Development and Evaluation of a MinION Full-Length 16S rDNA Sequencing Analysis Pipeline for Rapid Diagnosis of Animal Gastrointestinal Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DNA Extraction
2.2. MinION Full-Length 16S rDNA Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Sensitivity and Specificity Assessment of the MinION Full-Length 16S rDNA Analysis Pipeline in Pathogen Detection Based on Salmonella-Contaminated Fecal Samples
2.5. Clinical Sample Collection and Sequencing Analysis
3. Results
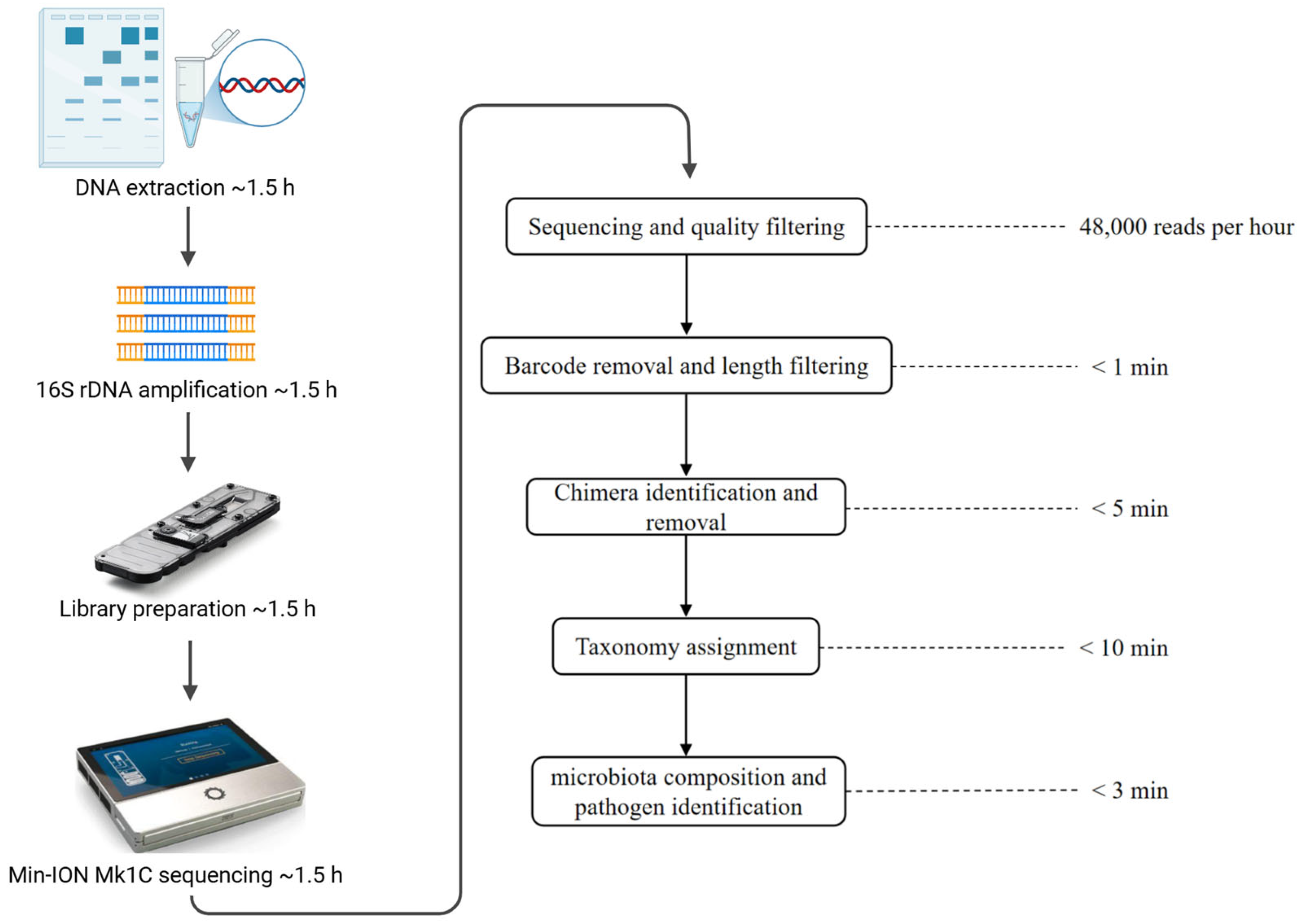
3.1. Development of Sample-to-Answer MinION Full-Length 16S rDNA Sequencing Analysis Pipeline
- porechop -i S1.fastq|seqkit seq -m 1000 -M 1600 - > S1.1-1.6kb.fq
