Abstract
Soil erosion has caused the loss of black soil and exposed the soil parent material in the cultivated layer of sloping farmland in Northeast China. Straw return (STR) and manure fertilization (MF) are critical measures to improve soil quality and crop yield. However, the effect of STR and MF on the soil properties of the parent material remains unclear. We conducted a 1-year pot experiment in the field using the soil parent material of degraded black soil to evaluate the effects of STR and MF on soil nutrients, microbial community, and soybean yield. We analyzed these effects using two treatments (STR and MF) in three soybean growth stages (seedling, flowering, and maturity) and a control group (CK). The MF treatment had higher α and β diversity of soil microbial than the CK during all soybean growth stages. Similarly, STR had higher soil microbial α diversity at the maturity stage and lower diversity at the seedling stage. Co-occurrence network analysis suggested that STR and MF increased the proportion of positively correlated edges in soil bacterial and fungal networks compared to the CK. Notably, the treatments enriched beneficial taxa, such as Schizothecium (fungi) and Massilia (bacteria), which are associated with organic matter decomposition and nitrogen cycling. STR and MF significantly improved soil organic matter, total nitrogen, and carbon-nitrogen ratio (p < 0.05). Structural equation modeling (SEM) revealed that STR and MF directly increased soybean yield. This effect was primarily mediated by the significantly higher soil organic matter, total carbon, total nitrogen, and carbon-to-nitrogen ratio in the treatments than in the CK (p < 0.05). In summary, STR and MF improved soil fertility and soil microbial community diversity of degraded black soil. This study provides scientific methods to improve the fertility of degraded black soil and increase soybean production in the short term.
1. Introduction
The black soil region of Northeast China is an important commercial grain production base and is regarded as “the hometown of soybeans” [1]. However, inappropriate land development and utilization have caused topsoil loss of sloping farmland at rates of 0.3–1 cm annually. Consequently, the average soil layer thickness has decreased from 60–80 cm in the 1950s to 20–30 cm at present [2,3]. Continued land degradation has caused the complete disappearance of the black soil layer in some areas of sloping farmland, exposing the soil parent material [4,5], which has less organic matter and a worse soil structure than the black soil, resulting in reduced grain yields and threatening China’s food security [6,7]. These severely degraded areas still need to be used as arable land to protect the arable land minimum of China, so it is critical to rapidly restore the soil fertility of degraded black soils to maintain grain production in Northeast China. Meanwhile, Soybean is a relatively low-tilled crop, which can increase soil nitrogen content through nitrogen fixation and improve soil fertility [8]. In addition, previous studies found that short-term STR could increase soybean yields while reducing corn yields by 30% in this region [9].
The addition of organic materials (i.e., straw and manure fertilization) is crucial for improving soil quality and crop yield [10,11]. Numerous studies have shown that applying organic materials improved soil structure, water-holding capacity, and nutrient availability and content [12,13,14,15]. Moreover, soil microbes are crucial in maintaining soil quality in farmland ecosystems [16]. The application of organic material substantially improved soil microbial richness, diversity, and functional gene abundance [14,17]. Long-term (44-year) applications of MF increased the relative abundance of Nitrospira and Gemmatimonas, which were significantly positively correlated with soybean yield in Northeast China [18]. Meanwhile, the STR treatment provided nutrients for soil microorganisms, increased soil microbial diversity, and optimized microbial community structure [12,19,20]. Furthermore, improving soil organic matter, nutrient cycling, and carbon sequestration, and increasing soil fertility and crop yields [21,22,23].
The utilization of straw and manure fertilizers has become a critical priority for sustainable agriculture in the black soil region of Northeast China [14,24,25]. Several studies have demonstrated that the application of STR and MF can improve soil structure, increase soil nutrients, and maintain crop yields in this region [15,26,27]. However, few studies have analyzed the addition of straw and MF on soil quality and crop yields in the significantly eroded areas, i.e., regions where the soil parent material is exposed. We hypothesized that the application of organic materials can modulate microbial structure and function by improving soil fertility, thereby enhancing soybean productivity in the soil parent material of degraded black soil in Northeast China. Our objectives were to (1) evaluate the short-term effects of STR and manure fertilization (MF) on soil microbial community composition and abundance in degraded black soil, (2) examine the relationships between soil microbial communities, soil physicochemical properties, and crop yields, and (3) identify suitable practices for rapidly improving soil fertility and crop productivity. These results can provide a scientific basis for the sustainable utilization of arable land in Northeast China.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
The field experiment was conducted at the Hailun Monitoring and Research Station of Mollisol Erosion, Chinese Academy of Sciences (47°21′ N, 126°50′ E), in Hailun City, Heilongjiang Province. The mean annual air temperature is 1.5 °C. The ≥10 °C accumulated temperature ranges from 2400 to 2500 °C, and the mean annual sunshine duration ranges from 2600 to 2800 h. The area has a temperate continental monsoon climate with a mean annual precipitation of 530 mm, 65% of which falls from June to August. The frost-free period is approximately 120 days.
2.2. Experimental Design
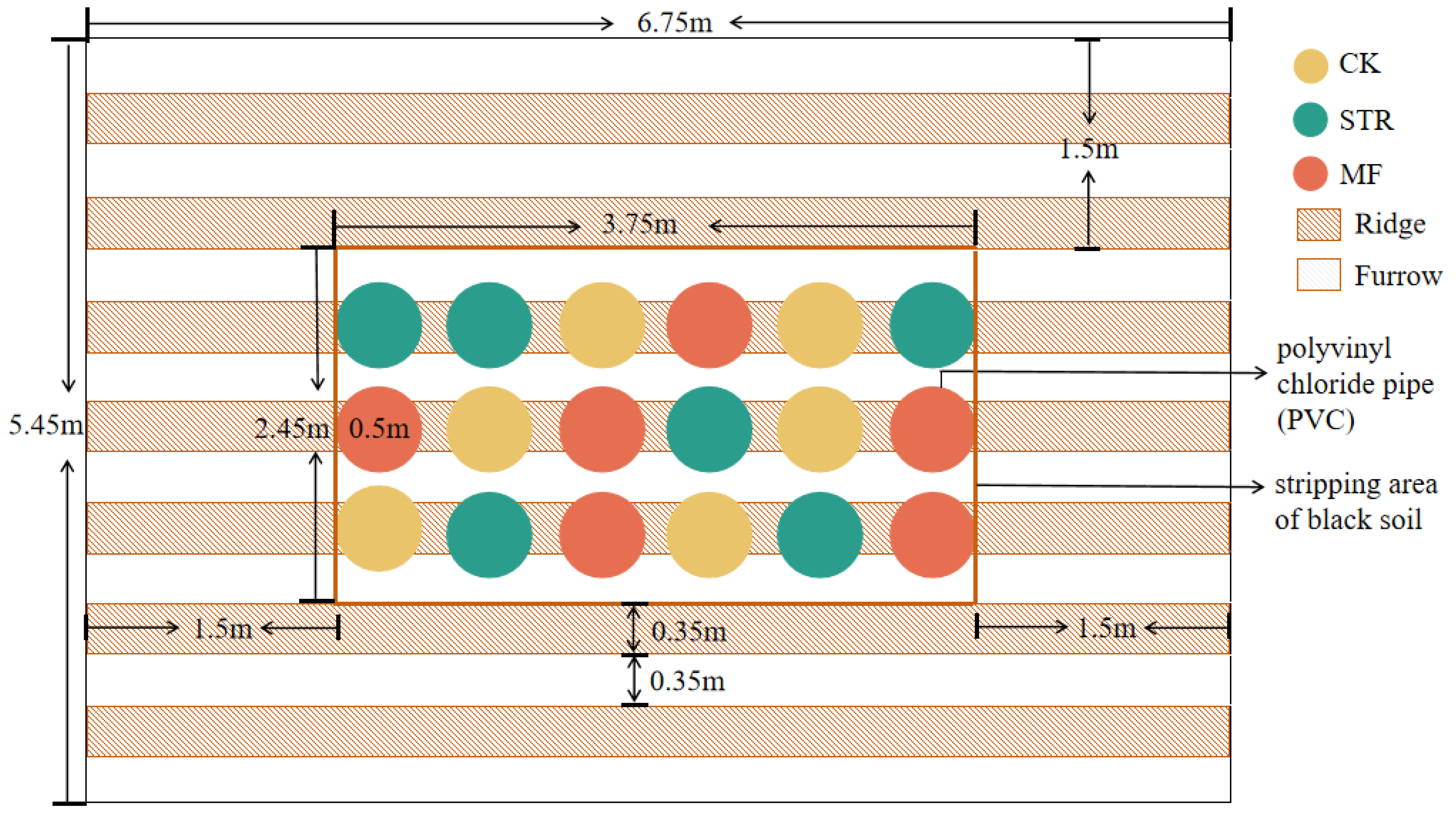
Experiment plots were established in the autumn of 2022. We conducted pot experiments in the field (Figure 1). An experimental farmland area (3.75 m length × 2.45 m width × 0.45 m height) was selected, and the naturally degraded soil was removed. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes (0.5 m in diameter and 0.5 m in height) were placed into the experimental area to delineate farmland ridges. The bottoms of the PVC pipes were covered with nylon mesh (30 μm) to exclude roots and facilitate soil moisture movement [28]. The PVC pipes were filled with the air-dried parent material of the black soil (bulk density: 1.50 g/cm3) [29], which was passed through a 2 cm sieve to ensure homogeneity. The soil properties are listed in Table 1. To control boundary effects, the spatial interval between each plot was 20 cm, and the height and depth of the PVC pipes were 50 cm and 45 cm, respectively. This means that the PVC pipe was 5 cm higher than the surface ground, which was beneficial to prevent the plot from being mixed into the plot during the snowmelt and rainy periods. Meanwhile, the plastic films were covered in the plots to reduce the impact of wind erosion before sowing in spring. In addition, a 1.5-meter-wide buffer planted with soybeans was created around the perimeter of the experimental site to protect the site from external influences. The spaces between the PVC pipes were backfilled with the removed soil.
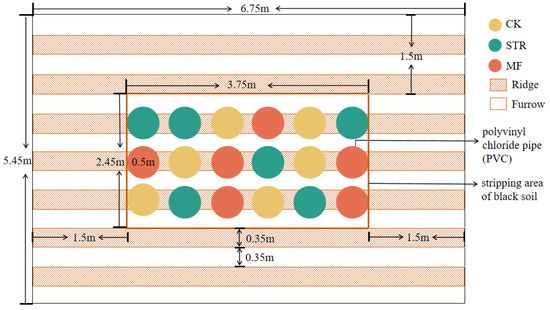
Figure 1.
Experimental plot. CK: the control treatment without the additions of straw and manure fertilization; STR: Straw returning; MF: Manure fertilization.

Table 1.
The initial soil properties of parent material.
The field experiment plots included two treatments (STR and MF) and a control group. We used a randomized complete block design with six replications. The MF treatment was 1.5 t/hm2, with an average organic matter content of 47 g/kg. The STR treatment consisted of applying crushed maize straw at a rate of 10 t/hm2, with an average total organic carbon content (TC) of 44 g/kg and total nitrogen content (TN) of 4 g/kg. The manure fertilization and crushed corn straw were evenly incorporated into the 0–20 cm soil layer in autumn 2022. Ten soybeans were planted in each plot, combining the regional survey data, and the same field managements were applied to all the plots. Inorganic fertilizer was applied to the treatment and control plots based on the typical fertilizer amount in the area at 20.25 kg N/ha, 51.75 kg P/ha, and 15.00 kg K/ha to provide soil nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium [9,30].
