Urinary Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Essential Oil Countermeasures in a One Health Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of the Strain
2.2. Definitive Identification
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Essential Oil and Antiseptic Susceptibility Testing
3. Results
3.1. Cultural Characterization
3.2. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
3.3. Essential Oil Susceptibility Testing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holt, K.E.; Wertheim, H.; Zadoks, R.N.; Baker, S.; Whitehouse, C.A.; Dance, D.; Jenney, A.; Connor, T.R.; Hsu, L.Y.; Severin, J.; et al. Genomic analysis of diversity, population structure, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae, an urgent threat to public health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3574–E3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karampatakis, T.; Tsergouli, K.; Behzadi, P. Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Virulence Factors, Molecular Epidemiology and Latest Updates in Treatment Options. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; Tang, H.L.; Chiou, C.S.; Lin, Y.C.; Chiang, M.K.; Tung, K.C.; Lai, Y.C.; Lu, M.C. Prevalence and Virulence Profiles of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated From Different Animals. Vet. Med. Sci. 2025, 11, e70243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Antimicrobial Resistance, Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae—Global Situation. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2024-DON527 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Marques, C.; Menezes, J.; Belas, A.; Aboim, C.; Cavaco-Silva, P.; Trigueiro, G.; Telo Gama, L.; Pomba, C. Klebsiella pneumoniae causing urinary tract infections in companion animals and humans: Population structure, antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blin, C.; Passet, V.; Touchon, M.; Rocha, E.P.; Brisse, S. Metabolic diversity of the emerging pathogenic lineages of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1881–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, T.S.; Opstrup, K.V.; Christiansen, G.; Rasmussen, P.V.; Thomsen, M.E.; Justesen, D.L.; Schønheyder, H.C.; Lausen, M.; Birkelund, S. Complement mediated Klebsiella pneumoniae capsule changes. Microbes Infect. 2020, 22, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapelle, C.; Gaborit, B.; Dumont, R.; Dinh, A.; Vallee, M. Treatment of UTIs due to Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-producers: How to use new antibiotic drugs? A narrative review. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filev, R.; Lyubomirova, M.; Bogov, B.; Kolevski, A.; Pencheva, V.; Kalinov, K.; Rostaing, L. Urinary Tract Infections Caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae and Prolonged Treatment with Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, G.; Chao, X.; Xie, L.; Wang, H. The characteristic of virulence, biofilm and antibiotic resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, S.; Murphy, C.N. Epidemiology and virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae. In Urinary Tract Infections: Molecular Pathogenesis and Clinical Management; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; pp. 435–457. [Google Scholar]
- Tarnagda, H.; Sagna, T.; Nadembega, W.M.; Ouattara, A.K.; Traoré, L.; Ouedraogo, R.A.; Bado, P.; Bazie, B.V.; Bouda, N.; Zongo, L.; et al. Prevalence and Antibiotic Resistance of Urinary Tract Pathogens, with Molecular Identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, and Acinetobacter spp., Using Multiplex Real-Time PCR. Am. J. Mol. Biol. 2024, 14, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochońska, D.; Brzychczy-Włoch, M. Klebsiella pneumoniae–Taxonomy, Occurrence, Identification, Virulence Factors and Pathogenicity. Adv. Microbiol. 2024, 63, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diago-Navarro, E.; Calatayud-Baselga, I.; Sun, D.; Khairallah, C.; Mann, I.; Ulacia-Hernando, A.; Sheridan, B.; Shi, M.; Fries, B.C. Antibody-based immunotherapy to treat and prevent infection with hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2017, 24, e00456-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosillo, N.; Taglietti, F.; Granata, G. Treatment options for colistin resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Present and future. