Advances in Donkey Disease Surveillance and Microbiome Characterization in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Search Methodology
3. Donkey Disease Surveillance Research in China
| Causative Agent | Clinical Manifestations/Findings | Treatment | Host/Model System | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial pathogens | ||||
| Salmonella abortus equi | 61 cases of abortion S. abortus equi was confirmed through serological and molecular testing | Minocycline | Donkey | [26,73] |
| Antibiotic resistance bacteria (Proteus mirabilis and Klebsiella pneumoniae) isolated from donkey meat | Potential public health concern | Donkey | [71] | |
| Coxiella burnetii; Salmonella | Isolated S. abortus equi from 45 donkeys that experienced abortions C. burnetii isolated from 17 donkeys with abortion and confirmed through real-time PCR | Donkey and mouse | [74,75] | |
| Streptococcus equi Subspecies zooepidemicus, Escherichia coli and Acinetobacter spp. | Serological, histopathalogical, and molecular diagnosis of endometritis induced bacteria | Donkey | [38,76,77,78,79] | |
| Streptococcus equi | Strangles with fever and respiratory distress Isolated S. equi from strangles epidemic on donkey farms | Donkey | [80,81] | |
| Viral pathogens | ||||
| EHV8 | Viral encephalitis with neurological disorder | Mouse and Donkey | [53] | |
| EHV8 | Abortion and respiratory distress | Donkey | [23,54] | |
| EHV8 | Inflammation and respiratory distress | Mouse lung | [56] | |
| EHV8 | Abortion | Donkey | [52] | |
| EHV1 | Abortion and respiratory distress | Mouse and Donkey | [50,51] | |
| EHV8 | Significantly reduced inflammation and oxidative stress in mouse lung by activating AMPK and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways | Cepharanthine | Mouse, NBL-6, and RK-13 cells. | [82] |
| EHV8 | Inhibited virus infection | Blebbistatin | Mouse, rabbit kidney (RK-13), and Madin–Darby Bovine Kidney (MDBK) cells | [59] |
| EHV8 | CoPP induced HO-1 inhibit EqHV-8 replication in susceptible cells through its metabolite biliverdin, which acts via PKCβ/ERK1/ERK2 and NO/cGMP/PKG signaling pathways | CoPP | Mouse, NBL-6, and RK-13 cells. | [57,61] |
| EqHV-8 | Rutin prevented EqHV-8 induced infection and oxidative stress via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway | Rutin | Mouse, MDBK, and RK-13 cells. | [58] |
| Hepatitis E virus genotypes 3 and 4 | Potential public health concern | Donkey | [62] | |
| Kirkoviruses | Intestinal inflammation and Diarrhea | Donkey | [83] | |
| Astro-virus | Diarrhea | Donkey | [63] | |
| Equine corona virus | Fever, anorexia, and diarrhea | Donkey | [84] | |
| Rotavirus | Enteritis | Donkey | [85] | |
| Equine influenza virus (H3N8 subtype) | High fever, cough, nasal discharge, enteritis, and abortion | Donkey | [86,87] | |
| Porcine circovirus 3 | Reproductive disorders including abortion | Donkey | [88] | |
| Parasitic pathogens | ||||
| Tetratrichomonas buttreyi and Pentatrichomonas hominis | Causes diarrhea and has potential for zoonotic transmission | Donkey | [89] | |
| Giardia duodenalis and Cryptosporidium spp. | Diarrhea and potential public health concern | Donkey | [25,90] | |
| Giardia duodenalis | Diarrhea and potential public health concern | Donkey | [64] | |
| Entamoeba sp. RL9 and Entamoeba equi | Diarrhea and potential public health concern | Donkey | [67] | |
| Theileria equi, Babesia caballi | Piroplasmosis (fever, anaemia, oedema, weight loss, icterus) | Donkey | [65,91] | |
| Theileria equi, Babesia caballi | Piroplasmosis (fever, anaemia, oedema, weight loss, icterus) | Donkey | [92] | |
| Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia duodenalis and Enterocytozoon bieneusi | Diarrhea and potential public health concern | Donkey | [68] | |
| Sarcocystis species (Sarcocystis bertrami, S. equicanis and S. fayeri) | Muscle damage, myositis, encephalitis, diarrhea, and weight loss | Donkey | [93,94] | |
| Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Blastocysti | Diarrhea and potential public health concern | Donkey | [95] | |
| Parascaris univalens and Parascaris equorum | Hepatitis, pneumonitis, respiratory disorders, intestinal obstruction, and even mortality if their hosts are untreated | Donkey | [96] | |
| Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Giardia duodenalis | Diarrhea and potential public health concern | Donkey | [97] | |
| Enterocytozoon bieneusi | Diarrhea and potential public health concern | Donkey | [98] | |
| Cryptosporidium | Diarrhea and potential public health concern | Donkey | [99,100] | |
| Toxoplasma gondii isolated from serum, meat and milk of donkey | Swollen lymph nodes, headaches, fever, fatigue, abortion, and muscle aches and pains | Donkey | [69,101,102,103] | |
| Enterocytozoon bieneusi | Diarrhea and potential public health concern | Donkey | [66] | |
| Neospora spp. (N. caninum) | Miscarriages, myositis, and pneumonia | Donkey | [104] | |
| Habronema muscae and H. majus | Diarrhea and intestinal ulceration | Donkey | [105] | |
| High concentrate feeds, Age pasture time and water source | Infundibular caries | Donkey | [106] |
4. The Intestinal Microbiota of Donkeys: Distribution, Function, and Physiological Significance
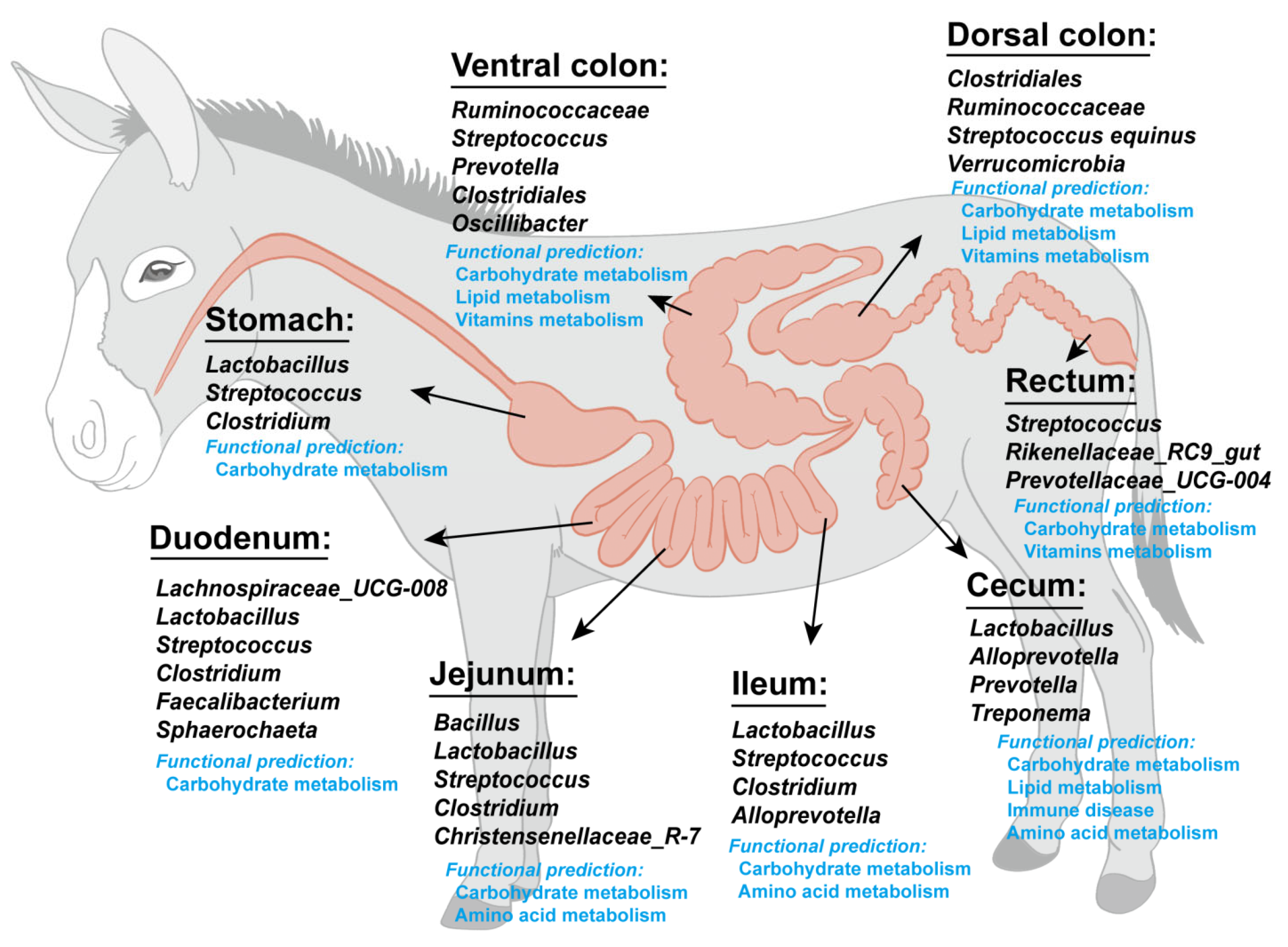
4.1. Microbiota Composition of Different Intestinal Segments