2.3. Soil Sampling and Measurement
Soil samples were collected at 0–20 cm soil depth during the soybean growth stages, sowing (May), flowering (July), and maturity (October). The mixed soil samples of the three sampling points were stored in sealed plastic bags. They were divided into two parts. One part was air-dried and passed through a 0.25 mm sieve to measure soil physicochemical properties. The other part was stored at −20 °C before analyzing soil microbial communities. Soil pH was determined using a potentiometer with a fixed ratio of 1:2.5 soil to water. Soil total carbon (TC) and total nitrogen (TN) were measured using an elemental analyzer (Vario EL, Langenselbold, Germany). Soil temperature and soil moisture were measured using a FieldScout TDR 350 (Aurora, IL, USA).
2.4. Soil DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
Soil DNA was extracted from 0.5 g of a fresh soil sample using the PowerSoil DNA Isolation Kit (Mo Bio, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The quantity and quality of the extracted DNA were assessed using a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Wilmington, DE, USA) and a Qubit 3.0 Fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Wilmington, DE, USA), respectively. The bacterial 16S rRNA gene was amplified with primer pair 338F (5′-ACTCCTACGGAGGCAGCAG-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′) [31]. The fungal internal transcribed spacer (ITS) regions were amplified with primers TS1F (5′-GGAAGTAAAAGTCGTAACAAGG-3′) and ITS2R (5′-GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC-3′) [32]. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reaction mixture consisted of 4 μL of 5× FastPfu Buffer, 2 μL of dNTPs (2 mmol/L), 0.8 μL each of forward and reverse primers (5 μmol/L), 2 μL of DNA template, 0.4 μL of Taq polymerase (5 U/μL), and ddH2O for a final volume of 20 μL [33]. The PCR cycle included initial denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min, followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 58 °C for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 1 min. The PCR product was extracted from a 2% agarose gel and purified using the PCR Clean-Up Kit (YuHua, Shanghai, China). Paired-end sequenced on an Illumina Nextseq2000 platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). The sequencing and analysis of the soil samples were conducted using an Illumina Miseq platform (Meiji Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The raw sequencing data were quality-filtered using Fastp (version 0.19.6) to remove low-quality base sequences. Sequence clustering was performed using Uparse (version 11.0) with a 97% similarity threshold for operational taxonomic unit (OTU) designation. After rarefaction analysis based on the minimum sequence count across samples, 34,740 high-quality sequences were retained and clustered into 3234 OTUs. Taxonomic annotation was performed using the Ribosomal Database Project’s (RDP) Bayesian classification algorithm and the Silva SSU128 16S rRNA and fungal 18S rRNA reference databases. Alpha diversity was calculated using Mothur (version 1.30.2). The original data were processed by EXCEL 2011 software and then were normalized by using descriptive Statistics from the SPSS 26.0 software (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA): One-way ANOVA and Duncan’s multiple-range test were used to determine statistically significant differences in the soil physiochemical properties, microbial diversity and crop yields between treatments. In this study, the Kolmogorov–Smirnov statistical test for the analysis of homogeneity of variance was conducted.
The beta diversity pattern was assessed using principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) and analysis of similarities (ANOSIM) to identify significant microbial community differences between treatments. The co-occurrence network was constructed by using the top 150 OTUs with strong correlations (Spearman’s |r| > 0.7, p < 0.01), and the results were visualized using Gephi 0.10.0. Structural equation modeling (SEM) was used to analyze the direct and indirect effects of different organic materials on the degraded black soil’s properties, soil microorganisms, and crop yields.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
MF increased soil pH, TC, TN, and soil organic matter (SOM) during all the soybean growth periods. The SOM content was significantly higher (p < 0.05) in the MF treatment in the seeding (23.96%), flowering (43.4%), and maturity (40.81%) stages than in the CK (Table 2). The STR treatment increased the TC, TN, and SOM contents. The average values of the TC, TN, and SOM in the MF treatment were 66.28%, 36.17%, and 45.79% higher in the MF treatment than in the CK (p < 0.05). Similarly, the average values of the TC, TN, and SOM in the STR treatment were 53.67%, 21.28, and 28.47% higher in the STR treatment than in the CK.

Table 2.
Soil physical and chemical properties of soil under different organic materials returned to the field.
Moreover, a significantly higher carbon-nitrogen ratio (C/N ratio) was observed in the STR and MF treatments than in the CK in the flowering and maturity stages. No significant differences in soil moisture and soil temperature occurred in the treatments during the soybean growth season. In addition, the TC, TN, and SOM in the STR and MF treatments were higher in the flowering and maturity stages than in the seedling stage.
3.2. Bacterial and Fungal Diversities
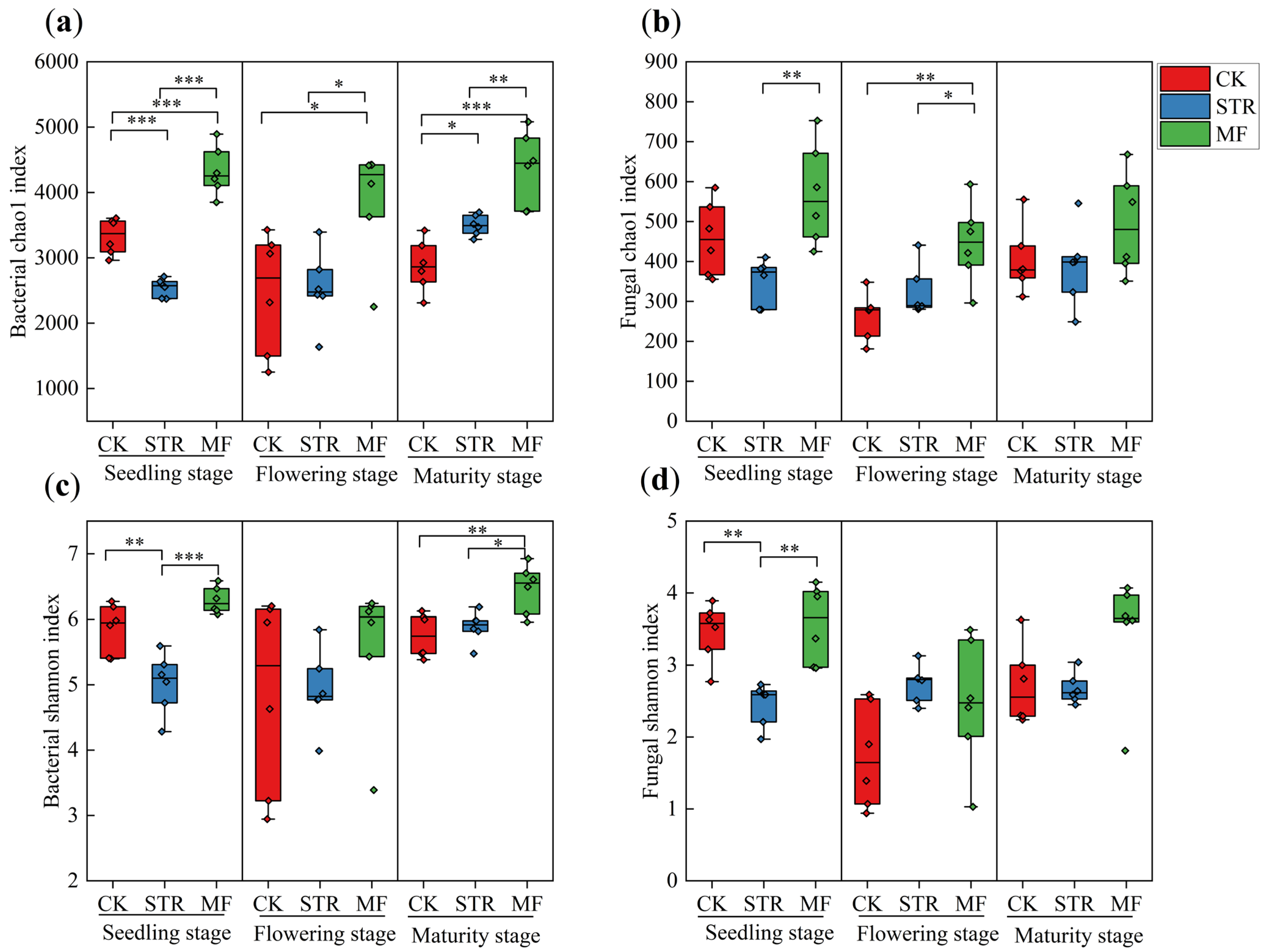
The alpha diversity of soil bacteria (the Chao1 and Shannon indices) was significantly lower in the STR treatment than the CK in the seeding stage (p < 0.05) (Figure 2a,c). In contrast, the Chao1 index was significantly higher in STR than in the CK in the maturity stage (p < 0.05). No significant difference in the Shannon index was found between STR and CK in the flowering and maturity stages. The Chao1 and Shannon indices were higher in the MF treatment than in the CK, especially in the seeding and maturity stages (p < 0.05) (Figure 2a,c).
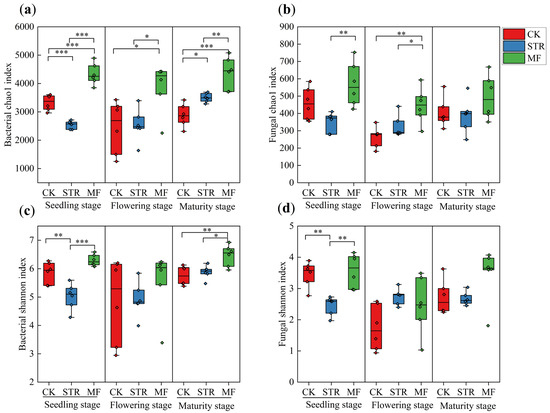
Figure 2.
Effect of the application of straw return (STR) and manure fertilization (MF) on the Alpha diversity index of bacteria (a,c) and fungi (b,d) in different periods. Note: *, ** and *** represented at p < 0.05, p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively.
STR significantly reduced soil fungal alpha diversity in the seeding stage, whereas no significant differences were observed in the flowering and maturity stages (Figure 2b,d). No significant differences in the alpha diversity of soil fungi were observed between MF and CK during the growing season (Figure 2b,d).