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Marr, C.M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, 10–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, P.; Hu, D. The making of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, P.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yu, Y. A global perspective on the convergence of hypervirulence and carbapenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 25, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, K.A.; Miller, V.L. The intersection of capsule gene expression, hypermucoviscosity and hypervirulence in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2020, 54, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Ferrer, S.; Peñaloza, H.F.; Budnick, J.A.; Bain, W.G.; Nordstrom, H.R.; Lee, J.S.; Van Tyne, D. Finding order in the chaos: Outstanding questions in Klebsiella pneumoniae pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, 10–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochan, T.J.; Nozick, S.H.; Medernach, R.L.; Cheung, B.H.; Gatesy, S.W.; Lebrun-Corbin, M.; Mitra, S.D.; Khalatyan, N.; Krapp, F.; Qi, C.; et al. Genomic surveillance for multidrug-resistant or hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae among United States bloodstream isolates. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.Y.; Ong, E.L. Positive string test in hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess. Oxf. Med. Case Rep. 2022, 4, omac035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. Klebsiella pneumoniae population genomics and antimicrobial-resistant clones. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 944–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.H.; Porto, W.F.; de Faria, C., Jr.; Dias, S.C.; Alencar, S.A.; Pickard, D.J.; Hancock, R.E.; Franco, O.L. Genomic insights into the diversity, virulence and resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae extensively drug resistant clinical isolates. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Yang, X.; Chan, E.W.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S. Klebsiella species: Taxonomy, hypervirulence and multidrug resistance. EBioMedicine 2022, 79, 103998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2023; Volume M100. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, M.M.; Wick, R.R.; Watts, S.C.; Cerdeira, L.T.; Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. A genomic surveillance framework and genotyping tool for Klebsiella pneumoniae and its related species complex. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, V.B.; Singh, B.B.; Priyadarshi, N.; Chauhan, N.K.; Rajamohan, G. Role of novel multidrug efflux pump involved in drug resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, G.; Saigal, S.; Elongavan, A. Action and resistance mechanisms of antibiotics: A guide for clinicians. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 33, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, A.; Henquet, S.; Compain, F.; Genel, N.; Arlet, G.; Decré, D. Partition locus-based classification of selected plasmids in Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica spp.: An additional tool. J. Microbiol. Methods 2015, 110, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkey, J.; Cottingham, H.; Tokolyi, A.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Cerdeira, L.; de Oliveira Garcia, D.; Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. Linear plasmids in Klebsiella and other Enterobacteriaceae. Microb. Genom. 2022, 8, 000807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Norman, A.; Hansen, L.H.; Sørensen, S.J. Conjugative plasmids: Vessels of the communal gene pool. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2275–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doménech-Sánchez, A.