The Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium Bacillus cereus LpBc-47 Can Alleviate the Damage of Saline–Alkali Stress to Lilium pumilum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Microbial Diversity Analysis
2.3. Screening and Identification of Endophytic Bacteria
2.4. Screening of Bacteria with Growth-Promoting and Saline–Alkali Tolerance
2.5. Physiological and Biochemical Identification of LpBc-47
2.6. The Whole Genome Sequencing of LpBc-47
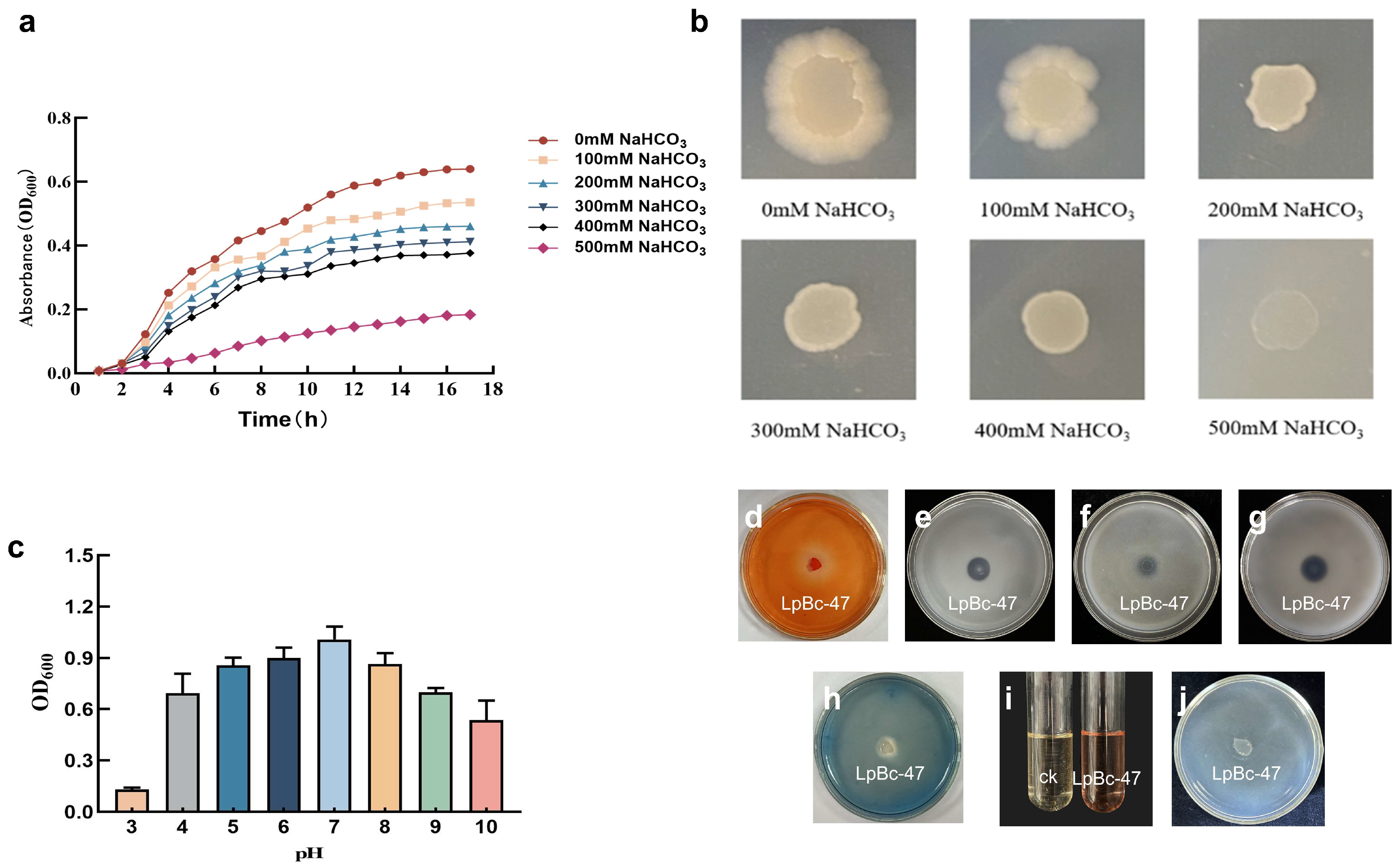
2.7. Growth Conditions and Growth Promoting Characteristics of LpBc-47
2.8. Construction of GFP-Labelled LpBc-47
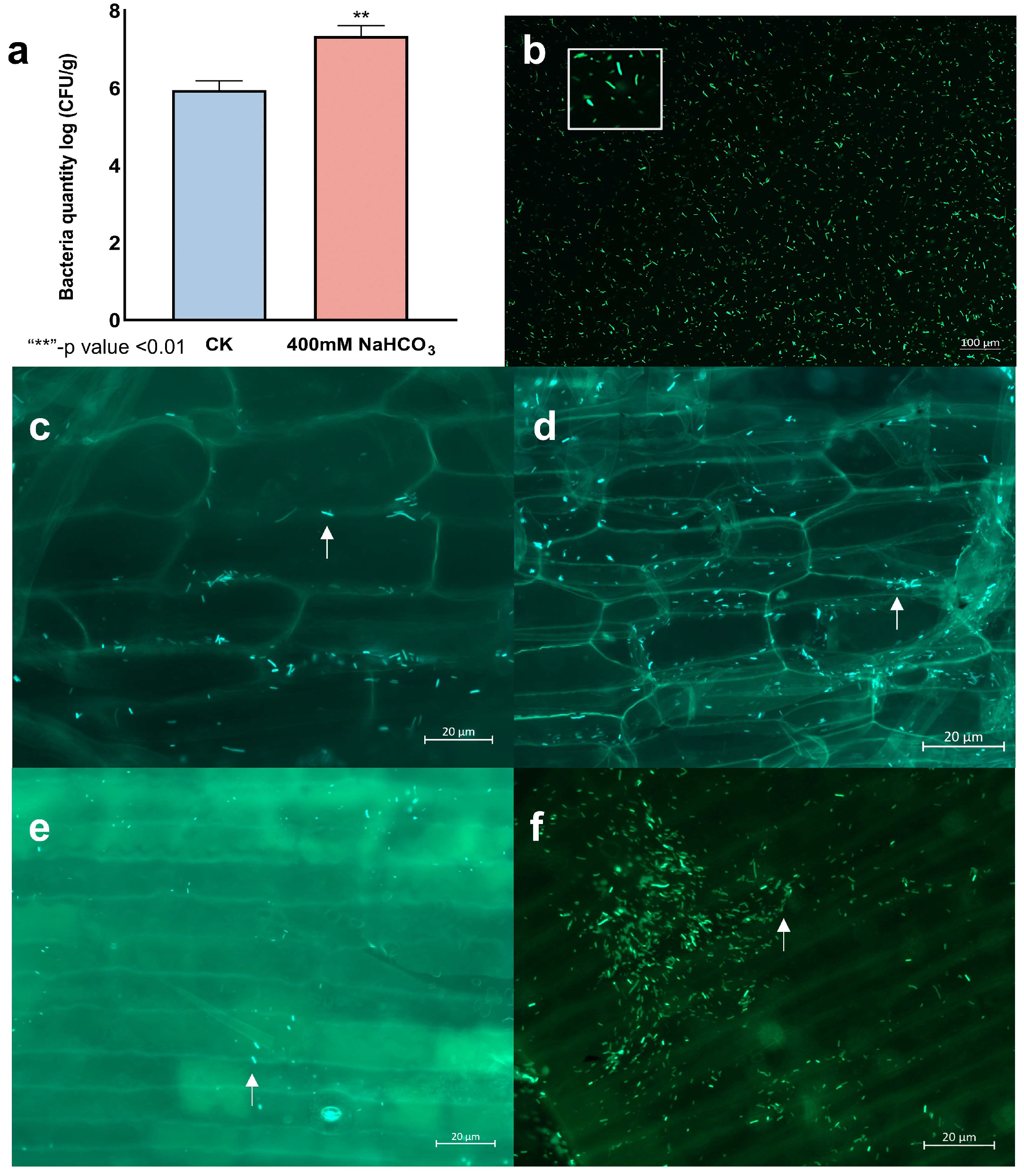
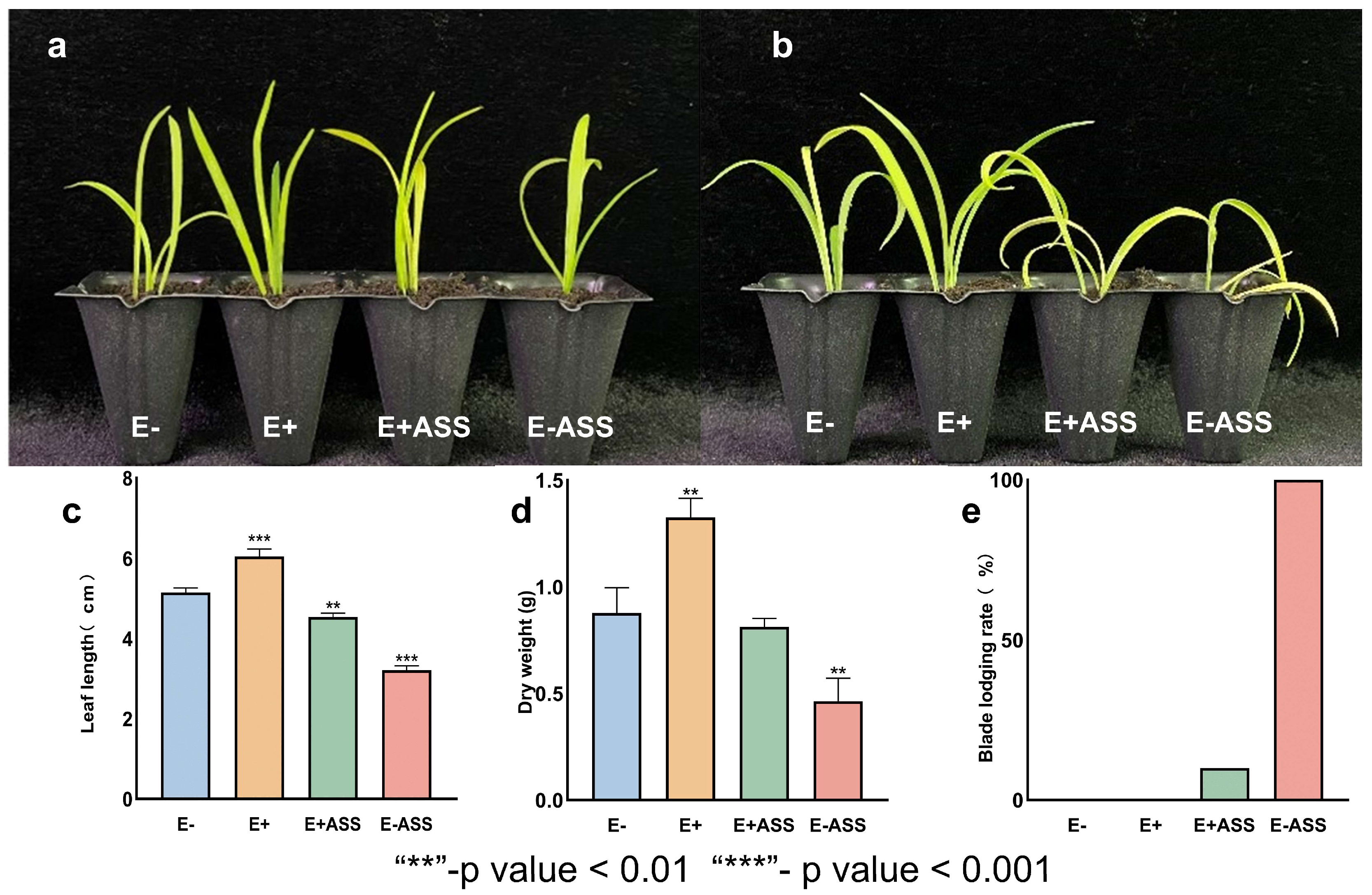
2.9. LpBc-47 Promotes the Growth of L. pumilum and Improves Its Salt Tolerance
3. Results
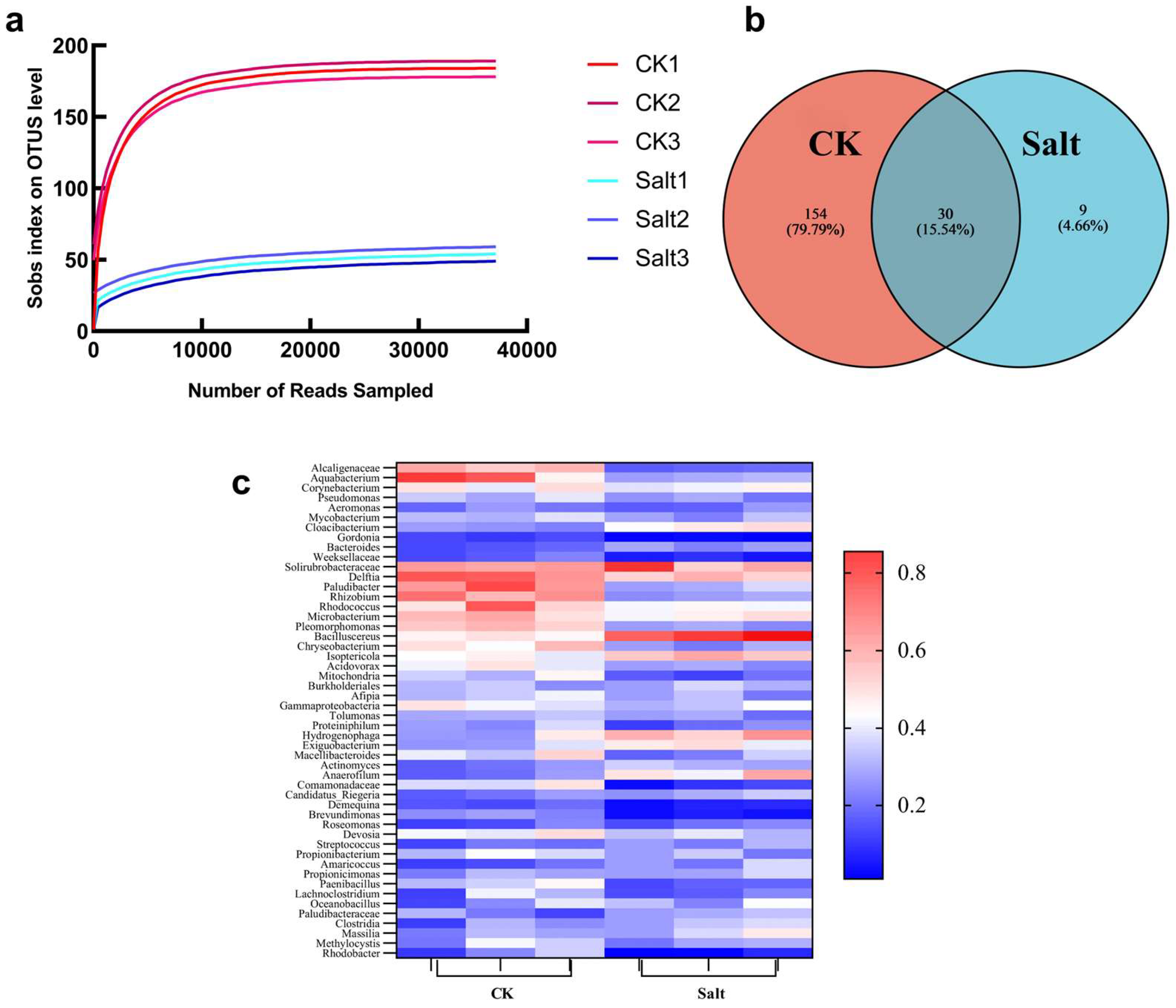
3.1. Microbial Diversity Analysis
3.2. Screening and Identification of Endophytic Bacteria
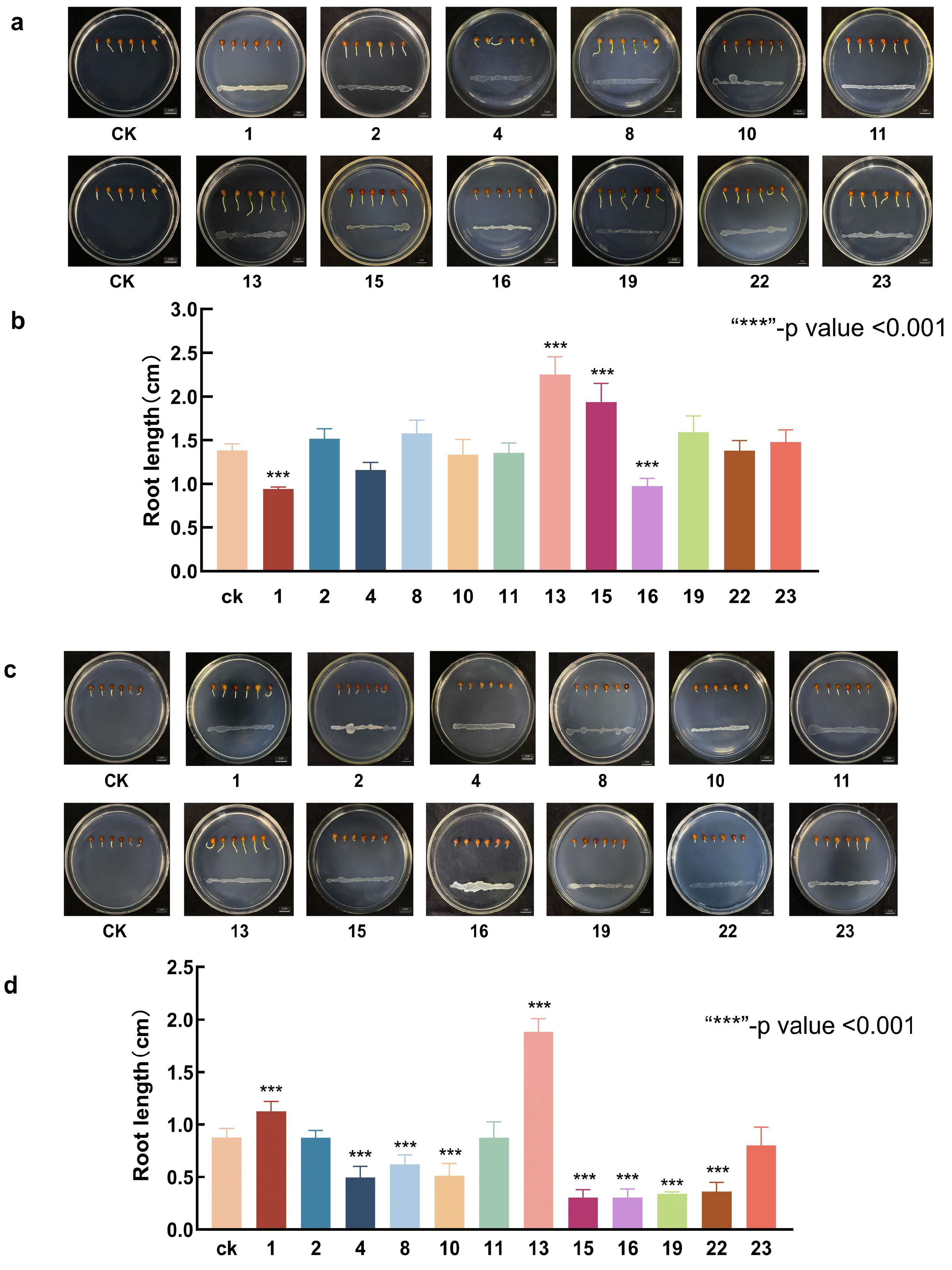
3.3. Screening of Bacteria with Growth-Promoting and Saline–Alkali Tolerance
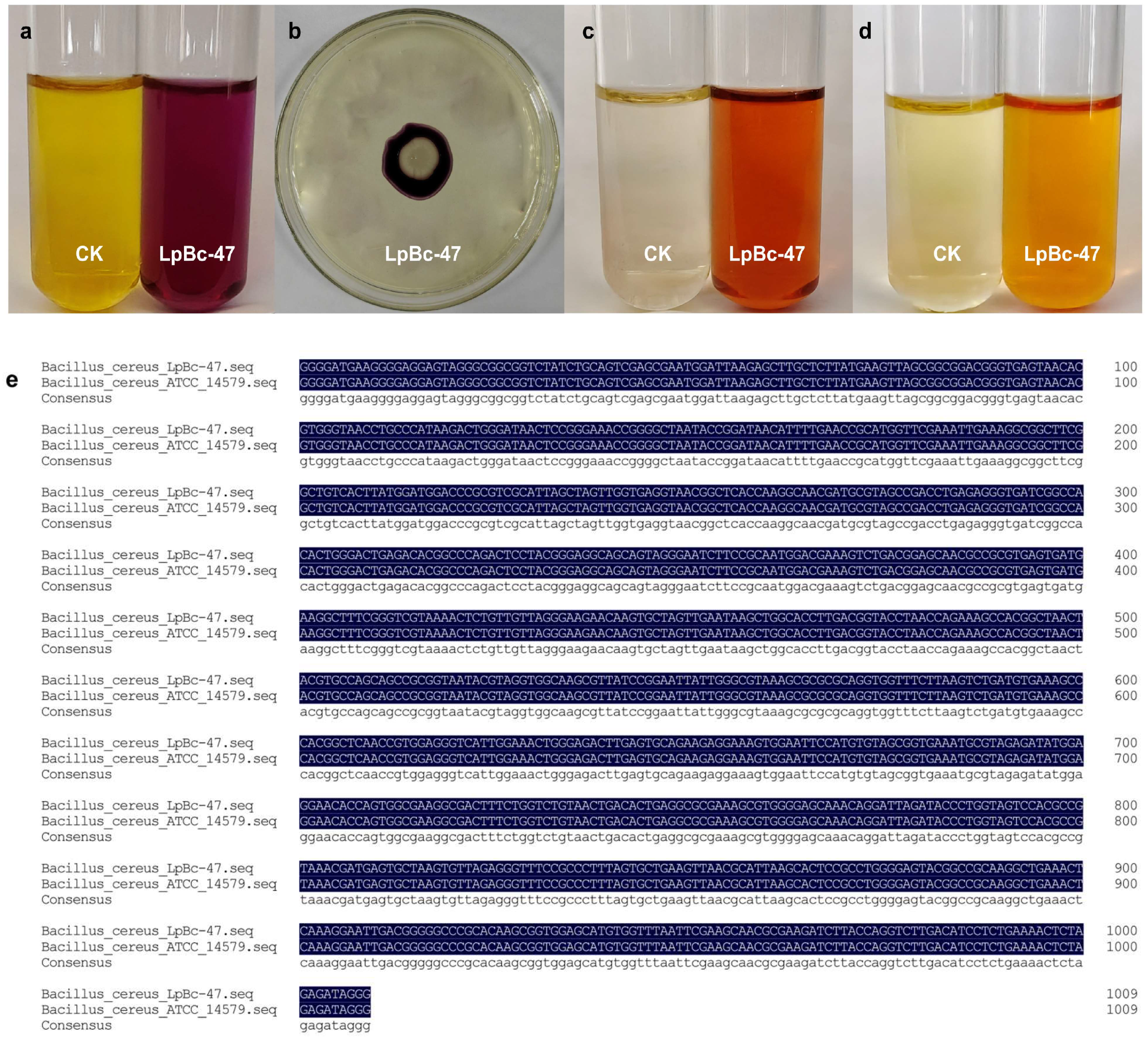
3.4. Identification of Bacteria
3.5. Genomic Analysis of LpBc-47
3.6. LpBc-47 Promotes the Growth of L. pumilum and Improves Plant Salt Tolerance
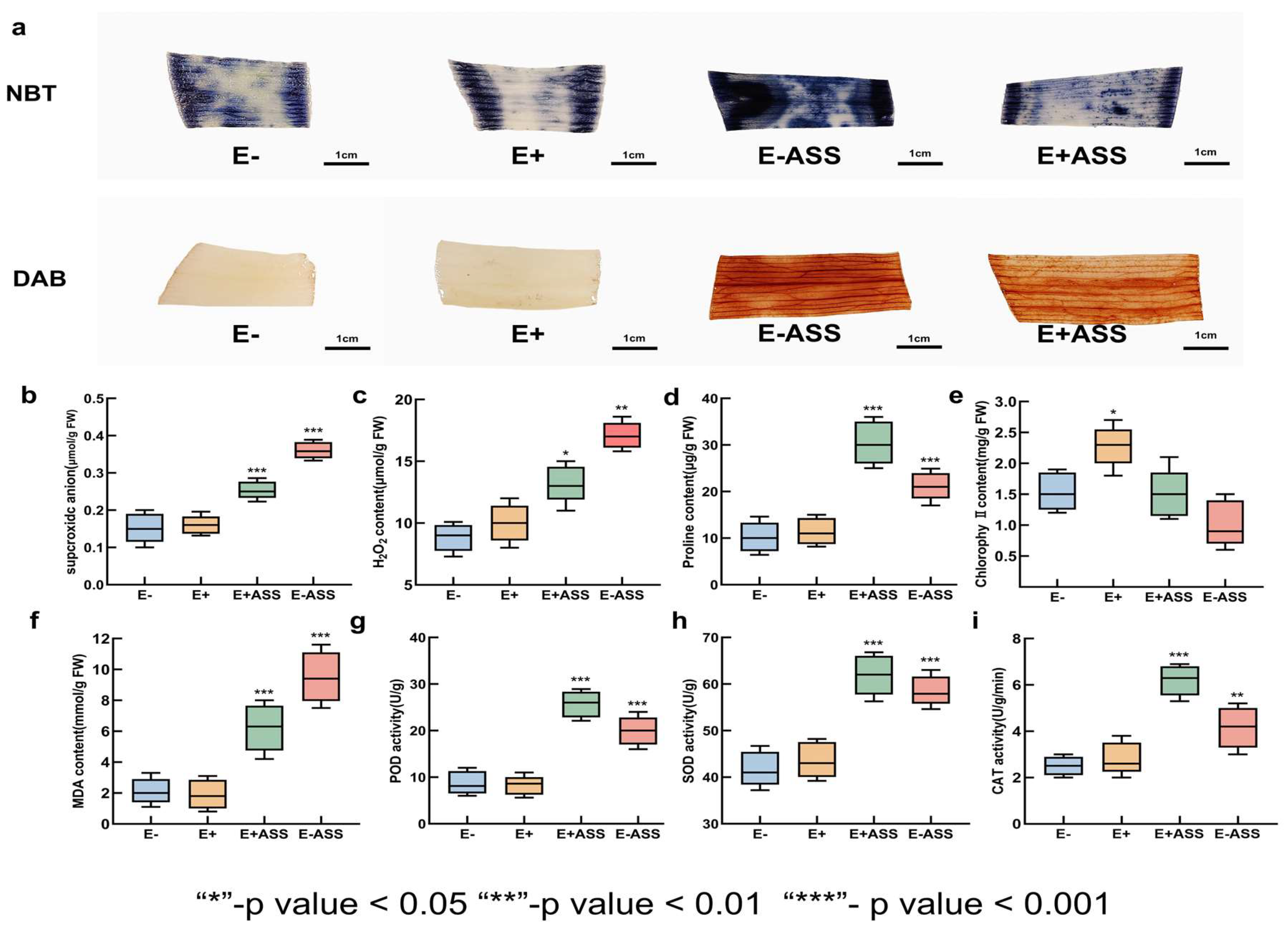
3.7. Measurement of Physiological Indexes After Bacteria Treatment Under Salt Stress
4. Discussion
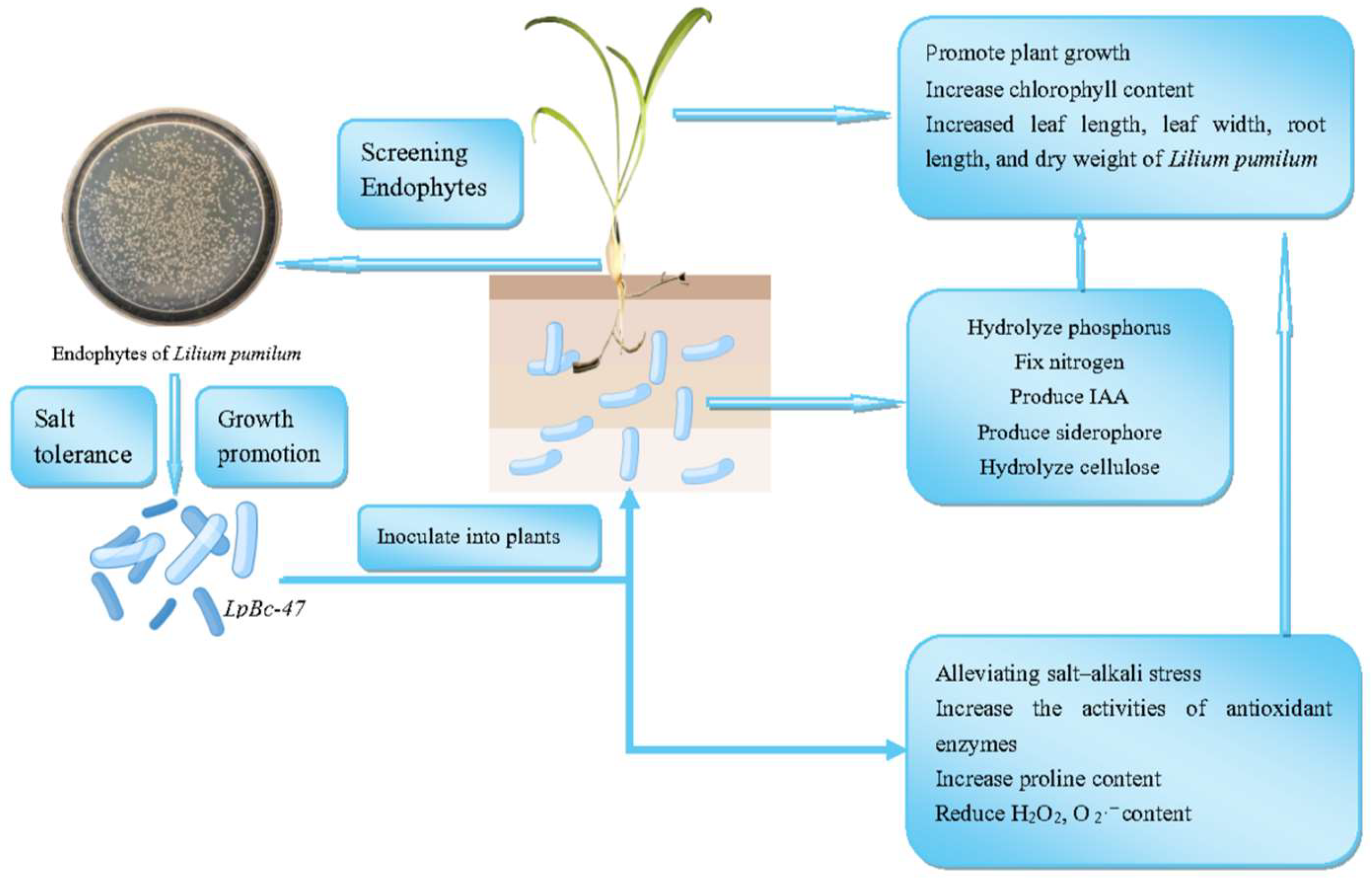
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LB | Lysogeny broth |
| PGPB | Plant growth-promoting bacteria |
| GFP | Green fluorescently labeled protein |
| NA | Nutrient agar |
References
- Zhou, D.; Hu, J.; Li, Q.; Huang, Y. Research progress of salt-affected land in Songnen Plain. Chin. J. Ecol. 2025, 44, 1671. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.; Wang, X.; Dong, Y.; Li, G.; Chang, X.; Zhang, L.; Jin, S. The gene increased NaHCO3 resistance by enhancing lignin or ROS scavenging in the Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Biol. 2022, 24, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Fu, L.; Wang, Z.; Gai, M.; Wang, C. Polyploidy induction and identification of Lilium pumilum and Lilium davidii var. unicolor based on somatic embryogenesis. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2018, 45, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Tan, M.; Yan, H.; So, K.; Zhang, Y. Transcriptome responses to salt stress in roots and leaves of Lilium pumilum. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 309, 111622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Cao, Y.; Bi, M.; Wang, P.; Liang, R.; Yang, P.; Ming, J. A Na+/H+ antiporter-encoding salt overly sensitive 1 gene, LpSOS1, involved in positively regulating the salt tolerance in Lilium pumilum. Gene 2023, 874, 147485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Guo, X.-Z.; Xu, Y.; Liu, D.-H.; Wang, H.-Y.; Guo, L.