Identification and Pathogenicity Analysis of Huaxiibacter chinensis Qf-1 in Mink (Neogale vison)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Bacterial Isolation
2.3. Morphological, Physiological, and Biochemical Analysis of Strain QF-1
2.4. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Construction of Phylogenetic Tree
2.5. Genome Sequencing and Analysis of Average Nucleotide Identity (ANI)
2.6. Bacterial Challenge Infection Assay
3. Results
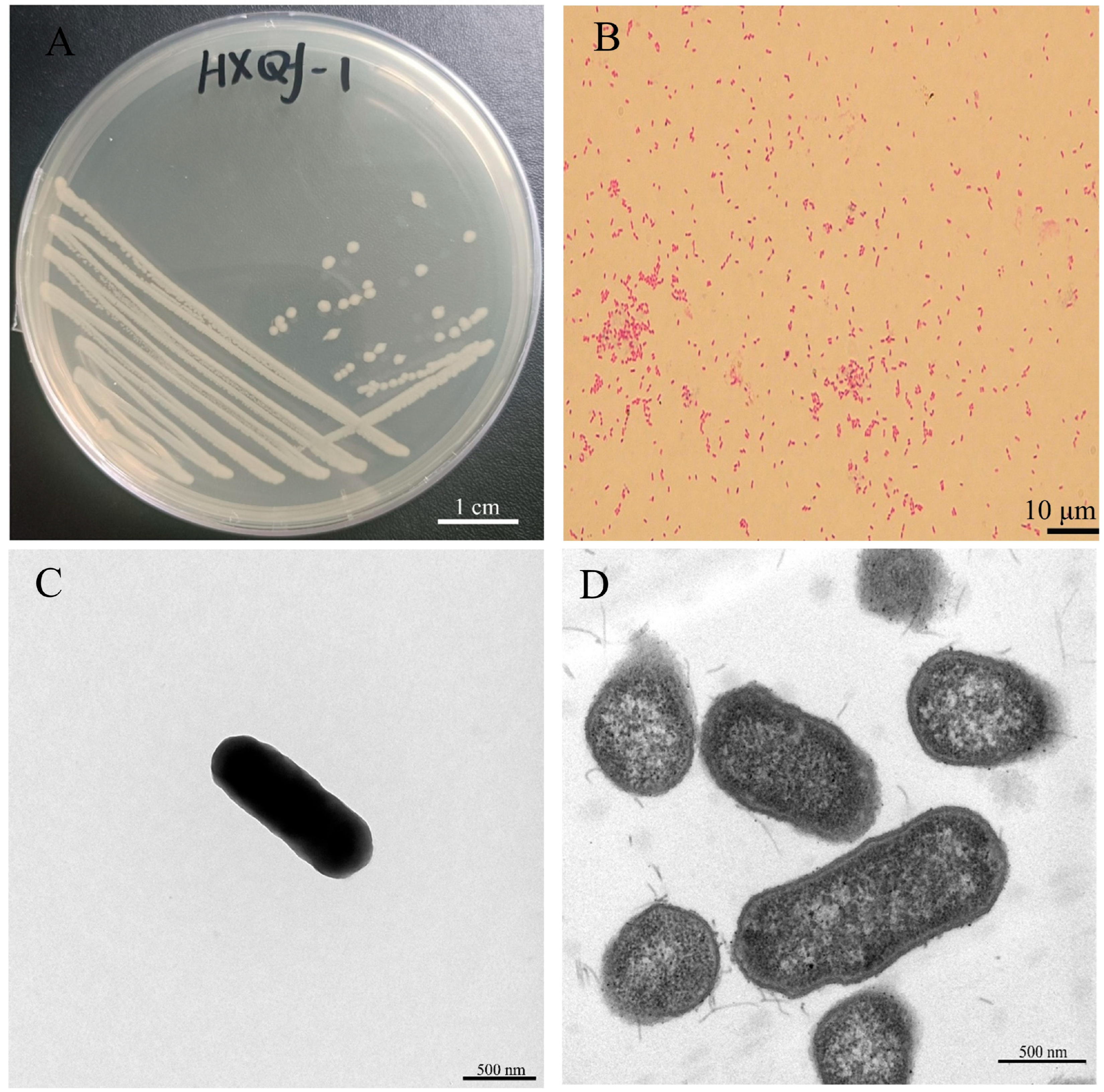
3.1. Morphological Characteristics of Pathogenic Bacterial Strain of Qf-1
3.2. Growth Curve and the Standard Growth Curve of Qf-1
3.3. Molecular Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis
3.4. Biochemical Characterization of Qf-1 Using Biolog Gen III Microtest System
3.5. Observations of HE Staining and Bacterial Changes in Infected Tissue by H. chinensis Qf-1
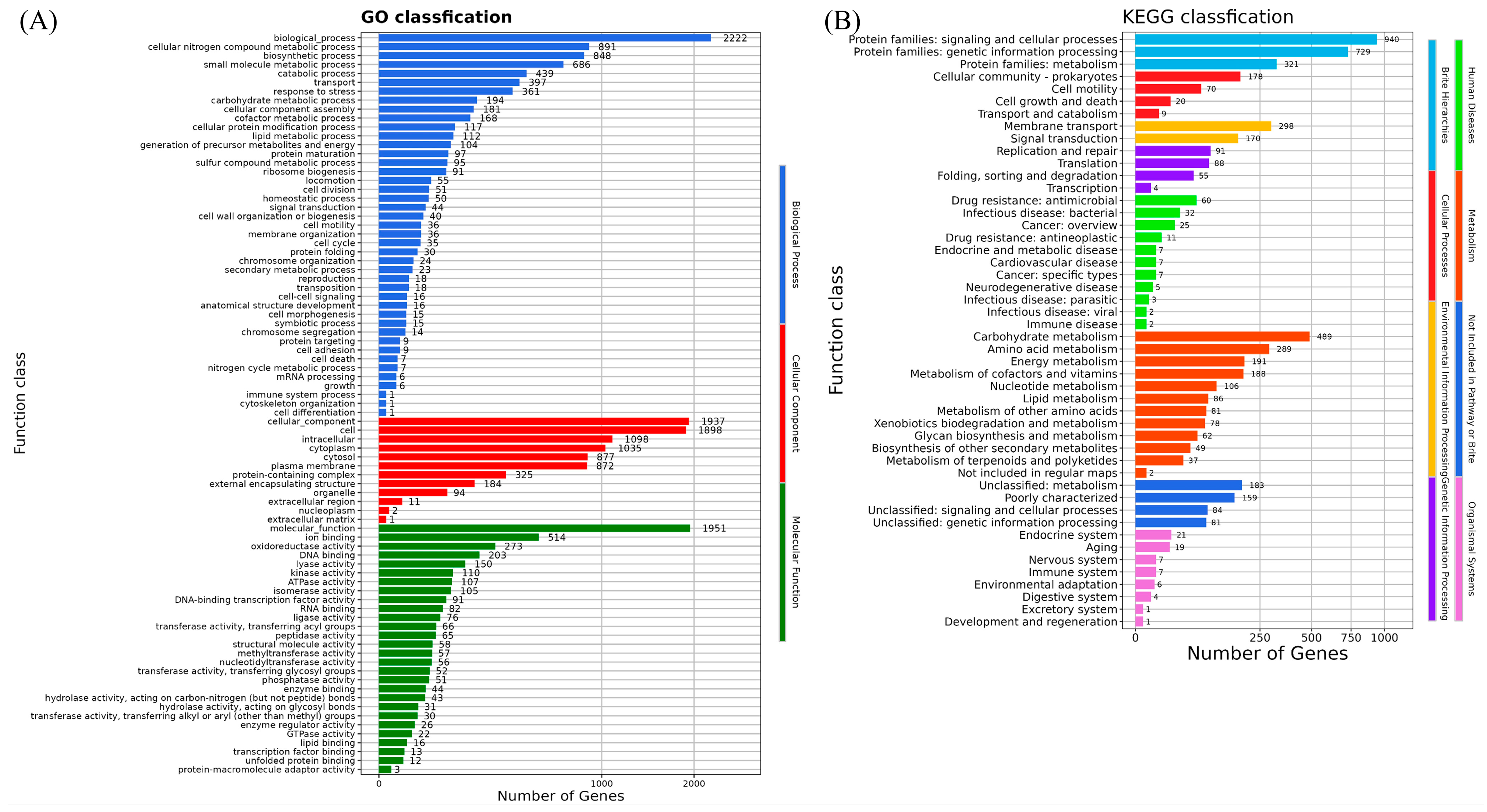
3.6. Whole-Genome Analyses of Strain H. chinensis Qf-1
3.7. Pathogenic Potential Analysis of Strain H. chinensis Qf-1
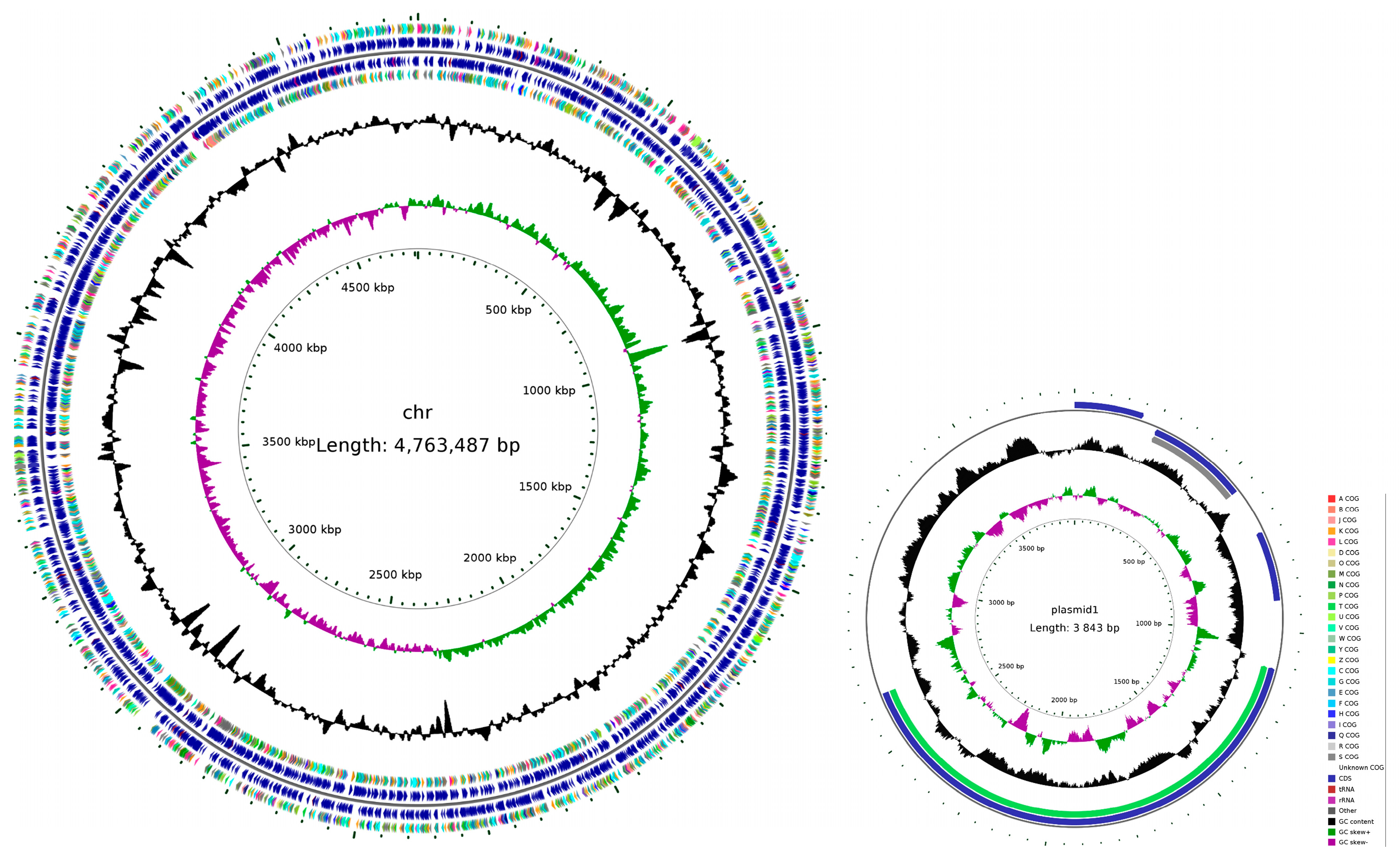
3.8. Genome Assembly Completion Mapping of Strain H. chinensis Qf-1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peacock, T.P.; Barclay, W.S. Mink farming poses risks for future viral pandemics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2303408120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, N.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.-S.; Shao, X.-Q.; Zhang, S.-Q.; Wang, F.-X.; Tan, B.; Tian, F.-L.; Cheng, S.-P.; Wen, Y.-J. Detection and Characterization of Avastrovirus Associated with Diarrhea Isolated from Minks in China. Food Environ. Virol. 2014, 6, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Hu, B.; Fan, H.; Zhang, H.; Lian, S.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Yan, X.; Wang, S.; Bai, X. Molecular Epidemiology of Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli Causing Hemorrhagic Pneumonia in Mink in Northern China. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 781068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, L.; Li, J.; Fang, B.; Huang, X. Molecular epidemiology, antimicrobial susceptibility, and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis genotyping of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from mink. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 82, 256–263. [Google Scholar]