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; Hernández-Allés, S.; del Carmen Conejo, M.; Pascual, A.; Tomás, J.M.; Albertí, S.; Benedí, V.J. Role of Klebsiella pneumoniae OmpK35 porin in antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 3332–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyres, K.L.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Froumine, R.; Tokolyi, A.; Gorrie, C.L.; Lam, M.M.; Duchêne, S.; Jenney, A.; Holt, K.E. Distinct evolutionary dynamics of horizontal gene transfer in drug resistant and virulent clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLoS Gen. 2019, 15, e1008114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorduijn, D.J.; Rooijakkers, S.H.; van Schaik, W.; Bardoel, B.W. Complement resistance mechanisms of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Immunobiology 2016, 221, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedrakyan, A.; Gevorgyan, Z.; Zakharyan, M.; Arakelova, K.; Hakobyan, S.; Hovhannisyan, A.; Aminov, R. Molecular Epidemiology and In-Depth Characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates from Armenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Li, Y.; Ren, P.; Tian, D.; Chen, W.; Fu, P.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Jiang, X. Molecular epidemiology of hypervirulent carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 661218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Héritier, C.; Tolün, V.; Nordmann, P. Emergence of oxacillinase-mediated resistance to imipenem in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, G.-A.; Codiță, I.; Szekely, E.; Șerban, R.; Ruja, G.; Tălăpan, D. Ghid Privind Enterobacteriaceele Producătoare de Carbapenemaze; Institutul National de Sanatate Publica: Bucharest, Romania, 2016; ISBN 978-973-0-22283-8. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.K.; Yusoff, K.; Ajat, M.; Thomas, W.; Abushelaibi, A.; Akseer, R.; Lim, S.H.; Lai, K.S. Disruption of KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae membrane via induction of oxidative stress by cinnamon bark (Cinnamomum verum J. Presl) essential oil. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Li, K.; Ji, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Shi, M.; Mi, Z. Carbapenem and cefoxitin resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae strains associated with porin OmpK36 loss and DHA-1 β-lactamase production. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2013, 44, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournomiti, M.; Kimbaris, A.; Mantzourani, I.; Plessas, S.; Theodoridou, I.; Papaemmanouil, V.; Kapsiotis, I.; Panopoulou, M.; Stavropoulou, E.; Bezirtzoglou, E.E.; et al. Antimicrobial activity of essential oils of cultivated oregano (Origanum vulgare), sage (Salvia officinalis), and thyme (Thymus vulgaris) against clinical isolates of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella oxytoca, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 23289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Sun, Z.; Wang, T.; Yang, M.; Liu, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Antimicrobial activity of eugenol against carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and its effect on biofilms. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 139, 103924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzaro, F.; Fratianni, F.; De Martino, L.; Coppola, R.; De Feo, V. Effect of essential oils on pathogenic bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 1451–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motley, M.P.; Fries, B.C. A new take on an old remedy: Generating antibodies against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in a postantibiotic world. MSphere 2017, 2, 10–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisso Ndezo, B.; Tokam Kuaté, C.R.; Dzoyem, J.P. Synergistic antibiofilm efficacy of thymol and piperine in combination with three aminoglycoside antibiotics against Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilms. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 1, 7029944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Rajivgandhi, G.N.; Ramachandran, G.