-P.; Zhang, Y. Advances in interaction between medicinal plants and rhizosphere microorganisms. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2020, 45, 2023–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunatha, N.; Manjunatha, N.; Li, H.; Sivasithamparam, K.; Jones, M.G.; Edwards, I.; Wylie, S.J.; Agarrwal, R. Fungal endophytes from salt-adapted plants confer salt tolerance and promote growth in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) at early seedling stage. Biorxiv-Microbiol. 2022, 168, 001225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Nie, K. Discovery of Endophytes in Lily cells. J. Wuhan Bot. Res. 1986, 4, 107–110+211–212. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Li, G.; Peng, L. Distribution and transmission of intracellular bacteria in lily tissue. J. Wuhan Bot. Res. 1989, 5, 101–106+205–206. [Google Scholar]
- Jibril, S.M.; Yan, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yunying, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, C. Highly diverse microbial community of regenerated seedlings reveals the high capacity of the bulb in lily, Lilium brownii. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1387870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Liu, S.; Ma, W.; Han, J.; Cao, H.; Zhang, X.; Liao, X. Screening and identification of Endophytic Antagonistic Bacteria Against Botrytis cinerea from Lilium davidii and optimization of fermentation conditions. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2022, 48, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yi, X.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Gao, J. Isolation and identification of a lily endophytic bacterium Burkholderia sp.fjb-2 and its in vitro antibacterial and growth promoting effect. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2022, 4, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Gao, J.; Zhang, M.; Xue, J.; Zhang, X. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Ld-08 isolated from Lilium davidii exhibits antifungal and growth-promoting properties. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Gao, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X.; Moe, T.S.; Du, Y.; Yang, F.; Xue, J.; Zhang, X. Isolation and characterization of plant growth-promoting endophytic bacteria Bacillus stratosphericus LW-03 from Lilium wardii. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reut, A.; Biglova, A.; Allayarova, I.; Aliniaeifard, S.; Gruda, N.S.; Lastochkina, O. Alteration of growth, phenology, and yield of lily flowers through the synergetic effect of light spectra and endophytic bacterial priming. South Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 167, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Qin, L.; Xu, X.; Shen, H.; Yang, X. Bacillus paralicheniformis RP01 Enhances the Expression of Growth-Related Genes in Cotton and Promotes Plant Growth by Altering Microbiota inside and outside the Root. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drobniewski, F.A. Bacillus cereus and related species. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1993, 6, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkova, I.; Dobrzyński, J.; Kowalczyk, P.; Bełżecki, G.; Kramkowski, K. Plant Growth Promotion Using Bacillus cereus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, B.; Deng, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Li, H.; Wang, J. Molecular Identification and Growth Promoting Mechanisms of 14 Bacillus Strains Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2021, 42, 789–799. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Liu, H.; Ning, Z.; Bian, Z.; Zeng, L.; Xie, D. Inoculation with Bacillus cereus DW019 modulates growth, yield and Rhizospheric Microbial Community of Cherry Tomato. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, G.-J.; Kim, Y.-M.; Lee, I.-J.; Song, K.-S.; Rhee, I.-K. Growth promotion of red pepper plug seedlings and the production of gibberellins by Bacillus cereus, Bacillus macroides and Bacillus pumilus. Biotechnol. Lett. 2004, 26, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Tan, J.; Chen, F.; Hao, D. Colonization of Bacillus cereus NJSZ-13, a species with nematicidal activity in Masson pine (Pinus massoniana Lamb.). J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, F.; Sun, M.; Liang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Yu, F.; Rengel, Z.; Li, H. Bicarbonate rather than high pH in growth medium induced Fe-deficiency chlorosis in dwarfing rootstock quince A (Cydonia oblonga Mill.) but did not impair Fe nutrition of vigorous rootstock Pyrus betulifolia. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1237327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Fu, X.; Wang, Q.; Mei, R. Cloning and characterization of Fe-SOD gene from Bacillus cereus M22. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2007, 37, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.-H.; Cox, J.M. Development and application of a centrifugation-plating method to study the biodiversity of Bacillus species in rice products. Food Control 2010, 21, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mete, A.; Coşansu, S.; Demirkol, O.; Ayhan, K. Amino acid decarboxylase activities and biogenic amine formation abilities of lactic acid bacteria isolated from shalgam. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y. Comparison of the ability of three bacterial species to catabolize starch. J. Hubei Univ. Med. 2003, 22, 182–183. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Shi, M.; Wan, W.; Wang, Z.; Ji, S.; Yang, F.; Jin, S.; Zhang, J. Maize Endophytic Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria Peribacillus simplex Can Alleviate Plant Saline and Alkaline Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Ma, L.; Zhou, W. An improved differential medium for cellulose decomposing microorganisms. J. Cellul. Sci. 2004, 12, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nautiyal, C.S. An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 170, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tong, J.; Dong, M.; Akhtar, K.; He, B.J.P. Isolation, identification and characterization of nitrogen fixing endophytic bacteria and their effects on cassava production. Peer J. 2022, 10, e12677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Yu, Q. Analysis of the Potassium-Solubilizing Priestia megaterium Strain NK851 and Its Potassium Feldspar-Binding Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, X.; Shen, P.; Xie, Z.-X. High-sensitive detection method for siderophores from pseudomonas. Microbiology 1992, 33, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Gang, S.; Sharma, S.; Saraf, M.; Buck, M.; Schumacher, J. Analysis of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) production in Klebsiella by LC-MS/MS and the Salkowski method. Bio-Protoc. 2019, 9, e3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Zeng, X.; Li, Y. Effects of ACC deaminase on symbiotic nitrogen fixation and competitive nodulation in Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 and Sinorhizobium fredii HH103. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2019, 38, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, A.; Pang, Q. Enhancement of sulfur metabolism and antioxidant machinery confers Bacillus sp. Jrh14-10–induced alkaline stress tolerance in plant. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 203, 108063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Yusuf, M.A.; Singh, P.; Sardar, M.; Sarin, N.B. Histochemical detection of superoxide and H2O2 accumulation in Brassica juncea seedlings. Bio-Protoc. 2014, 4, e1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltabayeva, A.; Sagi, M. Determination of ROS Generated by Arabidopsis Xanthine Dehydrogenase1 (AtXDH1) Using Nitroblue Tetrazolium (NBT) and 3,3′-Diaminobenzidine (DAP). In ROS Signaling in Plants Methods and Protocols; Corpas, F.J., Palma, J.M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.R.; Kim, C.S.; Park, T.; Choi, Y.-S.; Lee, K.-H. Optimization of the ninhydrin reaction and development of a multiwell plate-based high-throughput proline detection assay. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 556, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, J.; Guo, Z.; Tan, H.; Zhu, X. A simple colorimetric method for determination of hydrogen peroxide in plant tissues. Plant Growth Regul. 2006, 49, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Su, W.; Li, H.; Guo, Z. Abscisic acid improves drought tolerance of triploid bermudagrass and involves H2O2− and NO-induced antioxidant enzyme activities. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 47, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadgórska-Socha, A.; Kafel, A.; Kandziora-Ciupa, M.; Gospodarek, J.; Zawisza-Raszka, A. Accumulation of heavy metals and antioxidant responses in Vicia faba plants grown on monometallic contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, U.; Oba, S. Catalase, superoxide dismutase and ascorbate-glutathione cycle enzymes confer drought tolerance of Amaranthus tricolor. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, T.-T.; Li, T.-T.; Tian, Y.-Y.; Wang, L.-F.; Liu, W.-C. Jasmonic acid promotes leaf senescence through MYC2-mediated repression of CATALASE2 expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2020, 299, 110604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishad, R.; Ahmed, T.; Rahman, V.J.; Kareem, A. Modulation of plant defense system in response to microbial interactions. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Gao, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, F.; Du, Y.; Moe, T.S.; Munir, I.; Xue, J.; Zhang, X. The Endophytic Bacteria Bacillus velezensis Lle-9, Isolated from Lilium leucanthum, Harbors Antifungal Activity and Plant Growth-Promoting Effects. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.S.; Gao, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, F.; Du, Y.; Moe, T.S.; Munir, I.; Xue, J.; Zhang, X. Isolation and Characterization of Plant Growth-Promoting Endophytic Bacteria Paenibacillus polymyxa SK1 from Lilium lancifolium. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8650957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.-l.; Khan, M.S.; Sun, Y.-c.; Xue, J.; Du, Y.; Yang, C.; Chebotar, V.K.; Tikunov, V.S.; Rubanov, I.N.; Chen, X.; et al. Characterization of an Endophytic Antagonistic Bacterial Strain Bacillus halotolerans LBG-1-13 with Multiple Plant Growth-Promoting Traits, Stress Tolerance, and Its Effects on Lily Growth. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5960004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, H.; Fu, C.; Li, J.; Xiang, J.; Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Qin, L. Diversity changes of rhizosphere and endophytic bacteria in Allium senescens L. under drought stress and rewatering. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1571736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Tang, L.; Cui, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Guo, C. Saline-alkali stress reduces soil bacterial community diversity and soil enzyme activities. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 1356–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Song, Y. Toward understanding the genetic bases underlying plant-mediated “cry for help” to the microbiota. IMeta 2022, 1, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Li, Y.; Chai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ding, M. SigB regulates stress resistance, glucose starvation, MnSOD production, biofilm formation, and root colonization in Bacillus cereus 905. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 5943–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauveron, G.; Slomianny, C.; Henry, C.; Faille, C. Variability among Bacillus cereus strains in spore surface properties and influence on their ability to contaminate food surface equipment. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 110, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beattie, S.; Williams, A. Detection of toxigenic strains of Bacillus cereus and other Bacillus spp. with an improved cytotoxicity assay. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 28, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Ali, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, W.-C. Transgenic Arabidopsis expressing acdS gene of Pseudomonas veronii-KJ alleviate the adverse effects of salt and water-logging stress. Plant Breed. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Yan, D.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y. AcdS gene of Bacillus cereus enhances salt tolerance of seedlings in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2022, 36, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, P.M.; Stuckey, D.C. Biofilms, bubbles and boundary layers–A new approach to understanding cellulolysis in anaerobic and ruminant digestion. Water Res. 2016, 104, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Qiu, S.; Xie, X.; Wang, X. Research progress on phosphorus-dissolving fungi. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2010, 38, 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Sarikhani, M.R.; Oustan, S.; Ebrahimi, M.; Aliasgharzad, N. Isolation and identification of potassium-releasing bacteria in soil and assessment of their ability to release potassium for plants. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, A.P.D.d.; Sala, V.M.R.; Cardoso, E.J.B.N.; Labanca, E.G.; Cipriano, M.A.P. Nitrogen metabolism and growth of wheat plant under diazotrophic endophytic bacteria inoculation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 107, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Johri, B.N. Growth promoting influence of siderophore-producing Pseudomonas strains GRP3A and PRS9 in maize (Zea mays L.) under iron limiting conditions. Microbiol. Res. 2003, 158, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tu, W. Growth promoting activity of siderophore secreting bacteria for peanut plant under nickel stress. Microbiol. China 2017, 44, 1882–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manshur, T.A.; Fauzan, I.A.; Junianti, E. Indole Acetic Acid (IAA) Producing Bacteria from Saline Paddy Soil in Kebumen. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Purwokerto, Indonesia, 5–7 November 2018; p. 012006. [Google Scholar]