4.2. Composition of the Gut Microbiota at Different Physiological Stages
4.3. Composition of the Gut Microbiota in Different Geographical Regions
4.4. Influence of Diets and Environmental Stressors on the Composition of the Gut Microbiota
4.5. Microbiota Composition and Donkey Diseases
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, M.Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Liang, H.; Wei, L.; Huang, B.; Kou, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chai, W.; et al. A review of genetic resources and trends of omics applications in donkey research: Focus on China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1366128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Khan, M.Z.; Chai, W.; Ullah, Q.; Wang, C. Exploring genetic markers: Mitochondrial DNA and genomic screening for biodiversity and production traits in donkeys. Animals 2023, 13, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyiti, S.; Kelimu, A. Donkey industry in China: Current aspects, suggestions, and future challenges. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2021, 102, 103642. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, B.; Ren, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Chai, W. An investigation of genetic diversity in three Dezhou donkey original breeding farms. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Liu, G.; Wang, C. A survey report on the donkey original breeding farms in China: Current aspects and future prospective. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1126138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Shi, S.; Li, J.; Tang, C.; Han, Y.; Xie, P. A survey of smallholder farms regarding demographics, health care, and management factors of donkeys in northeastern China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 626622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Liang, H.; Zahoor Khan, M.; Ren, W.; Huang, B.; Chen, Y.; Xing, S.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, C. Comprehensive transcriptomic analysis unveils the interplay of mRNA and LncRNA expression in shaping collagen organization and skin development in Dezhou donkeys. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1335591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ren, W.; Peng, Y.; Khan, M.Z.; Liang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Kou, X.; Wang, L.; et al. Elucidating the role of transcriptomic networks and DNA methylation in collagen deposition of Dezhou donkey skin. Animals 2024, 14, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Shi, X.; Liu, Z.; Ren, W.; Wang, X.; Huang, B.; Kou, X.; Liang, H.; Wang, C.; Chai, W. A novel A > G polymorphism in the intron 1 of LCORL gene is significantly associated with hide weight and body size in Dezhou donkey. Animals 2022, 12, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.; Chen, W.; Li, M.; Ren, W.; Huang, B.; Kou, X.; Ullah, Q.; Wei, L.; Wang, T.; Khan, A.; et al. Is there sufficient evidence to support the health benefits of including donkey milk in the diet? Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1404998. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Sun, L.; Du, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, W.; Man, L.; Zhu, M.; Liu, G.; Khan, M.Z.; Wang, C. Characterization and discrimination of donkey milk lipids and volatiles across lactation stages. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Luo, X.; Yue, X. Characterization and nutrition assessment of amino acids in different domains between donkey colostrum and mature milk. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 132, 106345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Sun, M.; Shi, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, B.; Kou, X.; Liang, H.; Chen, Y.; et al. Effects of roughage on the lipid and volatile-organic-compound profiles of donkey milk. Foods 2023, 12, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, J.; Ning, J.; Bai, X.; Cao, X.; Yue, X.; Yang, M. Identification and analysis of miRNAs expression profiles in human, bovine, and donkey milk exosomes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 126321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Huang, F.; Du, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, C. Analysis of the differentially expressed proteins in donkey milk in different lactation stages. Foods 2023, 12, 4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Q.; Liu, G.; Wang, C. Effects of donkey milk on oxidative stress and inflammatory response. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e13935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, L.; Du, X.; Ren, W.; Man, L.; Chai, W.; Zhu, M.; Liu, G.; Wang, C. Characterization of lipids and volatile compounds in boiled donkey meat by lipidomics and volatilomics. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 3445–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhu, M.; Gong, Y.; Wang, C. Identification and functional prediction of lncRNAs associated with intramuscular lipid deposition in Guangling donkeys. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1410109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Ma, Q.; Khan, M.Z.; Zhu, M.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Chai, W. Data-independent acquisition method for in-depth proteomic screening of donkey meat. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.; Qu, H.; Ma, Q.; Zhu, M.; Li, M.; Zhan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Yao, H.; Li, Z.; et al. RNA-seq analysis identifies differentially expressed genes in different types of donkey skeletal muscles. Anim. Biotechnol. 2023, 34, 1786–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, N.; Wei, Z.; Liu, G.; Pasha, R.H.; Khan, M.A. Study on the extracting technology for antioxidant oligopeptides from donkey meat by two-step enzymatic hydrolysis. Pak. J. Zool. 2022, 54, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Li, S.; Ma, H.; Akhtar, M.F.; Tan, Y.; Wang, T.; Liu, W.; Khan, A.; Khan, M.Z.; Wang, C. An overview of infectious and non-infectious causes of pregnancy losses in equine. Animals 2024, 14, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, W. Detection of equine herpesvirus antibodies in large-scale donkey farms in Liaocheng area. Vet. Med. Sci. 2024, 10, e70016. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zeng, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Qu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J. Reproductive disorders in donkeys: Current evidence and update. Animals 2024, 14, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Tuo, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, F.; Chuai, L.; Qi, M.; Jing, B. Occurrence and genetic characteristics of Giardia duodenalis in donkeys in Xinjiang, China. Parasite 2023, 30, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, K.J.; Sun, Y.H.; Cui, L.Y.; Meng, X.; Jiang, G.M.; Zhao, F.W.; Li, J.J. Abortion in donkeys associated with Salmonella abortus equi infection. Equine Vet. J. 2019, 51, 756–759. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, X.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, F.; Zhang, X.; Khan, M.Z.; Wu, B.; Wang, H.; Gong, Y.; Wang, C.; Ma, Q.; et al. Insights into the donkey hindgut microbiome using metagenome-assembled genomes. Animals 2024, 14, 3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Guo, J.; Shi, W.; Tong, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Xiang, Z.; Qin, C. Metagenomic analysis reveals the community composition of the microbiome in different segments of the digestive tract in donkeys and cows: Implications for microbiome research. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Q.; Shi, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, C. Integrated multi-omics reveals novel microbe-host lipid metabolism and immune interactions in the donkey hindgut. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1003247. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, T.; Liang, K.; Li, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W.; Qu, H.; Dong, B.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Q.; et al. Spatial variations in the microbiota: Comparative analysis of microbial composition and predicted functions across different intestinal segments and feces in donkeys. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1494926. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Han, Q.; Hu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, H.; Zhang, H.; Qu, Y.; Shi, D.; et al. Comparative analysis of composition and spatial variations in the foregut microbiota of male and female donkeys. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 16, 1532265. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Bou, G.; Su, S.; Xing, J.; Qu, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Dugarjaviin, M. Microbial diversity within the digestive tract contents of Dezhou donkeys. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Yue, Y.; Kou, X.; Hou, W.; Wang, M.; Yang, X.; Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, C. Dynamic distribution of skin microorganisms in donkeys at different ages and various sites of the body. Animals 2023, 13, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, C. Could weaning remodel the oral microbiota composition in donkeys? An exploratory study. Animals 2022, 12, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Holyoak, R.; Liu, B.; Li, J. Investigation of oral microbiome in donkeys and the effect of dental care on oral microbial composition. Animals 2020, 10, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Mi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Holyoak, G.R.; Yi, Z.; Wu, R.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, S. Endometrial and vaginal microbiome in donkeys with and without clinical endometritis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 884574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Huang, F.; Du, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, G. Microbial quality of donkey milk during lactation stages. Foods 2023, 12, 4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoyizha, W.; Wu, X.; Zhang, M.; Guo, X.; Li, H.; Liao, X. Comparative analysis of microbial diversity in donkey milk from Xinjiang and Shandong of China through high-throughput sequencing. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, H.; Jafari, H.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z.; Su, J.; Wang, F.; Yang, G.; Sun, M.; Cheng, J.; et al. Metabolic changes before and after weaning in Dezhou donkey foals in relation to gut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1306039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, X.; Bai, D.; Yu, J.