Microbial Food Safety and Antimicrobial Resistance in Foods: A Dual Threat to Public Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
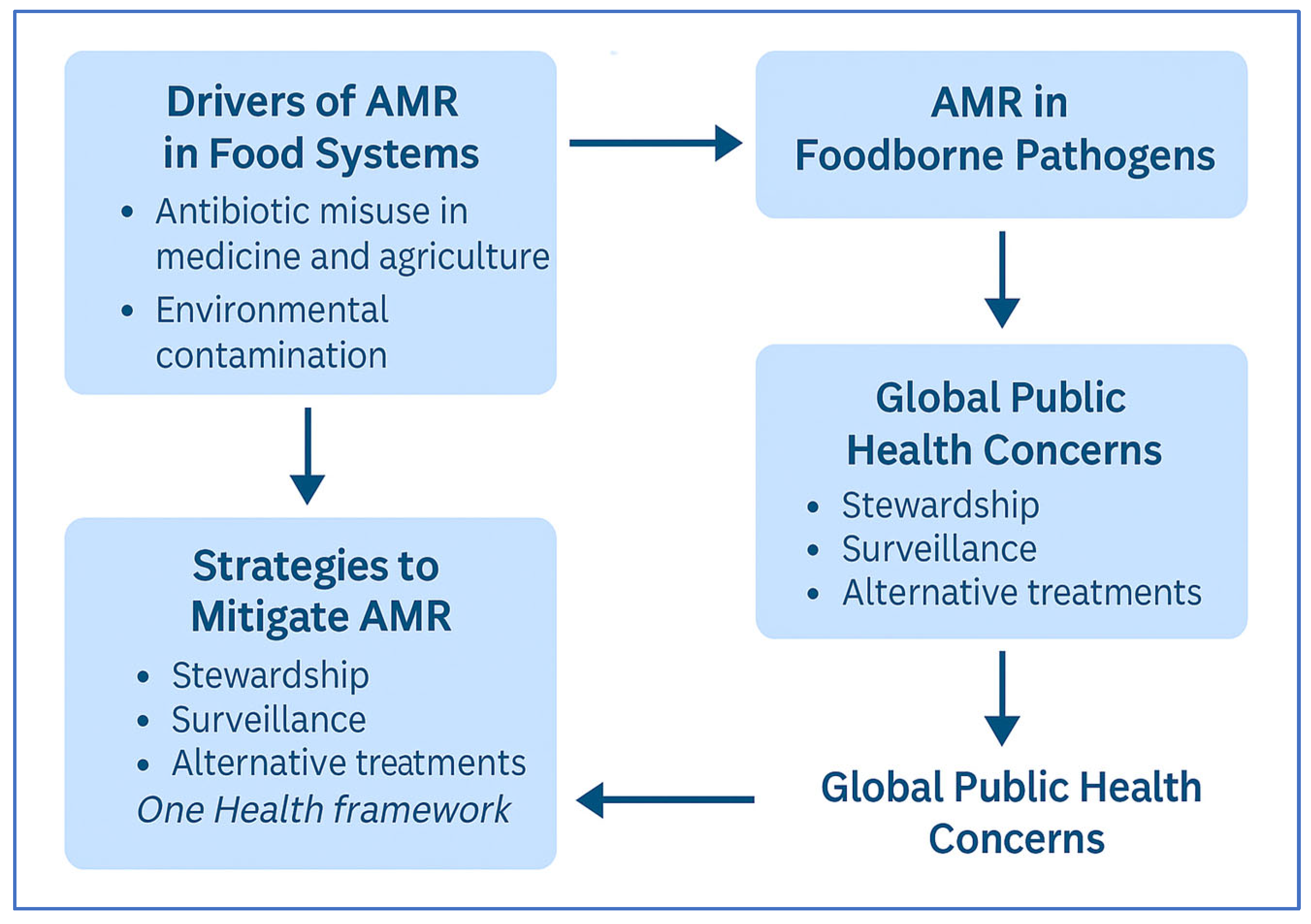
3. Foodborne Pathogens and the Burden of AMR
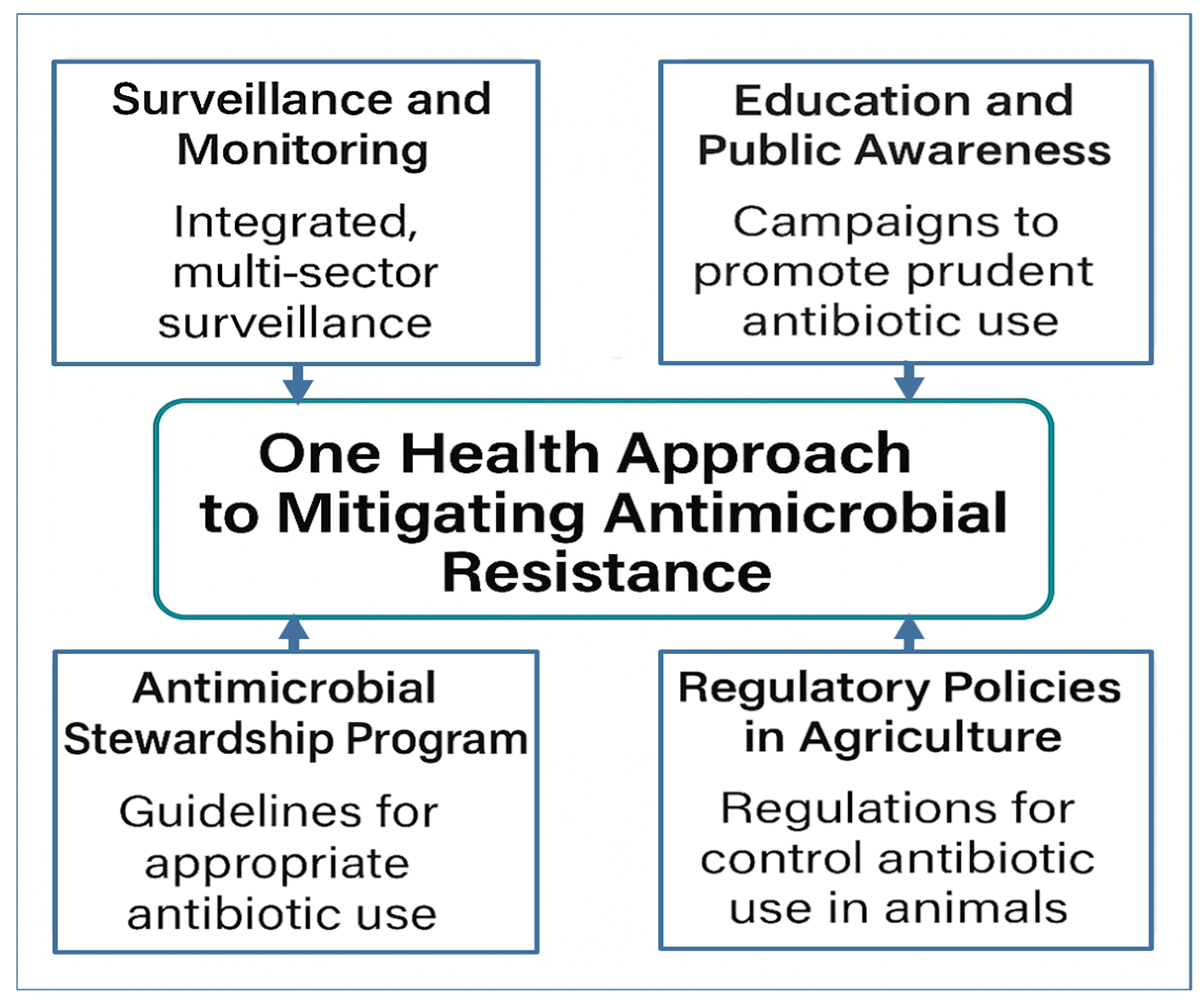
4. One Health Approach to Mitigating AMR
4.1. Conceptual Framework of One Health in AMR
4.2. Drivers of AMR Across Sectors
4.2.1. Human Health Sector
4.2.2. Animal Health and Agriculture
4.2.3. Environmental Sector
4.3. Surveillance and Monitoring
4.4. Interventions and Strategies
4.4.1. Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs (ASPs)
4.4.2. Regulatory Policies in Agriculture
4.4.3. Environmental Management
4.5. Research and Innovation
4.6. Education and Public Awareness
4.7. Global Collaboration and Policy Frameworks
5. AMR and Food Safety: A Neglected Link in One Health
5.1. Prevalence of Resistant Strains in Foods
5.2. Sources of Contamination
5.3. Biochemical and Molecular Mechanisms of AMR in Foodborne Pathogens
5.4. Prevention of Contamination
5.5. Detection Methods for AMR in Foods
5.6. Legislation and Policy
5.7. Implications for Food Security
6. Strategic Priorities and Challenges in One Health AMR Mitigation
6.1. Operationalizing One Health: Bridging Policy and Practice
6.2. Innovation and Equity: Addressing the Access Gap
6.3. Enhancing Surveillance: Integrating Environmental Data
6.4. From Awareness to Behavior Change
6.5. Strengthening Global Policy Frameworks
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verraes, C.; Van Boxstael, S.; Van Meervenne, E.; Van Coillie, E.; Butaye, P.; Catry, B.; De Schaetzen, M.-A.; Van Huffel, X.; Imberechts, H.; Dierick, K. Antimicrobial resistance in the food chain: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 2643–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, V.; Arsenov, D.; Thakur, M.; Kumar, A.; Khokhar, A.; Seth, C.S.; Kumar, R. The science of food safety and their health impacts. J. Geochem. Explor. 2024, 267, 107596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, B.M.; Levy, S.B. Food animals and antimicrobials: Impacts on human health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbergeld, E.K.; Graham, J.; Price, L.B. Industrial food animal production, antimicrobial resistance, and human health. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2008, 29, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landers, T.F.; Cohen, B.; Wittum, T.E.; Larson, E.L. A review of antibiotic use in food animals: Perspective, policy, and potential. Public Health Rep. 2012, 127, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manyi-Loh, C.; Mamphweli, S.; Meyer, E.; Okoh, A. Antibiotic use in agriculture and its consequential resistance in environmental sources: Potential public health implications. Molecules 2018, 23, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobrega, D.B.; Tang, K.L.; Caffrey, N.P.; De Buck, J.; Cork, S.C.; Ronksley, P.E.; Polachek, A.J.; Ganshorn, H.; Sharma, N.; Kastelic, J.P. Prevalence of antimicrobial resistance genes and its association with restricted antimicrobial use in food-producing animals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allel, K.; Day, L.; Hamilton, A.; Lin, L.; Furuya-Kanamori, L.; Moore, C.E.; Van Boeckel, T.; Laxminarayan, R.; Yakob, L. Global antimicrobial-resistance drivers: An ecological country-level study at the human–animal interface. Lancet Planet. Health 2023, 7, e291–e303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The European Union summary report on antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2016. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05182. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, T.P.; Bu, D.; Carrique-Mas, J.; Fèvre, E.M.; Gilbert, M.; Grace, D.; Hay, S.I.; Jiwakanon, J.; Kakkar, M.; Kariuki, S. Antibiotic resistance is the quintessential One Health issue. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 110, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendonk, T.U.; Manaia, C.M.; Merlin, C.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Cytryn, E.; Walsh, F.; Bürgmann, H.; Sørum, H.; Norström, M.; Pons, M.-N. Tackling antibiotic resistance: The environmental framework. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nethathe, B.; Matsheketsheke, P.A.; Mashau, M.E.; Ramashia, S.E. Microbial safety of ready-to-eat food sold by retailers in Thohoyandou, Limpopo province, South Africa. Cogent Food Agric. 2023, 9, 2185965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization, W.H. GLASS Manual for Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Common Bacteria Causing Human Infection. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- O’Neill, J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations. 2016. Available online: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.5555/20173071720 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Woolhouse, M.; Ward, M.; Van Bunnik, B.; Farrar, J. Antimicrobial resistance in humans, livestock and the wider environment. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.L. Environmental pollution by antibiotics and by antibiotic resistance determinants. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2893–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammie, S.L.; Hughes, J.M. Antimicrobial resistance, food safety, and one health: The need for convergence. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 7, 287–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, A.; van Klinken, R.D.; Jones, D.; Wang, J. Consumers’ perspectives on antibiotic use and antibiotic resistance in food animals: A systematic review. npj Sci. Food 2025, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.W.-T.; Ng, I.C.-F.; Wong, E.Y.-K.; Wong, I.T.-F.; Sze, R.P.-P.; Chan, K.-Y.; So, T.-Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fung, S.K.-Y.; Wong, S.C.-Y. Comprehensive identification of pathogenic microbes and antimicrobial resistance genes in food products using nanopore sequencing-based metagenomics. Food Microbiol. 2024, 121, 104493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.L.; Caffrey, N.P.; Nóbrega, D.B.; Cork, S.C.; Ronksley, P.E.; Barkema, H.W.; Polachek, A.J.; Ganshorn, H.; Sharma, N.; Kellner, J.D. Restricting the use of antibiotics in food-producing animals and its associations with antibiotic resistance in food-producing animals and human beings: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Planet. Health 2017, 1, e316–e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The FAO Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance 2016–2020. 2016. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/70dd55f7-3348-4895-b651-76308101cb45/content (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States; US Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 67–100. [Google Scholar]
- Hollis, A.; Ahmed, Z. The path of least resistance: Paying for antibiotics in non-human uses. Health Policy 2014, 118, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, Á.; Sweeney, S.; McKernan, C.; Benson, T.; Dean, M. Consumer perception and understanding of the risks of antibiotic use and antimicrobial resistance in farming. Agric. Hum. Values 2023, 40, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasimanickam, V.; Kasimanickam, M.; Kasimanickam, R. Antibiotics use in food animal production: Escalation of antimicrobial resistance: Where are we now in combating AMR? Med. Sci. 2021, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adebisi, Y.A. Balancing the risks and benefits of antibiotic use in a globalized world: The ethics of antimicrobial resistance. Glob. Health 2023, 19, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havelaar, A.H.; Kirk, M.D.; Torgerson, P.R.; Gibb, H.J.; Hald, T.; Lake, R.J.; Praet, N.; Bellinger, D.C.; De Silva, N.R.; Gargouri, N. World Health Organization global estimates and regional comparisons of the burden of foodborne disease in 2010. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxminarayan, R.; Duse, A.; Wattal, C.; Zaidi, A.K.; Wertheim, H.F.; Sumpradit, N.; Vlieghe, E.; Hara, G.L.; Gould, I.M.; Goossens, H. Antibiotic resistance—The need for global solutions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 1057–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujat Choy, S.; Neumann, E.-M.; Romero-Barrios, P.; Tamber, S. Contribution of Food to the Human Health Burden of Antimicrobial Resistance. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2024, 21, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriksen, R.S.; Munk, P.; Njage, P.; Van Bunnik, B.; McNally, L.; Lukjancenko, O.; Röder, T.; Nieuwenhuijse, D.; Pedersen, S.K.; Kjeldgaard, J. Global monitoring of antimicrobial resistance based on metagenomics analyses of urban sewage. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Tan, A.; Zhao, F.; Wang, F.; Gong, H.; Lai, Y.; Huang, Z. Global distribution of antimicrobial resistance genes in aquaculture. One Health Adv. 2025, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H. A review of antibiotics, antibiotic resistant bacteria, and resistance genes in aquaculture: Occurrence, contamination, and transmission. Toxics 2023, 11, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Nagano, I.; Masunaga, S.; Kitazawa, D.; Matsuda, H. Antibiotics, antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and resistance genes in aquaculture: Risks, current concern, and future thinking. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 11054–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.; Gray, J.; Chandry, P.S.; Fox, E.M. Phenotypic and genotypic analysis of antimicrobial resistance among Listeria monocytogenes isolated from Australian food production chains. Genes 2018, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unicomb, L.E.; Fullerton, K.E.; Kirk, M.D.; Stafford, R.J. Outbreaks of campylobacteriosis in Australia, 2001 to 2006. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2009, 6, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieczorek, K.; Osek, J. Antimicrobial resistance mechanisms among Campylobacter. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 340605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2020/2021. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e07867. [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn, B.M. CDC establishes global networks to combat antimicrobial resistance. JAMA 2022, 327, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2018/2019. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06490. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.; Yang, G.