Regulatory Mechanisms of Exogenous Acyl-Homoserine Lactones in the Aerobic Ammonia Oxidation Process Under Stress Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reactor Operation and Experimental Design
2.2. Illumina MiSeq Sequencing and Sequence Processing
2.3. qPCR Assay of amoA Genes
- -
- AOA amoA genes: archaea-amoA F/R (Francis et al., 2005);
- -
- AOB amoA genes: amoA-1F/1R (Rotthauwe et al., 1997);
- -
- Comammox amoA genes: com amoA AF/SR (Shao and Wu, 2021).
3. Results and Discussion
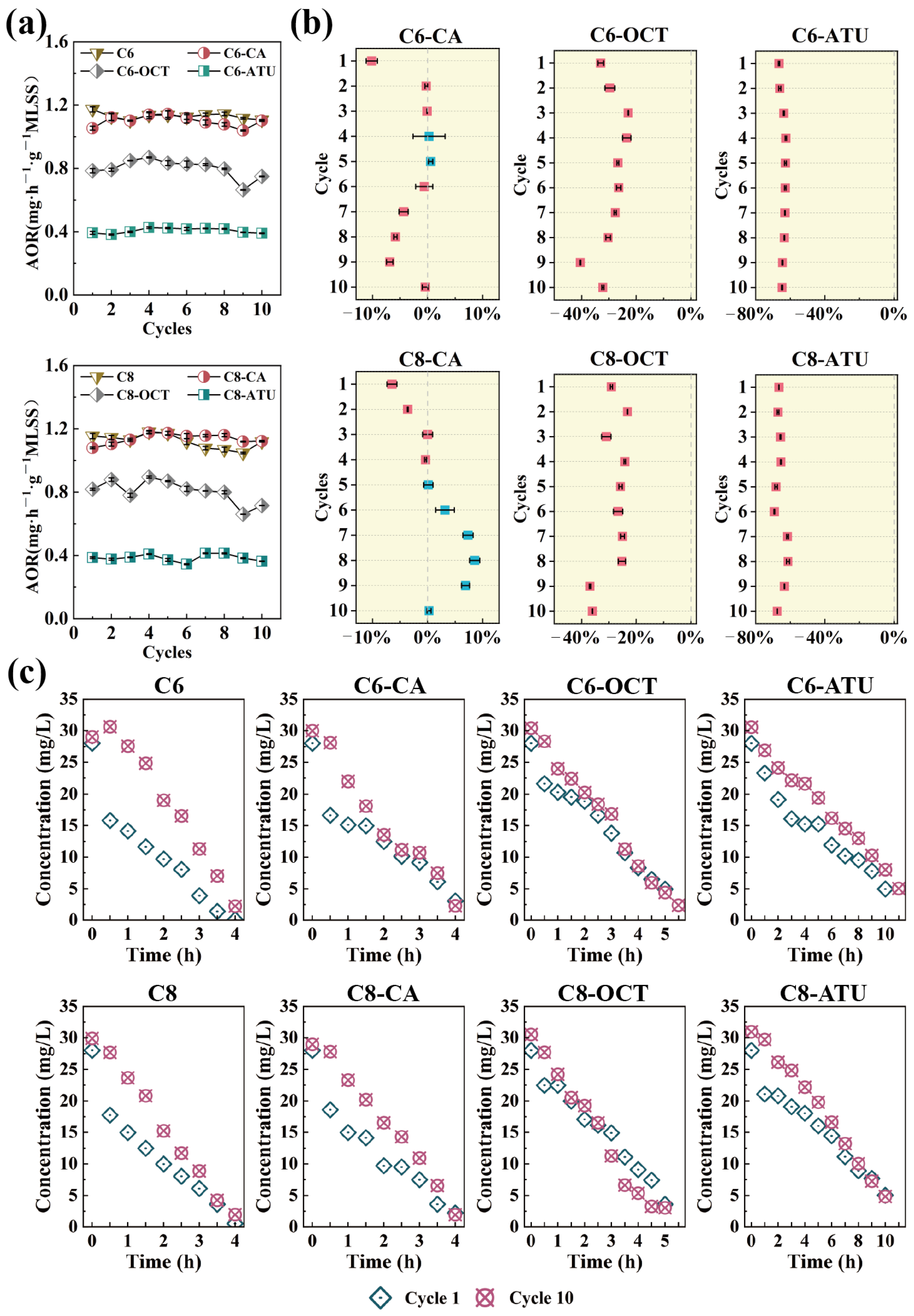
3.1. Effects of AHLs on Ammonia Oxidization
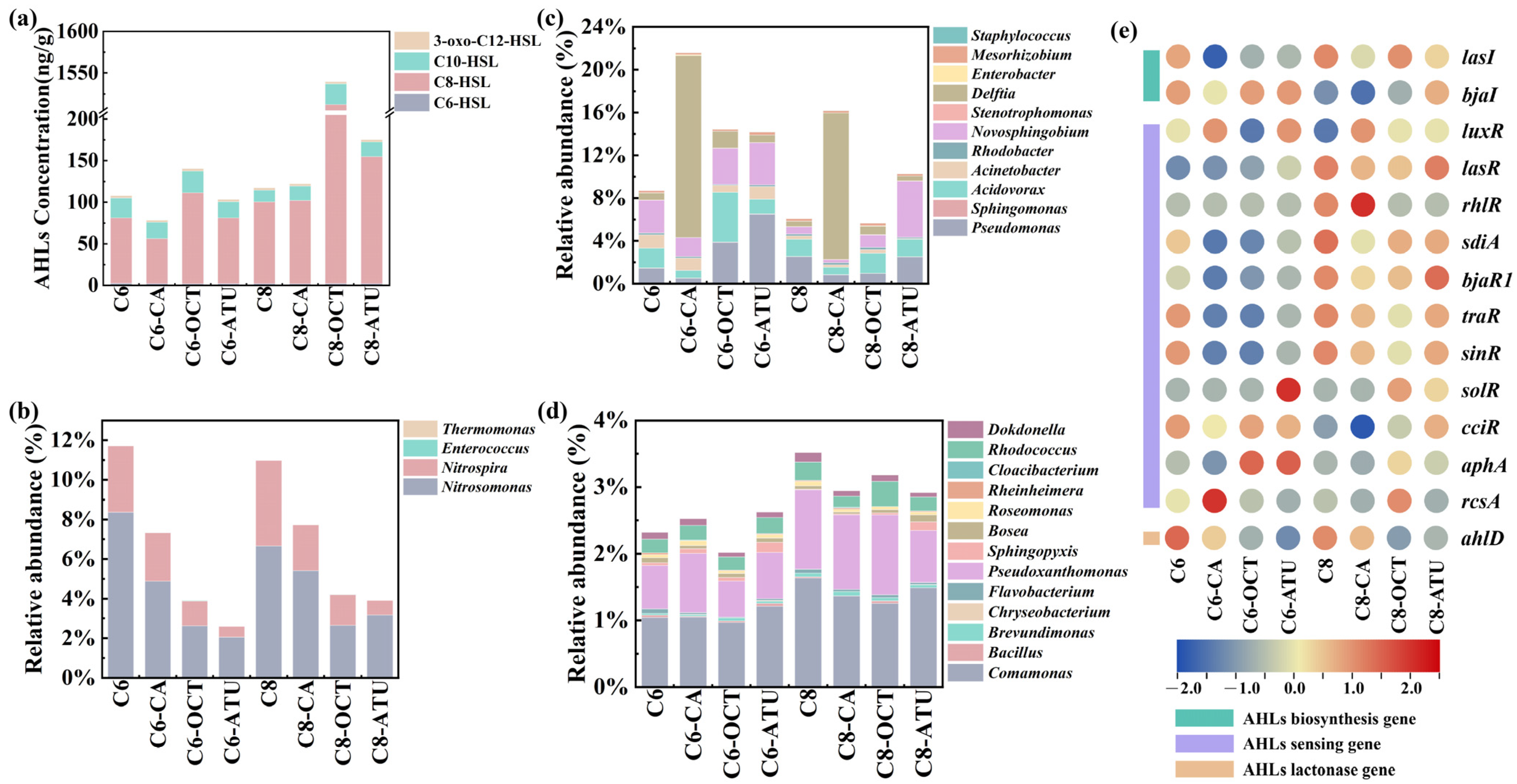
3.2. Functional Gene Abundance and AOM Diversity
3.3. Impact of AHL Addition on QS/QQ Bacteria and Genes
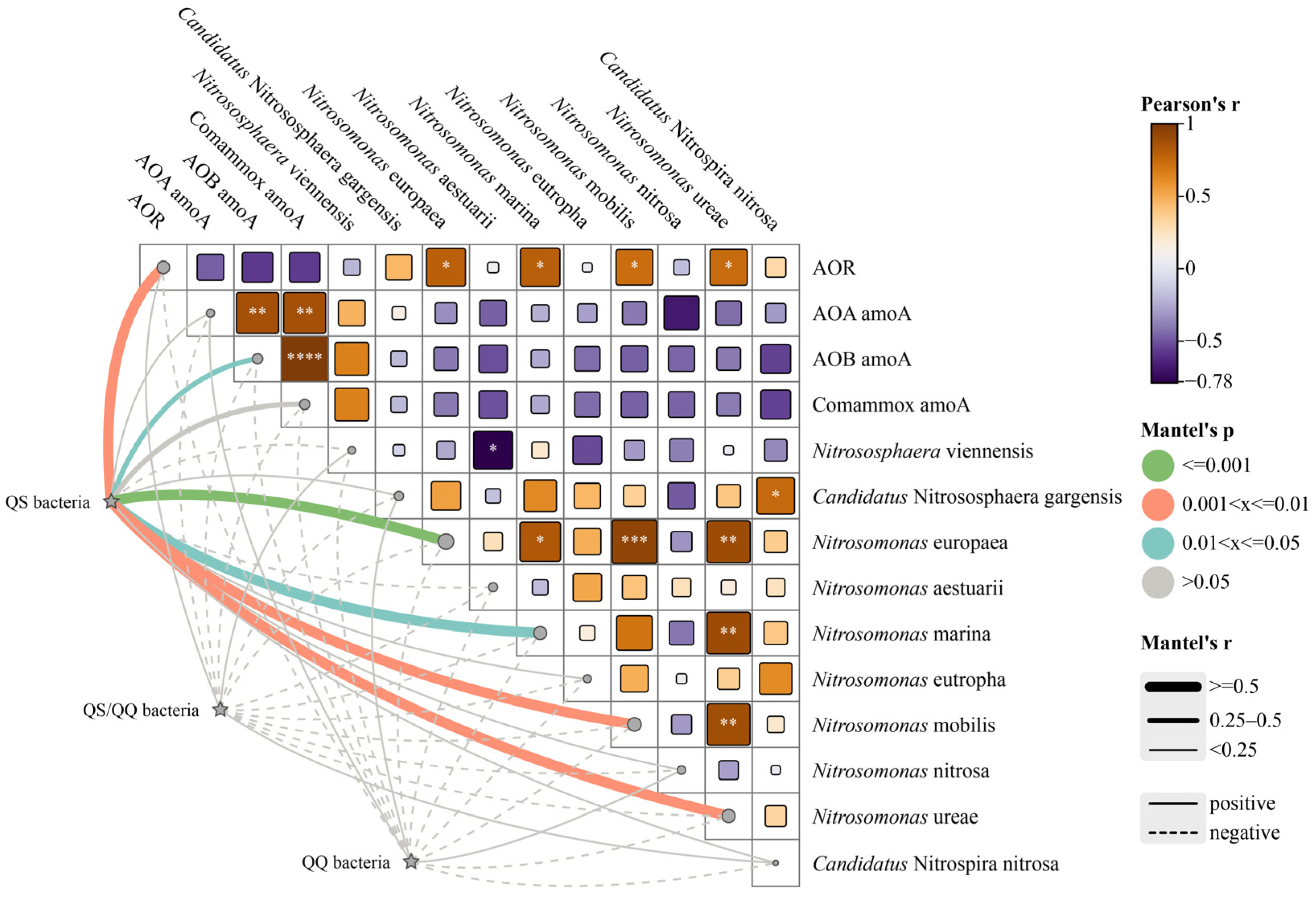
3.4. Potential Interactions Between AHL-Related Bacteria and the Ammonia Oxidation Process
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, Z.; Hu, S.; Chen, D.; Zhu, B. From Production to Consumption: A Coupled Human-Environmental Nitrogen Flow Analysis in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2025–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Dodds, W.K. Nutrients, eutrophication and harmful algal blooms along the freshwater to marine continuum. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2019, 6, e1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuypers, M.M.M.; Marchant, H.K.; Kartal, B. The microbial nitrogen-cycling network. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, M.K.; Straka, L. New directions in biological nitrogen removal and recovery from wastewater. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 57, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martikainen, P.J. Heterotrophic nitrification–An eternal mystery in the nitrogen cycle. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 168, 108611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhao, Z.; Tian, Z.; Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; He, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, M. Comammox bacteria predominate among ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in municipal but not in refinery wastewater treatment plants. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, C.E.; Lücker, S. Complete ammonia oxidation: An important control on nitrification in engineered ecosystems? Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 50, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.Y.; Gao, J.; Pan, K.; Li, D.; Dai, H.; Li, X. Temporal heterogeneity and temperature response of active ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in winter in full-scale wastewater treatment plants. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Bello, M.O.; Meng, Y.; Prosser, J.I.; Gubry-Rangin, C. Selective inhibition of ammonia oxidising archaea by simvastatin stimulates growth of ammonia oxidising bacteria. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 141, 107673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.; Du, Z.; Behrens, S. Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria Maintain Abundance but Lower amoA-Gene Expression during Cold Temperature Nitrification Failure in a Full-Scale Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e02571-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, H.J.; Cameron, K.C.; Podolyan, A.; Robinson, A. Effect of soil moisture status and a nitrification inhibitor, dicyandiamide, on ammonia oxidizer and denitrifier growth and nitrous oxide emissions in a grassland soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 73, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Xue, B.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Shen, Z.; Bo, L.; Qiu, Z.; et al. Horizontal transfer of the multidrug resistance plasmid RP4 inhibits ammonia nitrogen removal dominated by ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Water Res. 2022, 217, 118434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Fujiwara, T.; Hidaka, T.; Nishimura, F.; Nakanishi, T.; Terada, A.; Hori, T. Evaluation of nitrous oxide emission during ammonia retention from simulated industrial wastewater by microaerobic activated sludge process. Water Res. 2023, 247, 120780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauder, L.A.; Ross, A.A.; Neufeld, J.D. Nitric oxide scavengers differentially inhibit ammonia oxidation in ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria. Fems Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363, fnw052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chapman, S.J.; Nicol, G.W.; Yao, H. Nitrification and nitrifiers in acidic soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, S.; Ma, S.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Z.; Lu, C. Effects of commonly used nitrification inhibitors—Dicyandiamide (DCD), 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP), and nitrapyrin—On soil nitrogen dynamics and nitrifiers in three typical paddy soils. Geoderma 2020, 380, 114637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginestet, P.; Audic, J.M.; Urbain, V.V.; Block, J.C. Estimation of Nitrifying Bacterial Activities by Measuring Oxygen Uptake in the Presence of the Metabolic Inhibitors Allylthiourea and Azide. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2266–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.E.; Vajrala, N.; Giguere, A.T.; Gitelman, A.I.; Bottomley, P.J. Use of Aliphatic n-Alkynes To Discriminate Soil Nitrification Activities of Ammonia-Oxidizing Thaumarchaea and Bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 6544–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Bai, S.H.; Omidvar, N.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, M. Insight into the functional mechanisms of nitrogen-cycling inhibitors in decreasing yield-scaled ammonia volatilization and nitrous oxide emission: A global meta-analysis. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, D.; Chu, X.; Huang, J.; Shu, Z.; Li, Y.; Jin, Y. Effects of exogenous signaling molecules on anaerobic sludge digestion: Quorum sensing and antibiotic resistance genes. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 414, 131624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ni, L.; Du, C.; Shi, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, S.; Li, Y. Decoding Microcystis aeruginosa quorum sensing through AHL-mediated transcriptomic molecular regulation mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 172101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Gao, W.; Sun, L.; Wang, P.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, G.; Li, W. Roles and regulation of quorum sensing in anaerobic granular sludge: Research status, challenges, and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 387, 129644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Dai, H. Transcriptome analysis expands underlying mechanisms of quorum sensing mediating heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification process at low temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 414, 131581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddela, N.R.; Sheng, B.; Yuan, S.; Zhou, Z.; Villamar-Torres, R.; Meng, F. Roles of quorum sensing in biological wastewater treatment: A critical review. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhuang, G. Identification of the release and effects of AHLs in anammox culture for bacteria communication. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Guan, Y.; Zeng, D.; He, K.; Wu, G. Metagenomics-based interpretation of AHLs-mediated quorum sensing in Anammox biofilm reactors for low-strength wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 344, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Sun, Y.; Li, T.; Meng, F.; Wu, G. Operational pattern affects nitritation, microbial community and quorum sensing in nitrifying wastewater treatment systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 677, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zhao, A.; Zhang, X.; Tang, P.; Li, D.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z. Potential role of N-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing in the adaptation of anammox granular sludge system to salinity stress. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 416, 131758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.J.; Hou, B.L.; Li, M.X. Cell adhesion, ammonia removal and granulation of autotrophic nitrifying sludge facilitated by N-acyl-homoserine lactones. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 196, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clippeleir, H.; Defoirdt, T.; Vanhaecke, L.; Vlaeminck, S.E.; Carballa, M.; Verstraete, W.; Boon, N. Long-chain acylhomoserine lactones increase the anoxic ammonium oxidation rate in an OLAND biofilm. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 90, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhuang, G. Realizing the role of N-acyl-homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing in nitrification and denitrification: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; He, J.; Yu, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J. A strategy to speed up formation and strengthen activity of biofilms at low temperature. RSC Adv. 2017, 37, 22788–22796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Xie, X.; Feng, F.; Huang, S.; Sun, Y. Impact of acyl-homoserine lactones on the response of nitrogen cycling in sediment to florfenicol stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Dong, D.; Hu, H.; Ren, H. AHLs-mediated quorum sensing threshold and its response towards initial adhesion of wastewater biofilms. Water Res. 2021, 194, 116925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, P.; He, J.; Li, J. Effects of AHLs inhibitors and exogenous AHLs on the stability and activity of Anammox granules at low temperatures. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 1576–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Hou, M.; Wu, X.; Zhuang, J.; Liu, Y. The effect of quorum sensing on performance of salt-tolerance aerobic granular sludge: Linking extracellular polymeric substances and microbial community. Biodegradation 2019, 30, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Duan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Liu, Y.; Bai, Z.; Ma, W.; Zhuang, G. Long- and short-chain AHLs affect AOA and AOB microbial community composition and ammonia oxidation rate in activated sludge. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 78, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; He, J.; Liu, J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J. Biofilm activity and sludge characteristics affected by exogenous N-acyl homoserine lactones in biofilm reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zheng, S.; Huo, Z.; Shi, B.; Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Ma, J.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, K. Effects of exogenous N-acyl-homoserine lactones on nutrient removal, sludge properties and microbial community structures during activated sludge process. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Hu, H. Potential roles of acyl homoserine lactones (AHLs) in nitrifying bacteria survival under certain adverse circumstances. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, E.O.; Read, H.W.; Pellitteri, M.C.; Hickey, W.J. Identification of acyl-homoserine lactone signal molecules produced by Nitrosomonas europaea strain Schmidt. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4906–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeon, K.M.; Cheong, W.S.; Oh, H.S.; Lee, W.N.; Hwang, B.K.; Lee, C.H.; Beyenal, H.; Lewandowski, Z. Quorum Sensing: A New Biofouling Control Paradigm in a Membrane Bioreactor for Advanced Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decho, A.W.; Norman, R.S.; Visscher, P.T. Quorum sensing in natural environments: Emerging views from microbial mats. Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.H.; Koh, K.S.; Xie, C.; Zhang, J.; Kjelleberg, S. Community quorum sensing signalling and quenching: Microbial granular biofilm assembly. Npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2015, 1, 15006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaki, S.; Sugiyama, R.; Okabe, S. Membrane fouling induced by AHL-mediated soluble microbial product (SMP) formation by fouling-causing bacteria co-cultured with fouling-enhancing bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Li, B.; Li, W.; Fang, F.; Tong, Z.; Yu, H. Outcompeting Presence of Acyl-Homoserine-Lactone (AHL)- Quenching Bacteria over AHL-Producing Bacteria in Aerobic Granules. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 3, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellbye, B.L.; Spieck, E.; Bottomley, P.J.; Sayavedrasoto, L.A. Acyl-Homoserine Lactone Production in Nitrifying Bacteria of the Genera Nitrosospira, Nitrobacter, and Nitrospira Identified via a Survey of Putative Quorum-Sensing Genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01540-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Inhibitor and Dose | Blank Control | Caffeic Acid, 100 μm | 1-Octyne, 0.03% v/v | ATU, 100 μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C6-HSL, 50 μM (GROUP 1) | C6 | C6-CA | C6-OCT | C6-ATU |
| C8-HSL, 50 μM (GROUP 2) | C8 | C8-CA | C8-OCT | C8-ATU |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, C.; Pan, K.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, X.; Su, Q.; Bi, X.; Ng, H. Regulatory Mechanisms of Exogenous Acyl-Homoserine Lactones in the Aerobic Ammonia Oxidation Process Under Stress Conditions. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030663
Qiu C, Pan K, Wei Y, Zhou X, Su Q, Bi X, Ng H. Regulatory Mechanisms of Exogenous Acyl-Homoserine Lactones in the Aerobic Ammonia Oxidation Process Under Stress Conditions. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(3):663. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030663
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Chen, Kailing Pan, Yuxuan Wei, Xiaolin Zhou, Qingxian Su, Xuejun Bi, and Howyong Ng. 2025. "Regulatory Mechanisms of Exogenous Acyl-Homoserine Lactones in the Aerobic Ammonia Oxidation Process Under Stress Conditions" Microorganisms 13, no. 3: 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030663
APA StyleQiu, C., Pan, K., Wei, Y., Zhou, X., Su, Q., Bi, X., & Ng, H. (2025). Regulatory Mechanisms of Exogenous Acyl-Homoserine Lactones in the Aerobic Ammonia Oxidation Process Under Stress Conditions. Microorganisms, 13(3), 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030663