- Canuti, M.; Pénzes, J.J.; Lang, A.S. A new perspective on the evolution and diversity of the genus Amdoparvovirus (family Parvoviridae) through genetic characterization, structural homology modeling, and phylogenetics. Virus Evol. 2022, 8, veac056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahedi, S.M.; Salek Ardestani, S.; Banabazi, M.H.; Clark, F. Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and diagnosis of Aleutian disease caused by Aleutian mink disease virus: A literature review with a perspective of genomic breeding for disease control in American mink (Neogale vison). Virus Res. 2023, 336, 199208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Miao, B.; Chen, N.; Chen, C.; Shao, T.; Zhang, X.; Chang, L.; Zhang, X.; Du, Q.; Huang, Y.; et al. SYNCRIP facilitates porcine parvovirus viral DNA replication through the alternative splicing of NS1 mRNA to promote NS2 mRNA formation. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, K.; Hammer, A.S.; Sørensen, C.M.; Heuer, O.E. Usage of antimicrobials and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance among bacteria from mink. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 133, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaisen, N.K.; Lassen, D.C.K.; Chriél, M.; Larsen, G.; Jensen, V.F.; Pedersen, K. Antimicrobial resistance among pathogenic bacteria from mink (Neovison vison) in Denmark. Acta Vet. Scand. 2017, 59, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.S.; Du, Y.; Wu, J.Q.; Tian, F.L.; Yu, X.J.; Wang, J.B. Vaccine resistant pseudorabies virus causes mink infection in China. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Saha, M.; Zhuang, Y.; Chang, L.; Xiao, L.; Wang, G. Pseudoalteromonas piscicida X-8 causes bleaching disease in farmed Saccharina japonica. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsuki, H.; Zhang, T.; Yahiro, K.; Toyomoto, T.; Sawa, T. Non-canonical inflammasome activation analysis in a mouse model of Citrobacter rodentium infection. STAR Protoc. 2022, 3, 101741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifa, A.Y.Z.; Bekhet, G. First isolation and characterization of the pathogenic Aeromonas veronii bv. veronii associated with ulcerative syndrome in the indigenous Pelophylax ridibundus of Al-Ahsaa, Saudi Arabia. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 117, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evol. Int. J. Org. Evol. 