- minimap2 -x ava-ont -g 500 S1.1-1.6kb.fq S1.1-1.6kb.fq > S1.1-1.6kb.overlap.pafyacrd -i S1.1-1.6kb.overlap.paf -o S1.1-1.6kb.report.yacrd -c 4 -n 0.4 scrubb -i S1.1-1.6kb.fq -o S1.1-1.6kb.scrubb.fq
- minimap2 -a -x map-ont --secondary = no -t 46 rrnDB-16S_rRNA.name.fasta S1.1-1.6kb.scrubb.fq > S1.1-1.6kb.scrubb.rrn.samcut -f1,3,14 S1.1-1.6kb.scrubb.rrn.sam |grep ‘AS:i’ |sed ‘s/AS:i://g’ |awk ‘{if ($3≥1500) print $0}’ > S1.1-1.6kb.result.txt
3.2. Sensitivity and Specificity Assessment of the Developed Pipeline in Pathogen Detection Based on Salmonella-Contaminated Fecal Samples
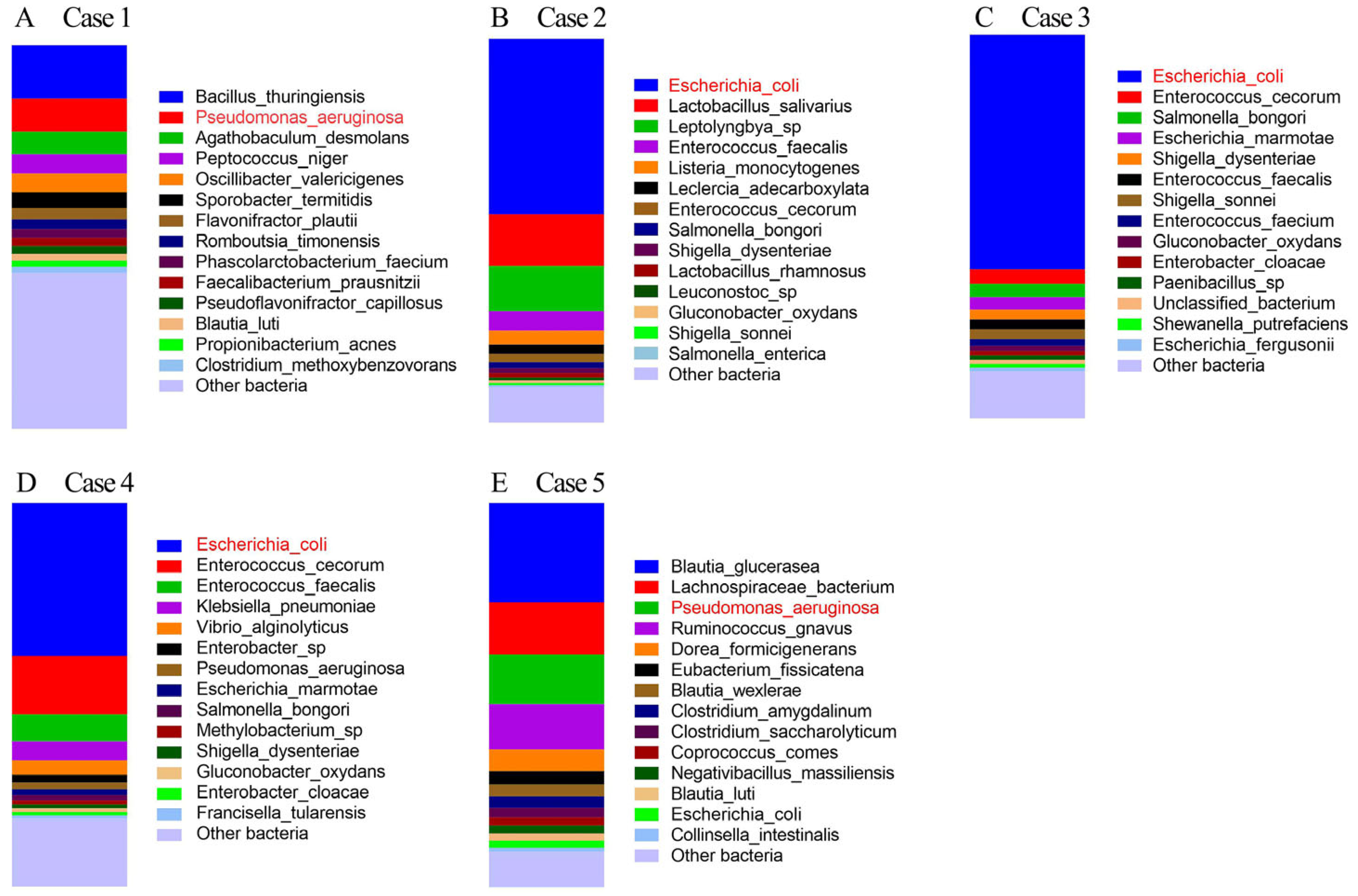
3.3. Evaluation of the Developed MinION Full-Length 16S rDNA Sequencing Pipeline in Animal Gastrointestinal Disease Diagnosis Practices
- Case 1.
