Detection of Group B Streptococcus (GBS) from Antenatal Screening, Maternal GBS Colonization and Incidence of Early-Onset Neonatal Disease (GBS-EOD): A National Survey, December 2022 to February 2023, Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Ethical Approval
3. Results
3.1. Compliance to the Online Survey
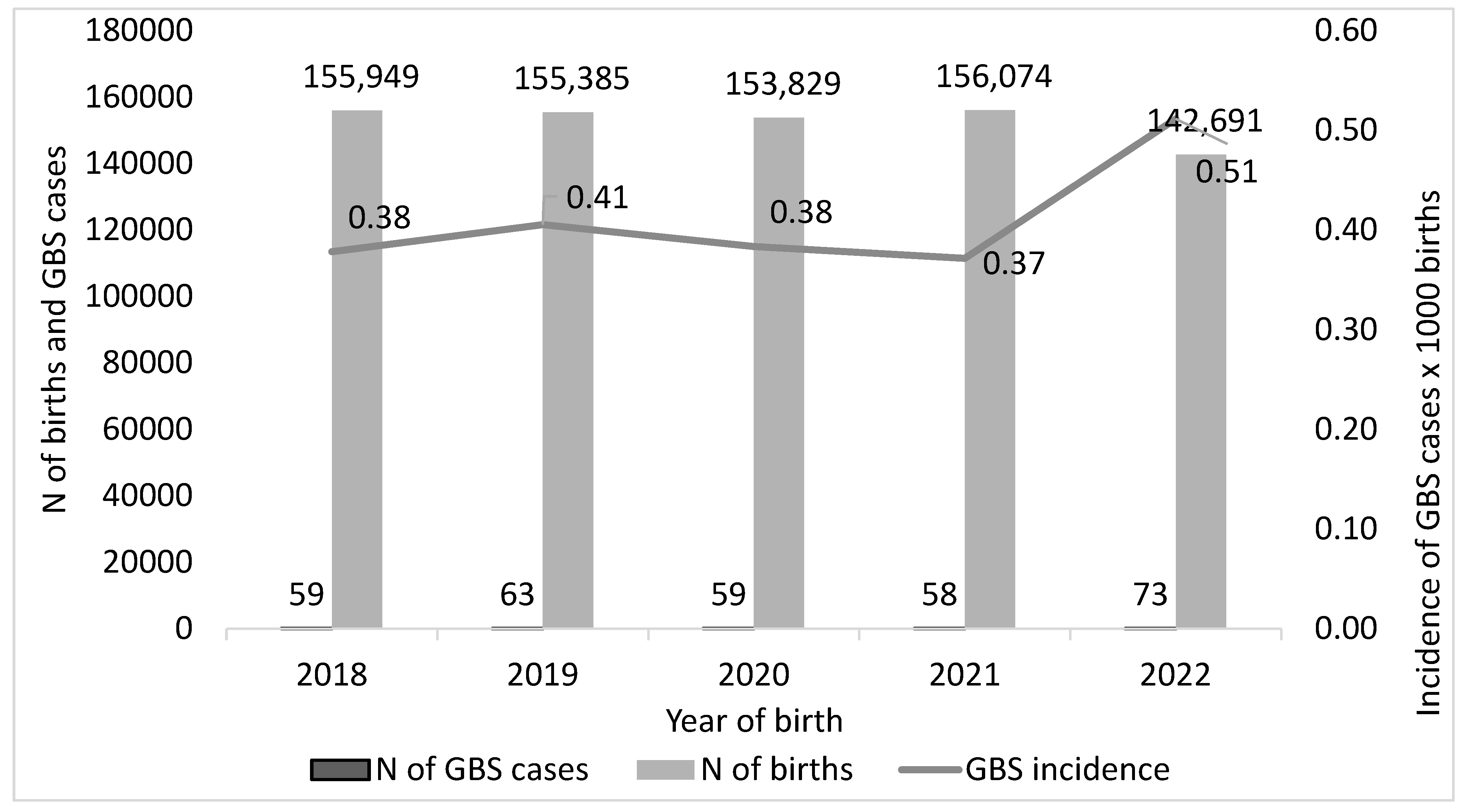
3.2. GBS-EOD Incidence over Time
3.3. Maternal GBS Colonization
3.4. Detection and Identification of GBS at the Antenatal Screening
3.5. GBS-EOD Neonates Born to Mothers Negative or Positive for AGBSS
3.6. Antibiotic Resistance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coggins, S.A.; Puopolo, K.M. Neonatal Group B Streptococcus Disease. Pediatr. Rev. 2024, 45, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs-Steinberg, C.; Roth, P. Early-Onset Sepsis in Newborns. Pediatr. Rev. 2023, 44, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuel, G.; Twentymanm, J.; Noble, K.; Eastman, A.J.; Aronoff, D.M.; Seepersaud, R.; Rajagopal, L.; Adams Waldorf, K.M. Group B streptococcal infections in pregnancy and early life. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2025, 38, e0015422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoff, S.P.; Boyer, K.M. Prevention of early-onset neonatal group B streptococcal disease. Pediatrics 1997, 99, 866–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Lin, X.Z. Updates in prevention policies of early-onset group B streptococcal infection in newborns. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2021, 62, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steer, P.J.; Russell, A.B.; Kochhar, S.; Cox, P.; Plumb, J.; Rao, G.G. Group B streptococcal disease in the mother and newborn—A review. