Deciphering the Language of Intestinal Microbiota Associated with Sepsis, Organ Failure, and Mortality in Patients with Alcohol-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure (ACLF): A Pioneer Study in Latin America
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Recruiting Participants
2.2. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Amplicon Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. LPS Quantification
3. Results
3.1. Cross-Sectional Study and Clinical Characteristics of Recruited Patients
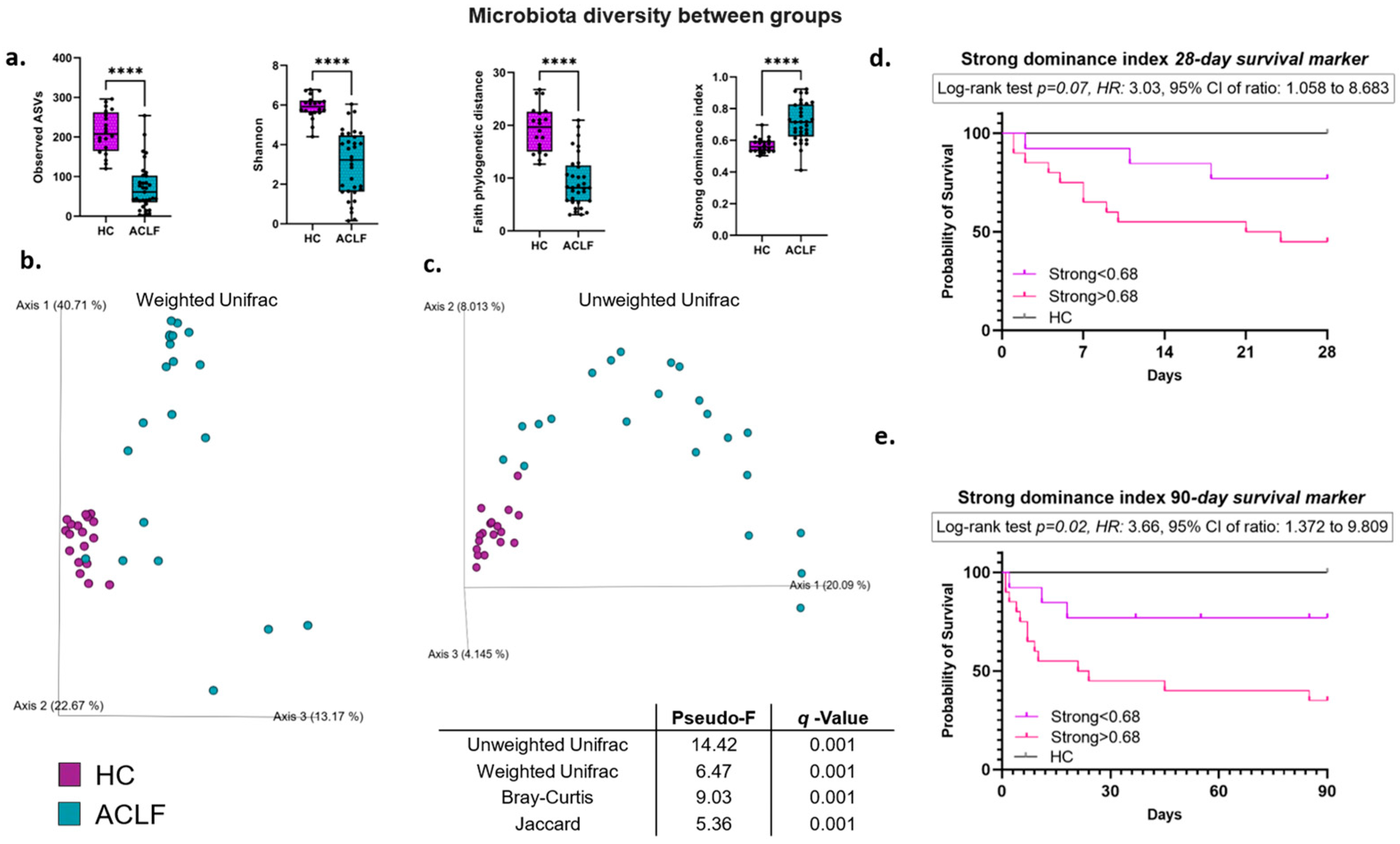
3.2. Intestinal Microbiota Alpha and Beta Diversity
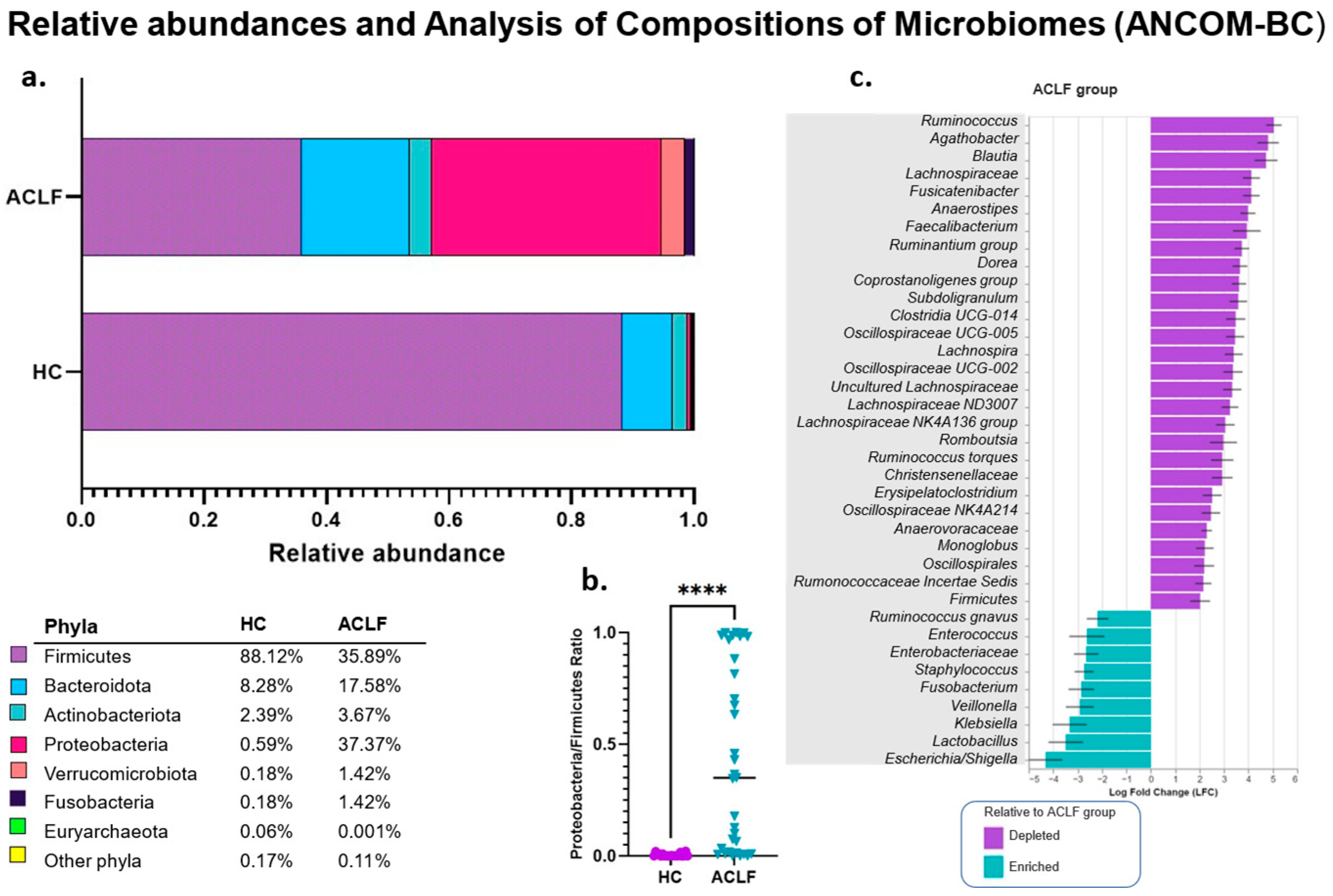
3.3. Analysis of the Relative and Differential Bacterial Taxonomy of the Intestinal Microbiota
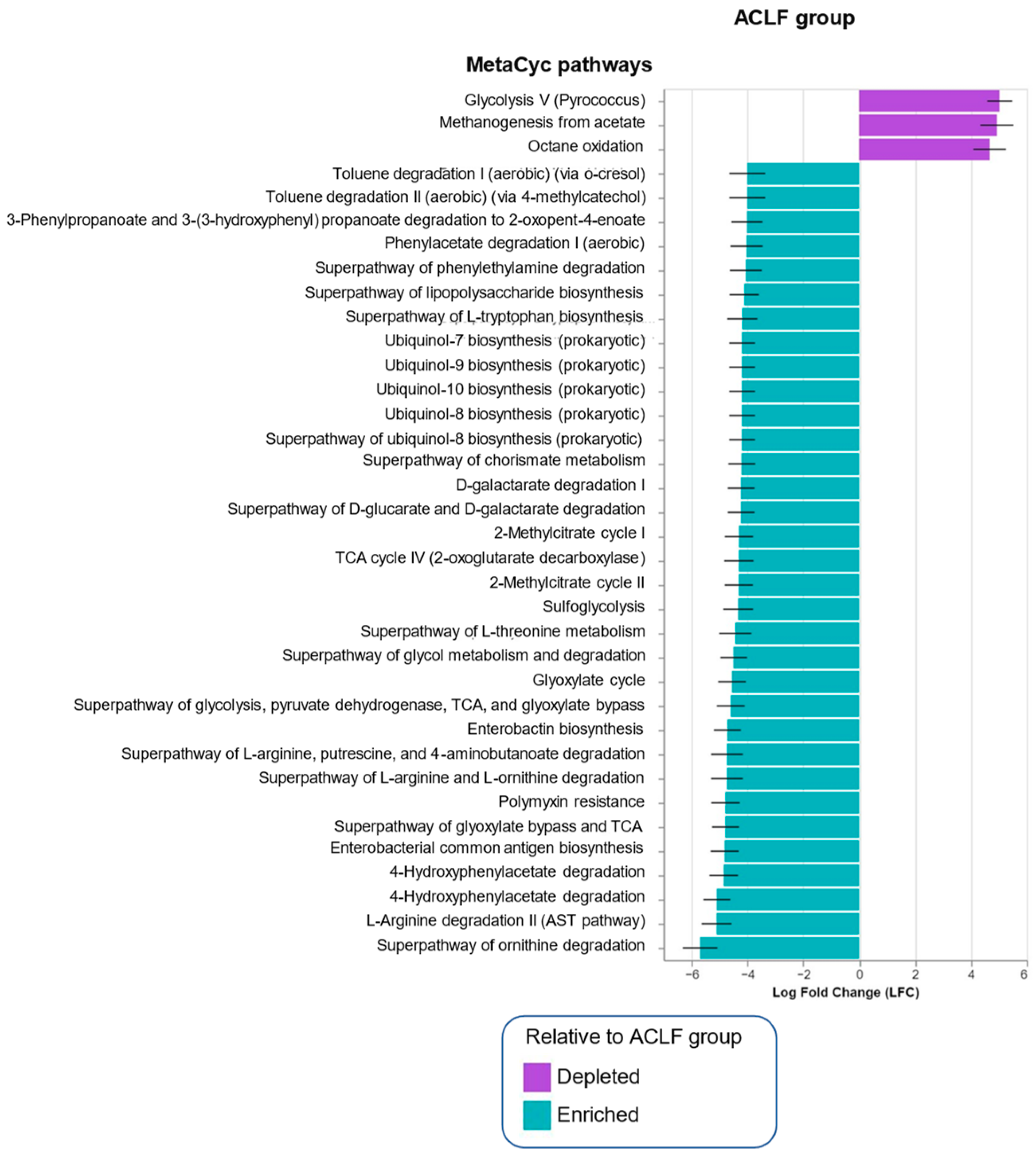
3.4. Functional Metagenomic Profiles
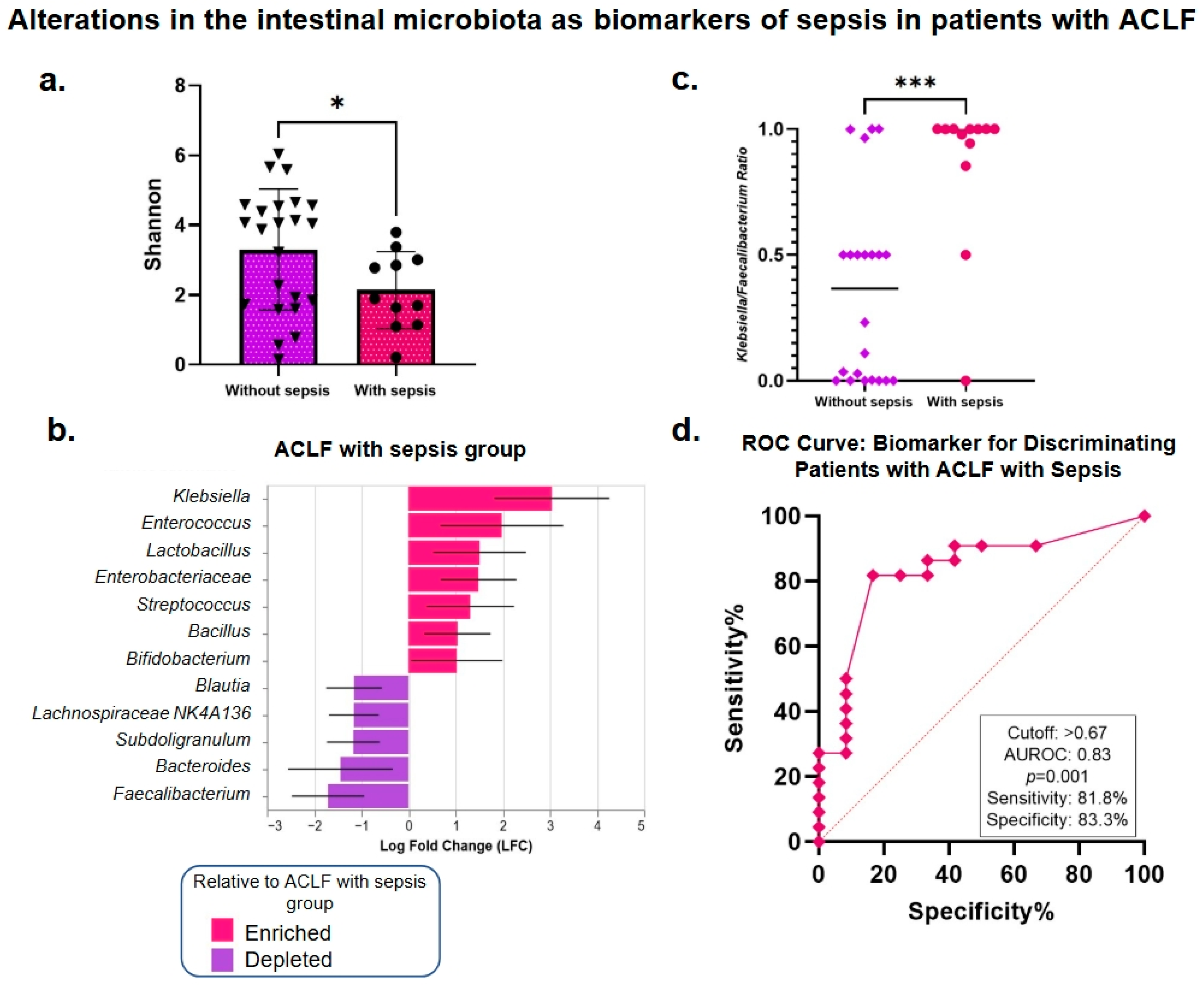
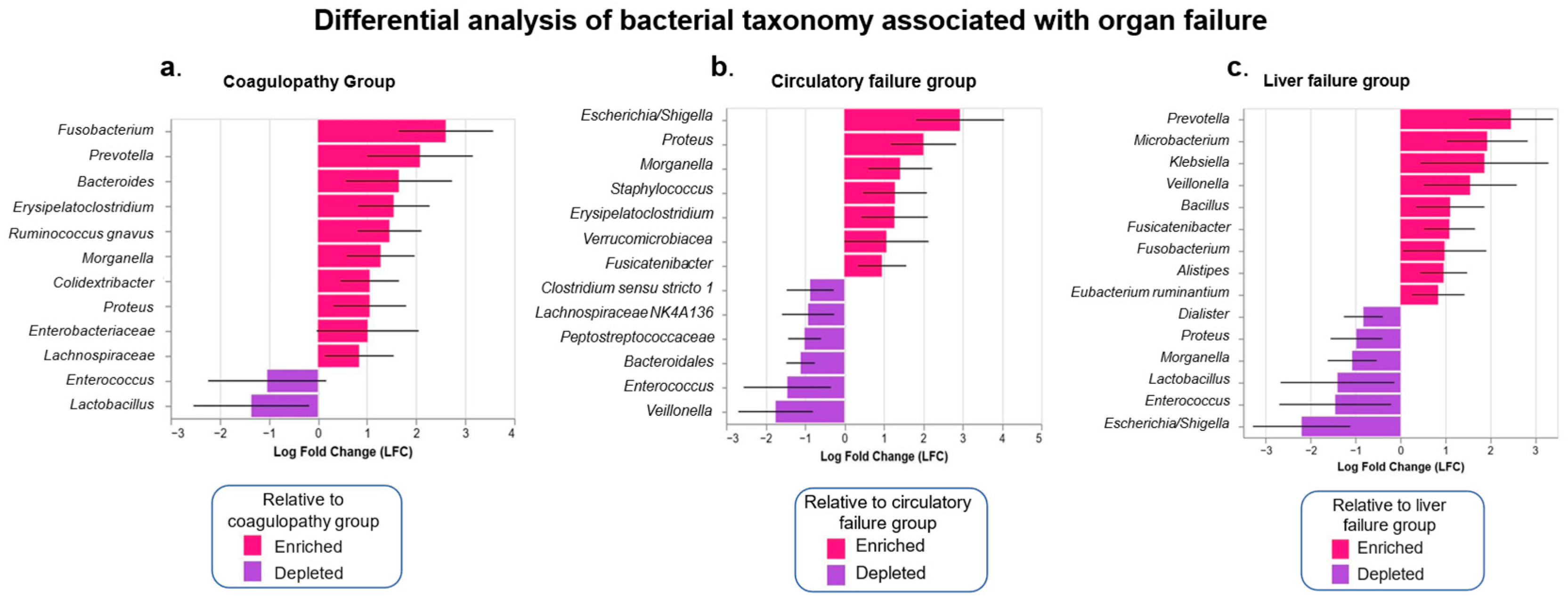
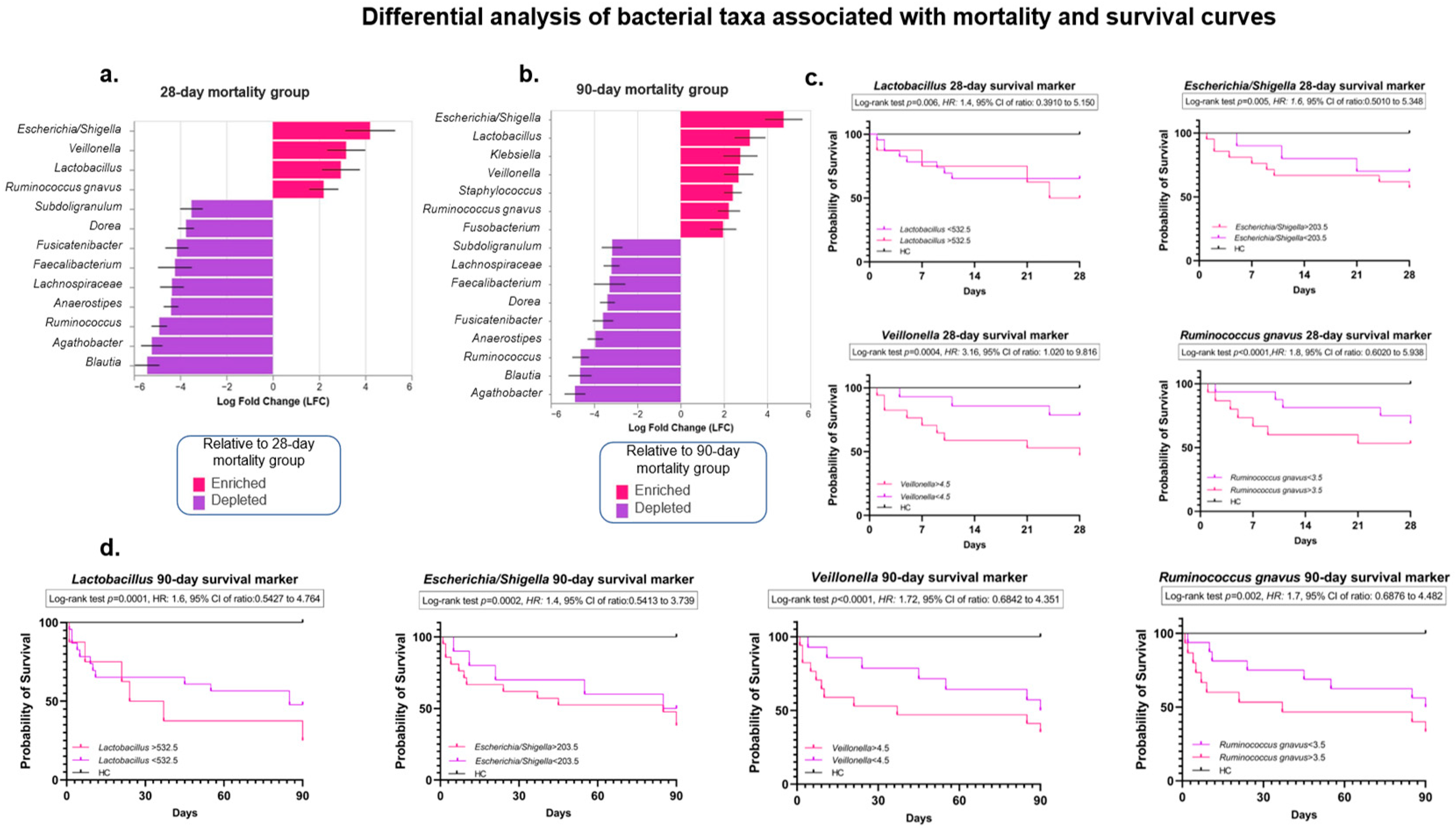
3.5. Analysis of the Intestinal Microbiota Related to Sepsis, Organ Failure, and Mortality
3.6. Quantification of Serum LPS Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- INEGI. 2023. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/contenidos/saladeprensa/boletines/2024/EDR/EDR2023_ene-dic.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2023).
- Arroyo, V.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Ginès, P. Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure: A New Syndrome That Will Re-Classify Cirrhosis On Behalf of the Investigators of the EASL-CLIF Consortium CANONIC Study. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S131–S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, C.; Bajaj, J.S. The Microbiome in Cirrhosis and Its Complications. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltazar-Díaz, T.A.; González-Hernández, L.A.; Aldana-Ledesma, J.M.; Peña-Rodríguez, M.; Vega-Magaña, A.N.; Zepeda-Morales, A.S.M.; López-Roa, R.I.; del Toro-Arreola, S.; Martínez-López, E.; Salazar-Montes, A.M.; et al. Escherichia/Shigella, SCFAs, and Metabolic Pathways—The Triad That Orchestrates Intestinal Dysbiosis in Patients with Decompensated Alcoholic Cirrhosis from Western Mexico. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Vargas, H.E.; Reddy, K.R.; Lai, J.C.; O’Leary, J.G.; Tandon, P.; Wong, F.; Mitrani, R.; White, M.B.; Kelly, M.; et al. Association Between Intestinal Microbiota Collected at Hospital Admission and Outcomes of Patients With Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 756–765.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Qian, G.; Fang, D.; Shi, D.; Guo, L.; Li, L. Gut Dysbiosis in Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure and Its Predictive Value for Mortality. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, C.; Guilly, S.; Da Silva, K.; Llopis, M.; Le-Chatelier, E.; Huelin, P.; Carol, M.; Moreira, R.; Fabrellas, N.; De Prada, G.; et al. Alterations in Gut Microbiome in Cirrhosis as Assessed by Quantitative Metagenomics: Relationship With Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure and Prognosis. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 206–218.E13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslennikov, R.; Ivashkin, V.; Efremova, I.; Poluektova, E.; Shirokova, E.; Maslennikov, R.; Poluektova, E.; Maslennikov, R. Gut-Liver Axis in Cirrhosis: Are Hemodynamic Changes a Missing Link? World J. Clin. Cases 2021, 9, 9320–9332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H. Leaky Gut and Gut-Liver Axis in Liver Cirrhosis: Clinical Studies Update. Gut Liver 2021, 15, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albillos, A.; de Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The Gut-Liver Axis in Liver Disease: Pathophysiological Basis for Therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelli, M.; Franza, L.; Pignataro, G.; Ojetti, V.; Covino, M.; Piccioni, A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Franceschi, F. Interaction between Lipopolysaccharide and Gut Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremova, I.; Maslennikov, R.; Medvedev, O.; Kudryavtseva, A.; Avdeeva, A.; Krasnov, G.; Romanikhin, F.; Diatroptov, M.; Fedorova, M.; Poluektova, E.