3.3. β Diversity of Bacterial and Fungal Communities Under the Addition of Different Organic Materials
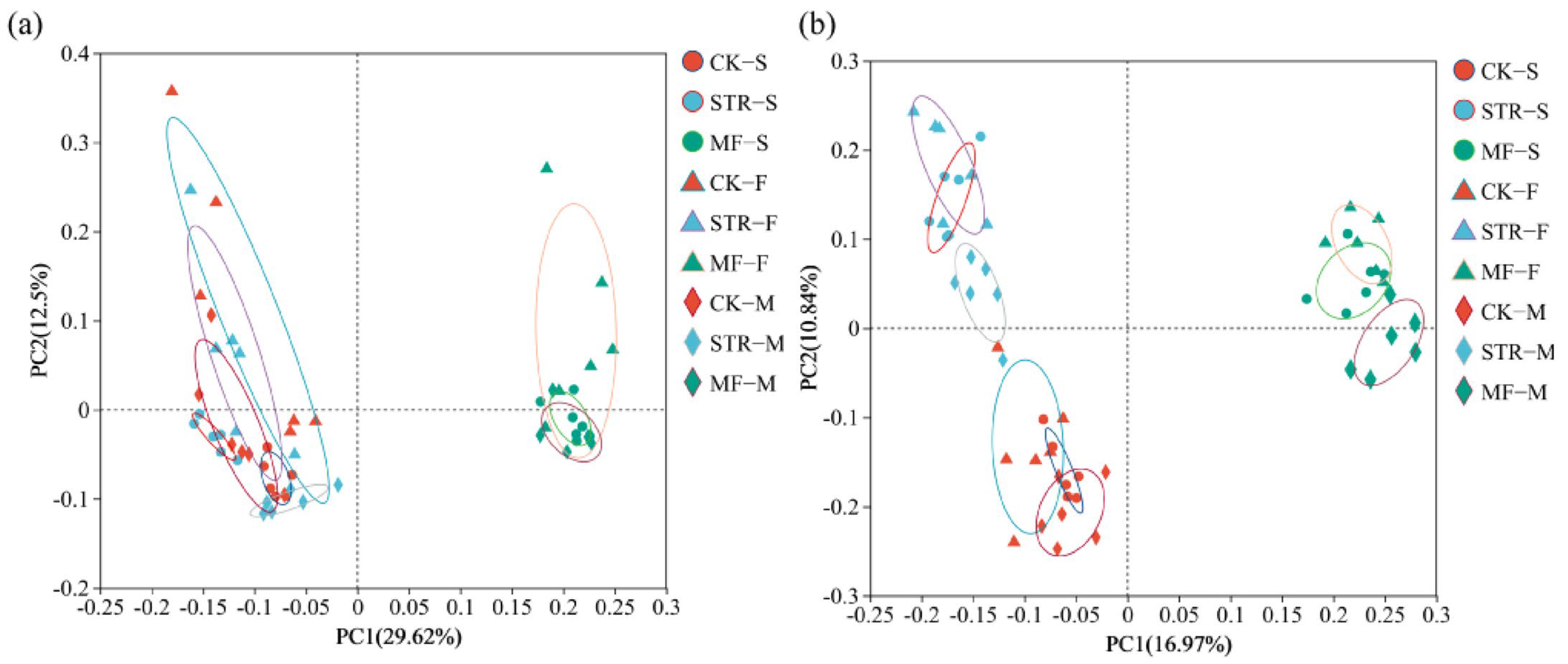
The PCoA revealed significant differences in bacterial and fungal communities among the treatments (Figure 3). PC1 and PC2 accounted for 29.62% and 12.50% of the total variance in bacterial community structure (Figure 3a) and 16.97% and 10.84% of the variance in fungal community structure, respectively (Figure 3b). The bacterial and fungal communities of the CK group and the STR treatment were widely separated from those of the MF treatment along the PC1 axis, suggesting similar microbial community structures in the CK and STR. Thus, we classified them into CK + STR and MF groups. Significant differences in the soil bacterial community were observed between samples collected at different times (seedling stages and flowering stages). However, the fungal communities at the seeding and maturity stages clustered together and were distinct from those at the flowering stage, indicating that the crop growth period significantly affected soil microbial community structure.
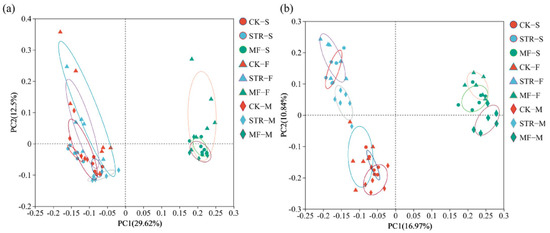
Figure 3.
Principal coordinate analysis of soil bacterial (a) and fungal (b) communities under the addition of different organic materials (PCoA). Note: CK: the control treatment without the additions of straw and manure fertilization; STR: Straw returning; MF: Manure fertilization; S, F, M, represent the seedling, flowering, and maturity stages, respectively.
3.4. Composition of Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Different Soybean Growth Stages
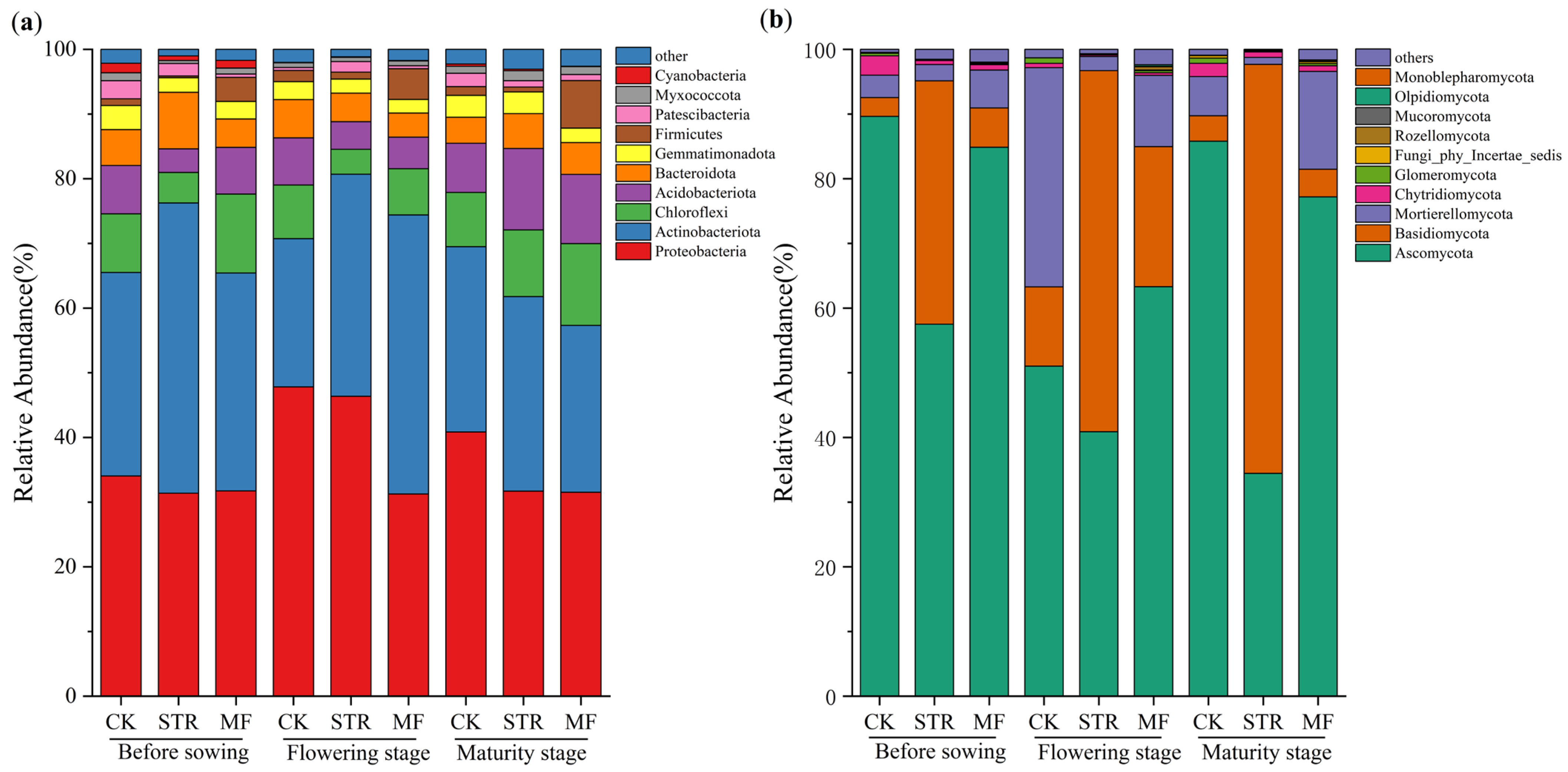
The bacterial community was analyzed at multiple taxonomic levels. High-throughput sequencing identified 32 phyla, 89 classes, 209 orders, 331 families, and 666 genera. At the phylum level, the dominant bacterial phyla in all treatments exhibited relative consistency during the crop growth season, including Proteobacteria, Actinobacteriota, Chloroflexi, Acidobacteriota, and Bacteroidota. These accounted for 86.19–93.35% of the total bacterial abundance (Figure 4a). The abundance of Actinobacteriota was higher in the STR and MF treatments than in the CK, while the relative abundance of Proteobacteria was lower. Moreover, the relative abundance of Chloroflexi and Acidobacteriota in STR was higher in the maturity stage than in the seedling and flowering stages. The relative abundance of Firmicutes in the MF treatment increased significantly during the crop growth period (p < 0.05).
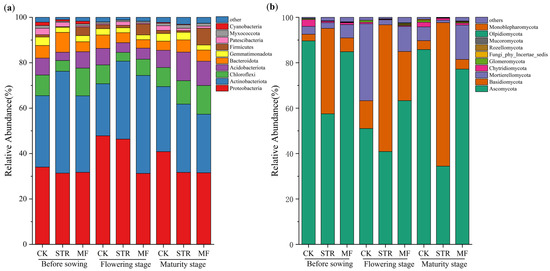
Figure 4.
Effect of the application of straw return and manure fertilization on the top 10 species phylum relative abundance of soil bacterial community (a) and fungal community (b).
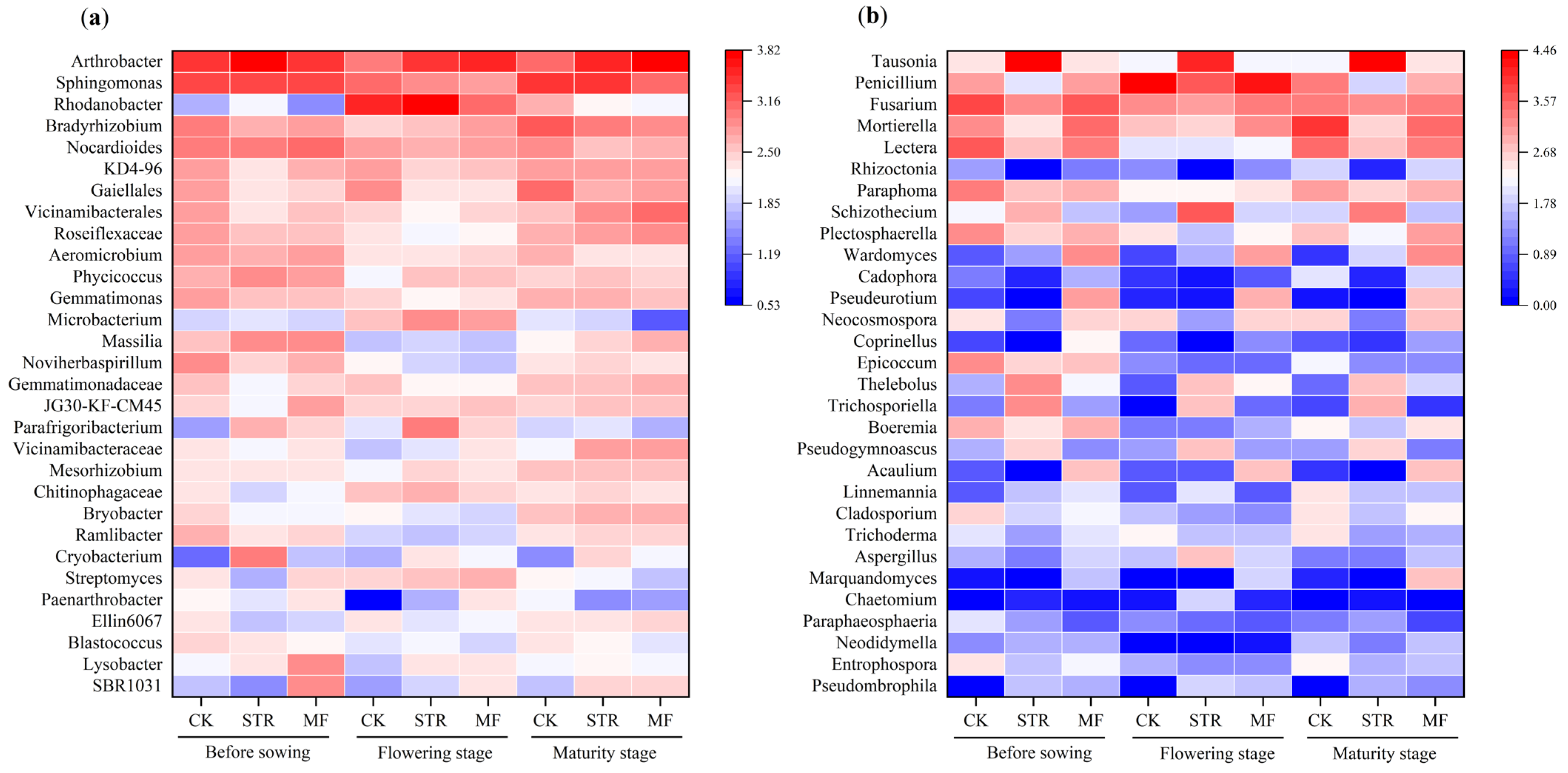
The MF significantly decreased the abundance of Gemmatimonas and Sphingomonas (Figure 5a). In contrast, STR decreased the abundance of Gemmatimonas but enhanced the abundance of Arthrobacter during the soybean growing stages. The abundance of Rhodanobacteria in the three treatments was highest in the flowering stage.