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 252, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.W.; Yap, S.F.; Murdan, S.; Zainudin, Z.; Abdul Hamid, H.; Emamjomeh, M.; Mohd Desa, M.N.; Sither Joseph, N.M.; Azmai Amal, M.N.; Amin-Nordin, S. Maternal and neonatal group B Streptococcus colonisation: A systematic review and the meta-analysis of matched-pair studies. Acta Paediatr. 2024, 113, 892–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.J.; Edwards, M.S. Group B streptococcal infections. In Infectious Diseases of the Fetus and Newborn Infant, 4th ed.; Remington, J., Klein, J.O., Eds.; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1995; pp. 980–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Stafford, I.A.; Rodrigue, E.; Berra, A.; Adams, W.; Heard, A.J.; Hagan, J.L.; Stafford, S.J. The strong correlation between neonatal early-onset Group B Streptococcal disease and necrotizing enterocolitis. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2018, 223, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National System Guideline (SNGL). Uncomplicated Pregnancy; Guideline 20/2010. Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/materno/pdf/LG_Gravidanza.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2025). (In Italian).
- National System Guideline (SNGL). Antenatal Care for Uncomplicated Pregnancy; PART ONE. Section 1—Information for Pregnant Women. Section 2—Screening for Infections in Pregnancy. Guideline 1/2023. 2023. Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/itoss/pdf/LG-Gravidanza-Fisiologica-Parte1_protetto.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2025). (In Italian).
