Abstract
Streptococcus suis serotype 2 (SS2) is an important zoonotic pathogen that seriously harms the swine industry and human health. However, its pathogenic mechanisms are largely unknown, and the few virulence factors reported so far are insufficient to systematically explain its infectious and pathogenic mechanisms. In preliminary research, we identified a gene named G22 encoding a hypothetical secreted protein that may be closely associated with the high-level pathogenicity of S. suis. In this study, we constructed deletion and complementation strains of the G22 gene through homologous recombination and explored its roles in the pathogenicity and susceptibility of S. suis to environmental stresses through in vitro and in vivo experiments. The deletion of G22 clearly influenced the typical capsular structure of SS2 and impaired the bacterium’s growth in a medium containing hydrogen peroxide (showing a growth reduction of 32.98% ± 5.23% compared to the wild-type strain SC19, p < 0.001) or with a low pH (with a growth inhibition of 17.44% ± 1.9% relative to the wild-type strain SC19, p < 0.01). ΔG22 also showed reduced survival in whole blood and in RAW 264.7 macrophages (with a survival reduction of 16.44% ± 2.29% compared to the wild-type, p < 0.001). The deletion of G22 also sharply attenuated the virulence of SS2 in a mouse infection model (reducing the mortality rate by 50% ± 0.04%, p < 0.05). We also demonstrated that G22 is required for the adhesion and invasion of SS2 in host cells. An RNA sequencing analysis revealed that 50 genes were differentially expressed in the ΔG22 and wild-type strains: 23 upregulated and 37 downregulated. Many of the genes are involved in carbohydrate metabolism and the synthesis of virulence-associated factors. Several genes associated with the phosphotransferase system were significantly upregulated in strain ΔG22. In summary, G22 plays a role in the morphological development and pathogenesis of the highly virulent SS2 strain SC19.
1. Introduction
Streptococcus suis (S. suis) is an important emerging zoonotic agent that causes septicemia, meningitis, endocarditis, arthritis, septicemia, meningitis, and even sudden death in humans. Although S. suis is considered a major swine pathogen, it is increasingly being isolated from a wide range of mammalian species and from birds [1]. S. suis has spread worldwide and has caused enormous economic losses in the swine industry in recent years because it causes high morbidity and mortality [2]. S. suis infections in humans are most often restricted to workers in close contact with pigs or swine byproducts [3]. However, two extensive outbreaks of SS2 in humans in China in 1998 and 2005 raised serious concerns for public health and changed our perception that human SS2 infections were only sporadic [1,4]. Almost all of the known strains of SS2 mainly infect swine and humans [5]. Serotype 2 is the serotype most frequently isolated from diseased pigs in the majority of countries [6], and most research has focused on this serotype [5]. However, the molecular pathogenesis of S. suis-induced infectious disease is still unclear, and our understanding of it is fragmentary [4,7], which hampers our attempts to control the diseases caused by S. suis [8].
A repertoire of S. suis virulence determinants undoubtedly plays a role in human infections because S. suis has been suggested to cause community-acquired disease [9]. Many SS2 virulence factors have been reported, some of which are considered critical, including glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh), suilysin (Sly), Eno, and capsular polysaccharide (Cps) [10]. For example, a deficiency in O-acetyl-homoserine sulfhydrylase (OAHS) reduces the expression of Eno and thus inhibits SC19-induced endothelial cell apoptosis, ultimately alleviating the damage caused by SC19 to the blood–brain barrier (BBB). Although the virulence of SC19-ΔOAHS is significantly reduced, it still induces a good immune response in mice against infection by a homologous strain [11]. Cps not only forms the basis for serotyping but also protects the bacterium from phagocytosis [12]. Catabolite control protein A (CcpA) is involved in metabolic gene regulation in various bacteria [13] and is the major mediator of carbon catabolite repression (CCR), repressing gene expression in response to excess sugar during growth [14,15,16]. Bacterial growth, hemolysin production, biofilm formation, and capsule expression are also influenced by CcpA depletion in other streptococci [17,18]. CcpA only indirectly affects certain pathogenic proteins, thus reducing virulence [19]. Although several virulence factors have been shown to play roles in the early stages of infection, the roles of other virulence factors remain unclear [20]. Therefore, further investigations into the pathogenesis of known and unknown virulence factors will extend our understanding of the pathogenesis of, and prevent infection by, this bacterium [21].
In a previous study, we analyzed the genomic sequences of 1634 S. suis isolates from 14 countries and classified them into nine Bayesian analysis of population structure (BAPS) groups. Among them, BAPS group 7 represented a dominant group of virulent S. suis associated with human infections, which were most commonly sequence type 1 (ST1) and ST7 (included in clonal complex 1 [CC1]). We proposed that this cluster constituted a novel human-associated clade (HAC) that had diversified from swine S. suis isolates. A genome-wide association study was used to identify 25 HAC-specific genes. These genes may contribute to an increased risk of human infection and could be used as markers for HAC identification [22]. The G22 gene, annotated as a secretory protein gene, was one of these 25 HAC-specific genes. Based on these findings, we hypothesize that the G22 protein plays a crucial role in the pathogenicity of SS2 and that its inactivation may lead to the attenuation of virulence. Specifically, we propose that the G22 protein contributes to the virulence of S. suis by modulating the expression of key virulence factors and influencing host–pathogen interactions. To test this hypothesis and clarify the biological functions of the G22 protein, we used homologous recombination to construct a gene knockout mutant, ΔG22, of SC19. Comprehensive experiments showed clear morphological changes and the attenuation of pathogenicity in the mutant strain. An RNA sequencing analysis suggested that the inactivation of G22 resulted in the up- or downregulation of many genes involved in carbohydrate metabolism or encoding virulence-related factors. Our results provide new insights into the pathogenesis of SS2 and extend our understanding of this pathogen.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Plasmids
The S. suis strain and plasmids used in this study are given in Table 1. In this study, we used SS2 strain SC19, one of the representative Chinese virulent strains that were isolated from a diseased pig during an outbreak in the Sichuan province of China [23]. The SS2 strains were cultured at 37 °C in tryptic soy broth (TSB) or on tryptic soy agar (Difco, Detroit, MI, USA) (TSA) plates containing 10% newborn bovine serum (Sijiqing Biological Engineering Materials Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China). E. coli strains were cultured on Luria–Bertani (LB) broth or LB agar plates at 37 °C. During selection procedures, spectinomycin (Spc; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was added at concentrations of 100 μg/mL for S. suis and 50 μg/mL for Escherichia coli to maintain plasmid stability. DMEM culture medium (Gibco, Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) including 10% fetal calf serum (Gibco, Carlsbad, CA, USA) was used to culture the human laryngeal epithelial cell line (HEp-2) and Raw264.7 macrophage cell line at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 humidified atmosphere. SS2 strain SC19 was selected as the wild-type (WT) strain. Strain SC19 and the G22-deletion mutant ∆G22 were cultured in TSB or on TSA plates containing 10% newborn bovine serum (Sijiqing Biological Engineering Materials Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China) at 37 °C under 5% CO2. When the pSET4s plasmid contained Spc, the concentration of Spc in the medium was 100 µg/mL.

