The Role of Quantitative Real-Time PCR in the Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Diagnosis: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ledoux, M.P.; Herbrecht, R. Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kousha, M.; Tadi, R.; Soubani, A.O. Pulmonary aspergillosis: A clinical review. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2011, 20, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Feys, S.; Carvalho, A.; Clancy, C.J.; Gangneux, J.-P.; Hoenigl, M.; Lagrou, K.; Rijnders, B.J.A.; Seldeslachts, L.; Vanderbeke, L.; van de Veerdonk, F.L.; et al. Influenza-associated and COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients. Lancet Respir. Med. 2024, 12, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadena, J.; Thompson, G.R.; Thomas, F. Patterson, Aspergillosis: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 35, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoth, F.; Calandra, T. Pulmonary aspergillosis: Diagnosis and treatment. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2022, 31, 220114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Denis, J.; Forouzanfar, F.; Herbrecht, R.; Toussaint, E.; Kessler, R.; Sabou, M.; Candolfi, E.; Letsher-Bru, V. Evaluation of Two Commercial Real-Time PCR Kits for Aspergillus DNA Detection in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid in Patients with Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis. J. Mol. Diagn. 2018, 20, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Arvanitis, M.; Ziakas, P.D.; Zacharioudakis, I.M.; Zervou, F.N.; Caliendo, A.M.; Mylonakis, E. PCR in diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis: A meta-analysis of diagnostic performance. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 3731–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Available online: https://fpcri.eu/wp-content/uploads/2014/11/A-proposed-standard-for-Aspergillus-PCR.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2024).
- Available online: https://c.peervoice.com/programs/140200557/downloads/PV_practiceaids_QVJ.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2024).
- Donnelly, J.P.; Chen, S.C.; Kauffman, C.A.; Steinbach, W.J.; Baddley, J.W.; Verweij, P.E.; Clancy, C.J.; Wingard, J.R.; Lockhart, S.R.; Groll, A.H.; et al. Revision and Update of the Consensus Definitions of Invasive Fungal Disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer and the Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bassetti, M.; Azoulay, E.; Kullberg, B.J.; Ruhnke, M.; Shoham, S.; Vazquez, J.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Calandra, T. EORTC/MSGERC Definitions of Invasive Fungal Diseases: Summary of Activities of the Intensive Care Unit Working Group. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72 (Suppl. S2), S121–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbert, S.; Meyer, I.; Palous, M.; Brossas, J.Y.; Uzunov, M.; Touafek, F.; Gay, F.; Trosini-Desert, V.; Fekkar, A. Aspergillus PCR in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Aspergillosis in Patients with Hematological and Non-hematological Conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chabi, M.L.; Goracci, A.; Roche, N.; Paugam, A.; Lupo, A.; Revel, M.P. Pulmonary aspergillosis. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2015, 96, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmidis, C.; Denning, D.W. The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis. Thorax 2015, 70, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warris, A. The biology of pulmonary aspergillus infections. J. Infect. 2014, 69 (Suppl. S1), S36–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, G.R., 3rd; Patterson, T.F. Pulmonary aspergillosis: Recent advances. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 32, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hites, M.; Goicoechea Turcott, E.W.; Taccone, F.S. The role of galactomannan testing to diagnose invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ferns, R.B. Evaluation of the role of real-time PCR in the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis. Leuk. Lymphoma 2006, 47, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Li, X.; Guo, W.; Shangguan, Y.; Xia, J.; Feng, X.; Sheng, C.; Ji, Z.; Ding, C.; Xu, K. The Utility of Real-Time PCR, Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing, and Culture in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid for Diagnosis of Pulmonary Aspergillosis. J. Mol. Diagn. 2024, 26, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulska, M.; Furfaro, E.; De Carolis, E.; Drago, E.; Pulzato, I.; Borghesi, M.L.; Zappulo, E.; Raiola, A.M.; Grazia, C.D.; Del Bono, V.; et al. Use of Aspergillus fumigatus real-time PCR in bronchoalveolar lavage samples (BAL) for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis, including azole-resistant cases, in high risk haematology patients: The need for a combined use with galactomannan. Med. Mycol. 2019, 57, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Townsend, L.; Martin-Loeches, I. Invasive Aspergillosis in the Intensive Care Unit. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Trovato, L.; Scalia, G.; Domina, M.; Oliveri, S. Environmental Isolates of Multi-Azole-Resistant Aspergillus spp. in Southern Italy. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Calvo, M.; Lauricella, F.; Mellini, A.M.; Scalia, G.; Trovato, L. Isavuconazole and Amphotericin B Synergic Antifungal Activity: In Vitro Evaluation on Pulmonary Aspergillosis Molds Isolates. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Qi, G.; Hao, L.; Gan, Y.; Xin, T.; Lou, Q.; Xu, W.; Song, J. Identification of closely related species in Aspergillus through Analysis of Whole-Genome. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1323572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

