Molecular Characterization, Antibiotic Resistance, and Biofilm Formation of Escherichia coli Isolated from Commercial Broilers from Four Chinese Provinces
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Bacterial Isolation and Primary Identification
2.3. Molecular Identification of E. coli
2.4. Molecular Identification of E. coli Serotypes and Virulence Genes
2.5. Antibiotic Susceptibility of E. coli Isolates
2.6. Biofilm Formation Assay of E. coli Isolates
2.7. Pathogenicity Assay of E. coli Isolates for Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) Strains
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
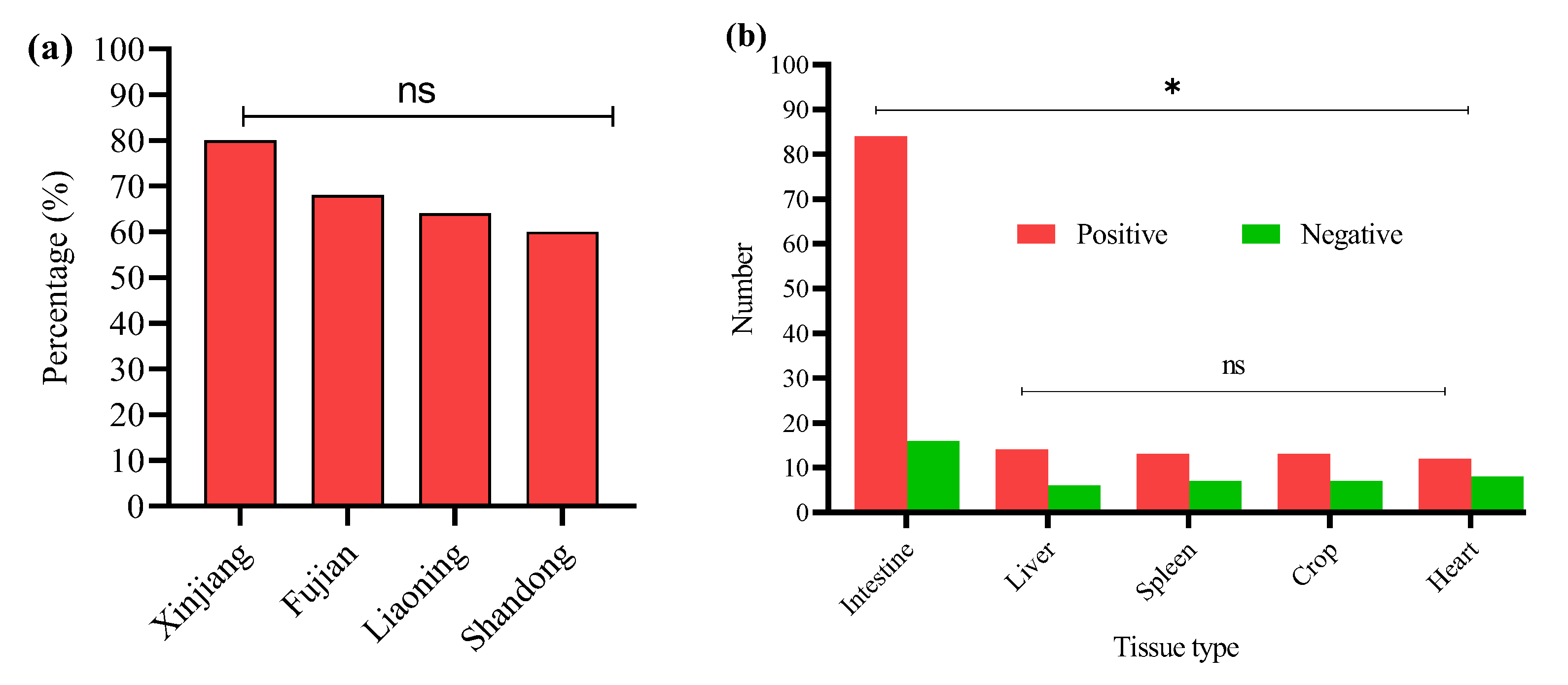
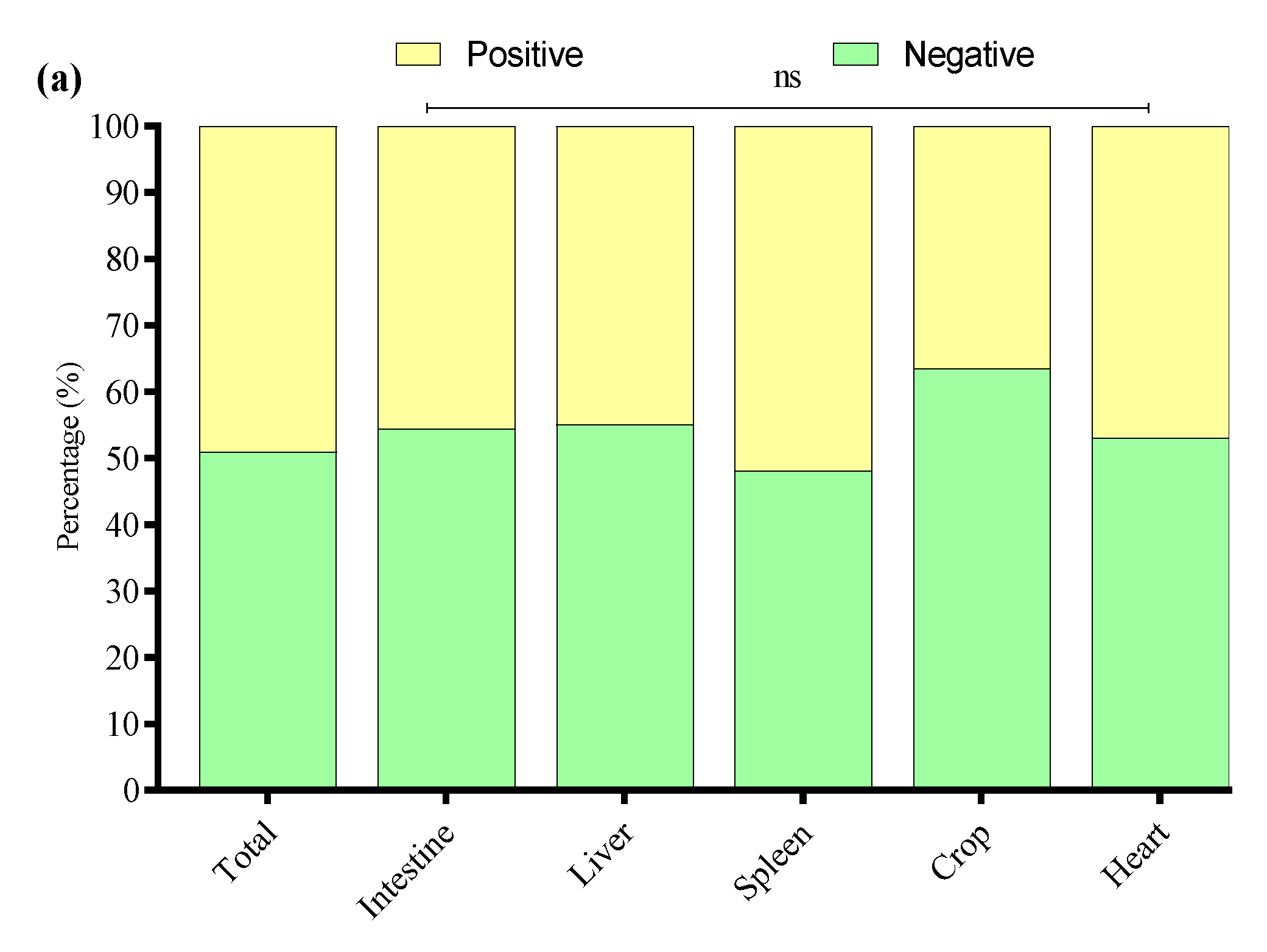
3.1. Detection of E. coli isolates
3.2. Detection of O-Serotypes in E. coli-Positive Samples
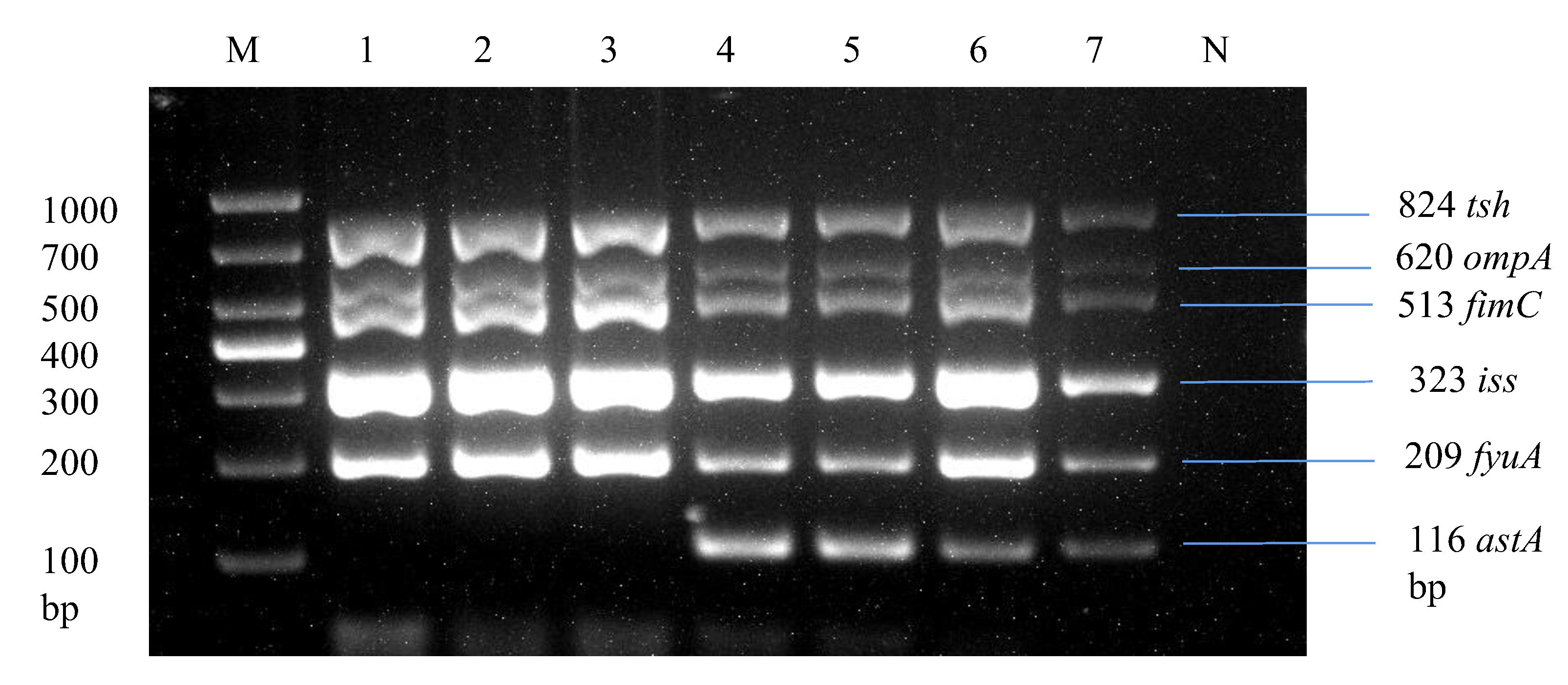
3.3. Detection Rate of Virulence Genes in Positive O-Serotype Samples
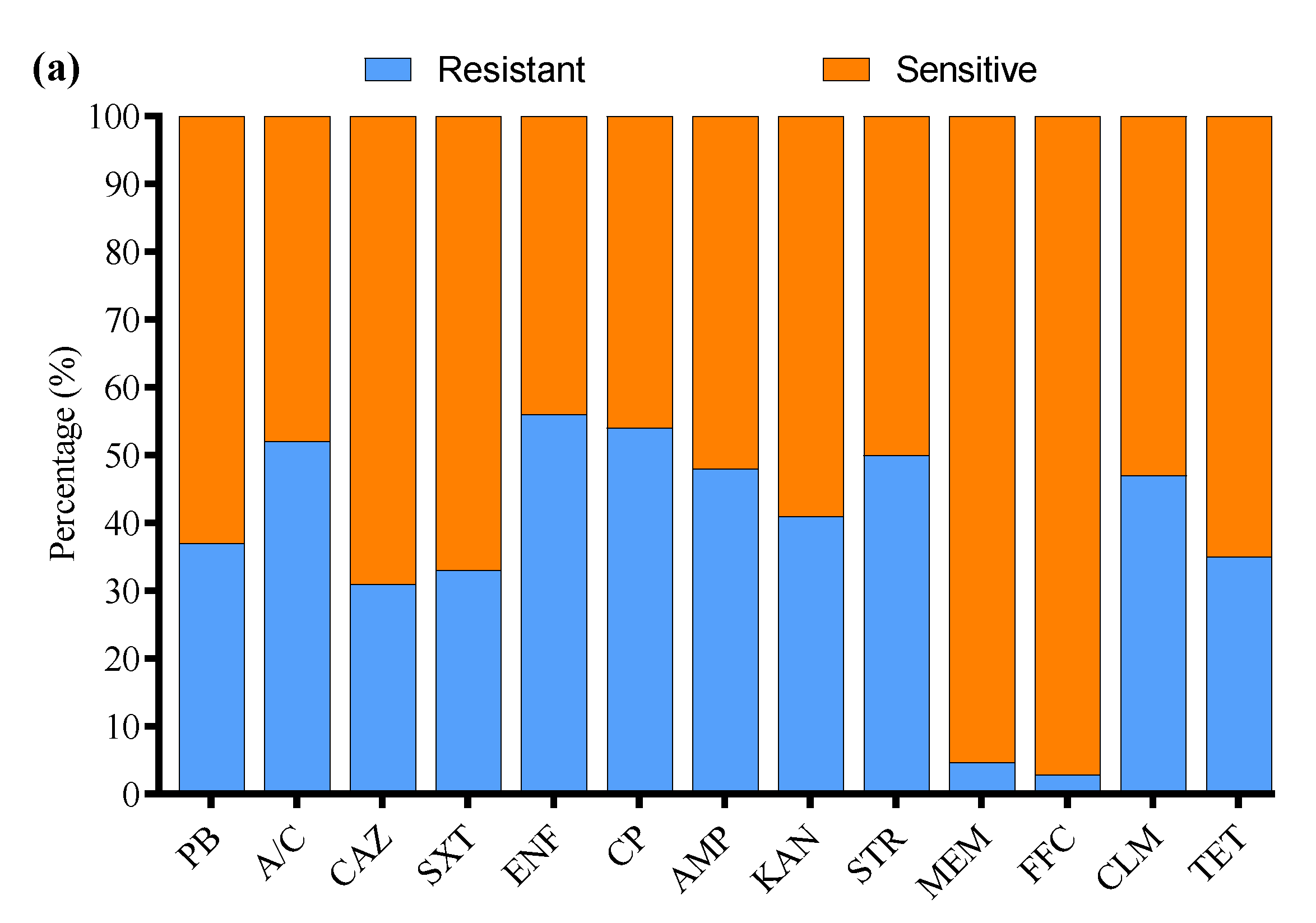
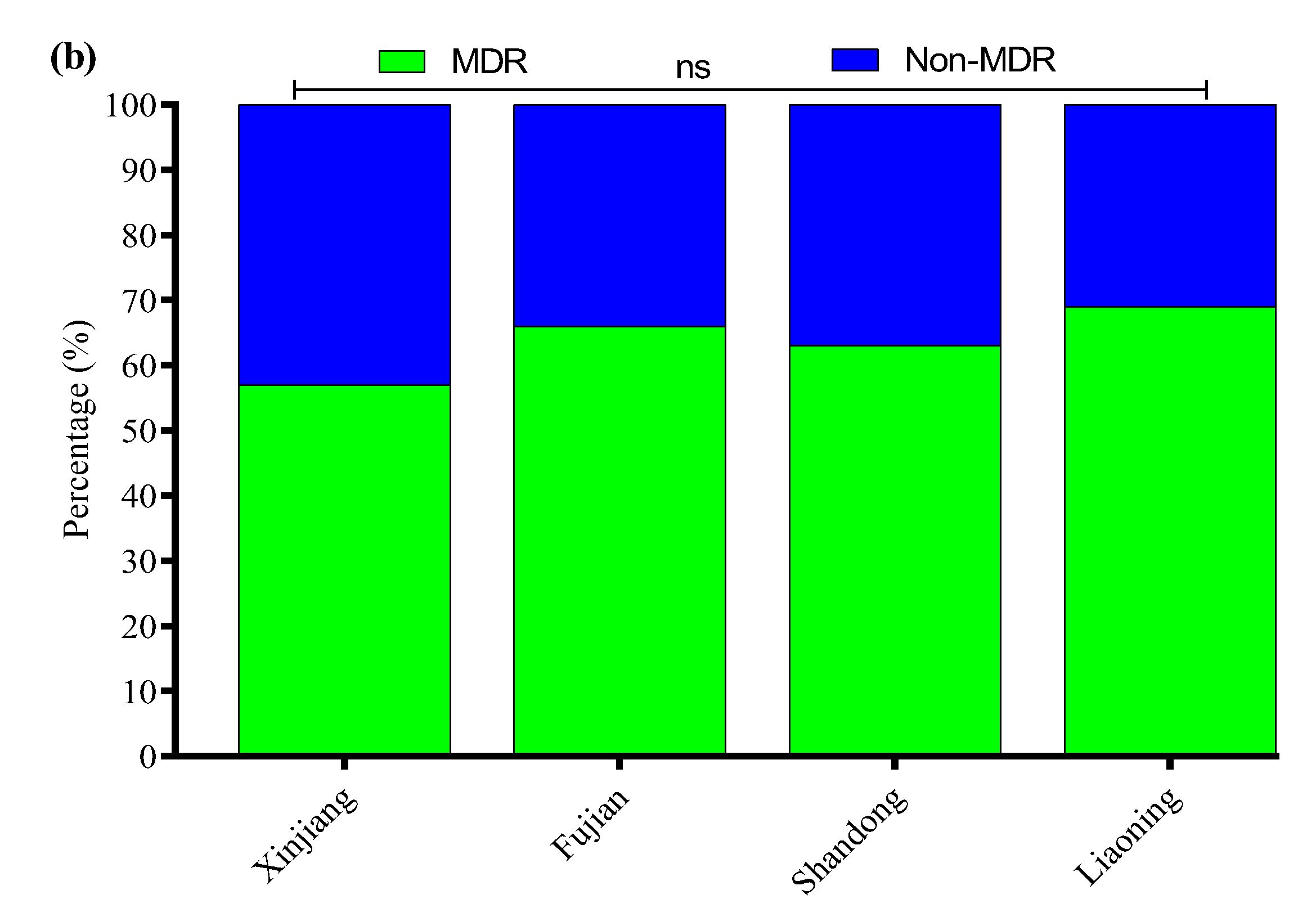
3.4. Antibiotic Susceptibility Profile
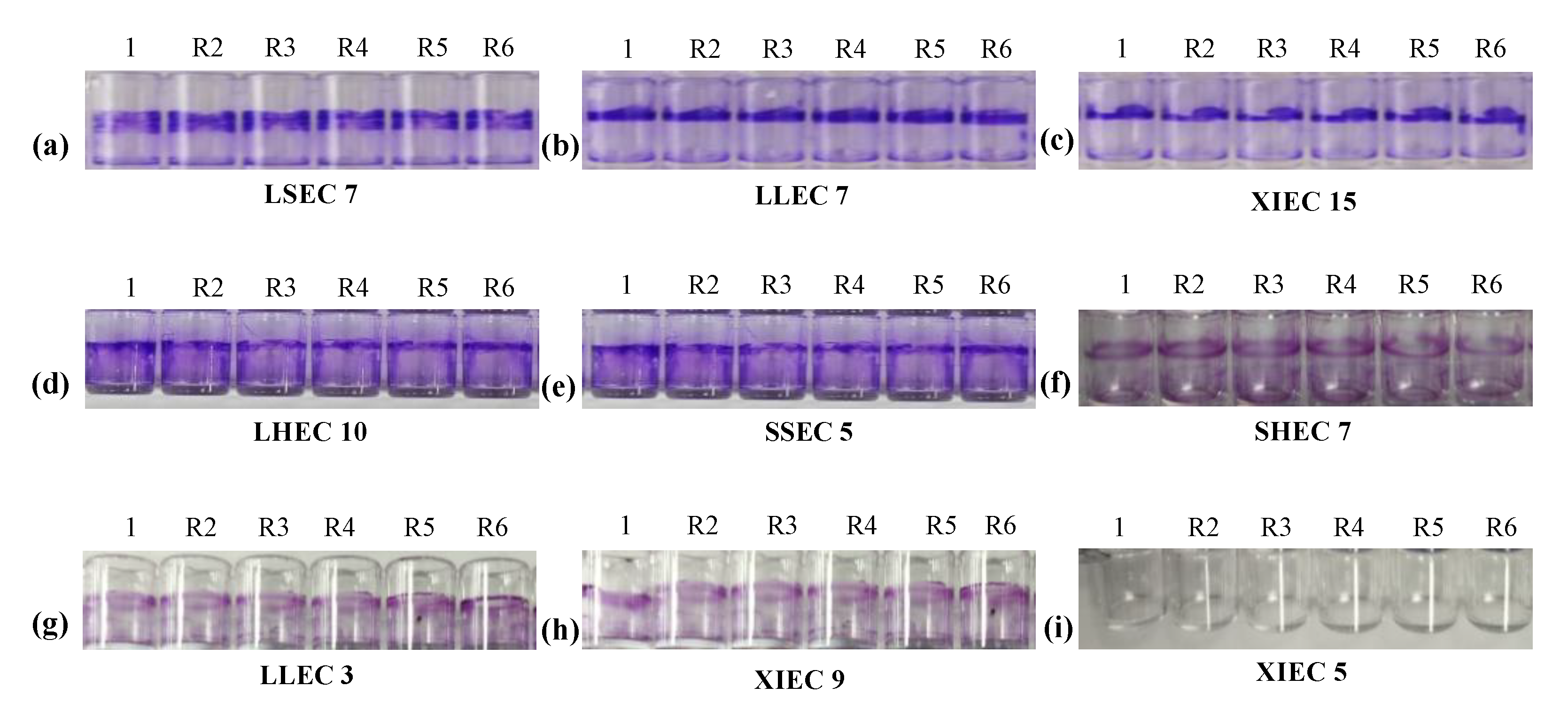
3.5. Biofilm Formation Ability
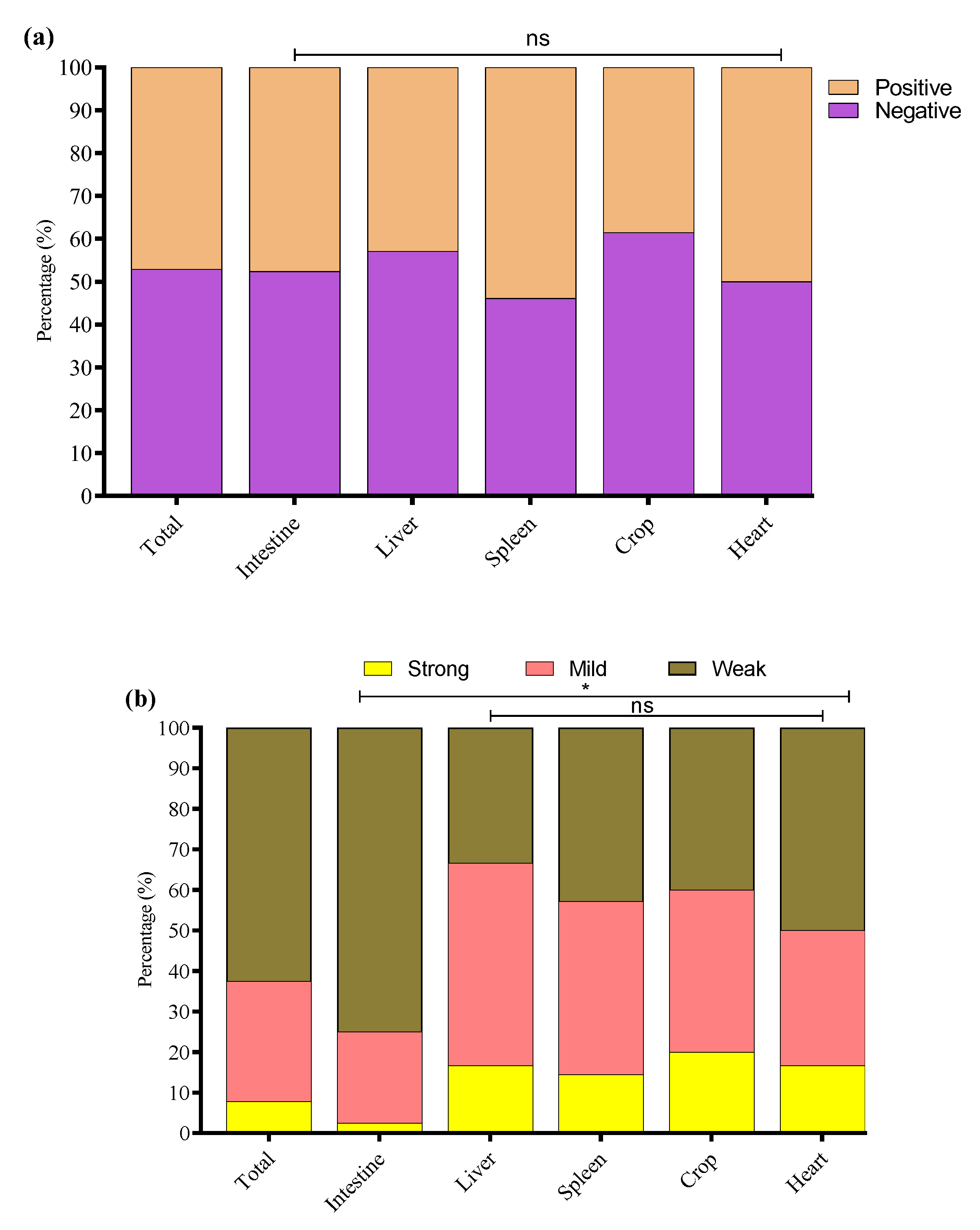
3.6. Detection of APEC Strains in E. coli Isolates
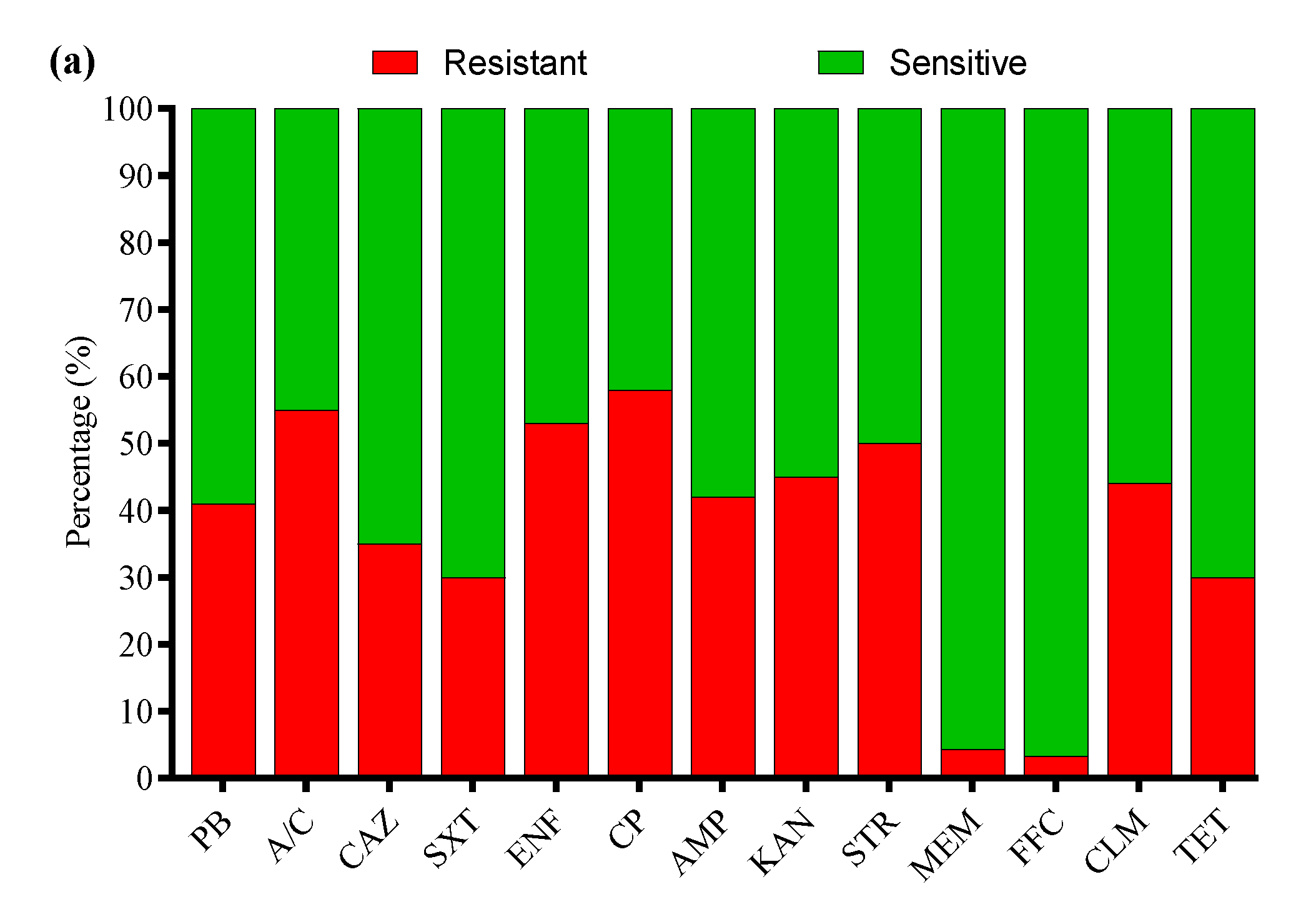
3.7. Antibiotic Susceptibility Profile of APEC Strains
3.8. Biofilm Formation of APEC Strains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PB | Polymyxin B |
| A/C | Amoxicillin/Clavulanate |
| CAZ | Ceftazidime |
| SXT | Sulfamethoxazole/Trimethoprim |
| ENF | Enrofloxacin |
| CP | Cefepime |
| AMP | Ampicillin |
| KAN | Kanamycin |
| STR | Streptomycin |
| MEM | Meropenem |
| FFC | Florfenicol |
| CLM | Clindamycin |
| TET | Tetracycline |
References
- Sannes, M.R.; Kuskowski, M.A.; Owens, K.; Gajewski, A.; Johnson, J.R. Virulence factor profiles and phylogenetic background of Escherichia coli isolates from veterans with bacteremia and uninfected control subjects. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 190, 2121–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathayat, D.; Lokesh, D.; Ranjit, S.; Rajashekara, G. Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC): An Overview of Virulence and Pathogenesis Factors, Zoonotic Potential, and Control Strategies. Pathogens 2021, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fancher, C.A.; Zhang, L.; Kiess, A.S.; Adhikari, P.A.; Dinh, T.T.N.; Sukumaran, A.T. Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli and Clostridium perfringens: Challenges in No Antibiotics Ever Broiler Production and Potential Solutions. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghunaim, H.; Abu-Madi, M.A.; Kariyawasam, S. Advances in vaccination against avian pathogenic Escherichia coli respiratory disease: Potentials and limitations. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 172, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellata, M. Human and avian extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli: Infections, zoonotic risks, and antibiotic resistance trends. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 916–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Wannemuehler, Y.; Kariyawasam, S.; Johnson, J.R.; Logue, C.M.; Nolan, L.K. Prevalence of avian-pathogenic Escherichia coli strain O1 genomic islands among extraintestinal and commensal E. coli isolates. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 2846–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Tang, M.; Awan, F.; Aqib, A.I.; Hao, R.; Ahmad, S.; Wang, S.; Shang, R.; Pu, W. Genomic Characterization of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL) Producing E. coli Harboring blaOXA−1-catB3-arr-3 Genes Isolated From Dairy Farm Environment in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2024, 17, 3526395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collingwood, C.; Kemmett, K.; Williams, N.; Wigley, P. Is the Concept of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli as a Single Pathotype Fundamentally Flawed? Front. Vet. Sci. 2014, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agunos, A.; Carson, C.; Léger, D. Antimicrobial therapy of selected diseases in turkeys, laying hens, and minor poultry species in Canada. Can. Vet. J. 2013, 54, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.M.; Barbieri, N.L.; de Oliveira, A.L.; Willis, D.; Nolan, L.K.; Logue, C.M. Characterizing avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) from colibacillosis cases, 2018. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Jiang, W.; Chen, Z.; Yin, H.; Huang, C.; Han, X. Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC): Current insights and future challenges. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; An, C.; Bao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jernigan, R.L.; Lithio, A.; Nettleton, D.; Li, L.; Wurtele, E.S.; Nolan, L.K.; et al. ArcA Controls Metabolism, Chemotaxis, and Motility Contributing to the Pathogenicity of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 3545–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarowska, J.; Futoma-Koloch, B.; Jama-Kmiecik, A.; Frej-Madrzak, M.; Ksiazczyk, M.; Bugla-Ploskonska, G.; Choroszy-Krol, I. Virulence factors, prevalence and potential transmission of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from different sources: Recent reports. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, N.L.; Vande Vorde, J.A.; Baker, A.R.; Horn, F.; Li, G.; Logue, C.M.; Nolan, L.K. FNR Regulates the Expression of Important Virulence Factors Contributing to the Pathogenicity of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Meng, Q.; Wang, S.; Han, X.; Han, Y.; Ding, C.; Dai, J.; Yu, S. Multiplex PCR assay for detection of virulence genes in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 2014, 54, 696–702. [Google Scholar]
- Shoaib, M.; Tang, M.; Aqib, A.I.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wen, Y.; Hou, X.; Xu, J.; Hao, R.; Wang, S.; et al. Dairy farm waste: A potential reservoir of diverse antibiotic resistance and virulence genes in aminoglycoside- and beta-lactam-resistant Escherichia coli in Gansu Province, China. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; He, Z.; Geng, X.; Tang, M.; Hao, R.; Wang, S.; Shang, R.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Pu, W. The emergence of multi-drug resistant and virulence gene carrying Escherichia coli strains in the dairy environment: A rising threat to the environment, animal, and public health. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1197579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballén, V.; Gabasa, Y.; Ratia, C.; Sánchez, M.; Soto, S. Correlation Between Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Determinants and Biofilm Formation Ability Among Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli Strains Isolated in Catalonia, Spain. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 803862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijavec, M.; Müller-Premru, M.; Zakotnik, B.; Žgur-Bertok, D. Virulence factors and biofilm production among Escherichia coli strains causing bacteraemia of urinary tract origin. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limoli, D.H.; Jones, C.J.; Wozniak, D.J. Bacterial Extracellular Polysaccharides in Biofilm Formation and Function. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Q.; Shoaib, M.; Chengye, W.; Zhu, Z.; Wei, X.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, J. The prevalent dynamic and genetic characterization of mcr-1 encoding multidrug resistant Escherichia coli strains recovered from poultry in Hebei, China. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 38, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, J.E.; Blanco, M.; Mora, A.; Jansen, W.H.; García, V.; Vázquez, M.L.; Blanco, J. Serotypes of Escherichia coli isolated from septicaemic chickens in Galicia (northwest Spain). Vet. Microbiol. 1998, 61, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Siek, K.E.; Giddings, C.W.; Doetkott, C.; Johnson, T.J.; Nolan, L.K. Characterizing the APEC pathotype. Vet. Res. 2005, 36, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knöbl, T.; Moreno, A.M.; Paixão, R.; Gomes, T.A.; Vieira, M.A.; da Silva Leite, D.; Blanco, J.E.; Ferreira, A.J. Prevalence of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) clone harboring sfa gene in Brazil. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 437342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Xie, F.; Wang, X.; Dai, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W. Epidemiological investigation and drug resistance analysis of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) of Wenchang chickens in Hainan, China. Avian Pathol. 2025. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Guo, G.; Hu, Z.; Miao, J.; Dong, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, X.; Han, X.; et al. O145 may be emerging as a predominant serogroup of Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 266, 109358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Meng, Q.; Dai, J.; Han, X.; Han, Y.; Ding, C.; Liu, H.; Yu, S. Development of an allele-specific PCR assay for simultaneous sero-typing of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli predominant O1, O2, O18 and O78 strains. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronco, T.; Stegger, M.; Olsen, R.H.; Sekse, C.; Nordstoga, A.B.; Pohjanvirta, T.; Lilje, B.; Lyhs, U.; Andersen, P.S.; Pedersen, K. Spread of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli ST117 O78:H4 in Nordic broiler production. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, M.P.; Schoeni, J.L. Isolation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from retail fresh meats and poultry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1987, 53, 2394–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, P.; Blanc, V.; Mora, A.; Dahbi, G.; Blanco, J.E.; Blanco, M.; López, C.; Andreu, A.; Navarro, F.; Alonso, M.P.; et al. Isolation and characterization of potentially pathogenic antimicrobial-resistant Escherichia coli strains from chicken and pig farms in Spain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2799–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, N.; Nakahigashi, K.; Baba, T.; Robert, M.; Soga, T.; Kanai, A.; Hirasawa, T.; Naba, M.; Hirai, K.; Hoque, A.; et al. Multiple high-throughput analyses monitor the response of E. coli to perturbations. Science 2007, 316, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.B.; Yoon, M.Y.; Ha, J.S.; Seo, K.W.; Noh, E.B.; Son, S.H.; Lee, Y.J. Molecular characterization of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli from broiler chickens with colibacillosis. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, A.L.; Newman, D.M.; Sato, Y.; Noel, A.; Rauk, B.; Nolan, L.K.; Barbieri, N.L.; Logue, C.M. Characterization of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) Associated With Turkey Cellulitis in Iowa. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ievy, S.; Islam, M.S.; Sobur, M.A.; Talukder, M.; Rahman, M.B.; Khan, M.F.R.; Rahman, M.T. Molecular Detection of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) for the First Time in Layer Farms in Bangladesh and Their Antibiotic Resistance Patterns. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Wannemuehler, Y.; Doetkott, C.; Johnson, S.J.; Rosenberger, S.C.; Nolan, L.K. Identification of minimal predictors of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli virulence for use as a rapid diagnostic tool. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3987–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, M.; Luitel, H.; Devkota, B.; Bhattarai, R.K.; Phuyal, S.; Panthi, P.; Shrestha, A.; Chaudhary, D.K. Antibiotic resistance pattern and virulence genes content in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) from broiler chickens in Chitwan, Nepal. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewers, C.; Janssen, T.; Kiessling, S.; Philipp, H.C.; Wieler, L.H. Molecular epidemiology of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) isolated from colisepticemia in poultry. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 104, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) Report 2023; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Lv, X.; Niu, X.; Yu, F.; Zuo, J.; Bao, Y.; Yin, H.; Huang, C.; Nawaz, S.; Zhou, W.; et al. Effect of nutritional and environmental conditions on biofilm formation of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 4236–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumin, Y.M.; Yüksel, G.; Özad Düzgün, A. Investigation of virulence factor genes and biofilm formation of antibiotic resistant clinical E.coli isolates. Microb. Pathog. 2025, 199, 107257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewers, C.; Janssen, T.; Kiessling, S.; Philipp, H.C.; Wieler, L.H. Rapid detection of virulence-associated genes in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli by multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Avian Dis. 2005, 49, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, Z.; Akay, S.; Ejder, N.; Özad Düzgün, A. Determination of the Cytotoxicity and Antibiofilm Potential Effect of Equisetum arvense Silver Nanoparticles. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 196, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPeake, S.J.; Smyth, J.A.; Ball, H.J. Characterisation of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) associated with colisepticaemia compared to faecal isolates from healthy birds. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 110, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solà-Ginés, M.; Cameron-Veas, K.; Badiola, I.; Dolz, R.; Majó, N.; Dahbi, G.; Viso, S.; Mora, A.; Blanco, J.; Piedra-Carrasco, N.; et al. Diversity of Multi-Drug Resistant Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) Causing Outbreaks of Colibacillosis in Broilers during 2012 in Spain. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naundrup Thøfner, I.C.; Poulsen, L.L.; Bisgaard, M.; Christensen, H.; Olsen, R.H.; Christensen, J.P. Longitudinal Study on Causes of Mortality in Danish Broiler Breeders. Avian Dis. 2019, 63, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovanardi, D.; Campagnari, E.; Ruffoni, L.S.; Pesente, P.; Ortali, G.; Furlattini, V. Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli transmission from broiler breeders to their progeny in an integrated poultry production chain. Avian Pathol. 2005, 34, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, S.; Bailie, M.; Yaqoob, A.; Khanum, S.; Fatima, K.; Altaf, A.; Ahmed, I.; Shah, S.T.A.; Munawar, J.; Zehra, Q.A.; et al. Characterization of two novel lytic bacteriophages having lysis potential against MDR avian pathogenic Escherichia coli strains of zoonotic potential. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naves, P.; del Prado, G.; Huelves, L.; Gracia, M.; Ruiz, V.; Blanco, J.; Dahbi, G.; Blanco, M.; del Carmen Ponte, M.; Soriano, F. Correlation between virulence factors and in vitro biofilm formation by Escherichia coli strains. Microb. Pathog. 2008, 45, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Johnson, S.J.; Nolan, L.K. Complete DNA sequence of a ColBM plasmid from avian pathogenic Escherichia coli suggests that it evolved from closely related ColV virulence plasmids. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 5975–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, C.; Brash, M.L.; Slavic, D.; Boerlin, P.; Ouckama, R.; Weis, A.; Petrik, M.; Philippe, C.; Barham, M.; Guerin, M.T. Evaluating Virulence-Associated Genes and Antimicrobial Resistance of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Isolates from Broiler and Broiler Breeder Chickens in Ontario, Canada. Avian Dis. 2018, 62, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carli, S.; Ikuta, N.; Lehmann, F.K.; da Silveira, V.P.; de Melo Predebon, G.; Fonseca, A.S.; Lunge, V.R. Virulence gene content in Escherichia coli isolates from poultry flocks with clinical signs of colibacillosis in Brazil. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 2635–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, X.; Huo, S. Molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant avian pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from septicemic broilers. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewers, C.; Li, G.; Wilking, H.; Kiessling, S.; Alt, K.; Antáo, E.M.; Laturnus, C.; Diehl, I.; Glodde, S.; Homeier, T.; et al. Avian pathogenic, uropathogenic, and newborn meningitis-causing Escherichia coli: How closely related are they? Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 297, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, H.; Akrami, F.; Bouakkaz, S.; Dozois, C.M. Prevalence of specific serogroups, antibiotic resistance and virulence factors of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) isolated from clinical cases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 194, 106843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, G.; Reeves, P. Biosynthesis of O-antigens: Genes and pathways involved in nucleotide sugar precursor synthesis and O-antigen assembly. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 2503–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, E.R.; Yasir, M.; Turner, A.K.; Wain, J.; Charles, I.G.; Webber, M.A. Massively parallel transposon mutagenesis identifies temporally essential genes for biofilm formation in Escherichia coli. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.; Mirani, Z.A.; Pirzada, Z.A. Phylogenetic Group B2 Expressed Significant Biofilm Formation among Drug Resistant Uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Libyan J. Med. 2021, 16, 1845444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düzgün, A.; Okumuş, F.; Saral, A.; Çiçek, A.; Cinemre, S. Determination of antibiotic resistance genes and virulence factors in Escherichia coli isolated from Turkish patients with urinary tract infection. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2019, 52, e20180499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özad Düzgün, A.; Yüksel, G. Detection of virulence factor genes, antibiotic resistance genes and biofilm formation in clinical Gram-negative bacteria and first report from Türkiye of K.oxytoca carrying both blaOXA-23 and blaOXA-51 genes. Biologia 2023, 78, 2245–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeispour, M.; Ranjbar, R. Antibiotic resistance, virulence factors and genotyping of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naziri, Z.; Kilegolan, J.A.; Moezzi, M.S.; Derakhshandeh, A. Biofilm formation by uropathogenic Escherichia coli: A complicating factor for treatment and recurrence of urinary tract infections. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 117, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, T.A.; Preethishree, P.; Ashwini; Pai, V. Bacterial Profile of Urinary Tract Infections: Evaluation of Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance Pattern of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 14, 2577–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detho, H.; Bano, S.; Tunio, S.A.; Abbasi, S.M.; Ahmed, M. Biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance in uropathogenic Escherichia coli: The quest for effective treatment of urinary tract infections. Pure Appl. Biol. (PAB) 2023, 13, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastegar, E.; Malekzadegan, Y.; Khashei, R.; Hadi, N. Quinolone resistance and biofilm formation capability of uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolates from an Iranian inpatients’ population. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 8073–8079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattahi, S.; Kafil, H.S.; Nahai, M.R.; Asgharzadeh, M.; Nori, R.; Aghazadeh, M. Relationship of biofilm formation and different virulence genes in uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolates from Northwest Iran. GMS Hyg. Infect. Control 2015, 10, Doc11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laconi, A.; Tolosi, R.; Apostolakos, I.; Piccirillo, A. Biofilm Formation Ability of ESBL/pAmpC-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from the Broiler Production Pyramid. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trusz, A.; Gorlach, J.; Gazda, D.; Piekarska, K. Biofilm formation in the drinking water distribution system, on selected pipe materials in flow reactors–preliminary investigations. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2024, 24, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, D.; Silva, A.R.; Fernandes, R.; Serra, P.; Barros, M.M.; Campos, A.M.; Oliveira, R.; Silva, S.; Almeida, C.; Castro, J. Emerging Approaches for Mitigating Biofilm-Formation-Associated Infections in Farm, Wild, and Companion Animals. Pathogens 2024, 13, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


