Probiotic Supplementation Improves Gut Microbiota in Chronic Metabolic and Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases Among Chinese Adults over 60: Study Using Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Cohorts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Probiotic Strains
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Study Cohorts
2.4. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Cohorts
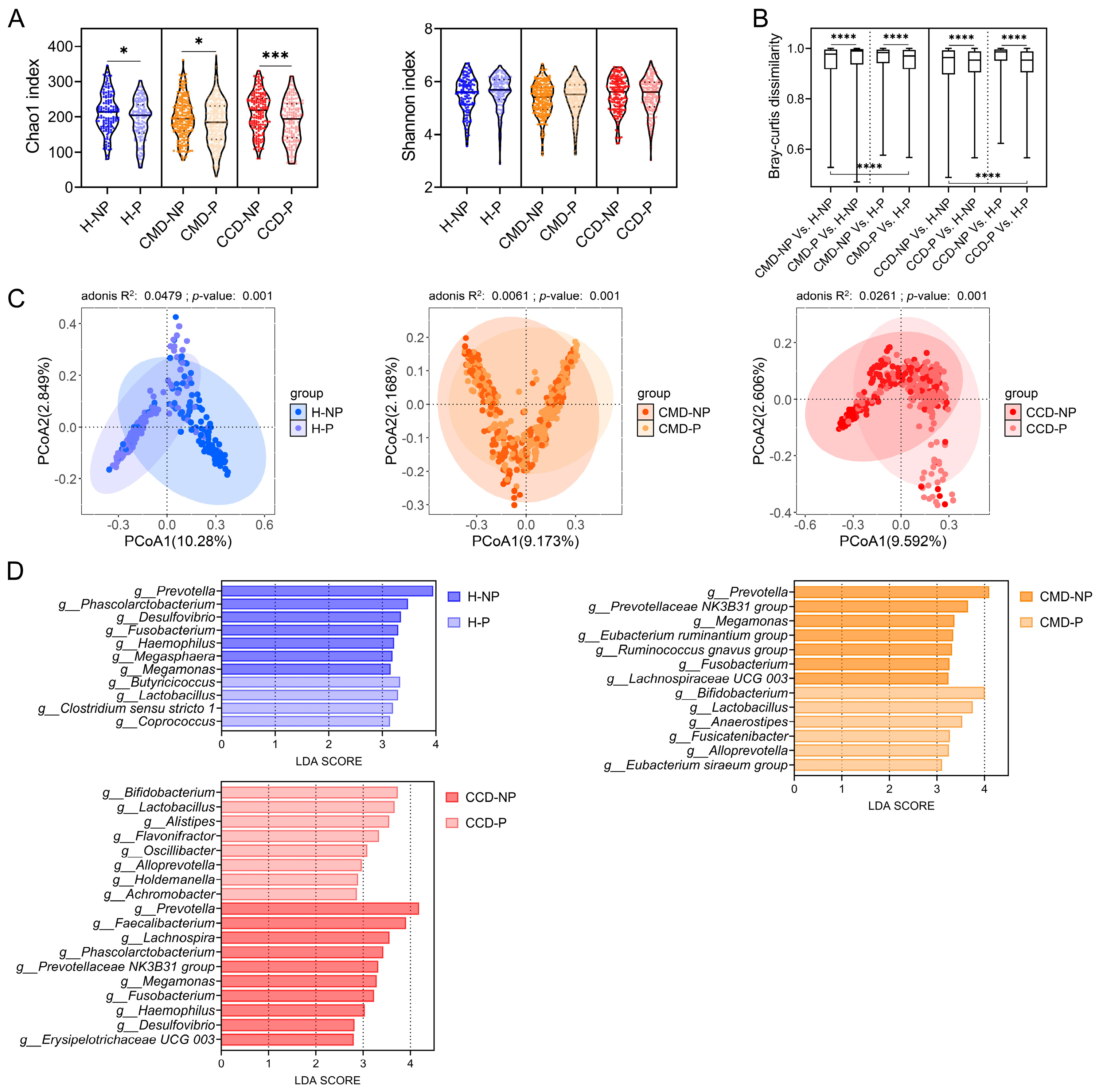
3.2. Patients with CMD or CCD Exhibit Differences in Gut Microbiota Composition Compared to Healthy Controls
3.3. Probiotic Supplementation Promotes Abundance of Beneficial Bacteria in the CMD and CCD Groups
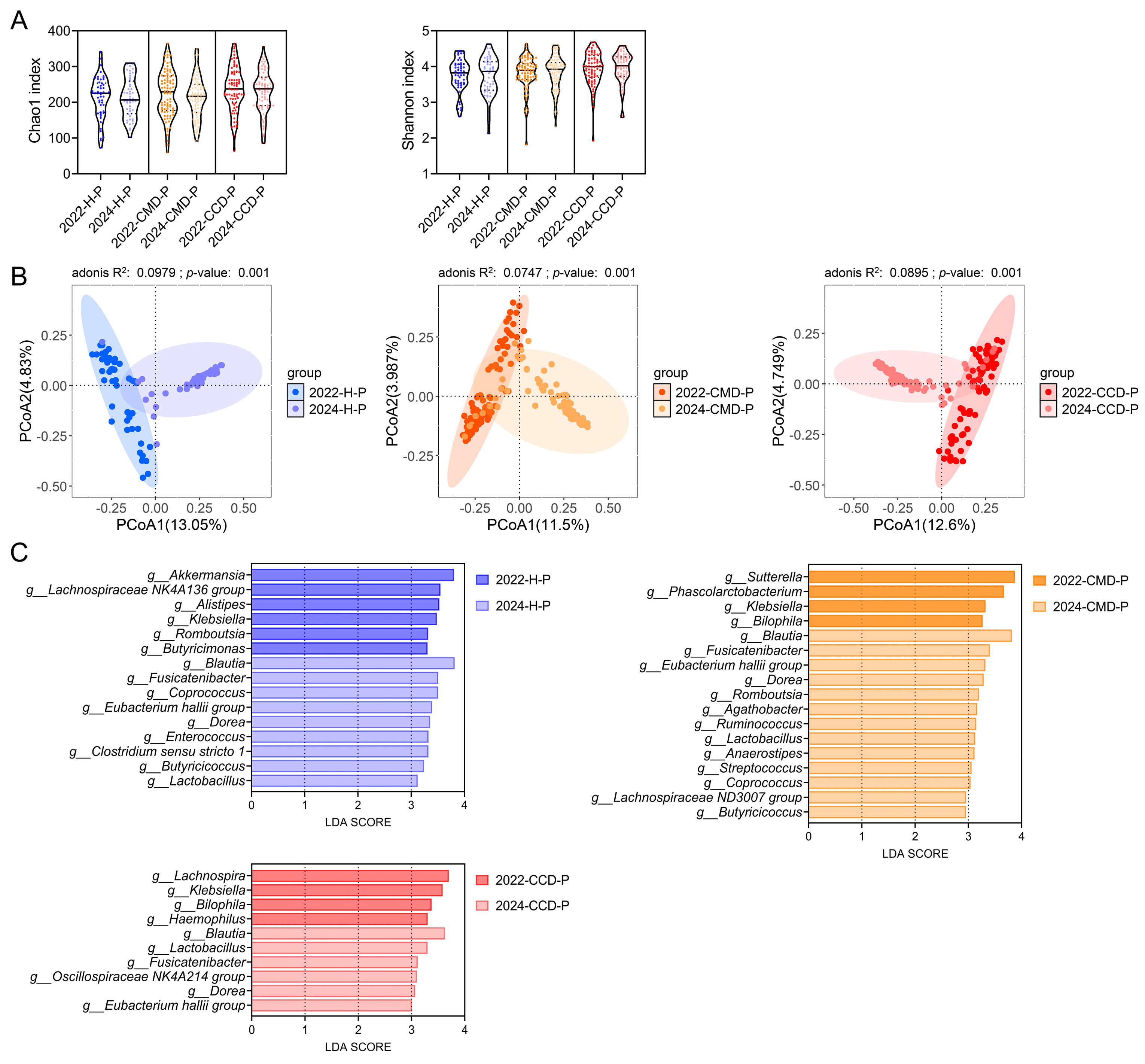
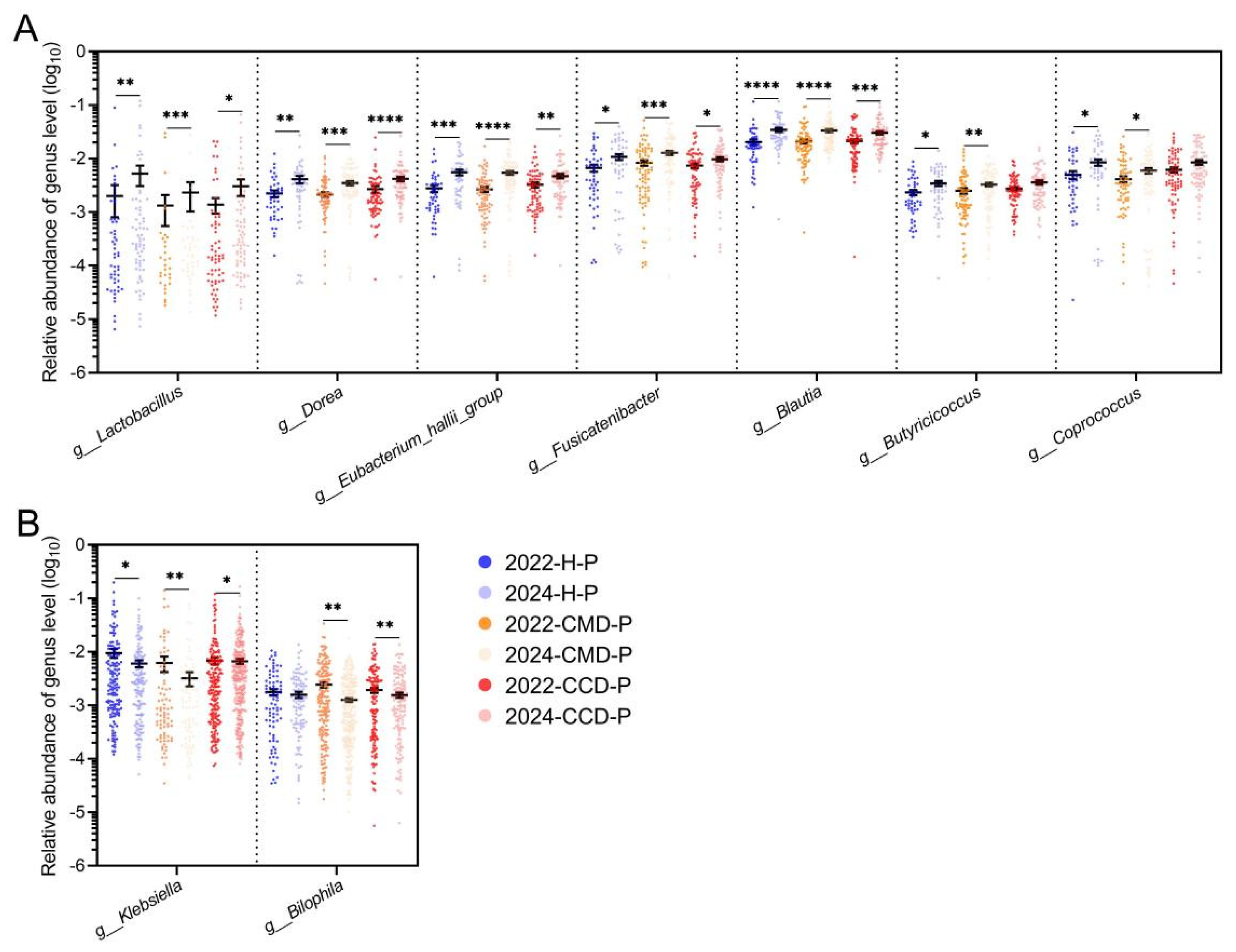
3.4. Long-Term Probiotic Supplementation Inhibits Gut Pathobionts in the CMD and CCD Groups While Increases the Abundance of Beneficial Bacteria
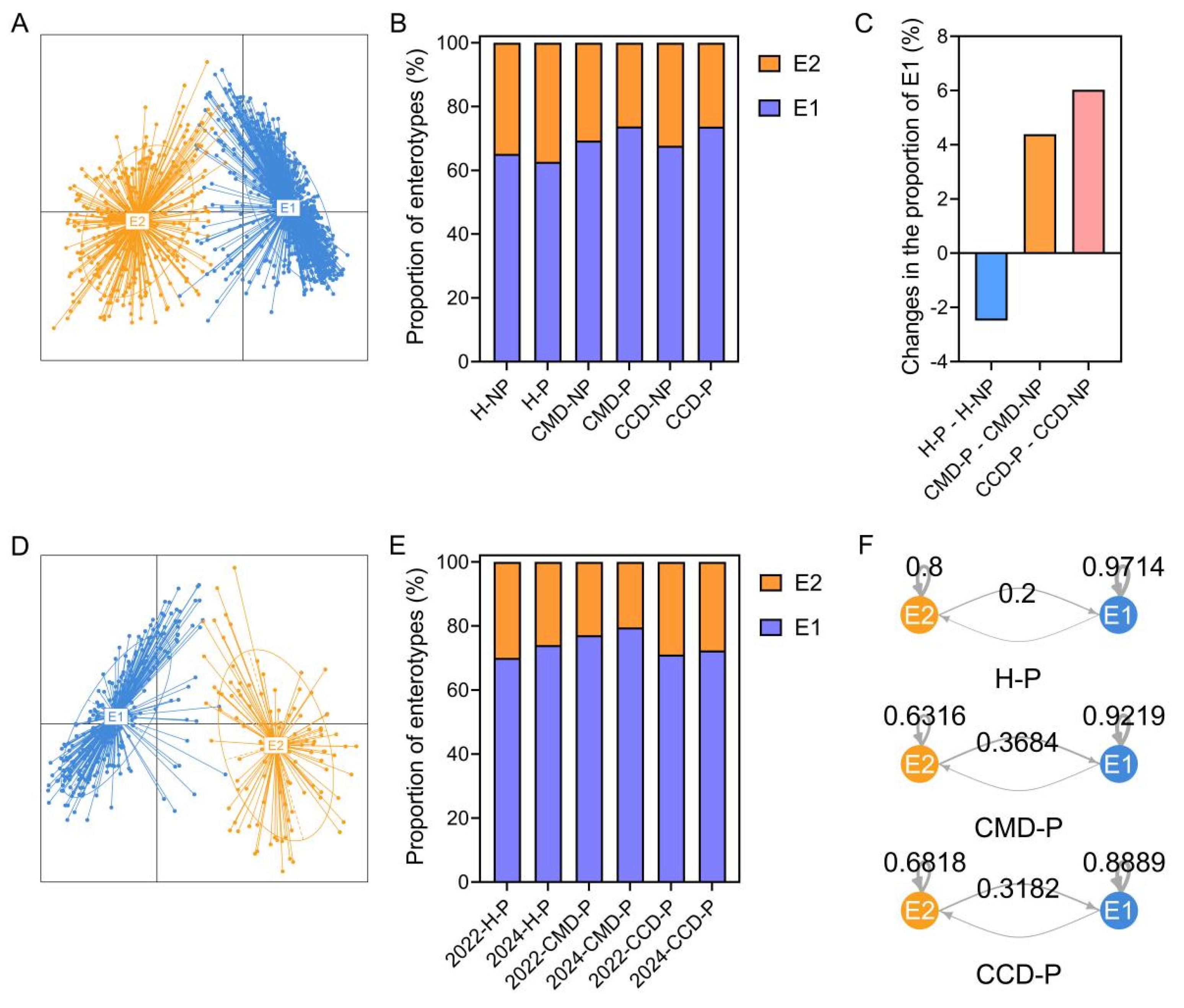
3.5. The Modulatory Effect of Probiotic Supplementation on Gut Enterotype in the CMD and CCD Groups than in the Healthy Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, C.H.; Zhu, F.; Qin, T.T. Relationships between Chronic Diseases and Depression among Middle-aged and Elderly People in China: A Prospective Study from CHARLS. Curr. Med. Sci. 2020, 40, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Li, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Ma, H.; Gao, J.; Wu, J.; Shen, H.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, N.; et al. The prevalence of multiple non-communicable diseases among middle-aged and elderly people: The Shanghai Changfeng Study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Wei, J.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Hou, G.; Meng, L.; Xin, Y.; Jiang, X. Role of the gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes and related diseases. Metabolism 2021, 117, 154712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastroch, M.; Ussar, S.; Keipert, S. Gut microbes controlling blood sugar: No fire required. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 443–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Tao, J.; Tian, G.; Wu, S.; Liu, W.; Cui, Q.; Geng, B.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the development of hypertension. Microbiome 2017, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.K.; Panyod, S.; Liu, P.Y.; Chen, C.C.; Kao, H.L.; Chuang, H.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Zou, H.B.; Kuo, H.C.; Kuo, C.H.; et al. Characterization of TMAO productivity from carnitine challenge facilitates personalized nutrition and microbiome signatures discovery. Microbiome 2020, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Weng, J.; Yan, J.; Zeng, Y.; Hao, Q.; Sheng, H.; Hua, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wen, Z.; Wu, Z.; et al. Puerarin alleviates atherosclerosis via the inhibition of Prevotella copri and its trimethylamine production. Gut 2024, 73, 1934–1943. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.Y.; Huang, F.Q.; Lao, X.; Lu, Y.; Gao, X.; Alolga, R.N.; Yin, K.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; et al. Integrated metagenomics identifies a crucial role for trimethylamine-producing Lachnoclostridium in promoting atherosclerosis. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2022, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.Q.; Yuan, L.X.; Sun, M.Y.; Wang, C.; Liang, E.M.; Li, Y.H.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.O.; Wu, D.; Lin, G.Z.; et al. Prevalence and patterns of multimorbidity in chronic diseases in Guangzhou, China: A data mining study in the residents’ health records system among 31708 community-dwelling elderly people. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e056135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, M.; Fu, Y.; Zhong, H.L.; Gou, W.; Jiang, Z.; Liang, Y.; Miao, Z.; Xu, J.J.; Huynh, T.; Wahlqvist, M.L.; et al. Mapping the human gut mycobiome in middle-aged and elderly adults: Multiomics insights and implications for host metabolic health. Gut 2022, 71, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettinger, G.; Macdonald, K.; Reid, G.; Burton, J.P. The influence of the human microbiome and probiotics on cardiovascular health. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdes, A.M.; Walter, J.; Segal, E.; Spector, T.D. Role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. BMJ 2018, 361, k2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavelle, A.; Sokol, H. Understanding and predicting the efficacy of FMT. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1759–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D.; Petitfils, C.; De Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; El-Omar, E.M. What defines a healthy gut microbiome. Gut 2024, 73, 1893–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paulo Farias, D.; de Araujo, F.F.; Neri-Numa, I.A.; Pastore, G.M. Prebiotics: Trends in food, health and technological applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baunwall, S.; Lee, M.M.; Eriksen, M.K.; Mullish, B.H.; Marchesi, J.R.; Dahlerup, J.F.; Hvas, C.L. Faecal microbiota transplantation for recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 29–30, 100642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baunwall, S.; Andreasen, S.E.; Hansen, M.M.; Kelsen, J.; Hoyer, K.L.; Ragard, N.; Eriksen, L.L.; Stoy, S.; Rubak, T.; Damsgaard, E.; et al. Faecal microbiota transplantation for first or second Clostridioides difficile infection (EarlyFMT): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paaske, S.E.; Baumwall, S.; Rubak, T.; Birn, F.H.; Ragard, N.; Kelsen, J.; Hansen, M.M.; Svenningsen, L.; Krarup, A.L.; Fernis, C.; et al. Real-world effectiveness of fecal microbiota transplantation for first or second Clostridioides difficile infection. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 23, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, G.; Khan, A.; Budryn, G.; Grzelczyk, J. Probiotic products from laboratory to commercialization. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 155, 104807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torp, A.M.; Bahl, M.I.; Boisen, A.; Licht, T.R. Optimizing oral delivery of next generation probiotics. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.E.; Merenstein, D.J.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Rastall, R.A. Probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: From biology to the clinic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britton, R.A.; Hoffmann, D.E.; Khoruts, A. Probiotics and the microbiome-how can we help patients make sense of probiotics? Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Q.; Yin, Y.; Yan, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, F.; Mcclements, D.J. Encapsulation of multiple probiotics, synbiotics, or nutrabiotics for improved health effects: A review. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2022, 309, 102781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahamsson, T.R. Not all probiotic strains prevent necrotising enterocolitis in premature infants. Lancet 2016, 387, 624–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costeloe, K.; Hardy, P.; Juszczak, E.; Wilks, M.; Millar, M.R. Bifidobacterium breve BBG-001 in very preterm infants: A randomised controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suez, J.; Zmora, N.; Zilberman-Schapira, G.; Mor, U.; Dori-Bachash, M.; Bashiardes, S.; Zur, M.; Regev-Lehavi, D.; Ben-Zeev, B.R.; Federici, S.; et al. Post-antibiotic gut mucosal microbiome reconstitution is impaired by probiotics and improved by autologous FMT. Cell 2018, 174, 1406–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severyn, C.J.; Bhatt, A.S. With probiotics, resistance is not always futile. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, L.E.; Gahche, J.J.; Herrick, K.A.; Davis, C.D.; Potischman, N.; Vargas, A.J. Nonfood prebiotic, probiotic, and synbiotic use has increased in US adults and children from 1999 to 2018. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.Y.; Nam, Y.D. Gut microbiome in healthy aging versus those associated with frailty. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2278225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, X.; Wu, S. Gut microbiota and aging. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 3509–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Shi, X.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, L.; Xu, L.; Cai, J. Gut microbes in cardiovascular diseases and their potential therapeutic applications. Protein Cell 2021, 12, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Companys, J.; Pla-Paga, L.; Calderon-Perez, L.; Llaurado, E.; Sola, R.; Pedret, A.; Valls, R.M. Fermented dairy products, probiotic supplementation, and cardiometabolic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 834–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; Mcmurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Gregory, C.J. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D643–D648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; Mcdonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Thurber, R.L.V.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.M.; et al. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digiulio, D.B.; Callahan, B.J.; Mcmurdie, P.J.; Costello, E.K.; Lyell, D.J.; Robaczewska, A.; Sun, C.L.; Goltsman, D.S.; Wong, R.J.; Shaw, G.; et al. Temporal and spatial variation of the human microbiota during pregnancy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11060–11065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorov, S.D.; Baretto, P.A.; Venema, K.; Holzapfel, W.H.; Chikindas, M.L. Recommendations for the use of standardised abbreviations for the former Lactobacillus genera, reclassified in the year 2020. Benef. Microbes 2023, 15, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.; Harris, H.; Mattarelli, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wu, H.; Yao, H.; Pan, W.; Su, M.; Chen, T.; Su, W.; Wang, Y. Rotundic acid protects against metabolic disturbance and improves gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes rats. Nutrients 2019, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Guo, P.; Mao, R.; Ren, Z.; Wen, J.; Yang, Q.; Yan, T.; Yu, J.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y. Gut microbiota signature of obese adults across different classifications. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 3933–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rossen, T.M.; Ooijevaar, R.E.; Kuyvenhoven, J.P.; Eck, A.; Bril, H.; Buijsman, R.; Boermeester, M.A.; Stockmann, H.; de Korte, N.; Budding, A.E. Microbiota composition and mucosal immunity in patients with asymptomatic diverticulosis and controls. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Xu, R.; Chen, X.; Yang, C.; Jiang, F.; Shen, Y.; Li, Q.; Fang, F.; Li, Y.; Shen, X. Characterization of gut microbiota in adults with coronary atherosclerosis. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhao, E.; Li, L.; Zhao, S.; Mao, H.; Deng, J.; Ji, W.; Li, Y.; Gao, Q.; Zeng, S.; et al. Alteration and clinical potential in gut microbiota in patients with cerebral small vessel disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1231541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Han, H.; Fu, X.; Liu, A.; Zhan, Y.; Qiu, H.; Ma, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Metformin reduces blood glucose in treatment-naive type 2 diabetes by altering the gut microbiome. Can. J. Diabetes 2022, 46, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.; Hu, J.; Chen, H.; Geng, F.; Nie, S. Arabinoxylan ameliorates type 2 diabetes by regulating the gut microbiota and metabolites. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Ge, Y.; Du, H.; Li, Q.; Xu, X.; Yi, H.; Wu, X.; Kuang, T.; Fan, G.; Zhang, Y. Berberis kansuensis extract alleviates type 2 diabetes in rats by regulating gut microbiota composition. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 273, 113995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Figueroa-Romero, C.; Noureldein, M.; Hinder, L.M.; Sakowski, S.A.; Rumora, A.E.; Petit, H.; Savelieff, M.G.; Hur, J.; Feldman, E.L. Gut microbiota in a mouse model of obesity and peripheral neuropathy associated with plasma and nerve lipidomics and nerve transcriptomics. Microbiome 2023, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, S.; Matsuoka, T.; Hosomi, K.; Park, J.; Nishimura, M.; Murakami, H.; Konishi, K.; Miyachi, M.; Kawashima, H.; Mizuguchi, K.; et al. Characteristic gut bacteria in high barley Cconsuming Japanese individuals without hypertension. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, L.; Baharlooeian, M.; Terasawa, M.; Shimada, Y.; Nishimura, N. Beneficial effects of seaweed-derived components on metabolic syndrome via gut microbiota modulation. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1173225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Tao, J.; Xiao, S.; Jiang, S.; Shang, E.; Zhu, Z.; Qian, D.; Duan, J. Xiexin Tang improves the symptom of type 2 diabetic rats by modulation of the gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranaivo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Alligier, M.; Van Den Berghe, L.; Sothier, M.; Lambert-Porcheron, S.; Feugier, N.; Cuerq, C.; Machon, C.; Neyrinck, A.M.; et al. Chitin-glucan supplementation improved postprandial metabolism and altered gut microbiota in subjects at cardiometabolic risk in a randomized trial. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X. Probiotics regulate gut microbiota: An effective method to improve immunity. Molecules 2021, 26, 6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, L.J.; Viciani, E.; Kumar, N. Genome watch: Microbial diversity knows no borders. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunk, T.; Kollmann, T.; Patole, S. Probiotics to prevent early-life infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 378–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, W.; Al-Kaabi, M.M.; Akram, N.N.; Kassim, M.; Pantazi, A.C. Probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease; a deep dive into their impact on disease course and associated health risks. Curr. Med. Chem. 2024, 31, 4807–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Shen, R.; Qin, H. Gut microbiota alteration after long-term consumption of probiotics in the elderly. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, N.B.; Bryrup, T.; Allin, K.H.; Nielsen, T.; Hansen, T.H.; Pedersen, O. Alterations in fecal microbiota composition by probiotic supplementation in healthy adults: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.C.; Herraiz, A.; Tigre, S.; Llama-Palacios, A.; Hernandez, M.; Ciudad, M.J.; Collado, L. Evidence of the beneficial impact of three probiotic-based food supplements on the composition and metabolic activity of the intestinal microbiota in healthy individuals: An ex vivo study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryaznova, M.; Smirnova, Y.; Burakova, I.; Syromyatnikov, M.; Chizhkov, P.; Popov, E.; Popov, V. Changes in the human gut microbiome caused by the short-term impact of lactic acid bacteria consumption in healthy people. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2024, 16, 1240–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udayappan, S.; Manneras-Holm, L.; Chaplin-Scott, A.; Belzer, C.; Herrema, H.; Dallinga-Thie, G.M.; Duncan, S.H.; Stroes, E.; Groen, A.K.; Flint, H.J.; et al. Oral treatment with Eubacterium hallii improves insulin sensitivity in db/db mice. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2016, 2, 16009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.G.; Kounatidis, D.; Tsilingiris, D.; Panagopoulos, F.; Christodoulatos, G.S.; Evangelopoulos, A.; Karampela, I.; Dalamaga, M. The Role of Next-Generation Probiotics in Obesity and Obesity-Associated Disorders: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, C.; Liu, R.; Hou, H.; Luo, Q.; Yu, Q.; Ouyang, H.; Feng, Y.; et al. alpha-D-1,3-glucan from Radix Puerariae thomsonii improves NAFLD by regulating the intestinal flora and metabolites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 299, 120197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Silva, C.; Kashani, A.; Hansen, T.H.; Pinna, N.K.; Anjana, R.M.; Dutta, A.; Saxena, S.; Stoy, J.; Kampmann, U.; Nielsen, T.; et al. Trans-ethnic gut microbiota signatures of type 2 diabetes in Denmark and India. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, A.; Yao, X.; Strappe, P.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, Q.; Guo, T. Starch acylation of different short-chain fatty acids and its corresponding influence on gut microbiome and diabetic indexes. Food Chem. 2022, 389, 133089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yu, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Q.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wu, C. Strain-level screening of human gut microbes identifies Blautia producta as a new anti-hyperlipidemic probiotic. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2228045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farras, M.; Martinez-Gili, L.; Portune, K.; Arranz, S.; Frost, G.; Tondo, M.; Blanco-Vaca, F. Modulation of the Gut Microbiota by Olive Oil Phenolic Compounds: Implications for Lipid Metabolism, Immune System, and Obesity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Lopez, Y.E.; Neri-Rosario, D.; Esquivel-Hernandez, D.A.; Padron-Manrique, C.; Vazquez-Jimenez, A.; Sanchez-Castaneda, J.P.; Giron-Villalobos, D.; Mendoza-Ortiz, C.; Reyes-Escogido, M.L.; Evia-Viscarra, M.L.; et al. Effect of metformin and metformin/linagliptin on gut microbiota in patients with prediabetes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Gao, J.; Yu, C.; Zhao, W.; Chen, N.; Valencak, T.G.; Ren, D. Lactobacillus rhamnosus ZJUIDS07 ameliorates type 2 diabetes in mice through the microbiome-gut-pancreas axis. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Yu, L.; Zhang, C.; Ni, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Zhai, Q.; Tian, F. Prebiotic activity of chitooligosaccharides and their ability to alleviate necrotizing enterocolitis in newborn rats. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 299, 120156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Liao, Y.; Qin, T.; Zhang, D.; Lai, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals a Dynamic Bacterial Linkage between the Captive White Rhinoceros and Its Environment. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0092123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, L.M.T. How important are fatty acids in human health and can they be used in treating diseases? Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2420765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chiou, J. Potential Benefits of Probiotics and Prebiotics for Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Chen, H.; Gao, Y.; An, N.; Li, X.; Pan, X.; Yang, X.; Tian, L.; Sun, J.; Xiong, X.; et al. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and hypertension: Mechanism and treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modrego, J.; Ortega-Hernandez, A.; Goirigolzarri, J.; Restrepo-Cordoba, M.A.; Bauerl, C.; Cortes-Macias, E.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, S.; Esteban-Fernandez, A.; Perez-Villacastin, J.; Collado, M.C.