.; Garza-Ramos, G.; Hernández-Durán, M.; Franco-Cendejas, R.; Loarca, D.; Romero-Martínez, D.; Nguyen, P.T.D.; Maeda, T.; González-Pedrajo, B.; Díaz-Guerrero, M.; et al. AiiM Lactonase Strongly Reduces Quorum Sensing Controlled Virulence Factors in Clinical Strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated From Burned Patients. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandan, K.; Vittal, R.R. Quorum Quenching Activity of AiiA Lactonase KMMI17 from Endophytic Bacillus Thuringiensis KMCL07 on AHL- Mediated Pathogenic Phenotype in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 132, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-W.; Xuan, C.-G.; Lu, C.-H.; Guo, S.; Yu, J.-F.; Asif, M.; Jiang, W.-J.; Zhou, Z.-G.; Luo, Z.-Q.; Zhang, L.-Q. AidB, a Novel Thermostable N-Acylhomoserine Lactonase from the Bacterium bosea sp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02065-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rémy, B.; Plener, L.; Decloquement, P.; Armstrong, N.; Elias, M.; Daudé, D.; Chabrière, É. Lactonase Specificity Is Key to Quorum Quenching in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guendouze, A.; Plener, L.; Bzdrenga, J.; Jacquet, P.; Rémy, B.; Elias, M.; Lavigne, J.-P.; Daudé, D.; Chabrière, E. Effect of Quorum Quenching Lactonase in Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Comparison with Quorum Sensing Inhibitors. Front. Microbiol 2017, 8, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Cheng, P.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Xiong, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Yi, H.; Du, H.; et al. Effects of a Novel Anti-Biofilm Peptide CRAMP Combined with Antibiotics on the Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 152, 104660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aflakian, F.; Rad, M.; Hashemitabar, G.; Lagzian, M.; Ramezani, M. Design and Assessment of Novel Synthetic Peptides to Inhibit Quorum Sensing-Dependent Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biofouling 2022, 38, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroven, K.; Putzeys, L.; Swinnen, A.-L.; Hendrix, H.; Paeshuyse, J.; Lavigne, R. The Phage-Encoded Protein PIT2 Impacts Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing by Direct Interaction with LasR. iScience 2023, 26, 107745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Taylor, V.L.; Bona, D.; Tsao, Y.; Stanley, S.Y.; Pimentel-Elardo, S.M.; McCallum, M.; Bondy-Denomy, J.; Howell, P.L.; Nodwell, J.R.; et al. A Phage-Encoded Anti-Activator Inhibits Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 571–583.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xu, Z.; Cao, R.; Li, J.; Wu, C.-J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H. Effects of Hydroxyl Group in Cyclo(Pro-Tyr)-like Cyclic Dipeptides on Their Anti-QS Activity and Self-Assembly. iScience 2023, 26, 107048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, G.S.; Sajayan, A.; Priyadharshini, G.; Balakrishnan, A.; Prathiviraj, R.; Sabu, A.; Selvin, J. A Novel Anti-Infective Molecule Nesfactin Identified from Sponge Associated Bacteria Nesterenkonia sp. MSA31 against Multidrug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 157, 104923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.W.; Shin, M.K.; Park, H.-R.; Kim, S.; Lee, B.; Yoo, J.S.; Chi, W.-J.; Sung, J.-S. PA-Win2: In Silico-Based Discovery of a Novel Peptide with Dual Antibacterial and Anti-Biofilm Activity. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, P.; Luscher, A.; Siriwardena, T.; Michetti, M.; Que, Y.-A.; Rahme, L.G.; Reymond, J.-L.; Raffoul, W.; Van Delden, C.; Applegate, L.A.; et al. Antimicrobial Peptide Dendrimers and Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors in Formulating Next-Generation Anti-Infection Cell Therapy Dressings for Burns. Molecules 2021, 26, 3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xiao, X.; Qi, Y.; Lin, X.; Hu, H.; Shi, M.; Zhou, M.; Jiang, W.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; et al. Host-Defense-Peptide-Mimicking β-Peptide Polymer Acting as a Dual-Modal Antibacterial Agent by Interfering Quorum Sensing and Killing Individual Bacteria Simultaneously. Research 2023, 6, 0051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, D.M.; Dahabiyeh, L.A.; Abdelrazig, S.; Alqudah, D.A.; Al-Bakri, A.G. Micafungin Effect on Pseudomonas aeruginosa Metabolome, Virulence and Biofilm: Potential Quorum Sensing Inhibitor. AMB Express 2023, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.-K.; Ng, S.-K.; Chen, Y.-E.; Lee, Y.-C.; Demeter, F.; Herczeg, M.; Borbás, A.; Chiu, C.-H.; Lan, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-L.; et al. Rhamnose Binding Protein as an Anti-Bacterial Agent-Targeting Biofilm of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasu, E.N.; Ahor, H.S.; Borquaye, L.S. Peptide Mix from Olivancillaria Hiatula Interferes with Cell-to-Cell Communication in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 5313918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Mujawar, S.; Yasmin, A.; Perveen, S.; Malik, P.A.; Gill, M.S.A.; Chohan, T.A. Targeting Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa with High-Affinity Inhibitors: A High-Throughput Screening and in-Silico Analysis. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2025, 117, 108419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szemerédi, N.; Kincses, A.; Rehorova, K.; Hoang, L.; Salardón-Jiménez, N.; Sevilla-Hernández, C.; Viktorová, J.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Spengler, G. Ketone- and Cyano-Selenoesters to Overcome Efflux Pump, Quorum-Sensing, and Biofilm-Mediated Resistance. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadkhah, F.; Moniri, F.; Zamani, H.; Hadavi, M. Anti-Virulence Effects of Diclofenac Sodium in Combination with Gentamicin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Attenuation of Quorum Sensing Related Traits and Efflux Pump Systems. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkumari, J.; Borkotoky, S.; Reddy, D.; Mohanty, S.K.; Kumavath, R.; Murali, A.; Suchiang, K.; Busi, S. Anti-Quorum Sensing and Anti-Biofilm Activity of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1: Insights from In Vitro, In Vivo and In Silico Studies. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 226, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsheredy, A.; El-Soudany, I.; Elsherbini, E.; Metwally, D.; Ghazal, A. Effect of Azithromycin and Phenylalanine-Arginine Beta-Naphthylamide on Quorum Sensing and Virulence Factors in Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2021, 13, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valastyan, J.S.; Shine, E.E.; Mook, R.A.; Bassler, B.L. Inhibitors of the PqsR Quorum-Sensing Receptor Reveal Differential Roles for PqsE and RhlI in Control of Phenazine Production. bioRxiv 2025. bioRxiv:2025.02.10.637488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Brenner, N.; Brice, J.; Klein-Seetharaman, J.; Sarkar, S.K. Cephalosporins Interfere With Quorum Sensing and Improve the Ability of Caenorhabditis elegans to Survive Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 598498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Hou, S.; Xing, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, J.; Xiao, J.; Lin, F. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of the Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Molecules 2024, 29, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyahyawy, O.Y.; Munshi, R.M.; Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Abualsunun, W.; Abbas, H.A.; Salem, I.M.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Nazeih, S.I. Reprofiling Lamivudine as an Antibiofilm and Anti-Pathogenic Agent against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. AMB Express 2025, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, T.; Tateda, K.; Kimura, S.; Ishii, Y.; Ito, H.; Yoshida, H.; Kimura, T.; Yamaguchi, K. A Low Concentration of Azithromycin Inhibits the mRNA Expression of N-Acyl Homoserine Lactone Synthesis Enzymes, Upstream of lasI or rhlI, in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 22, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolaki, K.; Gagaletsios, L.A.; Papagiannitsis, C.C.; Petinaki, E. Macrolides Impact the Growth Ability of Clinical Pseudomonas aeruginosa through Quorum-Sensing Systems. J. Chemother. 2024, 36, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Zhao, K.; Li, H.; Liu, K.; Li, J.; Chu, Y.; Prithiviraj, B.; Yue, B.; Zhang, X. Antibacterial and Anti-Virulence Effects of Furazolidone on Trueperella Pyogenes and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, K.; et al. Furazolidone Reduces the Pathogenesis of Trueperella Pyogenes and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Co-Infection in a Mouse Model. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldelli, V.; D’Angelo, F.; Pavoncello, V.; Fiscarelli, E.V.; Visca, P.; Rampioni, G.; Leoni, L. Identification of FDA-Approved Antivirulence Drugs Targeting the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing Effector Protein PqsE. Virulence 2020, 11, 652–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seleem, N.M.; Abd El Latif, H.K.; Shaldam, M.A.; El-Ganiny, A. Drugs with New Lease of Life as Quorum Sensing Inhibitors: For Combating MDR Acinetobacter Baumannii Infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1687–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Shen, W.; Liu, J.-S.; Jia, A.-Q. 2-Hydroxymethyl-1-Methyl-5-Nitroimidazole, One Siderophore Inhibitor, Occludes Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 955952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collalto, D.; Giallonardi, G.; Fortuna, A.; Meneghini, C.; Fiscarelli, E.; Visca, P.; Imperi, F.; Rampioni, G.; Leoni, L. In Vitro Activity of Antivirulence Drugs Targeting the Las or Pqs Quorum Sensing Against Cystic Fibrosis Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 845231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, V.; Golberg, K.; Teralı, K.; Ozer, N.; Kramarsky-Winter, E.; Marks, R.S.; Kushmaro, A. Assessing the Molecular Targets and Mode of Action of Furanone C-30 on Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing. Molecules 2021, 26, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Cázares, N.; Castillo-Juárez, I.; García-Contreras, R.; Castro-Torres, V.A.; Díaz-Guerrero, M.; Rodríguez-Zavala, J.S.; Quezada, H.; González-Pedrajo, B.; Martínez-Vázquez, M. A Brominated Furanone Inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing and Type III Secretion, Attenuating Its Virulence in a Murine Cutaneous Abscess Model. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensah, C.N.; Ampomah, G.B.; Mensah, J.O.; Gasu, E.N.; Aboagye, C.I.; Ekuadzi, E.; Boadi, N.O.; Borquaye, L.S. N-Alkylimidazole Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Wu, T.-Q.; Xiong, Y.-S.; Ni, H.-B.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, W.-C.; Chu, S.-P.; Ju, S.-Q.; Yu, J. Ibuprofen-Mediated Potential Inhibition of Biofilm Development and Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Life Sci. 2019, 237, 116947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.-J.; Choi, H.; Hong, S.; Moon, H.R.; Lee, J.-H. Antipathogenic Compounds That Are Effective at Very Low Concentrations and Have Both Antibiofilm and Antivirulence Effects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0024921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, S.; Ham, S.-Y.; Kwon, H.; Kim, H.-S.; Moon, S.; Lee, J.-H.; Lim, T.; Son, S.-H.; Park, H.