Table 1.
Strains and plasmids used in this study.
2.2. Construction of G22 Gene Knockout Strain and Complementary Strain
To cause the deletion of G22 in the SC19 strains, we utilized the thermosensitive suicide vector pSET4s, derived from S. suis-E. coli [24]. Initially, the specific primers outlined in Table 2 were employed to amplify the two flanking regions adjacent to the target gene. Subsequently, these regions were fused through overlap-extension PCR. Following purification, the resultant PCR products were treated with BamH1 and EcoRI restriction enzymes. Concurrently, the temperature-sensitive vector pSET4s was ligated with the digested PCR fragments to facilitate the cloning of the desired gene. Electroporation was then utilized to introduce the recombinant vectors into competent SS2 SC19 cells. The cultivation of the transformed cells took place at 28 °C for 36 h in media supplemented with Cm and Spc. We subsequently screened for vector-loss mutants, which had undergone homologous recombination via a double-crossover event, replacing their wild-type (WT) allele with a genetic segment harboring the G22 deletion. The verification of the mutant cells was carried out using PCR with the primer pairs W1/W2 (to differentiate between the WT and mutant based on amplicon size) and N1/N2 (to confirm the absence of G22).

Table 2.
Oligonucleotide primers used in this study.
For complementation purposes, the target gene, along with its putative promoter sequences, was amplified from the SC19 genome via PCR and cloned into the E. coli-S. suis shuttle vector pSET2 [25], generating recombinant plasmids. These plasmids were then electroporated into the ΔG22 mutant cells. Furthermore, complementation strains (CΔG22) were selected using Spc and validated by PCR. The sequences of all primers utilized in this study are detailed in Table 2.
2.3. Growth Characteristics and Genetic Stability of Mutant Strains
The experiment involved the separate inoculation of WT SC19, its mutant derivative ΔG22, and the complemented strain CΔG22; all strains reached equivalent viable counts (~108 CFU/mL) at OD600 = 0.6 before the inoculation, each diluted to a 1:100 ratio, into 100 mL aliquots of TSB. These cultures were then incubated at 37 °C with shaking at 180 rpm. To monitor bacterial growth, optical density measurements at a wavelength of 600 nm (OD600) were taken using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay reader (Smart Spec Plus, Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) every hour for a duration of 20 h. This experimental setup was repeated across three independent biological replicates to ensure the reliability of the results.
2.4. Observation with Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analyses were conducted following established protocols [26]. Cells from the SS2 strains SC19, ΔG22, and CΔG22 were collected at an optical density (OD600) of 0.6 and subsequently fixed overnight in 2.5% glutaraldehyde. Following this, the samples underwent post-fixation with 2% osmium tetroxide for two hours and were dehydrated through a graded ethanol series. The dehydrated specimens were then embedded in epoxy resin for sectioning. Ultrastructural examinations were performed using an H-7650 TEM instrument (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) to assess the morphological features of the bacterial cells.
2.5. Survival Assays of SS2 in H2O2, at High Temperature, and Under Acidic Conditions
To assess stress tolerance, we executed the following methodology. Initially, bacterial suspensions of the WT, ΔG22 mutant, and complemented CΔG22 strains were propagated and adjusted to an OD600 nm of 0.6 in TSB medium; all strains reached equivalent viable counts (~108 CFU/mL). Subsequently, 100 μL aliquots of each strain were individually subjected to various stress conditions: heat stress at temperatures of 40 °C, 41 °C, and 42 °C; acid stress mediated by acetic acid at pH 4, pH 5, and pH 6, all maintained at 37 °C; and oxidative stress induced by 10 mM H2O2, also at 37 °C. These stressed cultures were incubated for 1 h under their respective conditions. Concurrently, untreated strains were incubated at 37 °C for 1 h, serving as negative controls. To quantify the stress-induced survival, serial dilutions of the bacterial suspensions under all conditions were plated onto TSA plates. The colony-forming unit (CFU) counts under each stress scenario were then determined. The survival rate under a given stress was calculated as a percentage, using the formula [(CFU under stress)/(CFU in negative control)] × 100%, adopting a previously established methodology [27]. This experimental protocol was independently replicated three times to ensure reproducibility and statistical robustness.
2.6. Adhesion and Invasion Assays in Caco-2 and HEp-2 Cells
We utilized human laryngeal cancer epithelial cells (HEp-2) and human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells (Caco-2) to conduct adhesion and invasion assays for SS2, as described previously, with some modifications [21]. These two cell lines had previously been used to study interactions with SS2 strains [9,28]. These cell lines were purchased from Pricella Biotechnology Co., Ltd. and Warner Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China), respectively. Strains were streaked on TSA containing 10% fetal bovine serum and incubated for 16 h on 37 °C. The cultures were then used to inoculate fresh TSB containing 10% newborn bovine serum and cultured overnight. For the adhesion assay, bacterial strains were collected at the mid-exponential growth phase (OD600 = 0.6) via centrifugation and subsequently washed twice with PBS; all strains reached equivalent viable counts (~108 CFU/mL) before inoculation. The bacteria were then resuspended in a DMEM culture medium lacking antibiotics to achieve a concentration of 5 × 107 CFU/mL before being added to 24-well tissue culture plates containing HEp-2 and Caco-2 cells. The plates were incubated at 37 °C for 2 h. Infected cells were rinsed three times with PBS to remove unbound bacteria. The number of adherent bacteria was determined by plating serial 10-fold dilutions on TSB agar plates and incubating them at 37 °C for 12 h to count the colonies that had formed. The invasion assay procedure was similar to that of the adhesion assay, with the exception that extracellular and surface bacteria were eliminated using streptomycin (100 ng/mL) and penicillin (100 ng/mL). Each assay was carried out in triplicate to ensure reproducibility.
