The Role of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Erectile Dysfunction: From Pathophysiology to Treatment Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
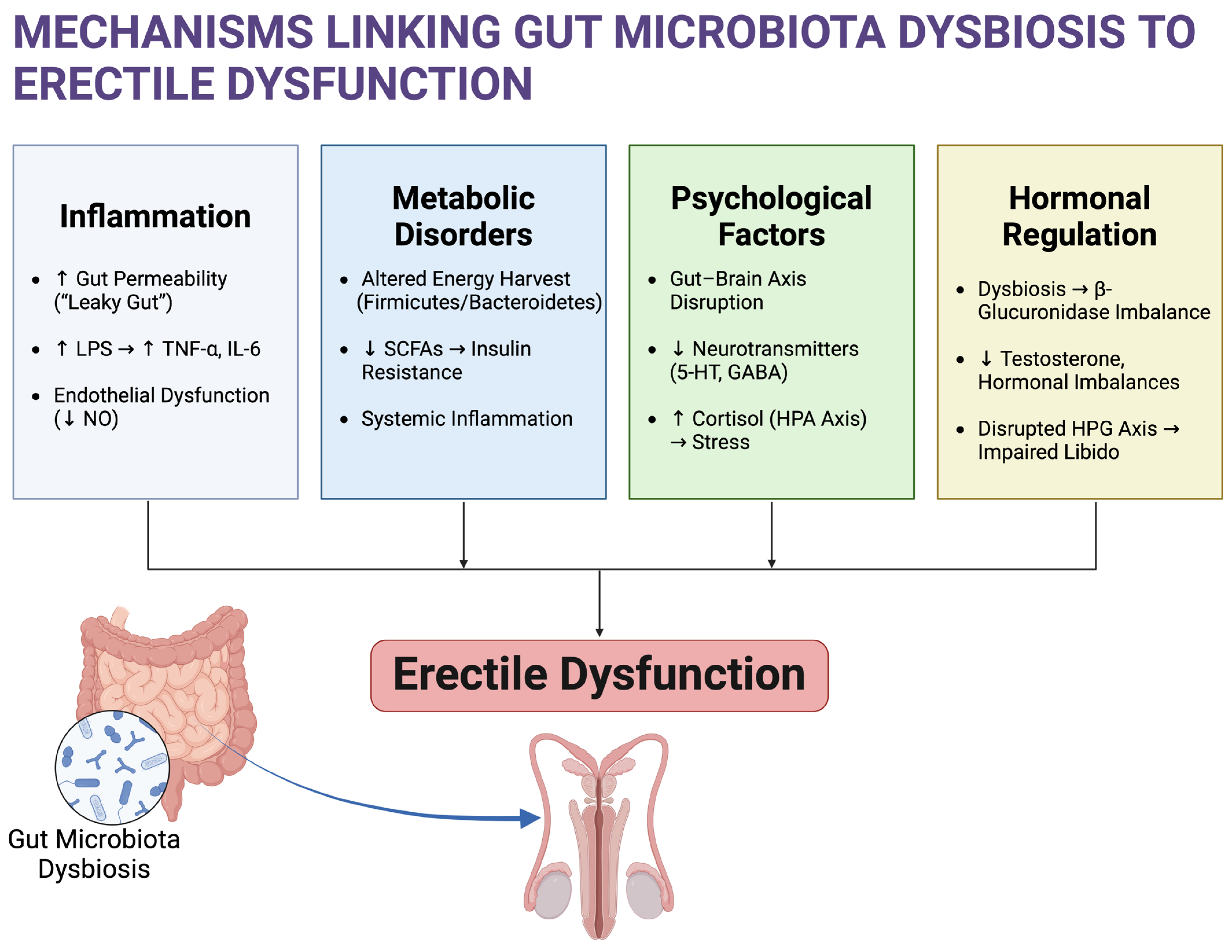
2. Potential Mechanisms Linking Gut Microbiota and ED
2.1. Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction
2.2. Metabolic Disorders and ED
2.3. Psychological Factors
2.4. Hormonal Regulation
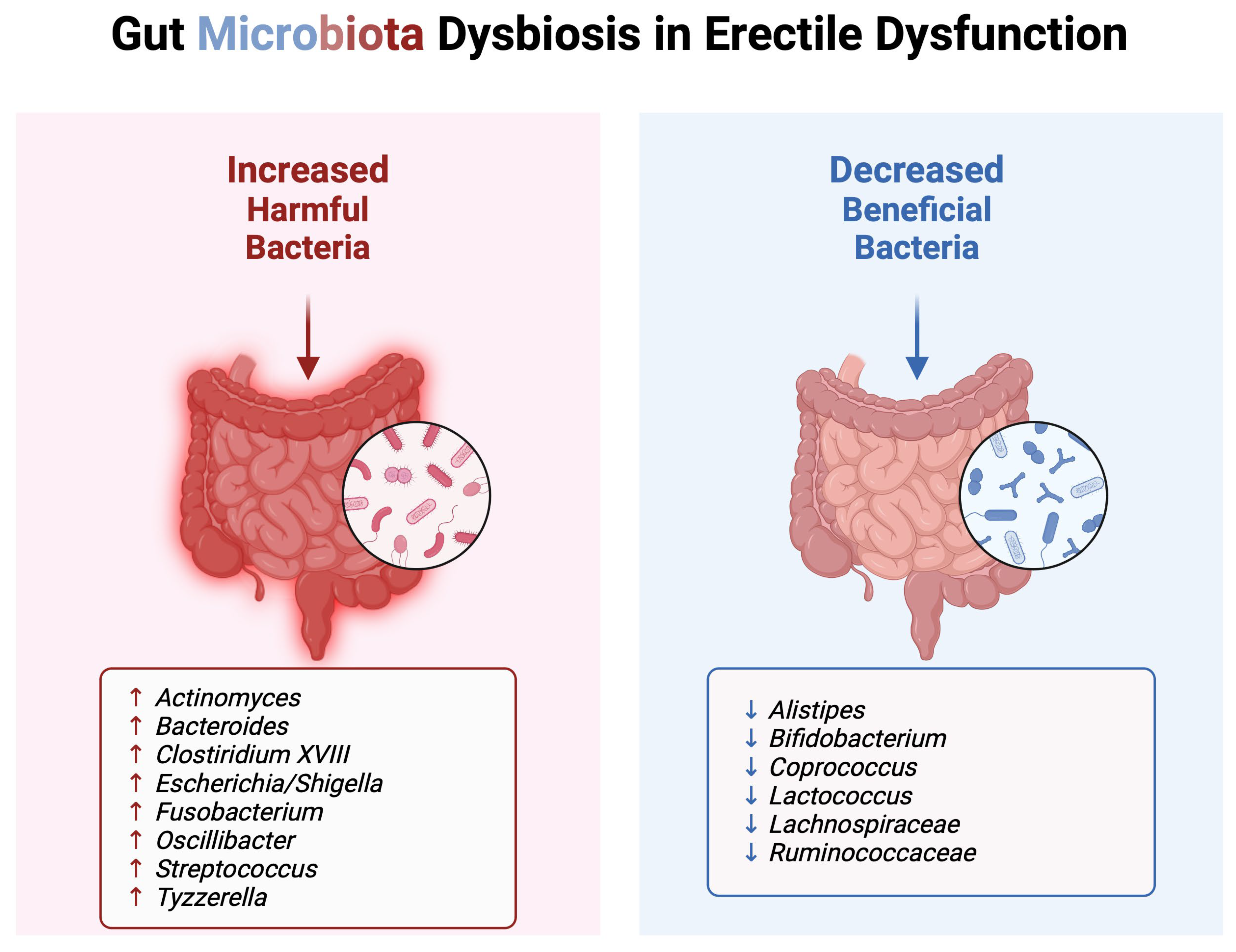
3. Alterations in Gut Microbiota Composition in ED Patients
3.1. Harmful Bacteria
3.1.1. Actinomyces
3.1.2. Bacteroides
3.1.3. Clostridium XVIII
3.1.4. Escherichia/Shigella
3.1.5. Fusobacterium
3.1.6. Oscillibacter
3.1.7. Streptococcus
3.1.8. Tyzzerella
3.2. Beneficial Bacteria
3.2.1. Alistipes
3.2.2. Coprococcus
3.2.3. Lactococcus
3.2.4. Lachnospiraceae
3.2.5. Ruminococcaceae
3.3. Consideration of Covariables and Summary of Key Taxa
4. Potential Biomarkers and Diagnostic Tools
5. Therapeutic Implications
6. Future Directions in Treatment Strategies
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rinkuniene, E.; Gimzauskaite, S.; Badariene, J.; Dzenkeviciute, V.; Kovaite, M.; Cypiene, A. The Prevalence of Erectile Dysfunction and Its Association with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients after Myocardial Infarction. Medicina 2021, 57, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitta, R.M.; de Lima Queiroga, L.; Louzada, A.C.S.; Ritti-Dias, R.M.; Kaufmann, O.G.; Wolosker, N. What are the Main Risk Factors Associated with Erectile Dysfunction in the Elderly? A Cross-Sectional Study of 2436 Brazilian Elderly Men. Clin. Interv. Aging 2023, 18, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yannas, D.; Frizza, F.; Vignozzi, L.; Corona, G.; Maggi, M.; Rastrelli, G. Erectile Dysfunction Is a Hallmark of Cardiovascular Disease: Unavoidable Matter of Fact or Opportunity to Improve Men’s Health? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herkommer, K.; Meissner, V.H.; Dinkel, A.; Jahnen, M.; Schiele, S.; Kron, M.; Ankerst, D.P.; Gschwend, J.E. Prevalence, lifestyle, and risk factors of erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, and low libido in middle-aged men: First results of the Bavarian Men’s Health-Study. Andrology 2024, 12, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallanzy, J.; Kron, M.; Goethe, V.E.; Kohn, F.M.; Schmautz, M.; Arsov, C.; Hadaschik, B.; Imkamp, F.; Gschwend, J.E.; Herkommer, K. Erectile Dysfunction in 45-Year-Old Heterosexual German Men and Associated Lifestyle Risk Factors and Comorbidities: Results From the German Male Sex Study. Sex. Med. 2019, 7, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltsas, A.; Zikopoulos, A.; Dimitriadis, F.; Sheshi, D.; Politis, M.; Moustakli, E.; Symeonidis, E.N.; Chrisofos, M.; Sofikitis, N.; Zachariou, A. Oxidative Stress and Erectile Dysfunction: Pathophysiology, Impacts, and Potential Treatments. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 8807–8834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivalacqua, T.J.; Usta, M.F.; Champion, H.C.; Kadowitz, P.J.; Hellstrom, W.J. Endothelial dysfunction in erectile dysfunction: Role of the endothelium in erectile physiology and disease. J. Androl. 2003, 24, S17–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Mannucci, E.; Mansani, R.; Petrone, L.; Bartolini, M.; Giommi, R.; Forti, G.; Maggi, M. Organic, relational and psychological factors in erectile dysfunction in men with diabetes mellitus. Eur. Urol. 2004, 46, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Liu, X.; Yang, P.; Ma, Y.; Gao, P.; Gao, J.