-D.; Byun, Y. Discovery and Characterization of Pure RhlR Antagonists against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 8388–8407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yang, X.; Zeng, Q.; Li, H.; Fu, R.; Du, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chu, Y.; et al. Repurposing Dimetridazole and Ribavirin to Disarm Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence by Targeting the Quorum Sensing System. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 978502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabir, S.; Suresh, D.; Subramoni, S.; Das, T.; Bhadbhade, M.; Black, D.S.; Rice, S.A.; Kumar, N. Thioether-Linked Dihydropyrrol-2-One Analogues as PqsR Antagonists against Antibiotic Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Bioorg Med. Chem. 2021, 31, 115967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukarieh, F.; Mashabi, A.; Richardson, W.; Oton, E.V.; Romero, M.; Roberston, S.N.; Grossman, S.; Sou, T.; Liu, R.; Halliday, N.; et al. Design and Evaluation of New Quinazolin-4(3H)-One Derived PqsR Antagonists as Quorum Sensing Quenchers in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 2666–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, S.; Soukarieh, F.; Richardson, W.; Liu, R.; Mashabi, A.; Emsley, J.; Williams, P.; Cámara, M.; Stocks, M.J. Novel Quinazolinone Inhibitors of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing Transcriptional Regulator PqsR. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 208, 112778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-H.; She, M.-T.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Liu, Y.-F.; Zhong, D.-X.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Zheng, J.-X.; Sun, N.; Wong, W.-L.; Lu, Y.-J. Novel Quinoline-Based Derivatives as the PqsR Inhibitor against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 2167–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelsamie, A.S.; Hamed, M.M.; Schütz, C.; Röhrig, T.; Kany, A.M.; Schmelz, S.; Blankenfeldt, W.; Hirsch, A.K.H.; Hartmann, R.W.; Empting, M. Discovery and Optimization of Thiazole-Based Quorum Sensing Inhibitors as Potent Blockers of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pathogenicity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 276, 116685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, W.; Ma, Y.-C.; Bai, B.; Sun, G.; Zhang, S.; Chang, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, X.; et al. Design and Synthesis of 4-Fluorophenyl-5-Methylene-2(5H)-Furanone Derivatives as Potent Quorum Sensing Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 8441–8463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abo-Dya, N.E.; Agha, K.A.; Abbas, H.A.; Abu-Kull, M.E.; Alahmdi, M.I.; Osman, N.A. Hybrid N-Acylcysteines as Dual-Acting Matrix Disruptive and Anti-Quorum Sensing Agents Fighting Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms: Design, Synthesis, Molecular Docking Studies, and In Vitro Assays. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 19879–19891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.Y.; Ammar, Y.A.; Abu-Elghait, M.; Salem, M.A.; Assiri, M.A.; Ali, T.E.; Ragab, A. Development of Novel Indolin-2-One Derivative Incorporating Thiazole Moiety as DHFR and Quorum Sensing Inhibitors: Synthesis, Antimicrobial, and Antibiofilm Activities with Molecular Modelling Study. Bioorg Chem. 2022, 119, 105571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukarieh, F.; Gurnani, P.; Romero, M.; Halliday, N.; Stocks, M.; Alexander, C.; Cámara, M. Design of Quorum Sensing Inhibitor-Polymer Conjugates to Penetrate Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. ACS Macro Lett. 2023, 12, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Lin, Y.; Yao, H.; Liu, Y.; Xi, Y.; Li, M.; Mao, A. Effect of L-HSL on Biofilm and Motility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Its Mechanism. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Meng, Y.; Yang, M.-H.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhao, J.-F.; Sun, P.-H.; Chen, W.-M. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel 3-Hydroxypyridin-4(1H)-Ones Based Hybrids as Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 259, 115665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, P.; Zhou, L.; Li, S.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Y. Inhibitory Effects of 1,3-Diaminopropane on the Biofilm Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa via Interaction with Quorum Sensing System. J. Cent. South Univ. Med. Sci. 2021, 46, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hou, J.-S.; Li, Y.-B.; Miao, Z.-Y.; Sun, P.-H.; Lin, J.; Chen, W.-M. Novel 2-Substituted 3-Hydroxy-1,6-Dimethylpyridin-4(1H)-Ones as Dual-Acting Biofilm Inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 10921–10945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, T.F.; Leitão, M.M.; Cerqueira, N.M.F.S.A.; Sousa, S.F.; Borges, A.; Simões, M. Montelukast and Cefoperazone Act as Antiquorum Sensing and Antibiofilm Agents against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 135, lxae088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Li, J.; Yang, D.; Du, J.; Li, J.; Lin, S.; Zhou, H.; Sun, P.; Xu, J. Multidimensional Criteria for Virtual Screening of PqsR Inhibitors Based on Pharmacophore, Docking, and Molecular Dynamics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborda, P.; Alcalde-Rico, M.; Chini, A.; Martínez, J.L.; Hernando-Amado, S. Discovery of Inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence through the Search for Natural-like Compounds with a Dual Role as Inducers and Substrates of Efflux Pumps. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 7396–7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajani, A.S.; Jangi, E.; Davodi, M.; Golmakaniyoon, S.; Ghodsi, R.; Soheili, V.; Fazly Bazzaz, B.S. Anti-Quorum Sensing Potential of Ketoprofen and Its Derivatives against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Insights to In Silico and In Vitro Studies. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 5123–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soukarieh, F.; Mashabi, A.; Richardson, W.; Oton, E.V.; Romero, M.; Dubern, J.-F.; Robertson, S.N.; Lucanto, S.; Markham-Lee, Z.; Sou, T.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of New 1H-Benzo[d]Imidazole Based PqsR Inhibitors as Adjuvant Therapy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 1008–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nketia, P.B.; Manu, P.; Osei-Poku, P.; Kwarteng, A. Phenazine Scaffolds as a Potential Allosteric Inhibitor of LasR Protein in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2025, 19, 11779322251319594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Li, Q.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Ye, X.; Wang, H. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Benzoheterocyclic Sulfoxide Derivatives as Quorum Sensing Inhibitors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Enzyme. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2023, 38, 2175820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, A.J.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Taher, E.S.; Mohamed, M.F.A.; Youns, M.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Al-Mahmoudy, A.M.M. Synthesis, Antimicrobial, Anti-Virulence and Anticancer Evaluation of New 5(4H)-Oxazolone-Based Sulfonamides. Molecules 2022, 27, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alotaibi, H.F.; Alotaibi, H.; Darwish, K.M.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Ali, M.A.M.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Alshawwa, S.Z. The Anti-Virulence Activities of the Antihypertensive Drug Propranolol in Light of Its Anti-Quorum Sensing Effects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia Marcescens. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayat, M.T.; Abbas, H.A.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Khayyat, A.N.; Alharbi, M.; Darwish, K.M.; Elhady, S.S.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Safo, M.K.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities of Gliptins against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.A.; Shaldam, M.A.; Eldamasi, D. Curtailing Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Sitagliptin. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saqr, A.A.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Shaldam, M.A.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Abbas, H.A. A Novel Use of Allopurinol as A Quorum-Sensing Inhibitor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rabia, M.W.; Asfour, H.Z.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Bazuhair, M.A.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Abbas, H.A.; Mansour, B.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Seleem, N.M. Cilostazol Is a Promising Anti-Pseudomonal Virulence Drug by Disruption of Quorum Sensing. AMB Express 2024, 14, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.M.; Abbas, H.A.; Askoura, M.M. Repositioning Secnidazole as a Novel Virulence Factors Attenuating Agent in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 127, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Sun, L.; Hu, X.; Nie, T.; Pang, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Li, C.; Yao, K.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Ostarine Attenuates Pyocyanin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Interfering with Quorum Sensing Systems. J. Antibiot. 2021, 74, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleem, N.M.; Atallah, H.; Abd El Latif, H.K.; Shaldam, M.A.; El-Ganiny, A.M. Could the Analgesic Drugs, Paracetamol and Indomethacin, Function as Quorum Sensing Inhibitors? Microb. Pathog. 2021, 158, 105097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Srivastava, N.; Devi, B.; Kumar, L.; Kumar, R.; Kumar Yadav, A. Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and In Silico Study of N-(2- and 3-Pyridinyl)Benzamide Derivatives as Quorum Sensing Inhibitors against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202201191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, F.D.S.; Alves, C.F.D.S.; Machado, A.K.; Siqueira, J.D.; Santos, T.D.; Mizdal, C.R.; Moreira, K.S.; Teixeira Carvalho, D.; Bonez, P.C.; Urquhart, C.G.; et al. Molecular Docking, Quorum Quenching Effect, Antibiofilm Activity and Safety Profile of Silver-Complexed Sulfonamide on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biofouling 2021, 37, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naga, N.G.; El-Badan, D.E.; Mabrouk, M.E.M.; Rateb, H.S.; Ghanem, K.M.; Shaaban, M.I. Innovative Application of Ceftriaxone as a Quorum Sensing Inhibitor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dong, E.; Ma, S. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 2-Phenoxyalkylhydrazide Benzoxazole Derivatives as Quorum Sensing Inhibitors with Strong Antibiofilm Effect. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 5721–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arami, N.; Tajani, A.S.; Hashemi, M.; Rezaei, T.; Ghodsi, R.; Soheili, V.; Bazzaz, B.S.F. Targeted Inhibition of PqsR in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 Quorum-Sensing Network by Chalcones as Promising Antibacterial Compounds. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2025, 52, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.A.K.S.; Rudden, M.; Smyth, T.J.; Dooley, J.S.G.; Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Natural Quorum Sensing Inhibitors Effectively Downregulate Gene Expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence Factors. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3521–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitão, M.M.; Vieira, T.F.; Sousa, S.F.; Borges, F.; Simões, M.; Borges, A. Dual Action of Benzaldehydes: Inhibiting Quorum Sensing and Enhancing Antibiotic Efficacy for Controlling Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 191, 106663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhoury, N.E.; Mansour, S.; Abdel-Halim, M.; Hamed, M.M.; Empting, M.; Boese, A.; Loretz, B.; Lehr, C.-M.; Tammam, S.N. Nanoparticles in Liposomes: A Platform for Increased Antibiotic Selectivity in Multidrug Resistant Bacteria in Respiratory Tract Infections. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2025, 15, 1193–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Mei, L.; Si, Y.; Wu, J.; Shao, J.; Wang, T.; Yan, G.; Wang, C.; Wu, D. Sodium New Houttuyfonate Affects Transcriptome and Virulence Factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Controlled by Quorum Sensing. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 572375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, J.; Mortensen, K.T.; Nørskov, A.; Qvortrup, K.; Yang, L.; Tan, C.H.; Nielsen, T.E.; Givskov, M. Itaconimides as Novel Quorum Sensing Inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, B.; Peng, A.-Y.; Mao, Z.-W.; Xia, W. Inhibition of Quorum-Sensing Regulator from Pseudomonas aeruginosa Using a Flavone Derivative. Molecules 2022, 27, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Mao, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Du, A.; Wang, H. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Phenyloxadiazole Sulfoxide Derivatives as Potent Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Inhibitors. Molecules 2023, 28, 3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, B.K.; Li, A.; Seyedsayamdost, M.R. Identification of the Hypertension Drug Guanfacine as an Antivirulence Agent in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chembiochem 2019, 20, 2005–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trognon, J.; Vera, G.; Rima, M.; Stigliani, J.-L.; Amielet, L.; El Hage, S.; Lajoie, B.; Roques, C.; El Garah, F. Investigation of Direct and Retro Chromone-2-Carboxamides Based Analogs of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing Signal as New Anti-Biofilm Agents. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajera, G.; Henriksen, N.; Cox, B.; Kothari, V. Identification of Anti-Pathogenic Activity Among In Silico Predicted Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasR or Nitric Oxide Reductase (NOR). Drug Target Insights 2023, 17, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Hou, X.; Quan, C.; Chen, M. Widespread Existence of Quorum Sensing Inhibitors in Marine Bacteria: Potential Drugs to Combat Pathogens with Novel Strategies. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Almada, K.; González-Acosta, B.; Borges-Souza, J.M.; Aguila-Ramírez, R.N. Marine Bacteria Associated with Shallow Hydrothermal Systems in the Gulf of California with the Capacity to Produce Biofilm Inhibiting Compounds. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 1477–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, S.J.; Ain, Q.; Khan, S.J.; Jalil, A.; Siddiqui, M.F.; Ahmad, T.; Badshah, M.; Adnan, F. Targeting Acyl Homoserine Lactones (AHLs) by the Quorum Quenching Bacterial Strains to Control Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarudheen, N.; Rao, K.V.B. Fatty Acyl Compounds from Marine Streptomyces griseoincarnatus Strain HK12 against Two Major Bio-Film Forming Nosocomial Pathogens; an In Vitro and In Silico Approach. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 127, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cong, M.; Deng, S.; Chen, Y.; Pang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liao, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, J. New 24-Membered Macrolactines from an Arctic Bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SCSIO 41392 and Their Anti-Pathogenicity Evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-D.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Niu, W.-X.; Hong, J.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, J.-H. Multifaceted Antipathogenic Activity of Two Novel Natural Products, Chermesiterpenoid B and Chermesiterpenoid B Seco Acid Methyl Ester, Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Biotechnol. 2025, 18, e70101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, L.; Wu, H.; Zhao, C.; Gong, Q.; Yu, W. Cladodionen Is a Potential Quorum Sensing Inhibitor Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-Y.; Le, D.D.; Kim, W.-G. Curvularin Isolated From Phoma Macrostoma Is an Antagonist of RhlR Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 913882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Sun, S.; Li, L.; Dai, X.; Li, H.; He, Q.; Zhu, H. Tyrosol from Marine Fungi, a Novel Quorum Sensing Inhibitor against Chromobacterium violaceum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Bioorg Chem. 2019, 91, 103140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, A.; Mabudi, H.; Tajbakhsh, E.; Roomiani, L.; Momtaz, H. Optimizing Chitosan Derived from Metapenaeus Affinis: A Novel Anti-Biofilm Agent against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. AMB Express 2024, 14, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.-X.; Liu, J.-S.; Wang, Y.-J.; Tang, S.; Wang, D.-Y.; Deng, S.-M.; Jia, A.-Q. Actinomycin D: A Novel Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing Inhibitor from the Endophyte Streptomyces cyaneochromogenes RC1. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alford, M.A.; Mann, S.; Akhoundsadegh, N.; Hancock, R.E.W. Competition between Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus Is Dependent on Intercellular Signaling and Regulated by the NtrBC Two-Component System. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talaat, R.; Abu El-Naga, M.N.; El-Bialy, H.A.A.; El-Fouly, M.Z.; Abouzeid, M.A. Quenching of Quorum Sensing in Multi-Drug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Insights on Halo-Bacterial Metabolites and Gamma Irradiation as Channels Inhibitors. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2024, 23, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, G.; Sun, C.; Wu, S. Volatile Organic Compounds Produced by a Deep-Sea Bacterium Efficiently Inhibit the Growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Mar. Drugs. 2024, 22, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S. Transcriptional Profiling of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 in Response to Anti-Biofilm and Anti-Infection Agent Exopolysaccharide EPS273. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Ashraf, S.A.; Surti, M.; Awadelkareem, A.M.; Snoussi, M.; Hamadou, W.S.; Bardakci, F.; Jamal, A.; Jahan, S.; et al. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum-Derived Biosurfactant Attenuates Quorum Sensing-Mediated Virulence and Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Chromobacterium violaceum. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Zhao, L.; Lv, K.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.; Gong, Q.; Yu, W. Citrinin Is a Potential Quorum Sensing Inhibitor against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Yan, Y.; Chen, S.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Quorum Sensing Inhibitors from Marine Bacteria Oceanobacillus sp. XC22919. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 1819–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, N.; Ghosh, M.; Jain, D.; Sinha, R.; Khare, S.K. Inhibition and Eradication of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms by Secondary Metabolites of Nocardiopsis Lucentensis EMB25. RSC Med. Chem. 2023, 14, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Ren, J.; Xue, Y.; Xie, G.; Gao, J.; Fu, Q.; Shao, P.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, M.; Ding, F. Palmitoleic Acid Inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing Activation and Protects Lungs from Infectious Injury. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malešević, M.; Di Lorenzo, F.; Filipić, B.; Stanisavljević, N.; Novović, K.; Senerovic, L.; Polović, N.; Molinaro, A.; Kojić, M.; Jovčić, B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing Inhibition by Clinical Isolate Delftia Tsuruhatensis 11304: Involvement of N-Octadecanoylhomoserine Lactones. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.D.; Patel, H.; Saiyad, S.M.; Bajpai, B. Effect of a Phthalate Derivative Purified from Bacillus Zhangzhouensis SK4 on Quorum Sensing Regulated Virulence Factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 191, 106664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onbas, T.; Osmanagaoglu, O.; Kiran, F. Potential Properties of Lactobacillus Plantarum F-10 as a Bio-Control Strategy for Wound Infections. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 1110–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, R.; Chanishvili, N.; Caplin, J.; Kakabadze, E.; Bakuradze, N.; Makalatia, K.; Cooper, I. Antibiofilm Potential of Purified Environmental Bacteriophage Preparations against Early Stage Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 1657–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, M.H.; Elgaml, A.; Abdel Bar, F.M.; Badria, F.A. Antimicrobial and Antiquorum-Sensing Activity of Ricinus Communis Extracts and Ricinine Derivatives. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 1556–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, N.F.; Wang, J.; Kundukad, B.; Oluwabusola, E.T.; Goh, D.X.Y.; Phyo, M.Y.; Tong, J.J.L.; Kjelleberg, S.; Tan, L.T. Cyclopropane-Containing Specialized Metabolites from the Marine Cyanobacterium cf. Lyngbya sp. Molecules 2023, 28, 3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oluwabusola, E.T.; Katermeran, N.P.; Poh, W.H.; Goh, T.M.B.; Tan, L.T.; Diyaolu, O.; Tabudravu, J.; Ebel, R.; Rice, S.A.; Jaspars, M. Inhibition of the Quorum Sensing System, Elastase Production and Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Psammaplin A and Bisaprasin. Molecules 2022, 27, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloyi, I.T.; Adeosun, I.J.; Yusuf, A.A.; Cosa, S. In Silico and In Vitro Screening of Antipathogenic Properties of Melianthus comosus (Vahl) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete-Kertész, I.; Berkl, Z.; Buda, K.; Fenyvesi, É.; Szente, L.; Molnár, M. Quorum Quenching Effect of Cyclodextrins on the Pyocyanin and Pyoverdine Production of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, S.; Hassan, N.; Rafiq, M.; Hassan, F.; Rehman, M.; Iqbal, N.; Ali, H.; Hasan, F.; Kang, Y.-Q. Biofilms as Battlefield Armor for Bacteria against Antibiotics: Challenges and Combating Strategies. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshammari, M.; Ahmad, A.; AlKhulaifi, M.; Al Farraj, D.; Alsudir, S.; Alarawi, M.; Takashi, G.; Alyamani, E. Reduction of Biofilm Formation of Escherichia coli by Targeting Quorum Sensing and Adhesion Genes Using the CRISPR/Cas9-HDR Approach, and Its Clinical Application on Urinary Catheter. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askoura, M.; Almalki, A.J.; Lila, A.S.A.; Almansour, K.; Alshammari, F.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Alteration of Salmonella enterica Virulence and Host Pathogenesis through Targeting sdiA by Using the CRISPR-Cas9 System. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyman, L.J.; Tanner, M.P.; Rosario-Meléndez, N.; Peters, J.M.; Mandel, M.J.; van Kessel, J.C. Mobile-CRISPRi as a Powerful Tool for Modulating Vibrio Gene Expression. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e0006524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshobary, M.E.; Badawy, N.K.; Ashraf, Y.; Zatioun, A.A.; Masriya, H.H.; Ammar, M.M.; Mohamed, N.A.; Mourad, S.; Assy, A.M. Combating Antibiotic Resistance: Mechanisms, Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens, and Novel Therapeutic Approaches: An Updated Review. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Fang, L.; Tan, S.; Yu, M.; Li, X.; He, S.; Wei, Y.; Li, G.; Jiang, J.; Wu, M. Type I CRISPR-Cas Targets Endogenous Genes and Regulates Virulence to Evade Mammalian Host Immunity. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 1273–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha KesavanNair, L. Computational Design of Guide RNAs and Vector to Knockout LasR Gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Gene Genome Ed. 2023, 6, 100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Lahiri, D.; Nag, M.; Sarkar, T.; Pati, S.; Edinur, H.A.; Kumar, M.; Mohd Zain, M.R.A.; Ray, R.R. Precision Targeting of Food Biofilm-Forming Genes by Microbial Scissors: CRISPR-Cas as an Effective Modulator. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 964848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghavami, S.; Pandi, A. Chapter Five—CRISPR Interference and Its Applications. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Singh, V., Ed.; Reprogramming the Genome: Applications of CRISPR-Cas in Non-mammalian Systems Part B; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 123–140. [Google Scholar]
