Ecological Modulation of Soil Microbial Communities by Fertilization Regimes: Insights from Castor Bean Cake, Chemical Fertilizers, and Organic Fertilizer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Collection and Treatments
2.2. DNA Extraction, Library Construction, and Sequencing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis and Community Assembly Mechanisms
2.5. Data Availability
3. Results
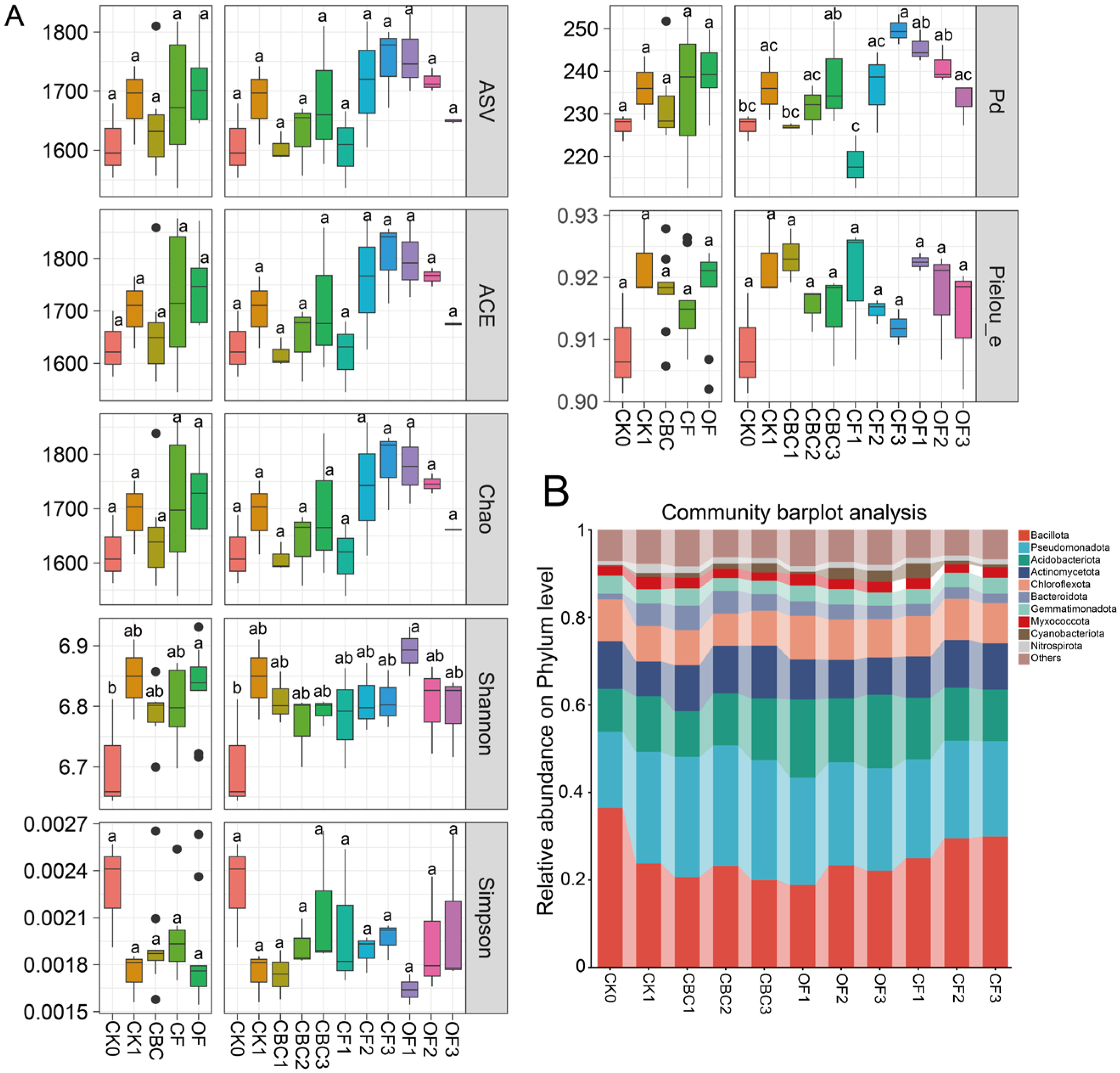
3.1. Effects of Different Fertilization Treatments on Soil Bacterial Community Composition and Alpha Diversity
3.2. Effects of Different Fertilization Treatments on Soil Bacterial Beta Diversity
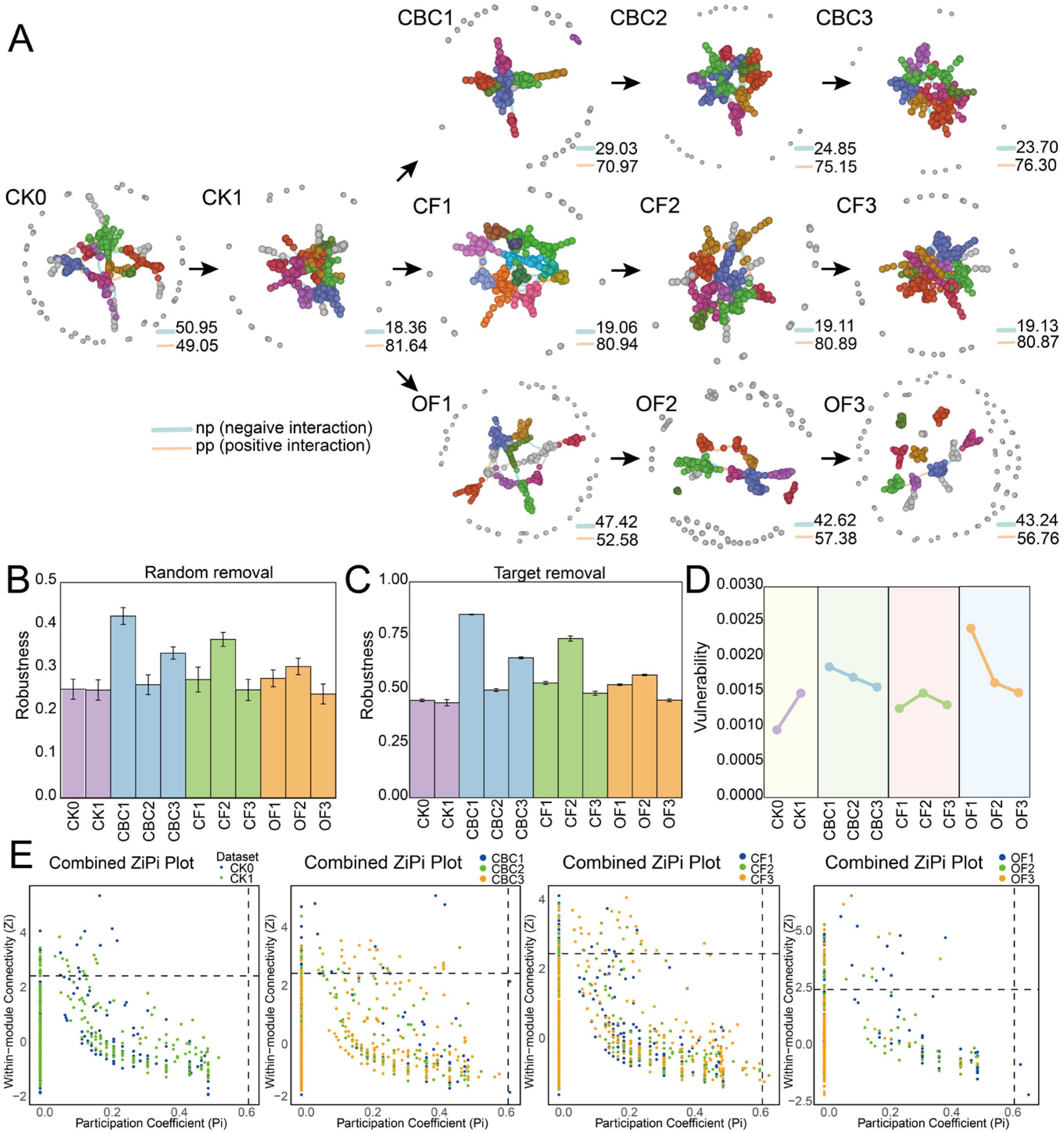
3.3. Bacterial Co-Occurrence Network Dynamics Under Different Fertilizer Treatments
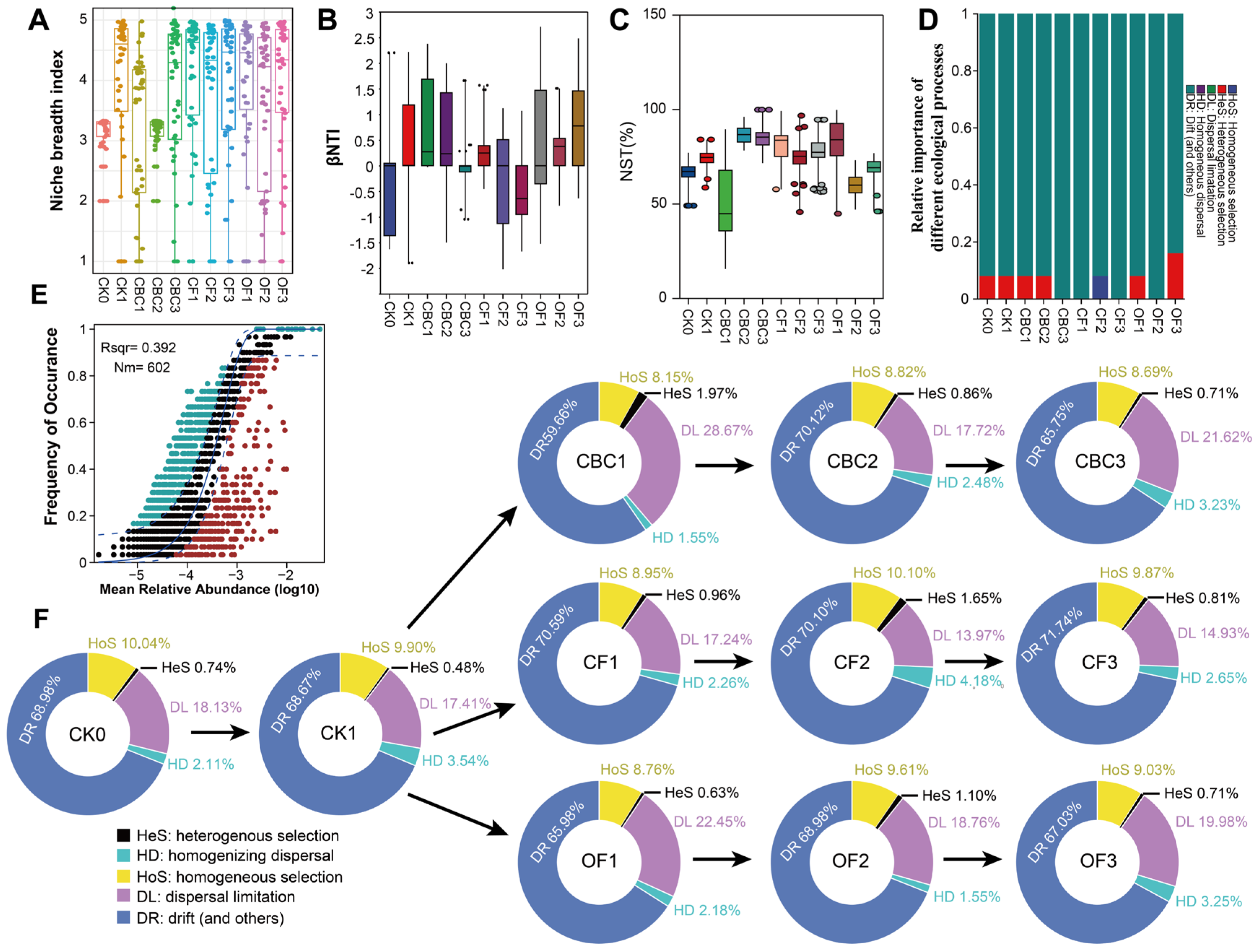
3.4. Assembly Mechanisms of Bacterial Communities Under Fertilization Regimes
4. Discussion
4.1. Castor Cake Application Promotes the Enrichment of Functional Bacterial Phyla and Diversity Recovery
4.2. Castor Cake Mediates Microbial Community Restructuring Through Nutrient and Enzyme System Modulation
4.3. Effects of Different Fertilizers Application on Soil Microbial Ecological Network
4.4. Stochastic and Deterministic Processes Structure Bacterial Community Assembly
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hemathilake, D.; Gunathilake, D. Agricultural productivity and food supply to meet increased demands. In Future Foods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 539–553. [Google Scholar]