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, X. The Association between the Gut Microbiota and Erectile Dysfunction. World J. Men’s Health 2024, 42, 772–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L. Role and Mechanism of Gut Microbiota in Human Disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 625913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, R.D., Jr.; Pontefract, B.A.; Mishcon, H.R.; Black, C.A.; Sutton, S.C.; Theberge, C.R. Gut Microbiome: Profound Implications for Diet and Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo-Roman, A.; Pagan-Zayas, N.; Velazquez-Rivera, L.I.; Torres-Ventura, A.C.; Godoy-Vitorino, F. Insights into Gut Dysbiosis: Inflammatory Diseases, Obesity, and Restoration Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltsas, A.; Zachariou, A.; Markou, E.; Dimitriadis, F.; Sofikitis, N.; Pournaras, S. Microbial Dysbiosis and Male Infertility: Understanding the Impact and Exploring Therapeutic Interventions. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarova, S.; Umbayev, B.; Masoud, A.R.; Kaiyrlykyzy, A.; Safarova, Y.; Tsoy, A.; Olzhayev, F.; Kushugulova, A. The Links Between the Gut Microbiome, Aging, Modern Lifestyle and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, H. The impact of metabolites derived from the gut microbiota on immune regulation and diseases. Int. Immunol. 2020, 32, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajeri, M.H.; Brummer, R.J.M.; Rastall, R.A.; Weersma, R.K.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Faas, M.; Eggersdorfer, M. The role of the microbiome for human health: From basic science to clinical applications. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasaly, N.; de Vos, P.; Hermoso, M.A. Impact of Bacterial Metabolites on Gut Barrier Function and Host Immunity: A Focus on Bacterial Metabolism and Its Relevance for Intestinal Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 658354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Sun, X.; Oh, S.F.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Geva-Zatorsky, N.; Jupp, R.; Mathis, D.; Benoist, C.; et al. Microbial bile acid metabolites modulate gut RORgamma(+) regulatory T cell homeostasis. Nature 2020, 577, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, N.; Su, X.; Gao, Y.; Yang, R. Gut-Microbiota-Derived Metabolites Maintain Gut and Systemic Immune Homeostasis. Cells 2023, 12, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Li, H.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Liu, H.; Chen, H.; Lu, M. The Gut Microbiome and Sex Hormone-Related Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 711137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Hatakeyama, S.; Imai, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Yoneyama, T.; Mori, K.; Yoneyama, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Nakaji, S.; Ohyama, C. The association between gut microbiome and erectile dysfunction: A community-based cross-sectional study in Japan. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020, 52, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Niu, Y.; Guo, H.; Jin, X.; Liu, F. Pyroptosis and inflammation-mediated endothelial dysfunction may act as key factors in the development of erectile dysfunction (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2023, 28, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, N.; Hatakeyama, S.; Momota, M.; Hamaya, T.; Tobisawa, Y.; Yoneyama, T.; Okamoto, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Yoneyama, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; et al. Relationships of low-grade systemic inflammation and nutritional status with erectile dysfunction severity in men on dialysis. Andrology 2022, 10, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Pan, Y.; Niu, S.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, X. Characteristics of Gut Microbiota in Patients with Erectile Dysfunction: A Chinese Pilot Study. World J. Men’s Health 2024, 42, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohm, T.V.; Meier, D.T.; Olefsky, J.M.; Donath, M.Y. Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Immunity 2022, 55, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, A.L.; Stephens, J.W.; Harris, D.A. Intestinal microbiota and their metabolic contribution to type 2 diabetes and obesity. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2021, 20, 1855–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randeni, N.; Bordiga, M.; Xu, B. A Comprehensive Review of the Triangular Relationship among Diet-Gut Microbiota-Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheithauer, T.P.M.; Rampanelli, E.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Vallance, B.A.; Verchere, C.B.; van Raalte, D.H.; Herrema, H. Gut Microbiota as a Trigger for Metabolic Inflammation in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 571731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Tian, J.X.; Lian, F.M.; Li, M.; Liu, W.K.; Zhen, Z.; Liao, J.Q.; Tong, X.L. Therapeutic mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine to improve metabolic diseases via the gut microbiota. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigalou, C.; Paraschaki, A.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Aftzoglou, K.; Bezirtzoglou, E.; Tsakris, Z.; Vradelis, S.; Stavropoulou, E. Alterations of gut microbiome following gastrointestinal surgical procedures and their potential complications. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1191126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, V.; Ditu, L.M.; Pircalabioru, G.G.; Picu, A.; Petcu, L.; Cucu, N.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Gut Microbiota, Host Organism, and Diet Trialogue in Diabetes and Obesity. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppas, S.; Pansieri, C.; Piovani, D.; Danese, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Tsantes, A.G.; Brunetta, E.; Tsantes, A.E.; Bonovas, S. The Brain-Gut Axis: Psychological Functioning and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suda, K.; Matsuda, K. How Microbes Affect Depression: Underlying Mechanisms via the Gut-Brain Axis and the Modulating Role of Probiotics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonali, S.; Ray, B.; Ahmed Tousif, H.; Rathipriya, A.G.; Sunanda, T.; Mahalakshmi, A.M.; Rungratanawanich, W.; Essa, M.M.; Qoronfleh, M.W.; Chidambaram, S.B.; et al. Mechanistic Insights into the Link between Gut Dysbiosis and Major Depression: An Extensive Review. Cells 2022, 11, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiak, B.; Loniewski, I.; Marlicz, W.; Frydecka, D.; Szulc, A.; Rudzki, L.; Samochowiec, J. The HPA axis dysregulation in severe mental illness: Can we shift the blame to gut microbiota? Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 102, 109951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, T.; Dalziel, J.; Coad, J.; Roy, N.; Butts, C.; Gopal, P. The Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis and Resilience to Developing Anxiety or Depression Under Stress. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.H.; Kim, N.; Nam, R.H.; Choi, S.I.; Jang, J.Y.; Lee, H.N. Changes in Gut Microbiome upon Orchiectomy and Testosterone Administration in AOM/DSS-Induced Colon Cancer Mouse Model. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 55, 196–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Park, Y.H.; Sim, M.; Kim, S.A.; Joung, H.; Shin, D.M. Serum level of sex steroid hormone is associated with diversity and profiles of human gut microbiome. Res. Microbiol. 2019, 170, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeri, F.; Endres, K. How biological sex of the host shapes its gut microbiota. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2021, 61, 100912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tang, L.; Zhai, D.; Song, M.; Li, W.; Xu, S.; Jiang, S.; Meng, H.; Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. The role of the sex hormone-gut microbiome axis in tumor immunotherapy. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2185035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Yang, Z.; Fu, G.; Chen, Y. Gut microbiota composition may be an indicator of erectile dysfunction. Microb. Biotechnol. 2024, 17, e14403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, M.L.; Gozal, D.; Pires, G.N.; Tufik, S. Exploring the potential relationships among obstructive sleep apnea, erectile dysfunction, and gut microbiota: A narrative review. Sex. Med. Rev. 2023, 12, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.I.; Bongiorno, D.; Bonomo, C.; Musso, N.; Stefani, S.; Sokolakis, I.; Hatzichristodoulou, G.; Falcone, M.; Cai, T.; Smarrazzo, F.; et al. The relationship between the gut microbiota, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and erectile dysfunction. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2023, 35, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, E.; Joshy, G.; Abhayaratna, W.P.; Kritharides, L.; Macdonald, P.S.; Korda, R.J.; Chalmers, J.P. Erectile dysfunction severity as a risk marker for cardiovascular disease hospitalisation and all-cause mortality: A prospective cohort study. PLoS Med. 2013, 10, e1001372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.; Rosas, S.E. Erectile dysfunction and coronary artery calcification in incident dialysis patients. J. Nephrol. 2021, 34, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakodimos, I.; Ziogou, A.; Giannakodimos, A.; Mitakidi, E.; Kaltsas, A.; Kratiras, Z.; Chrisofos, M. Renal Actinomycosis in Humans-A Narrative Review. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansara, T.; Majmundar, M.; Doshi, R.; Ghosh, K.; Saeed, M. A Case of Life-threatening Actinomyces turicensis Bacteremia. Cureus 2020, 12, e6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, J.D.; Chen, C.Y.; Knox, N.C.; Marrie, R.A.; El-Gabalawy, H.; de Kievit, T.; Alfa, M.; Bernstein, C.N.; Van Domselaar, G. A comparative study of the gut microbiota in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases-does a common dysbiosis exist? Microbiome 2018, 6, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofilis, P.; Sagris, M.; Oikonomou, E.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Siasos, G.; Tsioufis, C.; Tousoulis, D. Inflammatory Mechanisms Contributing to Endothelial Dysfunction. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Mei, Y.; Xu, R.; Zhang, H.; Feng, X. Causal effects of gut microbiota on erectile dysfunction: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1257114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhogaria, B.; Bhowmik, P.; Kundu, A. Correlation between human gut microbiome and diseases. Infect. Med. 2022, 1, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atarashi, K.; Tanoue, T.; Shima, T.; Imaoka, A.; Kuwahara, T.; Momose, Y.; Cheng, G.; Yamasaki, S.; Saito, T.; Ohba, Y.; et al. Induction of colonic regulatory T cells by indigenous Clostridium species. Science 2011, 331, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostadmohammadi, S.; Nojoumi, S.A.; Fateh, A.; Siadat, S.D.; Sotoodehnejadnematalahi, F. Interaction between Clostridium species and microbiota to progress immune regulation. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2022, 69, 89–103. [Google Scholar]
