Changes in L-Carnitine Metabolism Affect the Gut Microbiome and Influence Sexual Behavior Through the Gut–Testis Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Object of Study
2.2. Experiment Design
2.3. Test to Assess Sexual Behavior
2.4. Measurement of Gene Expression
2.5. Extraction and Assessment of DNA Quality and Quantity
2.6. Library Preparation and Sequencing on the DNBSEQ-G50 Platform
2.7. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
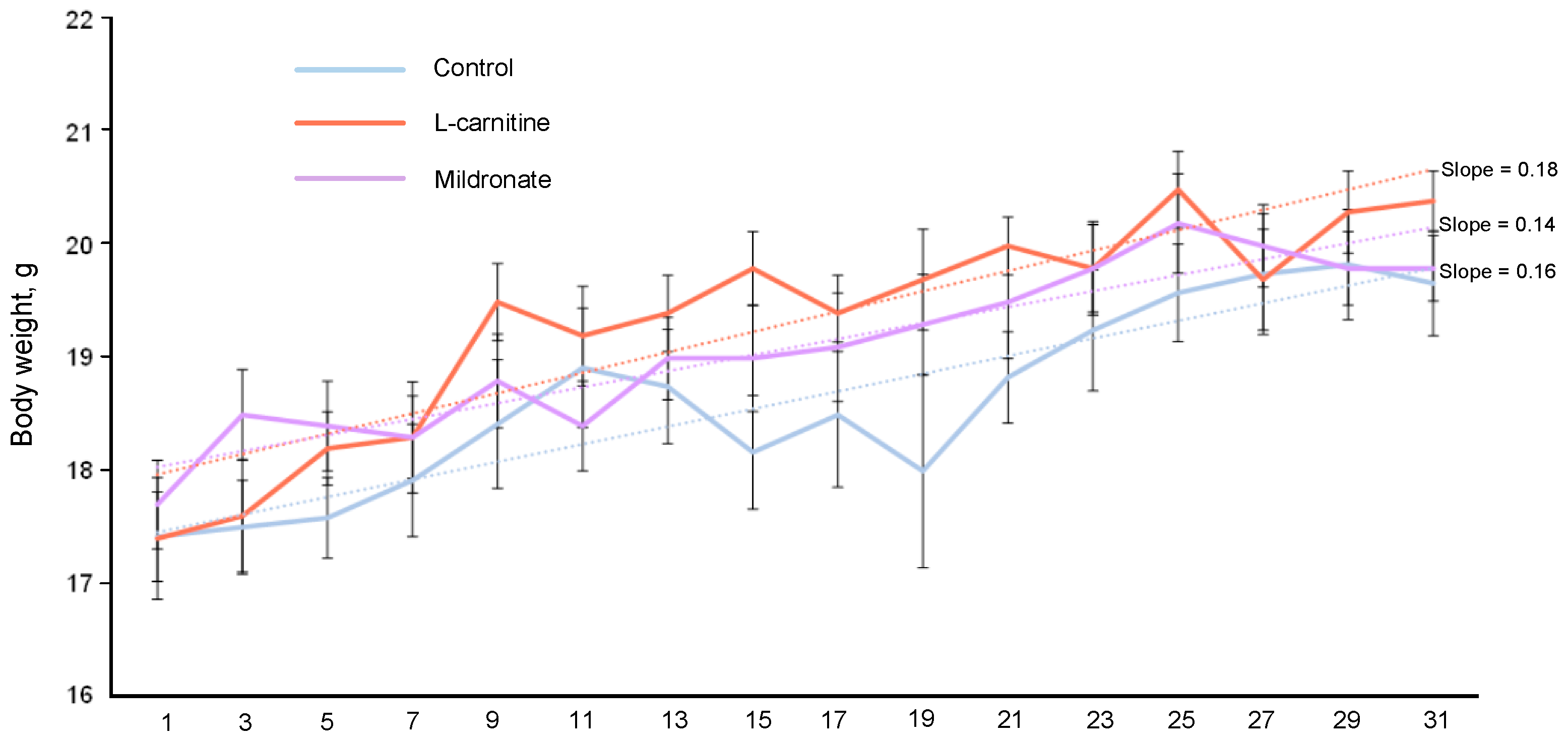
3.1. Dynamics of Body Weight of Mice
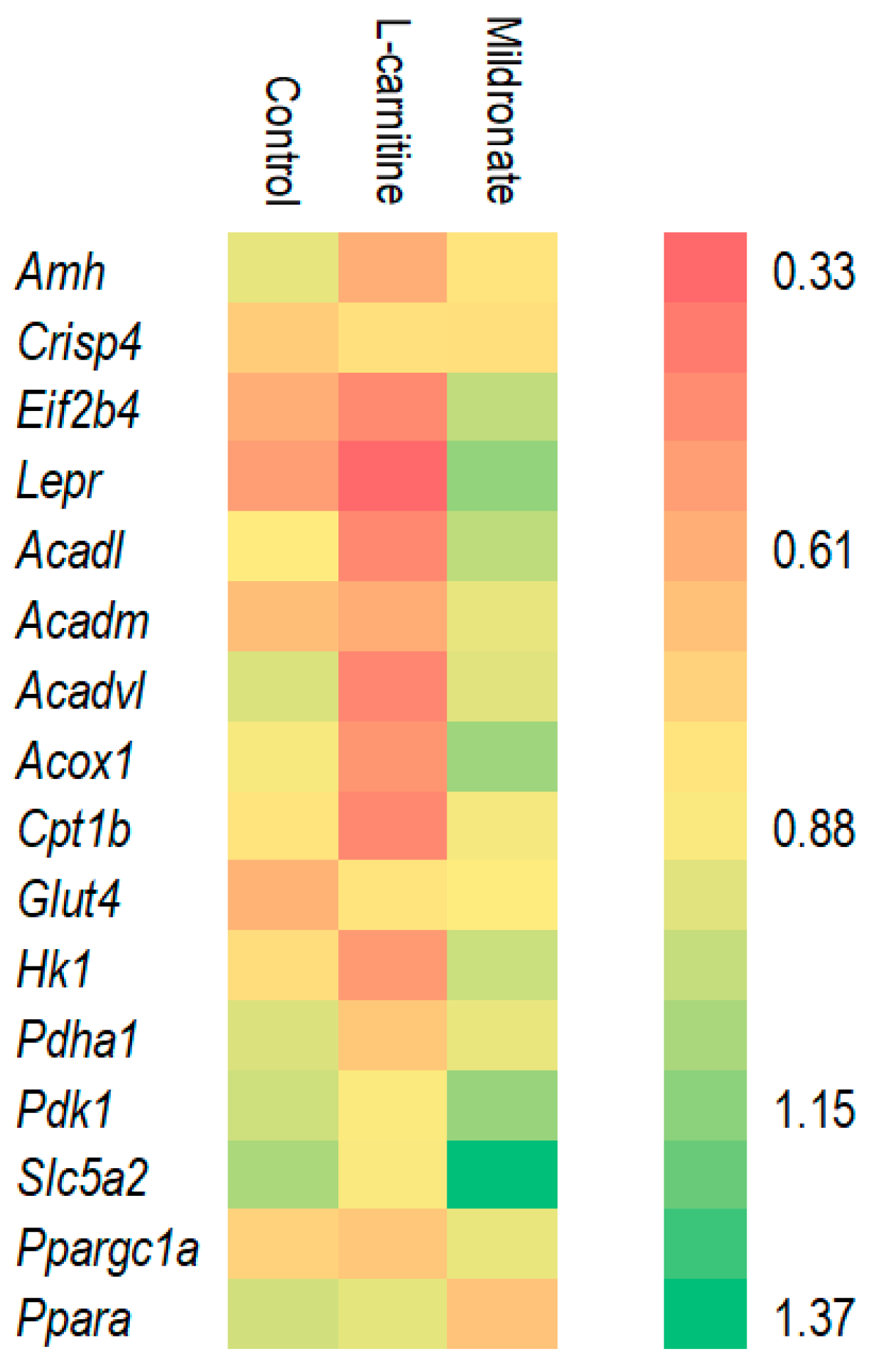
3.2. Assessment of Gene Expression Levels
3.3. Assessment of the Sexual Behavior of Male Mice
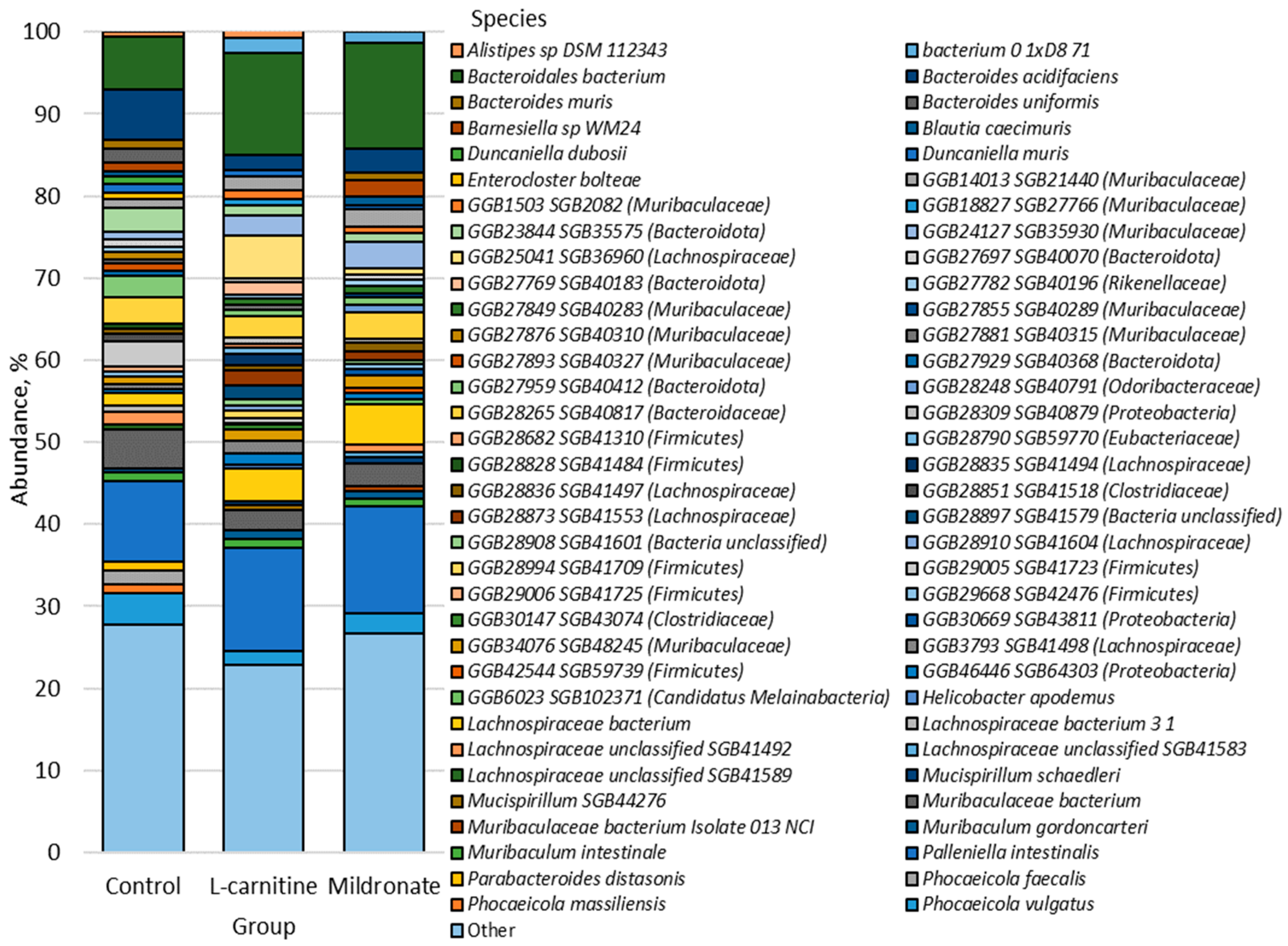
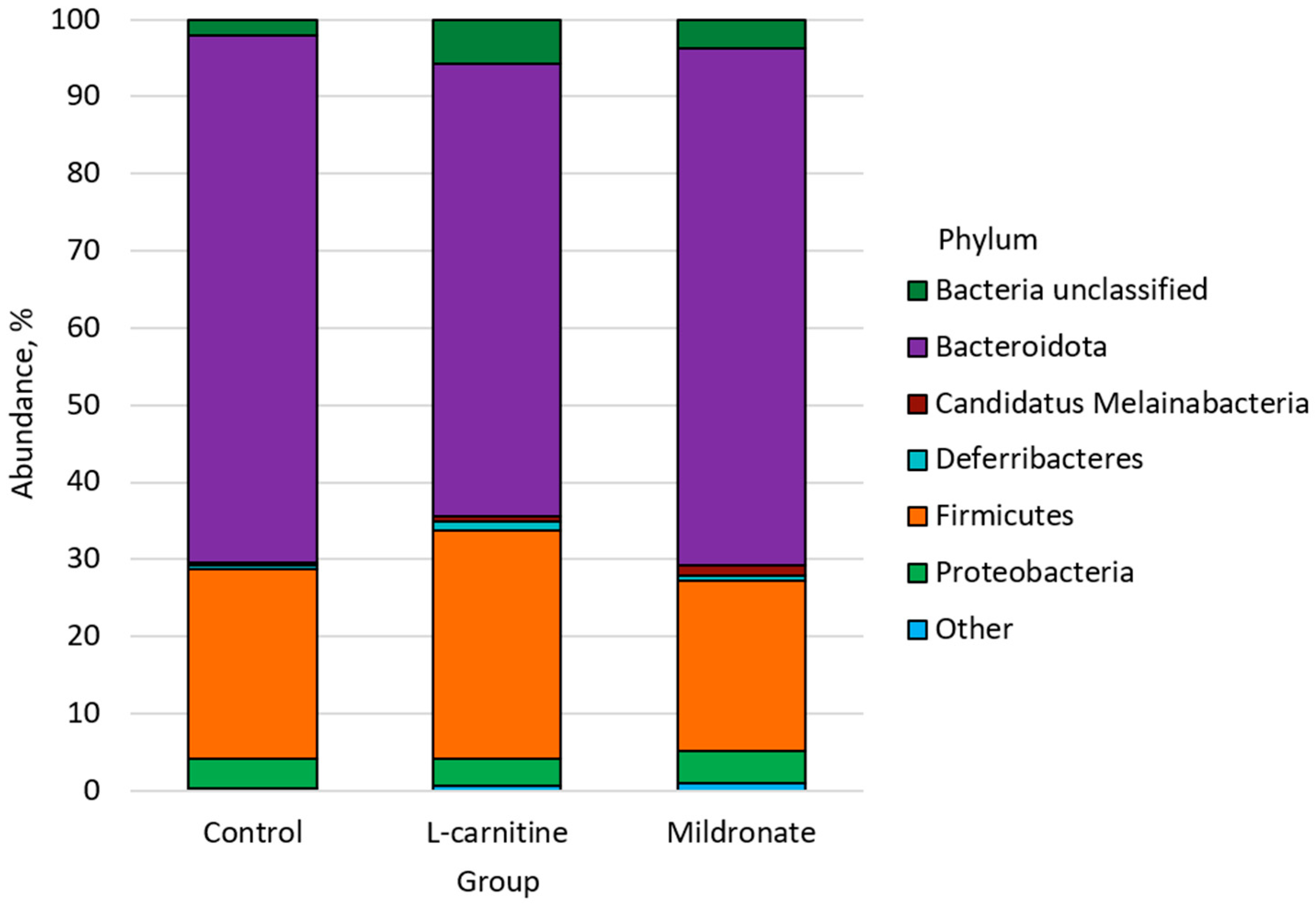
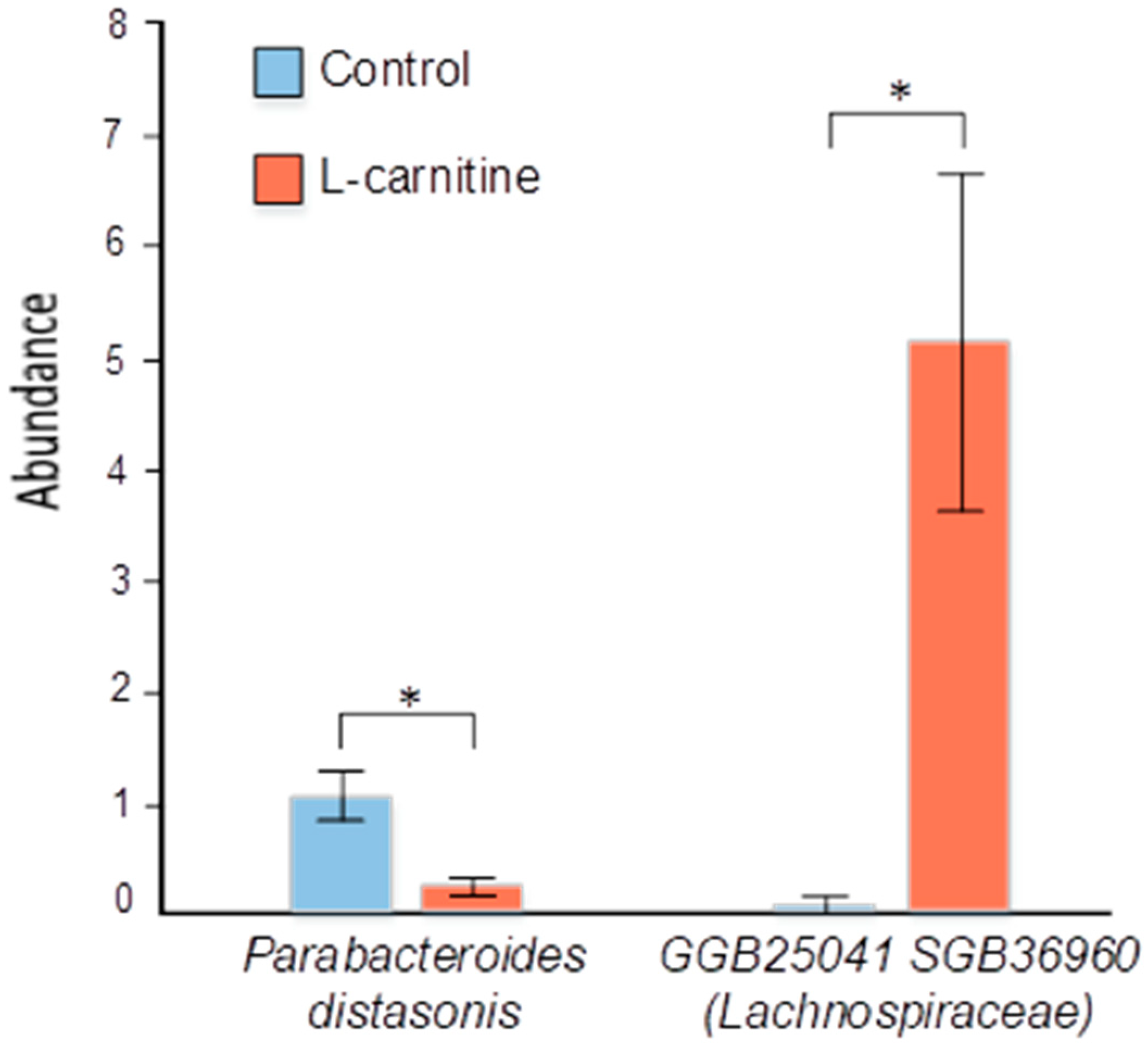
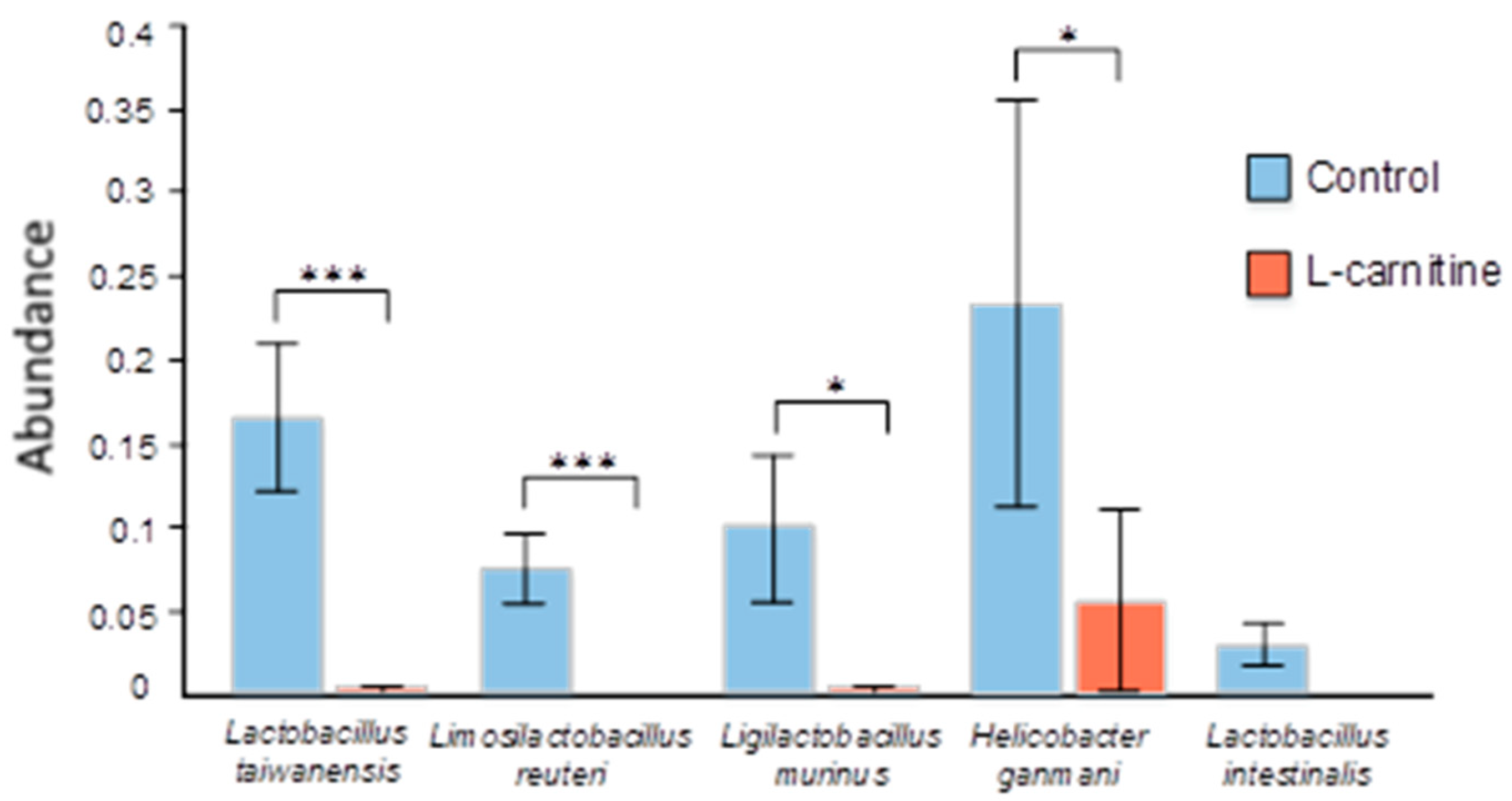
3.4. Gut Microbiome Analysis
3.5. Evaluation of Correlations Between Bacterial Content and Physiological Indices of Male Mice
4. Discussion
4.1. Gene Expression Changes
4.2. Сhanges in Sexual Behavior
4.3. Mechanism of Action of the Gut–Testis Axis
4.4. The Impact of Changing Bacterial Strains
4.4.1. Firmicutes
4.4.2. Bacteroidota
4.4.3. Proteobacteria
4.4.4. Deferribacteres
4.4.5. Tenericutes
4.4.6. Other
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UDB | Union Database |
| cDNA | Complementary DNA |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| dsDNA | Double-stranded DNA |
| ssDNA | Single-stranded DNA |
| PE | Paired end |
| FCL | Flow cell large |
| FCS | Flow cell small |
| MetaPhlAn | Metagenomic phylogenetic analysis |
| MaAsLin | Multivariate analysis by linear models |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NOS | Nitric oxide synthase |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| PYY | Peptide YY |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon like peptide-1 |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| SCFAs | Short-chain fatty acids |
| GPx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| StAR | Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein |
References
- Mateus, F.G.; Moreira, S.; Martins, A.D.; Oliveira, P.F.; Alves, M.G.; de Lourdes Pereira, M. L-Carnitine and Male Fertility: Is Supplementation Beneficial? J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkhovich, B.Z.; Shutenko, Z.V.; Meirena, D.V.; Khagi, K.B.; Mezapuķe, R.J.; Molodchina, T.N.; Kalviņs, I.J.; Lukevics, E. 3-(2,2,2-Trimethylhydrazinium)propionate (THP)—A novel gamma-butyrobetaine hydroxylase inhibitor with cardioprotective properties. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1988, 37, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambrova, M.; Makrecka-Kuka, M.; Vilskersts, R.; Makarova, E.; Kuka, J.; Liepinsh, E. Pharmacological Effects of Meldonium: Biochemical Mechanisms and Biomarkers of Cardiometabolic Activity. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 113, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liepinsh, E.; Vilskersts, R.; Skapare, E.; Svalbe, B.; Kuka, J.; Cirule, H.; Pugovics, O.; Kalvinsh, I.; Dambrova, M. Mildronate Decreases Carnitine Availability and Up-Regulates Glucose Uptake and Related Gene Expression in the Mouse Heart. Life Sci. 2008, 83, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volodina, D.E.; Gureev, A.P.; Shaforostova, E.A.; Gryaznova, M.V.; Ignatyeva, D.A.; Popov, V.N. Effect of L-Carnitine and Mildronate on the Mitochondrial Metabolism of Heart and Bacterial Composition of the Gut Microbiome in Ageing Mice. Life Sci. 2022, 293, 120333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudino Dos Santos, J.C.; Oliveira, L.F.; Noleto, F.M.; Gusmão, C.T.P.; Brito, G.A.d.C.; Viana, G.S.d.B. Gut-Microbiome-Brain Axis: The Crosstalk between the Vagus Nerve, Alpha-Synuclein and the Brain in Parkinson’s Disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 2611–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Jayasena, C.N.; Dhillo, W.S. Regulation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Testicular Axis: Pathophysiology of Hypogonadism. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 51, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, Z. Exploring the Role of Gut Microbiome in Male Reproduction. Andrology 2022, 10, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GitHub.com. Available online: https://github.com/s-andrews/FastQC/blob/master/fastqc (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Dodt, M.; Roehr, J.T.; Ahmed, R.; Dieterich, C. FLEXBAR-Flexible Barcode and Adapter Processing for Next-Generation Sequencing Platforms. Biology 2012, 1, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast Gapped-Read Alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Míguez, A.; Beghini, F.; Cumbo, F.; McIver, L.J.; Thompson, K.N.; Zolfo, M.; Manghi, P.; Dubois, L.; Huang, K.D.; Thomas, A.M.; et al. Extending and Improving Metagenomic Taxonomic Profiling with Uncharacterized Species Using MetaPhlAn 4. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, B.P.; Silva, A.M.; Martins, A.D.; Monteiro, M.P.; Sousa, M.; Oliveira, P.F.; Alves, M.G. Effect of Leptin in Human Sertoli Cells Mitochondrial Physiology. Reprod. Sci. 2021, 28, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degrace, P.; Demizieux, L.; Gresti, J.; Tsoko, M.; André, A.; Demaison, L.; Clouet, P. Fatty Acid Oxidation and Related Gene Expression in Heart Depleted of Carnitine by Mildronate Treatment in the Rat. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2004, 258, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gureev, A.P.; Shaforostova, E.A.; Vitkalova, I.Y.; Sadovnikova, I.S.; Kalinina, Y.I.; Cherednichenko, V.R.; Reznikova, K.A.; Valuyskikh, V.V.; Popov, V.N. Long-Term Mildronate Treatment Increased Proteobacteria Level in Gut Microbiome, and Caused Behavioral Deviations and Transcriptome Change in Liver, Heart and Brain of Healthy Mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 398, 115031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-M.; Li, L.-Y.; Qin, X.; Degrace, P.; Demizieux, L.; Limbu, S.M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.-L.; Li, D.-L.; Du, Z.-Y. Inhibited Carnitine Synthesis Causes Systemic Alteration of Nutrient Metabolism in Zebrafish. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.B.S. Direct and Indirect Effects of Leptin on Adipocyte Metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanayem, B.I.; Bai, R.; Kissling, G.E.; Travlos, G.; Hoffler, U. Diet-Induced Obesity in Male Mice Is Associated with Reduced Fertility and Potentiation of Acrylamide-Induced Reproductive Toxicity. Biol. Reprod. 2010, 82, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agmo, A. Male Rat Sexual Behavior. Brain Res. Protoc. 1997, 1, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjakste, N.; Baumane, L.; Boucher, J.-L.; Dzintare, M.; Meirena, D.; Sjakste, J.; Lauberte, L.; Kalvinsh, I. Effects of Gamma-Butyrobetaine and Mildronate on Nitric Oxide Production in Lipopolysaccharide-Treated Rats. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 94, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Involvement of Nitric Oxide Production in the Mildronate Mechanism of Action. Pharmacol. Rev. Commun. 2002, 12, 163–170. [CrossRef]
- Toda, N.; Ayajiki, K.; Okamura, T. Nitric Oxide and Penile Erectile Function. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 106, 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, F.; Borgmann, H.; Struck, J.P.; Salem, J.; Kuru, T.H. Antioxidant Supplementation on Male Fertility-A Systematic Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooshesh, L.; Nateghian, Z.; Aliabadi, E. Evaluation of L-Carnitine Potential in Improvement of Male Fertility. J. Reprod. Infertil. 2023, 24, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaw, S.C.; Wong, Z.Z.; Anderson, R.; Martins da Silva, S. L-Carnitine and l-Acetylcarnitine Supplementation for Idiopathic Male Infertility. Reprod. Fertil. 2020, 1, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazza, T.; Scalise, M.; Console, L.; Galluccio, M.; Giangregorio, N.; Tonazzi, A.; Pochini, L.; Indiveri, C. Carnitine Traffic and Human Fertility. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 230, 116565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, F.; Hassanpour, A.; Poost-Pasand, A.; Noorafshan, A.; Karbalay-Doust, S. Protective Effects of L-Carnitine and Homogenized Testis Tissue on the Testis and Sperm Parameters of Busulfan-Induced Infertile Male Rats. Iran. J. Reprod. Med. 2013, 11, 693–704. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, L.; Zhao, R.; Hu, G.; Dai, G.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Xue, B. Chronic Oral Administration of L-Carnitine Induces Testicular Injury: In Vivo Evidence. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2025, 57, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Cheng, W.; Shang, H.; Wei, H.; Deng, C. The Interplay between Androgen and Gut Microbiota: Is There a Microbiota-Gut-Testis Axis. Reprod. Sci. 2022, 29, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zou, H.; Xu, H.; Cao, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J. The potential influence and intervention measures of gut microbiota on sperm: It is time to focus on testis-gut microbiota axis. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1478082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaj, H.W.; Li, Z.; Shan, T.; Dai, P.; Zhu, P.; Li, Y.; Alsiddig, M.A.; Abdelghani, E.; Li, C. Effects of dietary sodium butyrate on reproduction in adult breeder roosters. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2018, 196, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Yan, X.; Chen, L.; Ma, X.; Tang, X.; Zhong, R.; Sun, Z.; Agarwal, M.; Zhang, H.; et al. Gut microbiota-testis Axis: FMT mitigates high-fat diet-diminished male fertility via improving systemic and testicular metabolome. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0002822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jian, Y.P.; Zhang, Y.N.; Li, Y.; Gu, L.T.; Sun, H.H.; Liu, M.D.; Zhou, H.L.; Wang, Y.S.; Xu, Z.X. Short-chain fatty acids in diseases. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaniyi, K.S.; Akintayo, C.O.; Oniyide, A.A.; Omoaghe, A.O.; Oyeleke, M.B.; Fafure, A.A. Acetate supplementation restores testicular function by modulating Nrf2/PPAR-γ in high fat diet-induced obesity in Wistar rats. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2021, 20, 1685–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; He, T.; Becker, S.; Zhang, G.; Li, D.; Ma, X. Butyrate: A Double-Edged Sword for Health? Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From Dietary Fiber to Host Physiology: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Key Bacterial Metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Zeng, X.; Wang, S.; Zeng, X.; Yang, G.; Ye, C.; Cai, S.; Chen, M.; Li, S.; Qiao, S. Butyrate drives the acetylation of histone H3K9 to activate steroidogenesis through PPARγ and PGC1α pathways in ovarian granulosa cells. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Cai, S.; Wang, S.; Zeng, X.; Ye, C.; Chen, M.; Zeng, X.; Qiao, S. Maternal short and medium chain fatty acids supply during early pregnancy improves embryo survival through enhancing progesterone synthesis in rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 69, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Vyavahare, S.; Duchesne Blanes, I.L.; Berger, F.; Isales, C.; Fulzele, S. Microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolism: Impacts on health, aging, and disease. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 183, 112319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Xin, F.Z.; Xue, Y.; Hu, Z.; Han, Y.; Ma, F.; Zhou, D.; Liu, X.L.; Cui, A.; Liu, Z.; et al. Indole-3-propionic acid inhibits gut dysbiosis and endotoxin leakage to attenuate steatohepatitis in rats. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsar, T.; Razak, S.; Trembley, J.H.; Khan, K.; Shabbir, M.; Almajwal, A.; Alruwaili, N.W.; Ijaz, M.U. Prevention of testicular damage by indole derivative MMINA via upregulated StAR and CatSper channels with coincident suppression of oxidative stress and inflammation: In Silico and in vivo validation. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconi, E.; Palma, G.; De Biase, D.; Luciano, A.; Barbieri, M.; de Nigris, F.; Bruzzese, F. Microbiota Effect on Trimethylamine N-Oxide Production: From Cancer to Fitness—A Practical Preventing Recommendation and Therapies. Nutrients 2023, 15, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A.; Garrity, G.M. Valid Publication of the Names of Forty-Two Phyla of Prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 005056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statovci, D.; Aguilera, M.; MacSharry, J.; Melgar, S. The Impact of Western Diet and Nutrients on the Microbiota and Immune Response at Mucosal Interfaces. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, E.B. Differences in Microbiome and Virome between Cattle and Horses in the Same Farm. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 33, 1042–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, N.; Zhao, L. An Opportunistic Pathogen Isolated from the Gut of an Obese Human Causes Obesity in Germfree Mice. ISME J. 2013, 7, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio: A Relevant Marker of Gut Dysbiosis in Obese Patients? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, E.S.; Viardot, A.; Psichas, A.; Morrison, D.J.; Murphy, K.G.; Zac-Varghese, S.E.K.; MacDougall, K.; Preston, T.; Tedford, C.; Finlayson, G.S.; et al. Effects of Targeted Delivery of Propionate to the Human Colon on Appetite Regulation, Body Weight Maintenance and Adiposity in Overweight Adults. Gut 2015, 64, 1744–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, S.; Nirmalkar, K.; Hoyo-Vadillo, C.; García-Espitia, M.; Ramírez-Sánchez, D.; García-Mena, J. Gut Microbiome Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Obesity in Children. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hylander, B.L.; Qiao, G.; Cortes Gomez, E.; Singh, P.; Repasky, E.A. Housing Temperature Plays a Critical Role in Determining Gut Microbiome Composition in Research Mice: Implications for Experimental Reproducibility. Biochimie 2023, 210, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameyama, K.; Itoh, K. Intestinal Colonization by a Lachnospiraceae Bacterium Contributes to the Development of Diabetes in Obese Mice. Microbes Environ. 2014, 29, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaplana, T.; Miele, S.; Tolonen, A.C. Lachnospiraceae Are Emerging Industrial Biocatalysts and Biotherapeutics. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1324396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, A.; Scoggin, K.; Gupta, J.; Threadgill, D.W.; Andrews-Polymenis, H.L. Using the Collaborative Cross to Identify the Role of Host Genetics in Defining the Murine Gut Microbiome. Microbiome 2023, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, E.; Corr, S.C. Lactobacillus Spp. for Gastrointestinal Health: Current and Future Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 840245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Harris, H.M.B.; Mattarelli, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A Taxonomic Note on the Genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 Novel Genera, Emended Description of the Genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and Union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahiddine, F.Y.; You, I.; Park, H.; Kim, M.J. Commensal Lactobacilli Enhance Sperm Qualitative Parameters in Dogs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 888023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayat, M.; Koohpeyma, F.; Montazeri-Najafabady, N.; Dabbaghmanesh, M.H.; Asmarian, N.; Hosseini, S.I. The effects of modest intake of soy milk enriched with Lactobacillus casei and omega-3 on the testis parameters in diabetic rats: A stereological study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2025, 57, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talarico, T.L.; Casas, I.A.; Chung, T.C.; Dobrogosz, W.J. Production and Isolation of Reuterin, a Growth Inhibitor Produced by Lactobacillus Reuteri. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1988, 32, 1854–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uwaezuoke, S.N.; Ayuk, A.C.; Eze, J.N.; Odimegwu, C.L.; Ndiokwelu, C.O.; Eze, I.C. Postnatal Probiotic Supplementation Can Prevent and Optimize Treatment of Childhood Asthma and Atopic Disorders: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 956141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, C.; Schmidt, S.; Garbe, E.; Röhmel, J.; Giersiepen, K. Effects of the Regular Intake of the Probiotic Lactobacillus Reuteri (DSM 17938) on Respiratory and Gastrointestinal Infections in a Workplace Setting: A Double-Blind Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. BMC Nutr. 2015, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, M.; Lacey, S.; Doolan, A.; Goodbody, E.; Seamans, K. The Effect of Lactobacillus Reuteri Supplementation in Helicobacter Pylori Infection: A Placebo-Controlled, Single-Blind Study. BMC Nutr. 2018, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liang, L.; Lv, P.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y. Effects of Non-Viable Lactobacillus Reuteri Combining with 14-Day Standard Triple Therapy on Helicobacter Pylori Eradication: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Jung, I.S.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, J.H. The Probiotics Lacticaseibacillus paracasei, Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus, and Limosilactobacillus fermentum Enhance Spermatozoa Motility Through Mitochondrial Function-Related Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Huang, Z.; Duan, B.; Li, Q.; Song, Z.; He, D. A Multiplying Delay-Locked Loop Design with Low Jitter and High Linearity. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Integrated Circuits, Technologies and Applications (ICTA), Xi’an, China, 28–30 October 2022; pp. 38–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Peng, X.; Shu, L.; Long, C.; Tan, Z. Intestinal Microbiota Characteristics of Mice Treated with Folium Senna Decoction Gavage Combined with Restraint and Tail Pinch Stress. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Liu, X. Characteristics of Gut Microbiota in Patients with Asthenozoospermia: A Chinese Pilot Study. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, D.A.; Александрoвна, К.Д.; Lapin, S.V.; Владимирoвич, Л.С.; Gubonina, I.V.; Владимирoвна, Г.И. Bile acid dysmetabolism in inflammatory bowel diseases. Alm. Clin. Med. 2023, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.R.; Haileselassie, Y.; Nguyen, L.P.; Tropini, C.; Wang, M.; Becker, L.S.; Sim, D.; Jarr, K.; Spear, E.T.; Singh, G.; et al. Dysbiosis-Induced Secondary Bile Acid Deficiency Promotes Intestinal Inflammation. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 659–670.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellwag, E.J.; Hylemon, P.B. 7alpha-Dehydroxylation of Cholic Acid and Chenodeoxycholic Acid by Clostridium Leptum. J. Lipid Res. 1979, 20, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Ma, X. Dietary nutrients mediate crosstalk between bile acids and gut microbes in animal host metabolism. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 63, 9315–9329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kaoutari, A.; Armougom, F.; Gordon, J.I.; Raoult, D.; Henrissat, B. The Abundance and Variety of Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes in the Human Gut Microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.D.; Jing, J.; Liu, S.S.; Mu, Y.P.; Peng, L.L.; Yan, Y.J.; Xiao, G.M.; Bi, X.Y.; et al. Impairment of Spermatogenesis and Sperm Motility by the High-Fat Diet-Induced Dysbiosis of Gut Microbes. Gut 2020, 69, 1608–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, J.; Xu, P.; Wang, X.; Xing, Z.; Dong, S.; Li, G.; Yao, X.; Guo, R.; Feng, T.; Yao, W.; et al. Enterotypes in Asthenospermia Patients with Obesity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Nie, Q.; Zhang, S.; He, H.; Zuo, S.; Chen, C.; Yang, J.; Chen, H.; Hu, J.; Li, S.; et al. Parabacteroides Distasonis Ameliorates Insulin Resistance via Activation of Intestinal GPR109a. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeji, J.C.; Sarikonda, D.K.; Hopperton, A.; Erkkila, H.L.; Cohen, D.E.; Martinez, S.P.; Cominelli, F.; Kuwahara, T.; Dichosa, A.E.K.; Good, C.E.; et al. Parabacteroides Distasonis: Intriguing Aerotolerant Gut Anaerobe with Emerging Antimicrobial Resistance and Pathogenic and Probiotic Roles in Human Health. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1922241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaifem, J.; Mendes-Frias, A.; Wolter, M.; Steimle, A.; Garzón, M.J.; Ubeda, C.; Nobre, C.; González, A.; Pinho, S.S.; Cunha, C.; et al. Akkermansia Muciniphila and Parabacteroides Distasonis Synergistically Protect from Colitis by Promoting ILC3 in the Gut. mBio 2024, 15, e0007824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Huang, J.F.; Cheng, Y.; Dai, M.Y.; Zhu, W.F.; Yang, X.W.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Li, F. Polyamine metabolism links gut microbiota and testicular dysfunction. Microbiome 2021, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegg, A.E. The function of spermine. IUBMB Life 2014, 66, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Akbar, M.T.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhi, L.; Shen, Q. Exploration of the Muribaculaceae Family in the Gut Microbiota: Diversity, Metabolism, and Function. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Palatinszky, M.; Pereira, F.C.; Nguyen, J.; Fernandez, V.I.; Mueller, A.J.; Menolascina, F.; Daims, H.; Berry, D.; Wagner, M.; et al. An Automated Raman-Based Platform for the Sorting of Live Cells by Functional Properties. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, J.C.; Pehrsson, E.C.; Blaser, M.J.; Sandhu, K.; Gao, Z.; Wang, B.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Contreras, M.; Noya-Alarcón, Ó.; et al. The Microbiome of Uncontacted Amerindians. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, M.; Luo, C.; Lu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Shi, J. Prebiotic Mannan-Oligosaccharides Augment the Hypoglycemic Effects of Metformin in Correlation with Modulating Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5821–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Shi, H.; Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, B.; Zhuoga, D.; Luo, M.; et al. Berberine alters the gut microbiota metabolism and impairs spermatogenesis. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2024, 57, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, N.-R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.-W. Proteobacteria: Microbial Signature of Dysbiosis in Gut Microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirpuri, J.; Raetz, M.; Sturge, C.R.; Wilhelm, C.L.; Benson, A.; Savani, R.C.; Hooper, L.V.; Yarovinsky, F. Proteobacteria-Specific IgA Regulates Maturation of the Intestinal Microbiota. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, S.E.; Winter, M.G.; Xavier, M.N.; Thiennimitr, P.; Poon, V.; Keestra, A.M.; Laughlin, R.C.; Gomez, G.; Wu, J.; Lawhon, S.D.; et al. Host-Derived Nitrate Boosts Growth of E. Coli in the Inflamed Gut. Science 2013, 339, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.A.; Koren, O.; Goodrich, J.K.; Johansson, M.E.V.; Nalbantoglu, I.; Aitken, J.D.; Su, Y.; Chassaing, B.; Walters, W.A.; González, A.; et al. Transient Inability to Manage Proteobacteria Promotes Chronic Gut Inflammation in TLR5-Deficient Mice. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Pan, L.; Cheng, J.; Wang, X.; Zheng, L.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H. High-Fat-Diet-Induced Gut Microbiome Changes in Mice. Stress. Brain 2022, 2, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.X.; Deng, Z.C.; Liu, M.; Huang, Y.X.; Yang, J.C.; Sun, L.H. Heat Stress Impairs Male Reproductive System with Potential Disruption of Retinol Metabolism and Microbial Balance in the Testis of Mice. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 3373–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, C.G.; Kocsis, A.G.; Hart, M.L.; Crim, M.J.; Myles, M.H.; Franklin, C.L. Pathogenicity of Helicobacter Ganmani in Mice Susceptible and Resistant to Infection with H. Hepaticus. Comp. Med. 2015, 65, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, H.-O.; Ouis, I.