2.7. Anti-Phagocytosis Analysis in RAW 264.7 Macrophages
To assess the intracellular survival capacity of bacteria, murine RAW264.7 macrophages were propagated in DMEM medium fortified with 10% FBS, then distributed into 24-well plates at a density of 4 × 105 cells per well, following an adapted protocol from the prior literature [29]. Prior to infection, bacterial cultures in the logarithmic phase were harvested by centrifugation, rinsed twice with sterile PBS, and redispersed in fresh DMEM devoid of serum. The macrophages were subsequently challenged with these bacteria at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 100. Following a 2 h co-incubation period at 37 °C under a 5% CO2 atmosphere, the macrophages were subjected to extensive washing with PBS and maintained in DMEM supplemented with 1% FBS and antibiotics (streptomycin, 100 ng/mL; penicillin, 100 ng/mL) throughout the experimental duration. To quantify intracellular bacterial survival, infected cells were sampled 2 h post-antibiotic treatment. After triplicate washes with sterile PBS, the macrophages were lysed using 0.02% Triton X-100 (Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) at 37 °C for 15 min, thereby releasing the intracellular bacteria. The resultant lysates underwent serial dilutions and were plated onto TSA agar, followed by overnight incubation at 37 °C. Colony forming units (CFUs) were enumerated to ascertain the intracellular bacterial load. To track the dynamics of bacterial survival over time relative to the initial intracellular bacterial count, a relative CFU (rCFU) metric was employed, calculated as the ratio of CFUs at a given time point (x) to the CFUs at the starting time point (0), adapted from the methodology described by Cumley [30]. This experimental design incorporated three independent biological replicates, each replicated technically in triplicate to ensure robust statistical analysis.
2.8. Whole-Blood Bactericidal Assay
The survival of SS2 in whole blood was determined as described in previous studies [31]. Briefly, each bacterial suspension was incubated at 37 °C for 5 h under static conditions and then centrifuged at 6000 rpm for 5 min. The pellets were suspended in PBS and the microbial concentrations adjusted to 104 CFU/mL. SC19 (100 µL) or an equal volume of ∆G22 and C∆G22 was added to 900 µL of fresh heparinized pig blood from clinically healthy pigs for 3 h at 37 °C. The initial bacterial volume was set to 100%, and the percentage of remaining bacteria was recorded at this time point (after 3 h). Each assay was performed as three independent biological replicates.
2.9. Experimental Infection of Mice
Overnight cultures of SS2 strains SC19 and ∆G22 were washed twice with PBS and suspended in PBS. Twenty-four 6-week-old female BALB/c mice were randomly divided into three groups, with eight mice in each. They were challenged with 200 µL of PBS containing 5 × 108 colony-forming units (CFUs) of SC19 or ∆G22 or with 200 µL of PBS as the blank control. The infected mice were monitored daily for 7 days. Clinical symptoms and deaths were observed and recorded postinfection. Another 18 BALB/c mice were divided into three groups and injected intraperitoneally with 5 × 107 CFU per mouse, to examine the invasion and colonization capacities of SS2 strains SC19 and ∆G22. At 24 h postinfection, the infected mice were killed, and brain, blood, spleen, lung, and liver samples were collected. The numbers of colonizing bacteria were measured by plating diluted samples onto TSA containing 10% newborn bovine serum. The present study was carried out in strict adherence with the ethical standards for animal experimentation set forth by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Hubei Academy of Preventive Medicine/Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention. The experimental protocol was meticulously reviewed and approved by the IACUC, with the assigned ethics approval number 202310190. Throughout the research, we upheld the highest standards of animal care and welfare, ensuring that all procedures were consistent with national and international guidelines on the humane treatment of animals. This included the implementation of measures to alleviate pain and distress, such as the appropriate use of anesthesia and analgesia, as well as the application of the 3R principle—Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement—to optimize scientific rigor while minimizing animal usage.
2.10. RNA Sequencing Analysis
The total RNAs of WT and ΔG22 cultures were extracted in the late exponential phase with the Total RNA Isolation Kit (Shanghai Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China). RNA libraries were constructed and Illumina sequencing was performed on an Illumina HiSeq™ sequencer (Novogene, Beijing, China). The complete genomic sequence of SC19 (accession number: CP020863) was used as the reference genome against which the processed reads from each sample were aligned with Bowtie2. The DESeq R package (1.18.0) was used to identify the differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The DEGs were functionally annotated with the NCBI, ENSEMBL, Gene Ontology (GO), UniProt, and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) databases and a NCBI BLAST+ (version 2.13.0) alignment analysis.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using GraphPad Prism 8.3.0 software (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Appropriate statistical tests were selected based on the nature of the data and the experimental design. For normally distributed data with equal variances, one-sample t-tests or unpaired t-tests were used to compare differences between two groups. For comparisons among multiple groups, one-way ANOVA was employed. When data did not meet the assumptions of normality or equal variances, non-parametric tests such as the Mann–Whitney U test or Kruskal–Wallis test were utilized. For in vivo virulence experiments, survival was analyzed using the LogRank test. All statistical tests were two-tailed, and a p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Identification of G22 Gene Knockout Strain and Complementary Strain
The deletion of the G22 gene was verified with PCR using the primers listed in Table 1. As shown in Figure 1B, a large fragment (1347 bp) was amplified from the SC19 genome with the external primers (W1/W2) of G22, and a small genome fragment (1026 bp) was amplified from the ∆G22 and C∆G22 genome. The fragments in ∆G22 were smaller than those from the parent strain SC19 (Figure 1; Supplementary Materials, Figure S1). A small fragment (202 bp) was amplified from the SC19 and C∆G22 genome with the internal primers (N1/N2) of G22. And no fragment was amplified from the ∆G22 genome with the internal primers of G22 (Figure 1B). In summary, we successfully deleted the G22 gene.
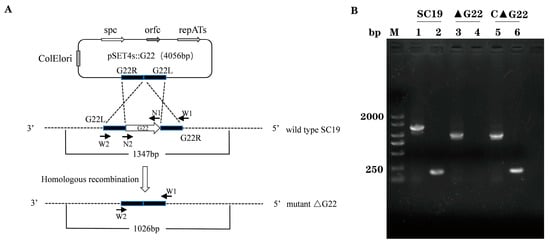
Figure 1.
Identification of G22 gene knockout strain and complementary strain. (A) G22 knockout technology roadmap. G22L: Upstream fragment amplification of G22. G22R: Downstream fragment amplification of G22. W1/W2: Identification outside the homologous region. N1/N2: Identification of the internal fragment of G22. (B) Confirmation of the ∆G22 mutant (M, DNA Marker, Lanes 1, 3, and 5 were amplified with the external primers W1/W2. Lanes 2, 4, and 6 were amplified with the internal primers N1/N2).
