Germination and Outgrowth of Bacillus subtilis Spores Deficient in BER and DisA Unveil Alternative Genetic Checkpoints
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain and Culture Conditions
2.2. Determination of Spore Germination and Outgrowth
2.3. Analysis of Spontaneous and H2O2- or MMS-Induced Mutation Frequencies
2.4. Fluorescence Microscopy
2.5. Isolation and Quantitation of Chromosomal DNA
2.6. Detection of Oxidative DNA Damage
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
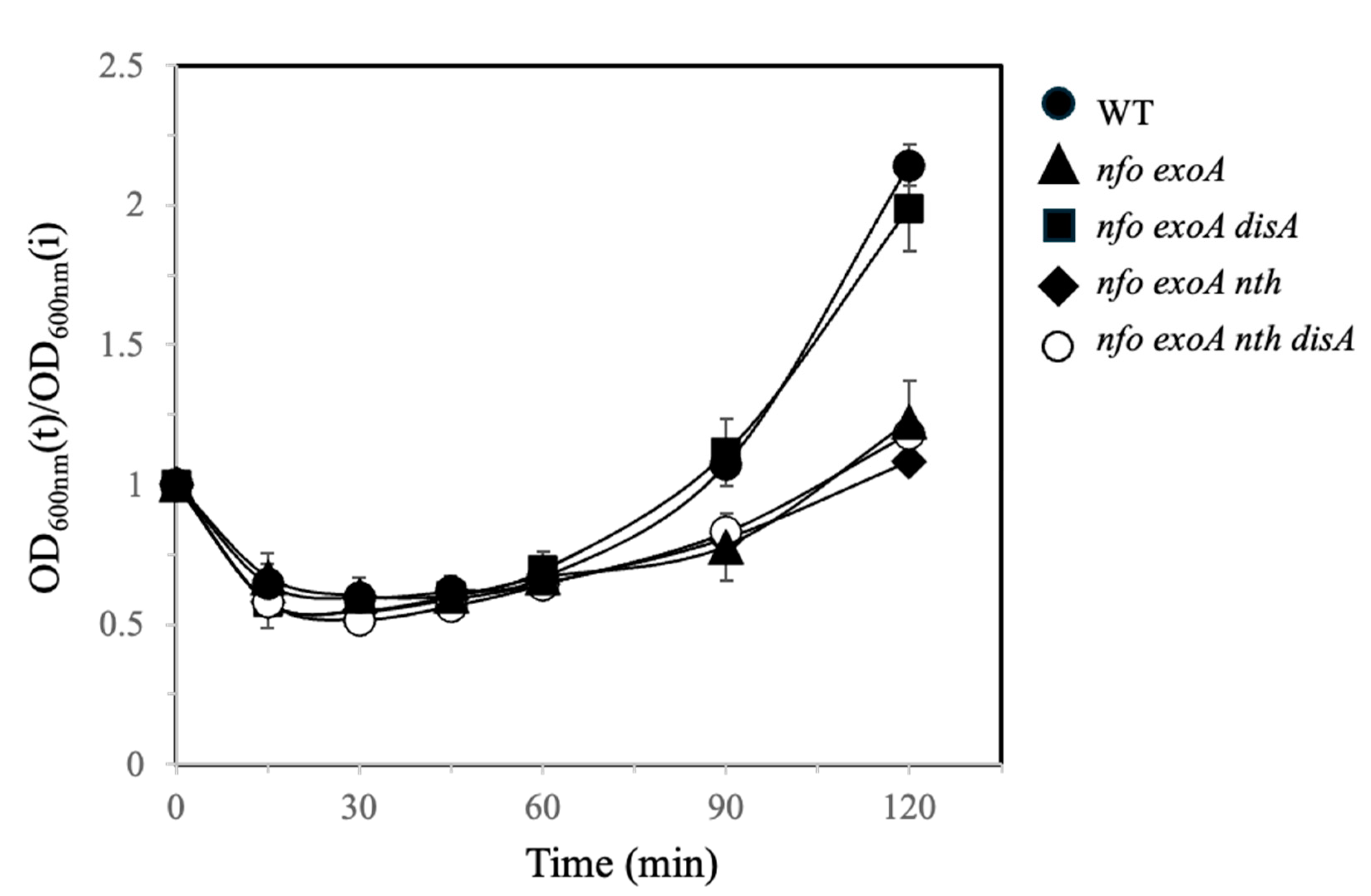
3.1. Analysis of Germination and Outgrowth of B. subtilis Spores Deficient for APEs and DisA
3.2. Effect of H2O2 and MMS During Germination/Outgrowth of B. subtilis Spores Deficient in AP-Endonucleases and DisA
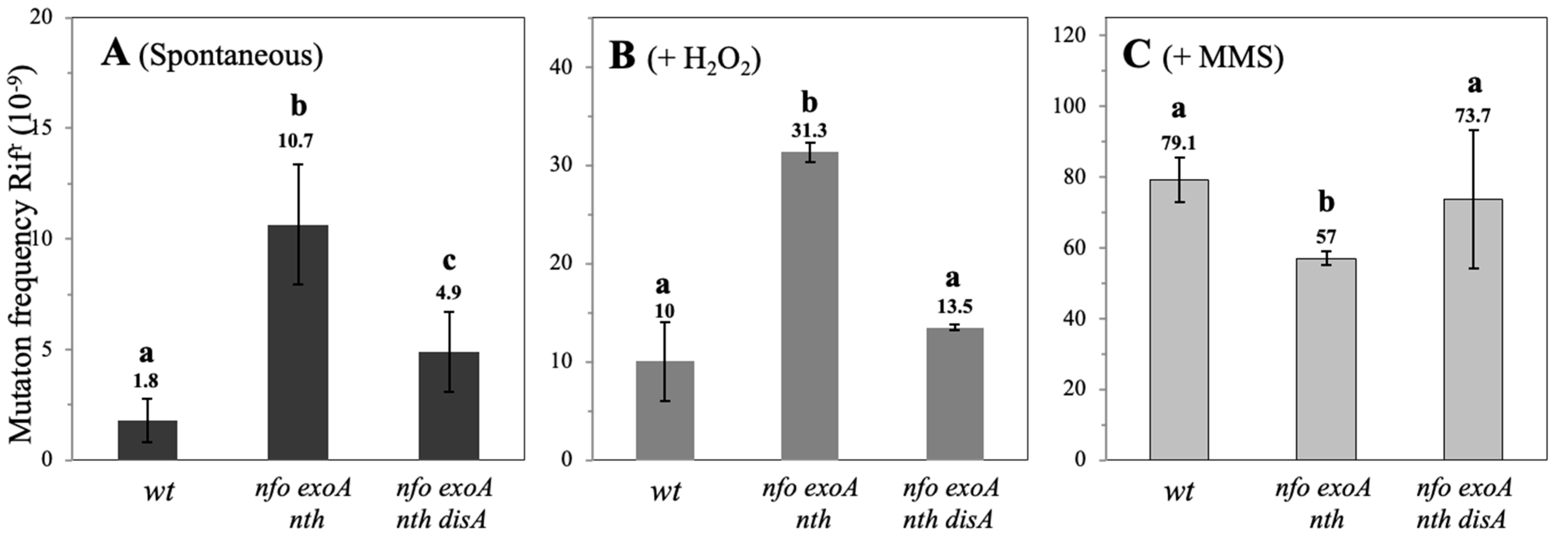
3.3. Spontaneous, H2O2- and MMS-Induced Mutagenesis During B. subtilis Spore Outgrowth
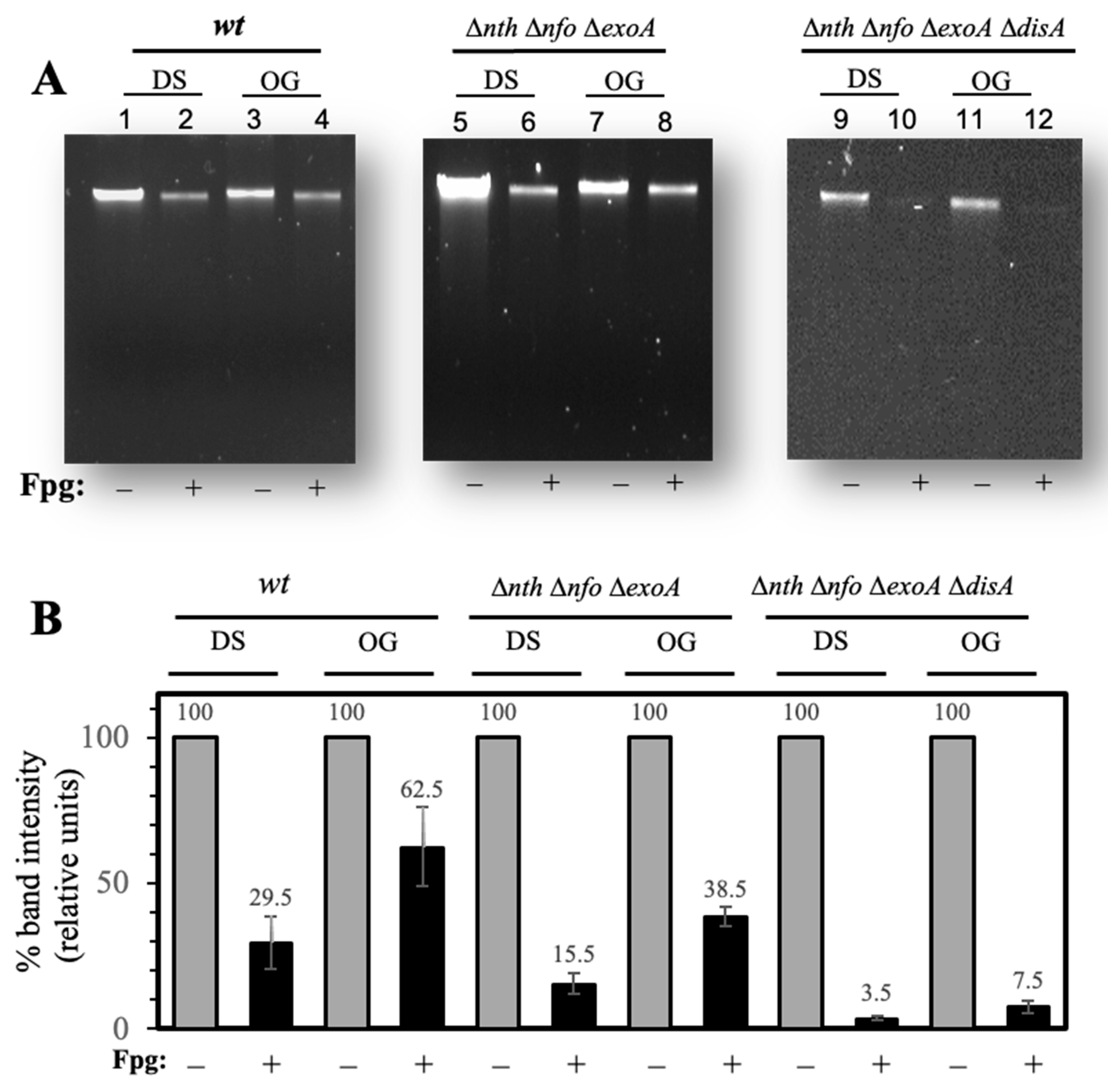
3.4. Determination of 8-OxoG and FapyGua Lesions by Alkaline DNA Electrophoresis (AGE)
3.5. Chromosome Replication Is Delayed During Outgrowth of B. subtilis Spores Deficient for APEs and DisA
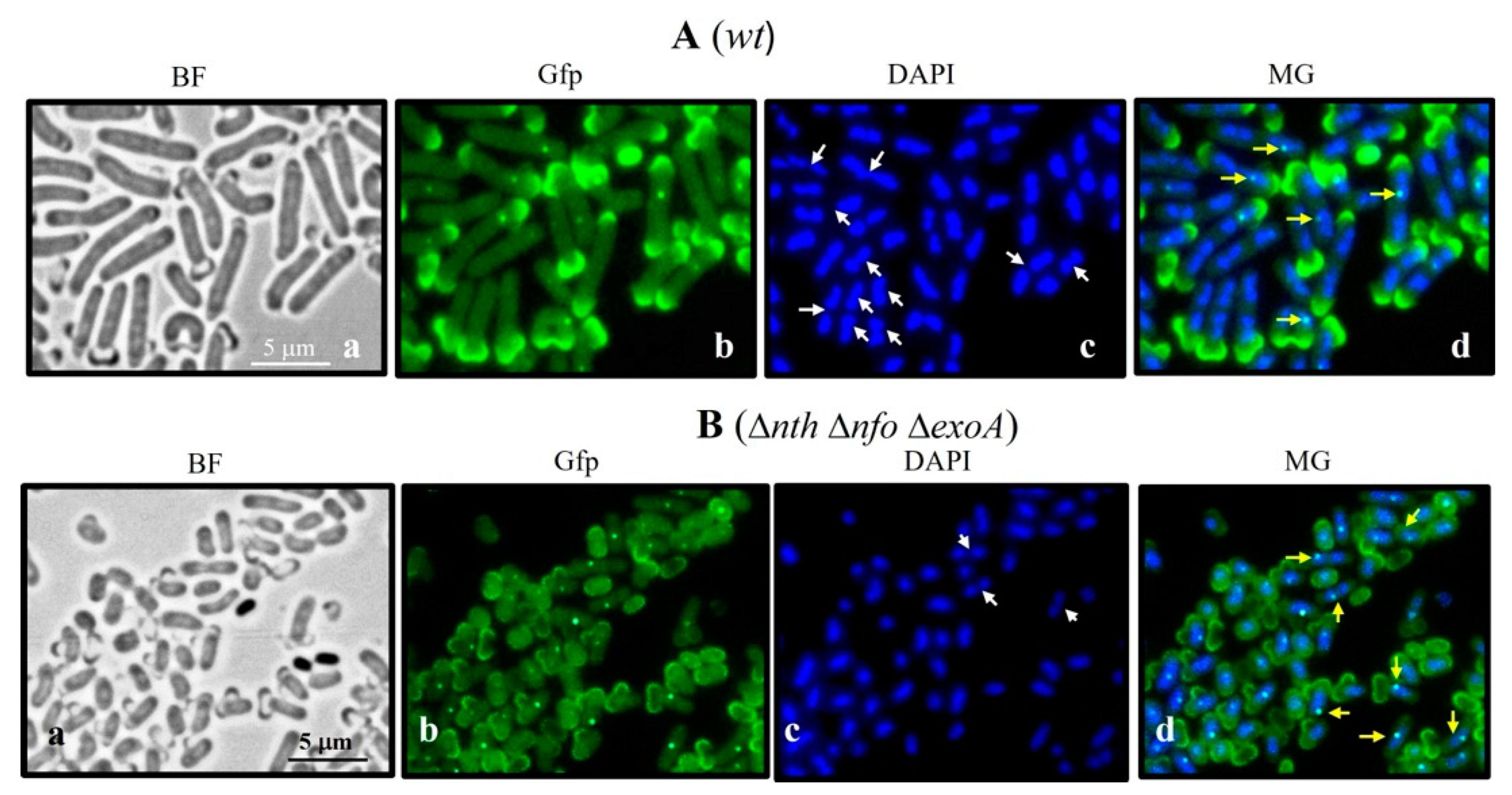
3.6. DisA Foci Synthesis in Outgrowing B. subtilis Spores Deficient and Proficient for APEs
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pedraza-Reyes, M.; Abundiz-Yañez, K.; Rangel-Mendoza, A.; Martínez, L.E.; Barajas-Ornelas, R.C.; Cuéllar-Cruz, M.; Leyva-Sánchez, H.C.; Ayala-García, V.M.; Valenzuela-García, L.I.; Robleto, E.A. Bacillus subtilis stress-associated mutagenesis and developmental DNA repair. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2024, 88, e0015823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errington, J. Regulation of endospore formation in Bacillus subtilis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 1, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piggot, P.J.; Hilbert, D.W. Sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2004, 7, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setlow, B.; Setlow, P. Role of DNA repair in Bacillus subtilis spore resistance. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 3486–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paidhungat, M.; Setlow, P. Spore germination and outgrowth. In Bacillus subtilis and Its Relatives: From Genes to Cells; Hoch, J.A., Losick, R., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 537–548. [Google Scholar]