- Kachhadia, R.; Kapadia, C.; Singh, S.; Gandhi, K.; Jajda, H.; Alfarraj, S.; Ansari, M.J.; Danish, S.; Datta, R. Quorum Sensing Inhibitory and Quenching Activity of Bacillus cereus RC1 Extracts on Soft Rot-Causing Bacteria Lelliottia Amnigena. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 25291–25308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Nandi, S.; Basu, T. Nano-Antibacterials Using Medicinal Plant Components: An Overview. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 768739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, J.C.; Domingues, J.M.; Miranda, C.S.; Silva, A.F.G.; Homem, N.C.; Amorim, M.T.P.; Felgueiras, H.P. Bioactivity of Chitosan-Based Particles Loaded with Plant-Derived Extracts for Biomedical Applications: Emphasis on Antimicrobial Fiber-Based Systems. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattah, R.A.F.A.; Fathy, F.E.Z.Y.; Mohamed, T.A.H.; Elsayed, M.S. Effect of Chitosan Nanoparticles on Quorum Sensing-Controlled Virulence Factors and Expression of LasI and RhlI Genes among Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates. AIMS Microbiol. 2021, 7, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micale, N.; Citarella, A.; Molonia, M.S.; Speciale, A.; Cimino, F.; Saija, A.; Cristani, M. Hydrogels for the Delivery of Plant-Derived (Poly)Phenols. Molecules 2020, 25, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.Y.; Lin, B.-S.; Hu, P.-S.; Huang, T.-Y.; Huang, Y.-K. Nanoparticles of Cs0.33WO3 as Antibiofilm Agents and Photothermal Treatment to Inhibit Biofilm Formation. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 28144–28154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Lee, S.-H.; Byun, Y.; Park, H.-D. 6-Gingerol Reduces Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Formation and Virulence via Quorum Sensing Inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinam, P.; Vijay Kumar, H.S.; Viswanathan, P. Eugenol Exhibits Anti-Virulence Properties by Competitively Binding to Quorum Sensing Receptors. Biofouling 2017, 33, 624–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Ravichandran, V.; Zhang, N.; Wang, H.; Bian, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, A. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing by Natural Products: Virtual Screening, Evaluation and Biomolecular Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, M.; Yadav, V.K.; Singh, P.K.; Sharma, D.; Narvi, S.S.; Agarwal, V. Exploring the Impact of Parthenolide as Anti-Quorum Sensing and Anti-Biofilm Agent against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Life Sci. 2018, 199, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernando-Amado, S.; Alcalde-Rico, M.; Gil-Gil, T.; Valverde, J.R.; Martínez, J.L. Naringenin Inhibition of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing Response Is Based on Its Time-Dependent Competition With N-(3-Oxo-Dodecanoyl)-L-Homoserine Lactone for LasR Binding. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Gaikwad, S.; Nagar, S.; Kulshrestha, S.; Vaidya, V.; Nawani, N.; Pawar, S. Biofilm Inhibition and Anti-Quorum Sensing Activity of Phytosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles against the Nosocomial Pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biofouling 2019, 35, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Chhibber, S.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, M.; Harjai, K. Zingerone Silences Quorum Sensing and Attenuates Virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Fitoterapia 2015, 102, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.K.; Chauhan, M.; Dhingra, N.; Chhibber, S.; Harjai, K. Terpinen-4-Ol Attenuates Quorum Sensing Regulated Virulence Factors and Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Future Microbiol. 2020, 15, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parai, D.; Banerjee, M.; Dey, P.; Chakraborty, A.; Islam, E.; Mukherjee, S.K. Effect of Reserpine on Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing Mediated Virulence Factors and Biofilm Formation. Biofouling 2018, 34, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samreen; Qais, F.A.; Ahmad, I. Anti-Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Inhibitory Effect of Some Medicinal Plants against Gram-Negative Bacterial Pathogens: In Vitro and In Silico Investigations. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiga, A.; Ampomah-Wireko, M.; Li, H.; Fan, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zhen, H.; Kpekura, S.; Wu, C. Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors: A Particular Focus on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 281, 117008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimzadeh, M.; Greco, G.; Farmani, A.; Nourian, A.; Pourhajibagher, M.; Taherkhani, A.; Alikhani, M.Y.; Bahador, A. Biofilm Inhibition of Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Using Green-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles and Colistin. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukarieh, F.; Williams, P.; Stocks, M.J.; Cámara, M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing Systems as Drug Discovery Targets: Current Position and Future Perspectives. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 10385–10402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S.K.; Vrla, G.D.; Fröhlich, K.S.; Gitai, Z. Surface Association Sensitizes Pseudomonas aeruginosa to Quorum Sensing. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanek, K.A.; Schumacher, M.L.; Mallery, C.P.; Shen, S.; Li, L.; Paczkowski, J.E. Quorum-Sensing Synthase Mutations Re-Calibrate Autoinducer Concentrations in Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to Enhance Pathogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, K.; Zhao, C.Y.; Mei, M.; Diggle, S.P. Frequency of Quorum-Sensing Mutations in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains Isolated from Different Environments. Microbiology 2022, 168, 001265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlichter Kadosh, Y.; Muthuraman, S.; Nisaa, K.; Ben-Zvi, A.; Karsagi Byron, D.L.; Shagan, M.; Brandis, A.; Mehlman, T.; Gopas, J.; Saravana Kumar, R.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Attenuation by a Di-Hydroxy Derivative of Piperlongumine (PL-18). Biofilm 2024, 8, 100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simanek, K.A.; Paczkowski, J.E. Resistance Is Not Futile: The Role of Quorum Sensing Plasticity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections and Its Link to Intrinsic Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brindhadevi, K.; LewisOscar, F.; Mylonakis, E.; Shanmugam, S.; Verma, T.N.; Pugazhendhi, A. Biofilm and Quorum Sensing Mediated Pathogenicity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Process Biochem. 2020, 96, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-X.; Xu, Z.-H.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Tian, J.; Weng, L.-X.; Wang, L.-H. A New Quorum-Sensing Inhibitor Attenuates Virulence and Decreases Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostylev, M.; Kim, D.Y.; Smalley, N.E.; Salukhe, I.; Greenberg, E.P.; Dandekar, A.A. Evolution of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum-Sensing Hierarchy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7027–7032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koul, S.; Prakash, J.; Mishra, A.; Kalia, V.C. Potential Emergence of Multi-Quorum Sensing Inhibitor Resistant (MQSIR) Bacteria. Indian J. Microbiol. 2016, 56, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeske, A.; Arce-Rodriguez, A.; Thöming, J.G.; Tomasch, J.; Häussler, S. Evolution of Biofilm-Adapted Gene Expression Profiles in lasR-Deficient Clinical Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2022, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.-P.; Xu, Y.-H.; Wang, Z.-X.; Fang, Y.-P.; Shen, J.-L. Overexpression of MexAB-OprM Efflux Pump in Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch. Microbiol. 2016, 198, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelraheem, W.M.; Yassin, H.I.; Zaki, S.; Esmail, M.A.M. Zinc Sulfate Acts as an Efflux Pump Inhibitor on Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2025, 41, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinduti, P.A.; George, O.W.; Ohore, H.U.; Ariyo, O.E.; Popoola, S.T.; Adeleye, A.I.; Akinwande, K.S.; Popoola, J.O.; Rotimi, S.O.; Olufemi, F.O.; et al. Evaluation of Efflux-Mediated Resistance and Biofilm Formation in Virulent Pseudomonas aeruginosa Associated with Healthcare Infections. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bové, M.; Bao, X.; Sass, A.; Crabbé, A.; Coenye, T. The Quorum-Sensing Inhibitor Furanone C-30 Rapidly Loses Its Tobramycin-Potentiating Activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms during Experimental Evolution. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0041321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, M.; Yu, C.; Li, J.; Zhou, X. Biofilm Formation: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Targets. Mol. Biomed. 2023, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.Y.; Prentice, E.L.; Webber, M.A. Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance in Biofilms. npj Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchadi, B.V.; Derringer, J.J.; Detweiler, A.K.; Taylor, I.R. PqsE Adapts the Activity of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum-Sensing Transcription Factor RhlR to Both Autoinducer Concentration and Promoter Sequence Identity. J. Bacteriol. 2025, 7, e00516-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampomah-Wireko, M.; Luo, C.; Cao, Y.; Wang, H.; Nininahazwe, L.; Wu, C. Chemical Probe of AHL Modulators on Quorum Sensing in Gram-Negative Bacteria and as Antiproliferative Agents: A Review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 226, 113864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Ahator, S.D.; Zhang, L.-H. Molecular Mechanisms of Phosphate Stress Activation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing Systems. mSphere 2020, 5, e00119-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyżek, P. Challenges and Limitations of Anti-Quorum Sensing Therapies. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.N.; Saafan, A.E.; Ahmedy, A.; El Gebaly, E.; Khairalla, A.S. Two Novel Synthetic Peptides Inhibit Quorum Sensing-Dependent Biofilm Formation and Some Virulence Factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondil, V.S.; Kalaiyarasan, T.; Bharti, V.K.; Chhibber, S. Antibiofilm Potential of Seabuckthorn Silver Nanoparticles (SBT@AgNPs) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Feng, T.; Du, R.; Tian, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.-H. Heterologous Expression of the Marine-Derived Quorum Quenching Enzyme MomL Can Expand the Antibacterial Spectrum of Bacillus Brevis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Li, L.; Pan, L.; Zhu, H. Anti-Quorum-Sensing Activity of Tryptophan-Containing Cyclic Dipeptides. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikdar, R.; Elias, M. Quorum Quenching Enzymes and Their Effects on Virulence, Biofilm and Microbiomes: A Review of Recent Advances. Expert Rev. Anti Infect Ther. 2020, 18, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetta, H.F.; Ramadan, Y.N.; Rashed, Z.I.; Alharbi, A.A.; Alsharef, S.; Alkindy, T.T.; Alkhamali, A.; Albalawi, A.S.; Battah, B.; Donadu, M.G. Quorum Sensing Inhibitors: An Alternative Strategy to Win the Battle against Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) Bacteria. Molecules 2024, 29, 3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.-W.; Jia, A.-Q.; Jiang, H.; Li, P.-L.; Chen, H.; Tan, X.-J.; Liu, E.-Q. 1-(4-Amino-2-Hydroxyphenyl)Ethanone from Phomopsis Liquidambari Showed Quorum Sensing Inhibitory Activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesic, B.; Starkey, M.; He, J.; Hazan, R.; Rahme, L.G. Quorum Sensing Differentially Regulates Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type VI Secretion Locus I and Homologous Loci II and III, Which Are Required for Pathogenesis. Microbiology 2009, 155, 2845–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; He, Q.; Li, L.; Yu, X.; Sun, S.; Zhu, H. Exploring the Quorum Sensing Inhibition of Isolated Chrysin from Penicillium Chrysogenum DXY-1. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 111, 104894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaeger, L.N.; Ranieri, M.R.M.; Chee, J.; Karabelas-Pittman, S.; Rudolph, M.; Giovannoni, A.M.; Harvey, H.; Burrows, L.L. A Genetic Screen Identifies a Role for oprF in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Stimulation by Subinhibitory Antibiotics. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tang, W.S.; Liu, S.Y.; Khoo, B.L.; Chua, S.L. Juglone as a Natural Quorum Sensing Inhibitor against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pqs-Mediated Virulence and Biofilms. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2024, 7, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Almpani, M.; Maura, D.; Kitao, T.; Ferrari, L.; Fontana, S.; Bergamini, G.; Calcaterra, E.; Pignaffo, C.; Negri, M.; et al. Tackling Recalcitrant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections in Critical Illness via Anti-Virulence Monotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.-H.; Cai, W.-J.; He, X.-W.; Song, H.-L.; Gao, J.; Yang, Y.-L.; Zhou, J. A Review of Advances & Potential of Applying Nanomaterials for Biofilm Inhibition. npj Clean Water 2024, 7, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, X.; Wang, D. Treatment with Paeoniflorin Increases Lifespan of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infected Caenorhabditis elegans by Inhibiting Bacterial Accumulation in Intestinal Lumen and Biofilm Formation. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1114219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadakkan, K.; Sathishkumar, K.; Mapranathukaran, V.O.; Ngangbam, A.K.; Nongmaithem, B.D.; Hemapriya, J.; Nair, J.B. Critical Review on Plant-Derived Quorum Sensing Signaling Inhibitors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 151, 107649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakumar, G.; Mao, L.; Bao, T.; Wen, W.; Wang, S.; Gomathi, T.; Gnanasundaram, N.; Rebezov, M.; Shariati, M.A.; Chung, I.-M.; et al. Yttrium Oxide Nanoparticle Synthesis: An Overview of Methods of Preparation and Biomedical Applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theuretzbacher, U. The Global Resistance Problem and the Clinical Antibacterial Pipeline. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak, M.; Pankowski, J.A.; Kwiatek, A.; Grygorcewicz, B.; Karczewska-Golec, J.; Sadowska, K.; Golec, P. An Effective Antibiofilm Strategy Based on Bacteriophages Armed with Silver Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, A.I.; El-Ganiny, A.M.; Eissa, A.G.; Noureldin, N.A.; Nazeih, S.I. Miconazole and Phenothiazine Hinder the Quorum Sensing Regulated Virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Antibiot. 2024, 77, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, B.; Ahmad, S.; Thai, T.D.; Eyun, S.-I.; Na, D. Rational Drug Design for Pseudomonas aeruginosa PqsA Enzyme: An In Silico Guided Study to Block Biofilm Formation. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 577316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshaer, S.L.; Shaaban, M.I. Inhibition of Quorum Sensing and Virulence Factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Biologically Synthesized Gold and Selenium Nanoparticles. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddeboina, K.; Yada, B.; Kumari, S.; McHale, C.; Pal, D.; Durden, D.L. Recent Advances in Multitarget-Directed Ligands via In Silico Drug Discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 103904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, J.; Magalhães, R.P.; de la Oliva Roque, V.M.; Simões, M.; Pratas, D.; Sousa, S.F. TargIDe: A Machine-Learning Workflow for Target Identification of Molecules with Antibiofilm Activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2023, 37, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Kushveer, J.S.; Khan, M.I.K.; Pagal, S.; Meena, C.K.; Murali, A.; Dhayalan, A.; Venkateswara Sarma, V. 2,4-Di-Tert-Butylphenol Isolated From an Endophytic Fungus, Daldinia Eschscholtzii, Reduces Virulence and Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Morita, Y.; Ishige, S.; Kai, K.; Kawasaki, K.; Matsushita, K.; Ogura, K.; Miyoshi-Akiyama†, T.; Shimizu, T. Effects of Quorum Sensing–Interfering Agents, Including Macrolides and Furanone C-30, and an Efflux Pump Inhibitor on Nitrosative Stress Sensitivity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 2024, 170, 001464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Long, J.; Jin, Y.; Chen, S.; Duan, G.; Yang, H. The Application of CRISPR-Cas System in Staphylococcus aureus Infection. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Wu, Y. A Review on Colloidal Delivery Vehicles Using Carvacrol as a Model Bioactive Compound. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rano, S.; Bhaduri, A.; Singh, M. Nanoparticle-Based Platforms for Targeted Drug Delivery to the Pulmonary System as Therapeutics to Curb Cystic Fibrosis: A Review. J. Microbiol. Methods 2024, 217, 106876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parihar, A.; Prajapati, B.G.; Paliwal, H.; Shukla, M.; Khunt, D.; Devrao Bahadure, S.; Dyawanapelly, S.; Junnuthula, V. Advanced Pulmonary Drug Delivery Formulations for the Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.G.; Sanchez Rangel, U.J.; Franklin, A.; Oda, H.; Wang, Z.; Chang, J.; Fox, P.M. Topical Antibiotic Elution in a Collagen-Rich Hydrogel Successfully Inhibits Bacterial Growth and Biofilm Formation In Vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00136-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.D.; Jarman, E.H.; Kuppalli, K.; Murphy, M.J.; Longaker, M.T.; Gurtner, G.; Fox, P.M. Successful Topical Treatment of Human Biofilms Using Multiple Antibiotic Elution from a Collagen-Rich Hydrogel. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackman, G.; Garcia-Fernandez, M.J.; Lenoir, J.; De Meyer, L.; Remon, J.-P.; De Beer, T.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Coenye, T. Dressings Loaded with Cyclodextrin-Hamamelitannin Complexes Increase Staphylococcus aureus Susceptibility Toward Antibiotics Both in Single as Well as in Mixed Biofilm Communities. Macromol. Biosci. 2016, 16, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, S.; Kvich, L.; Xu, Y.; Thomsen, T.R.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Thaarup, I. Development of a Tri-Species Wound Model for Studying Fungal-Bacterial Interactions and Antimicrobial Therapies. Biofilm 2025, 9, 100256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Q.; Liu, R.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Zhou, X.; Yu, O.Y.; Chu, C.-H.; Cheng, L.; Ren, B.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Wraps around Candida albicans and Synergistically Escapes from Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1422440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, N.; Jeong, J.; Yoon, D.; Kim, S.; Choi, J. Global Metabolomics Approach in In Vitro and In Vivo Models Reveals Hepatic Glutathione Depletion Induced by Amorphous Silica Nanoparticles. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 293, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xie, X.; Li, R.; You, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J. Development and Characterization of LasR Immobilized Monolithic Column for Screening Active Ingredients as Quorum Sensing Inhibitors Against P. Aeruginosa in Natural Products. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2025, 19, 2051–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maneira, C.; Chamas, A.; Lackner, G. Engineering Saccharomyces Cerevisiae for Medical Applications. Microb. Cell Fact. 2025, 24, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León-Félix, J.; Villicaña, C. The Impact of Quorum Sensing on the Modulation of Phage-Host Interactions. J. Bacteriol. 2021, 203, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subhaswaraj, P.; Barik, S.; Macha, C.; Chiranjeevi, P.V.; Siddhardha, B. Anti Quorum Sensing and Anti Biofilm Efficacy of Cinnamaldehyde Encapsulated Chitosan Nanoparticles against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. LWT 2018, 97, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.; Ahmed, N.; Rehman, A. ur Recent Applications of PLGA Based Nanostructures in Drug Delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.; Ham, S.-Y.; Nam, S.; Kim, M.; Lee, K.Y.; Park, H.-D.; Byun, Y. Recent Advance in Small Molecules Targeting RhlR of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Agha, A.S.A.; Al-Samydai, A.; Aburjai, T. New Frontiers in CRISPR: Addressing Antimicrobial Resistance with Cas9, Cas12, Cas13, and Cas14. Heliyon 2025, 11, e42013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banala, V.T.; Mukherjee, D.; Mahajan, S.; Singh, P.K. Chapter 20—Current Status of FDA-Approved Marketed Nano Drug Products: Regulatory Considerations. In Multifunctional Nanocarriers; Mehra, N.K., Srivastava, S., Madan, J., Singh, P.K., Eds.; Micro and Nano Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 501–521. ISBN 978-0-323-85041-4. [Google Scholar]
- Milewska, S.; Niemirowicz-Laskowska, K.; Siemiaszko, G.; Nowicki, P.; Wilczewska, A.Z.; Car, H. Current Trends and Challenges in Pharmacoeconomic Aspects of Nanocarriers as Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 6593–6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CARB-X Is Funding a German Team of Scientists to Develop a New Treatment for Difficult-to-Treat Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections in Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Carb-X. Available online: https://carb-x.org/carb-x-news/carb-x-is-funding-a-german-team-of-scientists-to-develop-a-new-treatment-for-difficult-to-treat-pseudomonas-aeruginosa-infections-in-cystic-fibrosis-patients/ (accessed on 10 January 2019).