3.2. Characterization of Mutant Strain ∆G22
We examined the phenotypes of ∆G22 and C∆G22. Growth curves indicated few differences between ∆G22, C∆G22, and SC19 (Figure 2A), so the deletion of the G22 gene did not greatly affect the growth characteristics of ∆G22. To investigate whether Cps (cellular polysaccharide) was altered by G22 deficiency, we examined the mutant ∆G22, complemented C∆G22, and SC19 strains with TEM. The Cps structure and composition of SC19 and C∆G22 are basically consistent (Figure 2B,D). Surprisingly, the Cps structure and composition of ∆G22 differ markedly from those of SC19 (Figure 2C). The Cps structure of ∆G22 shows irregular matrix deposition with visible spatial discontinuities, indicating that the G22 protein is involved in the synthesis or regulation of Cps.
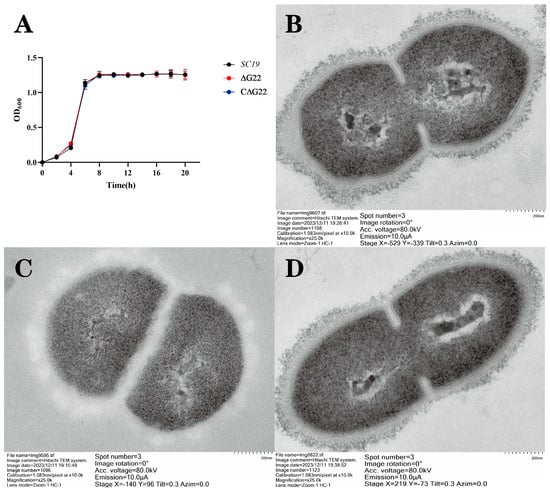
Figure 2.
(A) Growth characteristics of SC19, ∆G22, and C∆G22. Transmission electron micrographs of SC19 (B), ∆G22 (C), and C∆G22 (D).
3.3. Role of G22 in Oxidative Stress Tolerance of SS2
To investigate the effect of deleting the G22 gene on the stress tolerance of SS2, we compared the survival of SS2 strains SC19 and ∆G22 under the stress imposed by H2O2, high-temperature, or acidic conditions. Compared with that of the SC19 and C∆G22 strains, the survival rate of ΔG22 was significantly lower than that of SC19 under acidic conditions, high temperatures, and in the presence of H2O2 (both p < 0.01; Figure 3A–C). No significant difference was found in the survival rates of three strains at a high temperature 42 °C (Figure 3C). These results indicate that G22 is important in the bacterium’s resistance to oxidative stress and could affect the antioxidant capacity, high-temperature resistance, and acid resistance of SS2.
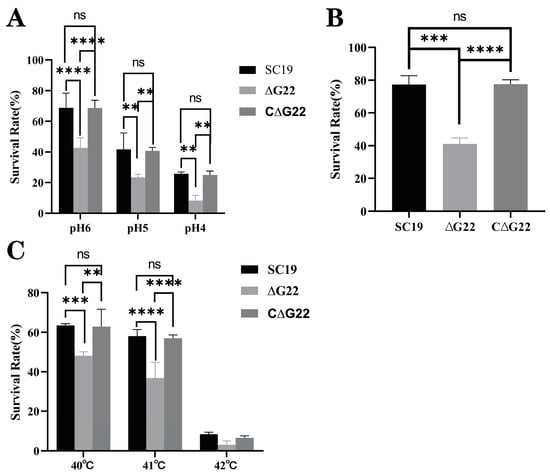
Figure 3.
Survival capacities of SC19, ∆G22, and C∆G22 under stress imposed by acid (A), H2O2 (B), or high temperatures (C). Data represent the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. ‘ns’, ‘**’, ‘***’, and ‘****’ indicate significant difference values with ‘p > 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.001, and p < 0.0001’, respectively.
3.4. Role of G22 in Adhesion to and Invasion of Host Cells by SS2
The effect of G22 deletion on the in vitro adhesion and invasion of cells by SS2 was investigated in the Caco-2 and HEp-2 cell lines. The results indicated that the adhesion of ∆G22 to Caco-2 cells was significantly lower than that of SC19 (p < 0.01; Figure 4B). Similarly, the invasion of Caco-2 cells by ∆G22 was markedly lower than that by SC19 (p < 0.001; Figure 4D), consistent with the results in HEp-2 cells (p < 0.001; Figure 4A,C). The adherence rates and invasion rates of host cells did not differ significantly between SC19 and C∆G22. These findings suggest that the G22 protein contributes to the adhesion and invasion of its host cells by SS2.
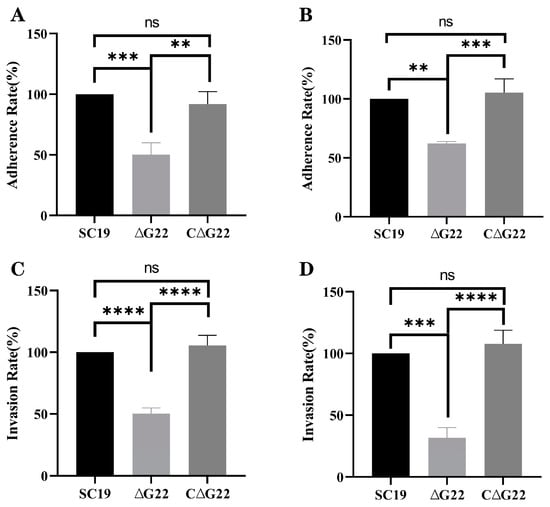
Figure 4.
Involvement of G22 in adhesion and invasion of host cells by SS2. (A) Adherence rates of SC19, ∆G22, and C∆G22 in HEp-2 cells. (B) Adherence rates of SC19, ∆G22, and C∆G22 in Caco-2 cells. (C) Invasion rates of SC19, ∆G22, and C∆G22 in HEp-2 cells. (D) Invasion rates of SC19, ∆G22, and C∆G22 in Caco-2 cells. Data represent the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. ‘ns’, ‘**’, ‘***’, and ‘****’ indicate significant difference values with ‘p > 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.001, and p < 0.0001’, respectively.
3.5. Role of G22 in Resistance of SS2 to Host Cell Phagocytosis and Whole-Blood Resistance Assay
These results showed that the phagocytosis rate of the SS2 strain ∆G22 was significantly higher than that of the SS2 strain SC19 (p < 0.001). This indicates that the deletion of G22 made the bacterium more easily phagocytosed by RAW 264.7 cells than the WT SC19 (Figure 5A) was. In a pig blood resistance assay, ΔG22 was more vulnerable to the bactericidal effect of blood and was less viable when exposed to pig blood than strain SC19 (Figure 5B). Phagocytosis rates and bacterial killing did not differ significantly between SC19 and C∆G22. These results indicate that the deletion of the G22 gene reduced the opsonic killing and pathogenic effect of SS2.