- Calmasini, F.B.; Klee, N.; Webb, R.C.; Priviero, F. Impact of Immune System Activation and Vascular Impairment on Male and Female Sexual Dysfunction. Sex. Med. Rev. 2019, 7, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Bai, M.; Ning, X.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Dong, R.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S. Expansion of Escherichia-Shigella in Gut Is Associated with the Onset and Response to Immunosuppressive Therapy of IgA Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 2276–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatro, J.B.; Romero, L.I.; Beasley, D.; Steere, A.C.; Reichlin, S. Borrelia burgdorferi and Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharides induce nitric oxide and interleukin-6 production in cultured rat brain cells. J. Infect. Dis. 1994, 169, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Guo, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, F.; Wen, S.; Liu, Y.; Ren, W.; Zhang, X.; Shang, Y.; Gao, M.; et al. Predominance of Escherichia-shigella in Gut Microbiome and Its Potential Correlation with Elevated Level of Plasma Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha in Patients with Tuberculous Meningitis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0192622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltazar-Diaz, T.A.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, L.A.; Aldana-Ledesma, J.M.; Pena-Rodriguez, M.; Vega-Magana, A.N.; Zepeda-Morales, A.S.M.; Lopez-Roa, R.I.; Del Toro-Arreola, S.; Martinez-Lopez, E.; Salazar-Montes, A.M.; et al. Escherichia/Shigella, SCFAs, and Metabolic Pathways-The Triad That Orchestrates Intestinal Dysbiosis in Patients with Decompensated Alcoholic Cirrhosis from Western Mexico. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comtois, A.S.; El-Dwairi, Q.; Laubach, V.E.; Hussain, S.N. Lipopolysaccharide-induced diaphragmatic contractile dysfunction in mice lacking the inducible nitric oxide synthase. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 1975–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chou, P.S.; Hung, W.C.; Yang, I.H.; Kuo, C.M.; Wu, M.N.; Lin, T.C.; Fong, Y.O.; Juan, C.H.; Lai, C.L. Predicting Adverse Recanalization Therapy Outcomes in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients Using Characteristic Gut Microbiota. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.C.; Chua, L.L.; Yap, S.H.; Khang, T.F.; Leng, C.Y.; Raja Azwa, R.I.; Lewin, S.R.; Kamarulzaman, A.; Woo, Y.L.; Lim, Y.A.L.; et al. Enrichment of gut-derived Fusobacterium is associated with suboptimal immune recovery in HIV-infected individuals. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Sun, J.; Wei, L.; Jiang, H.; Hu, C.; Yang, J.; Huang, Y.; Ruan, B.; Zhu, B. Altered gut microbiota correlate with different immune responses to HAART in HIV-infected individuals. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Isnard, S.; Lin, J.; Fombuena, B.; Peng, X.; Nair Parvathy, S.; Chen, Y.; Silverman, M.S.; Routy, J.P. Treating From the Inside Out: Relevance of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation to Counteract Gut Damage in GVHD and HIV Infection. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Long, Y.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, T.; Zheng, L.; Wang, K.; Tang, Q. Specific gut microbiota may increase the risk of erectile dysfunction: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1216746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Qin, Z.; Yi, B.; Xie, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yang, K.; Zhang, H. Inflammatory cytokine profiles in erectile dysfunction: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1342658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, H.; Kohanawa, M. Endogenous interleukin-6 plays a crucial protective role in streptococcal toxic shock syndrome via suppression of tumor necrosis factor alpha production. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 3745–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Q.; Chen, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, F.; Yu, G.; Yan, X.; Zhang, J. Correlation between gut microbiota diversity and psychogenic erectile dysfunction. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2021, 10, 4412–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, B.J.; Wearsch, P.A.; Veloo, A.C.M.; Rodriguez-Palacios, A. The Genus Alistipes: Gut Bacteria With Emerging Implications to Inflammation, Cancer, and Mental Health. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesic, D.; Lugovic Mihic, L.; Ozretic, P.; Lojkic, I.; Buljan, M.; Situm, M.; Zovak, M.; Vidovic, D.; Mijic, A.; Galic, N.; et al. Association of Gut Lachnospiraceae and Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria. Life 2023, 13, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.; Zhang, B. Genetically proxied intestinal microbiota and risk of erectile dysfunction. Andrology 2024, 12, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Serrano, A.M.; Skoug, C.; Axling, U.; Korhonen, E.R.; Teixeira, C.; Ahren, I.L.; Mukhopadhya, I.; Boteva, N.; Martin, J.; Scott, K.; et al. Butyrate-producing bacteria as probiotic supplement: Beneficial effects on metabolism and modulation of behaviour in an obesity mouse model. Benef. Microbes 2024, 16, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Ma, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, W. Ruminococcaceae_UCG-013 Promotes Obesity Resistance in Mice. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Relman, D.A. Thinking about the microbiome as a causal factor in human health and disease: Philosophical and experimental considerations. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2020, 54, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.M.; Hammad, M.A.; Barham, D.W.; Toma, R.; El-Khatib, F.M.; Dianatnejad, S.; Nguyen, J.; Towe, M.; Choi, E.; Wu, Q.; et al. Comparison of the gut microbiome composition between men with erectile dysfunction and a matched cohort: A pilot study. Andrology 2024, 12, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Lorusso, E.; Fosso, B.; Pesole, G. A comprehensive overview of microbiome data in the light of machine learning applications: Categorization, accessibility, and future directions. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1343572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, J.; West, N.P.; Cox, A.J. Comparison of four DNA extraction methods for 16s rRNA microbiota profiling of human faecal samples. BMC Res. Notes 2023, 16, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snigdha, S.; Ha, K.; Tsai, P.; Dinan, T.G.; Bartos, J.D.; Shahid, M. Probiotics: Potential novel therapeutics for microbiota-gut-brain axis dysfunction across gender and lifespan. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 231, 107978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Ho, C.L. Recent Development of Probiotic Bifidobacteria for Treating Human Diseases. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 770248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhong, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Gao, X. Therapeutic and Improving Function of Lactobacilli in the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular-Related Diseases: A Novel Perspective From Gut Microbiota. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 693412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsimardou, A.; Patoulias, D.; Zografou, I.; Siskos, F.; Stavropoulos, K.; Imprialos, K.; Tegou, Z.; Boulmpou, A.; Georgopoulou, V.; Hatzipapa, N.; et al. The Impact of Metabolic Syndrome Components on Erectile Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Metabolites 2023, 13, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchin, S.; Bertin, L.; Bonazzi, E.; Lorenzon, G.; De Barba, C.; Barberio, B.; Zingone, F.; Maniero, D.; Scarpa, M.; Ruffolo, C.