- Zhao, K.; Yang, X.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Yan, C.; Li, J.S.; Liu, H.; Du, L.; Wu, Y.; et al. Evolution of lasR Mutants in Polymorphic Pseudomonas aeruginosa Populations Facilitates Chronic Infection of the Lung. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, M.; Behera, P.R.; Bhuyan, P.P.; Singh, L.; Pradhan, B. Algal Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Activity: Current Research Status and Future Prospectives. Drugs Drug Candidates 2023, 2, 554–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, A.; Noei, M.; Askarinia, M.; Khoshbayan, A.; Farahani, A.; Chegini, Z. Inhibitory Effect of Natural Compounds on Quorum Sensing System in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Helpful Promise for Managing Biofilm Community. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1350391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, A.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Nandi, A.; Sinha, A.; Kar, S.; Manoharan, N.; Mitra, S.; Mojumdar, A.; Panda, P.K.; Patro, S.; et al. Phage Delivered CRISPR-Cas System to Combat Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens in Gut Microbiome. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, C.; Ho, D.; Hamed, M.M.; Abdelsamie, A.S.; Röhrig, T.; Herr, C.; Kany, A.M.; Rox, K.; Schmelz, S.; Siebenbürger, L.; et al. A New PqsR Inverse Agonist Potentiates Tobramycin Efficacy to Eradicate Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
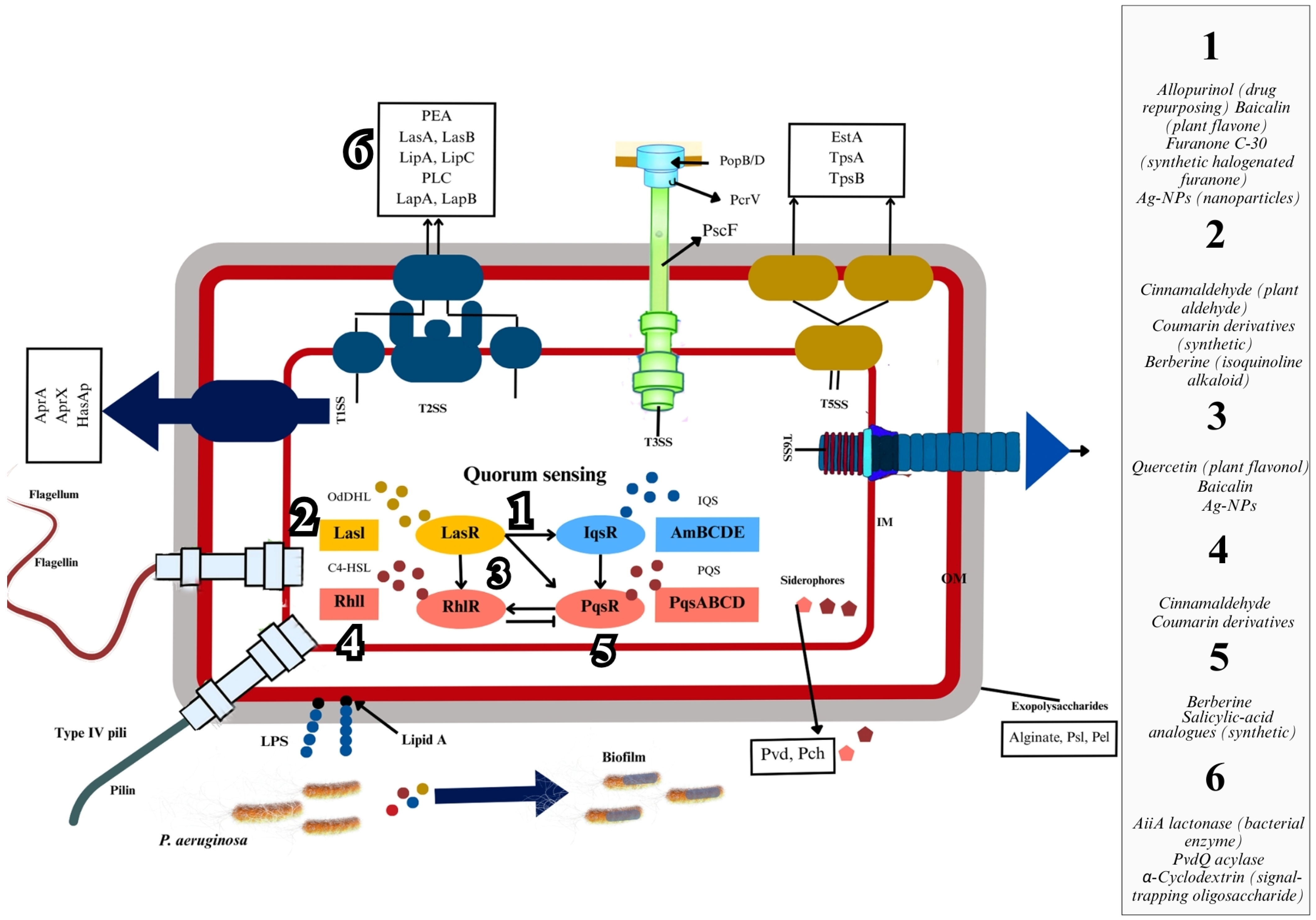
| Inhibitor Name | Plant/Source | Target QS Component |
|---|---|---|
| Diallyl Disulfide (Compound 2i) | Allium sativum | LasR |
| Astragaloside IV | Astragalus membranaceus | MexAB-OprM efflux pump |
| Ortho-Vanillin | Benzaldehyde derivative | RhlR |
| Berberine | Berberis species | PqsA |
| Bistorta officinalis (BIO) | Bistorta officinalis | LasR |
| Boeravinone O | Boerhavia diffusa | LasR |
| Cajaninstilbene Acid (CSA) 3o | Cajanus cajan | lasB, pqsA |
| Carvone (Caraway EO) | Carum carvi (Caraway) | LasR, CviR |
| Lutein | Chlorella pyrenoidosa (Algae) | LasI, LasR, RhlI, RhlR |
| Caffeine | Coffea arabica (Coffee) | LasR, LasI |
| Sulforaphane | Cruciferous vegetables (e.g., broccoli) | Lux-type receptors (TraR, QscR, CviR) |
| Bakuchiol | Cullen corylifolium | PqsR |
| Diphysa americana Extract | Diphysa americana | QS-regulated virulence factors |
| Panchvalkal (Polyherbal) | Ficus spp. and Albizzia lebbec | Nitric oxide reductase (NOR) |
| Phillyrin | Forsythia suspensa | QS signaling network |
| Fragaria vesca Extract | Fragaria vesca (Wild strawberry) | AI-1, AI-2 signaling |
| 6-Gingerol | Ginger (Zingiber officinale) | QscR, LasR, PqsR, RhlR |
| Hibiscus sabdariffa Extract | Hibiscus sabdariffa | QS-regulated virulence factors |
| Compound 5f (Ligustilide derivative) | Ligusticum chuanxiong (Chinese lovage) | LasR/LasB |
| Mangiferin Derivatives | Mangifera indica (Mango) | LasR |
| Methyl Gallate (MG) | Mangifera indica (Mango) | LasR, LasI |
| 1,8-Cineole | Musa paradisiaca (Banana) | Las, Rhl systems |
| Thymoquinone | Nigella sativa (Black seed) | LasR, RhlR, PqsR |
| Falcarindiol | Notopterygium incisum | lasI, lasR, rhlI, rhlR, lasB |
| Carvacrol | Oregano, Thyme | LasI, LasR, BswR |
| Paeonol | Paeonia suffruticosa (Tree peony) | Las, Rhl, Pqs systems |
| American Ginseng Extract (AGE) | Panax quinquefolius | Swarming, swimming motility |
| Persicaria maculosa (PEM) | Persicaria maculosa | LasR |
| Psoralen | Psoralea corylifolia | LasR, RhlR, PqsR |
| Salvia sclarea Essential Oil | Salvia sclarea | Las, Rhl systems |
| Cinnamoyl Hydroxamates (CHA, MCHA) | Synthetic (Cinnamoyl derivatives) | RhlI/R system |
| Coumarin-Chalcone C9 | Synthetic (Coumarin-Chalcone conjugate) | LasR, PqsR |
| Isovanillin | Synthetic/Vanilla derivatives | las, pqs systems |
| Syzygium aromaticum Extract | Syzygium aromaticum (Clove) | QS signal molecules |
| Trigonelline Hydrochloride | Trigonella foenum-graecum (Fenugreek) | Las, Rhl, Pqs pathways |
| Wild Blueberry Extract | Vaccinium angustifolium | lasI, lasR, rhlI, rhlR |
| Vanillin | Vanilla planifolia | PqsR |
| Quercetin | Various plants (e.g., onions, apples) | QS proteins |
| Ginger Extract | Zingiber officinale | lasI, lasR, rhlI, rhlR |
| Inhibitor Name | Molecule Used in Nanoparticle | Target Component of QS |
|---|---|---|
| P-AgNPs | Silver nanoparticles (propolis extract) | AHL-mediated signaling pathways |
| AgCS@AC NPs | Silver nanoparticles, chitosan, acylase I | AHLs (degradation) |
| AgNPs (Eruca sativa) | Silver nanoparticles | Pyocyanin, LasA/B proteases, exopolysaccharides (QS-regulated virulence factors) |
| AgNPs (Ducrosia flabellifolia) | Silver nanoparticles | AHLs, Las/Rhl systems |
| AgNPs | Silver nanoparticles | QS-related genes, PQS biosynthesis, virulence factors (pyocyanin, elastase, rhamnolipids) |
| SBT@AgNPs | Silver nanoparticles (Seabuckthorn extract) | AHLs (degradation) |
| AgNP + 4NPO | Silver nanoparticles, 4-nitropyridine N-oxide | Las, Rhl, Pqs systems |
| Pb-AgNPs | Silver nanoparticles (Piper betle extract, eugenol) | LasR, LasI, MvfR |
| ZnO-NPs (orange peel) | Zinc oxide nanoparticles | lasI gene (AHL synthase) |
| Zinc Oxide Nanospikes (ZNs) | Zinc oxide | Las, Rhl, Pqs systems |
| ZnC-NCs | Zinc oxide/curcumin nanocomposites | LasR, RhlR |
| Eugenol_Au NPs | Gold nanoparticles (eugenol) | QS signaling pathways, ROS-mediated disruption |
| Fe3O4@EUG | Magnetite nanoparticles (eugenol) | QS signaling (exact target unspecified) |
| SLNs (Ofloxacin + Eugenol) | Solid lipid nanoparticles (eugenol) | QS-regulated virulence factors |
| Eugenol nanoemulsion | Eugenol nanoemulsion | lasI, rhlI genes |
| SeNPs | Selenium nanoparticles | LasI, LasR, RhlI, RhlR, MvfR |
| SeNPs | Selenium nanoparticles | AHL biosynthesis |
| TDN | Titanium dioxide nanoparticles | lasI, lasR, rhlI, rhlR, pqsA, pqsR genes |
| mBTL-CANPs | Calcium alginate nanoparticles (meta-bromo-thiolactone) | LasR, RhlR |
| CeO2 NPs | Cerium dioxide nanoparticles | AHL-mediated QS (via halogenated compounds) |
| QSINPs (ajoene) | Chitosan/dextran sulfate nanoparticles (ajoene) | QS-regulated virulence factors (pyocyanin, rhamnolipids) |
| Y2O3 nanospheres | Yttrium oxide nanoparticles | AHL-mediated QS |