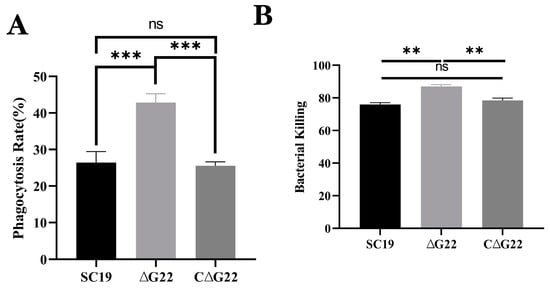
Figure 5.
Effects of G22 gene deficiency on pathogenicity phenotype of SS2. (A) Phagocytic rates of SC19, ∆G22, and C∆G22 in Raw 264.7 cells. (B) Growth indices of SC19, ∆G22, and C∆G22 in pig blood. Data represent the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. ‘ns’, ‘**’, and ‘***’ indicate significantly different values with p > 0.05, p < 0.01, and p < 0.001, respectively.
3.6. Knockout of G22 Significantly Reduces Mortality
BALB/c mice were infected with 5 × 108 CFU of SC19 or an equal quantity of ∆G22. As shown in Figure 6, 80% of mice infected with SC19 died within 3 days. In contrast, 80% of mice infected with ∆G22 survived for 7 days postinfection. These results indicate that G22 deficiency significantly reduced the virulence of SS2 in these mice.
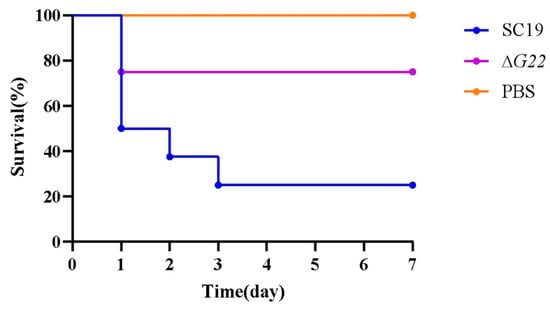
Figure 6.
Survival curves of SC19 and ∆G22 in a mouse infection model. Survival was analyzed using the LogRank test. Twenty-four BALB/c mice were randomly divided into three groups, with eight mice in each.
3.7. Colonization of Mouse Tissues by WT and ∆G22 Strains
To evaluate the inflammatory responses of animals infected with the WT and mutant strains, plasma mediators of inflammation were evaluated after 24 h of infection. The cause of the reduced virulence of ∆G22 was investigated by determining the cytokine concentrations in the blood and the bacterial loads in different organs after infection with ∆G22 or SC19. The numbers of SC19 cells recovered from the blood (Figure 7A) and brain (Figure 7E) were significantly higher than those of the mutant strain ∆G22 (both p < 0.001). The bacterial loads of SC19 in the brain and blood were 105/mL, whereas the bacterial loads of ∆G22 in the brain and blood were < 103/mL. These results indicate that resistance to the bactericidal effect of blood was significantly reduced. The spleen (Figure 7B), lung (Figure 7C), and liver (Figure 7D) samples showed similar colonization rates to the brain and blood. The bacterial loads of SC19 were higher in mice than those of ∆G22. These results indicate that the deletion of G22 increased microbial clearance from the host tissues of infected mice.
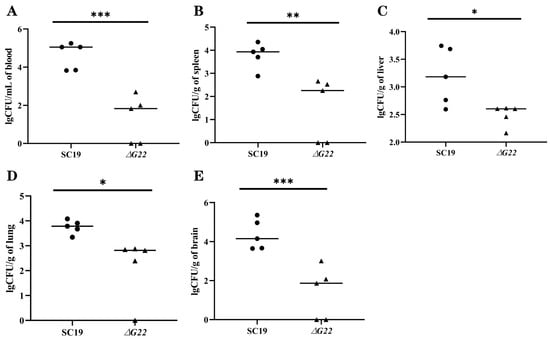
Figure 7.
Colonization of various tissues of mice by SC19 and ∆G22. (A) Bacterial burdens in the blood of BALB/c mice at 24 h postinfection. (B) Bacterial burdens in spleen tissues of BALB/c mice at 24 h postinfection. (C) Bacterial burdens in liver tissues of BALB/c mice at 24 h postinfection. (D) Bacterial burdens in lung tissues of BALB/c mice at 24 h postinfection. (E) Bacterial burdens in brain tissues of BALB/c mice at 24 h postinfection. Data represent the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. ‘*’, ‘**’, and ‘***’ indicate significantly different values with p < 0.05, p < 0.01, and p < 0.001, respectively.
3.8. Significant Bacterial Transcriptomic Changes with G22 Gene Deletion
To investigate the molecular regulatory mechanisms of the G22 gene in the pathogenic process of S. suis, we performed a comparative analysis of gene transcription levels between WT SC19 and the G22 knockout strain (∆G22) using RNA sequencing technology. Our findings revealed that the deletion of G22 resulted in the differential expression of 50 genes, with 23 genes being upregulated and 27 being downregulated (Figure 8A, Supplementary Figure S2). These differentially expressed genes (DEGs) are implicated in various biological functions, highlighting the pivotal role of G22 in the regulation of cellular processes in S. suis. Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis indicated that the DEGs were significantly enriched in 158 categories, predominantly related to biological processes such as sugar metabolic processes, carbohydrate transport processes, and transmembrane transport processes (Supplementary Figure S3). This suggests that G22 plays a crucial role in modulating biological processes that influence the cellular dynamics of S. suis. Furthermore, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway annotation demonstrated that the DEGs were involved in 29 metabolic pathways, with a significant focus on the phosphotransferase system (PTS) and fructose and mannose metabolism, as well as glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism (Figure 8B).
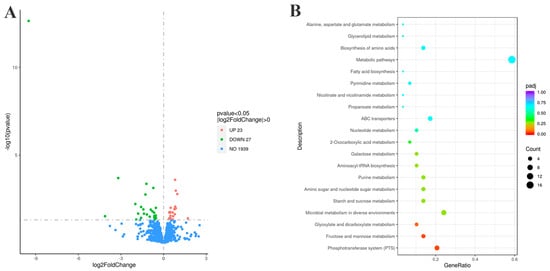
Figure 8.
