The Effect of Selected Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on the Growth of Cotton Plants in Salinized Farmlands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Identification of PSBs
2.1.1. Culture Mediums
2.1.2. Isolation of PSBs
2.1.3. Morphological and Molecular Identification of PSBs
2.1.4. Determination of the Phosphorus-Solubilizing Ability of PSBs
2.1.5. Determination of Organic Acid Content and IAA Production
2.1.6. Determination of Enzyme Production by PSBs
2.2. Experiment on PSBs’ Potential for Cotton Growth Promotion
2.2.1. Experimental Site and Materials
2.2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Test Methods
2.3.1. Determination of Soil Properties
2.3.2. Soil Metagenomics
2.3.3. Determination of Cotton Growth Indicators and Yield
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphological and Molecular Identification of PSBs
3.2. Phosphate-Solubilizing and Growth-Promoting Ability of PSBs
3.3. Effects of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on Bacterial Diversity and Community Structure in Cotton Rhizosphere Soil
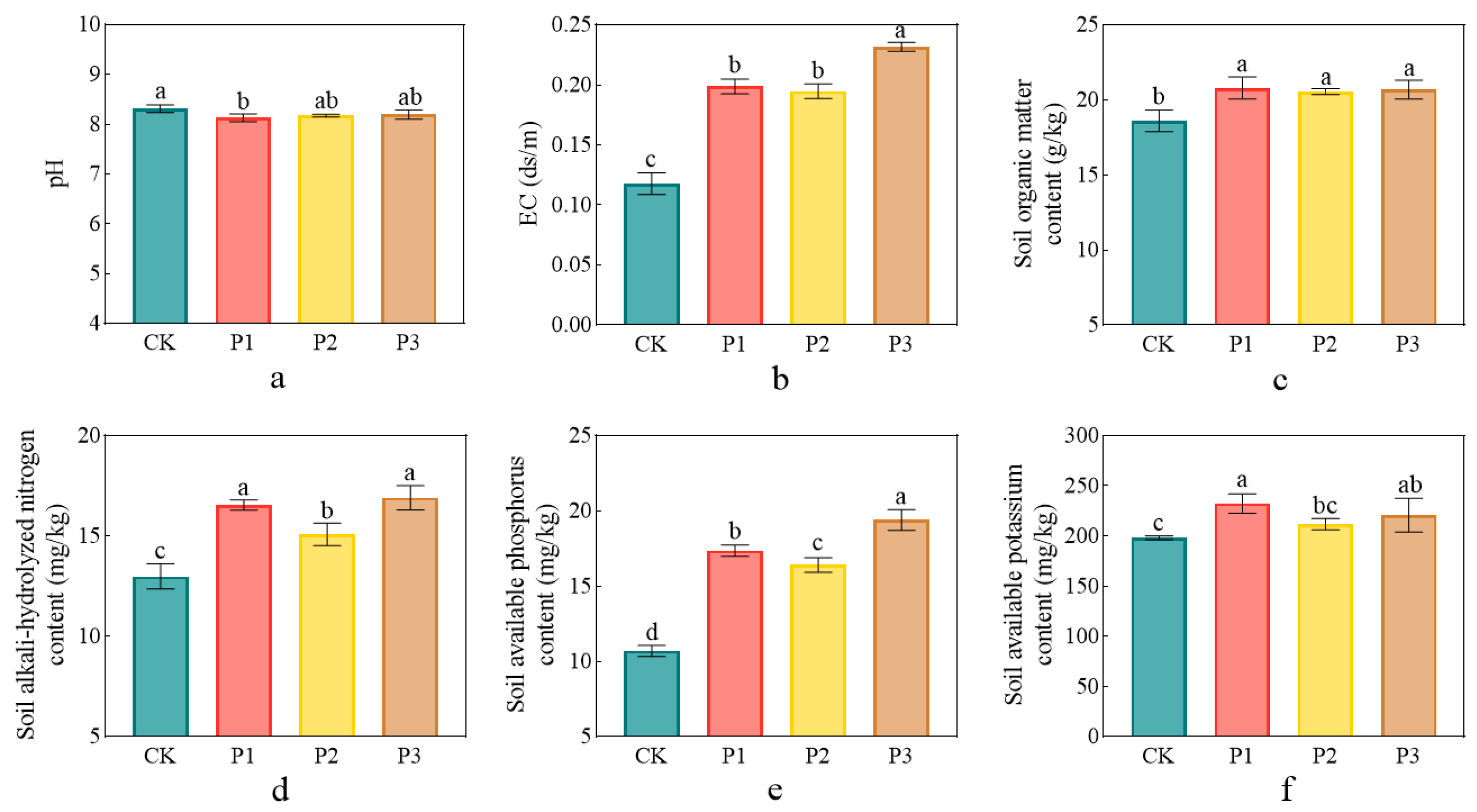
3.4. Impact of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on Soil Properties
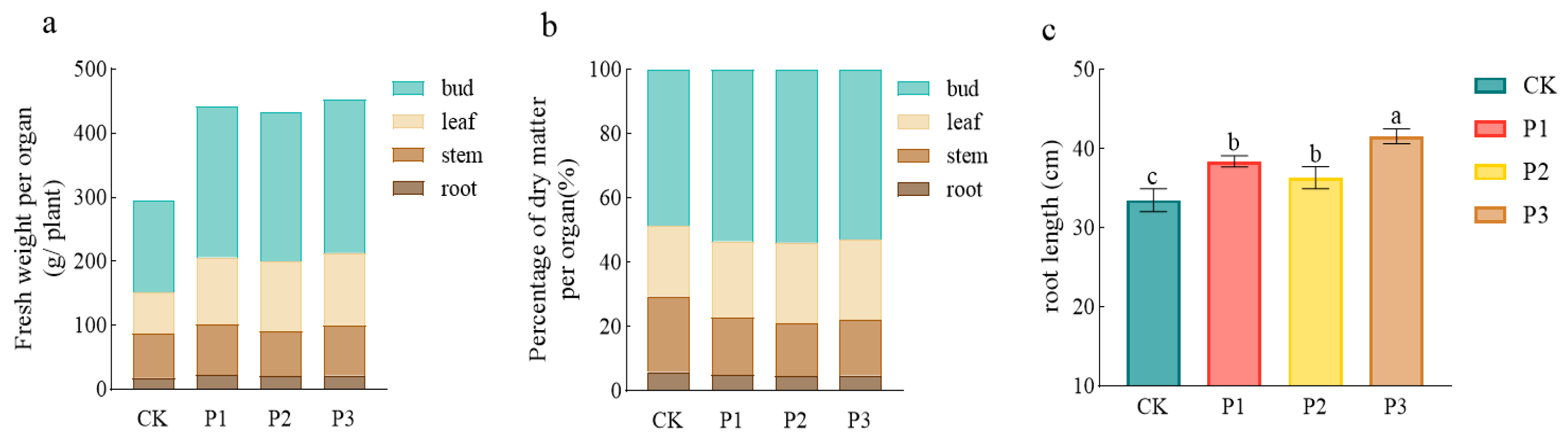
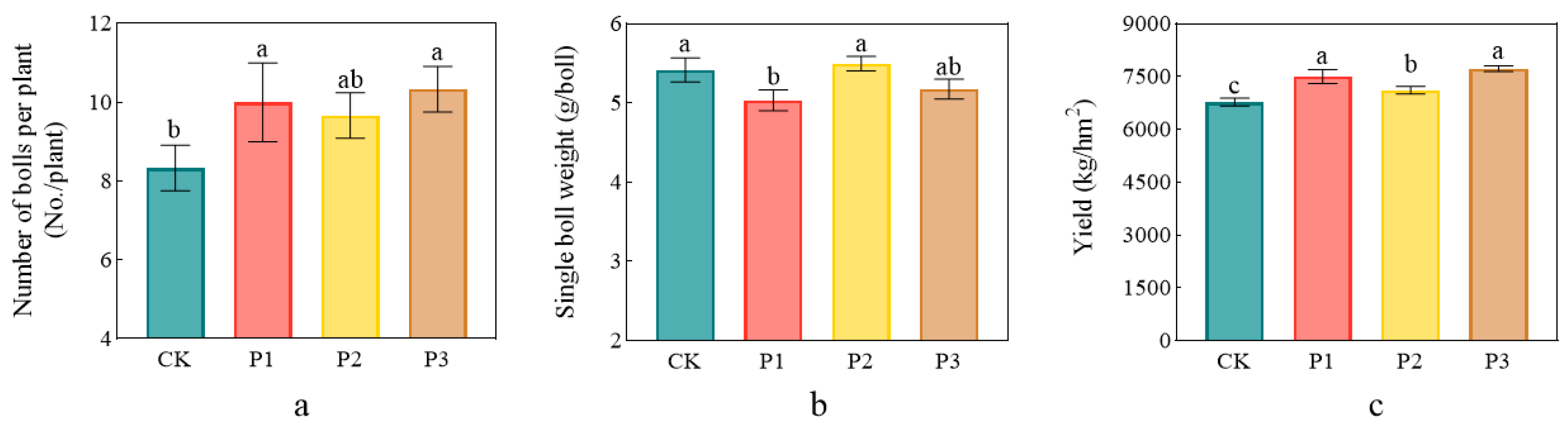
3.5. Growth Promoting Effect of PSBs
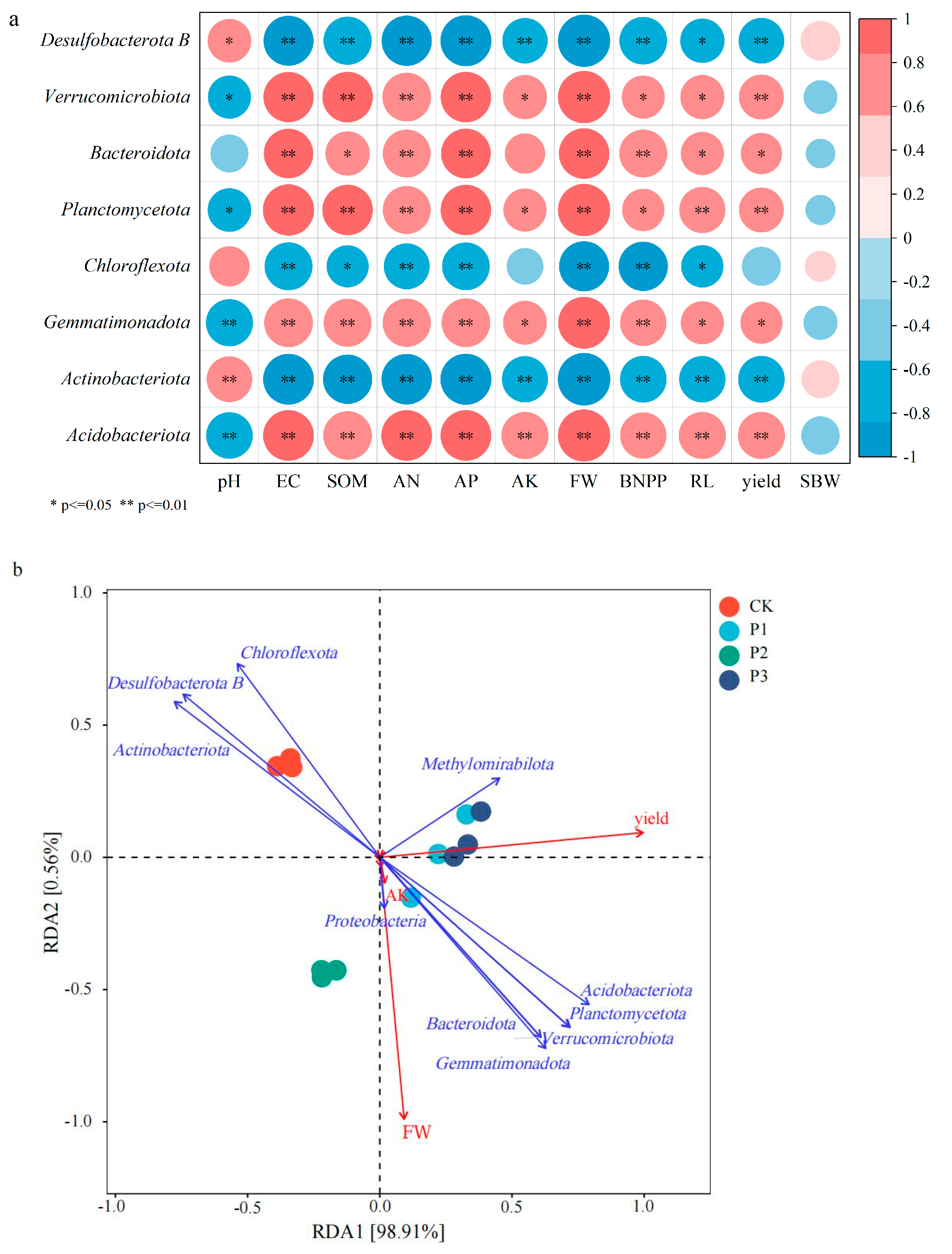
3.6. Correlation and Redundancy Analysis (RDA) Between Soil Microorganisms and Cotton Growth