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, M.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Y.; Pevzner, P.A. Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Concepcion, G.T.; Feng, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, H. Haplotype-resolved de novo assembly using phased assembly graphs with hifiasm. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Nie, F.; Xie, S.Q.; Zheng, Y.F.; Dai, Q.; Bray, T.; Wang, Y.X.; Xing, J.F.; Huang, Z.J.; Wang, D.P.; et al. Efficient assembly of nanopore reads via highly accurate and intact error correction. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An Integrated Tool for Comprehensive Microbial Variant Detection and Genome Assembly Improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T. The enveomics collection: A toolbox for specialized analyses of microbial genomes and metagenomes. PeerJ Prepr. 2016, 4, e1900v1. [Google Scholar]
- Galperin, M.Y.; Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V. Expanded microbial genome coverage and improved protein family annotation in the COG database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D261–D269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D457–D462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, B.; Zheng, D.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. VFDB 2025: An integrated resource for exploring anti-virulence compounds. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D871–D877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Ge, Q.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Yin, Y. dbCAN3: Automated carbohydrate-active enzyme and substrate annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W115–W121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abby, S.S.; Néron, B.; Ménager, H.; Touchon, M.; Rocha, E.P. MacSyFinder: A program to mine genomes for molecular systems with an application to CRISPR-Cas systems. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, R.; Brandmaier, S.; Kleine, F.; Tischler, P.; Heinz, E.; Behrens, S.; Niinikoski, A.; Mewes, H.W.; Horn, M.; Rattei, T. Sequence-based prediction of type III secreted proteins. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, S.; Feng, Y.; Zong, Z. Huaxiibacter chinensis gen. nov., sp. nov., recovered from human sputum. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 005484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faust, K.; Sathirapongsasuti, J.F.; Izard, J.; Segata, N.; Gevers, D.; Raes, J.; Huttenhower, C. Microbial co-occurrence relationships in the human microbiome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grier, A.; McDavid, A.; Wang, B.; Qiu, X.; Java, J.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Yang, H.; Holden-Wiltse, J.; Kessler, H.A.; Gill, A.L.; et al. Neonatal gut and respiratory microbiota: Coordinated development through time and space. Microbiome 2018, 6, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, E.K.; Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Fierer, N.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R. Bacterial community variation in human body habitats across space and time. Science 2009, 326, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.; Blaser, M.J. The human microbiome: At the interface of health and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, E.K.; Carlisle, E.M.; Bik, E.M.; Morowitz, M.J.; Relman, D.A. Microbiome assembly across multiple body sites in low-birthweight infants. Mbio 2013, 4, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P.V.; Brabb, T.; Pekow, C.; Vasbinder, M.A. Administration of substances to laboratory animals: Routes of administration and factors to consider. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2011, 50, 600–613. [Google Scholar]
- Goris, J.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Klappenbach, J.A.; Coenye, T.; Vandamme, P.; Tiedje, J.M. DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Gu, T.; Zhou, J.; Chen, F.; Li, S. Investigating the gut bacteria structure and function of hibernating bats through 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing and culturomics. mSystems 2025, 10, e0146324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Minamino, T.; Namba, K.; Macnab, R.M. Substrate specificity classes and the recognition signal for Salmonella type III flagellar export. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 2485–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucidi, M.; Capecchi, G.; Spagnoli, C.; Basile, A.; Artuso, I.; Persichetti, L.; Fardelli, E.; Capellini, G.; Visaggio, D.; Imperi, F.; et al. The response to desiccation in Acinetobacter baumannii. Virulence 2025, 16, 2490209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chu, Y.F.; Zhong, L.G.; Xu, J.P.; Liang, L.Y.; Long, T.F.; Fang, L.X.; Sun, J.; Liao, X.P.; et