Transcriptomic profiles of strains ∆G22 and SC19. (A) Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes (upregulated genes are shown in red, and downregulated genes are shown in green). (B) KEGG metabolic pathways of differentially expressed genes.
Specifically, the analysis of the PTS indicated that all 14 upregulated genes were associated with this system, including 4 operon genes (manLMN) related to mannose and the fructose-specific IIC component (fruA) (Figure 8B). We hypothesize that the absence of G22 may enhance the phosphorylation of fructose and mannose, which could indirectly inhibit the phosphorylation and transport of glucose, thereby downregulating the expression of virulence factors in S. suis and ultimately attenuating the virulence of the SC19 strain. Furthermore, the absence of G22 resulted in the decreased expression of glnA within the Two-Component System (TCS), which is implicated in the intracellular accumulation of glutamine. This alteration likely contributes to a weakened expression of associated virulence factors, leading to the attenuation of the bacterium’s virulence (Supplementary Figure S4). Additionally, the deletion of G22 caused a reduction in the expression of lacD within the Quorum Sensing (QS) system, which subsequently affected the expression of the virulence factor SpeB, further contributing to the observed decrease in pathogenicity (Supplementary Figure S5).
In summary, transcriptomic analysis underscores the multifaceted role of the G22 gene in regulating key biological processes and metabolic pathways, ultimately influencing the pathogenicity of S. suis.
4. Discussion
S. suis is a zoonotic bacterial pathogen that causes lethal infections in pigs and humans [32]. Among all the S. suis serotypes, SS2 is regarded as the most important and virulent zoonotic agent and is responsible for infections in swine and humans [7]. Therefore, clarifying the molecular mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of S. suis is crucial in the development of novel and effective prophylactic and therapeutic strategies. Although our knowledge of the pathogenesis of S. suis has improved in recent years, the precise involvement of most of its putative virulence factors remains poorly understood, and further studies are required to clarify it [33].
In this study, we defined the phenotypic differences between strains SC19 and ∆G22 to characterize the function of G22 in terms of the pathogenicity of SS2, to extend our understanding of this zoonotic pathogen. Comparative growth curves showed that the deletion of the G22 gene had no effect on bacterial growth. However, it reduced the cytotoxicity, adhesion, and invasion of SC19 in Caco-2 and HEp-2 cells, indicating that G22 contributes to the adhesion to and invasion of host cells by SS2. G22 deletion also rendered the bacterium more easily phagocytosed by RAW 264.7 cells than SC19. In a pig blood resistance assay, ΔG22 was more vulnerable to the bactericidal effect of blood than SC19 and was less viable when exposed to pig blood. The deletion of G22 reduced the antioxidant capacity and acid resistance of SS2. The G22 protein mediates SS2 infection by affecting bacterial invasion, phagocytosis resistance, and virulence. This evidence suggests that G22 is one of the multifunctional factors that play an essential role in the virulence and pathogenesis of SS2. A previous study showed that the lacD gene is generally distributed in SS2 strains, which encodes a novel metabolism-related factor that contributes to stress tolerance, antimicrobial resistance, and virulence modulation, as moonlighting roles in SS2 [21]. As the most important virulence factor of S. suis, Cps also prevents host phagocytes from phagocytizing and killing the bacterium [34]. There are several similarities between G22 and the abovementioned virulence factors. However, the pathogenesis of the G22 virulence factor requires further investigation in future research.
As previously reported, infected mice developed the typical clinical symptoms of S. suis disease, including septicemia, meningitis, and septic shock, followed by clinical signs of central nervous system (CNS) dysfunction [35]. We experimentally infected mice to evaluate the inflammatory response of animals infected with strains SC19 and ∆G22. The results indicated that the normal resistance to the bactericidal effect of blood and the BBB-damaging ability of SC19 were significantly reduced in ∆G22 and that the deletion of G22 increased microbial clearance from the tissues of infected mice. The survival rate of strain ΔG22 in a microenvironment of H2O2-induced oxidative stress was also greatly reduced compared with that of SC19. Consistent with previous findings, the reduced tolerance of ∆G22 for oxidative stress may be an important factor in the reduced survival of the mutant in infected mouse tissues, because ∆G22 is probably less well adapted to the host environment during infection [26]. This is consistent with our experimental finding that the BBB-damaging ability of ∆G22 was significantly reduced.
The SS2 biofilm structure is complex and may contain lipoprotein, Cps, and host-derived fibrin, although most bacterial biofilms are predominantly composed of a polysaccharide matrix. Extracellular polysaccharides can be categorized into different types based on their apparent morphology: mucin-like protein (also known as ‘mucoid’), which generally creates a resilient outer membrane that adheres to the cell surface through intermolecular hydrogen bonds and other non-covalent bonds, also known as ‘Cps’ [36]. The Cps of SS2 strains is composed of glucose, galactose, N-acetylglucosamine, rhamnose, and sialic acid, which are synthesized by the capsule synthesis clusters [37]. Transmission electron microscopic analysis of SC19 and ∆G22 showed that the capsular structure of ∆G22 had irregular matrix deposition with visible spatial discontinuities. This differs from previous reports, in which the capsule of the deletion mutant strain was thinner than that of the WT [37,38].
We investigated the transcriptome-level changes in SC19 in response to the deletion of G22 to determine how G22 regulates the high-level pathogenicity of SS2. The deletion of G22 led to the differential expression of 50 genes, among which several encoded potential virulence-associated factors. The first was associated with the phosphotransferase system (PTS). The G22 deletion altered the expression of fourteen PTS-related genes, all of which were upregulated. These included four genes in the mannose-specific PTS (manL, manM, manN, and manO), as well as the fructose-specific IIC component gene fruA. Therefore, we speculate that the deletion of G22 promoted the phosphorylation of fructose and mannose [39,40,41], thereby indirectly inhibiting the phosphorylation and transport of glucose, inhibiting the expression of virulence factors, and ultimately reducing the virulence of S. suis SC19. The deletion of G22 also reduced the expression of glnA in the two-component system (TCS), which, we speculate, affected the accumulation of intracellular glutamine in S. suis, weakening the expression of related virulence factors and ultimately reducing the virulence of S. suis [42,43]. The third virulence-associated system affected was the quorum sensing system (QSS). The loss of G22 reduced the expression of lacD in the QSS, which affected the expression of the virulence factor SpeB, also weakening bacterial virulence. Therefore, we investigated whether G22 is involved in the virulence of SS2 [21,44] because there is sparse experimental evidence of the biological function of G22 in SS2 pathogenicity. Our integrative omics analyses reveal that secreted protein G22 is a master virulence coordinator in S. suis. Key findings demonstrate that G22 deletion triggers capsular disorganization (30% reduction in CPS thickness), impaired host interaction, and compromised stress resistance, concurrent with the significant upregulation of PTS components and glycolytic genes. This tripartite regulatory pattern suggests that G22 functions as a metabolic–capsular coupler—a novel mechanism where extracellular capsule biogenesis is energetically coupled with intracellular carbon flux via PTS-mediated ATP generation. While analogous nutrient sensing systems exist in Klebsiella pneumoniae [45], the direct linkage of CPS synthesis to sugar phosphotransferase activity represents an evolutionary innovation in S. suis pathogenicity. Future studies should delineate whether G22 acts as a PTS substrate chaperone or phosphatase modulator to bridge these pathways.