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Su, S.; Zhao, Y.; Bou, G.; et al. The composition and predictive function of the fecal microbiota differ between young and adult donkeys. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 596394. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Shang, S.; Chen, J.; Yan, J.; Wei, Q.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, H. Comparison of the gut microbiota in the Tibetan wild ass (Equus kiang) collected from high and low altitude. Pak. J. Zool. 2020, 52, 2281. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Ma, Z.; Du, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, G.; Zhou, M. Methionine alters the fecal microbiota and enhances the antioxidant capacity of lactating donkeys. Animals 2025, 15, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Yin, G.; Hui, F.; Guo, X.; Shi, B.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, S. Effects of dietary energy level on antioxidant capability, immune function, and rectal microbiota in late gestation donkeys. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1308171. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Xing, J.; Qi, X.; Lu, T.; Jin, Y.; Akhtar, M.F.; Li, L.; Liu, G. Effects of concentrate feeding sequence on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, VFA production, and fecal microbiota of weaned donkeys. Animals 2023, 13, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Xie, L.; Xing, J.; Lu, T.; Qi, X.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; Akhtar, M.F.; Jin, Y.; Liu, G. Effects of concentrate feeding sequence on VFA production, and cecal microbiota of Dezhou donkeys by metagenomic technology. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1401980. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, X.Y.; Li, X.B.; Ma, C.; Chen, H.; Yang, F. Growth performance, nutrient digestibility, fecal microbial diversity and volatile fatty acid, and blood biochemical indices of suckling donkeys fed diets supplemented with multi-enzymes. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Q.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, C. Metabolic alterations during gestation in Dezhou donkeys and the link to the gut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 801976. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Jiang, G.; Ji, C.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, W.; Feng, P.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Liu, H.; Liu, G.; et al. Effects of long-distance transportation on blood constituents and composition of the nasal microbiota in healthy donkeys. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 338. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, S.; Yi, Z.; Holyoak, R.; Wang, T.; Ding, Z.; Li, J. Nasopharyngeal microbiomes in donkeys shedding Streptococcus equi subspecies equi in comparison to healthy donkeys. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 645627. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, L.; Li, L.; Yang, R.; You, A.; Khan, M.Z.; Yu, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, C.; et al. Equine herpesvirus-1 induced respiratory disease in Dezhou donkey foals: Case study from China, 2024. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, P.; Pan, J.; Dang, Y.; Yang, E.; Jia, C.; Duan, R.; Tian, S.; Palidan, N.; Kuang, L.; Wang, C.; et al. First identification and isolation of equine herpesvirus type 1 in aborted fetal lung tissues of donkeys. Virol. J. 2024, 21, 117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Hu, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, G.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Ren, H.; Li, L. Identification of equine herpesvirus 8 in donkey abortion: A case report. Virol. J. 2022, 19, 10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Hu, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, T.; Hu, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ren, H.; et al. The emergence of viral encephalitis in donkeys by equid herpesvirus 8 in China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 840754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Xi, C.; Yu, Y.; Liu, W.; Akhtar, M.F.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, L. Characteristics and epidemiological investigation of equid herpesvirus 8 in donkeys in Shandong, China. Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Xi, C.; Geng, Y.; Tian, W.; Li, L.; Wang, T.; Zhao, J. Pathogenicity and host cytokines response of EqHV-8 infection in C57BL/6J mice. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 186, 106506. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Wang, T.; Ren, H.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, L. Characterizing the pathogenesis and immune response of equine herpesvirus 8 infection in lung of mice. Animals 2022, 12, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, S.; Hu, X.; Geng, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, W.; Zhao, J.; Tian, W.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Heme oxygenase-1 is an equid alphaherpesvirus 8 replication restriction host protein and suppresses viral replication via the PKCβ/ERK1/ERK2 and NO/cGMP/PKG pathway. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e03220-23. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhou, H.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Xu, M.; et al. Rutin prevents EqHV-8-induced infection and oxidative stress via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1386462. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Cui, X.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Khan, M.Z.; Wang, C.; et al. Blebbistatin as a novel antiviral agent targeting equid herpesvirus type 8. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1390304. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Hu, L.; Li, R.; Ren, H.; Li, S.; Sun, Q.; Ding, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, L. Hyperoside inhibits EHV-8 infection via alleviating oxidative stress and IFN production through activating JNK/Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. J. Virol. 2024, 98, e00159-24. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Hu, X.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Shen, F.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, T. Cobalt protoporphyrin blocks EqHV-8 infection via IFN-α/β production. Animals 2023, 13, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, P.; Zhao, F.; Yan, S.; Wang, C.; Fu, Q.; Hao, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhong, H.; Tang, M.; Hui, W.; et al. Detection of hepatitis E virus genotypes 3 and 4 in donkeys in northern China. Equine Vet. J. 2020, 52, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.J.; Li, J.; Tu, Q.H.; Xu, S.; Liu, W.L.; Li, Y.; Bai, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, W.H.; Xiao, Y.Q.; et al. Identification of a novel astrovirus from intestinal tissue of a donkey foal with severe diarrhea in China. Zool. Res. 2023, 44, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.W.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, T.H.; Xiao, H.D.; Su, N.; Tao, M.F.; Wu, Z.X.; Zhang, Z.D.; Zhu, X.Q.; Xie, S.C. Prevalence and multilocus genotyping of Giardia duodenalis in donkeys in Shanxi Province, North China. Animals 2023, 13, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Cao, M.; Yu, F.; Zhao, A.; Tao, D.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, M. Molecular detection of piroplasms in domestic donkeys in Xinjiang, China. Vet. Med. Sci. 2024, 10, e1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, D.M.; Ma, J.G.; Li, F.C.; Hou, J.L.; Zheng, W.B.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhu, X.Q. Occurrence of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in donkeys (Equus asinus) in China: A public health concern. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.D.; Xiao, H.D.; Wang, D.Y.; Su, N.; Liu, X.Z.; Wang, Z.R.; Xie, S.C.; Zhu, X.Q.; Zhang, S.; Gao, W.W. Molecular prevalence and associated risk factors of Entamoeba spp. in donkeys in Shanxi Province, North China. Parasites Vectors 2025, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Fan, W.; Yi, C.; Liu, H.X.; Ding, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Su, X.; Liu, Y. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia duodenalis and Enterocytozoon bieneusi in donkeys of Inner Mongolia, Northern China. Acta Parasitol. 2025, 70, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Zhao, S.; Wang, N.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Liu, M.; Jin, W.; Meng, Y.; Jia, L. Molecular occurrence and risk factors for Toxoplasma gondii infection in equids in Jilin, China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, Z.J.; Meng, Q.F. Detection of specific IgG-antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii in the serum and milk of domestic donkeys during lactation in China: A potential public health concern. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 760400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Duan, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, H.; Wu, R.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J. Antimicrobial resistance profiling of pathogens from cooked donkey meat products in Beijing area in One Health context. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Gao, N.; Waller, A.S.; Cook, F.R.; Fan, S.; Yuan, D.; Du, Y.; Li, F.; Norimine, J.; Zhu, W. An outbreak of strangles associated with a novel genotype of Streptococcus equi subspecies equi in donkeys in China during 2018. Equine Vet. J. 2019, 51, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Su, J.; Chu, X.; Wang, C. Pharmacokinetics and ex vivo pharmacodynamics of minocycline against Salmonella abortus equi in donkey plasma and tissue cage fluid. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 135, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Qi, P.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, W. Characterization of Salmonella isolated from donkeys during an abortion storm in China. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 161, 105080. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Wu, J.; Ma, W.; Yang, Y.; Lv, L.; Cai, J.; Liu, Z.; He, J.; Shang, Y.; Li, Z.; et al. Molecular detection and characterization of Coxiella burnetii in aborted samples of livestock in China. Acta Trop. 2024, 254, 107163. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Yu, F.; Holyoak, G.R.