| Zeolite 4A | Zeolite 4A | Adsorption of AHLs (3-oxo-C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL) |
| Inhibitor Name | Type | Origin | QS Factor Inhibited |
|---|---|---|---|
| Micafungin | Lipopeptide | Semi-synthetic | Biofilm-related genes (alginate, 1,3-β-D-glucan, pellicles); QS virulence factors |
| Nesfactin | Lipopeptide | Nesterenkonia sp. MSA31 | las and rhl systems (via AHL degradation: 3-oxo-C12-HSL, C4-HSL) |
| CRAMP | Peptide | Host (cathelicidin-related) | lasR, lasI, rhlR, rhlI |
| WSF, FASK, YDVD | Peptide | Synthetic | LasR |
| Cyclo(Pro-Tyr)-like cyclic dipeptides | Peptide | Synthetic | LasR, Rhl systems |
| G3, C8G2 | Peptide | Synthetic | LasR |
| β-peptide polymer (20:80-Bu:DM) | Peptide | Synthetic | las, rhl, pqs systems |
| PA-Win2 | Peptide | Pardosa astrigera (spider) | Las, Pqs, Rhl systems |
| Tryptophan-containing CDPs | Peptide | Synthetic | rhl, pqs systems |
| LIVRHK, LIVRRK | Peptide | Synthetic | lasI, lasR, rhlI, rhlR |
| Peptide mix (Olivancillaria hiatula) | Peptide | Olivancillaria hiatula (marine snail) | QS-regulated virulence factors (biofilm, pyoverdine, pyocyanin, proteases) |
| PIT2 | Protein | Pseudomonas phage LMA2 | lasR, lasI, rsaL, prpL, lasA, pqsH |
| YtnP | Protein | Bacillus velezensis | AHLs (Las and Rhl systems) |
| Aqs1 | Protein | Pseudomonas phage DMS3 | LasR |
| AiiM lactonase | Protein | Bacterial (source unspecified) | AHLs (Las, Rhl systems) |
| rHPLOE | Protein | Tachypleus tridentatus (horseshoe crab) | Rhl system components (di-rhamnolipids, Psl) |
| AidB | Protein | Bosea sp. | AHLs (Las, Rhl systems) |
| MomL | Protein | Marine-derived (expressed in B. brevis) | AHLs (Las, Rhl systems) |
| AiiA lactonase KMMI17 | Protein | Bacillus thuringiensis KMCL07 | AHLs (Las, Rhl systems) |
| Inhibitor Name | Type of Inhibitor | Chemical/Pharmaceutical Class | QS Factor(s) Inhibited |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphate ester derivative of chrysin | Allosteric LasR inhibitor | Flavonoid derivative | LasR |
| Halogenated phenazine compounds | Phenazine derivatives | LasR | |
| 1,3,4-oxadiazoles (15, 23) | Competitive antagonist | 1,3,4-oxadiazoles | PQS system |
| 6f (1H-benzimidazole) | 1H-benzimidazole-based | PqsR | |
| QZN 34 | 3-C3NH2-7Cl-C9-QZN derivative | PqsR | |
| Propyl gallate (PG) | Alkyl gallate | LasR, RhlR | |
| Compound 30 | Alkynyl ketone | RhlR | |
| Y-31 | Amino-tetrahydro-oxazinone | LasR, RhlR, PqsR | |
| Paracetamol | Analgesic (NSAID) | LasR | |
| Cilostazol | Antiplatelet/vasodilator | LasR, RhlR | |
| 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, vanillin, syringaldehyde | Benzaldehydes | LasR | |
| Benzimidazolium salts (2, 3) | Benzimidazolium salts | LasR | |
| 6b | Benzoheterocyclic sulfoxide derivative | LasR | |
| Benzothiazole-2-thiol (7) | Benzothiazole derivative | LasB | |
| GBr | Brominated furanone | LasR | |
| Cefoperazone | Cephalosporin antibiotic | PQS system | |
| Ceftriaxone (CRO) and CRON | Cephalosporin antibiotics | LasR, LasI, PqsR | |
| 6n (chromone-2-carboxamide) | Chromone-2-carboxamide | PqsR | |
| L-HSL | Cyclic butyrolactone derivative | LasR, RhlR, PqsR | |
| Sitagliptin | DPP-4 inhibitor | LasR, RhlR | |
| Furanone C-30 | Furanone | LasR, RhlR | |
| 23e (4-fluorophenyl-furanone) | Furanone derivative | Las, Rhl | |
| 5-HMF | Hydroxymethylfurfural | LasR, RhlR | |
| Itaconimides (e.g., 18a) | Itaconimide | LasR, RhlR, PqsR | |
| NOI, NDI | N-alkylimidazole derivatives | LasR | |
| D88 (N-Aryl Malonamide) | N-Aryl Malonamide (NAM) | PqsR | |
| Secnidazole | Nitroimidazole antibiotic | lasI, lasR, rhlI, rhlR, pqsA, pqsR | |
| Dimetridazole, Ribavirin | Nitroimidazole, nucleoside analog | LasR, RhlR, PqsR | |
| Ibuprofen | NSAID | Rhl system (C4-HSL) | |
| Ketoprofen, G20 | NSAID derivatives | PqsR | |
| 5b (phenyloxadiazole sulfoxide) | Phenyloxadiazole sulfoxide | LasR | |
| P2-QSI (polymer conjugate) | Polymer-PqsR inhibitor conjugate | PqsR | |
| 5d (N-pyridinylbenzamide) | Pyridinylbenzamide derivative | Las/Rhl | |
| Ketone-/cyano-selenoesters | Selenoesters | AI-1/AI-2 pathways | |
| PqsR inhibitors (small molecules) | Small molecules | PqsR | |
| Sulfamethoxazole-silver complex (SMTZAg) | Sulfonamide-metal complex | LasR | |
| 7g | Thioether-linked dihydropyrrol-2-one | PqsR | |
| Allopurinol | Xanthine oxidase inhibitor | LasR, RhlR | |
| Propranolol | β-adrenergic receptor blocker | lasR, rhlR, pqsR | |
| Cephalosporins (cefepime, ceftazidime, ceftriaxone) | β-lactam antibiotics | LasR, PqsR, CviR | |
| Triazole nucleoside mimics | Triazole nucleoside | PqsA | |
| Thiazolo-indolin-2-one derivatives (7a, 4, 12) | Dual PqsR/DHFR inhibitor | Thiazole-indole hybrids | PqsR |
| 10d | 3-hydroxy-1,6-dimethylpyridin-4-one | FpvA receptor | |
| Levamisole | QS gene downregulator | Anthelmintic | lasI, lasR, rhlI, rhlR, lasB |
| Chloroquine | Antimalarial | lasI, lasR, rhlI, rhlR, lasB | |
| Sodium New Houttuyfonate (SNH) | Fatty acid derivative | rhlI, pqsA | |
| Erythromycin | Macrolide antibiotic | lasI, lasR, rhlI, rhlR, pqsA, pqsR | |
| Furazolidone | Nitrofuran antibiotic | lasR, rhlR, pqsR | |
| Ostarine | Selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) | lasR, rhlI, rhlR, pqsA-E, pqsH | |
| trans-Cinnamaldehyde (CA) | Aldehyde | lasI, lasR, rhlI, rhlR | |
| Guanfacine | Antihypertensive | QseC/QseB homolog | |
| 1,3-DMP | Diamine | lasR | |
| Compound 11f (L-homoserine analog) | L-homoserine lactone analog | lasI, lasR, rhlI, rhlR, pqsA, pqsR | |
| Furazolidone | Nitrofuran antibiotic | lasR, rhlR, pqsR | |
| HMMN | Nitroimidazole | lasR, rhlR, pqsR | |
| NAC derivatives (4d, 4h) | LasR antagonist | N-Acylcysteine derivatives | LasR |
| OBS 9a, 9b, 9f | Oxazolone-sulfonamide hybrids | LasR | |
| 2-Difluoromethylpyridine derivatives (1, 5, 6) | Pyridine derivatives | LasR | |
| Chalcone derivatives (5H, Nme2) | PqsR antagonist | Chalcones | PqsR |
| Compound 61 | Quinazolin-4(3H)-one derivative | PqsR | |
| Quinazolinone derivatives (11a, 11b) | Quinazolinone-based compounds | PqsR | |
| Clofoctol | Chlorinated phenolic ether | PqsR | |
| HIPS-1635 | Nanoparticle-in-liposome formulation | PqsR | |
| Thiazole-based QSIs (27, 34) | Thiazole derivatives | PqsR | |