In addition to the findings presented in this study, several limitations should be acknowledged. Firstly, although mouse models and cell cultures were used to investigate the pathogenicity and virulence of SS2, there may be differences between these models and natural infections in pigs or humans. Therefore, the results obtained from animal experiments and cell cultures may not fully reflect the actual situation in vivo. Secondly, the study focused on a specific virulent strain, SC19, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other strains or serotypes of S. suis. Future studies should explore the role of the G22 gene in different strains and serotypes to validate the current findings. Thirdly, the pathogenesis of S. suis infections is complex and involves multiple factors. The current study only explored the role of the G22 gene, and other genes and proteins may also play crucial roles in the virulence and pathogenesis of S. suis. Therefore, further research is needed to elucidate the entire pathogenic mechanism.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms13040774/s1, Supplementary Figure S1. Comparison of sequences of SC19 and ∆G22. The consensus sequences are indicated in red. Supplementary Figure S2. Hierarchical cluster diagram of differential genes of SC19 and ∆G22.The expression genes are clustered in rows in each heatmap, and the isolates are shown in columns. The numbers in the end in isolates representing each of the three biological replica. High expression genes are represented in red and low expression genes are represented in blue. Supplementary Figure S3. The significantly enriched GO terms of the DEGs of SC19 and ∆G22. The top 30 significantly enriched GO terms are shown. The X-axis indicates the enriched GO terms, and the Y-axis indicates the number of the DEGs for each GO term. The GO terms in red color belonged to biological processes, those in green belonged to cellular components, and those in blue belonged to molecular function. The GO terms with a corrected p-value < 0.05 were considered to be significantly enriched. Supplementary Figure S4. KEGG metabolic pathway for the Two-Component System (TCS). Low expression genes are highlighted in green. Supplementary Figure S5. KEGG metabolic pathway for the Quorum Sensing (QS) system. Low expression genes are highlighted in green.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.D. and X.C.; methodology, Y.T., S.F. and Z.L.; software, Y.T. and S.F.; validation, X.C. and X.D.; for-mal analysis, Y.T. and S.F.; investigation, S.F. and X.D.; resources, Y.Z. and X.D.; data curation, Y.T. and S.F.; writing—original draft preparation, S.F.; writing—review and editing, S.F., Y.T., X.C., Z.L., Y.H., Y.F. and J.L.; visualization, Y.T., S.F. and X.D.; supervision, X.D.; project administration, X.D.; funding acquisition, X.D. and X.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation Project (2022CFB945), and Hubei Provincial Department of Education Scientific and Technological Research Project (Q20211612).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Hubei Academy of Preventive Medicine/Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention (protocol code 202310190 and date of approval 16 October 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw sequencing datasets from this study have been curated and deposited in the Sequence Read Archive of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) under accession number PRJNA1130436, promoting data sharing and reproducibility in future research. The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors state that they have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- Gottschalk, M.; Segura, M.; Xu, J. Streptococcus suis infections in humans: The Chinese experience and the situation in North America. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2007, 8, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goyette-Desjardins, G.; Auger, J.-P.; Xu, J.; Segura, M.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcus suis, an important pig pathogen and emerging zoonotic agent—An update on the worldwide distribution based on serotyping and sequence typing. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 3, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Nahuel, F.; Mariela, S.; Daniel, G.; Marcelo, G. Virulence factors involved in the pathogenesis of the infection caused by the swine pathogen and zoonotic agent Streptococcus suis. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 259–279. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Cao, M.; Hu, D.; Wang, C. Streptococcus suis infection. Virulence 2014, 5, 477–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Q.; Xu, Q.; Lan, Z.; Wu, Z. Comparative Genome Analysis of TwoStreptococcus suis Serotype 8 Strains Identifies Two New Virulence-Associated Genes. Animals 2024, 14, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisselink, H.J.; Smith, H.E.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Peperkamp, K.; Vecht, U. Distribution of capsular types and production of muramidase-released protein (MRP) and extracellular factor (EF) of Streptococcus suis strains isolated from diseased pigs in seven European countries. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 74, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Fei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, G.; Shi, H.; Zhang, W. The biological role of MutT in the pathogenesis of the zoonotic pathogen Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Virulence 2021, 12, 1538–1549. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Wang, C.; Feng, Y.; Yang, W.; Song, H.; Chen, Z.; Yu, H.; Pan, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome caused by Streptococcus suis serotype 2. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e151. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, H.; Shiming, F.; Geng, Z.; Anusak, K.; Xiabing, C.; Xingxing, D.; Lin, T.; Jinquan, L. Genome analysis provides insight into hyper-virulence of Streptococcus suis LSM178, a human strain with a novel sequence type 1005. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23919. [Google Scholar]
- Segura, M.; Fittipaldi, N.; Calzas, C.; Gottschalk, M. Critical Streptococcus suis Virulence Factors: Are They All Really Critical? Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 585–599. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, W.; Hexiang, J.; Fengyang, L.; Xuan, J.; Jun, W.; Shaopeng, W.; Yi, S.; Yanyan, T.; Hong, C.; Yu, S.; et al. O-acetyl-homoserine sulfhydrylase deficient Streptococcus suis serotype 2 strain SC19 becomes an avirulent strain and provides immune protection against homotype infection in mice. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 288, 109943. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.; Qin, W.; Zhu, H.; Wang, X.; Jiang, J.; Hu, J. How Streptococcus suis serotype 2 attempts to avoid attack by host immune defenses. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2019, 52, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willenborg, J.; Koczula, A.; Fulde, M.; Greeff, A.D.; Beineke, A.; Eisenreich, W.; Huber, C.; Seitz, M.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Goethe, R. FlpS, the FNR-like Protein of Streptococcus suis Is an Essential, Oxygen-Sensing Activator of the Arginine Deiminase System. Pathogens 2016, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kietzman, C.C.; Caparon, M.G. CcpA and LacD.1 affect temporal regulation of Streptococcus pyogenes virulence genes. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, T.; Wolfgang, H. Global control of sugar metabolism: A gram-positive solution. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2002, 82, 59–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zomer, A.L.; Buist, G.; Larsen, R.; Kok, J.; Kuipers, O.P. Time-resolved determination of the CcpA regulon of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris MG1363. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 1366–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelburne, S.A., III; Keith, D.; Horstmann, N.; Sumby, P.; Davenport, M.T.; Graviss, E.A.; Brennan, R.G.; Musser, J.M. A direct link between carbohydrate utilization and virulence in the major human pathogen group A Streptococcus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1698–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.T.; Burne, R.A. Functional Genomics Approach to Identifying Genes Required for Biofilm Development by Streptococcus mutans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willenborg, J.; Fulde, M.; De Greeff, A.; Rohde, M.; Smith, H.E.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Goethe, R. Role of glucose and CcpA in capsule expression and virulence of Streptococcus suis. Microbiology 2011, 157, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tu, T.; Yao, X.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Z.; Ren, M.; Zhang, G.; Yu, Y.; Lu, A.; Wang, Y. Pan-genome analysis of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 highlights genes associated with virulence and antibiotic resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1362316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaowu, J.; Lexin, Z.; Dongbo, Z. Deletion of lacD gene affected stress tolerance and virulence of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. J. Microbiol. 2022, 60, 948–959. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Chao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, W.; Fischetti, V.A.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Li, J. The global emergence of a novel Streptococcus suis clade associated with human infections. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e13810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Jing, H.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Zu, R.; Luo, L.; et al. Human Streptococcus suis outbreak, Sichuan, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamatsu, D.; Osaki, M.; Sekizaki, T. Thermosensitive Suicide Vectors for Gene Replacement in Streptococcus suis. Plasmid 2001, 46, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, D.; Osaki, M.; Sekizaki, T. Construction and Characterization of Streptococcus suis—Escherichia coli Shuttle Cloning Vectors. Plasmid 2001, 45, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.F.; Liu, W.Q.; Zhang, C.Y.; Gao, T.; Zheng, L.L.; Qiu, D.X.; Li, L.; Zhou, R. The involvement of MsmK in pathogenesis of the Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Microbiol. Open 2017, 6, e00433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, J.; Roy, A.C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, X.; Pan, Z.; Yao, H. Role of ClpX and ClpP in Streptococcus suis serotype 2 stress tolerance and virulence. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 223–225, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, D.; Zong, B. Orphan response regulator CovR plays positive regulative functions in the survivability and pathogenicity of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 isolated from a pig. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 19, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, Y.; Ni, Y.; Zhou, J.; Han, L.; Yu, Z.; Mao, A.; Wang, D.; Fan, H.; He, K. The Redox-Sensing Regulator Rex Contributes to the Virulence and Oxidative Stress Response of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumley, N.J.; Smith, L.M.; Anthony, M.; May, R.C. The CovS/CovR acid response regulator is required for intracellular survival of group B Streptococcus in macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 1650–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhu, J.; Chang, H.; Gao, X.; Gao, C.; Wei, X.; Yuan, F.; Bei, W. The CodY regulator is essential for virulence in Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Zhao, L.; Hu, Q.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, G.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Huang, Q.; et al. Screening for Virulence-Related Genes via a Transposon Mutant Library of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Using a Galleria mellonella Larvae Infection Model. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servane, P.; David, R.; Anaïs, B.; Masatoshi, O.; JeanPhilippe, A.; Mariela, S.; Marcelo, G. Role of Maturation of Lipoproteins in the Pathogenesis of the Infection Caused by Streptococcus suis Serotype 2. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, A.; Sun, X.; Jin, M. HP1717 Contributes to Streptococcus suis Virulence by Inducing an Excessive Inflammatory Response and Influencing the Biosynthesis of the Capsule. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esgleas, M.; Dominguez-Punaro, M.D.L.C.; Li, Y.; Harel, J.E.; Dubreuil, J.D.; Gottschalk, M. Immunization with SsEno fails to protect mice against challenge with Streptococcus suis serotype 2. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 294, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Shen, Y.; Yuan, S.; Quan, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Yi, L.; Wang, Y. Methyl anthranilate deteriorates biofilm structure of Streptococcus suis and antagonizes the capsular polysaccharide defence effect. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 62, 106996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, W.; Ma, J.; Pan, Z.; Yao, H. Identification of an Autorepressing Two-Component Signaling System That Modulates Virulence in Streptococcus suis Serotype 2. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, 10–128. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Q.; He, P.; Wang, D.; Ma, J.; Zhong, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Q.; Pan, Z.; Yao, H. An Auto-Regulating Type II Toxin-Antitoxin System Modulates Drug Resistance and Virulence in Streptococcus suis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 671706. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, W. Contribution of nadR to the cell growth and virulence of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 288, 109928. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, Y.; Nagasawa, R.; Senpuku, H. Inhibiting effects of fructanase on competence-stimulating peptide-dependent quorum sensing system in Streptococcus mutans. J. Infect. Chemother. 2017, 23, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disi, L.; JinMing, F.; Jingjie, W.; Long, L.; Li, X.; Feiyu, L.; Jing, Y.; Bei, L. The Fructose-Specific Phosphotransferase System of Klebsiella pneumoniae is regulated by global regulator CRP and link to virulence and growth. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86, 10–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Haber, A.; Friedman, S.; Lobel, L.; Burg-Golani, T.; Sigal, N.; Rose, J.; Livnat-Levanon, N.; Lewinson, O.; Herskovits, A.A. L-glutamine Induces Expression of Listeria monocytogenes Virulence Genes. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Wang, H.; Han, X.; Li, W.; Xue, M.; Qi, K.; Chen, X.; Ni, J.; Deng, R.; Shang, F.; et al. The two-component system, BasSR, is involved in the regulation of biofilm and virulence in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Avian Pathol. 2020, 49, 532–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Das, S.; Burne, R.A. Utilization of lactose and galactose by Streptococcus mutans: Transport, toxicity, and carbon catabolite repression. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 2434–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjaitan, N.S.; Horng, Y.T.; Chien, C.C.; Yang, H.C.; You, R.I.; Soo, P.C. The PTS Components in Klebsiella pneumoniae Affect Bacterial Capsular Polysaccharide Production and Macrophage Phagocytosis Resistance. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).