The Effects of Polymer–Nitrogen Fertilizer on Biomes in Drip-Irrigated Wheat Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Sampling
2.4. Measurements
2.4.1. High-Throughput Sequencing
2.4.2. Metabolome Measurement
2.4.3. Measurement of Soil Enzyme Activity
2.4.4. Measurement of Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon and Nitrogen
2.4.5. Measurement of Soil Aggregates
2.4.6. Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
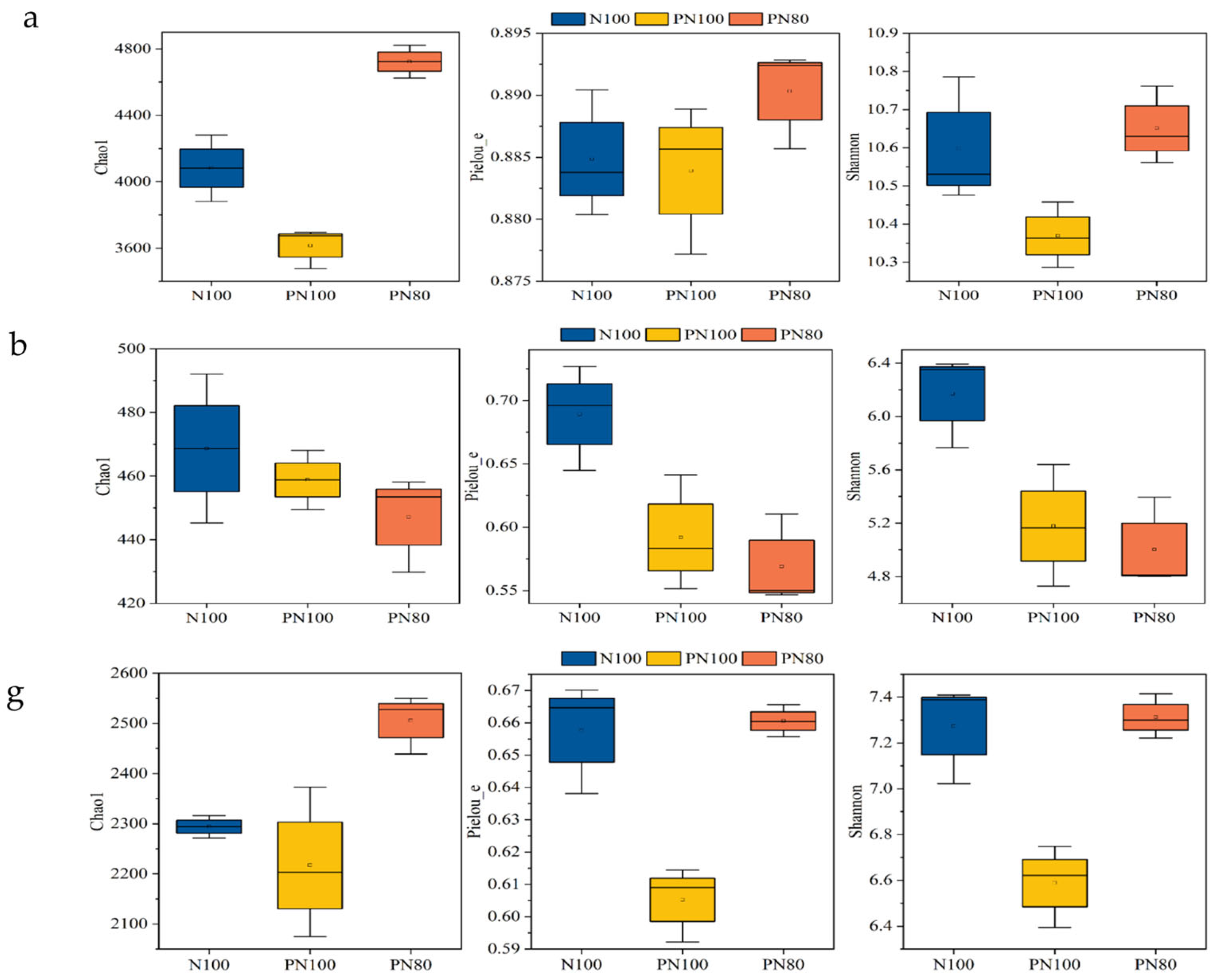
3.1. Effects of Combined Application of PPM and Nitrogen Fertilizer on the α-Diversity Indices of Soil Biocommunity
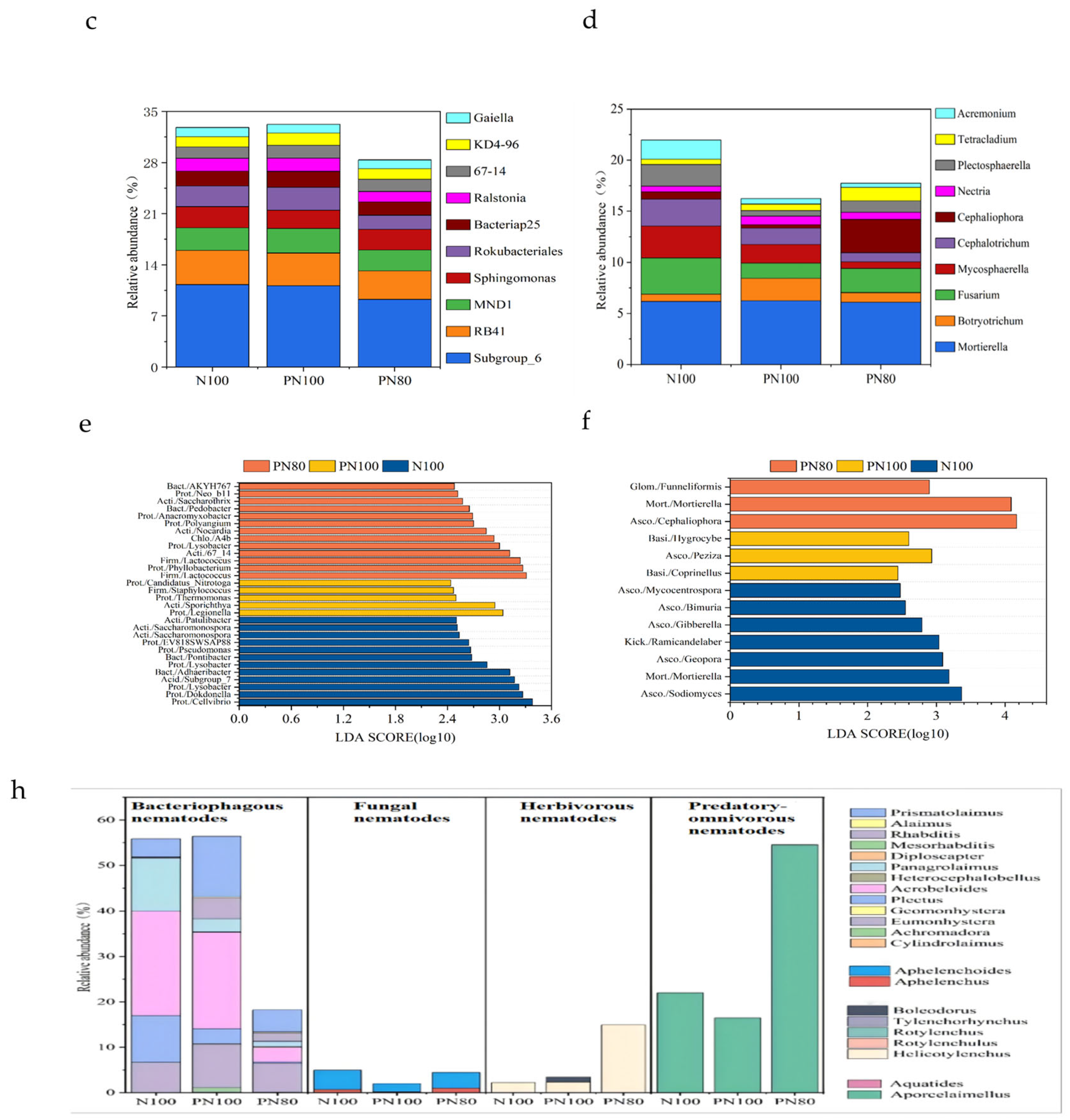
3.2. Effects of Combined Application of PPM and Nitrogen Fertilizer on the Soil Biocommunity Structure and Abundance
3.3. Analysis of Differential Abundance of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities
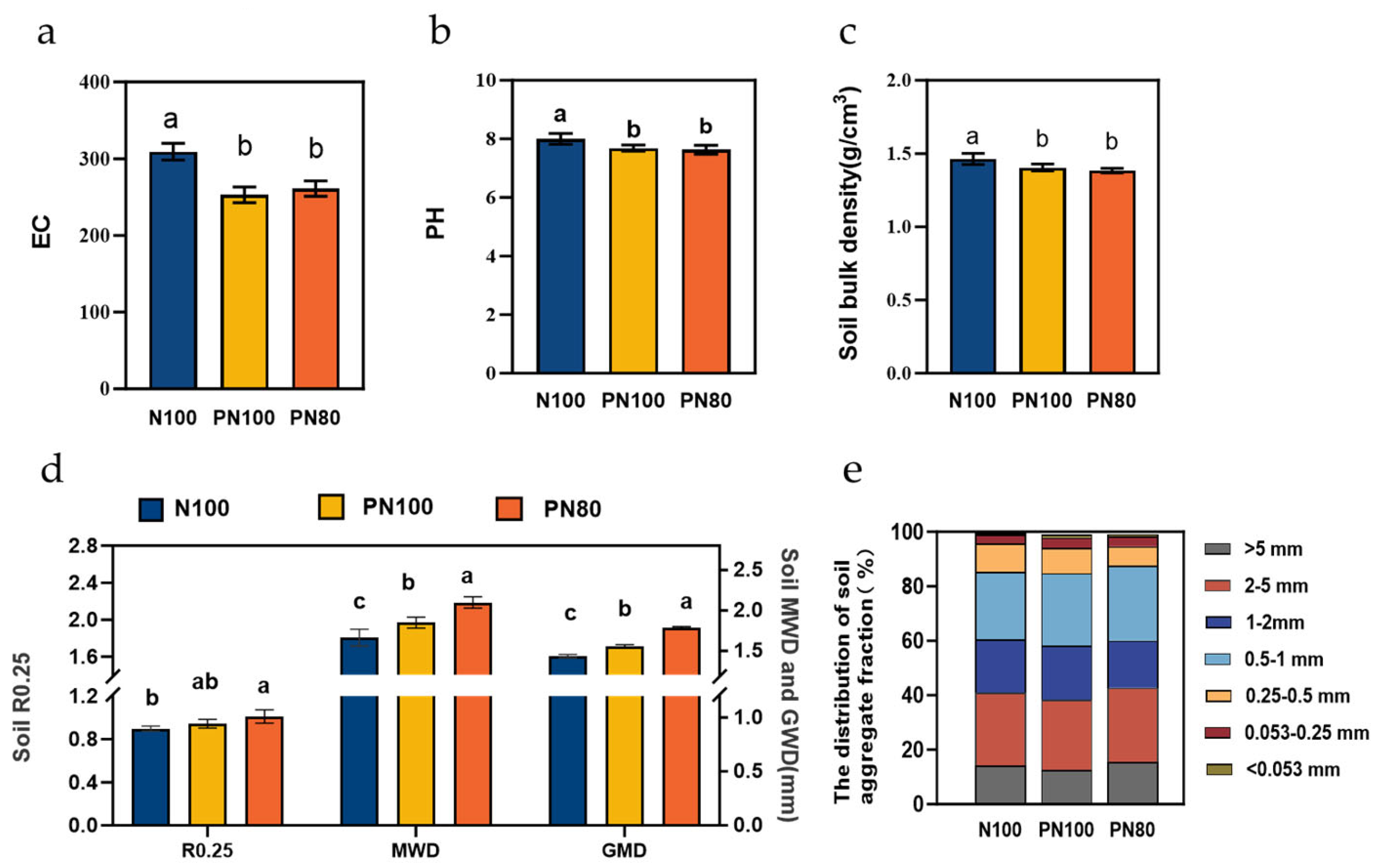
3.4. Effects of Combined Application of Polymer and Nitrogen Fertilizer on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Enzyme Activities
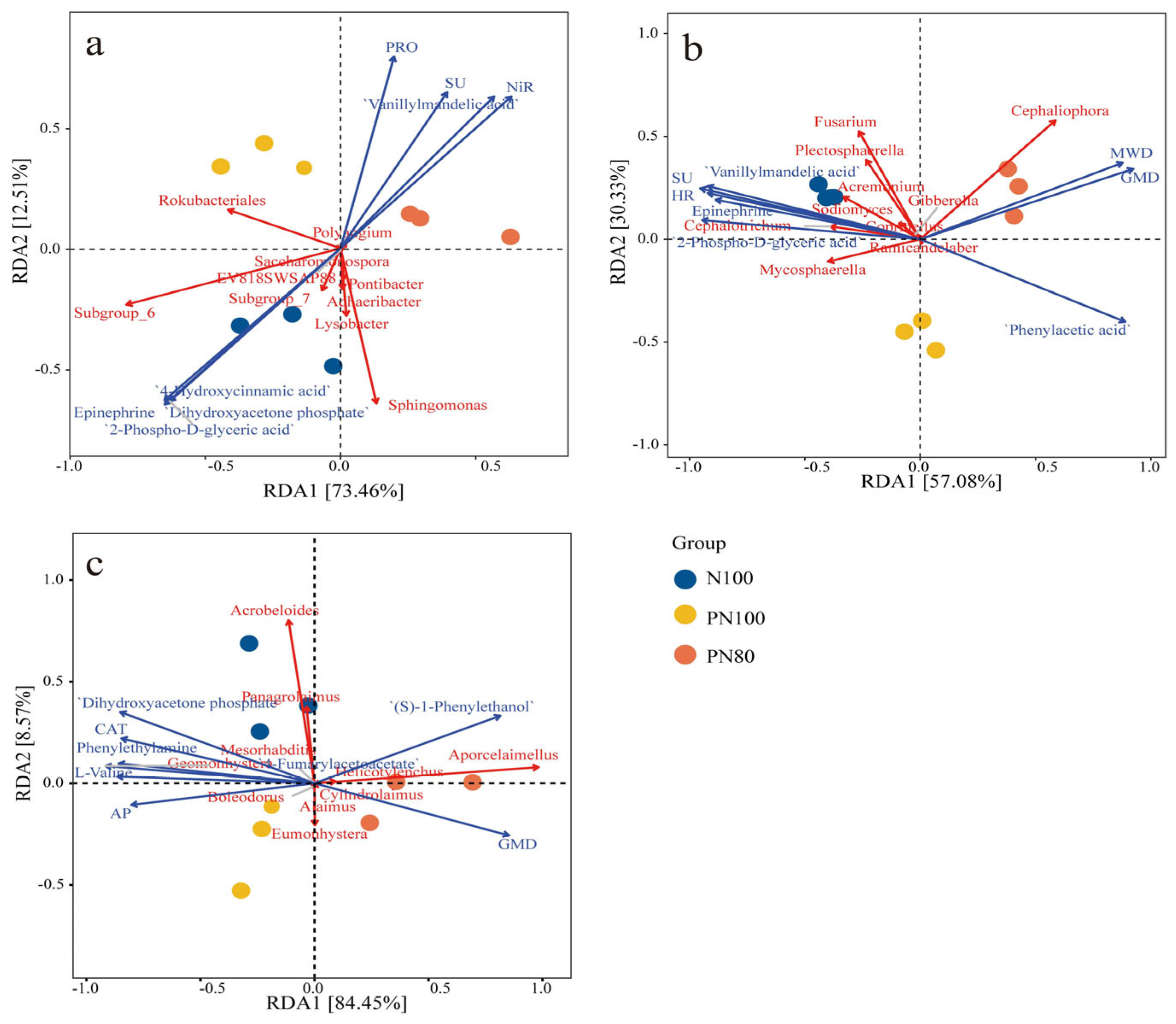
3.5. RDA of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Biocommunities
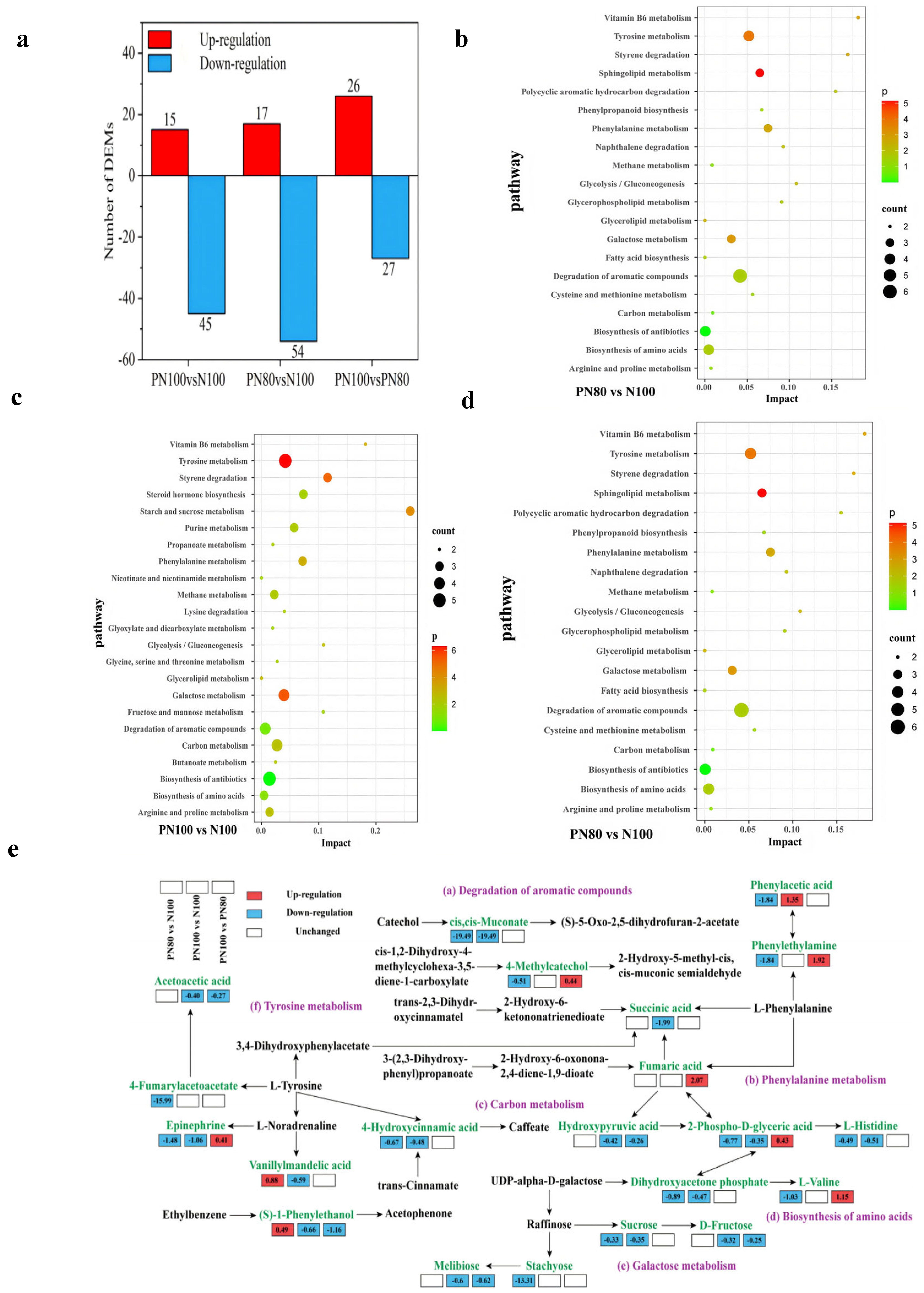
3.6. Soil Metabolome Characteristics and Pathway Analysis
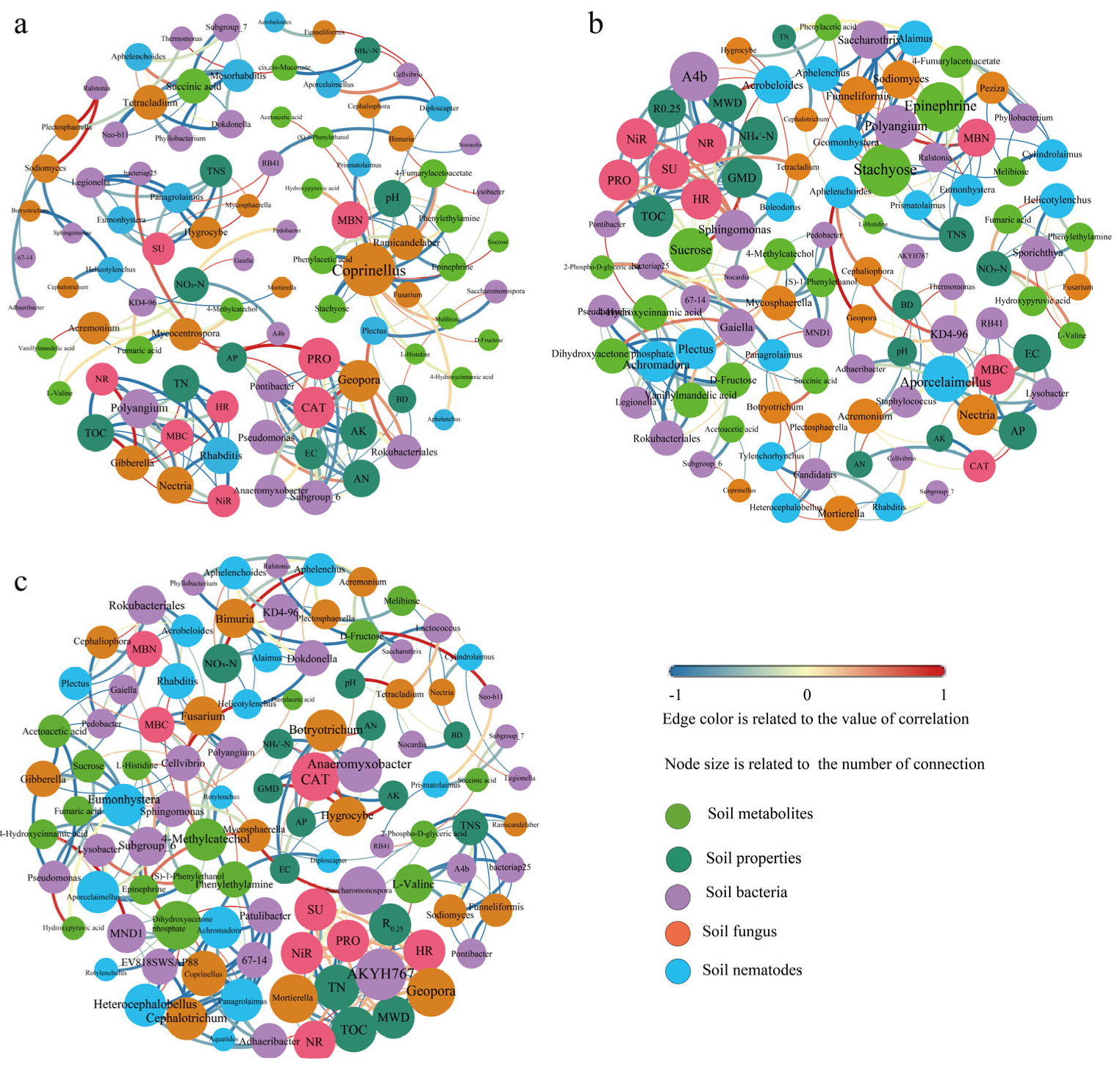
3.7. Correlation Network Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Xiao, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Jiang, Y.; Yao, M.; Li, X. The effect of phosphorus content on wheat root-associated prokaryotic community depends on growth stage and variety. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2024, 88, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Z.R.; Xu, Y.; Virk, A.L.; Liu, M.; Pei, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, C. Organic fertilizer substitution benefits microbial richness and wheat yield under warming. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 174007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, B.; Ma, M.; Guan, D.; Qin, J. Thirty four years of nitrogen fertilization decreases fungal diversity and alters fungal community composition in black soil in northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 95, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebber, D.P.; Richards, V.R. A meta-analysis of the effect of organic and mineral fertilizers on soil microbial diversity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 175, 104450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, W.; Zhao, J.; Xue, C.; Zhang, G.; Ran, W.; Wang, B.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R. Significant alteration of soil bacterial communities and organic carbon decomposition by different long-term fertilization management conditions of extremely low-productivity arable soil in South China. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1907–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Shen, C. Soil microbiome response to reduced nitrogen supply in an over-fertilized wheat-maize system. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.J.; Feng, Q.; Wei, Y.P.; Li, C.S.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, B.G. Effects of saline water irrigation and fertilization regimes on soil microbial metabolic activity. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Wu, H.; Bei, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Effect of different fertilization practices on soil microbial community in a wheat–maize rotation system. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olfs, H.W.; Blankenau, K.; Brentrup, F.; Jasper, J.; Link, A.; Lammel, J. Soil-and plant-based nitrogen-fertilizer recommendations in arable farming. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2005, 168, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, X.; Feng, S.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Yu, Z.; Bian, W.; Sun, D.; et al. Optimization of controlled-release urea application based on the winter wheat yield. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 151, 126987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Peng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhuge, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H. Effect of bag-controlled release fertilizer on nitrogen loss, greenhouse gas emissions, and nitrogen applied amount in peach production. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Chang, D.; Shao, C.; Cui, W.; Lu, X.; Dong, W.; Liu, Y. Effects of polymer conditioner and nitrogen fertilizer application on nitrogen absorption and utilization of drip-irrigated wheat in arid areas. Agronomy 2024, 14, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Yin, J.; Eeswaran, R.; Gunaratnam, A.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H. Interacting effects of water and compound fertilizer on the resource use efficiencies and fruit yield of drip-fertigated Chinese wolfberry (Lycium barbarum L.). Technol. Hortic. 2024, 4, e019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Fan, H.; Wang, J.; An, M. Effects of polymer materials on soil physicochemical properties and bacterial community structure under drip irrigation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 150, 103456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, L.; Hartmann, M.; Engbersen, N.; Six, J.; Schöb, C. Positive effects of crop diversity on productivity driven by changes in soil microbial composition. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 660749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.B.; Roley, S.S.; Duncan, D.S.; Guo, J.; Quensen, J.F.; Yu, H.Q.; Tiedje, J.M. Long-term excess nitrogen fertilizer increases sensitivity of soil microbial community to seasonal change revealed by ecological network and metagenome analyses. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 108349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Yin, Y.; Tong, Q.; Gong, Z.; Shi, Y. Multi-omics analysis of excessive nitrogen fertilizer application: Assessing environmental damage and solutions in potato farming. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 284, 116916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, Y.M.