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Human Health: From Metabolic Pathways to Current Therapeutic Implications. Life 2024, 14, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasquez, E.C.; Pereira, T.M.C.; Peotta, V.A.; Baldo, M.P.; Campos-Toimil, M. Probiotics as Beneficial Dietary Supplements to Prevent and Treat Cardiovascular Diseases: Uncovering Their Impact on Oxidative Stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 3086270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, W.; Li, Q.; Yu, J. Gut microbiota modulation: A novel strategy for prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2020, 39, 4925–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airola, C.; Severino, A.; Porcari, S.; Fusco, W.; Mullish, B.H.; Gasbarrini, A.; Cammarota, G.; Ponziani, F.R.; Ianiro, G. Future Modulation of Gut Microbiota: From Eubiotics to FMT, Engineered Bacteria, and Phage Therapy. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofikitis, N.; Kaltsas, A.; Dimitriadis, F.; Rassweiler, J.; Grivas, N.; Zachariou, A.; Kaponis, A.; Tsounapi, P.; Paterakis, N.; Karagiannis, A.; et al. The Effect of PDE5 Inhibitors on the Male Reproductive Tract. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 2697–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Bacterial Genus/Family | Key Metabolites | Proposed Role in ED | Mechanistic Pathway(s) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actinomyces | Unknown or LPS-like components | - Enriched in ED patients; negatively correlates with erectile function scores - Elevates TNF-α, IL-6, contributing to endothelial dysfunction | Inflammation, endothelial injury, possible gut barrier disruption | [24,47,48,49,50,51] |
| Bacteroides | Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), bile acid metabolites | - Associated with increased systemic inflammation and vascular impairment - Often linked to diets high in saturated fats | Inflammation, gut barrier compromise | [21,52] |
| Escherichia/Shigella | LPS, pro-inflammatory metabolites | - Elevates TNF-α, IL-6, impairing NO availability - Contributes to oxidative stress, potentially disrupting hormone balance | Inflammation, oxidative stress, metabolic/hormonal dysregulation | [56,57,58,59,60] |
| Fusobacterium | LPS, other inflammatory mediators | - Linked to compromised gut barrier, increased bacterial translocation - Induces vascular dysfunction and immune cell death | Inflammation, gut barrier disruption | [61,62,63,64] |
| Oscillibacter | Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs; e.g., butyrate) | - Positively associated with ED risk - Linked to pro-inflammatory states, metabolic issues (insulin resistance, obesity) | Inflammation, metabolic dysregulation, possible mood interactions | [65] |
| Streptococcus | Possibly LPS-like components, other virulence factors | - Raises TNF-α, IL-6, disrupting NO signaling - Linked to cardiovascular disorders and vascular inflammation | Inflammation, endothelial dysfunction | [66,67,68] |
| Tyzzerella | Pro-inflammatory metabolites (not fully characterized) | - Elevated in ED, associated with CVD and metabolic syndrome - May exacerbate oxidative stress, impairing vascular health | Inflammation, oxidative stress | [51] |
| Alistipes | Sulfonolipids, SCFAs (e.g., propionate, butyrate) | - Reduced in ED patients; exerts anti-inflammatory, gut-protective effects - May inhibit TNF-α, IL-6 via von Willebrand factor receptor antagonism | Anti-inflammation, gut barrier support | [21,69] |
| Coprococcus | Butyrate and other SCFAs | - Decreased in ED; correlates with reduced metabolic and vascular complications - Supports endothelial function by mitigating inflammation | Anti-inflammation, endothelial support | [24] |
| Lactococcus | SCFAs, bacteriocins, lactate | - Depleted in ED; helps maintain gut barrier and lower systemic inflammation - Reduced levels linked to increased gut permeability and vascular risk | Gut barrier integrity, immune modulation | [51] |
| Lachnospiraceae | SCFAs (butyrate, propionate), varies by genus | - Some taxa (e.g., Roseburia) produce butyrate (anti-inflammatory), others linked to pro-inflammatory states - Disruption can affect lipid metabolism, endocrine function, and NO bioavailability | Inflammation, lipid metabolism, NO signaling | [70,71,72] |