- Setlow, P. Spore germination. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenhart, J.S.; Schroeder, J.W.; Walsh, B.W.; Simmons, L.A. DNA Repair and Genome Maintenance in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2012, 76, 530–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domian, I.J.; Quon, K.C.; Shapiro, L. Cell type-specific phosphorylation and proteolysis of a transcriptional regulator controls the G1-to-S transition in a bacterial cell cycle. Cell 1997, 90, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Cao, C.; Lutkenhaus, J. Inhibition of FtsZ polymerization by SulA, an inhibitor of septation in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2885–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehne, F.M.; Schroder-Tittmann, K.; Eijlander, R.T.; Herzberg, C.; Hewitt, L.; Kaever, V.; Lewis, R.J.; Kuipers, O.P.; Tittmann, K.; Stülke, J. Control of the diadenylate cyclase CdaSin Bacillus subtilis: An autoinhibitory domain limits cyclic di-AMP production. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 21098–21107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberkampf, M.; Hamiot, A.; Altamirano-Silva, P.; Bellés-Sancho, P.; Tremblay, Y.D.N.; DiBenedetto, N.; Seifert, R.; Soutourina, O.; Bry, L.; Dupuy, B.; et al. c-di-AMP signaling is required for bile salt resistance, osmotolerance, and long-term host colonization by Clostridioides difficile. Sci. Signal. 2022, 15, eabn8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireton, K.; Grossman, A. A developmental checkpoint couples the initiation of sporulation to DNA replication in Bacillus subtilis. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 1566–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongiorni, C.; Stoessel, R.; Perego, M. Negative regulation of Bacillus anthracis sporulation by the Spo0E family of phosphatases. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 2637–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, B.M.; Cartman, S.T.; Minton, N.P.; Butala, M.; Rupnik, M. The SOS Response Master Regulator LexA Is Associated with Sporulation, Motility and Biofilm Formation in Clostridium difficile. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, S.S.; Ibarra-Rodriguez, J.R.; Barajas-Ornelas, R.C.; Ramírez-Guadiana, F.H.; Obregón-Herrera, A.; Setlow, P.; Pedraza-Reyes, M. Interaction of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonucleases Nfo and ExoA with the DNA integrity scanning protein DisA in the processing of oxidative DNA damage during Bacillus subtilis spore outgrowth. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas-Pacheco, J.M.; Urtiz-Estrada, N.; Martínez-Cadena, G.; Yasbin, R.E.; Pedraza-Reyes, M. YqfS from Bacillus subtilis is a spore protein and a new functional member of the type IV apurinic/apyrimidinic-endonuclease family. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 5380–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barajas-Ornelas, R.d.C.; Ramírez-Guadiana, F.H.; Juárez-Godínez, R.; Ayala-García, V.M.; Robleto, E.A.; Yasbin, R.E.; Pedraza-Reyes, M. Error-Prone Processing of Apurinic/Apyrimidinic (AP) Sites by PolX Underlies a Novel Mechanism That Promotes Adaptive Mutagenesis in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 3012–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, J.R.; Orozco, A.D.; Rojas, J.A.; López, K.; Setlow, P.; Yasbin, R.E.; Pedraza-Reyes, M. Role of the Nfo and ExoA Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonucleases in repair of DNA damage during outgrowth of Bacillus subtilis spores. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 2031–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejerano-Sagie, M.; Oppenheimer-Shaanan, Y.; Berlatzky, I.; Rouvinski, A.; Meyerovich, M.; Ben-Yehuda, S. A Checkpoint Protein That Scans the Chromosome for Damage at the Start of Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Cell 2006, 125, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela-García, L.I.; Ayala-García, V.M.; Regalado-García, A.G.; Setlow, P.; Pedraza-Reyes, M. Transcriptional coupling (Mfd) and DNA damage scanning (DisA) coordinate excision repair events for efficient Bacillus subtilis spore outgrowth. Microbiologyopen 2018, 7, e00593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, C.; Machón, C.; Briggs, G.S.; Smits, W.K.; Soultanas, P. Untwisting of the DNA helix stimulates the endonuclease activity of Bacillus subtilis Nth at AP sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Zhang, Q.-M.; Takao, M.; Yasui, A.; Yonei, S. Escherichia coli Nth and human hNTH1 DNA glycosylases are involved in removal of 8-oxoguanine from 8-oxoguanine/guanine mispairs in DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 1975–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagyan, I.; Noback, M.; Bron, S.; Paidhungat, M.; Setlow, P. Characterization of yhcN, a new forespore-specific gene of Bacillus subtilis. Gene 1998, 212, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J. Experiments in Molecular Genetics; Cold Spring Harbor Lab: Long Island, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer, P.; Millet, J.; Aubert, J.P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1965, 54, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, W.L.; Setlow, B.; Setlow, P. Binding of DNA in vitro by a small, acid-soluble spore protein from Bacillus subtilis and the effect of this binding on DNA topology. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 6900–6906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-García, V.M.; Valenzuela-García, L.I.; Setlow, P.; Pedraza-Reyes, M. Aag hypoxanthine-DNA glycosylase is synthesized in the forespore compartment and involved in counteracting the genotoxic and mutagenic effects of hypoxanthine and alkylated bases in DNA during Bacillus subtilis sporulation. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 3345–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak, K.J.; Simmons, L.A. Bacterial DNA excision repair pathways. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazra, T.K.; Muller, J.G.; Manuel, R.C.; Burrows, C.J.; Lloyd, R.S.; Mitra, S. Repair of hydantoins, one electron oxidation product of 8-oxoguanine, by DNA glycosylases of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 1967–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, C.; North, M.; Erixon, K.; Walters, K.; Jenssen, D.; Goldman, A.S.H.; Helleday, T. Methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) produces heat-labile DNA damage but no detectable in vivo DNA double-strand breaks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 3799–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, A.; Jaruga, P.; Bohr, V.A.; Grollman, A.P.; Dizdaroglu, M. Kinetics of excision of purine lesions from DNA by Escherichia coli Fpg protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchou, J.; Bodepudi, V.; Shibutani, S.; Antoshechkin, I.; Miller, J.; Grollman, A.; Johnson, F. Substrate Specificity of Fpg Protein. Recognition and cleavage of oxidatively damaged DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 15318–15324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boal, A.K.; Yavin, E.; Lukianova, O.A.; O’Shea, V.L.; David, S.S.; Barton, J.K. DNA-bound redox activity of DNA repair glycosylases containing [4Fe-4S] clusters. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 8397–8407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanchan, S.; Mehrotra, R.; Chowdhury, S. In Silico Analysis of the Endonuclease III Protein Family Identifies Key Residues and Processes During Evolution. J. Mol. Evol. 2015, 81, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denver, D.R.; Swenson, S.L.; Lynch, M. An evolutionary analysis of the helix-hairpin-helix superfamily of DNA repair glycosylases. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keijser, B.J.F.; Ter Beek, A.; Rauwerda, H.; Schuren, F.; Montijn, R.; Van Der Spek, H.; Brul, S. Analysis of temporal gene expression during Bacillus subtilis spore germination and outgrowth. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 3624–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppenheimer-Shaanan, Y.; Wexselblatt, E.; Katzhendler, J.; Yavin, E.; Ben-Yehuda, S. c-di-AMP reports DNA integrity during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. EMBO Rep. 2011, 12, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.