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S.; Kuzyakov, Y. Effects of biochar and polyacrylamide on decomposition of soil organic matter and C-labeled alfalfa residues. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Gai, S.; Tang, C.; Jin, Y.; Cheng, K.; Antonietti, M.; Yang, F. Artificial humic acid improves maize growth and soil phosphorus utilization efficiency. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 179, 104587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Wang, K.; Fan, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. Effects of polymer materials on the transformation and utilization of soil nitrogen and yield of wheat under drip irrigation. Soil Use Manag. 2021, 37, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianfeng, L.; Lili, S.; Yunjian, H.; Guiling, Z.; Peihong, D. Quality Characters of Wheat Varieties in Spring Series: Analysis and Evaluation. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2021, 37, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- An, M.; Chang, D.; Hong, D.; Fan, H.; Wang, K. Metabolic regulation in soil microbial succession and niche differentiation by the polymer amendment under cadmium stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, H.; Zhen, L.; Jian, Z. Improvement of indophenol blue colorimetric method on activity of urease in soil. J. Civ. Archit. Environ. Eng. 2012, 34, 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, K.; Hayano, K. Seasonal variation of soil protease activities and their relation to proteolytic bacteria and Bacillus spp in paddy field soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1995, 27, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankeberger, W.T.; Johanson, J.B. Method of measuring invertase activity in soils. Plant Soil 1983, 74, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmagid, H.M.; Tabatabai, M.A. Nitrate reductase activity of soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Liu, W.; Zhu, L.; Yan, X. Different forms and proportions of exogenous nitrogen promote the growth of alfalfa by increasing soil enzyme activity. Plants 