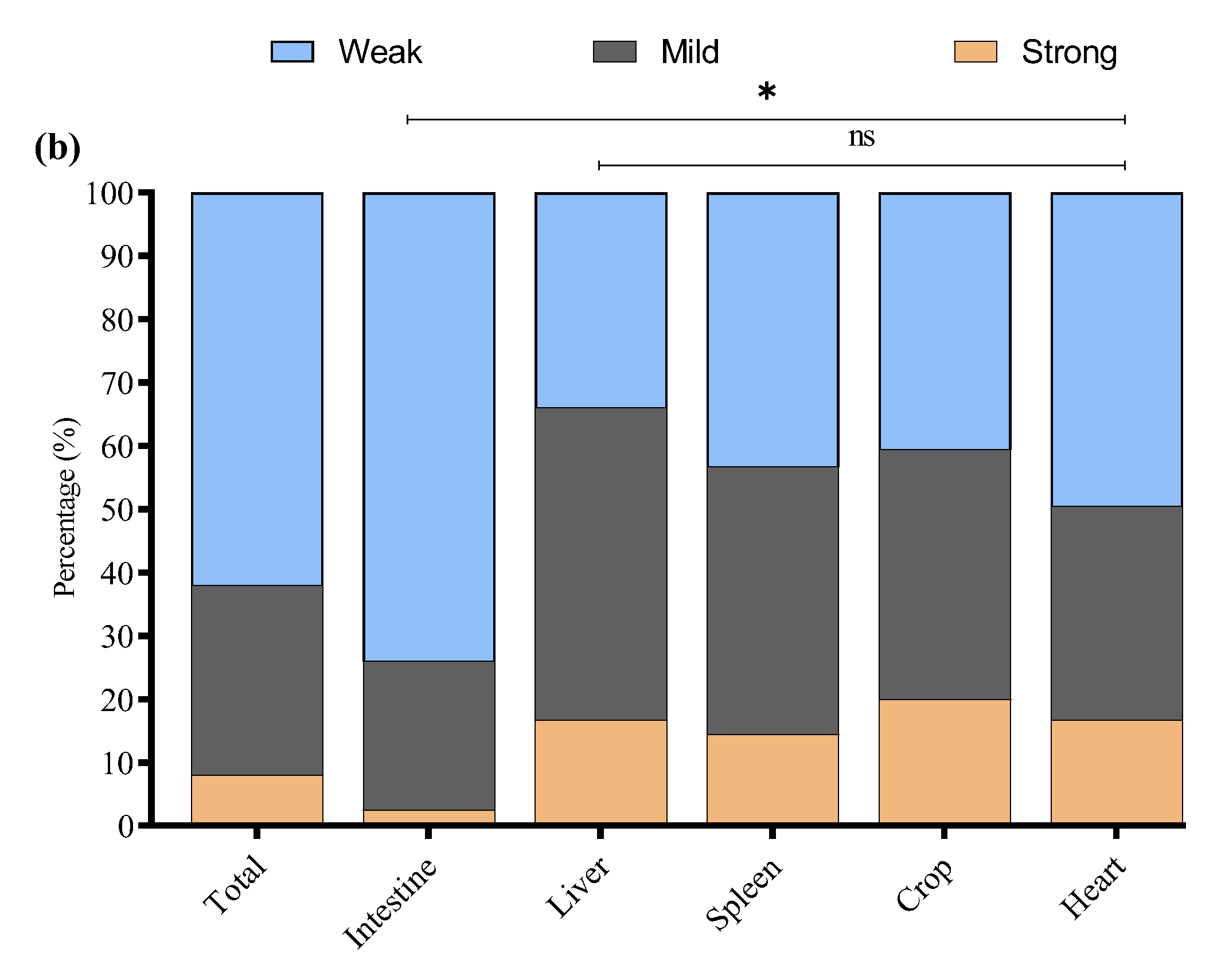
| Gene | Description | Size (bp) | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serotypes | |||||
| gnd-F | Serotype O1 | 263 | CGATGTTGAGCGCAAGGTTG | 57 | [27] |
| rfbO1-R | CATTAGGTGTCTCTGGCACG | ||||
| rfbO2-R | Serotype O2 | 355 | GATAAGGAATGCACATCGCC | ||
| rfbO18-R | Serotype O18 | 459 | AGAAGCATTGAGCTGTGGAC | ||
| rfbO78-R | Serotype O78 | 623 | TAGGTATTCCTGTTGCGGAG | ||
| O8-F O8-R | Serotype O8 | 448 | CCAGAGGCATAATCAGAAATAACAG GCAGAGTTAGTCAACAAAAGGTCAG | 53 | [25,26] |
| O9-F O9-R | Serotype O9 | 1235 | CGTCGGCAAGGCGTATAAATA CCCAGAAATCCATGCTC | ||
| O21-F O21-R | Serotype O21 | 209 | CTGCTGATGTCGCTATTATTGCTG TGAAAAAAAGGGAAACAGAAGAGCC | ||
| O102-F O102-R | Serotype O102 | 1025 | TCCGGTAAGTATCTTACGGCA GCACCAAATAGCGAAATACCA | ||
| O128-F O128-R | Serotype O128 | 782 | ATGATTTCTTACGGAGTGC CTCTAACCTAATCCCTCCC | ||
| O145-F O145-R | Serotype O145 | 132 | TTCGCGCACAGCATGGTTAT TACAATGCACCGCAAACAGT | ||
| Virulence genes | |||||
| iroN | Iron acquisition | 553 | F: AATCCGGCAAAGAGACGAACCGCCT R: GTTCGGGCAACCCCTGCTTTGACTTT | 63 | [35] |
| iutA | 302 | F: GGCTGGACATCATGGGAACTGG R: CGTCGGGAACGGGTAGAATCG | |||
| ompT | Protectins | 496 | F: TCATCCCGGAAGCCTCCCTCACTACTAT R: TAGCGTTTGCTGCACTGGCTTCTGATAC | ||
| ompA | 620 | F: ATGATGGTCATCCGTCCCGT R: ATCAGTTCTGCAATAAATGC | |||
| iss | 323 | F: CAGCAACCCGAACCACTTGATG R: AGCATTGCCAGAGCGGCAGAA | |||
| hlyE | Toxins | 450 | F: GGCCACAGTCGTTTAGGGTGCTTACC R: GGCGGTTTAGGCATTCCGATACTCAG | ||
| astA | 116 | F: TGCCATCAACACAGTATATCC R: TCAGGTCGCGAGTGACGGC | 57 | [36] | |
| papC | Adhesins | 501 | F: TGATATCACGCAGTCAGTAGC R: CCGGCCATATTCACATAA | 60 | |
| tsh | 824 | F: ACTATTCTCTGCAGGAAGTC R: CTTCCGATGTTCTGAACGT | |||
| ibeA | Invasins | 171 | F: AGGCAGGTGTGCGCCGCGTAC R: TGGTGCTCCGGCAAACCATGC | 63 | [35] |
| iucD | Aerobactin synthesis | 613 | F: GAAGCATATGACACAATCCTG R: CAGAGTGAAGTCATCACGCAC | 54 | [15,37] |
| vat | Vacuolating autotransporter toxin | 939 | F: TCCATGCTTCAACGTCTCAGAG R: CTGTTGTCAGTGTCGTGAACG | ||
| cvi/cva | Structural genes of colicin V operon | 598 | F: TCCAAGCGGACCCCTTATAG R: CGCAGCATAGTTCCATGCT | 57 | |
| fimC | Type 1 fimbriae (D-mannose-specific adhesin) | 513 | F: TATGTTGGCTTTGAAATGGG R: ATCCAGAGCAGCCTGACCTT | 63 | |
| fyuA | Ferric yersinia uptake | 209 | F: GGCGGCGTGCGCTTCTCGCA R: CGCAGTAGGCACGATGTTGTA | ||
| Province | Coefficient | Std. Error | z | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liaoning | −0.178 | 0.423 | −0.422 | 0.673 |
| Shandong | −0.348 | 0.419 | −0.832 | 0.405 |
| Xinjiang | +0.633 | 0.466 | +1.358 | 0.174 |
| Serotype | Shandong (n = 34) | Fujian (n = 30) | Liaoning (n = 32) | Xinjiang (n = 40) | Positive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rfbO1 | 2 (5.9%) ns | 4 (13.3%) ns | 2 (6.3%) ns | 2 (5.0%) ns | 10 (7.4%) |
| rfbO2 | 5 (14.7%) ns | 2 (6.7%) ns | 2 (6.3%) ns | 3 (7.5%) ns | 12 (8.8%) |
| O8 | 5 (14.7%) ns | 3 (10.0%) ns | 4 (12.5%) ns | 5 (12.5%) ns | 17 (12.5%) |