- Case 2.
- Case 3.
- Case 4.
- Case 5.
- Case 6.
- Case 7.
- Case 8.
- Case 9.
- Case 10.
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IBD | Inflammatory Bowel Disease |
| SPF | Specific Pathogen Free |
References
- Allen, H. Reportable animal diseases in the United States. Zoonoses Public Health 2012, 59, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.S.; Farnsworth, M.L.; Malmberg, J.L. Diseases at the livestock-wildlife interface: Status, challenges, and opportunities in the United States. Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 110, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbs, E.C.; Colling, A.; Gurung, R.B.; Allen, J. The potential of diagnostic point-of-care tests (POCTs) for infectious and zoonotic animal diseases in developing countries: Technical, regulatory and sociocultural considerations. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1835–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.A.; Rammah, S.S.; Sheweita, S.A.; Haroun, M.; El-Sayed, L.H. Development of immunization trials against Pasteurella multocida. Vaccine 2014, 32, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, R.W.; Williams, S.H.; Beckett, S.D. Farm economic impacts of bovine Johne’s disease in endemically infected Australian dairy herds. Aust. Vet. J. 2016, 94, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingg, D.; Steinbach, S.; Kuhlgatz, C.; Rediger, M.; Schüpbach-Regula, G.; Aepli, M.; Grøneng, G.M.; Dürr, S. Epidemiological and Economic Evaluation of Alternative On-Farm Management Scenarios for Ovine Footrot in Switzerland. Front. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkilä, A.M.; Liski, E.; Pyörälä, S.; Taponen, S. Pathogen-specific production losses in bovine mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9493–9504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.H.; Barbour, A.G.; Oliver, J.H.; Lane, R.S.; Dumler, J.S.; Dennis, D.T.; Persing, D.H.; Azad, A.F.; McSweegan, E. Emerging bacterial zoonotic and vector-borne diseases. Ecological and epidemiological factors. JAMA 1996, 275, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, M.; Ranucci, E.; Romagnoli, P.; Giaccone, V. Antimicrobial resistance: A global emerging threat to public health systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2857–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäumler, A.J.; Sperandio, V. Interactions between the microbiota and pathogenic bacteria in the gut. Nature 2016, 535, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb Ware, J.K.; Larsen, J.W.; Kluver, P. Financial effect of bovine Johne’s disease in beef cattle herds in Australia. Aust. Vet. J. 2012, 90, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windsor, P.A. Paratuberculosis in sheep and goats. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 181, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schokker, D.; Zhang, J.; Vastenhouw, S.A.; Heilig, H.G.; Smidt, H.; Rebel, J.M.; Smits, M.A. Long-lasting effects of early-life antibiotic treatment and routine animal handling on gut microbiota composition and immune system in pigs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresse, R.