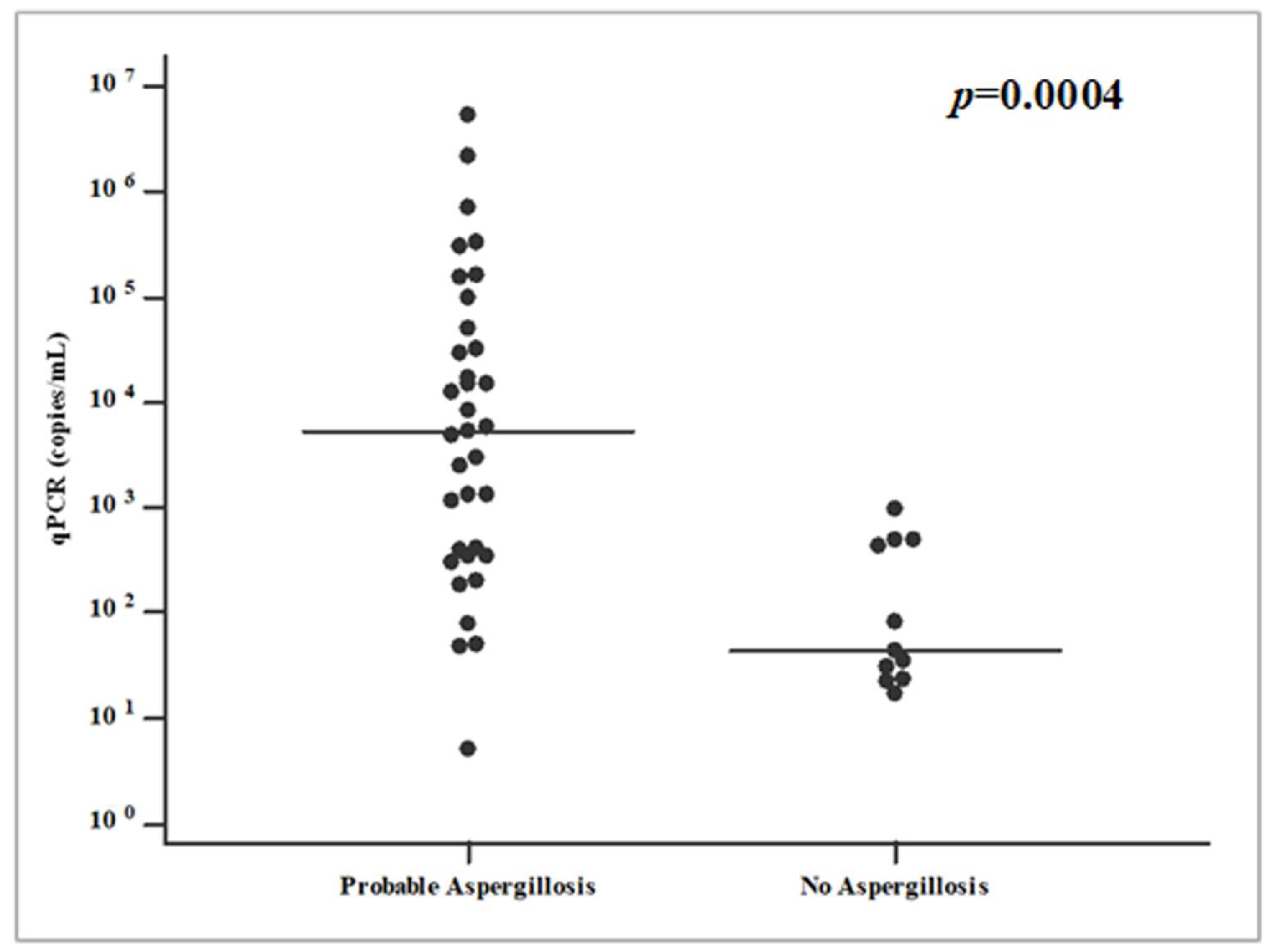
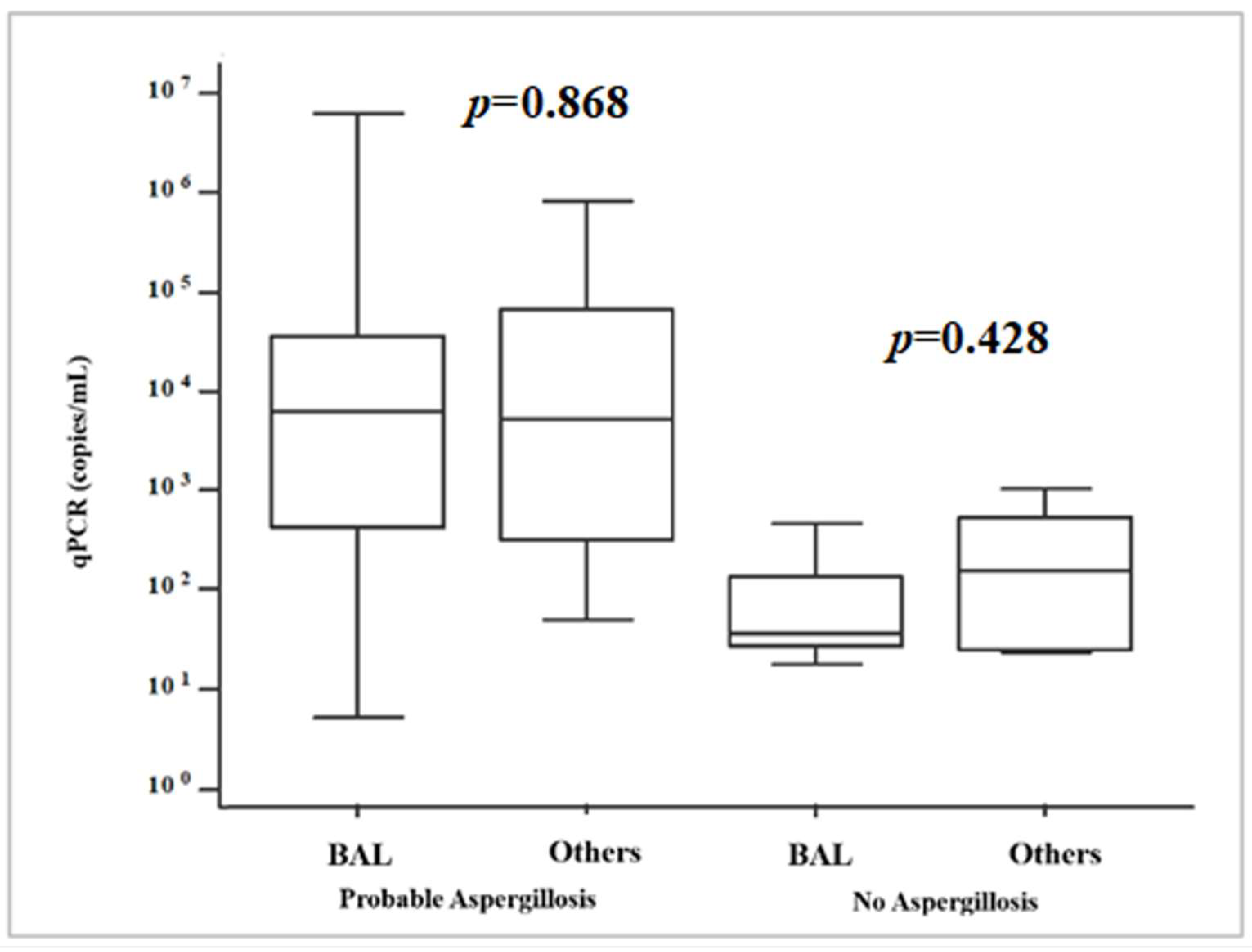
| Patients and Risk Factors | Total (n = 62) | Probable IPA (n = 35) | No IPA (n = 27) | p a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex (%) | 30 (48.4) | 15 (42.8) | 9 (33.3) | 0.448 |
| Age, median years (range) | 79 (19 to 85) | 63 (19 to 85) | 66 (29 to 84) | 0.809 |
| Antifungal treatment (no., %) | 53 (85.5) | 35 (100%) | 19 (70.4) | <0.0001 |
| No. of patients (%) with a: | ||||
| Positive microscopy a | 32 (51.6) | 32 (91.4) | 0 | <0.0001 |
| Positive culture | 51 (82.2) | 33 (94.3) | 18 (66.7) | 0.005 |
| Positive GM b | 22 (75.9) | 17 (94.4) | 5 (45.4) | 0.005 |
| Positive PCR | 46 (74.2) | 35 (100) | 11 (40.7) | <0.0001 |
| No | Host Factors | Clinical Features | Respiratory Culture | GM a | PCR b | Antifungal Terapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chronic obstructive lung disease | Cavity | Negative | 8.46 | 5 | Itraconazole |
| 2 | Use of corticosteroids | Air crescent sign | A. fumigatus | 12.16 | 2,175,083 | Amphotericin B |
| 3 | COVID-19 | Dense, well-circumscribed lesions | A. terreus | 11.3 | 301,497 | Amphotericin B |
| 4 | Use of corticosteroids | Nodule | A. fumigatus | 5.7 | 155,877 | Amphotericin B |
| 7 | Severe influenza | Air crescent sign | A. niger | 3.4 | 5377 | Voriconazole |
| 8 | Multiple myeloma | Dense, well-circumscribed lesions | A. fumigatus | 6.9 | 8181 | Amphotericin B |
| 9 | HSCT | Dense, well-circumscribed lesions | A. niger | - | 48 | Amphotericin B |
| 10 | Neutrophil deficiency | Air crescent sign | A. niger | - | 713,875 | Amphotericin B |
| 11 | Chronic obstructive lung disease | Cavity | A. niger | - | 17,327 | Caspofungin |
| 12 | Hematological malignancies | Dense, well-circumscribed lesions | A. flavus | - | 330,791 | Amphotericin B |
| 14 | Treatment with immunosuppressant | Tracheobronchial ulceration | A. fumigatus | 1.3 | 302 | Voriconazole |
| 15 | Solid organ transplant | Nodule | Negative | 1.9 | 50 | Caspofungin |
| 17 | Acute leukemias | Nodule | A. terreus | - | 98,182 | Amphotericin B |
| 19 | Acute leukemias | Nodule | A. fumigatus | - | 2469 | Amphotericin B |
| 20 | Glucocorticoid treatment | Cavity | A. flavus | - | 162,433 | Amphotericin B |
| 25 | Chronic obstructive lung disease | Cavity | A. fumigatus | - | 181 | Caspofungin |
| 28 | Chronic obstructive lung disease | Cavity | A. fumigatus | - | 1167 | Voriconazole |
| 29 | Acute leukemias | Air crescent sign | A. terreus | 2.55 | 1295 | Amphotericin B |
| 31 | COVID-19 | Dense, well-circumscribed lesions | A. niger | 9.49 | 2937 | Amphotericin B |
| 34 | Treatment with immunosuppressant | Chronic obstructive lung disease | A. terreus | 2.44 | 14,560 | Caspofungin |