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Biomarkers of Intestinal Barrier Damage in Cirrhosis. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opal, S.M. Endotoxemia: Pathophysiological Background Endotoxins and Other Sepsis Triggers. Contrib. Nephrol. 2010, 167, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo, V.B.M. Systemic Inflammation and Organ Failure in Cirrhosis. In The Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure Syndrome (ACLF), Procedings of the 1st International Meeting on Systemic Inflammation and Organ Failure in Cirrhosis, Barcelona, Spain, 12 April 2016; Elsevier: Barcelona, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. Global Impacts of Western Diet and Its Effects on Metabolism and Health: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espino-Rosales, D.; Lopez-Moro, A.; Heras-González, L.; Jimenez-Casquet, M.J.; Olea-Serrano, F.; Mariscal-Arcas, M. Estimation of the Quality of the Diet of Mexican University Students Using DQI-I. Healthcare 2023, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, A.Q.; Curto Vilalta, A.; Momoyo Zitelli, P.; Pereira, G.; Goncalves, L.L.; Torre, A.; Diaz, J.M.; Gadano, A.C.; Mattos, A.Z.; Mendes, L.S.C.; et al. Genetic Ancestry, Race, and Severity of Acutely Decompensated Cirrhosis in Latin America. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 696–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, R.; Tonon, M.; Krag, A.; Angeli, P.; Berenguer, M.; Berzigotti, A.; Fernandez, J.; Francoz, C.; Gustot, T.; Jalan, R.; et al. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 461–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illumina. 16S Metagenomic Sequencing Library Preparation Preparing 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Amplicons for the Illumina MiSeq System. Available online: https://support.illumina.com/documents/documentation/chemistry_documentation/16s/16s-metagenomic-library-prep-guide-15044223-b.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Guerrini, C.J.; Botkin, J.R.; McGuire, A.L. Clarify the HIPAA Right of Access to Individuals’ Research Data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 850–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Gregory Caporaso, J. Optimizing Taxonomic Classification of Marker-Gene Amplicon Sequences with QIIME 2’s Q2-Feature-Classifier Plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, M.S.; O’Rourke, D.R.; Kaehler, B.D.; Ziemski, M.; Dillon, M.R.; Foster, J.T.; Bokulich, N.A. RESCRIPt: Reproducible Sequence Taxonomy Reference Database Management. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glöckner, F.O.; Yilmaz, P.; Quast, C.; Gerken, J.; Beccati, A.; Ciuprina, A.; Bruns, G.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Westram, R.; et al. 25 Years of Serving the Community with Ribosomal RNA Gene Reference Databases and Tools. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 261, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.-I.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A Novel Method for Rapid Multiple Sequence Alignment Based on Fast Fourier Transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielou, E.C. The Measurement of Diversity in Different Types of Biological Colledions. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A. Board of the Foundation of the Scandinavian Journal of Statistics Nonparametric Estimation of the Number of Classes in a Population Nonparametric Estimation of the Number of Classes in a Population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 11, 256–270. [Google Scholar]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Hamady, M.; Kelley, S.T.; Knight, R. Quantitative and Qualitative β Diversity Measures Lead to Different Insights into Factors That Structure Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1576–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A New Phylogenetic Method for Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Pirrung, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Knight, R. EMPeror: A Tool for Visualizing High-Throughput Microbial Community Data. GigaScience 2013, 2, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Peddada, S. Das Analysis of Compositions of Microbiomes with Bias Correction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo, H.H.; Hashimoto, D.A.; Caicedo, J.C.; Pentland, A.; Pisano, G.P. Overcoming Barriers to Early Disease Intervention. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera, P.; Kozlov, A.M.; Czech, L.; Morel, B.; Darriba, D.; Flouri, T.; Stamatakis, A. EPA-Ng: Massively Parallel Evolutionary Placement of Genetic Sequences. Syst. Biol. 2019, 68, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Doak, T.G. A Parsimony Approach to Biological Pathway Reconstruction/Inference for Genomes and Metagenomes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czech, L.; Barbera, P.; Stamatakis, A. Genesis and Gappa: Processing, Analyzing and Visualizing Phylogenetic (Placement) Data. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 3263–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Doebeli, M. Efficient Comparative Phylogenetics on Large Trees. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1053–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspi, R.; Altman, T.; Billington, R.; Dreher, K.; Foerster, H.; Fulcher, C.A.; Holland, T.A.; Keseler, I.M.; Kothari, A.; Kubo, A.; et al. The MetaCyc Database of Metabolic Pathways and Enzymes and the BioCyc Collection of Pathway/Genome Databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D459–D471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltazar-Díaz, T.A.; Andrade-Villanueva, J.F.; Sánchez-Álvarez, P.; Amador-Lara, F.; Holguín-Aguirre, T.; Sánchez-Reyes, K.; Álvarez-Zavala, M.; López-Roa, R.I.; Bueno-Topete, M.R.; González-Hernández, L.A. A Two-Faced Gut Microbiome: Butyrogenic and Proinflammatory Bacteria Predominate in the Intestinal Milieu of People Living with HIV from Western Mexico. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosselaere, F.; Vanderleyden, J. A Metabolic Node in Action: Chorismate-Utilizing Enzymes in Microorganisms. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2001, 27, 75–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, P.; Ji, Y. Biosynthesis of the Aromatic Amino Acids. EcoSal Plus 2008, 3, 458–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Q.; Terrault, N.A.; Tacke, F.; Gluud, L.L.; Arrese, M.; Bugianesi, E.; Loomba, R. Global Epidemiology of Cirrhosis—Aetiology, Trends and Predictions. Nat Rev Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.N.; Xue, F.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, W.; Hou, J.J.; Lv, Y.; Xiang, J.X.; Zhang, X.F. Global Burden of Liver Cirrhosis and Other Chronic Liver Diseases Caused by Specific Etiologies from 1990 to 2019. BMC Public Heal. 2024, 24, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Heuman, D.M.; Hylemon, P.B.; Sanyal, A.J.; White, M.B.; Monteith, P.; Noble, N.A.; Unser, A.B.; Daita, K.; Fisher, A.R.; et al. Altered Profile of Human Gut Microbiome Is Associated with Cirrhosis and Its Complications. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltazar-Díaz, T.A.; Riggen-Bueno, V.; Cortina-Romero, D.B.; Del Toro-Arreola, S.; Haramati, J.; Bastidas-Ramírez, B.E.; Bueno-Topete, M.R. Low-Diversity Microbiota and an Increased Metabolism of Arginine and Aromatic Amino Acids: A Hallmark of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Western Mexican Patients with Alcohol-Associated Cirrhosis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, W.L. Assessing Species Abundance Unevenness within and between Plant Communities. Commun. Ecol. 2002, 3, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltazar-Díaz, T.A.; Amador-Lara, F.; Andrade-Villanueva, J.F.; González-Hernández, L.A.; Cabrera-Silva, R.I.; Sánchez-Reyes, K.; Álvarez-Zavala, M.; Valenzuela-Ramírez, A.; Del Toro-Arreola, S.; Bueno-Topete, M.R. Gut Bacterial Communities in HIV-Infected Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome: Effects of the Therapy with Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitor-Based and Protease Inhibitor-Based Regimens. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggen-Bueno, V.; Del Toro-Arreola, S.; Baltazar-Díaz, T.A.; Vega-Magaña, A.N.; Peña-Rodríguez, M.; Castaño-Jiménez, P.A.; Sánchez-Orozco, L.V.; Vera-Cruz, J.M.; Bueno-Topete, M.R. Intestinal Dysbiosis in Subjects with Obesity from Western Mexico and Its Association with a Proinflammatory Profile and Disturbances of Folate (B9) and Carbohydrate Metabolism. Metabolites 2024, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzarotto, C.; Ronsoni, M.F.; Fayad, L.; Nogueira, C.L.; Luiza Bazzo, M.; Luz Narciso-Schiavon, J.; De Lucca Schiavon, L.; Buzaglo Dantas-Corrêa, E. Acute Phase Proteins in Complications of Cirrhosis. Ann. Hepatol. 2013, 12, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, A.C.; Longo, C.; Landeira, G.; Lausi, A.F.; Priore, G.; Gualano, G.; Domínguez, N.; Ruffillo, G.; Zulatto, C.; Di Bartolomeo, S.; et al. Las Infecciones Por Bacterias Multirresistentes En La Modifican El Pronóstico de Los Pacientes. Acta Gastroenterológica Latinoam. 2017, 47, 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, M.T.; Cresci, G.A.M. The Immunomodulatory Functions of Butyrate. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 6025–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From Dietary Fiber to Host Physiology: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Key Bacterial Metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Rodríguez, M.; Vega-Magaña, N.; García-Benavides, L.; Zepeda-Nuño, J.S.; Gutierrez-Silerio, G.Y.; González-Hernández, L.A.; Andrade-Villanueva, J.F.; Del Toro-Arreola, S.; Pereira-Suárez, A.L.; Bueno-Topete, M.R. Butyrate Administration Strengthens the Intestinal Epithelium and Improves Intestinal Dysbiosis in a Cholestasis Fibrosis Model. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Chávez, F.; Lopez, C.A.; Bäumler, A.J. Oxygen as a Driver of Gut Dysbiosis. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 105, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bert, F.; Johnson, J.R.; Ouattara, B.; Leflon-Guibout, V.; Johnston, B.; Marcon, E.; Valla, D.; Moreau, R.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.H. Genetic Diversity and Virulence Profiles of Escherichia Coli Isolates Causing Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis and Bacteremia in Patients with Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2709–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.M. The Immune Response to Prevotella Bacteria in Chronic Inflammatory Disease. Immunology 2017, 151, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldapa-Vega, G.; Pastelín-Palacios, R.; Isibasi, A.; Moreno-Eutimio, M.A.; López-Macías, C. Modulation of Immune Response by Bacterial Lipopolysaccharides. Rev. Alerg. Mex. 2016, 63, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botos, I.; Majdalani, N.; Mayclin, S.J.; McCarthy, J.G.; Lundquist, K.; Wojtowicz, D.; Barnard, T.J.; Gumbart, J.C.; Buchanan, S.K. Structural and Functional Characterization of the LPS Transporter LptDE from Gram-Negative Pathogens. Structure 2016, 24, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argentina Microbiología, R.D.; Ramírez-Mata, A.; Fernández-Domínguez, I.J.; Nuñez-Reza, K.J.; Xiqui-Vázquez Beatriz E Baca, M.L. PALABRAS CLAVE Networks Involving Quorum Sensing, Cyclic-Di-GMP and Nitric Oxide on Biofi Lm Production in Bacteria. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2014, 46, 242–255. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, R.T.; Brown, P.D. SpoT-Mediated Stringent Response Influences Environmental and Nutritional Stress Tolerance, Biofilm Formation and Antimicrobial Resistance in Klebsiella Pneumoniae. APMIS 2020, 128, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Nian, R.; Xian, M.; Li, F.; Zhang, H. Common Problems Associated with the Microbial Productions of Aromatic Compounds and Corresponding Metabolic Engineering Strategies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 41, 107548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Wendisch, V.F. Biotechnological Production of Aromatic Compounds of the Extended Shikimate Pathway from Renewable Biomass. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 257, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, R.; Jallu, S.; Singh, T.P. The Shikimate Pathway: Review of Amino Acid Sequence, Function and Three-Dimensional Structures of the Enzymes. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 41, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzin, V.; Galili, G. The Biosynthetic Pathways for Shikimate and Aromatic Amino Acids in Arabidopsis thaliana. Arab. Book 2010, 8, e0132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, A.; Cross, P.J.; Dobson, R.C.J.; Adams, L.E.; Savka, M.A.; Hudson, A.O. A Three-Ring Circus: Metabolism of the Three Proteogenic Aromatic Amino Acids and Their Role in the Health of Plants and Animals. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, S.; Jaswal, K.; Shiver, A.L.; Balecha, H.; Patra, T.; Chaba, R. A Genome-Wide Screen in Escherichia Coli Reveals That Ubiquinone Is a Key Antioxidant for Metabolism of Long-Chain Fatty Acids. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 20086–20099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroz, A.; Anderson, R.F.; Smith, R.A.J.; Murphy, M.P. Reactivity of Ubiquinone and Ubiquinol with Superoxide and the Hydroperoxyl Radical: Implications for in Vivo Antioxidant Activity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Pan, X.; Hao, D.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, S.; Peng, H.; Zhuang, Y. Causal Associations of Gut Microbiota and Metabolites on Sepsis: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1190230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, F.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Jia, X.; Li, N.; Wang, X.; Luo, Y.; Man, M.; et al. Gut Microbiota Composition and Changes in Patients with Sepsis: Potential Markers for Predicting Survival. MC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, W.; Zhang, S.; Qian, H.; Huang, S.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, D. Gut Microbiota and Sepsis and Sepsis-Related Death: A Mendelian Randomization Investigation. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1266230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, S.; Xiang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wei, W.; Long, X.; Han, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, F.; Xue, M.; et al. The Pathogens of Secondary Infection in Septic Patients Share a Similar Genotype to Those That Predominate in the Gut. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Chakravorty, S.; Yang, T.; Russo, T.A.; Newton, S.M.; Klebba, P.E. Siderophore-Mediated Iron Acquisition by Klebsiella Pneumoniae. J. Bacteriol. 