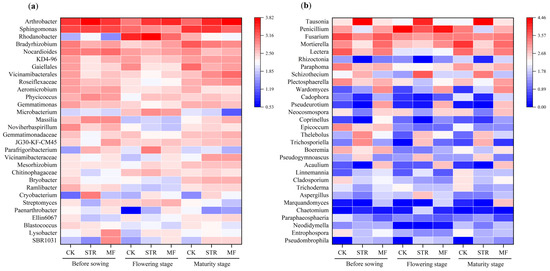
Figure 5.
Effect of adding different organic materials on the genus-level composition of soil bacterial community (a) and fungal community (b).
As shown in Figure 4b, 14 phyla, 42 classes, 86 orders, 166 families, and 304 genera of fungi were detected in the three treatments during the crop growth season. The dominant phyla included Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, and Mortierellycota, accounting for 96.32–98.43% of the relative abundance in all treatments (Figure 4b). STR significantly reduced the relative abundance of Ascomycota and Mortierellycota and increased the relative abundance of Basidiomycota (p < 0.05). The MF treatment increased the relative abundance of Basidiomycota at all growth stages and reduced the relative abundance of Ascomycota at the seeding and maturity stages. The changes in the abundance of Mortierellycota were opposite to those of Ascomycota at various stages in the MF treatment.
At the genus level, STR significantly increased the relative abundance of Tausonia, Schizothecium, Thelebolus, Pseudogymnocus, and Trichosporiella and decreased the abundance of Penicillium, Mortierella, Fusarium, Lectera, and Boeremia (p < 0.05). The abundance of Waromyces, Acaulium, and Pseudourotium was significantly higher in the MF treatment than in the CK (p < 0.05) (Figure 5b).
3.5. Effects of Different Organic Materials on Soil Microbial Co-Occurrence Network
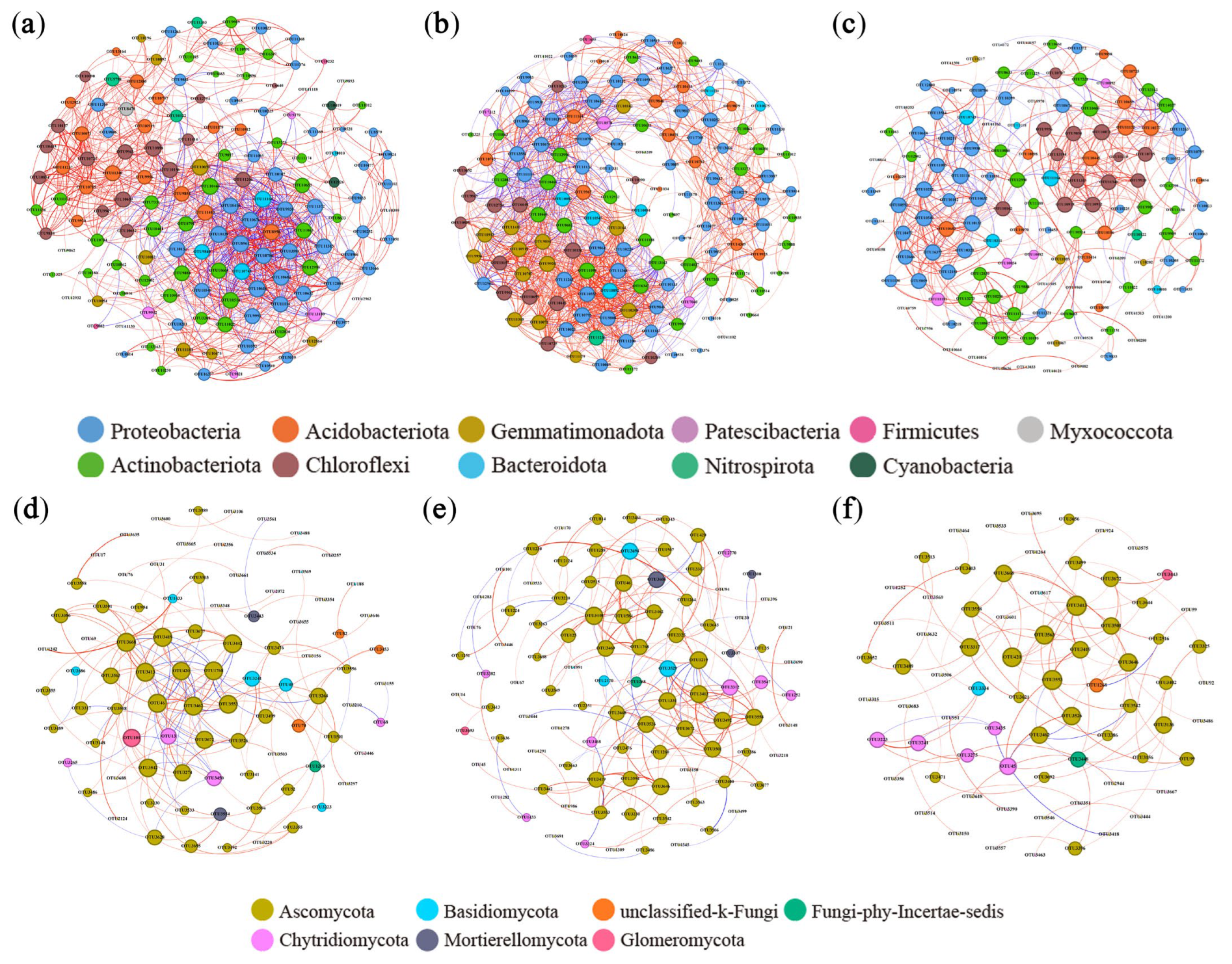
Co-occurrence networks of soil bacteria and fungi were constructed to analyze microbial community interactions in different organic material treatments (Figure 6). Higher proportions of positive correlations occurred between bacteria and fungi in the STR and MF treatments. The results demonstrate enhanced mutual synergistic interactions, metabolic efficiency, and environmental adaptability in microbial communities. The analysis of network topological parameters (Table 3) revealed that the graph density and number of edges were higher in the STR treatment than in the CK, indicating greater network complexity. The MF treatment had lower network complexity. The modularity coefficients were higher in STR and MF than in CK.
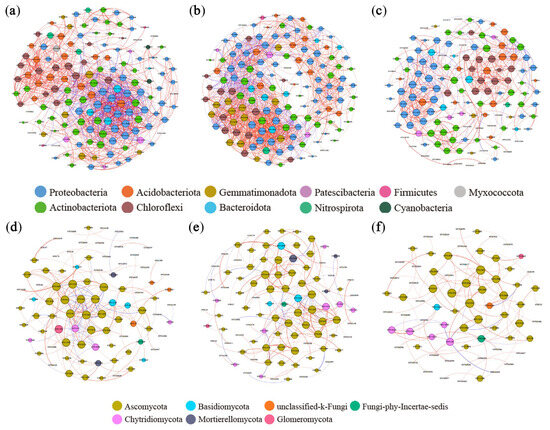
Figure 6.
Co-occurrence network of soil bacteria and fungi under the application of straw return and manure fertilization: (a) Bacterial CK; (b) Bacterial STR; (c) Bacterial MF; (d) Fungal CK; (e) Fungal STR; (f) Fungal MF. Nodes represented operational taxonomic units (OTUs) color-coded by different phyla and scaled proportionally to the number of connections (node degrees). Edges represented correlations between OTUs and were scaled proportionally to the weight of the edge. Connection lines at r > 0.7 (positive correlation, red) or r < −0.7 (negative correlation, blue) and p < 0.01.

Table 3.
Effects of different organic materials on topological properties of soil bacterial and fungal networks.
We identified the keystone species by calculating the degree centrality, closeness centrality, and betweenness centrality in different treatments. The keystone species in the co-occurrence network of bacterial communities were Chujaibacter and Ramlibacter in the CK, Vicinamibacteraceae and norank_o__IMCC26256 in the STR treatment, and Sphingomonas and Massilia in the MF treatment. In the fungal communities, the keystone species were Penicillium and Boeremia in the CK, Aspergillus and Schizothecium in the STR treatment, and Boeremia and Lectera in the MF treatment.
3.6. Soybean Yields
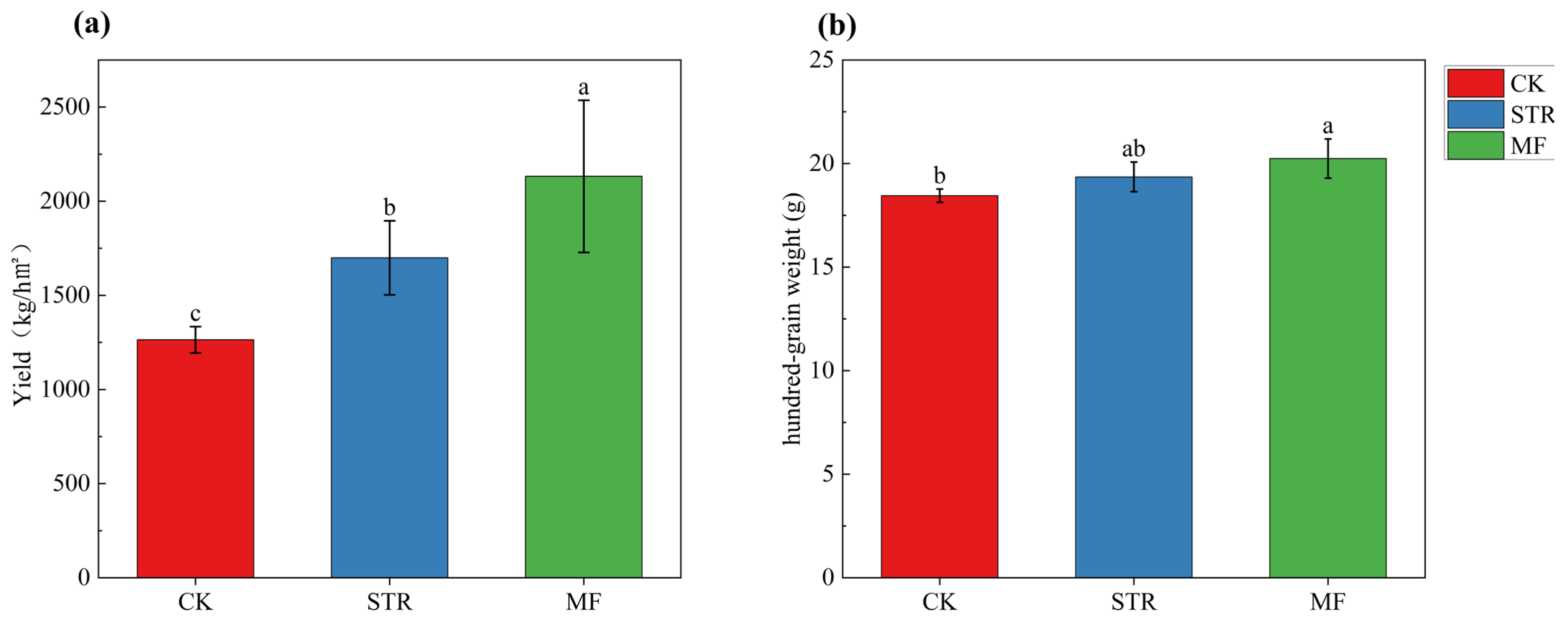
The STR and MF treatments significantly increased (p < 0.05) soybean yield by 34.52% and 68.8%, respectively (Figure 7). The hundred-grain weight of soybean was significantly higher in MF than in CK (p < 0.05), whereas no significant difference was found between the STR treatment and the CK.