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M.; Almanaa, T.N.; Manoharan, N. Preparative HPLC fraction of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis essential oil against biofilm forming Klebsiella pneumoniae. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 2853–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, S. Essential oils: Their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods—A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, J.S.; Karuppayil, S.M. A status review on the medicinal properties of essential oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 62, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassolé, I.H.N.; Juliani, H.R. Essential oils in combination and their antimicrobial properties. Molecules 2012, 17, 3989–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
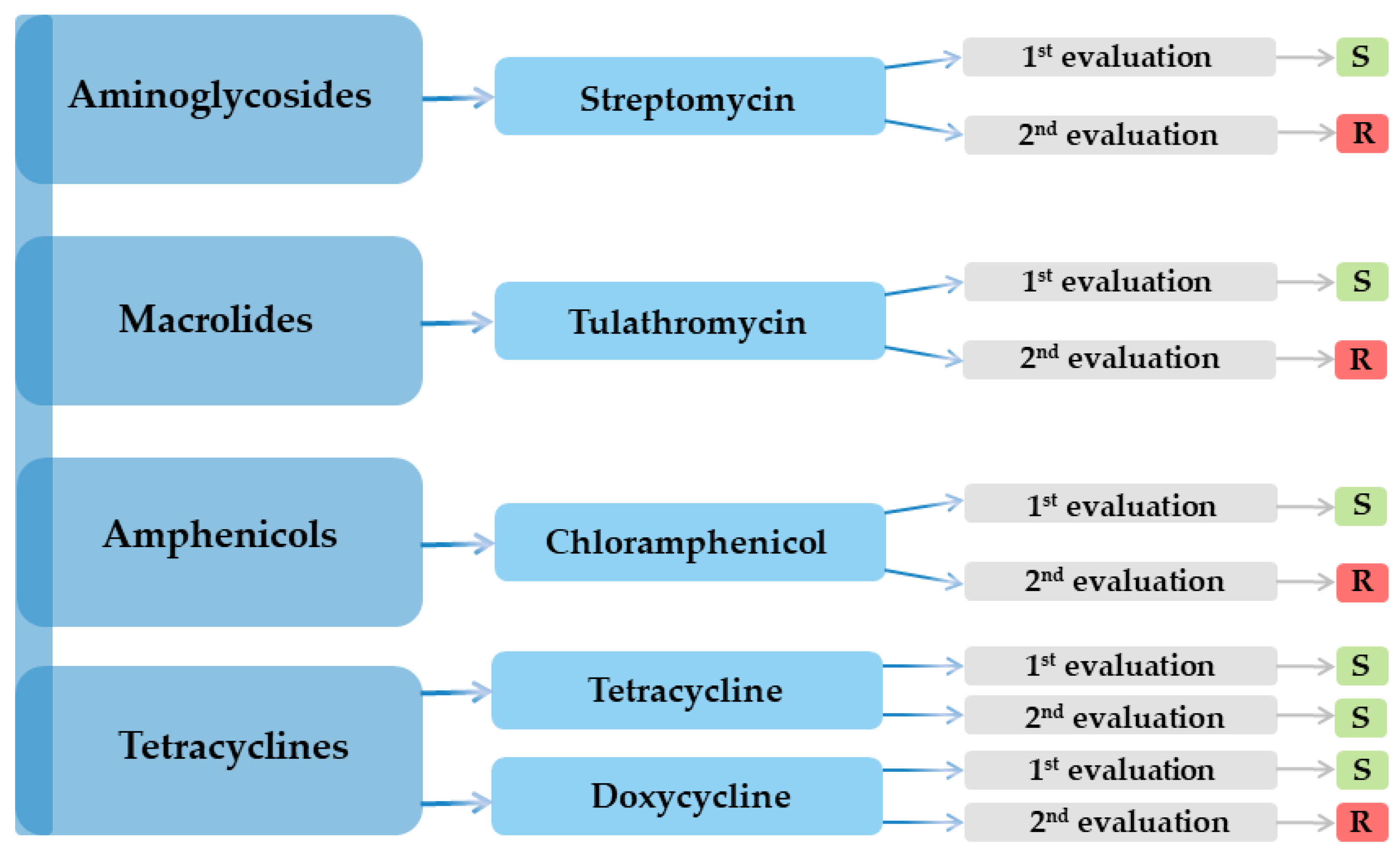
| Antimicrobial Class | Nr. | Antibiotic | Result | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Evaluation | 2nd Evaluation | |||
| Aminoglycosides | 1 | Amikacin (AK) | R | R |
| 2 | Streptomycin (S) | S | R | |
| 3 | Gentamicin (GME) | R | R | |
| Penicillins | 4 | Piperacillin (PRL) | R | R |
| 5 | Mecillinam (MEC) | R | R | |
| 6 | Amoxicillin–clavulanic acid (AMC) | R | R | |
| Macrolides | 7 | Azithromycin (AZM) | R | R |
| 8 | Tulathromycin (TUL) | S | R | |
| Cephalosporins 1st generation | 9 | Cefadroxil (CFR) | R | R |
| 2nd generation | 10 | Cefaclor (CEC) | R | R |
| 11 | Cefotetan (CTT) | R | R | |
| 12 | Cefuroxime (CXM) | R | R | |
| 13 | Cefamandole (MA) | R | R | |
| 3rd generation | 14 | Ceftriaxone (CRO) | R | R |
| 15 | Ceftazidime (CAZ) | R | R | |
| 16 | Cefoperazone (CEP) | R | R | |
| 17 | Ceftiofur (FUR) | R | R | |
| 18 | Cefixime (CFM) | R | R | |
| 19 | Ceftazidime-avibactam (CZA) | R | R | |
| 4th generation | 20 | Cefquinome (CFQ) | R | R |
| Carbapenems | 21 | Meropenem (MEM) | R | R |
| 22 | Imipenem (IMI) | R | R | |
| Fluoroquinolones | 23 | Norfloxacin (NX) | R | R |
| 24 | Ofloxacin (OFX) | R | R | |
| 25 | Marbofloxacin (MAR) | R | R | |
| Tetracyclines | 26 | Tetracycline (TET) | S | S |
| 27 | Doxycycline (DOX) | S | R | |
| Amphenicols | 28 | Chloramphenicol (C) | S | R |
| Chemotherapeutic agents | 29 | Nitrofurantoin (F) | R | R |
| Sulfonamides | 30 | Trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole (SXT) | R | R |
| International Name | Latin Name/Composition | Inhibition Area Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Palmarosa | Cymbopogon martini | 11 |
| Geranium | Pelargonium graveolens | R |
| Frankincense | Boswellia carteri | R |
| Laurel | Laurus nobilis | 12 |
| Tea tree | Melaleluca alternifolia | 20 |
| Citronella | Cymbopogon nardus | R |
| Thyme | Thymus vulgaris | 22 |
| Propolis | Apis mellifera propolis | R |
| Biomicin Urinar® (A20) | Origani aetheroleum + Cinnamomun verum + Salvia officinalis + Thymi aetheroleum | 12 (resistant colonies) |
| Biomicin Forte® (A3) | Thymi aetheroleum + Caryophylli floris aetheroleum | 30 |
| Methylene blue 3% | - | 13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mihu, M.-L.; Novac, C.Ş.; Crăciun, S.; Fiţ, N.I.; Bouari, C.M.; Nadăş, G.C.; Răpuntean, S. Urinary Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Essential Oil Countermeasures in a One Health Case Report. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081807
Mihu M-L, Novac CŞ, Crăciun S, Fiţ NI, Bouari CM, Nadăş GC, Răpuntean S. Urinary Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Essential Oil Countermeasures in a One Health Case Report. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081807
Chicago/Turabian StyleMihu, Mălina-Lorena, Cristiana Ştefania Novac, Smaranda Crăciun, Nicodim Iosif Fiţ, Cosmina Maria Bouari, George Cosmin Nadăş, and Sorin Răpuntean. 2025. "Urinary Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Essential Oil Countermeasures in a One Health Case Report" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081807
APA StyleMihu, M.-L., Novac, C. Ş., Crăciun, S., Fiţ, N. I., Bouari, C. M., Nadăş, G. C., & Răpuntean, S. (2025). Urinary Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Essential Oil Countermeasures in a One Health Case Report. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081807