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, T.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Dong, H.; Dai, S.; Chai, L.; Li, H.; Lv, Y.; Li, T.; et al. Trade-offs of organic amendment input on soil quality and crop productivity in saline-alkali land globally: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Agron. 2025, 164, 127471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balemi, T.; Negisho, K. Management of soil phosphorus and plant adaptation mechanisms to phosphorus stress for sustainable crop production: A review. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2012, 12, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.-Y.; Ye, Z.-C. China Statistics Abstract 2018; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Song, Y. Analysis on the development status of cotton production efficiency in Xinjiang. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2017, 45, 1020–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, S.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Guo, Z.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, G.; Wu, J. Effects of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria on the growth of maize seedling and bacterial community structure and phosphorus fractions in rhizosphere soil. China Soil Fertil. 2024; 80–88. [Google Scholar]
- Dejene, M.; Abera, G.; Desalegn, T. The effect of phosphorus fertilizer sources and lime on acidic soil properties of mollic rhodic nitisol in Welmera District, Central Ethiopia. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2023, 2023, 7002816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Ci, B.; Lu, X.; Feng, X.; Wen, S.; Ma, F. Effect of different NPK fertilization timing sequences management on soil-petiole system nutrient uptake and fertilizer utilization efficiency of drip irrigation cotton. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Huang, Y.; Nie, Q.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, X.; Guo, P.; Luo, P. Spatiotemporal variations and risk characteristics of potential non-point source pollution driven by LUCC in the loess plateau region, China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1253328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, M.; Whelan, M. Phosphorus activators contribute to legacy phosphorus availability in agricultural soils: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 522–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, P.; Das, S.; Shankhdhar, D.; Shankhdhar, S.C. Phosphate-Solubilizing Microorganisms: Mechanism and Their Role in Phosphate Solubilization and Uptake. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 21, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Rekha, P.D.; Arun, A.B.; Shen, F.T.; Lai, W.A.; Young, C.C. Phosphate solubilizing bacteria from subtropical soil and their tricalcium phosphate solubilizing abilities. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2006, 34, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, T.; Mao, Y.; Wang, F.; Yu, J.; Zhu, C. Current situation of agricultural non-point source pollution and its control. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2023, 234, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alori, E.T.; Glick, B.R.; Babalola, O.O. Microbial Phosphorus Solubilization and Its Potential for Use in Sustainable Agriculture. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ge, F.; Li, F.; Zhang, D.; Deng, S.; Tian, J. Intracellular Metabolomics Switching Alters Extracellular Acid Production and Insoluble Phosphate Solubilization Behavior in Penicillium oxalicum. Metabolites. 2020, 10, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.N. Plant Microbiomes for Sustainable Agriculture: Current Research and Future Challenges. In Plant Microbiomes for Sustainable Agriculture; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 25, pp. 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, M.; Ali, M.; Shahzad, K.; Ahmad, F.; Ikram, R.M.; Ishtiaq, M.; Alaraidh, I.A.; Al-hashimi, A.; Ali, H.M.; Zarei, T.; et al. Mitigation of Osmotic Stress in Cotton for the Improvement in Growth and Yield through Inoculation of Rhizobacteria and Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria Coated Diammonium Phosphate. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.; Hussain, M.B.; Zahir, Z.A.; Haq, T.U.; Matloob, A. Thermal Plasticity and Cotton Production Enhancing Attributes of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria from Cotton Rhizosphere. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 3885–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters-ScienceDirect. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.A.; Weber, R.P. Colorimetric Estimation Of Indoleacetic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1951, 26, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, B. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, Chian, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ranawat, B.; Bachani, P.; Singh, A.; Mishra, S. Enterobacter hormaechei as Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria for Improvement in Lycopersicum esculentum. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Cruz, N.D.; Meza-Contreras, J.C.; Escalante, F.M.E.; Macías-Rodríguez, M.E.; Salcedo-Perez, E.; González-García, Y. Phosphate Solubilization and Indole-Like Compounds Production by Bacteria Isolated From Forest Soil with Plant Growth Promoting Activity on Pine Seedlings. Geomicrobiol. J. 2020, 37, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.J.; Zhang, J.K.; Hou, R.N.; Jing, Z.Q.; Sun, Q.; Zhu, X.; Fu, L.X.; Zhang, F.Y.; Ren, H.L.; Guo, Z.J. In vitro screening of native rhizobacteria and selection of Bacillus atrophaeus for the biocontrol of pepper root rot in the Gansu Province, China. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2023, 48, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaylar, B.; Güllüce, M.; Karadayi, M.; Isaoglu, M. Rapid Detection of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria from Agricultural Areas in Erzurum. Curr. Microbiol. 2019, 76, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, M.; Yasmin, S.; Yahya, M.; Breitkreuz, C.; Tarkka, M.; Reitz, T. The wheat growth-promoting traits of Ochrobactrum and Pantoea species, responsible for solubilization of different P sources, are ensured by genes encoding enzymes of multiple P-releasing pathways. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 246, 126703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Zineb, A.; Trabelsi, D.; Ayachi, I.; Barhoumi, F.; Aroca, R.; Mhamdi, R. Inoculation with Elite Strains of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Enhances the Effectiveness of Fertilization with Rock Phosphates. Geomicrobiol. J. 2020, 37, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sheng, K.; Zheng, Q.; Hu, D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W. Inoculation with phosphate-solubilizing bacteria alters microbial community and activates soil phosphorus supply to promote maize growth. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Xie, J.; Xue, X.; Jiang, Y. Screening of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and their abilities of phosphorus solubilization and wheat growth promotion. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, O.S.; Fernandes, A.S.; Tupy, S.; Ferreira, T.G.; Almeida, L.N.; Creevey, C.J.; Santana, M.F. Insights into Plant Interactions and the Biogeochemical Role of the Globally Widespread Acidobacteriota Phylum. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Li, K.X.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Zhang, F.L.; Wang, F.H.; Sun, R.B. The impact of Verticillium wilt on community composition and assembly of cotton root endotrophic bacteria. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2024, 32, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Li, R.; Xiong, W.; Shen, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, B.; Ruan, Y.; Geisen, S.; Shen, Q.; Kowalchuk, G.A. Bio-organic fertilizers stimulate indigenous soil Pseudomonas populations to enhance