| 35 | Chronic obstructive lung disease | Cavity | A. flavus | - | 345 | Caspofungin |
| 36 | Acute leukemias | Air crescent sign | A. terreus | - | 12,356 | Caspofungin |
| 37 | Acute leukemias | Dense, well-circumscribed lesions | A. terreus | - | 4765 | Amphotericin B |
| 38 | Chronic obstructive lung disease | Cavity | A. terreus | - | 78 | Caspofungin |
| 41 | Acute leukemias | Air crescent sign | A. fumigatus | - | 15,185 | Amphotericin B |
| 42 | Chronic obstructive lung disease | Cavity | A. flavus | - | 1295 | Caspofungin |
| 43 | Hematological malignancies | Dense, well-circumscribed lesions | A. flavus | 1.33 | 29,271 | Amphotericin B |
| 44 | Chronic obstructive lung disease | Cavity | A. niger | 0.84 | 5872 | Itraconazole |
| 45 | Severe influenza | Air crescent sign | A. fumigatus | 2.72 | 391 | Caspofungin |
| 46 | Treatment with immunosuppressant | Dense, well-circumscribed lesions | A. flavus | - | 197 | Amphotericin B |
| 47 | Severe influenza | Dense, well-circumscribed lesions | A. terreus | - | 50,459 | Caspofungin |
| 48 | Chronic obstructive lung disease | Cavity | A. niger | 0.03 | 408 | Caspofungin |
| 49 | COVID-19 | Dense, well-circumscribed lesions | A. fumigatus | 6.34 | 5,345,000 | Amphotericin B |
| 50 | Severe influenza | Air crescent sign | A. fumigatus | 3.56 | 32,000 | Amphotericin B |
| 51 | Chronic obstructive lung disease | Cavity | A. fumigatus | 2.2 | 345 | Voriconazole |
| Techniques | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microscopy | 91.4 | 100 | 100 | 90 |
| Culture | 94.3 | 32.1 | 64.7 | 81.8 |
| GM * | 94.4 | 54.5 | 77.3 | 85.6 |
| PCR | 100 | 59.2 | 76.1 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trovato, L.; Calvo, M.; Palermo, C.I.; Scalia, G. The Role of Quantitative Real-Time PCR in the Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Diagnosis: A Retrospective Study. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020409
Trovato L, Calvo M, Palermo CI, Scalia G. The Role of Quantitative Real-Time PCR in the Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Diagnosis: A Retrospective Study. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(2):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020409
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrovato, Laura, Maddalena Calvo, Concetta Ilenia Palermo, and Guido Scalia. 2025. "The Role of Quantitative Real-Time PCR in the Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Diagnosis: A Retrospective Study" Microorganisms 13, no. 2: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020409
APA StyleTrovato, L., Calvo, M., Palermo, C. I., & Scalia, G. (2025). The Role of Quantitative Real-Time PCR in the Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Diagnosis: A Retrospective Study. Microorganisms, 13(2), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020409