al. Tobramycin-resistant small colony variant mutant of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium shows collateral sensitivity to nitrofurantoin. Virulence 2024, 15, 2356692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulin, G.; Méndez, A.A.E.; Figueroa, N.R.; Smith, C.; Folmer, M.P.; Serra, D.; Wade, J.T.; Checa, S.K.; Soncini, F.C. Integration of BrfS into the biofilm-controlling cascade promotes sessile Salmonella growth at low temperatures. Biofilm 2025, 9, 100254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Wang, L.; Zhai, R.; Ma, Q.; Liu, J.; Bao, C.; Zhang, H.; Sun, C.; Feng, X.; Gu, J.; et al. Trimeric autotransporter adhesins contribute to Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae pathogenicity in mice and regulate bacterial gene expression during interactions between bacteria and porcine primary alveolar macrophages. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2016, 109, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.L.; Fong, J.C.; Rule, C.; Rogers, A.; Yildiz, F.H.; Sandkvist, M. The Type II secretion system delivers matrix proteins for biofilm formation by Vibrio cholerae. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 4245–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, G.C.; Cisneros, D.A.; Delepierre, M.; Francetic, O.; Izadi-Pruneyre, N. 1H, 15N and 13C resonance assignments of PpdD, a type IV pilin from enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Biomol. NMR Assign. 2014, 8, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cao, Y.; Hu, X.; Lv, A. Rahnella aquatilis VgrG-mediated PANoptosis in macrophages of Carassius auratus by dual RNA-seq analysis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025, 158, 110155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Positive Reaction with the Following Substrates/Tests | ||
| D-Turanose | D-Glucuronic Acid | N-Acetyl-β-Dmannosamine |
| Glucuronamide | D-Saccharic Acid | N-Acetyl-D-Galactosamine * |
| L-Histidine | D-Gluconic Acid | D-Glucose-6-PO4 |
| L-Glutamic Acid | D-Galactose * | D-Fructose-6-PO4 |
| Acetic Acid | Glycyl-L-Proline | Bromo-Succinic Acid |
| L-Rhamnose * | Citric Acid | D-Lactic Acid Methyl Ester |
| Sucrose | Gentiobiose * | N-Acetyl-D-Glucosami |
| L-Lactic Acid | α-D-Glucose * | b-Methyl-D-Glucoside |
| D-Cellobiose * | D-Sorbito * | D-Mannose |