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J. Use of the endometrial histopathology to improve diagnosis of donkeys with endometritis. Equine Vet. Educ. 2024, 36, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, N.; Chen, C.; Ji, Y.; Guo, J.; Du, Y.; Gu, J.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, J.; Dong, J. Multi-locus sequence typing of Streptococcus equi subspecies zooepidemicus strains isolated from donkeys: A novel genotype associated with donkey infectious endometritis. Pak. Vet. J. 2023, 43, 838–841. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, B.; Mi, J.; Li, N.; Zhao, W.; Wu, R.; Holyoak, G.R.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility of bacterial isolates from donkey uterine infections, 2018–2021. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Du, Y.; Zheng, X.; Shu, S.; Suo, J.; Han, M.; Ma, X.; Huang, R.; Peng, W.; Fu, C.; et al. Endometritis in donkeys associated with Streptococcus equi subspecies zooepidemicus infection. Pak. Vet. J. 2020, 40, 537–539. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Lv, F.; Su, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B. Complete genome sequencing and comparative genomic analysis of three donkey Streptococcus equi subsp. equi isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1285027. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, N.; He, D.; Waller, A.; Gu, J.; Wang, T.; Han, W. Identification of a novel genotype of Streptococcus equi subspecies equi in a donkey suffering from strangles. Pak. Vet. J. 2019, 39, 609–611. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, L.; Sun, Y.; Khan, M.Z.; Yu, Y.; Ruan, L.; Chen, L.; Zhao, J.; Jia, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Protective role of cepharanthine against equid herpesvirus type 8 through AMPK and Nrf2/HO-1 pathway activation. Viruses 2024, 16, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, P.; Deng, H.; Duan, L.; Ren, M.; Song, X.; Wang, H.; Gulimire, D.; Kuang, L.; Xie, J. First detection of the occurrence and study of the genetic diversity of novel putative kirkoviruses in donkey in China. Virus Genes 2022, 58, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, P.F.; Gao, X.Y.; Ji, K.K.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.H.; Cheng, K.H.; Cui, N.; Zhu, M.L.; Hu, T.; Dong, X.; et al. Identification of a recombinant equine coronavirus in donkey, China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Liu, G.; Gao, N.; Suo, J.; Matthijnssens, J.; Li, S.; Yuan, D.; Du, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yamashita, N.; et al. A reassortant G3P[12] rotavirus A strain associated with severe enteritis in donkeys (Equus asinus). Equine Vet. J. 2022, 54, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Yongfeng, Y.; Xiaobo, S.; Nan, X.; Jingwen, Z.; Wenqiang, L. Detection of the epidemic of the H3N8 subtype of the equine influenza virus in large-scale donkey farms. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2020, 8, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Meng, F.; Sun, F.; Chen, M.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, H. Emergence of H3N8 equine influenza virus in donkeys in China in 2017. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 214, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chai, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Huang, Z.; Chen, L.; Guo, R.; Dong, Y.; Liu, M.; Zheng, Q.; et al. First detection and phylogenetic analysis of porcine circovirus 3 in female donkeys with reproductive disorders. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.D.; Zhang, S.; Lv, Y.H.; Zhang, Z.D.; Su, N.; Li, L.L.; Zhu, X.Q.; Xie, S.C.; Gao, W.W. First molecular detection and genetic characterization of Tetratrichomonas buttreyi and Pentatrichomonas hominis in Donkeys in Shanxi Province, China. Animals 2024, 14, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Jing, H.; Cao, J.; Yin, J.; Li, T.; Sun, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, X. Genotyping and subtyping of Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis isolates from two wild rodent species in Gansu Province, China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12178. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Xie, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Jia, L. First report of genetic diversity and risk factor analysis of equine piroplasm infection in equids in Jilin, China. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Xu, J.; Su, L.; Li, E.; Wang, S.; Hornok, S.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y. First molecular evidence of Babesia caballi and Theileria equi in imported donkeys from Kyrgyzstan. Pathogens 2024, 13, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wei, K.; Wu, Z.; Sun, J.; Hu, J.; Deng, S.; Tao, J. Morphological and molecular characterization of a Sarcocystis species infecting donkeys from China. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 2917–2926. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Sun, L.; Xiang, Z.; Li, N.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Li, Q.; Yang, F.; Song, J.; Morris, J.; et al. Morphological and molecular characteristics of Sarcocystis bertrami from horses and donkeys in China. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 252, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, T.H.; Jia, T.; Su, N.; Xie, S.C.; Li, S.; Tian, X.; Zhu, X.Q.; Liu, Q.; Gao, W.W. Prevalence and genotype/subtype distribution of Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Blastocystis in donkeys in Shanxi Province, North China. Parasitol. Res. 2024, 123, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Lu, Y.; Han, L.; Lu, M.; Guan, C.; Yu, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Exploration of Parascaris species in three different Equus populations in China. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 202. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Wang, R.; Guo, Y.; Li, N.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Zoonotic potential of Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Giardia duodenalis in horses and donkeys in northern China. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Jing, B.; Xing, J.; Tao, D.; Zhao, W.; Qi, M. Enterocytozoon bieneusi in donkeys from Xinjiang, China: Prevalence, molecular characterization, and the assessment of zoonotic risk. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 196. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, A.; Jing, B.; Zhang, L.; Liu, P.; Qi, M.; Zhao, W. Prevalence and genotypic identification of Cryptosporidium in free-ranging and farm-raised donkeys (Equus asinus asinus) in Xinjiang, China. Parasite 2020, 27, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Su, J.; Chahan, B.; Guo, Q.; Wang, T.; Yu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, N.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Different distribution of Cryptosporidium species between horses and donkeys. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 75, 103954. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, W.; Chen, L.; Shan, X.F.; Qian, A.D.; Meng, Q.F. First genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii infection in donkey meat slaughtered for human consumption in Shandong province, eastern China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 61, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.F.; Li, D.; Yao, G.Z.; Zou, Y.; Cong, W.; Shan, X.F. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection and variables associated with seropositivity in donkeys in eastern China. Parasite 2018, 25, 66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.X.; Shi, W.; Zhang, N.Z.; Shi, K.; Li, J.M.; Xu, P.; Zhao, Q.; Du, R. Prevalence and genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii in donkeys in northeastern China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 54, 455–457. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, W.; Nie, L.B.; Qin, S.Y.; Wang, W.L.; Qian, A.D.; Meng, Q.F. Prevalence of Neospora spp. in donkeys in China. Parasite 2018, 25, 16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jian, R.; Wang, S.W.; Zhang, W.X.; Zhang, L.P. Morphological and molecular identification of Habronema spp. (Nematoda: Habronematidae) from donkeys in Xinjiang, China, and notes on the taxonomical status of Habronema majus (Creplin, 1849) and H. microstoma (Schneider, 1866). Syst. Parasitol. 2017, 94, 511–525. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Sun, D.; Jiang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Gao, X. The epidemiology of infundibular caries in donkeys in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region of China and associated risk factors. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2022, 119, 104160. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, B.; Shi, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, C. Comparative analysis of bacterial diversity between the liquid phase and adherent fraction within the donkey caeco-colic ecosystem. Animals 2022, 12, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Shen, W.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Pan, Q.; Xie, T.; Ai, D.; et al. Comparison of gut microflora of donkeys in high and low altitude areas. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 964799. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, B.; Zhu, M.; Wang, C. The fibrolytic enzyme profiles and the composition of fungal communities in donkey cecum-colon ecosystem. Animals 2022, 12, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.; Dang, W.; Irwin, D.M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S. Unveiling the biogeography and potential functions of the intestinal digesta- and mucosa-associated microbiome of donkeys. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 596882. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, C. Dynamic alterations in the donkey fecal bacteria community and metabolome characteristics during gestation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 927561. [Google Scholar]