2024, 206, e0002424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namikawa, H.; Niki, M.; Niki, M.; Oinuma, K.I.; Yamada, K.; Nakaie, K.; Tsubouchi, T.; Tochino, Y.; Takemoto, Y.; Kaneko, Y.; et al. Siderophore Production as a Biomarker for Klebsiella Pneumoniae Strains That Cause Sepsis: A Pilot Study. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2022, 121, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson Toll, J.; Solà, E.; Perez, M.A.; Piano, S.; Cheng, A.; Subramanian, A.K.; Kim, W.R. Infections in Decompensated Cirrhosis: Pathophysiology, Management, and Research Agenda. Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 8, e0539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr O’hara, C.; Brenner, F.W.; Miller, J.M. Classification, Identification, and Clinical Significance of Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koronakis, V.; Cross, M.; Senior, B.; Koronakis, E.; Hughes, C. The Secreted Hemolysins of Proteus Mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, and Morganella morganii Are Genetically Related to Each Other and to the Alpha-Hemolysin of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1987, 169, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Livermore, D.M. Chromosomal 1-Lactamase Expression and Resistance to 3-Lactam Antibiotics in Proteus vulgaris and Morganella morganii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1988, 32, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Long, W.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, L.; Hamaker, B.R. Fiber-Utilizing Capacity Varies in Prevotella- versus Bacteroides-Dominated Gut Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, C.M.; Chen, K.F.; Lin, Y.; Ke, H.M.; Huang, H.Y.; Gong, Y.N.; Tsai, W.S.; You, J.F.; Lu, M.J.; Cheng, H.T.; et al. Predicting Clinical Outcomes of Cirrhosis Patients with Hepatic Encephalopathy From the Fecal Microbiome. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 8, 301–318.E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslennikov, R.; Ivashkin, V.; Efremova, I.; Alieva, A.; Kashuh, E.; Tsvetaeva, E.; Poluektova, E.; Shirokova, E.; Ivashkin, K. Gut Dysbiosis Is Associated with Poorer Long-Term Prognosis in Cirrhosis. World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Manoil, D.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Kotsakis, G.A. Veillonellae: Beyond Bridging Species in Oral Biofilm Ecology. Front. Oral Heal. 2021, 2, 774115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, A.; Rainer, F.; Bashir, M.; Leber, B.; Schmerboeck, B.; Klymiuk, I.; Groselj-Strele, A.; Durdevic, M.; Freedberg, D.E.; Abrams, J.A.; et al. Biomarkers for Oralization during Long-Term Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy Predict Survival in Cirrhosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ji, F.; Guo, J.; Shi, D.; Fang, D.; Li, L. Dysbiosis of Small Intestinal Microbiota in Liver Cirrhosis and Its Association with Etiology. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Honda, T.; Inukai, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Ito, T.; Imai, N.; Ishizu, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Kawashima, H. Identification of the Microbiome Associated with Prognosis in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubachs, J.; Ziemons, J.; Soons, Z.; Aarnoutse, R.; van Dijk, D.P.J.; Penders, J.; van Helvoort, A.; Smidt, M.L.; Kruitwagen, R.F.P.M.; Baade-Corpelijn, L.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acid Alterations in Cachectic Cancer Patients. J. Cachex Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 2007–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Fields, B.K.K.; Liang, T.; Dubé, M.P.; Politano, S. Veillonella Bacteremia in Alcoholic Hepatitis. Case Rep. Hepatol. 