| Ruminococcaceae (UCG-013) | SCFAs (especially butyrate) | - Increased abundance inversely linked to ED risk - Enhances endothelial function by reducing inflammation and oxidative damage | Anti-inflammation, endothelial protection | [65,71,73] |
| Study (Year) | Study Design/Population | Intervention/Exposure | Outcome Measures | Key Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Okamoto et al. (2020) | Cross-sectional, community-based study in Japan (n = 68 men) | No intervention; fecal samples collected for microbiota profiling | Prevalence of ED, gut microbial composition | Enrichment of Bacteroides and Escherichia/Shigella associated with higher ED severity. Study suggests a possible link between dysbiosis and ED. | [21] |
| Su et al. (2023) | Mendelian randomization analysis (population-level genetic data) | Genetic proxies for gut microbiota traits | Causal relationship between certain taxa and ED | Lachnospiraceae and Oscillibacter variants showed potential causal links to ED risk, providing genetic evidence for gut microbiota’s role in ED pathogenesis. | [65] |
| Kang et al. (2024) | Pilot observational study in China (n = 36 ED patients vs. 36 controls) | No intervention; 16S rRNA gene sequencing of stool samples | IIEF-5 scores, gut microbiota composition, inflammatory markers | ED group showed increased abundance of Actinomyces, decreased Ruminococcaceae spp. Negative correlation between Actinomyces load and erectile function. | [24] |
| Osman et al. (2024) | Case–control pilot study in the USA (n = 19 ED patients vs. 19 controls) | No intervention; stool sample analysis of microbial composition | Gut microbiota composition, ED severity | Identified differences in gut microbial diversity; suggested that specific taxa might influence inflammatory pathways contributing to ED. | [75] |
| Zhu et al. (2024) | Narrative synthesis of gut microbiota and ED studies | No direct intervention; overview of observational findings | ED-associated changes in gut microbiome | Summarized cross-sectional data linking dysbiosis to ED, highlighting potential inflammatory and metabolic pathways. Called for larger RCTs to confirm efficacy. | [9] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaltsas, A.; Giannakodimos, I.; Markou, E.; Adamos, K.; Stavropoulos, M.; Kratiras, Z.; Zachariou, A.; Dimitriadis, F.; Sofikitis, N.; Chrisofos, M. The Role of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Erectile Dysfunction: From Pathophysiology to Treatment Strategies. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020250
Kaltsas A, Giannakodimos I, Markou E, Adamos K, Stavropoulos M, Kratiras Z, Zachariou A, Dimitriadis F, Sofikitis N, Chrisofos M. The Role of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Erectile Dysfunction: From Pathophysiology to Treatment Strategies. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(2):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020250
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaltsas, Aris, Ilias Giannakodimos, Eleftheria Markou, Konstantinos Adamos, Marios Stavropoulos, Zisis Kratiras, Athanasios Zachariou, Fotios Dimitriadis, Nikolaos Sofikitis, and Michael Chrisofos. 2025. "The Role of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Erectile Dysfunction: From Pathophysiology to Treatment Strategies" Microorganisms 13, no. 2: 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020250
APA StyleKaltsas, A., Giannakodimos, I., Markou, E., Adamos, K., Stavropoulos, M., Kratiras, Z., Zachariou, A., Dimitriadis, F., Sofikitis, N., & Chrisofos, M. (2025). The Role of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Erectile Dysfunction: From Pathophysiology to Treatment Strategies. Microorganisms, 13(2), 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020250