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F.; Fleury, M.A.; Van de Wiele, T.; Forano, E.; Blanquet-Diot, S. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Postweaning Piglets: Understanding the Keys to Health. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 851–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, A.S.; Arnoult, M.H.; Ahmadi, B.V.; Rich, K.M.; Gunn, G.J.; Stott, A.W. Correction: A framework for estimating society’s economic welfare following the introduction of an animal disease: The case of Johne’s disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomel, B.B. Emerging and Re-Emerging Zoonoses of Dogs and Cats. Animals 2014, 4, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, I.; Maguire, J.H. Small animal zoonoses and immuncompromised pet owners. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2009, 24, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchodolski, J.S. Companion animals symposium: Microbes and gastrointestinal health of dogs and cats. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 89, 1520–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Bai, H.; Qu, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Du, Z.; Feng, L. Coinfection of Clostridium perfringens and Escherichia coli in gas-producing perianal abscess diagnosed by 16S rDNA sequencing: A case report. Gut Pathog. 2021, 13, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, B.; Pop, M.; Antonio, M.; Walker, A.W.; Mai, V.; Ahmed, D.; Oundo, J.; Tamboura, B.; Panchalingam, S.; Levine, M.M.; et al. Survey of culture, goldengate assay, universal biosensor assay, and 16S rRNA Gene sequencing as alternative methods of bacterial pathogen detection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3263–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Morris, A.J.; Murray, P.R.; Reller, L.B. Contemporary testing for enteric pathogens: The potential for cost, time, and health care savings. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 1776–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabel, J.R. An improved method for cultivation of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis from bovine fecal samples and comparison to three other methods. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1997, 9, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Q.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, W.; Yao, Y.; Su, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. Microbiological Diagnostic Performance of Metagenomic Next-generation Sequencing When Applied to Clinical Practice. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, S231–s240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zhou, C.; Wang, L.; Wei, S.; Shi, M.; Li, J.; Lin, L.; Liu, X. Clinical application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing for the diagnosis of suspected infection in adults: A cross-sectional study. Medicine 2024, 103, e37845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, C.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, X.; Zhao, X.; An, Y. Clinical Application of Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing for Suspected Infections in Patients with Primary Immunodeficiency Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 696403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.Y.; Miller, S.A. Clinical metagenomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.; Dong, R.; Yang, W.; Chen, L.; Lang, J.; Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Ma, S.