2021, 2021, 9947213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crost, E.H.; Coletto, E.; Bell, A.; Juge, N. Ruminococcus gnavus: Friend or Foe for Human Health. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 47, fuad014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefever, S.; Van Den Bossche, D.; Van Moerkercke, W.; D’Hondt, M.; Alegret Pampols, M.d.C.; Struyve, M.; De Bel, A.; Boudewijns, M. Ruminococcus gnavus Bacteremia, an Uncommon Presentation of a Common Member of the Human Gut Microbiota: Case Report and Literature Review. Acta Clin. Belg. Int. J. Clin. Lab. Med. 2019, 74, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.Y.; Groer, M.; Dutra, S.V.O.; Sarkar, A.; McSkimming, D.I. Gut Microbiota and Immune System Interactions. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, J.M.; Facklam, R.R.; Thornsberry, C. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Vancomycin-Resistant Leuconostoc, Pediococcus, and Lactobacillus Species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1990, 34, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May-Torruco, A.L.; Corona-Cruz, A.I.; Jiménez, A.L.L.; Cortés, N.G.; Vera, R.J. Sensibilidad y Resistencia a Antibióticos de Cepas Probióticas Empleadas En Productos Comerciales. Eur. Sci. J. ESJ 2020, 16, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, S.S.B.; Nagendra, V.; Hofmeyr, A. Probiotic Related Lactobacillus rhamnosus Endocarditis in a Patient with Liver Cirrhosis. IDCases 2018, 13, e00439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding-Theobald, E.; Maraj, B. Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis Due to Lactobacillus paracasei in Cirrhosis. Case Rep. Gastrointest. Med. 2018, 2018, 5714053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | HC (n = 20) | ACLF (n = 33) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 50.65 ± 10.13 | 49.12 ± 10.63 | 0.600 a |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.9 (24.4–27.2) | 23.8 (20.9–26.2) | 0.200 b |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 14.8 (14.0–15.6) | 9.02 (7.6–11.2) | <0.001 b |
| Platelets (10 9 /µL) | 231 (178.8–274.8) | 92.9 (78.3–123.4) | <0.001 b |
| White blood cells (10 9 /µL) | 5.9 (4.7–6.6) | 13.09 (7.7–22.3) | <0.001 b |
| Neutrophils (10 9 /µL) | 3.4 (2.4–4.08) | 11.3 (5.7–21.7) | <0.001 b |
| Lymphocytes (10 9 /µL) | 1.7 (1.5–2.1) | 0.91 (0.6–1.3) | <0.001 b |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.6 (0.5–0.8) | 8.2 (4.2–23.2) | <0.001 b |
| Direct bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.12 (0.1–1.15) | 3.5 (1.3–10.3) | <0.001 b |
| GGT (IU/L) | 23.5 (16.0–34.2) | 86 (27.2–166.5) | 0.003 b |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.5 (4.3–4.6) | 2.1 (1.7–2.2) | <0.001 b |
| ALT (IU/L) | 26 (15.5–37.7) | 28 (22–45) | 0.180 b |
| AST (IU/L) | 20 (15.2–29.7) | 68 (55–104) | <0.001 b |
| ALP (IU/L) | 73.5 (61.2–79) | 163 (83–200) | <0.001 b |
| Total protein (g/dL) | 7.1 (6.8–7.6) | 6 (4.8–6.4) | <0.001 b |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.78 (0.7–0.9) | 2.5 (1.1–3.8) | <0.001 b |
| Prothrombin time (s) | 11.4 (11.1–12.1) | 25.2 (20.2–32.3) | <0.001 b |
| INR | 1.07 (1.06–1.2) | 2.3 (1.8–2.6) | <0.001 b |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | N/A | 128 (124–135) | N/A |
| Child–Pugh class A/B/C | N/A | 0/0/33 | N/A |
| Child–Pugh score | N/A | 12 (11–13) | N/A |
| MELD-Na score | N/A | 33.5(28–38) | N/A |
| ACLF Grades I/II/III | N/A | 9/16/8 | N/A |
| CLIF-SOFA | N/A | 48 (39–51) | N/A |
| Platelet-to-neutrophil ratio | 1.7(1.2–2.2) | 8.9 (6.2–14.3) | <0.001 b |
| Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio | 1.8 (1.5–2.2) | 9.2 (6.5–21.1) | <0.001 b |
| APRI index | 0.19 (0.13–0.29) | 1.5 (1–2.3) | <0.001 b |
| FIB-4 index | 0.82 (0.63–1.57) | 7.4 (4.5–10.4) | <0.001 b |
| Presence of hepatic encephalopathy (n, %) | N/A | 28 (84.8) | N/A |