2022, 11, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Gawad, A.M.; Morsy, A.S.M. Integrated impact of organic and inorganic fertilizers on growth, yield of maize (Zea mays L.) and soil properties under Upper Egypt conditions. J. Plant Prod. 2017, 8, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okalebo, J.R.; Gathua, K.W.; Woomer, P.L. Laboratory Methods of Soil and Plant Analysis: A Working Manual Second Edition; Sacred Africa: Nairobi, Kenya, 2002; Volume 21, pp. 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mazurak, A.P. Effect of gaseous phase on water-stable synthetic aggregates. Soil Sci. 1950, 69, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, E. Aggregate structure and carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in native and cultivated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.J.; Wang, X.; Li, S.P.; Liu, X.T.; Liu, Z.P.; Lu, J.J.; Wu, X.P.; Xi, J.L.; Zhang, J.C.; Li, Y.S. Synergistic effects of soil moisture, aggregate stability and organic carbon distribution on wheat yield under no-tillage practice. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2021, 54, 596–607. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis 2021, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, Z.P.; Chen, B.L.; Jiang, P.A.; Sheng, J.D.; Liu, M.; Shen, X.; Ding, K. Parameters of fertilization effect on “Korla Fragrant Pear” tree. J. Fruit Sci. 2014, 31, 423–429. [Google Scholar]
- Wang Chao, W.C.; Liu DongWei, L.D.; Bai, E. Decreasing soil microbial diversity is associated with decreasing microbial biomass under nitrogen addition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, J.Z.; Liu, Y.R.; Zheng, Y.M. Effects of super absorbent polymers on soil microbial properties and Chinese cabbage (Brassica chinensis) growth. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Jackson, R.B. The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Tong, C.; Hu, K.; Zhou, B.; Xing, S.; Mao, Y. Biochar-fertilizer interaction modifies N-sorption, enzyme activities and microbial functional abundance regulating nitrogen retention in rhizosphere soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 140065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunihiro, M.; Ozeki, Y.; Nogi, Y.; Hamamura, N.; Kanaly, R.A. Benz [a] anthracene biotransformation and production of ring fission products by Sphingobium sp. strain KK22. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 4410–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, F.; Meng, Q.; Wang, Q.; Luo, S.; Chen, B.; Khan, K.Y.; Yang, X.; Feng, Y. Endophytic bacterium Sphingomonas SaMR12 promotes cadmium accumulation by increasing glutathione biosynthesis in Sedum alfredii Hance. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Nie, M. Enzymic moderations of bacterial and fungal communities on short-and long-term warming impacts on soil organic carbon. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Yang, L.; He, Q.P.; Xu, Y.L.; Zhu, Y.T.; Mi, Y.L.; Zhou, L.; Yang, S.-Z.; Gu, J.-D.; Mu, B.-Z. Gelling and reducing agents are potential carbon and energy sources in culturing of anaerobic microorganisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2025, 91, e0227624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatt, C.G.; Liu, Z.; Ludwig, M.; Kühl, M.; Jensen, S.I.; Bryant, D.A.; Ward, D.M. Temporal metatranscriptomic patterning in phototrophic Chloroflexi inhabiting a microbial mat in a geothermal spring. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podosokorskaya, O.A.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A.; Novikov, A.A.; Kolganova, T.V.; Kublanov, I.V. Ornatilinea apprima gen. nov., sp. nov., a cellulolytic representative of the class Anaerolineae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63 Pt 1, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holatko, J.; Hammerschmiedt, T.; Mustafa, A.; Kintl, A.; Radziemska, M.; Baltazar, T.; Jaskulska, I.; Malicek, O.; Latal, O.; Brtnicky, M. Carbon-enriched organic amendments differently affect the soil chemical, biological properties and plant biomass in a cultivation time-dependent manner. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2022, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.P.; Li, J.H.; Qi, Y.H.; Guo, W.; Li, X.; Li, M.Q. Effects of naked barley root rot on rhizosphere soil microorganisms and enzyme activity. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 5640–5649. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Que, Y.; Yu, D.; Wang, H. The influence of rhizosphere soil fungal diversity and complex community structure on wheat root rot disease. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.J.; Huang, H.; Ma, Z.G.; Zeng, D.Z.; Fu, J.; Zeng, C.J. Illumina high-throughput sequencing reveals fungal community composition and diversity in root and rhizosphere soil of health and root-rot Panax notoginseng. Food Ferment. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed Zubi, W.S.; Mohd, M.H.; Mohamed Nor, N.M.I.; Zakaria, L. Fusarium species in mangrove soil in northern peninsular Malaysia and the soil physico-chemical properties. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, L.W.; Bryden, W.L. Fusarium: A ubiquitous fungus of global significance. Microbiol. Aust. 2012, 33, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherm, B.; Balmas, V.; Spanu, F.; Pani, G.; Delogu, G.; Pasquali, M.; Migheli, Q. Fusarium culmorum: Causal agent of foot and root rot and head blight on wheat. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 323–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergård, M. Nematode assemblages in the rhizosphere of spring barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) depended on fertilisation and plant growth phase. Pedobiologia 2004, 48, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, B.S. Microbial-feeding nematodes and protozoa in soil: Their effectson microbial activity and nitrogen mineralization in decomposition hotspots and the rhizosphere. Plant Soil 1994, 164, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lu, Y. Decomposition of soil polymeric organic matter by Bacteroidetes and Clostridia: Progress and perspectives. Microbiol. China 