- Gamalero, E.; Lingua, G.; Glick, B.R. Ethylene, ACC, and the plant growth-promoting enzyme ACC deaminase. Biology 2023, 12, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, N.; Qian, C.; Hao, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, X.; Ghanem, O.M.; Salem, A.; Orban, Z.; Elwakeel, A.E.; et al. Hybrid Pennisetum colonization by Bacillus megaterium BM18-2 labeled with green fluorescent protein (GFP) under Cd stress. Arch. Microbiol. 2025, 207, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Wu, Q. Alleviation of drought stress by mycorrhizas is related to increased root H2O2 efflux in trifoliate orange. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, P.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Bi, Z.; Zhang, P. Effects of exogenous hydrogen peroxide on the physiological index of wheat seedlings under salt stress. Acta Bot. Boreal.-Occident. Sin. 2012, 32, 1796–1801. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Chen, F.; Liu, D.; Wan, Y.; Cao, Y. Effect of potash application on some enzyme content in rapeseed leaf. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2002, 24, 61–62, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Sun, J.; Guo, S.; Jin, C. Effects of calcium on antioxidant enzymes activities of cucumber seedlings under salt stress. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2010, 37, 1937–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; He, C.-X.; He, Z.-Q.; Zou, Z.-R.; Zhang, Z.-B. The effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on reactive oxyradical scavenging system of tomato under salt tolerance. Agric. Sci. China 2010, 9, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, J.; Lu, N. The characteristics of free proline distribution in various types of salt-resistant plants. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2006, 15, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Sang, T.; Tian, M.; Jahan, M.S.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Guo, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Shu, S. Effects of Bacillus cereus on Photosynthesis and Antioxidant Metabolism of Cucumber Seedlings under Salt Stress. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.-Y.; Wang, Y.-H.; Wu, F.; Wu, X.-Q. Dual inoculation with rhizosphere-promoting bacterium Bacillus cereus and beneficial fungus Peniophora cinerea improves salt stress tolerance and productivity in willow. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 268, 127280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Qiuli, W.; Duoyong, L.; Yuankui, C.; Yu, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X. RNA-seq reveals that multiple plant hormones are regulated by Bacillus cereus G2 in Glycyrrhiza uralensis subjected to salt stress. J. Plant Interact. 2021, 16, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, A.M.; Umesh, M.; Priyanka, K.; Preethi, K. Isolation of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacillus cereus from Soil and Its Use as a Microbial Inoculant. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Serial Number | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Priestia aryabhattai |