-M.; Yeamans, G.; Ross, C.A.; Yasbin, R.E. Roles of YqjH and YqjW, homologs of the Escherichia coli UmuC/DinB or Y superfamily of DNA polymerases, in stationary-phase mutagenesis and UV-induced mutagenesis of Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 2153–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patlán, A.G.; Corona, S.U.; Ayala-García, V.M.; Pedraza-Reyes, M. Non-canonical processing of DNA photodimers with Bacillus subtilis UV-endonuclease YwjD, 5′→3′ exonuclease YpcP and low-fidelity DNA polymerases YqjH and YqjW. DNA Repair 2018, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morohoshi, F.; Hayashi, K.; Munakata, N. Bacillus subtilis ada operon encodes two DNA alkyltransferases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 5473–5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruck, I.; Goodman, M.F.; O’Donnell, M. The Essential C Family DnaE Polymerase Is Error-prone and Efficient at Lesion Bypass. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 44361–44368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, B.; Torres, R.; Álamo, M.M.-D.; Ramos, C.; Ayora, S.; Alonso, J.C. Processing of stalled replication forks in Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2024, 48, fuad065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.S.; Cortez, D. New insights into abasic site repair and tolerance. DNA Repair 2020, 90, 102866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrin, M.K.E.; Foster, M.R.; Santana, C.M.; Choi, Y.; Jassal, A.S.; Rancic, S.J.; Greenwald, C.R.; Drucker, M.N.; Feldman, D.T.; Thrall, E.S. The translesion polymerase Pol Y1 is a constitutive component of the B. subtilis replication machinery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, 9613–9629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiala, K.A.; Suo, Z. Sloppy bypass of an abasic lesion catalyzed by a Y-family DNA polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 