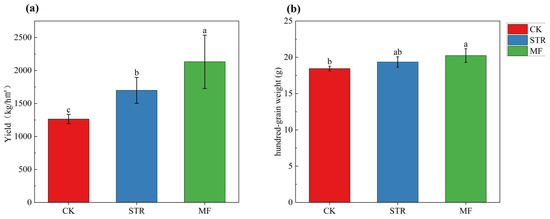
Figure 7.
Soybean yields (a) and hundred-grain weight (b) in the straw returning (STR) and manure fertilization (MF). Notes: Different lower-case letters represent the significant differences between the treatments (p < 0.05).
3.7. Relationship Between Soil Properties and Soybean Yield
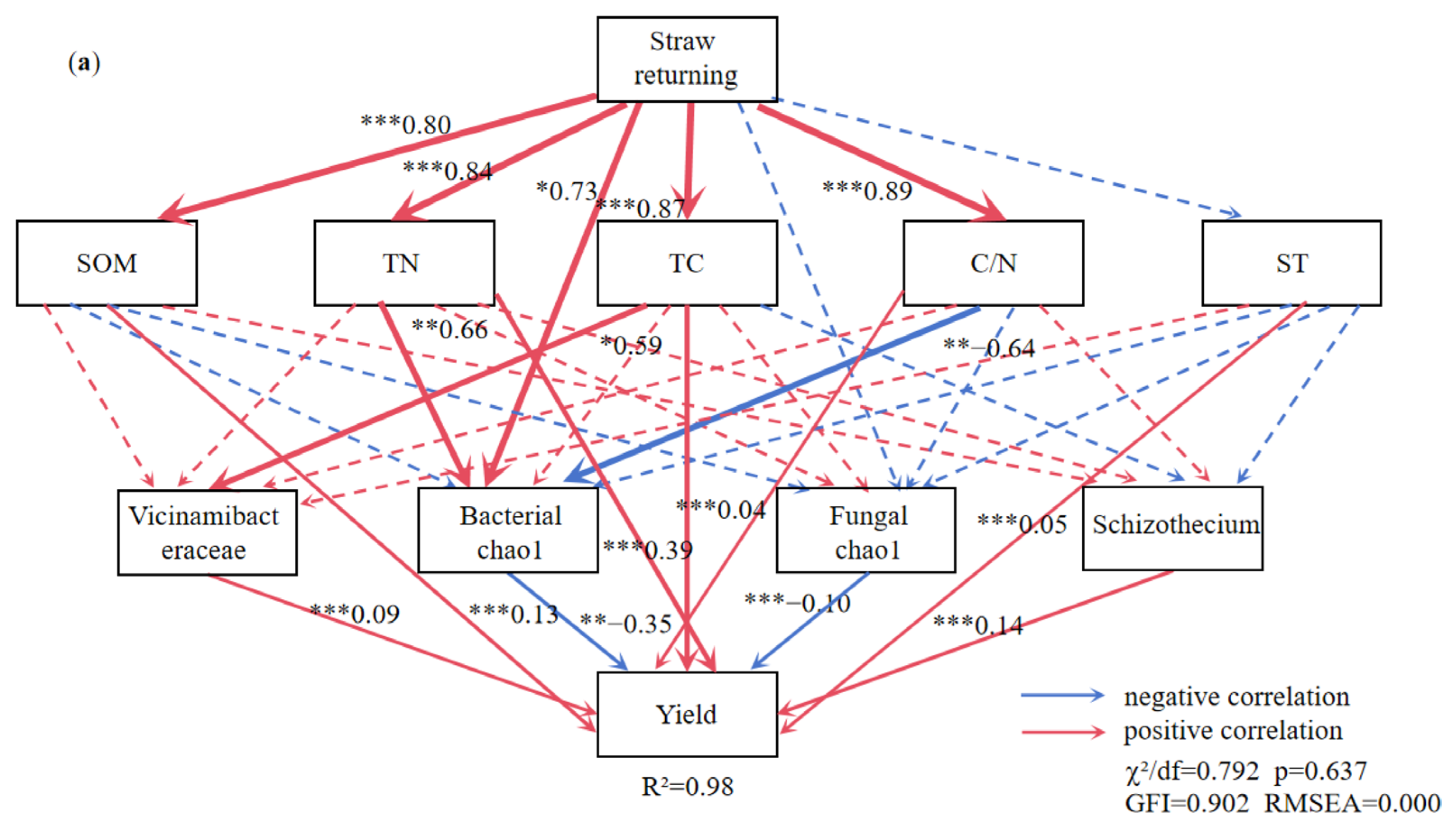
The TC, TN, SOM, C/N ratio, and the Chao1 index of soil bacterial diversity exhibited significant positive correlations with the STR treatment (Figure 8a). The SOM, TN, ST, C/N ratio, and the abundance of Schizothecium and Vicinamibacteraceae were significantly positively correlated, and the Chao1 index of soil bacterial and fungal diversity was significantly negatively correlated with the soybean yield (Figure 8a).
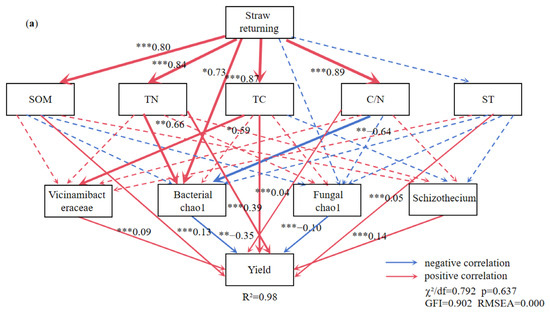
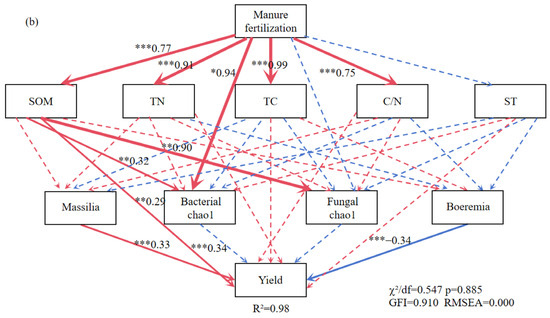
Figure 8.
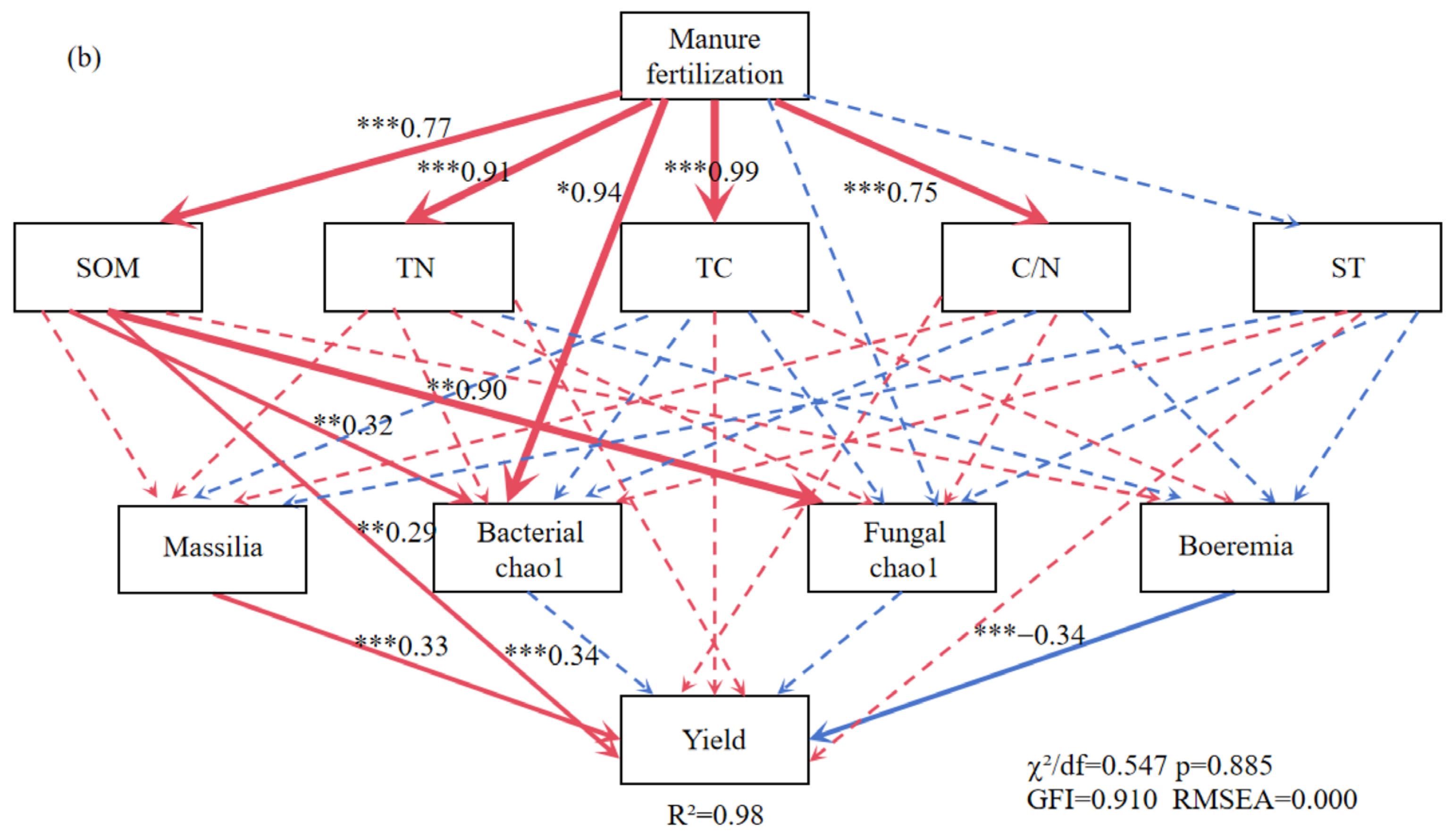
The structural equation model reveals the relationship between straw returning (a), manure fertilization (b). Note: ST: soil temperature; TC: soil total carbon; TN: soil total nitrogen; C/N: soil carbon-nitrogen ratio; SOM: soil organic matter. The red arrow indicates positive correlation and the blue arrow indicates negative correlation. Solid lines indicate significant correlation, dotted lines indicate insignificant, *, ** and *** represent p < 0.05, p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively, and the width of the arrow is proportional to the intensity of the path coefficient.
The MF treatment was positively related to SOM, TN, TC, and the C/N ratio (Figure 8b). The SOM was positively correlated with soybean yield and indirectly influenced soybean yield by moderating the Chao1 index of soil bacterial and fungal diversity. Massilia (a dominant bacterium in MF) was highly positively correlated with soybean yield. Figure 9 illustrates the effects of the indicators on soybean yield. Soil physicochemical properties had a larger influence on soybean yield than microbial factors in the STR treatments, whereas both factors had comparable effects in the MF treatment.