plant disease suppression. Microbiome 2020, 8, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Song, Y.; An, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhong, G. Soil Microorganisms: Their Role in Enhancing Crop Nutrition and Health. Diversity 2024, 16, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, M.; Sahoo, R.K.; Pradhan, C.; Tuteja, N.; Mohanty, S. Contribution of native phosphorous-solubilizing bacteria of acid soils on phosphorous acquisition in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Protoplasma Int. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 254, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, I.; Fahsi, N.; Hafidi, M.; Benjelloun, S.; Allaoui, A.; Biskri, L. Rhizospheric Phosphate Solubilizing Bacillus atrophaeus GQJK17 S8 Increases Quinoa Seedling, Withstands Heavy Metals, and Mitigates Salt Stress. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, M.; Bushra; Hussain, A.; Mumtaz, M.Z.; Najm-ul-Seher; Abbasi, G.H.; Nazli, F.; Pataczek, L.; Ali, H.M. Mineral-Solubilizing Bacteria-Mediated Enzymatic Regulation and Nutrient Acquisition Benefit Cotton’s (Gossypium hirsutum L.) Vegetative and Reproductive Growth. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

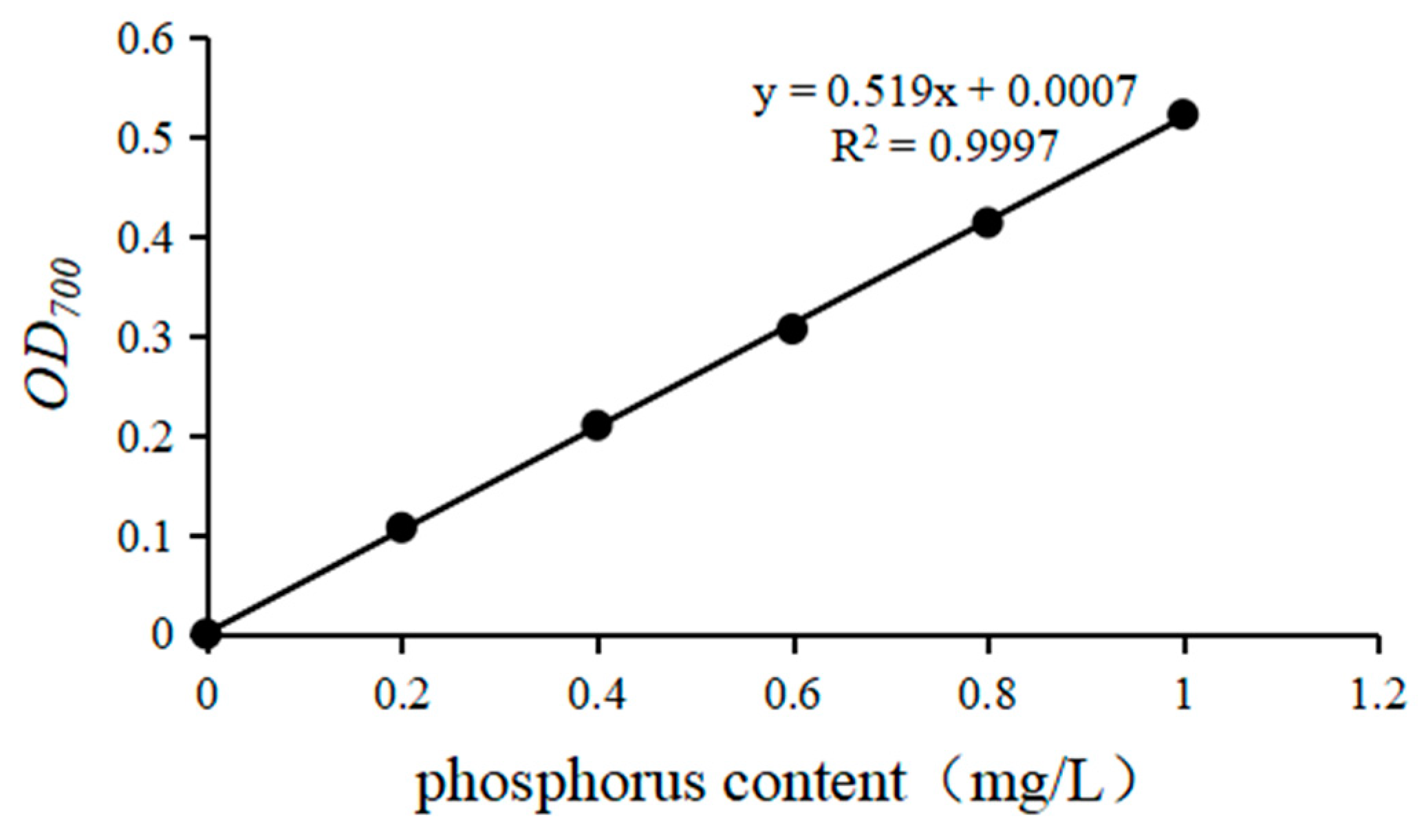
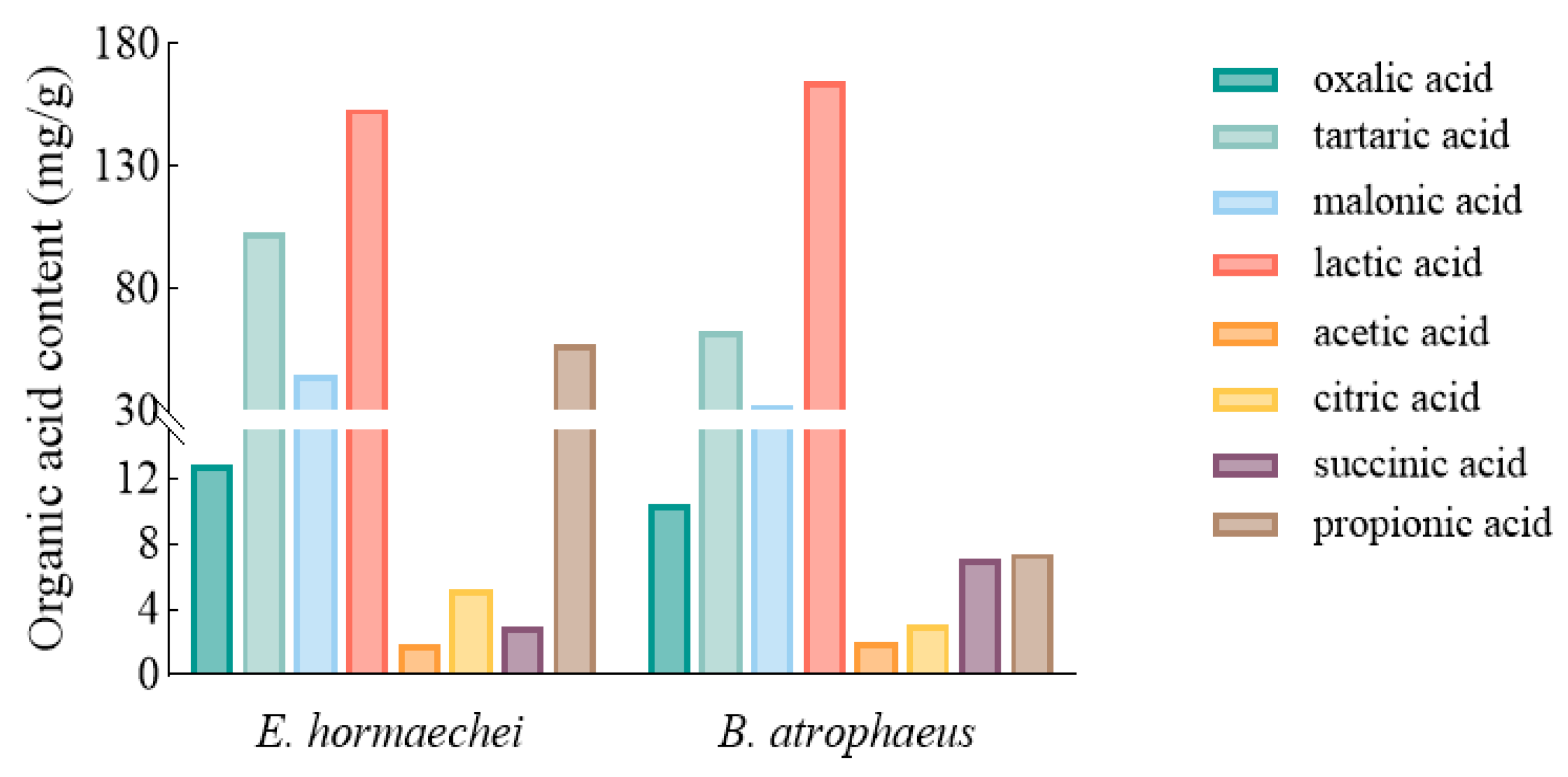
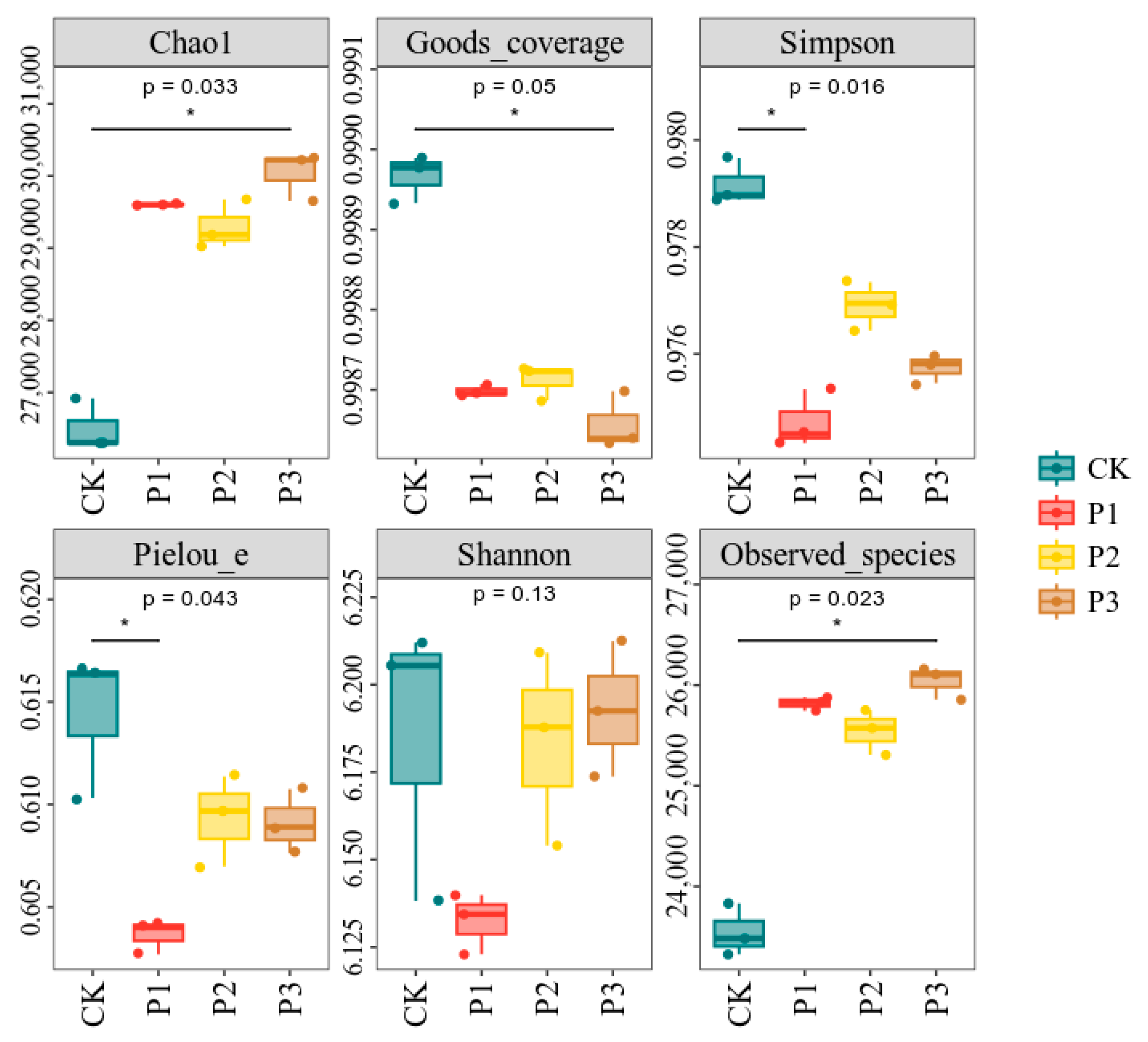
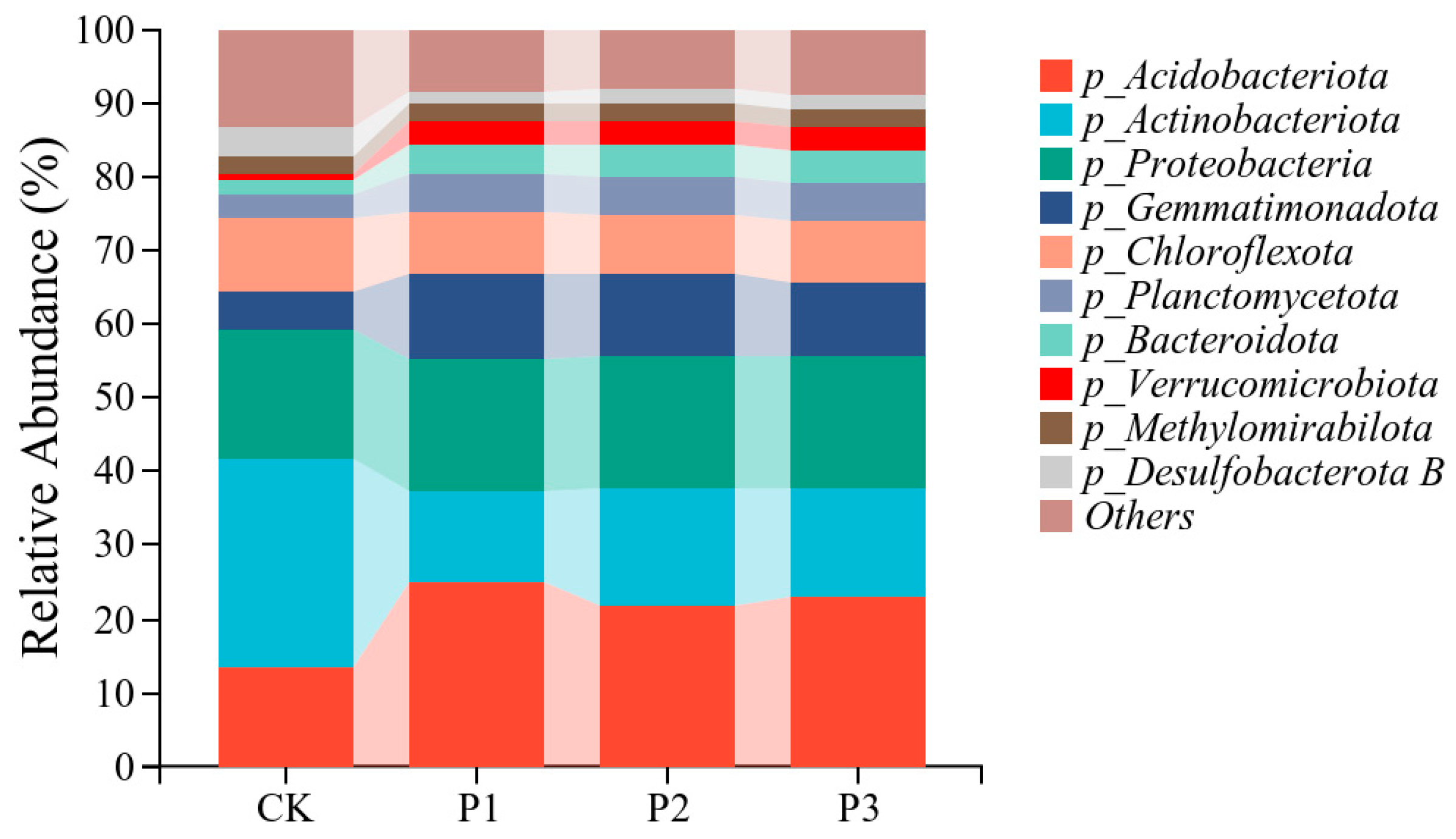
| Strain | Soluble Phosphorus Content (mg·L−1) | Indoleacetic Acid Content (ng·mL−1) | Acid Phosphatase Activity (μmol·min−1·mL−1) | Phytase Activity (μmol·min−1·mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. hormaechei | 294 ± 8.50 a | 359 ± 0.89 a | 0.293 ± 0.002 a | 0.289 ± 0.0012 a |
| B. atrophaeus | 231 ± 4.25 b | 215 ± 0.59 b | 0.230 ± 0.001 b | 0.262 ± 0.0004 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Sun, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, Z.; Fan, H.; Pan, X.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, K.; Yang, L. The Effect of Selected Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on the Growth of Cotton Plants in Salinized Farmlands. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051075
Wang T, Sun Y, Huang H, Li Z, Fan H, Pan X, Wang Y, Cao Y, Wang K, Yang L. The Effect of Selected Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on the Growth of Cotton Plants in Salinized Farmlands. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(5):1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051075
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tong, Yan Sun, Hong Huang, Ziwei Li, Hua Fan, Xudong Pan, Yiwen Wang, Yuxin Cao, Kaiyong Wang, and Le Yang. 2025. "The Effect of Selected Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on the Growth of Cotton Plants in Salinized Farmlands" Microorganisms 13, no. 5: 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051075
APA StyleWang, T., Sun, Y., Huang, H., Li, Z., Fan, H., Pan, X., Wang, Y., Cao, Y., Wang, K., & Yang, L. (2025). The Effect of Selected Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on the Growth of Cotton Plants in Salinized Farmlands. Microorganisms, 13(5), 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051075