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Ding, Y.; Su, Y.; Ye, Q.; Wu, S. High prevalence of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli in retail aquatic products in China and the first report of mcr-1-positive extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing E. coli ST2705 and ST10 in fish. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 408, 110449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, C.; De Paepe, K.; Galia, W.; De Bodt, J.; Chalancon, S.; Denis, S.; Leriche, F.; Vandekerkove, P.; Ballet, N.; Blanquet-Diot, S. Multi-targeted properties of the probiotic saccharomyces cerevisiae CNCM I-3856 against enterotoxigenic escherichia coli (ETEC) H10407 pathogenesis across human gut models. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1953246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, M.; Rahman, S.U.; Bilal, H.; Ullah, A.; Noman, S.M.; Zeng, M.; Yuan, Y.; Xie, Q.; Li, X.; Jiao, X. Incidence and molecular characterization of ESBL-producing and colistin-resistant Escherichia coli isolates recovered from healthy food-producing animals in Pakistan. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 1169–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Hu, H.-W.; Chen, Q.-L.; Singh, B.K.; Yan, H.; Chen, D.; He, J.-Z. Transfer of antibiotic resistance from manure-amended soils to vegetable microbiomes. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-G.; Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, Y.-S.; Zhang, T.; Gillings, M.R.; Su, J.-Q. Continental-scale pollution of estuaries with antibiotic resistance genes. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 16270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keet, R.; Rip, D. Listeria monocytogenes isolates from Western Cape, South Africa exhibit resistance to multiple antibiotics and contradicts certain global resistance patterns. AIMS Microbiol. 2021, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovic Fabijan, A.; Lin, R.C.; Ho, J.; Maddocks, S.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Iredell, J.R.; Westmead Bacteriophage Therapy Team. Safety of bacteriophage therapy in severe Staphylococcus aureus infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, G.; Popa, L.I.; Marutescu, L.; Gheorghe, I.; Popa, M.; Czobor Barbu, I.; Cristescu, R.; Chifiriuc, M.-C. Bacteriocins in the era of antibiotic resistance: Rising to the challenge. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijbom, M.; Büchner, F.L.; Saadah, N.H.; Numans, M.E.; De Boer, M.G. Determinants of inappropriate antibiotic prescription in primary care in developed countries with general practitioners as gatekeepers: A systematic review and construction of a framework. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e065006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, A.J.; Chipeta, M.G.; Haines-Woodhouse, G.; Kumaran, E.P.; Hamadani, B.H.K.; Zaraa, S.; Henry, N.J.; Deshpande, A.; Reiner, R.C.; Day, N.P. Global antibiotic consumption and usage in humans, 2000–2018: A spatial modelling study. Lancet Planet. Health 2021, 5, e893–e904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming-Dutra, K.E.; Hersh, A.L.; Shapiro, D.J.; Bartoces, M.; Enns, E.A.; File, T.M.; Finkelstein, J.A.; Gerber, J.S.; Hyun, D.Y.; Linder, J.A. Prevalence of inappropriate antibiotic prescriptions among US ambulatory care visits, 2010–2011. JAMA 2016, 315, 1864–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, L.A.; van Santen, K.L.; Weiner, L.M.; Dudeck, M.A.; Edwards, J.R.; Srinivasan, A. Antibiotic stewardship programs in US acute care hospitals: Findings from the 2014 National Healthcare Safety Network Annual Hospital Survey. Rev. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Core Elements of Hospital Antibiotic Stewardship Programs. 2024. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/hcp/core-elements/hospital.html (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Ardillon, A.; Ramblière, L.; Kermorvant-Duchemin, E.; Sok, T.; Zo, A.Z.; Diouf, J.-B.; Long, P.; Lach, S.; Sarr, F.D.; Borand, L. Inappropriate antibiotic prescribing and its determinants among outpatient children in 3 low-and middle-income countries: A multicentric community-based cohort study. PLoS Med. 2023, 20, e1004211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Pires, J.; Silvester, R.; Zhao, C.; Song, J.; Criscuolo, N.G.; Gilbert, M.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial resistance in animals in low-and middle-income countries. Science 2019, 365, eaaw1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, A.; Tirkaso, W.; Nicolli, F.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Cinardi, G.; Song, J. The future of antibiotic use in livestock. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citaristi, I. United Nations Environment Programme—UNEP. In The Europa Directory of International Organizations 2022; Routledge: London, UK, 2022; pp. 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, C.; Naughton, P.J.; Dooley, J.S.; Corcionivoschi, N.; Brooks, C. The spread of antimicrobial resistance in the aquatic environment from faecal pollution: A scoping review of a multifaceted issue. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández Salgueiro, M.; Cernuda Martínez, J.A.; Gan, R.K.; Arcos González, P. Climate change and antibiotic resistance: A scoping review. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2024, 16, e70008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, D.J.; Flach, C.-F. Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) Report 2022. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240062702 (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- ECDC. Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Europe 2022—EARS-Net Annual Report. 2022. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/surveillance-antimicrobial-resistance-europe-2022 (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC); European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Medicines Agency (EMA). Antimicrobial consumption and resistance in bacteria from humans and food-producing animals: Fourth joint inter-agency report on integrated analysis of antimicrobial agent consumption and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from humans and food-producing animals in the EU/EEA JIACRA IV–2019−2021. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e8589. [Google Scholar]
- CDC. National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (NARMS): About NARMS. 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/narms/about/index.html (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- The Fleming Fund. How the Fleming Fund Has Worked to Build Surveillance Capacity in LMICs Across Human and Animal Health Sectors. 2023. Available online: https://www.flemingfund.org/publications/how-the-fleming-fund-has-worked-to-build-surveillance-capacity-in-lmics-across-human-and-animal-health-sectors/ (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- FAO. FAO Assessment Tool for Laboratories and AMR Surveillance Systems (ATLASS); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2023; Available online: https://www.fao.org/antimicrobial-resistance/resources/tools/fao-atlass/en/ (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Argimón, S.; Masim, M.A.; Gayeta, J.M.; Lagrada, M.L.; Macaranas, P.K.; Cohen, V.; Limas, M.T.; Espiritu, H.O.; Palarca, J.C.; Chilam, J. Integrating whole-genome sequencing within the National Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Program in the Philippines. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyar, O.J.; Huttner, B.; Schouten, J.; Pulcini, C. What is antimicrobial stewardship? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, D.; Gladstone, B.P.; Burkert, F.; Carrara, E.; Foschi, F.; Döbele, S.; Tacconelli, E. Effect of antibiotic stewardship on the incidence of infection and colonisation with antibiotic-resistant bacteria and Clostridium difficile infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Menon, V.P.; Mohamed, Z.U.; Kumar, V.A.; Nampoothiri, V.; Sudhir, S.; Moni, M.; Dipu, T.; Dutt, A.; Edathadathil, F. Implementation and impact of an antimicrobial stewardship program at a tertiary care center in South India. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, ofy290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, F.; De, R.G.; Chakraborty, D.; Majumdar, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Sarkar, M.D.; Singh, T.; Patra, S.K.; Saha, S.; Rehman, J. Antimicrobial stewardship implementation in primary and secondary tier hospitals in India: Interim findings from a need assessment study using mixed method design. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahni, A.; Bahl, A.; Martolia, R.; Jain, S.K.; Singh, S.K. Implementation of antimicrobial stewardship activities in India. Indian J. Med. Spec. 2020, 11, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Aarestrup, F.M. The livestock reservoir for antimicrobial resistance: A personal view on changing patterns of risks, effects of interventions and the way forward. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Summary Report on Antimicrobials Sold or Distributed for Use in Food-Producing Animals. 2023. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/animal-veterinary/antimicrobial-resistance/2022-summary-report-antimicrobials-sold-or-distributed-use-food-producing-animals (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.-X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dar, O.A.; Hasan, R.; Schlundt, J.; Harbarth, S.; Caleo, G.; Dar, F.K.; Littmann, J.; Rweyemamu, M.; Buckley, E.J.; Shahid, M. Exploring the evidence base for national and regional policy interventions to combat resistance. Lancet 2016, 387, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, L.; Manaia, C.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Ploy, M.-C.; Michael, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.J.; Andremont, A.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Brandt, K.K.; de Roda Husman, A.M.; Fagerstedt, P.; Fick, J.; Flach, C.-F.; Gaze, W.H.; Kuroda, M. Critical knowledge gaps and research needs related to the environmental dimensions of antibiotic resistance. Environ. Int. 2018, 117, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedon, S.T.; García, P.; Mullany, P.; Aminov, R. Phage therapy: Past, present and future. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxminarayan, R.; Sridhar, D.; Blaser, M.; Wang, M.; Woolhouse, M. Achieving global targets for antimicrobial resistance. Science 2016, 353, 874–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, A.A.; Klumpe, H.E.; Luo, M.L.; Selle, K.; Barrangou, R.; Beisel, C.L. Programmable removal of bacterial strains by use of genome-targeting CRISPR-Cas systems. MBio 2014, 5, e00928-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; McBride, S.W.; Hullahalli, K.; Palmer, K.L.; Duerkop, B.A. Conjugative delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 for the selective depletion of antibiotic-resistant enterococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolti, O.; Suganthan, B.; Ramasamy, R.P. Lab-on-a-chip electrochemical biosensors for foodborne pathogen detection: A review of common standards and recent progress. Biosensors 2023, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, K.; Chandra, P. based miniaturized immunosensor for naked eye ALP detection based on digital image colorimetry integrated with smartphone. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 128, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, R.-L.E.; Natasha, N.T.; Edward, G.D. Regulatory Landscape and the Potential of Bacteriophage Applications in the United States’ Food Industry. J. Food Prot. 2025, 88, 100510. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez de la Lastra, J.M.; González-Acosta, S.; Otazo-Pérez, A.; Asensio-Calavia, P.; Rodríguez-Borges, V.M. Antimicrobial Peptides for Food Protection: Leveraging Edible Mushrooms and Nano-Innovation. Dietetics 2025, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, A.; Parekh, S.; Rathbone, J.; Del Mar, C.; Hoffmann, T. A systematic review of the public’s knowledge and beliefs about antibiotic resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttner, B.; Goossens, H.; Verheij, T.; Harbarth, S. Characteristics and outcomes of public campaigns aimed at improving the use of antibiotics in outpatients in high-income countries. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapot, L.; Sarker, M.S.; Begum, R.; Hossain, D.; Akter, R.; Hasan, M.M.; Bupasha, Z.B.; Bayzid, M.; Salauddin, M.; Parvej, M.S. Knowledge, attitudes and practices regarding antibiotic use and resistance among veterinary students in Bangladesh. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. World Antimicrobial Awareness Week. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/campaigns/world-amr-awareness-week/2024 (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- WHO. World Antimicrobial Awareness Week. 2015. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/events/detail/2015/11/16/default-calendar/world-antibiotic-awareness-week (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Codex Alimentarius Commission. Guidelines on Integrated Monitoring and Surveillance of Foodborne Antimicrobial Resistance (CXG 94-2021); FAO and WHO: Rome, Italy, 2021; Available online: https://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/sh-proxy/de/?lnk=1&url=https%3A%2F%2Fworkspace.fao.org%2Fsites%2Fcodex%2FStandards%2FCXG%2B94-2021%2FCXG_94e.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- CARB-X. Collaboration. 2024. Available online: https://globalamrhub.org/collaboration/ (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- WHO. Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) Report 2023. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240070424 (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Severino, N.; Reyes, C.; Fernandez, Y.; Azevedo, V.; Francisco, L.E.D.; Ramos, R.T.; Maroto-Martín, L.O.; Franco, E.F. Bacterial Foodborne Diseases in Central America and the Caribbean: A Systematic Review. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Satola, S.W.; Read, T.D. Genome-based prediction of bacterial antibiotic resistance. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01405-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, D. Food safety in low and middle income countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 10490–10507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Chang, J.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, H.; Liu, C.; Xiao, X.; Ji, X.; Yang, H. Prevalence and characteristics of the mcr-1 gene in retail meat samples in Zhejiang Province, China. J. Microbiol. 2022, 60, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhung, N.T.; Van, N.T.B.; Van Cuong, N.; Duong, T.T.Q.; Nhat, T.T.; Hang, T.T.T.; Nhi, N.T.H.; Kiet, B.T.; Hien, V.B.; Ngoc, P.T. Antimicrobial residues and resistance against critically important antimicrobials in non-typhoidal Salmonella from meat sold at wet markets and supermarkets in Vietnam. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 266, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phung, T.; Tran, T.; Pham, D.; To, A.; Le, H. Occurrence and molecular characteristics of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from ready-to-eat meats in Hanoi, Vietnam. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2020, 9, 8772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayode, A.J.; Okoh, A.I. Antimicrobial-resistant Listeria monocytogenes in ready-to-eat foods: Implications for food safety and risk assessment. Foods 2023, 12, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, W.A.; Ahmed, A.M.; Hegazy, Y.; Torky, H.A.; Shimamoto, T. High prevalence of ESBL and plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in Salmonella enterica isolated from retail meats and slaughterhouses in Egypt. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bort, B.; Martí, P.; Mormeneo, S.; Mormeneo, M.; Iranzo, M. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter spp. isolated from broilers throughout the supply chain in Valencia, Spain. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2022, 19, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasho, R.P.; Cho, J.Y. Veterinary antibiotics in animal waste, its distribution in soil and uptake by plants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Araújo, S.; Monteiro, A.; Eira, J.; Pereira, J.E.; Maltez, L.; Igrejas, G.; Lemsaddek, T.S.; Poeta, P. Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA in livestock: Antimicrobial resistance and genetic lineages. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazards, E.P.o.B.; Koutsoumanis, K.; Allende, A.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Bolton, D.; Bover-Cid, S.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; De Cesare, A.; Hilbert, F. Update of the list of QPS-recommended biological agents intentionally added to food or feed as notified to EFSA 14: Suitability of taxonomic units notified to EFSA until March 2021. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06689. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, A.K.; Zhang, L.; Yin, X.; Zhang, T.; Buckling, A.; Snape, J.; Gaze, W.H. Novel insights into selection for antibiotic resistance in complex microbial communities. MBio 2018, 9, e00969-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, E.D.; Dassanayake, R.P.; Bearson, S.M. Increasing antimicrobial susceptibility of MDR Salmonella with the efflux pump inhibitor 1-(1-Naphthylmethyl)-piperazine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 668, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalaf, A.A.; El-Ghareeb, W.R.; Raheem, S.M.; Seliem, M.M.; Shosha, A.M.; Elzawahry, R.R. A study on the prevalence of multidrug resistant food poisoning Salmonella spp. in camel meat and offal with a reduction trial using organic acids. J. Adv. Vet. Res. 2024, 14, 526–530. [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby, G.A.; Strahilevitz, J.; Hooper, D.C. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance. Plasmids Biol. Impact Biotechnol. Discov. 2015, 30, 475–503. [Google Scholar]
- Eaves, D.J.; Randall, L.; Gray, D.T.; Buckley, A.; Woodward, M.J.; White, A.P.; Piddock, L.J. Prevalence of mutations within the quinolone resistance-determining region of gyrA, gyrB, parC, and parE and association with antibiotic resistance in quinolone-resistant Salmonella enterica. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4012–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, A.; Gaballa, A.; Yang, H.; Yu, D.; Ernst, R.K.; Wiedmann, M. Site-selective modifications by lipid A phosphoethanolamine transferases linked to colistin resistance and bacterial fitness. mSphere 2024, 9, e00731-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racewicz, P.; Majewski, M.; Madeja, Z.E.; Łukomska, A.; Kubiak, M. Role of integrons in the proliferation of multiple drug resistance in selected bacteria occurring in poultry production. Br. Poult. Sci. 2020, 61, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, S.A.; Collignon, P.J. Antimicrobial resistance: A one health perspective. In Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria from Livestock and Companion Animals; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 521–547. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, V.T.; Smith, K.F.; Melvin, D.W.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A. Community assembly of a euryhaline fish microbiome during salinity acclimation. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 2537–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, A.; Tourdjman, M.; Leclercq, A.; Hamelin, E.; Laurent, E.; Fredriksen, N.; Van Cauteren, D.; Bracq-Dieye, H.; Thouvenot, P.; Vales, G. Real-time whole-genome sequencing for surveillance of Listeria monocytogenes, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.-N.; Gaston, J.M.; Dai, C.L.; Zhao, S.; Poyet, M.; Groussin, M.; Yin, X.; Li, L.-G.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.; Topp, E. An omics-based framework for assessing the health risk of antimicrobial resistance genes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. Electrochemical biosensors for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7. Talanta 2017, 162, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassini, A.; Högberg, L.D.; Plachouras, D.; Quattrocchi, A.; Hoxha, A.; Simonsen, G.S.; Colomb-Cotinat, M.; Kretzschmar, M.E.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Cecchini, M. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: A population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schar, D.; Klein, E.Y.; Laxminarayan, R.; Gilbert, M.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Global trends in antimicrobial use in aquaculture. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cella, E.; Giovanetti, M.; Benedetti, F.; Scarpa, F.; Johnston, C.; Borsetti, A.; Ceccarelli, G.; Azarian, T.; Zella, D.; Ciccozzi, M. Joining forces against antibiotic resistance: The one health solution. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delpy, L.; Astbury, C.C.; Aenishaenslin, C.; Ruckert, A.; Penney, T.L.; Wiktorowicz, M.; Ciss, M.; Benko, R.; Bordier, M. Integrated surveillance systems for antibiotic resistance in a One Health context: A scoping review. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global AMR R&D Hub. Situation Analysis: Antibiotic Use and Resistance Monitoring in LMICs—Gaps and Opportunities; Global AMR R&D Hub: Berlin, Germany, 2023; Available online: https://globalamrhub.org (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- World Health Organization. Regional Strategy on Antimicrobial Resistance 2023–2027; WHO SEARO: New Delhi, India, 2023; Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/searo/india/antimicrobial-resistance/rev-sea-hlm-407.pdf?sfvrsn=986ba503_2 (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Wirtz, V.J.; Hogerzeil, H.V.; Gray, A.L.; Bigdeli, M.; de Joncheere, C.P.; Ewen, M.A.; Gyansa-Lutterodt, M.; Jing, S.; Luiza, V.L.; Mbindyo, R.M. Essential medicines for universal health coverage. Lancet 2017, 389, 403–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Hu, L.-X.; Liu, Y.-S.; Zhao, J.-L.; He, L.-Y.; Ying, G.-G. Microalgae-based technology for antibiotics removal: From mechanisms to application of innovational hybrid systems. Environ. Int. 2021, 155, 106594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JPIAMR. Environmental Dimensions of Antimicrobial Resistance: Current Surveillance Approaches and Research Needs. 2022. Available online: https://www.jpiamr.eu/environment (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Leonard, A.F.; Zhang, L.; Balfour, A.J.; Garside, R.; Gaze, W.H. Human recreational exposure to antibiotic resistant bacteria in coastal bathing waters. Environ. Int. 2015, 82, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwu, E.E.; Oladele, D.A.; Enwuru, C.A.; Gogwan, P.L.; Abuh, D.; Audu, R.A.; Ogunsola, F.T. Antimicrobial resistance awareness and antibiotic prescribing behavior among healthcare workers in Nigeria: A national survey. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenssgen, M.J.; Charoenboon, N.; Zanello, G.; Mayxay, M.; Reed-Tsochas, F.; Lubell, Y.; Wertheim, H.; Lienert, J.; Xayavong, T.; Zaw, Y.K. Antibiotic knowledge, attitudes and practices: New insights from cross-sectional rural health behaviour surveys in low-income and middle-income South-East Asia. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e028224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwood, J.; Cabral, C.; Hay, A.D.; Ingram, J. Primary care clinician antibiotic prescribing decisions in consultations for children with RTIs: A qualitative interview study. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2016, 66, e207–e213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeker, D.; Knight, T.K.; Friedberg, M.W.; Linder, J.A.; Goldstein, N.J.; Fox, C.R.; Rothfeld, A.; Diaz, G.; Doctor, J.N. Nudging guideline-concordant antibiotic prescribing: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2014, 174, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.R.; Mathur, V.P. Anti-microbial resistance and dentistry. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2021, 32, 272–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirota, M.; Habersaat, K.B.; Betsch, C.; Bonga, D.L.; Borek, A.; Buckel, A.; Butler, R.; Byrne-Davis, L.; Caudell, M.; Charani, E. We must harness the power of social and behavioural science against the growing pandemic of antimicrobial resistance. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2024, 8, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kickbusch, I.; Szabo, M.M.C. A new governance space for health. Glob. Health Action 2014, 7, 23507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Quadripartite Key Recommendations and Priorities for the 2024 UNGA High-Level Meeting on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)—A Policy Brief. 2024. Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/policy-and-strategy/quadripartite-key-recommendations-and-priorities-2024-unga-high-level (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Amir, A.; Tellez, V.M. Leveraging the Antimicrobial Resistance Declarations of 2024 to Reduce the Burden of Drug-Resistant Infections. 2023. Available online: https://www.southcentre.int/policy-brief-137-14-march-2025/ (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- WHO. Integrated Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Foodborne Bacteria Application of a One Health Approach. 2017. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/255747/9789241512411-eng.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Tiseo, K.; Huber, L.; Gilbert, M.; Robinson, T.P.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals from 2017 to 2030. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwu, E.E.; Oladele, D.A.; Awoderu, O.B.; Afocha, E.E.; Lawal, R.G.; Abdus-Salam, I.; Ogunsola, F.T.; Audu, R.A. A national survey of public awareness of antimicrobial resistance in Nigeria. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Action Against Antimicrobial Resistance Requires a One Health Approach. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/publications/i/item/WHO-EURO-2024-9510-49282-73655?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 29 June 2025).