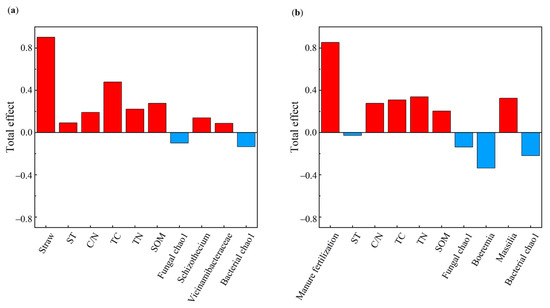
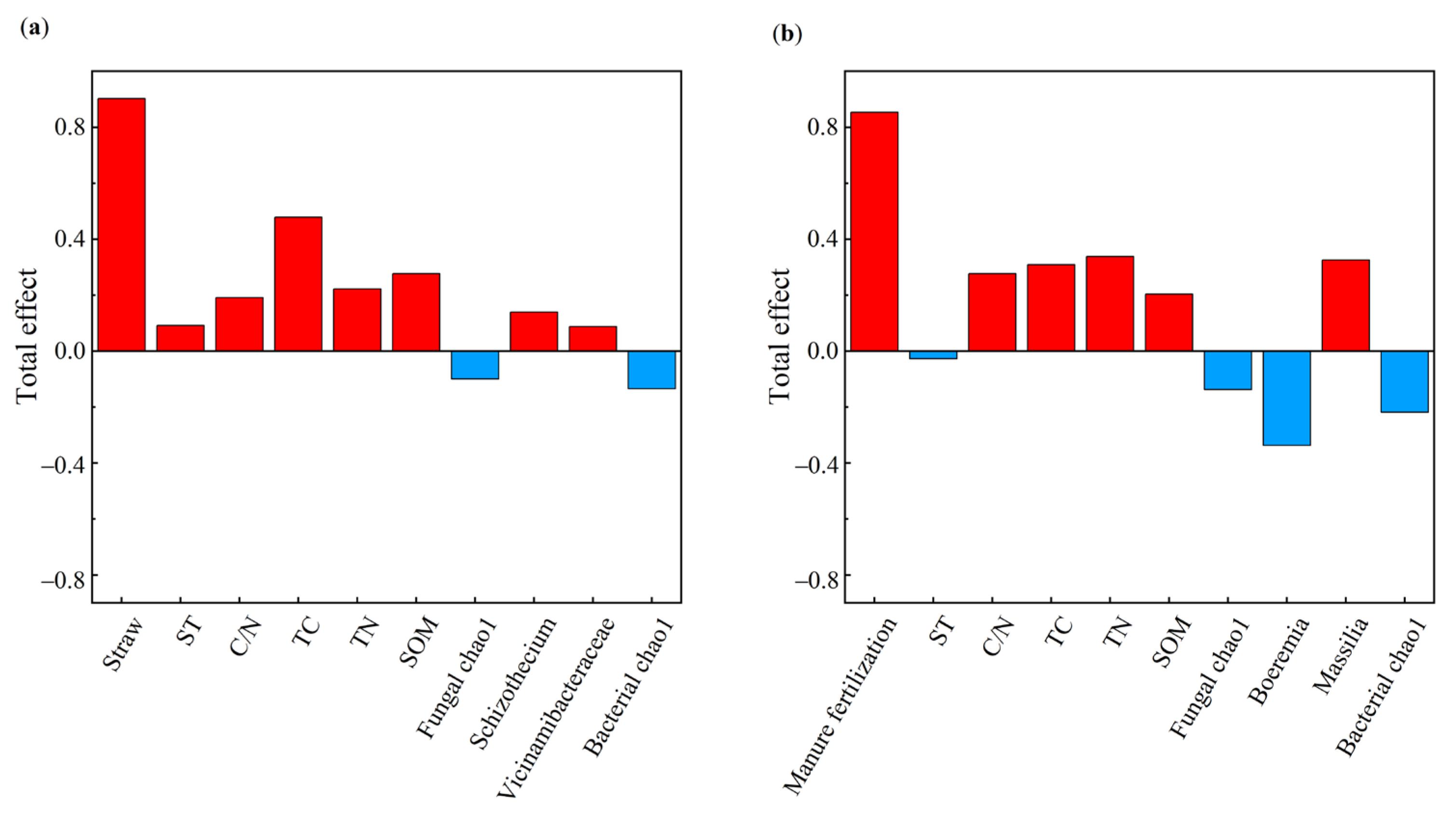
Figure 9.
Soil physical and chemical properties and microbial properties, and crop yield. (a,b) are the total impact of different variables on yield. Note: ST: soil temperature; TC: soil total carbon; TN: soil total nitrogen; C/N: soil carbon-nitrogen ratio; SOM: soil organic matter. The red bar represents the positive effect and the blue bar represents negative effect, respectively.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Straw Return and Manure Fertilization on Soil Microbial Diversity
Soil microorganisms are key indicators of soil quality and ecological functions. They are vital in maintaining farmland ecosystem sustainability [34]. A large number of studies have proved that long-term STR could increase α diversity of soil microorganisms [12,18,20]. However, the impact of short-term STR on soil microbial diversity remains debated. For instance, Liu et al. (2022) found that a 2-year STR experiment, across diverse regions of Jilin Province, revealed that α diversity of soil microbial communities exhibited significant decreases in specific areas while showing marked increases in others [35]. Wang et al. (2021) also demonstrated that different amount of straw retuning induced significant reductions in α diversity of soil fungal in short-term conditions [36]. These results are similar to our findings at the seedling stage. However, α diversity of soil microbial in STR treatment increased with time during the growing season. This was associated with the releases of substantial labile carbon in the initial stage of straw decomposition, creating nutrient-enriched conditions that selectively promote the proliferation of copiotrophic microorganisms (e.g., Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria), which thrive under high-resource availability [37]. Conversely, this process suppresses the activity of oligotrophic microorganisms adapted to nutrient-limited environments, thereby reducing bacterial diversity during the seedling stage [37,38]. Bacterial communities were dominant in the early-stage straw decomposition [39]. The intensive oxygen consumption creates hypoxic conditions that suppress aerobic fungal populations, reducing fungal diversity [36].
In contrast, MF had a more direct impact on soil nutrients, which showed MF treatment had higher α diversity of soil microbial than the CK during all soybean growth stages. Hence, MF treatment has stronger ecosystem functions and faster recovery from disturbances, contributing to ecological health and resilience. After the spring freeze–thaw cycles, some nutrients in the manure decomposed and were released into the soil, improving bacterial richness and diversity in the seedling stage. On the other hand, MF increased soil pH, alleviating soil acidification and reducing the inhibition of microbial growth [15,18,40]. This result aligns with the findings of Thompson (2017) [41], who used environmental samples and metadata from various regions worldwide and reported that soil microbial richness was the highest when the pH was near neutral, and the soil temperature was approximately 10 °C. Furthermore, the soil nutrient content in the STR treatment was higher in the flowering and maturity stages than in the seedling stage. This result can be attributed to rising temperatures enhancing straw decomposition and subsequent nutrient release [42]. Consequently, the soil nutrient content was higher in the STR treatment than in the CK during the flowering and maturity stages.
We also found that soil nutrients in the MF treatment increased during the crop growth season (Table 2). The MF treatment increased the richness and diversity of soil bacteria and fungi at all soybean growth stages. The primary reason is that the humified carbon in the manure is directly absorbed and utilized by crops, increasing the soil C/N ratio and stimulating the priming effect (PE) [43]. PE refers to a strong and short-term change in the turnover of soil organic matter caused by the supply of available fresh organic matter [44]. Various studies have pointed out that the PE significantly influences soil microbial communities, with its intensity primarily determined by the C/N ratio [44,45]. The high soil carbon-to-nutrient ratios induced by organic matter inputs promoted microbial nitrogen mineralization and drove a positive priming effect (PE) [45,46]. Another reason may be that MF treatment can significantly increase DOC and MBC in the soil’s labile organic carbon, which has a significant positive correlation with microbial growth [40].
4.2. Effects of Straw Return and Manure Fertilization on Soil Microbial Community Structure
The Acidobacteria are oligotrophic. The relative abundance of Acidobacteria in the seeding and flowering stage was lower in the STR and MF treatments than in the CK (Figure 4a). This result was due to the better adaptation of Acidobacteria to low-carbon environments [47]. These findings were similar to those of Zhang et al. (2021) [40], who observed that the application of a chemical fertilizer combined with STR and MF significantly reduced the relative abundance of Acidobacteria compared to no fertilizer treatment. Some studies found that the soil pH and carbon-to-nitrogen ratio substantially affected Acidobacteria [48,49]. In contrast, Liu et al. (2014) performed high-throughput sequencing and observed that the composition of Acidobacteria was not related to soil pH in the black soil area of Northeast China [49,50]. This result aligns with our findings; therefore, the significant increase in the relative abundance of Acidobacteria in the STR and MF treatments during the maturity stage was attributed to the C/N ratio. Moreover, Lauber et al. (2008) reported that the relative abundance of Acidobacteria was significantly positively correlated with the C/N ratio [51]. In this study, the relative abundance of Actinobacteriota in the STR and MF treatments increased during the seeding and flowering stages (Figure 4a). The Actinobacteriota are r-strategists with fast growth and require high availability of soil nutrients [52]. The relative abundance of Firmicutes was significantly higher in the MF treatment than in the CK in all growth stages, which was consistent with the findings of Ma et al. (2022) [52]. The relative abundance of Firmicutes was positively correlated with soil pH, TN, and other physicochemical properties [53]. In this study, the MF treatment increased soil nutrient content and PH. Some studies have found that Firmicutes were one of the dominant bacterial phyla in organic fertilizer treatment, and their relative abundance was positively correlated with SOM and crop yield [54,55,56].
At the genus level, the abundance of Gemmatimonas in the STR and MF treatments decreased during the crop growth stages, suggesting it was more adapted to oligotrophic environments [57]. This finding was also reported in other studies that observed a lower relative abundance of Gemmatimonas in STR than in non-STR treatments [12,20]. Despite Gemmatimonas belonging to the oligotrophic bacterium, soil denitrification exhibited a positive correlation with Gemmatimonas abundance. This suggests that the reduced populations of this bacterial group may decrease denitrification activity, potentially mitigating nitrogen loss while enhancing nitrate retention in soils [58]. We observed a lower abundance of Sphingomonas during the soybean growth period in the MF treatment than in the CK. Fang et al. (2024) obtained similar results [18]. The Sphingomonas is an oligotrophic bacterium that thrives in low-nutrient environments [59]. The MF treatment increased soil nutrient levels over time, reducing the abundance of Sphingomonas.
In the soil fungal communities, STR significantly increased the relative abundance of Basidiomycota at all crop growth stages, consistent with the findings of Zhang et al. (2021) [60]. Basidiomycota produce various peroxidases for lignin oxidation, which increases the lignin content and the decomposition rate of crop straw [57]. Therefore, the higher abundance of Basidiomycota significantly enhanced soil organic carbon accumulation capacity, and it was also a key factor in assessing land use effectiveness on maximizing carbon sequestration efficiency [61]. Song et al. (2022) found that the relative abundance of potential soil pathogens (Fusarium, Lectera, and Boeremia) was significantly positively correlated with Ascomycota and negatively correlated with Basidiomycota [62]. We observed similar results. Furthermore, the abundance of Boeremia and Fusarium significantly increased under continuous soybean monoculture, which was strongly associated with the elevated incidence of soybean root rot disease [63].
The STR treatment significantly increased the relative abundance of Tausonia at the genus level during all crop periods (p < 0.05). Tausonia is a well-documented saprophytic ascomycete crucial for organic matter degradation. It was associated with increased crop yields [64]. The relative abundance of Fusarium was lower in STR than in CK, which is consistent with the results reported by Tang et al. (2020) [65]. Some studies found that Fusarium species cause wilting and root rot diseases [62]. However, the STR treatment increased the relative abundance of inhibitory bacteria, such as Pseudogymnoascus and Schizothecium, reducing the relative abundance of Fusarium [66]. Moreover, the MF treatment significantly increased the abundance of Acaulium during all crop growth stages (p < 0.05). He et al. (2022) observed that Acaulium was the key microbial genus responsible for the degradation of cow dung and straw, increasing total sugar degradation [67].
4.3. Effects of Straw Return and Manure Fertilization on Key Species and Microbial Networks
The STR treatment increased the number of edges, average degree, and average clustering coefficient of the co-occurrence network of bacteria and fungi, indicating an increase in network complexity. As a result, closer interactions occurred among co-occurring species networks. The complexity of microbial ecological networks can directly reflect the stability and interactions of the ecosystem, such as positive (e.g., commensalism) and negative (e.g., competition) [68,69]. The nutrients and complex organic matter in straw need to be decomposed synergistically by multiple soil microorganisms, which leads to higher connectivity and complexity of the network [70]. Numerous studies have shown that long-term or short-term STR increases the soil microbial network complexity [18,35,71]. Notably, the MF treatment reduced the bacterial and fungal network complexity. This is mainly due to maintaining nutrient balance in the soil for MF treatment, thereby reducing the interactions between microbial communities for development [18,72,73].