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids Are Linked to Evolution of Heart Failure Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Xu, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhou, H.; Lasanajak, Y.; Fang, Y.; Tang, L.; Ye, L.; Li, X.; Cai, Z.; et al. Transplantation of fecal microbiota rich in short chain fatty acids and butyric acid treat cerebral ischemic stroke by regulating gut microbiota. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 148, 104403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecklu-Mensah, G.; Choo-Kang, C.; Maseng, M.G.; Donato, S.; Bovet, P.; Viswanathan, B.; Bedu-Addo, K.; Plange-Rhule, J.; Oti, B.P.; Forrester, T.E.; et al. Gut microbiota and fecal short chain fatty acids differ with adiposity and country of origin: The METS-microbiome study. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; An, Y.; Du, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, Y. Effects of short-chain fatty acids on blood glucose and lipid levels in mouse models of diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 199, 107041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Liu, J.; Xue, Y.; Kong, X.; Lv, C.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, B. Alteration of gut microbial profile in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Endocrine 2021, 73, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranaz, P.; Ramos-Lopez, O.; Cuevas-Sierra, A.; Martinez, J.A.; Milagro, F.I.; Riezu-Boj, J.I. A predictive regression model of the obesity-related inflammatory status based on gut microbiota composition. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 2261–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, R.; Hu, N. Alterations of gut microbiome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who had undergone cholecystectomy. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 320, E113–E121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Hernandez, D.; Dufoo-Hurtado, E.; Cruz-Hernandez, A.; Campos-Vega, R. Spent coffee grounds and its antioxidant dietary fiber promote different colonic microbiome signatures: Benefits for subjects with chronodisruption. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 185, 106431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.; Manneras-Holm, L.; Puschmann, R.; Wu, H.; Troise, A.D.; Nijsse, B.; Boeren, S.; Backhed, F.; Fiedler, D.; Devos, W.M. Conversion of dietary inositol into propionate and acetate by commensal Anaerostipes associates with host health. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.N.; Wang, Q.C.; Xu, W.; Yu, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C. The berberine-enriched gut commensal Blautia producta ameliorates high-fat diet (HFD)-induced hyperlipidemia and stimulates liver LDLR expression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Luo, Z.; Vandeputte, D.; He, L.; Li, M.; Di, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Multiomics Analyses with Stool-Type Stratification in Patient Cohorts and Blautia Identification as a Potential Bacterial Modulator in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes 2024, 73, 511–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosomi, K.; Saito, M.; Park, J.; Murakami, H.; Shibata, N.; Ando, M.; Nagatake, T.; Konishi, K.; Ohno, H.; Tanisawa, K.; et al. Oral administration of Blautia wexlerae ameliorates obesity and type 2 diabetes via metabolic remodeling of the gut microbiota. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, N.; He, J.; Ma, R.C.; Kong, A.P.; Chan, J.C.; Chow, E. The Relationship between Short-Chain Fermentable Carbohydrates (FODMAPs), Gut Microbiome, and Glucose Intolerance: An Exploratory Analysis. Diabetes 2022, 71, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Dong, W.; Fan, X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, G.; Zeng, X.; Ye, H. The polysaccharides from Auricularia auricula alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via modulating gut microbiota and bile acids metabolism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 246, 125662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, C.; Luukkonen, P.; Sadevirta, S.; Yki-Jarvinen, H.; Salonen, A. Impact of short-term overfeeding of saturated or unsaturated fat or sugars on the gut microbiota in relation to liver fat in obese and overweight adults. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, E.J.; Han, K.; Lim, T.J.; Lim, S.; Chung, M.J.; Nam, M.H.; Kim, H.; Nam, Y.D. Effect of probiotics on obesity-related markers per enterotype: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. EPMA J. 2020, 11, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honoki, H.; Fujisaka, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Oku, M.; Kondo, Y.; Nishimura, A.; Kado, T.; Bilal, M.; Enkaku, A.; Takikawa, A.; et al. Identification of gut microbes that prevents metabolic syndrome in healthy Japanese adults. Diabetes 2023, 72, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehlner-Peach, H.; Magnabosco, C.; Raghavan, V.; Scher, J.U.; Tett, A.; Cox, L.M.; Gottsegen, C.; Watters, A.; Wiltshire-Gordon, J.D.; Segata, N.; et al. Distinct polysaccharide utilization profiles of human intestinal Prevotella copri Isolates. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, R.; Yang, X.; Fang, C.; Yao, L.; Lv, J.; Wang, L.; Shi, M.; Zhang, W.; et al. Effects of Prevotella copri on insulin, gut microbiota and bile acids. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2340487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolhion, N.; Chassaing, B.; Nahori, M.A.; de Bodt, J.; Moura, A.; Lecuit, M.; Dussurget, O.; Berard, M.; Marzorati, M.; Fehlner-Peach, H.; et al. A Listeria monocytogenes bacteriocin can target the commensal Prevotella copri and modulate intestinal infection. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zhou, B.; Xia, X.; Chen, S.; Deng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, B.; Xu, H.; et al. Prevotella copri is associated with carboplatin-induced gut toxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpizar-Rodriguez, D.; Lesker, T.R.; Gronow, A.; Gilbert, B.; Raemy, E.; Lamacchia, C.; Gabay, C.; Finckh, A.; Strowig, T. Prevotella copri in individuals at risk for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.W.; Lee, E.M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Pruss, K.M.; Henrissat, S.; Chen, R.Y.; Kao, C.; Hibberd, M.C.; Lynn, H.M.; et al. Prevotella copri and microbiota members mediate the beneficial effects of a therapeutic food for malnutrition. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 922–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, H.; Liu, R.; Zhang, D.; Feng, Q.; Xie, X.; Hong, J.; et al. Analyses of gut microbiota and plasma bile acids enable stratification of patients for antidiabetic treatment. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, J.; Watanabe, K.; Jiang, J.; Matsuda, K.; Chao, S.H.; Haryono, P.; La-Ongkham, O.; Sarwoko, M.A.; Sujaya, I.N.; Zhao, L.; et al. Diversity in gut bacterial community of school-age children in Asia. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roager, H.M.; Licht, T.R.; Poulsen, S.K.; Larsen, T.M.; Bahl, M.I. Microbial enterotypes, inferred by the Prevotella-to-Bacteroides ratio, remained stable during a 6-month randomized controlled diet intervention with the new nordic diet. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjorth, M.F.; Blaedel, T.; Bendtsen, L.Q.; Lorenzen, J.K.; Holm, J.B.; Kiilerich, P.; Roager, H.M.; Kristiansen, K.; Larsen, L.H.; Astrup, A. Prevotella-to-Bacteroides ratio predicts body weight and fat loss success on 24-week diets varying in macronutrient composition and dietary fiber: Results from a post-hoc analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, L.; Roager, H.M.; Astrup, A.; Hjorth, M.F. Microbial enterotypes in personalized nutrition and obesity management. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessione, E. Lactic acid bacteria contribution to gut microbiota complexity: Lights and shadows. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintaric, M.; Langerholc, T. Probiotic Mechanisms Affecting Glucose Homeostasis: A Scoping Review. Life 2022, 12, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costea, P.I.; Hildebrand, F.; Arumugam, M.; Backhed, F.; Blaser, M.J.; Bushman, F.D.; de Vos, W.M.; Ehrlich, S.D.; Fraser, C.M.; Hattori, M.; et al. Enterotypes in the landscape of gut microbial community composition. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Darzi, Y.; Lima-Mendez, G.; Garcia, Y.R.; Okuda, S.; Vandeputte, D.; Valles-Colomer, M.; Hildebrand, F.; Chaffron, S.; et al. Species-function relationships shape ecological properties of the human gut microbiome. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fu, R.; Yang, Y.; Horz, H.; Guan, Y.; Lu, Y.; Lou, H.; Tian, L.; Zheng, S.; Liu, H.; et al. A metagenomic approach to dissect the genetic composition of enterotypes in Han Chinese and two Muslim groups. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Shi, Z.; Ren, H.; Xu, M.; Lu, J.; Yang, F.; Ye, C.; Wu, K.; Chen, M.; Xu, X.; et al. Divergent age-associated and metabolism-associated gut microbiome signatures modulate cardiovascular disease risk. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 1722–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmanski, T.; Diener, C.; Rappaport, N.; Patwardhan, S.; Wiedrick, J.; Lapidus, J.; Earls, J.C.; Zimmer, A.; Glusman, G.; Robinson, M.; et al. Gut microbiome pattern reflects healthy ageing and predicts survival in humans. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristics | Total (%) | CMD (%) | CCD (%) | H (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 1168) | (n = 547) | (n = 339) | (n = 282) | |
| Individuals with probiotic supplementation | 660 (56.51) | 335 (61.24) | 175 (51.62) | 150 (53.19) |
| Individuals without probiotic supplementation | 508 (43.49) | 212 (38.76) | 164 (48.38) | 132 (46.81) |
| Characteristics | Total | CMD-P | CCD-P | H-P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 418) | (n = 166) | (n = 152) | (n = 100) | |
| Sample collection | ||||
| 2022 (October–December) | 209 | 83 | 76 | 50 |
| 2024 (January–March) | 209 | 83 | 76 | 50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Dong, W.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Pan, Y.; Xiong, Q.; Lyu, N.; Zhu, B. Probiotic Supplementation Improves Gut Microbiota in Chronic Metabolic and Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases Among Chinese Adults over 60: Study Using Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Cohorts. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071507
Wang X, Dong W, Liu Q, Zeng X, Liu Y, Li Z, Pan Y, Xiong Q, Lyu N, Zhu B. Probiotic Supplementation Improves Gut Microbiota in Chronic Metabolic and Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases Among Chinese Adults over 60: Study Using Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Cohorts. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071507
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xi, Wanting Dong, Qiuying Liu, Xi Zeng, Yan Liu, Zheng Li, Yuanlong Pan, Qian Xiong, Na Lyu, and Baoli Zhu. 2025. "Probiotic Supplementation Improves Gut Microbiota in Chronic Metabolic and Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases Among Chinese Adults over 60: Study Using Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Cohorts" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071507
APA StyleWang, X., Dong, W., Liu, Q., Zeng, X., Liu, Y., Li, Z., Pan, Y., Xiong, Q., Lyu, N., & Zhu, B. (2025). Probiotic Supplementation Improves Gut Microbiota in Chronic Metabolic and Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases Among Chinese Adults over 60: Study Using Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Cohorts. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071507