| O9 | 4 (11.8%) ns | 4 (13.3%) ns | 3 (9.4%) ns | 4 (10.0%) ns | 15 (11.0%) |
| rfbO18 | 3 (8.8%) ns | 4 (13.3%) ns | 4 (12.5%) ns | 3 (7.5%) ns | 14 (10.3%) |
| O21 | 2 (5.9%) ns | 1 (3.3%) ns | 1 (3.1%) ns | 2 (5.0%) ns | 6 (4.4%) |
| rfbO78 | 2 (5.9%) ns | 4 (13.3%) ns | 3 (9.4%) ns | 2 (5.0%) ns | 11 (8.1%) |
| O102 | 3 (8.8%) ns | 3 (10.0%) ns | 3 (9.4%) ns | 7 (17.5%) ns | 16 (11.8%) |
| O128 | 2 (5.9%) ns | - | 5 (15.6%) ns | 6 (15.0%) ns | 13 (9.6%) |
| O145 | 6 (17.6%) ns | 5 (16.7%) ns | 5 (15.6%) ns | 6 (15.0%) ns | 22 (16.2%) |
| Virulence Genes | Xinjiang (n = 40) | Shandong (n = 34) | Liaoning (n = 32) | Fujian (n = 30) | Total Positive (n = 136) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ompA | 3 (7.5%) ns | 3 (8.8%) ns | 3 (9.3%) ns | 2 (6.6%) ns | 11 (8%) |
| astA | 4 (10%) ns | 2 (5.8%) ns | 2 (6.2%) ns | 2 (6.6%) ns | 10 (7.3%) |
| iss | 4 (10%) ns | 3 (8.8%) ns | 3 (9.3%) ns | 2 (6.6%) ns | 12 (8.8%) |
| ompT | 1(2.5%) ns | 1 (2.9%) ns | 1 (3.1%) ns | 1 (3.3%) ns | 4 (2.9%) |
| iroN | 3 (7.5%) ns | 1 (2.9%) ns | 1 (3.1%) ns | 1 (3.3%) ns | 6 (4.4%) |
| hlyE | 2 (5%) ns | 3 (8.8%) ns | 2 (6.2%) ns | 1 (3.3%) ns | 8 (5.8%) |
| iutA | 2 (5%) ns | 2 (5.8%) ns | 3 (9.3%) ns | 1 (3.3%) ns | 8 (5.8%) |
| papC | 2 (5%) ns | 3 (8.8%) ns | 3 (9.3%) ns | 3 (10%) ns | 11 (8%) |
| tsh | 3 (7.5%) ns | 4 (11.7%) ns | 4(12.5%) ns | 3 (10%) ns | 14 (10.2%) |
| ibeA | 4 (10%) ns | 2 (5.8%) ns | 1 (3.1%) ns | 3 (10%) ns | 10 (7.3%) |
| iucD | 2 (5%) ns | 1 (2.9%) ns | 1 (3.1%) ns | 3 (10%) ns | 7 (5.1%) |
| vat | 3 (7.5%) ns | 2 (5.8%) ns | 2 (6.2%) ns | 1 (3.3%) ns | 8 (5.8%) |
| cvi/cva | 1(2.5%) ns | 1 (2.9%) ns | 1 (3.1%) ns | 3 (10%) ns | 6 (4.4%) |
| fimC | 3 (7.5%) ns | 2 (5.8%) ns | 3 (9.3%) ns | 2 (6.6%) ns | 10 (7.3%) |
| fyuA | 3 (7.5%) ns | 4 (11.7%) ns | 2 (6.2%) ns | 2 (6.6%) ns | 11 (8%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nawaz, S.; Shoaib, M.; Huang, C.; Jiang, W.; Bao, Y.; Wu, X.; Nie, L.; Fan, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; et al. Molecular Characterization, Antibiotic Resistance, and Biofilm Formation of Escherichia coli Isolated from Commercial Broilers from Four Chinese Provinces. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051017
Nawaz S, Shoaib M, Huang C, Jiang W, Bao Y, Wu X, Nie L, Fan W, Wang Z, Chen Z, et al. Molecular Characterization, Antibiotic Resistance, and Biofilm Formation of Escherichia coli Isolated from Commercial Broilers from Four Chinese Provinces. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(5):1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051017
Chicago/Turabian StyleNawaz, Saqib, Muhammad Shoaib, Cuiqin Huang, Wei Jiang, Yinli Bao, Xiuyi Wu, Lianhua Nie, Wenyan Fan, Zhihao Wang, Zhaoguo Chen, and et al. 2025. "Molecular Characterization, Antibiotic Resistance, and Biofilm Formation of Escherichia coli Isolated from Commercial Broilers from Four Chinese Provinces" Microorganisms 13, no. 5: 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051017
APA StyleNawaz, S., Shoaib, M., Huang, C., Jiang, W., Bao, Y., Wu, X., Nie, L., Fan, W., Wang, Z., Chen, Z., Yin, H., & Han, X. (2025). Molecular Characterization, Antibiotic Resistance, and Biofilm Formation of Escherichia coli Isolated from Commercial Broilers from Four Chinese Provinces. Microorganisms, 13(5), 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051017