2022, 49, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Chomel, M.; Guittonny-Larchevêque, M.; Fernandez, C.; Gallet, C.; DesRochers, A.; Paré, D.; Jackson, B.G.; Baldy, V. Plant secondary metabolites: A key driver of litter decomposition and soil nutrient cycling. J. Ecol. 2016, 104, 1527–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homyak, P.M.; Slessarev, E.W.; Hagerty, S.; Greene, A.C.; Marchus, K.; Dowdy, K.; Iverson, S.; Schimel, J.P. Amino acids dominate diffusive nitrogen fluxes across soil depths in acidic tussock tundra. New Phytol. 2021, 231, 2162–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Luo, Y. N-induced shifts in tyrosine-derived metabolic networks regulate soil microbial C–N coupling. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 181, 109079. [Google Scholar]

| Treatment | Description |
|---|---|
| N100 | N fertilizer was applied at 300 kg·hm2 (traditional N application rate) |
| PN100 | 12 kg·hm2 of polymer PPM and 300 kg·hm2 of N fertilizer were applied |
| PN80 | 12 kg·hm2 of polymer PPM and 240 kg·hm2 of N fertilizer were applied |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Wei, C.; Zhang, S.; Fan, H.; Hong, D.; Huang, H.; Wang, K. The Effects of Polymer–Nitrogen Fertilizer on Biomes in Drip-Irrigated Wheat Soil. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061334
Sun Y, Wei C, Zhang S, Fan H, Hong D, Huang H, Wang K. The Effects of Polymer–Nitrogen Fertilizer on Biomes in Drip-Irrigated Wheat Soil. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061334
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yan, Chunying Wei, Shenglin Zhang, Hua Fan, Dashuang Hong, Hong Huang, and Kaiyong Wang. 2025. "The Effects of Polymer–Nitrogen Fertilizer on Biomes in Drip-Irrigated Wheat Soil" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061334
APA StyleSun, Y., Wei, C., Zhang, S., Fan, H., Hong, D., Huang, H., & Wang, K. (2025). The Effects of Polymer–Nitrogen Fertilizer on Biomes in Drip-Irrigated Wheat Soil. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061334