| Methyl Pyruvate | L-Alanine | D-Trehalose |
| 3-Methyl Glucose | D-Maltose * | L-Malic acid |
| Glycerol | Melibiose * | L-Aspartic Acid |
| L-Arginine | L-Serine | D-Mannitol * |
| Inosine | a-D-Lactose * | D-Galacturonic Acid |
| D-Fructose * | D-Salicin * | L-Galactonic Acid Lactine |
| Mucic Acid | L-Fucose * | |
| Weak Positive Reaction with the Following Substrates/Tests | ||
| Pectin | Nalidixic Acid | L-Pyroglutamic Acid |
| Quinic Acid | PH6 | c-Amino-Butyric Acid |
| Acetoacetic Acid | Vancomycin | β-Hydroxy-D, L-Butyric Acid |
| Dextrin | Sodium Lactate | a-Keto-Glutaric Acid |
| D-Raffinose | D-Malic Acid | |
| Tween40 | Formic Acid | |
| Negative Reaction with the Following Substrates/Tests | ||
| 1%NaCl | Potassium Tellurite | Fusidic Acid |
| D-Fucose * | D-Serine | Minocycline |
| Propanoic Acid | Sodium Bromate | a-Hydroxy-Butyric Acid |
| 4%NaCl | Guanidine HCl | Rifamycin SV |
| Myo-Inositol * | Aztreonam | a-Hydroxy-Butyric Acid |
| pH5 | Troleandomycin | Lincomycin |
| D-Arabitol * | Sodium Butyrate | N-Acetyl-D-Galactosam |
| Gelatin | Lithium Chloride | D-Aspartic Acid |
| Stachyose | 8%NaCl | p-Hydroxy-Phenylacetic Acid |
| D-Serine | Niaproof 4 | |
| Characteristic | Genome | Characteristic | Gnome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size of raw reads (bp) | 9,991,278 | CRISPRs | 7 |
| Size of total reads (bp) | 1,508,682,978 | VFDB | 192 |
| Size of clean reads (bp) | 9,768,592 | CARD | 143 |
| Genome size (Mb) | 4.77 | T3SS | 7 |
| GC content (%) | 48.99 | Coding gene annotated | 4445 |
| Total gene size (bp) | 4,168,185 | Coding gene assigned to eggNOG | 4149 |
| rRNA | 22 | Coding gene assigned to KEGG | 2916 |
| tRNA | 86 | Coding gene assigned to GO | 3573 |
| ncRNA | 130 | Coding gene assigned to Swiss-Prot | 3841 |
| TCS | 80 |
| ORF Name | Gene Name | VF_ID | CARD | T3SS | TNSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr_223 | aceA | VFG009263 | - | TRUE | - |
| chr_232 | pgi | VFG013531 | - | TRUE | - |
| chr_532 | lpxC | VFG013414 | ARO: 3003574 | - | - |
| chr_713 | hofB | VFG042799 | - | - | T4aP_pilB |
| chr_722 | ppdD | VFG042800 | - | - | T4aP_pilA |
| chr_723 | hemL | VFG013618 | - | TRUE | - |
| chr_769 | lpxA | VFG013394 | ARO: 3003573 | - | - |
| chr_794 | tssM1 | VFG035488 | - | - | T6SSi_tssM |
| chr_834 | clpV1 | VFG035568 | - | - | T6SSi_tssH |
| chr_836 | tssK1 | VFG035613 | - | - | T6SSi_tssK |
| chr_842 | tssC1 | VFG035762 | - | TRUE | - |