| 2 | Pseudomonas putida |
| 3 | Actinomycetota bacterium |
| 4 | Psychrobacter pulmonis |
| 5 | Novosphingobium resinovorum |
| 6 | Cytophaga sp. |
| 7 | Sphingobium baderi |
| 8 | Flavobacterium |
| 9 | Stenotrophomonas geniculate |
| 10 | Cellvibrio diazotrophicus |
| 11 | Flavobacterium microcysteis |
| 12 | Sphingomonas sp. |
| 13 | Bacillus cereus |
| 14 | Ureibacillus chungkukjangi |
| 15 | Bacillus luti |
| 16 | Pseudomonas psychrotolerans |
| 17 | Bacterium |
| 18 | Serratia |
| 19 | Lysinibacillus sphaericus |
| 20 | Acinetobacter |
| 21 | Bacillus megaterium |
| 22 | Paenibacillus amylolyticus |
| 23 | Bacillus pumilus |
| 24 | Exiguobacterium |
| Gene Function | Genes Number | Genes Name |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen compound metabolic process | 94 | Nif, nifD |
| Phosphorus metabolic process | 30 | PstA, pstB, pstC |
| Potassium ion transport | 88 | KdpC, KhtT |
| Indole acetic acid synthase activity | 6 | AdhR, aroA |
| Antioxidant activity | 10 | CAT, SOD, POD |
| Iron ion binding | 190 | EntS, dhbC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, M.; Zhang, L.; Sun, H.; Ji, S.; Cui, H.; Wan, W.; Liu, X.; Tian, A.; Yang, W.; Wang, X.; et al. The Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium Bacillus cereus LpBc-47 Can Alleviate the Damage of Saline–Alkali Stress to Lilium pumilum. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061248
Shi M, Zhang L, Sun H, Ji S, Cui H, Wan W, Liu X, Tian A, Yang W, Wang X, et al. The Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium Bacillus cereus LpBc-47 Can Alleviate the Damage of Saline–Alkali Stress to Lilium pumilum. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061248
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Miaoxin, Lingshu Zhang, Hao Sun, Shangwei Ji, Huitao Cui, Wenhao Wan, Xingyu Liu, Ao Tian, Wei Yang, Xinran Wang, and et al. 2025. "The Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium Bacillus cereus LpBc-47 Can Alleviate the Damage of Saline–Alkali Stress to Lilium pumilum" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061248
APA StyleShi, M., Zhang, L., Sun, H., Ji, S., Cui, H., Wan, W., Liu, X., Tian, A., Yang, W., Wang, X., Yang, F., & Jin, S. (2025). The Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium Bacillus cereus LpBc-47 Can Alleviate the Damage of Saline–Alkali Stress to Lilium pumilum. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061248