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; et al. Simultaneous detection and comprehensive analysis of HPV and microbiome status of a cervical liquid-based cytology sample using Nanopore MinION sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Komiya, S.; Yasumizu, Y.; Yasuoka, Y.; Mizushima, K.; Takagi, T.; Kryukov, K.; Fukuda, A.; Morimoto, Y.; Naito, Y.; et al. Full-length 16S rRNA gene amplicon analysis of human gut microbiota using MinION™ nanopore sequencing confers species-level resolution. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Holt, K.E. Performance of neural network basecalling tools for Oxford Nanopore sequencing. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Sipos, B.; Zhao, L. SeqKit2: A Swiss army knife for sequence and alignment processing. iMeta 2024, 3, e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marijon, P.; Chikhi, R.; Varré, J.S. yacrd and fpa: Upstream tools for long-read genome assembly. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 3894–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benítez-Páez, A.; Sanz, Y. Multi-locus and long amplicon sequencing approach to study microbial diversity at species level using the MinION™ portable nanopore sequencer. GigaScience 2017, 6, gix043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, H.; Yu, J.; Xu, X.; Sun, L.; Xu, X.; Yu, C.; Xu, F.; Huang, J.; et al. A balanced gut microbiota is essential to maintain health in captive sika deer. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 5659–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honneffer, J.B.; Minamoto, Y.; Suchodolski, J.S. Microbiota alterations in acute and chronic gastrointestinal inflammation of cats and dogs. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16489–16497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inness, V.L.; McCartney, A.L.; Khoo, C.; Gross, K.L.; Gibson, G.R. Molecular characterisation of the gut microflora of healthy and inflammatory bowel disease cats using fluorescence in situ hybridisation with special reference to Desulfovibrio spp. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2007, 91, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchodolski, J.S.; Markel, M.E.; Garcia-Mazcorro, J.F.; Unterer, S.; Heilmann, R.M.; Dowd, S.E.; Kachroo, P.; Ivanov, I.; Minamoto, Y.; Dillman, E.M.; et al. The fecal microbiome in dogs with acute diarrhea and idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchodolski, J.S.; Foster, M.L.; Sohail, M.U.; Leutenegger, C.; Queen, E.V.; Steiner, J.M.; Marks, S.L. The fecal microbiome in cats with diarrhea. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsilio, S.; Pilla, R.; Sarawichitr, B.; Chow, B.; Hill, S.L.; Ackermann, M.R.; Estep, J.S.