-S.; Stenram, U.; Ljungh, A.; Moran, A.P.; Wadström, T.; Al-Soud, W.A. High Prevalence of Helicobacter Species Detected in Laboratory Mouse Strains by Multiplex PCR-Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis and Pyrosequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 3781–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, B.R.; O’Rourke, J.L.; Vandamme, P.; On, S.L.; Lee, A. Helicobacter Ganmani Sp. Nov., a Urease-Negative Anaerobe Isolated from the Intestines of Laboratory Mice. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 1881–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Shi, M.; Zhu, F.-C.; Lian, C.-A.; He, L.-S. Genomic Evidence for the First Symbiotic Deferribacterota, a Novel Gut Symbiont from the Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent Shrimp Rimicaris Kairei. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1179935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Luan, Y.; Yue, X.; Xiang, F.; Mao, D.; Cao, Y.; Xiong, Z. Effects of Codonopis Bulleynana Forest Ex Diels on Deferribacteres in Constipation Predominant Intestine Tumor: Differential Analysis. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Shi, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, L.; Yi, R.; Su, H.; Sun, X. Oral Administration of a Mixture of Probiotics Protects against Food Allergy via Induction of CD103+ Dendritic Cells and Modulates the Intestinal Microbiota. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 55, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Zhang, M.N.; Wang, H.G.; Yang, X.Z.; Yu, C.G. Jatrorrhizine Alleviates Ulcerative Colitis via Regulating Gut Microbiota and NOS2 Expression. Gut Pathog. 2022, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Yu, Z.; Feng, P.; Ye, Z.; Li, R.; Liu, J.; Hu, J.; Kakade, A.; Liu, P.; Li, X. Lactobacillus Plantarum TW1-1 Alleviates Diethylhexylphthalate-Induced Testicular Damage in Mice by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Decreasing Inflammation. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Zhu, G.; Shi, Q.; Yang, S.; Ma, T.; Mishra, S.K.; Wen, A.; Xu, H.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Characterizing the Microbiota in Gastrointestinal Tract Segments of Rhabdophis Subminiatus: Dynamic Changes and Functional Predictions. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e00789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.-C.; Lian, C.-A.; He, L.-S. Genomic Characterization of a Novel Tenericutes Bacterium from Deep-Sea Holothurian Intestine. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grahnemo, L.; Kambur, O.; Lahti, L.; Jousilahti, P.; Niiranen, T.; Knight, R.; Salomaa, V.; Havulinna, A.S.; Ohlsson, C. Associations between Gut Microbiota and Incident Fractures in the FINRISK Cohort. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadmehrabi, S.; Tang, W.H.W. Gut Microbiome and Its Role in Cardiovascular Diseases. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2017, 32, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Strontium Chloride Improves Reproductive Function and Alters Gut Microbiota in Male Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bobe, G.; Revel, J.S.; Rodrigues, R.R.; Sharpton, T.J.; Fantacone, M.L.; Raslan, K.; Miranda, C.L.; Lowry, M.B.; Blakemore, P.R.; et al. Improvements in Metabolic Syndrome by Xanthohumol Derivatives Are Linked to Altered Gut Microbiota and Bile Acid Metabolism. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, e1900789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Zhou, X.; Lan, Z.; Tang, K.; Zhu, X.; Mo, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, M. Simotang Alleviates the Gastrointestinal Side Effects of Chemotherapy by Altering Gut Microbiota. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 32, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.C.; Hoffmann, C.; Mota, J.F. Gut Microbiota Is Associated with Adiposity Markers and Probiotics May Impact Specific Genera. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 1751–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacroce, L.; Imbimbo, C.; Ballini, A.; Crocetto, F.; Scacco, S.; Cantore, S.; Di Zazzo, E.; Colella, M.; Jirillo, E. Testicular immunity and its connection with the microbiota. physiological and clinical implications in the light of personalized medicine. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Han, W.; Zhan, G.; Li, S.; Jiang, X.; Wang, L.; Xiang, S.; Zhu, B.; Yang, L.; Luo, A.; et al. Abnormal Gut Microbiota Composition Contributes to the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Db/Db Mice. Aging 2019, 11, 10454–10467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrêa, R.; de Oliveira Santos, I.; Braz-de-Melo, H.A.; de Sant’Ana, L.P.; das Neves Almeida, R.; Pasquarelli-do-Nascimento, G.; Prado, P.S.; Kobinger, G.P.; Maurice, C.F.; Magalhães, K.G. Gut Microbiota Modulation Induced by Zika Virus Infection in Immunocompetent Mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelakis, E.; Bachar, D.; Yasir, M.; Musso, D.; Djossou, F.; Gaborit, B.; Brah, S.; Diallo, A.; Ndombe, G.M.; Mediannikov, O.; et al. Treponema Species Enrich the Gut Microbiota of Traditional Rural Populations but Are Absent from Urban Individuals. New Microbes New Infect. 2019, 27, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| № | Gene Name | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gapdh | F:5′-CATCACTGCCACCCAGAAGACTG-3′ R: 5′-ATGCCAGTGAGCTTCCCGTTCAG-3′ |
| 2 | Eif2b4 | F: 5′-GCTTGCAACAGGTAGCTTGT-3′ R: 5′-CCCCTCACTCACCTTGACAT-3′ |
| 3 | Crisp4 | F:5′-ATGGATGTGGGTATGGCAGT-3′ R: 5′-GCAGCTGAACTCCAACTCAC-3′ |
| 4 | Lepr | F: 5′-CTTTCCTGTGGACAGAACCAGC-3′ R: 5′-AGCACTGAGTGACTCCACAGCA-3′ |
| 5 | Amh | F:5′-CCGCTATTTGGTGCTAACCGTG-3′ R: 5′-AAGGCTTGCAGCTGATCGATGC-3′ |
| 6 | Acadl | F:5′-CCATGGCAAAATACTGGGCA-3′ R: 5′-TTGGTACCACCGTAGATCGG-3′ |
| 7 | Acadm | F:5′-AGGGTTTAGTTTTGAGTTGACGG-3′ R: 5′- CCCCGCTTTTGTCATATTCCG-3′ |
| 8 | Acadvl | F:5′-CTACTGTGCTTCAGGGACAAC-3′ R: 5′-CAAAGGACTTCGATTCTGCCC-3′ |
| 9 | Acox1 | F:5′-TAACTTCCTCACTCGAAGCCA-3′ R: 5′-AGTTCCATGACCCATCTCTGCC-3′ |
| 10 | Cpt1b | F:5′-AGGCACTTCTCAGCATGGTC-3′ R: 5′-CATCTCGAACATCCACCCGT-3′ |
| 11 | Glut4 | F:5′-CCTCCCGCCCTTAGTTG-3′ R: 5′-CTGCAAAGCGTAGGTACCA-3′ |
| 12 | Hk1 | F:5′-GTTCGAGAAGATGGTGAGCG-3′ R: 5′-AGAGTTCCCATCCCGTTTCA-3′ |
| 13 | Pdha1 | F:5′-GTTTTGGGCGTGGCTTCG-3′ R: 5′-GGCTTGCCGGCTTCTG-3′ |
| 14 | Pdk1 | F:5′-TCCTGGACTTCGGGTCAGT-3′ R: 5′-GTATGCTGAGCTCCAGGCCAA-3′ |
| 15 | Ppargc1a | F:5′-ATGTGTCGCCTTCTTGCTCT-3′ R: 5′-CACGACCTGTGTCGAGAAAA-3′ |
| 16 | Ppara | F:5′-AGAGCCCCATCTGTCCTCTC-3′ R: 5′-ACTGGTAGTCTGCAAAACCAAA-3′ |
| 17 | Slc5a2 | F:5′-TGGTGTTGGCTTGTGGTCTA-3′ R: 5′-ATGTTGCTGGCGAACAGAGA-3′ |
| Group | Observed Species | Shannon Index |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 204 | 3.64 |
| L-carnitine | 119 | 3.39 |
| Mildronate | 212 | 3.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babenkova, P.; Gureev, A.; Sadovnikova, I.; Burakova, I.; Smirnova, Y.; Pogorelova, S.; Morozova, P.; Gribovskaya, V.; Adzhemian, D.; Syromyatnikov, M. Changes in L-Carnitine Metabolism Affect the Gut Microbiome and Influence Sexual Behavior Through the Gut–Testis Axis. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081751
Babenkova P, Gureev A, Sadovnikova I, Burakova I, Smirnova Y, Pogorelova S, Morozova P, Gribovskaya V, Adzhemian D, Syromyatnikov M. Changes in L-Carnitine Metabolism Affect the Gut Microbiome and Influence Sexual Behavior Through the Gut–Testis Axis. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081751
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabenkova, Polina, Artem Gureev, Irina Sadovnikova, Inna Burakova, Yuliya Smirnova, Svetlana Pogorelova, Polina Morozova, Viktoria Gribovskaya, Dianna Adzhemian, and Mikhail Syromyatnikov. 2025. "Changes in L-Carnitine Metabolism Affect the Gut Microbiome and Influence Sexual Behavior Through the Gut–Testis Axis" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081751
APA StyleBabenkova, P., Gureev, A., Sadovnikova, I., Burakova, I., Smirnova, Y., Pogorelova, S., Morozova, P., Gribovskaya, V., Adzhemian, D., & Syromyatnikov, M. (2025). Changes in L-Carnitine Metabolism Affect the Gut Microbiome and Influence Sexual Behavior Through the Gut–Testis Axis. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081751