| Agency/Program | Key Role(s) | Coordination and Interaction |
|---|---|---|
| WHO | Oversees the GLASS, which standardizes AMR and antimicrobial consumption data—including for food and environment—across participating countries. | Works with FAO, WOAH, and United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) under the Quadripartite/Tripartite One Health alliance. |
| FAO | Implements the Progressive Management Pathway for AMR (PMP-AMR) to support agriculture in managing AMR and food safety. | Engages in One Health collaboration with WHO and WOAH and supports national AMR Action Plans. |
| WOAH | Develops veterinary antimicrobial use standards, monitors AMR in animals, and promotes stewardship. | Partners with WHO, FAO, and member countries through One Health initiatives. |
| GLASS | Collects harmonized data on AMR and antimicrobial consumption from human, animal, and environmental sectors. | Integrates regional networks (e.g., European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net), Central Asian and Eastern European Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance) and feeds data to WHO. |
| EFSA | Monitors AMR in food- and animal-origin samples within the EU. | Coordinates with European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) to support EU risk assessments and policy. |
| ECDC | Tracks AMR in human pathogens through EARS-Net and contributes to EU-level surveillance. | Collaborates with EFSA and national agencies under One Health. |
| NARMS | Monitors AMR in human, food, and animal bacterial samples via a One Health approach. | Led jointly by CDC, FDA, and USDA; supports data-driven interventions. |
| CDC Global AMR Lab and Response Network | Strengthens AMR detection capacity and rapid response through global lab networks. | Partners with international agencies; supports ~50 countries. |
| Global Leaders Group on AMR | Provides high-level advocacy and policy guidance to spur AMR action with a One Health lens. | Supported by a Quadripartite secretariat (WHO, FAO, WOAH, UNEP). |
| Study (Author, Year) | Country/Region | Food Type | Key Findings on AMR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tang et al. [99] | China | Retail pork and chicken meat | 13% E. coli carried mcr-1; most co-produced ESBLs, indicating co-resistance to critical antibiotics |
| Nhung et al. [100] | Vietnam | Retail meat | >50% Salmonella MDR; high resistance to fluoroquinolones and ESBLs |
| Adel et al. [103] | Egypt | Retail meats and slaughterhouse isolates | 82.4% S. enterica MDR; 41.2% ESBL producers; 67.6% carried plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes (qnrA, qnrB, qnrS) |
| Kayode & Okoh [102] | South Africa | RTE foods | 83.5% L. monocytogenes MDR; 53% resistant to ceftriaxone; 61.9% to trimethoprim; 62.9% to oxytetracycline |
| Bort et al. [104] | Spain | Broiler production chain | 97.6% Campylobacter resistant to ≥1 antibiotic; high resistance to fluoroquinolones and macrolides |
| Shafiq et al. [44] | Pakistan | Food-producing animals | ESBL-producing, colistin-resistant E. coli isolated from healthy animals |
| Zhang et al. [42] | China | Retail aquatic products | High prevalence of MDR E. coli; first report of mcr-1-positive ESBL-producing E. coli ST2705 and ST10 in fish |
| Thematic Area | Key Finding | Reference | Strategic Recommendation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microbial Food Safety and AMR Threats | High prevalence of MDR Salmonella, E. coli, L. monocytogenes, and Campylobacter in foods, especially ready-to-eat products across the EU | [41] | Implement farm-to-fork microbiological monitoring programs targeting RTE and minimally processed foods | [139] |
| Antibiotic Use in Food Production | Non-therapeutic use of antimicrobials (e.g., growth promotion) is a major AMR driver in livestock | [30] | Ban prophylactic antimicrobial use, enforce veterinary oversight, and promote stewardship in animal sectors | [139] |
| Environmental Reservoirs | Sewage and agricultural runoff harbor diverse AMR genes, reflecting environmental contamination | [32] | Integrate environmental samples (wastewater, manure, soil) into AMR surveillance; enhance pollution control | [139] |
| One Health Implementation | Fragmented governance hinders multisectoral coordination in AMR control | [122] | Establish inter-ministerial One Health coordination platforms and capacity building in risk analysis | [122] |
| Surveillance Gaps | Underrepresentation of animal and environmental data in national AMR systems | [41] | Broaden AMR surveillance to include metagenomic and wastewater approaches; support LMIC implementation | [32] |
| Innovation and Access Inequalities | Aquaculture AMU is rising (~93,000 t in 2017, projected +11.5% by 2030); LMIC diagnostics remain limited | [30,140] | Invest in affordable diagnostics in LMICs; support regional labs and rapid molecular tools | [140] |
| Behavior Change and Public Awareness | AMR awareness campaigns alone often fail to change prescribing behavior | [141] | Integrate behavioral nudges, peer comparison, and electronic prescribing feedback in stewardship | [133] |
| Policy and Governance Challenges | Global AMR strategies have variable national implementation; funding remains inadequate | [142] | Support local adaptation; embed AMR plans into national health and development agendas; secure sustainable financing | [141] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elbehiry, A.; Marzouk, E.; Abalkhail, A.; Edrees, H.M.; Ellethy, A.T.; Almuzaini, A.M.; Ibrahem, M.; Almujaidel, A.; Alzaben, F.; Alqrni, A.; et al. Microbial Food Safety and Antimicrobial Resistance in Foods: A Dual Threat to Public Health. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071592
Elbehiry A, Marzouk E, Abalkhail A, Edrees HM, Ellethy AT, Almuzaini AM, Ibrahem M, Almujaidel A, Alzaben F, Alqrni A, et al. Microbial Food Safety and Antimicrobial Resistance in Foods: A Dual Threat to Public Health. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071592
Chicago/Turabian StyleElbehiry, Ayman, Eman Marzouk, Adil Abalkhail, Husam M. Edrees, Abousree T. Ellethy, Abdulaziz M. Almuzaini, Mai Ibrahem, Abdulrahman Almujaidel, Feras Alzaben, Abdullah Alqrni, and et al. 2025. "Microbial Food Safety and Antimicrobial Resistance in Foods: A Dual Threat to Public Health" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071592
APA StyleElbehiry, A., Marzouk, E., Abalkhail, A., Edrees, H. M., Ellethy, A. T., Almuzaini, A. M., Ibrahem, M., Almujaidel, A., Alzaben, F., Alqrni, A., & Abu-Okail, A. (2025). Microbial Food Safety and Antimicrobial Resistance in Foods: A Dual Threat to Public Health. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071592