- Yancey, M.K.; Schuchat, A.; Brown, L.K.; Ventura, V.L.; Markenson, G.R. The accuracy of late antenatal screening cultures in predicting genital group B streptococcal colonization at delivery. Obstet. Gynecol. 1996, 88, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towers, C.V.; Rumney, P.J.; Asrat, T.; Preslicka, C.; Ghamsary, M.G.; Nageotte, M.P. The accuracy of late third-trimester antenatal screening for group B Streptococcus in predicting colonization at delivery. Am. J. Perinatol. 2010, 27, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filkins, L.; Hauser, J.R.; Robinson-Dunn, B.; Tibbetts, R.; Boyanton, B.L.; Revell, P. American Society for Microbiology Provides 2020 Guidelines for Detection and Identification of Group B Streptococcus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 59, e01230-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhudasia, M.B.; Flannery, D.D.; Pfeifer, M.R.; Puopolo, K.M. Updated Guidance: Prevention and Management of Perinatal Group B Streptococcus Infection. Neoreviews 2021, 22, e177–e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannery, D.D.; Ramachandran, V.; Schrag, S.J. Neonatal Early-Onset Sepsis: Epidemiology, Microbiology, and Controversies in Practice. Clin. Perinatol. 2025, 52, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boureka, E.; Krasias, D.; Tsakiridis, I.; Karathanasi, A.M.; Mamopoulos, A.; Athanasiadis, A.; Dagklis, T. Prevention of Early-Onset Neonatal Group B Streptococcal Disease: A Comprehensive Review of Major Guidelines. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2023, 78, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangerl, S.; Sundin, D.; Geraghty, S. Group B Streptococcus Screening Guidelines in Pregnancy: A Critical Review of Compliance. Matern. Child Health J. 2021, 25, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puopolo, K.M.; Lynfield, R.; Cummings, J.J.; AAP Committee on Fetus and Newborn; AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases. Management of Infants at Risk for Group B Streptococcal Disease. Pediatrics 2019, 144, e20191881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevention of Group B Streptococcal Early-Onset Disease in Newborns: ACOG Committee Opinion, Number 797. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 135, e51–e72. [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, B.P.; Procter, S.R.; Paul, P.; Chandna, J.; Lewin, A.; Seedat, F.; Koukounari, A.; Dangor, Z.; Leahy, S.; Santhanam, S.; et al. Group B Streptococcus infection during pregnancy and infancy: Estimates of regional and global burden. Lancet Glob Health 2022, 10, e807–e819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, M.L.; Dickson, B.F.R.; Sharland, M.; Williams, P.C.M. Beyond Early- and Late-onset Neonatal Sepsis Definitions: What are the Current Causes of Neonatal Sepsis Globally? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of the Evidence. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2024, 43, 1182–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verani, J.R.; McGee, L.; Schrag, S.J.; Division of Bacterial Diseases; National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevention of perinatal group B streptococcal disease—Revised guidelines from CDC, 2010. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2010, 59, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Madrid, L.; Seale, A.C.; Kohli-Lynch, M.; Edmond, K.M.; Lawn, J.E.; Heath, P.T.; Madhi, S.A.; Baker, C.J.; Bartlett, L.; Cutland, C.; et al. Infant Group B Streptococcal Disease Incidence and Serotypes Worldwide: Systematic Review and Meta-analyses. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65 (Suppl. S2), S160–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanduri, S.A.; Petit, S.; Smelser, C.; Apostol, M.; Alden, N.B.; Harrison, L.H.; Lynfield, R.; Vagnone, P.S.; Burzlaff, K.; Spina, N.L.; et al. Epidemiology of Invasive Early-Onset and Late-Onset Group B Streptococcal Disease in the United States, 2006 to 2015: Multistate Laboratory and Population-Based Surveillance. JAMA Pediatr. 2019, 173, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mynarek, M.; Bjellmo, S.; Lydersen, S.; Afset, J.E.; Andersen, G.L.; Vik, T. Incidence of invasive Group B Streptococcal infection and the risk of infant death and cerebral palsy: A Norwegian Cohort Study. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, A.; Spada, C.; Creti, R.; Ambretti, S.; Chiarabini, R.; Barozzi, A.; Pagano, R.; Sarti, M.; Pedna, M.M.; Fornaciari, S.; et al. Risk factors for group B Streptococcus early-onset disease: An Italian, area-based, case-control study. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020, 33, 2480–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creti, R.; Imperi, M.; Berardi, A.; Pataracchia, M.; Recchia, S.; Alfarone, G.; Baldassarri, L.; Italian Neonatal GBS Infections Working Group. Neonatal Group B Streptococcus Infections: Prevention Strategies, Clinical and Microbiologic Characteristics in 7 Years of Surveillance. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creti, R.; Imperi, M.; Berardi, A.; Lindh, E.; Alfarone, G.; Pataracchia, M.; Recchia, S.; The Italian Network On Neonatal And Infant GBS Infections. Invasive Group B Streptococcal Disease in Neonates and Infants, Italy, Years 2015–2019. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzialla, C.; Berardi, A.; Farina, C.; Clerici, P.; Borghesi, A.; Viora, E.; Scollo, P.; Stronati, M.; Task Force for group B streptococcal infections for the Italian Society of Neonatology; Italian Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists; et al. Strategies for preventing group B streptococcal infections in newborns: A nation-wide survey of Italian policies. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2017, 43, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters; Version 9.0; EUCAST: Växjö, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing—Twenty-Eighth Edition: M100; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- El Aila, N.A.; Tency, I.; Claeys, G.; Saerens, B.; Cools, P.; Verstraelen, H.; Temmerman, M.; Verhelst, R.; Vaneechoutte, M. Comparison of different sampling techniques and of different culture methods for detection of group B Streptococcus carriage in pregnant women. BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipson, E.H.; Palermino, D.A.; Robinson, A. Enhanced antenatal detection of group B Streptococcus colonization. Obstet. Gynecol. 1995, 85, 437–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votava, M.; Tejkalová, M.; Drábková, M.; Unzeitig, V.; Braveny, I. Use of GBS media for rapid detection of group B streptococci in vaginal and rectal swabs from women in labor. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2001, 20, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cao, S.; Ni, Y.; Chen, X.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Fu, J.; Zheng, L.; Tang, Z.; Ye, H. An improved procedure based on fluorescence immunochromatography for rapid detection of group B Streptococcus from enrichment cultures. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2025, 25, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero Méndez, A.; Reynoso de la Rosa, R.A.; Abreu Bencosme, M.E.; Sosa Ortiz, M.N.; Pichardo Beltré, E.; de la Cruz García, D.M.; Piñero Santana, N.J.; Bacalhau de León, J.C. Development and performance evaluation of a qPCR-based assay for the fully automated detection of group B Streptococcus (GBS) on the Panther Fusion Open Access system. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0005724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugelman, N.; Kleifeld, S.; Shaked-Mishan, P.; Assaf, W.; Marom, I.; Cohen, N.; Gruber, M.; Lavie, O.; Waisman, D.; Kedar, R.; et al. Group B Streptococcus real-time PCR may potentially reduce intrapartum maternal antibiotic treatment. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2022, 36, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, E.G.; Rodríguez, M.C.; Bartolomé, R.; Berjano, B.; Cabero, L.; Andreu, A. Evaluation of the Granada agar plate for detection of vaginal and rectal group B streptococci in pregnant women. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 2648–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furfaro, L.L.; Chang, B.J.; Payne, M.S. Detection of group B Streptococcus during antenatal screening in Western Australia: A comparison of culture and molecular methods. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Granger, J.; Spellerberg, B.; Asam, D.; Rosa-Fraile, M. Non-haemolytic and non-pigmented group b Streptococcus, an infrequent cause of early onset neonatal sepsis. Pathog. Dis. 2015, 73, ftv089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanquart, A.L.; Garnier, F.; Lauvray, T.; Mazeau, P.C.; Martinez, S.; Catalan, C.; Guigonis, V.; Bedu, A.; Mons, F.; Ponthier, L. Vaginal screening for group B Streptococcus using PCR in pregnant women with unknown colonization status: Impact on newborn monitoring for early-onset sepsis. Arch. Pediatr. 2024, 31, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, H.C., Jr.; Gray, E.; Pass, M.A.; Gray, B.M. Anorectal and vaginal carriage of group B streptococci during pregnancy. J. Infect. Dis. 1982, 145, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, M.W.; McLaughlin, J.C.; Gilson, G.J.; Wellhoner, M.F.; Nims, L.J. Increased recovery of group B Streptococcus by the inclusion of rectal culturing and enrichment. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1995, 21, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, J.D.; Hill, D.A.; Maxwell, B.D.; Boone, S.; Hoover, F.; Lense, J.J. The necessity of both anorectal and vaginal cultures for group B Streptococcus screening during pregnancy. J. Fam. Pract. 2000, 49, 447–448. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, G.G.; Khanna, P. To screen or not to screen women for Group B Streptococcus (Streptococcus agalactiae) to prevent early onset sepsis in newborns: Recent advances in the unresolved debate. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, 2049936120942424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finale, E.; Spadea, T.; Mondo, L.; Arnulfo, A.; Capuano, A.; Ghiotti, P.; Barbaglia, M.; Guala, A. Streptococcus agalactiae in pregnancy and the impact of recommendations on adherence to guidelines: An Italian area-based study. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022, 35, 7826–7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, G.; Lo Scalzo, L.; Giordano, M.; Giuffrè, M.; Trupiano, P.; Venezia, R.; Corsello, G. Group B Streptococcus colonization in pregnancy and neonatal outcomes: A three-year monocentric retrospective study during and after the COVID-19 pandemic. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2024, 50, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodolo, L.; Rossi, C.; Canale, C.; Barbaglia, M.; Prandi, G.; Ghiotti, P.; Agreiter, I.; Pagani, L.; Finale, E.; Cappuccia, N.; et al. Standardization and Enrichment of Culture Medium Improve Detection of Group B Streptococci during Prepartum Screening. J. Community Med. Health Educ. 2014, 4, 319. [Google Scholar]
- Sabroske, E.M.; Iglesias, M.A.S.; Rench, M.; Moore, T.; Harvey, H.; Edwards, M.; Baker, C.J.; Flores, A.R. Evolving antibiotic resistance in Group B Streptococci causing invasive infant disease: 1970–2021. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 93, 2067–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, K.; O’Halloran, F.; Cotter, L. A review of antibiotic resistance in Group B Streptococcus: The story so far. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 46, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Neonatal Infection: Antibiotics for Prevention and Treatment. NG195. 20 April 2021. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng195 (accessed on 17 June 2025).
- Plainvert, C.; Hays, C.; Touak, G.; Joubrel-Guyot, C.; Dmytruk, N.; Frigo, A.; Poyart, C.; Tazi, A. Multidrug-Resistant Hypervirulent Group B Streptococcus in Neonatal Invasive Infections, France, 2007–2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2721–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohrmann, F.; Hufnagel, M.; Kunze, M.; Afshar, B.; Creti, R.; Detcheva, A.; Kozakova, J.; Rodriguez-Granger, J.; Sørensen, U.B.S.; Margarit, I.; et al. Neonatal invasive disease caused by Streptococcus agalactiae in Europe: The DEVANI multi-center study. Infection 2023, 51, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohrmann, F.; Efstratiou, A.; Sørensen, U.B.S.; Creti, R.; Decheva, A.; Křížová, P.; Kozáková, J.; Rodriguez-Granger, J.; De La Rosa Fraile, M.; Margarit, I.; et al. Maternal Streptococcus agalactiae colonization in Europe: Data from the multi-center DEVANI study. Infection 2025, 53, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creti, R.; Imperi, M.; Berardi, A.; Angeletti, S.; Gherardi, G. Laboratory breakpoints for assessing high level gentamicin resistance in Streptococcus agalactiae: It is the time for a consensus. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 1050–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creti, R.; Imperi, M.; Khan, U.B.; Berardi, A.; Recchia, S.; Alfarone, G.; Gherardi, G. Emergence of High-Level Gentamicin Resistance in Streptococcus agalactiae Hypervirulent Serotype IV ST1010 (CC452) Strains by Acquisition of a Novel Integrative and Conjugative Element. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, K.; Arrieta, A.; Nieves, D.J.; Bhakta, K.; Tran, M.T.; Osborne, S.; Morphew, T. Ampicillin and Gentamicin Treatment for Early Onset Neonatal Sepsis: When One Size Does Not Fit All. Clin. Pediatr. 2023, 62, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridley, J.; Nelson, J. (Eds.) 2024 Nelson’s Pediatric Antimicrobial Therapy, 30th ed.; American Academy of Pediatrics: Itasca, IL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Capone, V.; Buttera, M.; Miselli, F.; Truocchio, S.; Iaccheri, M.; Auriti, C.; Creti, R.; Baroni, L.; Bedetti, L.; Benenati, B.; et al. Antimicrobial Therapies for Early-Onset Group B Streptococcal Sepsis: Insights from an Italian Multicenter Study. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, M.; Parodi, A.; Minghetti, D.; Ramenghi, L.A.; Palmero, C.; Ugolotti, E.; Medici, C.; Saffioti, C.; Castagnola, E. Early and Late Onset Neonatal Sepsis: Epidemiology and Effectiveness of Empirical Antibacterial Therapy in a III Level Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Region/Autonomous Province | Proportion of Compiled Questionnaires (%) | Participating Centres That Completed the Questionnaire (N) | Towns Where the Facilities Where Located (N) | Regional Population (1 January 2023) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lombardia | 22.0 | 48 | 31 | 9,976,509 |
| Calabria | 14.6 | 32 | 19 | 1,846,610 |
| Sicilia | 10.5 | 23 | 19 | 4,814,016 |
| Veneto | 11.0 | 24 | 20 | 4,849,553 |
| Toscana | 8.7 | 19 | 16 | 3,661,981 |
| Piemonte | 5.5 | 12 | 10 | 4,251,351 |
| Marche | 3.6 | 8 | 7 | 1,484,298 |
| Abruzzo | 2.8 | 6 | 5 | 1,272,627 |
| Friuli-Venezia Giulia | 2.8 | 6 | 4 | 1,194,248 |
| Lazio | 2.8 | 6 | 2 | 5,720,536 |
| Liguria | 2.8 | 6 | 3 | 1,507,636 |
| Puglia | 2.3 | 5 | 4 | 3,907,683 |
| PA Bolzano | 1.8 | 4 | 4 | 534,147 |
| Sardegna | 1.8 | 4 | 4 | 1,578,146 |
| Umbria | 1.8 | 4 | 4 | 856,407 |
| Campania | 1.4 | 3 | 3 | 5,609,536 |
| PA Trento | 1.4 | 3 | 1 | 542,996 |
| Emilia-Romagna | 0.9 | 2 | 2 | 4,437,578 |
| Basilicata | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 537,577 |
| Molise | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 290,636 |
| Valle d’Aosta | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 123,130 |
| Total | 100 | 218 | 161 | 58,997,201 |
| N of Newborns Per Year, Italy | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| data source: ISTAT | 439,747 | 420,084 | 404,892 | 400,249 | 393,333 |
| data source: GBS SURVEY total 763,928 | 155,949 | 155385 | 153,829 | 156,074 | 142,691 |
| ratio ISTAT/SURVEY | 2.8 | 2.7 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.8 |
| proportion (%) SURVEY/ISTAT | 35.5 | 37.0 | 38.0 | 39.0 | 36.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sabbatucci, M.; Clerici, P.; Creti, R. Detection of Group B Streptococcus (GBS) from Antenatal Screening, Maternal GBS Colonization and Incidence of Early-Onset Neonatal Disease (GBS-EOD): A National Survey, December 2022 to February 2023, Italy. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071438
Sabbatucci M, Clerici P, Creti R. Detection of Group B Streptococcus (GBS) from Antenatal Screening, Maternal GBS Colonization and Incidence of Early-Onset Neonatal Disease (GBS-EOD): A National Survey, December 2022 to February 2023, Italy. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071438
Chicago/Turabian StyleSabbatucci, Michela, Pierangelo Clerici, and Roberta Creti. 2025. "Detection of Group B Streptococcus (GBS) from Antenatal Screening, Maternal GBS Colonization and Incidence of Early-Onset Neonatal Disease (GBS-EOD): A National Survey, December 2022 to February 2023, Italy" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071438
APA StyleSabbatucci, M., Clerici, P., & Creti, R. (2025). Detection of Group B Streptococcus (GBS) from Antenatal Screening, Maternal GBS Colonization and Incidence of Early-Onset Neonatal Disease (GBS-EOD): A National Survey, December 2022 to February 2023, Italy. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071438