4.4. Relationship Between Soil Physical and Chemical Properties, Microbial Communities, and Crop Yields
Long-term STR and MF could increase soil nutrient content, promote soil microbial activities, and increase grain production, resulting in direct economic benefits. In addition, it can also improve soil structure and reduce soil erosion to generate indirect economic benefits [52,74]. In contrast, the short-term application of organic materials may not be completely decomposed into available nutrients, resulting in the limitation of soil nutrients and soil microbial activities, and ultimately leading to lower yields [75].
As illustrated in Figure 7a, STR and MF significantly increased soybean yield (p < 0.05). This finding is consistent with the observation that the addition of organic material increased crop yields by altering soil microbial communities and improving soil properties [12,54]. Our study demonstrated that the STR and MF treatments significantly increased soybean yield by improving the C/N ratio and TN (p < 0.05). Therefore, the soil TN content is vital in determining crop yields in degraded black soil areas, which is in line with previous studies [12,18]. Furthermore, the increased crop yield was related to soil microbial communities, such as Schizothecium and Massilia, which processed organic materials, indirectly improving soybean yield [76,77].
The Massilia participates in the transformation of ammonia and nitrate, while significantly modulating NH4+-N content in soil ecosystems [78]. In addition, the Massilia is also a key species that affects the characteristics of soil nitrogen retention and supply. Several studies have confirmed that Massilia is critical for soil nitrogen fixation and utilization [79]. In this study, the relative abundance of Massilia in the MF treatment was positively correlated with soybean yield, and Massilia was identified as a keystone species. This is supported by the findings of Qiao et al. (2019), who observed that the application of bio-organic fertilizers significantly increased the relative abundance of Massilia, which was strongly correlated with increased crop yields [80].
The Boeremia was the key fungal genus in the MF treatment [80]. Its abundance was significantly negatively correlated with grain yield. Previous studies have identified Boeremia and Lectera as potential pathogenic genera in leguminous plants [62]. SOM provides all essential nutrients, including primary nutrients, sulfur, and micronutrients, for crop growth and yields, particularly in soils with low fertility [81]. This study found that SOM was significantly positively correlated with soybean yield because it alters the relative abundance of bacteria and fungi (p < 0.01). The Schizothecium plays a critical role in regulating SOM transformation and nitrogen cycling dynamics. Ma et al. (2022) demonstrated that long-term STR treatment enhanced the abundance of Schizothecium, improved the cycling and transformation of SOM, and consequently increased SOM content through microbial-mediated mechanisms, which ultimately contributes to improving wheat yield [66]. The Schizothecium secreted cellulase to decompose straw, so it was significantly enriched in the STR treatment [39]. Meanwhile, its proliferation inhibited the ammonia oxidation and reduced nitrogen leaching, thereby increasing total nitrogen content [82].
The Vicinamibacteraceae is a genus in the Acidobacteria phylum, and it can increase the PE by decomposing the refractory soil organic matter [83,84]. In addition, the abundance of Vicinamibacteriaceae was positively correlated with mineral-associated organic carbon content and regulated the accumulation and depletion of SOC [85]. Guo et al. (2025) found that Vicinamibacteraceae was the main bacterial genus with different nitrogen fertilizer levels and was positively correlated with the available N content in the soil [86]. In this study, the Vicinamibacteraceae were also identified as keystone species in the STR treatment. They increased the efficiency of organic matter decomposition [87]. Our study demonstrated that SOM, TN, and the C/N ratio were positively correlated with the relative abundance of Vicinamibacteraceae, which is in agreement with other researchers [88]. Yin et al. (2022) observed that the relative abundance of Vicinamibacteraceae increased significantly after adding corn straw biochar and was highly positively correlated with soil nutrient availability, improving crop growth and yield [89].
Moreover, our study found that crop yield was positively correlated with the relative abundance of Schizothecium, cellulose-degrading bacteria highly enriched in soils to which straw has been returned [71]. They convert lignin and cellulose into humus, and their abundance is significantly positively correlated with wheat yield [14,71]. In summary, the short-term STR and MF applications improve soil nutrients, microbial diversity, and soybean yield. However, the short-term application of STR may result in limitations for soil properties and microbial diversity due to incomplete decomposition into available nutrients, potentially leading to lower yields compared to long-term application of STR treatment. Additionally, the initial decomposition products from the additions of STR and MF may not provide the same level of stability as long-term treatment, thereby affecting soil fertility and microbial community composition, which require continuous monitoring in the future.
5. Conclusions
STR and MF significantly increased soil nutrients and improved the α diversity of soil microorganisms. Notably, the MF treatment increased the abundance and diversity of the soil’s microbial community during the crop growth season. Soybean yield was significantly positively correlated with the abundance of Schizothecium (the key fungal group in the STR treatment) and Massilia (the key bacterial group in the MF treatment). Notably, the STR and MF treatments increased soybean yield by 34.52% and 68.8%, respectively. The MF treatment substantially increased soil nutrient content and significantly enhanced the diversity indices in all sampling periods. In summary, these findings support the use of short-term organic inputs as an emergency soil restoration practice in degraded black soil regions, with implications for climate-resilient agriculture and microbial ecosystem engineering.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms13051137/s1, Table S1: The fungal genus in straw return (STR) and manure fertilization (MF)treatments; Table S2: The bacterial genus in STR and MT treatments.
Author Contributions
Methodology, J.W., D.M., Q.C. and J.L.; Software, Z.L.; Validation, J.D.; Formal analysis, J.D. and Z.L.; Investigation, J.D.; Resources, J.L.; Data curation, J.W.; Writing—original draft, J.D.; Writing—review & editing, D.M., Q.C. and J.L.; Visualization, Q.C.; Funding acquisition, Q.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42101281).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chen, Y.; Shi, W.; Aihemaitijiang, G.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, D.; Li, J. Hyperspectral inversion of heavy metal content in farmland soil under conservation tillage of black soils. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.; Zhong, X.; Peng, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Gao, L. Soil Quality Mediates the Corn Yield in a Thin-Layer Mollisol in Northeast China. Land 2023, 12, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Z.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.C.; Xu, S.G.; Zhang, H.W. Soil loss and conservation in the black soil region of Northeast China: A retrospective study. Environ. Sci. Policy 2010, 13, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Li, F.; Pan, H.; Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, J. The Effects of Natural Humus Material Amendment on Soil Organic Matter and Integrated Fertility in the Black Soil of Northeast China: Preliminary Results. Agronomy 2023, 13, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, F.; Huang, J.; Zhao, S.-w. Study on soil hydraulic properties of slope farmlands with different degrees of erosion degradation in a typical black soil region. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, A.; Li, L.; Zhu, H. Protection and Utilization of Black Land and Making Concerted and Unremitting Efforts for Safeguarding Food Security Promoted by Sci-tech InnovationCountermeasures in Conservation and Rational Utilization of Black Land. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 36, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lin, B.; Zheng, Q.; Yin, J. Characteristics and factors controlling the development of ephemeral gullies in cultivated catchments of black soil region, Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 96, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidian, P.; Ghorbani, H.R.; Farajpour, M. Achieving agricultural sustainability through soybean production in Iran: Potential and challenges. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, H.; Li, X.F.; Song, C.Y.; Cruse, R.M.; Zhang, X.Y. Effects of conservation tillage on corn and soybean yield in the humid continental climate region of Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 115, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, H.; Dong, Q.g.; Xia, L.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Zang, H.; Andersen, M.N.; Olesen, J.E.; Jorgensen, U.; et al. Ammoniated straw incorporation increases wheat yield, yield stability, soil organic carbon and soil total nitrogen content. Field Crops Res. 2022, 284, 108558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, S. Enhancing Sustainable Agriculture in China: A Meta-Analysis of the Impact of Straw and Manure on Crop Yield and Soil Fertility. Agriculture 2024, 14, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qian, R.; Han, Y.; Ji, Z.; Yang, Q.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Ma, K.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Jia, Z.; et al. Straw return can increase maize yield by regulating soil bacteria and improving soil properties in arid and semi-arid areas. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 161, 127389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Du, X.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Liang, W. Organic substitutions improve soil quality and maize yield through increasing soil microbial diversity. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 347, 131323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zhou, J.; Ongena, M.; Liu, W.; Wei, D.; Zhao, B.; Guan, D.; Jiang, X.; Li, J. Effect of long-term fertilization strategies on bacterial community composition in a 35-year field experiment of Chinese Mollisols. AMB Express 2018, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, X.; Ma, M.; Zhou, B.; Guan, D.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, J.; Cao, F.; Li, L.; Li, J. Effect of 35 years inorganic fertilizer and manure amendment on structure of bacterial and archaeal communities in black soil of northeast China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 105, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, P.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, N.; Dong, J.; Pang, H.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Z. Changes in soil organic carbon and microbial community under varying straw incorporation strategies. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 204, 104735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; He, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xia, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Chu, H.; Liu, W.; et al. Organic amendments enhance soil microbial diversity, microbial functionality and crop yields: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Gu, H.; Wan, S.; Xiao, Y. Effects of long-term combined application of organic and chemical fertilizers on bacterial community characteristics and soybean yields. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2024, 32, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xia, H.; Jiang, C.; Riaz, M.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Fan, X.; Xia, X. 14 year applications of chemical fertilizers and crop straw effects on soil labile organic carbon fractions, enzyme activities and microbial community in rice-wheat rotation of middle China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, C. Impacts of Various Straw-Returning Techniques on the Chemical Characteristics and Bacterial Diversity of Soil. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebber, D.P.; Richards, V.R. A meta-analysis of the effect of organic and mineral fertilizers on soil microbial diversity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 175, 104450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Song, J.; Fan, J.; Yan, C.; Dong, S.; Ma, C.; Gong, Z. Changes in soil organic carbon fractions and microbial community under rice straw return in Northeast China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Lin, X.; Guan, S.; Dou, S. Deep incorporation of corn straw benefits soil organic carbon and microbial community composition in a black soil of Northeast China. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 1266–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Zhang, G.; Chen, S.; Zhang, N.; Wang, C. Response of soil erosion resistance to straw incorporation amount in the black soil region of Northeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 357, 120801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuan, L.; Jia, J.; Chen, X.; Ma, J.; Zhao, J.; Liang, C.; Xie, H.; et al. Effects of no-tillage and stover mulching on the transformation and utilization of chemical fertilizer N in Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-C.; Zhao, Y.-W.; Wang, J.-Z.; Zhu, P.; Cui, X.; Han, X.-Z.; Xu, M.-G.; Lu, C.-A. The efficiency of long-term straw return to sequester organic carbon in Northeast China’s cropland. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J. Effects of Long-Term Straw Returning and Nitrogen Fertilizer Reduction on Soil Microbial Diversity in Black Soil in Northeast China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossfeld, S.; Gansert, D.; Thiele, B.; Kuhn, A.J.; Loesch, R. The dynamics of oxygen concentration, pH value, and organic acids in the rhizosphere of Juncus spp. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y. Chinese Soils, 2nd ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1987; pp. 20–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Guo, M.; Zhang, X.; Tian, J.; Zhou, P.; Chen, Z. Comparison of the effects of five long-term land use and management practices on runoff, soil erosion, and nutrient loss under natural rainfall in the Mollisol region of Northeast China. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2024, 49, 1606–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Ma, Z.; He, Z.; Zhao, W.; Wang, P.; Zhao, S.; Wang, D. Investigation on the Microbial Diversity of Fresh-Cut Lettuce during Processing and Storage Using High Throughput Sequencing and Their Relationship with Quality. Foods 2022, 11, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wang, P.; Devlin, A.T.; Xiao, S.; Shu, W.; Zhang, H.; Ding, M. Influence of Soil and Water Conservation Measures on Soil Microbial Communities in a Citrus Orchard of Southeast China. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, J.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, R.; Hua, X.; Liu, X.; Qi, H.; Seo, T. Microecological Shifts in the Rhizosphere of Perennial Large Trees and Seedlings in Continuous Cropping of Poplar. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, T.; Qadir, M.F.; Khan, K.S.; Eash, N.S.; Yousuf, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Manzoor, R.; ur Rehman, S.; Oetting, J.N. Unrevealing the potential of microbes in decomposition of organic matter and release of carbon in the ecosystem. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhao, H.; Hu, W.; Xu, C.; Chen, X. Short-Term Straw Returning Improves Quality and Bacteria Community of Black Soil in Northeast China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 1869–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Lin, X.; Tian, L.; Wang, X.; Ji, L.; Jin, F.; Tian, C. Effects of Short-Term Rice Straw Return on the Soil Microbial Community. Agriculture 2021, 11, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yu, A.; Chi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Han, X.; Liu, K.; Fan, Q.; Hu, X.; Che, R.; Liu, D. Organic carbon decomposition temperature sensitivity positively correlates with the relative abundance of copiotrophic microbial taxa in cropland soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 204, 105712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, P.; Xu, X.; Qiu, S.; Zhao, S. Characteristics of rice straw decomposition and bacterial community succession for 2 consecutive years in a paddy field in southeastern China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Landry, N.d.B.J.; Duan, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, X. The impact of Ricinus straw on tomato growth and soil microbial community. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1499302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, J.; Han, X.; Zou, W.; Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Feng, Y. Labile organic carbon fractions drive soil microbial communities after long-term fertilization. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 32, e01867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.R.; Sanders, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Amir, A.; Ladau, J.; Locey, K.J.; Prill, R.J.; Tripathi, A.; Gibbons, S.M.; Ackermann, G.; et al. A communal catalogue reveals Earth’s multiscale microbial diversity. Nature 2017, 551, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Yan, S.-S.; Jia, T.-Y.; Dong, S.-K.; Ma, C.-M.; Gong, Z.-P. Decomposition characteristics of rice straw returned to the soil in northeast China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2019, 114, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Guo, L.; Li, C.; Liu, M.; Wu, G.; Jiang, G. The total biomass nitrogen reservoir and its potential of replacing chemical fertilizers in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, K.; Sun, Y.; Zarebanadkouki, M.; Gaiser, T.; Seidel, S.; Pausch, J. Long-term continuous farmyard manure application increases soil carbon when combined with mineral fertilizers due to lower priming effects. Geoderma 2022, 428, 116216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Fang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Gao, W.; Yuan, H.; Kuzyakov, Y.; et al. Stoichiometric regulation of priming effects and soil carbon balance by microbial life strategies. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 169, 108669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Shahbaz, M.; Tang, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, P.; Alharbi, H.; Wu, J.; et al. Microorganisms maintain C:N stoichiometric balance by regulating the priming effect in long-term fertilized soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 167, 104033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.T.; Robeson, M.S.; Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. A comprehensive survey of soil acidobacterial diversity using pyrosequencing and clone library analyses. ISME J. 2009, 3, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sui, Y.; Yu, Z.; Yao, Q.; Shi, Y.; Chu, H.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. Diversity and distribution patterns of acidobacterial communities in the black soil zone of northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 95, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.; Qian, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Sui, X.; Zhang, X. Diversity and Composition of Soil Acidobacterial Communities in Different Temperate Forest Types of Northeast China. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sui, Y.; Yu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Chu, H.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. High throughput sequencing analysis of biogeographical distribution of bacterial communities in the black soils of northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C.L.; Strickland, M.S.; Bradford, M.A.; Fierer, N. The influence of soil properties on the structure of bacterial and fungal communities across land-use types. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; He, X.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, Q.; Xue, C.; Shen, Q. Long-Term Organic-Inorganic Fertilization Regimes Alter Bacterial and Fungal Communities and Rice Yields in Paddy Soil. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 890712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Shu, A.; Liu, J.; Shi, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, G.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, S.; et al. Effects of long-term fertilization with different substitution ratios of organic fertilizer on paddy soil. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shu, A.; Song, W.; Shi, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, G.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, S.; et al. Long-term organic fertilizer substitution increases rice yield by improving soil properties and regulating soil bacteria. Geoderma 2021, 404, 115287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Yin, J.; Li, D.; Wang, B.; Zhang, K.; Zheng, X.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, C.; et al. Productivity and quality of banana in response to chemical fertilizer reduction with bio-organic fertilizer: Insight into soil properties and microbial ecology. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 322, 107659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Qu, C.; Cheng, X.; Chen, Y.; Yan, H.; Wu, Q. Effect of different fertilization strategies on the yield, quality of Euryales Semen and soil microbial community. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1310366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekelae, M.; Donofrio, N.; de Vries, R. Plant biomass degradation by fungi. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2014, 72, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hao, D.-C.; Fan, S.; Xie, H.; Bao, X.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L. N2O Emission and Nitrification/Denitrification Bacterial Communities in Upland Black Soil under Combined Effects of Early and Immediate Moisture. Agriculture 2022, 12, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Kim, M.; Tripathi, B.M.; Kim, H.; Adams, J.M. Predictable communities of soil bacteria in relation to nutrient concentration and successional stage in a laboratory culture experiment. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1740–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lin, Z.; Que, Y.; Fallah, N.; Tayyab, M.; Li, S.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Abubakar, A.Y.; Zhang, H. Straw retention efficiently improves fungal communities and functions in the fallow ecosystem. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manici, L.M.; Caputo, F.; Fornasier, F.; Paletto, A.; Ceotto, E.; De Meo, I. Ascomycota and Basidiomycota fungal phyla as indicators of land use efficiency for soil organic carbon accrual with woody plantations. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Huang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, C.; Tao, B.; Zhang, W. Characteristics of Soil Fungal Communities in Soybean Rotations. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 926731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shi, C.; Wei, D.; Gu, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Cai, S.; Hu, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, W. Soybean continuous cropping affects yield by changing soil chemical properties and microbial community richness. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1083736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Feng, Y.; Bate, B.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Cui, J. Maize-Soybean Rotation and Intercropping Increase Maize Yield by Influencing the Structure and Function of Rhizosphere Soil Fungal Communities. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Xia, Y.; Fan, C.; Kou, J.; Wu, F.; Li, W.; Pan, K. Control of Fusarium wilt by wheat straw is associated with microbial network changes in watermelon rhizosphere. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Wei, J.-L.; Li, Z.-S.; Zhou, X.-L.; Zheng, F.-L.; Wu, X.-B.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.-H.; Tan, D.-S. Effects of Long-Term Straw Returning on Fungal Community, Enzyme Activity and Wheat Yield in Fluvo-aquic Soil. Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2022, 43, 4755–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, D.; He, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Shi, X.; Chater, C.C.C.; Yu, F. Characteristics of bacterial and fungal communities and their impact during cow manure and agroforestry biowaste co-composting. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 324, 116377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Xiong, X.; Tan, L.; Deng, Y.; Du, X.; Yang, X.; Hu, Q. Soil microbial community assembly and stability are associated with potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) fitness under continuous cropping regime. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, C.-E.T.; Kim, D.Y.; Sachdeva, R.; Caron, D.A.; Fuhrman, J.A. Top-down controls on bacterial community structure: Microbial network analysis of bacteria, T4-like viruses and protists. ISME J. 2014, 8, 816–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, D.J.; David, A.S.; Menges, E.S.; Searcy, C.A.; Afkhami, M.E. Environmental stress destabilizes microbial networks. ISME J. 2021, 15, 1722–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tang, C.; Yang, J.; Yao, R.; Wang, X.; Xie, W.; Ge, A.-H. Salinity-dependent potential soil fungal decomposers under straw amendment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, Y.; Ma, T.; Raza, W.; Li, J.; Howland, J.G.; Huang, Q.; Shen, Q. Impacts of inorganic and organic fertilization treatments on bacterial and fungal communities in a paddy soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 112, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wu, W.; Zeng, S.; Jiang, S.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, C.; Xu, Y.; et al. Bioorganic and silicon amendments alleviate early defoliation of pear trees by improving the soil nutrient bioavailability, microbial activity, and reshaping the soil microbiome network. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 173, 104383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, T.; Zheng, L.; Jing, X.; Hussain, H.A.; Zhang, Q. Enhancing soil multifunctionality through restoring erosion environment and microbial functions combined with organic manure and straw mulching. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 383, 109515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Zhu, X.; Cao, G. Effects of Years of Rice Straw Return on Soil Nitrogen Components from Rice-Wheat Cropped Fields. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yuan, T.; Ibrahim, M.; Wu, F. Rotational Strip Bean and Celery Intercropping Alters the Microbial Community to Improve Crop Yield and Soil Nutrients. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Zhu, G.; Qiu, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, W.; Tian, B.; et al. Quality traits drive the enrichment of Massilia in the rhizosphere to improve soybean oil content. Microbiome 2024, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holochova, P.; Maslanova, I.; Sedlacek, I.; Svec, P.; Kralova, S.; Kovarovic, V.; Busse, H.-J.; Stankova, E.; Bartak, M.; Pantucek, R. Description of Massilia rubra sp. nov., Massilia aquatica sp. nov., Massilia mucilaginosa sp. nov., Massilia frigida sp. nov., and one Massilia genomospecies isolated from Antarctic streams, lakes and regoliths. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 43, 126112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Deng, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, Z. DOM hydrophilic components of organic fertilizers increased the soil nitrogen retention capacity and succession of the microbial community. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1320302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Penton, C.R.; Xiong, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z.; Xu, X.; Li, R.; Shen, Q. Reshaping the rhizosphere microbiome by bio-organic amendment to enhance crop yield in a maize-cabbage rotation system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 142, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubeux, J.C.B., Jr.; Sollenberger, L.E.; Mathews, B.W.; Scholberg, J.M.; Santos, H.Q. Nutrient cycling in warm-climate grasslands. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Lv, H.; Zhou, W.; Liang, B. Microbial mechanism of crop residues addition in nitrogen leaching loss retention and soil ecosystem stability maintenance. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 31, 103194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-J.A.; Sun, J.; Mau, R.L.; Finley, B.K.; Compson, Z.G.; van Gestel, N.; Brown, J.R.; Schwartz, E.; Dijkstra, P.; Hungate, B.A. Labile carbon input determines the direction and magnitude of the priming effect. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 109, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Deng, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, S.; Richter, A.; Shibistova, O.; Guggenberger, G.; et al. C:N:P stoichiometry regulates soil organic carbon mineralization and concomitant shifts in microbial community composition in paddy soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2020, 56, 1093–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Ji, J.; Hao, X.; Yang, B.; Wang, W.; Xu, D.; Zhang, S.; et al. Long-Term Crop Rotation Revealed the Relationship Between Soil Organic Carbon Physical Fraction and Bacterial Community at Aggregate Scales. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Ren, Y.; Ren, G.; Zhang, S.; Feng, J. Impacts of Fertilizers with Varying Nitrogen Contents on Millet Yield and Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Communities: Implications for Sustainable Agricultural Development. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, L.; Huang, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, W.; Ai, C. Nitrogen Application and Rhizosphere Effect Exert Opposite Effects on Key Straw-Decomposing Microorganisms in Straw-Amended Soil. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Yuan, M.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Cui, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhou, S.; Song, A.; Huang, Y. Deciphering the differences of bacterial communities between high- and low-productive wheat fields using high-throughput sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1391428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Suo, F.; Zheng, Y.; You, X.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y. Biochar-compost amendment enhanced sorghum growth and yield by improving soil physicochemical properties and shifting soil bacterial community in a coastal soil. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1036837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).