| Lamivudine (LAM) | QS receptor binder | Nucleoside analog | LasR, RhlR, PqsR |
| Metformin and Vildagliptin | Antidiabetic drugs | LasR, RhlR, PqsR | |
| Doxazosin | QS protein antagonist | α-adrenoreceptor blocker | QseC, PmrA |
| Terazosin | QscR antagonist | α-adrenoreceptor blocker | QscR |
| β-Blockers (atenolol, esmolol, metoprolol) | QscR stabilizer | β-adrenergic receptor blockers | QscR |
| Azithromycin (AZM) | AHL production inhibitor | Macrolide antibiotic | AHL synthesis |
| MHY1383, MHY1387 | Non-competitive QSI | Synthetic small molecules | LasR, QscR, RhlR |
| Nitrofurazone | PqsE inhibitor | Nitrofuran antibiotic | PqsE |
| Inhibitor Name | Producing Species | Nature of Inhibitor | QS Factor(s) Inhibited |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolites (MELF) | Aspergillus quandricinctus | Fungal metabolites | AHL-mediated QS systems |
| Amylomacrolactines A–C | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SCSIO 41392 | Macrolactins | PQS system, pyocyanin production |
| Diketopiperazines (DKPs) | Bacillus cereus RC1 | Diketopiperazines | QS-regulated virulence factors (pyocyanin, motility) |
| AHL-degrading enzymes | Bacillus cereus, Bacillus subtilis, Pseudomonas spp. | Enzymes (lactonases, acylases) | AHL molecules |
| AHL-degrading enzymes | Bacillus spp., Vibrio alginolyticus | Enzymes (lactonases, acylases) | AHL molecules |
| Phthalate derivative | Bacillus zhangzhouensis SK4 | Phthalate derivative | LasR |
| Fungal extract | Blastobotrys parvus PPR3 | Fungal extract | LasR, RhlR |
| Cladodionen | Cladosporium sp. Z148 | Fungal metabolite | LasR, PqsR |
| C18-HSL analogs | Delftia tsuruhatensis 11304 | AHL analogs | Las, Rhl, Pqs systems |
| Hydrocinnamic acid | Enterobacter xiangfangensis | Organic acid | lasI, lasR, rhlI, rhlR |
| 3-Benzyl-hexahydro-pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione | Exiguobacterium indicum SJ16 | Cyclic dipeptide | las, rhl, pqs systems |
| Glabrol, Berberine, Fucoxanthin | Halophilic bacteria (e.g., Halomonas spp.) | Bioactive metabolites | las, rhl systems |
| Biosurfactant | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum | Biosurfactant | AHL signaling |
| Cell-free extract | Lactobacillus plantarum F-10 | Cell extract | QS-regulated virulence factors (las, rhl systems) |
| Lyngbyoic acid, Benderadiene | Lyngbya sp. | Specialized metabolites | LasR, RhlR |
| AHL-degrading enzymes | Marine actinobacteria | Enzymes (lactonases, acylases) | AHL molecules |
| Chitosan | Metapenaeus affinis | Polysaccharide | lasR, rhlR |
| Secondary metabolites | Nocardiopsis lucentensis EMB25 | Secondary metabolites | LasR, RhlR |
| 2-Methyl-N-(2′-phenylethyl) butyramide, etc. | Oceanobacillus sp. XC22919 | Butyramides, benzoate | AHL-mediated QS systems |
| Chermesiterpenoid B (Che B) and Che B Ester | Penicillium chermesinum | Terpenoids | LasR, QscR |
| Tyrosol | Penicillium chrysogenum DXY-1 | Phenolic compound | CviR (AHL receptor) |
| Citrinin | Penicillium sp. JH1 | Secondary metabolite | lasI, lasR, rhlI, rhlR, pqsA, pqsR |
| Curvularin | Phoma macrostoma | Aromatic compound | RhlR |
| 1-(4-amino-2-hydroxyphenyl)ethanone (AHE) | Phomopsis liquidambari | Fungal metabolite | lasI, lasR, rhlI, rhlR, pqsR |
| VOC-3.9 | Spongiibacter nanhainus CSC3.9 | Volatile organic compounds | LasR, RhlR, PqsB, AmbB |
| Actinomycin D | Streptomyces cyaneochromogenes RC1 | Antibiotic | lasI, lasR, rhlI, rhIR, pqsR |
| Fatty acyl compounds (e.g., 13Z-Octadecenal) | Streptomyces griseoincarnatus HK12 | Fatty acyl compounds | LasI |
| Tyramine, N-acetyltyramine | Vibrio alginolyticus M3-10 | Amines | AHL-mediated QS systems |
| Inhibitor Class | Representative Compound(s) | QS Target | Reported Activity Metric | Experimental System | Key Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microbial-Derived | Amylomacrolactine A, Citrinin | PQS, LasR/RhlR | Pyocyanin inhibition: 68.64% (Citrinin) | P. aeruginosa PAO1, clinical strains | Narrow-spectrum, production complexity |
| Curvularin | RhlR | Rhamnolipid reduction: 34.7% | P. aeruginosa PAO1, C. elegans | Weak LasR inhibition | |
| Plant-Derived | Thymoquinone, 6-Gingerol | LasR, RhlR, PqsR | Biofilm inhibition: 42.74% (6-Gingerol) | P. aeruginosa PAO1, murine models | Poor solubility, metabolic instability |
| Falcarindiol, Bakuchiol | LasR, PqsR | Elastase reduction: 35.7% (Falcarindiol) | Burned mouse model | Dose-dependent cytotoxicity | |
| Synthetic Compounds | Furanone C-30, Compound 5b | LasR, RhlR | IC50: 8.7 μM (Compound 5b) | P. aeruginosa PAO1, C. elegans | Hemolysis at high doses |
| Benzoheterocyclic sulfoxide (6b) | LasR | Biofilm inhibition: 40% at 300 μg/mL | P. aeruginosa PAO1 | Limited in vivo data | |
| Peptides | CRAMP, PA-Win2 | QS-regulated genes | Biofilm reduction: 91.05% (CRAMP) | P. aeruginosa biofilm assays | Proteolytic degradation |
| LIVRHK/LIVRRK peptides | LasI, RhlI | Virulence factor reduction: 61% (pyocyanin) | P. aeruginosa PAO1 | Short half-life in vivo | |
| Nanoparticles | AgNPs (propolis), ZnO-NPs | AHL degradation, LasR | Violacein inhibition: 75.24% (AgNPs) | C. violaceum CV026, P. aeruginosa | Cytotoxicity, environmental impact |
| Eugenol-functionalized NPs | LasR, RhlR | Pyocyanin reduction: 66% | Carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa | ROS-mediated host cell damage | |
| Enzymes | AiiA lactonase, MomL | AHL hydrolysis | Elastase reduction: >50% (AiiA) | P. aeruginosa clinical strains | Instability in physiological fluids |
| YtnP lactonase | AHL degradation | Biofilm inhibition: 90% | Simulated water filter system | Thermolability |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Touati, A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Tighilt, L.; Idres, T. Anti-QS Strategies Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081838
Touati A, Ibrahim NA, Tighilt L, Idres T. Anti-QS Strategies Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081838
Chicago/Turabian StyleTouati, Abdelaziz, Nasir Adam Ibrahim, Lilia Tighilt, and Takfarinas Idres. 2025. "Anti-QS Strategies Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081838
APA StyleTouati, A., Ibrahim, N. A., Tighilt, L., & Idres, T. (2025). Anti-QS Strategies Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081838