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S. Characterization of the fecal microbiome in cats with inflammatory bowel disease or alimentary small cell lymphoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampous, T.; Kay, G.L.; Richardson, H.; Aydin, A.; Baldan, R.; Jeanes, C.; Rae, D.; Grundy, S.; Turner, D.J.; Wain, J.; et al. Nanopore metagenomics enables rapid clinical diagnosis of bacterial lower respiratory infection. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Wang, H.; Cao, Z.; Gai, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, G.; Lu, L.; Luan, X. Antimicrobial resistance analysis and whole-genome sequencing of Salmonella enterica serovar Indiana isolate from ducks. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2022, 28, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soe Thu, M.; Sawaswong, V.; Chanchaem, P.; Klomkliew, P.; Campbell, B.J.; Hirankarn, N.; Fothergill, J.L.; Payungporn, S. Optimization of a DNA extraction protocol for improving bacterial and fungal classification based on Nanopore sequencing. Access Microbiol. 2024, 6, 000754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, J.A.; von Keyserlingk, M.A.; Fraser, D.; Weary, D.M. INVITED REVIEW: Farm size and animal welfare. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 5439–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggs, D.S.; Jongman, E.C.; Hemsworth, P.H.; Fisher, A.D. The effects of herd size on the welfare of dairy cows in a pasture-based system using animal- and resource-based indicators. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 3406–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Guo, X.; Yan, Z.; Wang, W.; Chen, B.; Ge, F.; Ye, B. A Comprehensive Analysis on Spread and Distribution Characteristic of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Livestock Farms of Southeastern China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.Y.; He, L.K.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, J.L.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Ying, G.G. Microbial diversity and antibiotic resistome in swine farm environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Chen, T.; Cao, Z.; Zhong, S.; Wen, X.; Mi, J.; Ma, B.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, N.; Liao, X.; et al. Antibiotic resistance genes in layer farms and their correlation with environmental samples. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.; Achmon, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Siame, B.A.; Leung, K.Y. Distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the environment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiken, T.; Leighton, F.A.; Fouchier, R.A.; LeDuc, J.W.; Peiris, J.S.; Schudel, A.; Stöhr, K.; Osterhaus, A.D. Public health. Pathogen surveillance in animals. Science 2005, 309, 1680–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Raudonis, R.; Glick, B.R.; Lin, T.J.; Cheng, Z. Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanisms and alternative therapeutic strategies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, R.; Gaschen, F.P.; Barr, J.W.; Olson, E.; Honneffer, J.; Guard, B.C.; Blake, A.B.; Villanueva, D.; Khattab, M.R.; AlShawaqfeh, M.K.; et al. Effects of metronidazole on the fecal microbiome and metabolome in healthy dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 1853–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, A.; Edlund, C.; Nord, C.E. Effect of antimicrobial agents on the ecological balance of human microflora. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2001, 1, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmoinen, J.; Mentula, S.; Heikkilä, M.; van der Rest, M.; Rajala-Schultz, P.J.; Donskey, C.J.; Frias, R.; Koski, P.; Wickstrand, N.; Jousimies-Somer, H.; et al. Orally administered targeted recombinant Beta-lactamase prevents ampicillin-induced selective pressure on the gut microbiota: A novel approach to reducing antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Hyde, E.R.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Knight, R. Dog and human inflammatory bowel disease rely on overlapping yet distinct dysbiosis networks. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, R.; Suchodolski, J.S. The Gut Microbiome of Dogs and Cats, and the Influence of Diet. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 51, 605–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

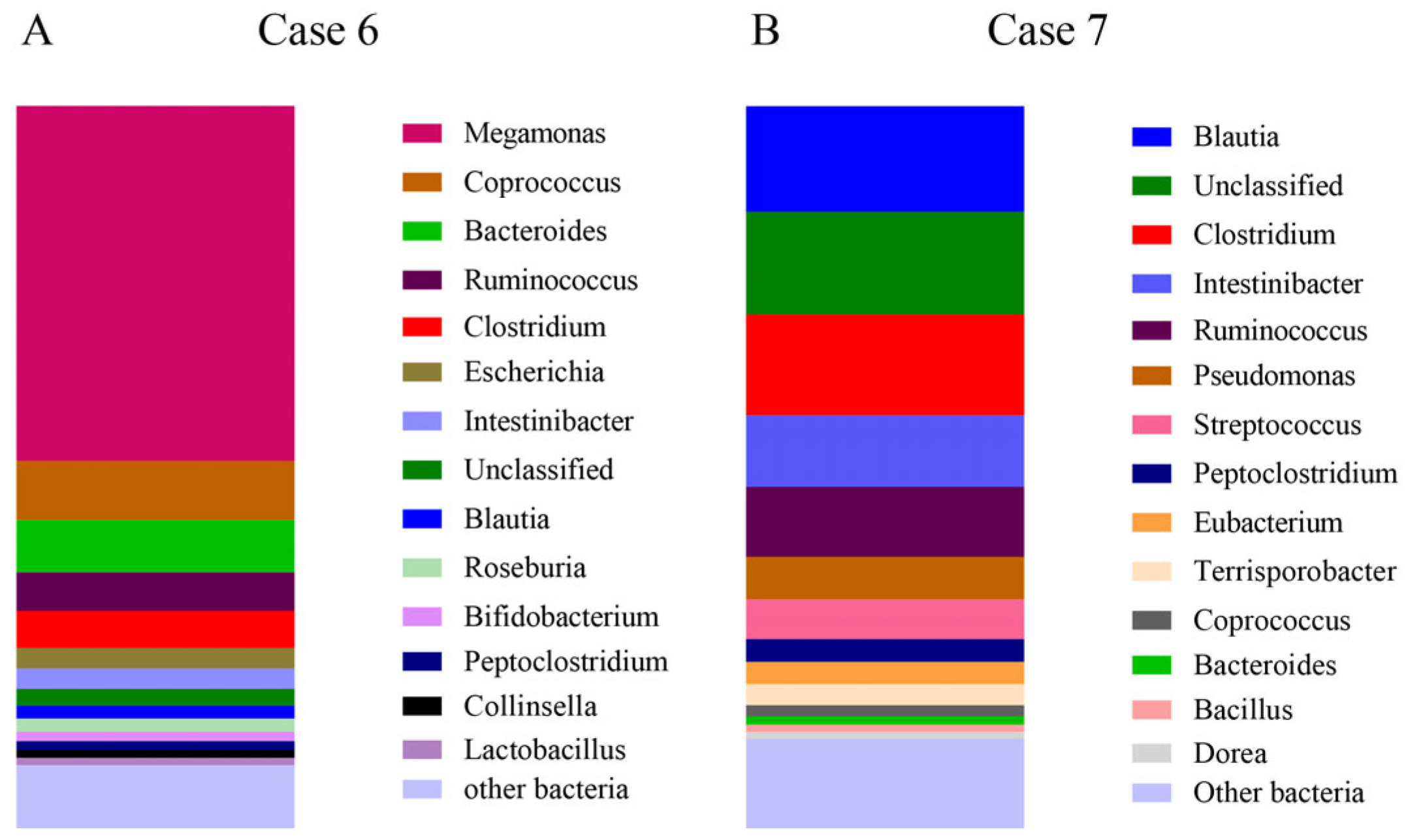
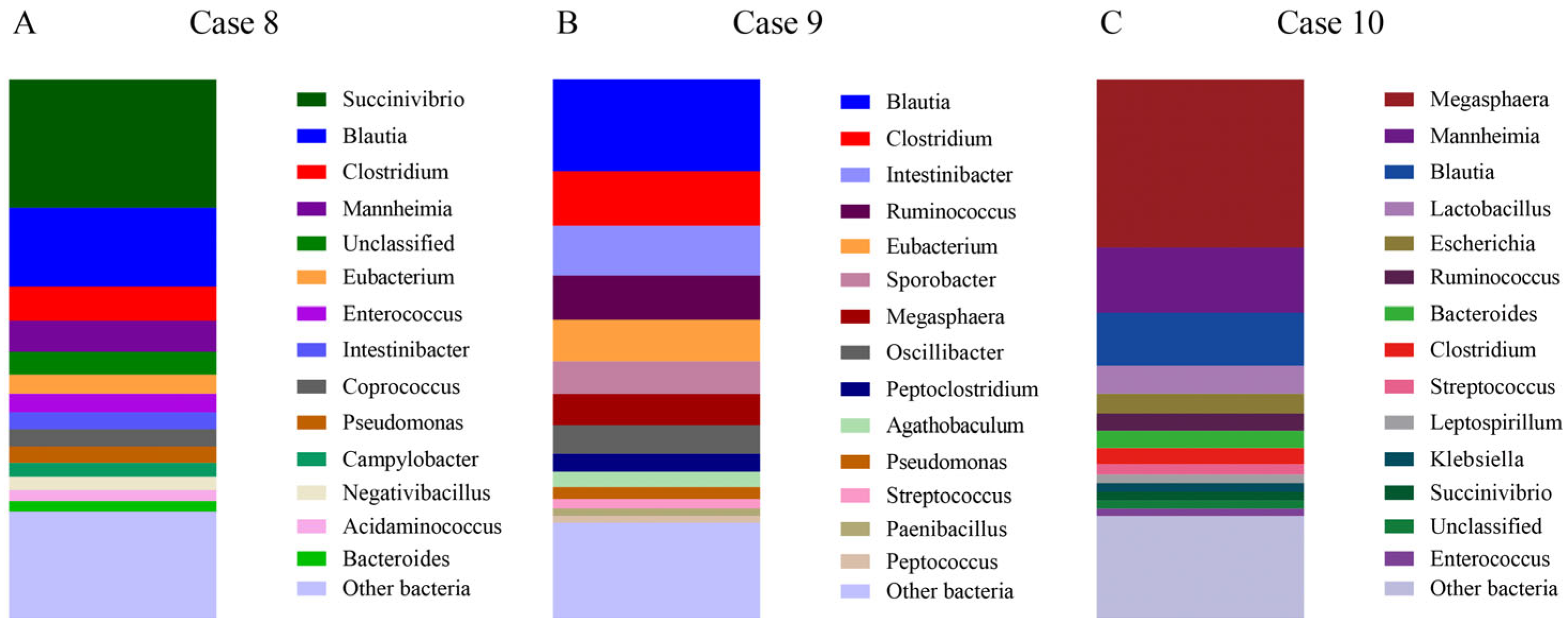
| Bacterial Group | Healthy Medians % (min–max%) | Active IBD Medians % (min–max%) | Case 6 | Case 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clostridiales | 78.1 (21–97) | 45.5 (1–94) | 24.8 | 49.6 |
| Clostridium | 33.7 (5–84) | 13.7 (0–82) | 5.1 | 14.0 |
| Ruminococcaceae | 16.0 (0–46) | 5.6 (0–54) | 0 | 0.1 |
| Faecalibacterium | 0.1 (0–16) | 0 (0–0) | 0 | 0 |
| Bacterial Group | Healthy Medians % (min–max%) | Active IBD Medians % (min–max%) | Case 8 | Case 9 | Case 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteroidales | 25.3 (1.2–56.4) | 16.6 (0.7–55.3) | 2.7 | 1.8 | 3.5 |
| Bifdobacterium | 1.2 (0–36.8) | 0.2 (0.1–38.9) | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, Y.; Pan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Gu, L.; Hou, M.; Liang, S.; Guo, J.; Jiao, X.; et al. Development and Evaluation of a MinION Full-Length 16S rDNA Sequencing Analysis Pipeline for Rapid Diagnosis of Animal Gastrointestinal Diseases. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040777
Zhong Y, Pan Q, Wang Y, Yu J, Li Y, Gu L, Hou M, Liang S, Guo J, Jiao X, et al. Development and Evaluation of a MinION Full-Length 16S rDNA Sequencing Analysis Pipeline for Rapid Diagnosis of Animal Gastrointestinal Diseases. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):777. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040777
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Ying, Qingyun Pan, Yu Wang, Jinyan Yu, Yaomen Li, Lifang Gu, Meicun Hou, Shenglong Liang, Jia Guo, Xinan Jiao, and et al. 2025. "Development and Evaluation of a MinION Full-Length 16S rDNA Sequencing Analysis Pipeline for Rapid Diagnosis of Animal Gastrointestinal Diseases" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040777
APA StyleZhong, Y., Pan, Q., Wang, Y., Yu, J., Li, Y., Gu, L., Hou, M., Liang, S., Guo, J., Jiao, X., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Development and Evaluation of a MinION Full-Length 16S rDNA Sequencing Analysis Pipeline for Rapid Diagnosis of Animal Gastrointestinal Diseases. Microorganisms, 13(4), 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040777