- Yahaya, S.M.; Mahmud, A.A.; Abdullahi, M.; Haruna, A. Recent advances in the chemistry of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium as fertilizers in soil: A review. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Wang, X. Precise application of water and fertilizer to crops: Challenges and opportunities. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1444560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Fatima, A.; Saha, S.; Sahoo, S.K.; Poddar, P. Environmental Pollution due to Improper Use of Chemical Fertilizers and Their Remediation. In Environmental Contaminants; Apple Academic Press: Palm Bay, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 203–219. [Google Scholar]
- Ramamoorthy, P.; Sathiyamurthi, S.; Pavithra, A.; Sivasakthi, M.; Praveen Kumar, S. Impact of Major Nutrients Fertilizer Application on Soil Pollution and Management Measures. In Soil, Water Pollution and Mitigation Strategies: A Spatial Approach; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 301–314. [Google Scholar]
- Rathod, S.V.; Saras, P.; Gondaliya, S.M. Environmental pollution: Threats and challenges for management. In Eco-Restoration of Polluted Environment; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ashitha, A.; Rakhimol, K. Fate of the conventional fertilizers in environment. In Controlled Release Fertilizers for Sustainable Agriculture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 25–39. [Google Scholar]
- Bhadu, A.; Singh, B.; Gulshan, T.; Kumawat, S.N.; Choudhary, R.K.; Farooq, F. Customized fertilizer: A key for enhanced crop production. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2022, 34, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, H.B.; Carolino, A.d.S.; Nunes, R.Z.d.A.; Macalia, C.M.; Ruzo, C.M.; Pinto, C.d.C.; Bezerra, J.d.A.; Campelo, P.H.; Ţălu, Ș.; de Souza, L.K. Advances in agricultural technology: A review of slow-release nanofertilizers and innovative carriers. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plant Anal. 2024, 55, 1849–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sindhu, S.S.; Kumar, R. Biofertilizers: An ecofriendly technology for nutrient recycling and environmental sustainability. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2022, 3, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Wang, Z.; He, Z.; Li, G.; Di, J.; Luo, R.; Wang, C.; Huang, F. Combining Ability, Heritability, and Heterosis for Seed Weight and Oil Content Traits of Castor Bean (Ricinus communis L.). Agronomy 2024, 14, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, V.; Sharma, R.K.; Bharambe, D. Investigation of rheological and thermal conductivity properties of castor oil nanofluids containing graphene nanoplatelets. Int. J. Thermophys. 2023, 44, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansdown, A.; Lee, S. Aviation lubricants. In Chemistry and Technology of Lubricants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 345–373. [Google Scholar]