8199–8206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swarge, B.; Abhyankar, W.; Jonker, M.; Hoefsloot, H.; Kramer, G.; Setlow, P.; Brul, S.; de Koning, L.J. Integrative Analysis of Proteome and Transcriptome Dynamics during Bacillus subtilis Spore Revival. mSphere 2020, 5, e00463-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Strain | Genotype and Description | Source or Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Strains (B. subtilis) | ||
| PS832 | Wild type, trp+, revertant of strain 168 | [23] |
| PERM454 | ∆nfo::neo ∆exoA::tet Neor Tetr | [18] |
| PERM769 | ∆nfo::neo ∆exoA::tet ∆nth:ery Neor Tetr Eryr | [17] |
| PERM1378 | ∆exoA::tet ∆nfo::neo ∆nth::ery ∆disA::cm Neor Tetr Eryr Cmr | This study |
| PERM1008 | PS832 disA-Gfp::ery EryR | This study |
| PERM1685 | ∆nfo::neo ∆exoA::tet ∆nth:cm disA-Gfp::ery Neor Tetr CmR Eryr | This study |
| Plasmids | ||
| pPERM1372 | pMutin4cat containing an internal region (307 bp) of disA; Cmr | [20] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rangel-Mendoza, A.; Valenzuela-García, L.I.; Robleto, E.A.; Pedraza-Reyes, M. Germination and Outgrowth of Bacillus subtilis Spores Deficient in BER and DisA Unveil Alternative Genetic Checkpoints. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040939
Rangel-Mendoza A, Valenzuela-García LI, Robleto EA, Pedraza-Reyes M. Germination and Outgrowth of Bacillus subtilis Spores Deficient in BER and DisA Unveil Alternative Genetic Checkpoints. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):939. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040939
Chicago/Turabian StyleRangel-Mendoza, Alejandra, Luz I. Valenzuela-García, Eduardo A. Robleto, and Mario Pedraza-Reyes. 2025. "Germination and Outgrowth of Bacillus subtilis Spores Deficient in BER and DisA Unveil Alternative Genetic Checkpoints" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040939
APA StyleRangel-Mendoza, A., Valenzuela-García, L. I., Robleto, E. A., & Pedraza-Reyes, M. (2025). Germination and Outgrowth of Bacillus subtilis Spores Deficient in BER and DisA Unveil Alternative Genetic Checkpoints. Microorganisms, 13(4), 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040939