- Lamoureux, C.; Surgers, L.; Fihman, V.; Gricourt, G.; Demontant, V.; Trawinski, E.; N’debi, M.; Gomart, C.; Royer, G.; Launay, N.; et al. Prospective Comparison Between Shotgun Metagenomics and Sanger Sequencing of the 16S rRNA Gene for the Etiological Diagnosis of Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 761873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, X.; Han, X.; Xu, S.; Zhao, L.; Hu, L.; Xu, T.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; et al. Comparative study of gut microbiota in Tibetan wild asses (Equus kiang) and domestic donkeys (Equus asinus) on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9032. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Du, M.; Zhang, G.; Lee, Y. Dietary energy level impacts the performance of donkeys by manipulating the gut microbiome and metabolome. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 694357. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Shi, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, S. Cecal microbial diversity and metabolome reveal a reduction in growth due to oxidative stress caused by a low-energy diet in donkeys. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Khan, M.Z.; Chen, Y.; Liang, H.; Kou, X.; Wang, X.; Ren, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z. Yeast polysaccharide supplementation: Impact on lactation, growth, immunity, and gut microbiota in Dezhou donkeys. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1289371. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Zhang, X.; Gao, W.; Ji, C.; Wang, Y.; Feng, P.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Zhao, F. Transport stress affects the fecal microbiota in healthy donkeys. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 2449–2457. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.Y.; Tong, M.M.; Li, L.; Hui, F.; Meng, F.Z.; Zhao, Y.L.; Guo, Y.M.; Guo, X.Y.; Shi, B.L.; Yan, S.M. Rectal microbiomes and serum metabolomics reveal the improved effect of Artemisia ordosica crude polysaccharides on the lactation performance, antioxidant status, and immune responses of lactating donkeys. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 6696–6716. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, Y.; Yu, J.; Xia, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. Remodeling of intestinal bacterial community and metabolome of Dezhou donkey induced by corn silage. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17032. [Google Scholar]
| Treatment/Factors | Gut Microbiota | Biological Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex and intestinal segments | Male Duodenum and jejunum: Streptococcus and Erysipelotrichaceae_UCG-002 Ileum: Sarcina and Streptococcus Female: Duodenum and jejunum: Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1, Acinetobacter, and NK4A214 Ileum: Amnipila, Terrisporobacter, and Luteimonas | Health and sex-wise microbiota information | [30] |
| Intestinal segments | Duodenum: Lachnospiraceae_UCG-008 and Sphaerochaeta jejunum: Christensenellaceae_R-7_group and Bacillus ileum: NK4A214_group and Alloprevotella UCG-005 Cecum; Lactobacillus Colon: Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1 and Chlamydia Feces: Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group and Prevotellaceae_UCG-004 | Body health, metabolism, and development of microbial additives. | [31] |
| Weaning | Verrucomicrobiales, Clostridia, Oscillospiraceae, Akkermansia, Rikenellaceae, Clostridia Oscillospiraceae, Campilobacterota, Lachnoclostridium, and Roseburia. | Metabolism and health | [39] |
| Methionine | Ruminococcus, Peptococcus, Anaeroplasma, and Methanocorpusculum | Antioxidant response and health | [42] |
| Artemisia ordosica crude polysaccharides | Improved colonization of beneficial bacteria, including Lactobacillus, Unclassified_f_Prevotellacea, Ruminococcus, and Fibrobacter genera. Decreased pathogenic bacterial colonization of the Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1 bacterial genus | Improved antioxidant response, lactational performance, and health | [118] |
| Corn Silage | Enhanced Bacteroidetes (Genera Prevotellaceae_UCG-003, Alloprevotella and Prevotella_1) and Firmicutes phyla (Genera Ruminococcaceae_NK4A214_group, Ruminococcaceae_UCG-010, Lachnospiraceae, and Ruminococcaceae_UCG-002) | Metabolism and intestinal health | [119] |
| Fibrolytic enzyme | Predominant fungi at phylum level were Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, and Neocallimastigomycota. Aspergillus, Wallemia, Phanerochaete, Fusarium, and Penicillium were detected as the dominant genera | Plant cell wall breakdown and digestion | [109] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, M.Z.; Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Li, M.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, W.; Ma, Q.; Wang, C. Advances in Donkey Disease Surveillance and Microbiome Characterization in China. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040749
Khan MZ, Li Y, Zhu M, Li M, Wang T, Zhang Z, Liu W, Ma Q, Wang C. Advances in Donkey Disease Surveillance and Microbiome Characterization in China. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):749. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040749
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Muhammad Zahoor, Yan Li, Mingxia Zhu, Mengmeng Li, Tongtong Wang, Zhenwei Zhang, Wenqiang Liu, Qingshan Ma, and Changfa Wang. 2025. "Advances in Donkey Disease Surveillance and Microbiome Characterization in China" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040749
APA StyleKhan, M. Z., Li, Y., Zhu, M., Li, M., Wang, T., Zhang, Z., Liu, W., Ma, Q., & Wang, C. (2025). Advances in Donkey Disease Surveillance and Microbiome Characterization in China. Microorganisms, 13(4), 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040749