| West-Haven grade (1/2/3/4) | N/A | 4/11/10/3 | N/A |
| Ascites (n, %) | N/A | 22 (66.7) | N/A |
| Upper gastrointestinal bleeding (n, %) | N/A | 9 (27.2) | N/A |
| Acute kidney injury (n, %) | N/A | 20 (60.6) | N/A |
| Lactulose (n, %) | N/A | 31 (93.9) | N/A |
| Mean arterial pressure (mmHg) | N/A | 75 (65–83) | N/A |
| Antibiotic usage (n, %) | N/A | 27 (81.8) | N/A |
| Ceftriaxone (n, %) | N/A | 21 (65.6) | N/A |
| Rifaximin (n, %) | N/A | 14 (46.7) | N/A |
| Piperacillin/tazobactam (n, %) | N/A | 5 (15.6) | N/A |
| Others (n, %) | N/A | 5 (15.6) | N/A |
| Use of proton pump inhibitors (n, %) | N/A | 22 (66.7) | N/A |
| Infection at admission (n, %) | N/A | 20 (60.6) | N/A |
| Active alcoholism (n, %) | N/A | 15 (45.5) | N/A |
| Urinary tract infection (n, %) | N/A | 6 (18.2) | N/A |
| Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (n, %) | N/A | 6 (18.2) | N/A |
| Pneumonia (n, %) | N/A | 3 (9.1) | N/A |
| SIRS (n, %) | N/A | 13 (39.4) | N/A |
| Sepsis (n, %) | N/A | 10 (30.3) | N/A |
| Septic shock (n, %) | N/A | 4 (12.1) | N/A |
| Kidney failure (n, %) | N/A | 19 (57.5) | N/A |
| Brain failure (n, %) | N/A | 13 (39.3) | N/A |
| Liver failure (n, %) | N/A | 14 (42.4) | N/A |
| Circulatory failure (n, %) | N/A | 10 (30.3) | N/A |
| Respiratory failure (n, %) | N/A | 3 (9.1) | N/A |
| Coagulopathy (n, %) | N/A | 11 (33.3) | N/A |
| 7-day mortality (n, %) | N/A | 7 (21.2) | N/A |
| 28-day mortality (n, %) | N/A | 13 (39.4) | N/A |
| 90-day mortality (n, %) | N/A | 20 (60.6) | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castaño-Jiménez, P.A.; Baltazar-Díaz, T.A.; González-Hernández, L.A.; García-Salcido, R.; Klimov-Kravtchenko, K.; Andrade-Villanueva, J.F.; Arellano-Arteaga, K.J.; Padilla-Sánchez, M.P.; Del Toro-Arreola, S.; Bueno-Topete, M.R. Deciphering the Language of Intestinal Microbiota Associated with Sepsis, Organ Failure, and Mortality in Patients with Alcohol-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure (ACLF): A Pioneer Study in Latin America. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051138
Castaño-Jiménez PA, Baltazar-Díaz TA, González-Hernández LA, García-Salcido R, Klimov-Kravtchenko K, Andrade-Villanueva JF, Arellano-Arteaga KJ, Padilla-Sánchez MP, Del Toro-Arreola S, Bueno-Topete MR. Deciphering the Language of Intestinal Microbiota Associated with Sepsis, Organ Failure, and Mortality in Patients with Alcohol-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure (ACLF): A Pioneer Study in Latin America. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(5):1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051138
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastaño-Jiménez, Paula Alejandra, Tonatiuh Abimael Baltazar-Díaz, Luz Alicia González-Hernández, Roxana García-Salcido, Ksenia Klimov-Kravtchenko, Jaime F. Andrade-Villanueva, Kevin Javier Arellano-Arteaga, Mayra Paola Padilla-Sánchez, Susana Del Toro-Arreola, and Miriam Ruth Bueno-Topete. 2025. "Deciphering the Language of Intestinal Microbiota Associated with Sepsis, Organ Failure, and Mortality in Patients with Alcohol-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure (ACLF): A Pioneer Study in Latin America" Microorganisms 13, no. 5: 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051138
APA StyleCastaño-Jiménez, P. A., Baltazar-Díaz, T. A., González-Hernández, L. A., García-Salcido, R., Klimov-Kravtchenko, K., Andrade-Villanueva, J. F., Arellano-Arteaga, K. J., Padilla-Sánchez, M. P., Del Toro-Arreola, S., & Bueno-Topete, M. R. (2025). Deciphering the Language of Intestinal Microbiota Associated with Sepsis, Organ Failure, and Mortality in Patients with Alcohol-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure (ACLF): A Pioneer Study in Latin America. Microorganisms, 13(5), 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051138