| chr_844 | hcpA | VFG041172 | - | T6SSi_tssD | |
| chr_845 | vgrGA | VFG035855 | - | - | T6SSi_tssI |
| chr_875 | phoE | VFG043568 | ARO: 3004122 | - | - |
| chr_1031 | acrB | VFG049136 | ARO: 3000216 | - | - |
| chr_1032 | acrA | VFG049125 | ARO: 3004042 | - | - |
| chr_1081 | fimF | VFG042684 | - | TRUE | - |
| chr_1471 | gspE | VFG007101 | - | - | T2SS_gspE |
| chr_1473 | outG | VFG040912 | - | - | T2SS_gspG |
| chr_1532 | msbA | VFG013253 | ARO: 3003950 | - | - |
| chr_1569 | ompA | VFG043544 | ARO: 3005044 | - | - |
| chr_1620 | csgD | VFG045791 | - | TRUE | - |
| chr_1651 | flgB | VFG043022 | - | - | Flg flgB |
| chr_1652 | flgC | VFG043075 | - | - | Flg flgC |
| chr_1653 | flgD | VFG043024 | - | TRUE | - |
| chr_1654 | flgE | VFG043077 | - | TRUE | - |
| chr_1655 | flgF | VFG043078 | - | TRUE | - |
| chr_1656 | flgG | VFG043079 | - | TRUE | Flg flgC |
| chr_1660 | flgK | VFG043083 | - | TRUE | - |
| chr_1661 | flgL | VFG043032 | - | TRUE | - |
| chr_1672 | fabG | VFG038840 | ARO: 3004049 | - | - |
| chr_1708 | phoQ | VFG021077 | ARO: 3007203 | - | - |
| chr_1709 | phoP | VFG000475 | ARO: 3003585 | - | - |
| chr_1815 | hemR | VFG012601 | - | TRUE | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Cai, H.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Shang, Y.; Wei, Q.; Sha, W.; Qi, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H. Identification and Pathogenicity Analysis of Huaxiibacter chinensis Qf-1 in Mink (Neogale vison). Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071604
Chen Y, Cai H, Wu X, Wang X, Shang Y, Wei Q, Sha W, Qi Y, Liu S, Zhang H. Identification and Pathogenicity Analysis of Huaxiibacter chinensis Qf-1 in Mink (Neogale vison). Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071604
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yao, Haotian Cai, Xiaoyang Wu, Xibao Wang, Yongquan Shang, Qinguo Wei, Weilai Sha, Yan Qi, Shuli Liu, and Honghai Zhang. 2025. "Identification and Pathogenicity Analysis of Huaxiibacter chinensis Qf-1 in Mink (Neogale vison)" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071604
APA StyleChen, Y., Cai, H., Wu, X., Wang, X., Shang, Y., Wei, Q., Sha, W., Qi, Y., Liu, S., & Zhang, H. (2025). Identification and Pathogenicity Analysis of Huaxiibacter chinensis Qf-1 in Mink (Neogale vison). Microorganisms, 13(7), 1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071604