- Meneses, A.J.G.; Pompeu, R.; Salles, H.O.; Costa, C.D.S.; Rogério, M.C.P.; de Andrade, I.R.A.; Furtado, R.N.; de Medeiros, A.N.; Pereira, P.L.; Cândido, M.J.D. Nutritional parameters and productive performance of grazing sheep using castor bean cake as supplement or fertilizer. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2024, 56, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneses, A.J.G.; Pompeu, R.; Salles, H.O.; da Silva Vieira, L.; Teixeira, M.; Rogério, M.C.P.; Sousa, A.M.P.; Pereira, P.L.; Cândido, M.J.D. Castor bean cake for the control of parasites in pasture-finished sheep. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2022, 54, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Sousa, V.F.; Dias, T.J.; Costa, J.E.; de Oliveira Maia Júnior, S.; Henschel, J.M.; Costa, R.N.M.; Pereira, W.E.; Linné, J.A. Castor Bean Cake Mitigates Saline Stress in Basil Plants. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 3969–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Luo, R.; Yin, M.; Wang, Z.; Su, Z.; Gu, X.; Hu, X.; Zhang, C.; Huang, F. Castor bean meal fertilizer improves peanut yield and quality by regulating the soil physicochemical environment and soil enzyme activities. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 4681–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Kumar, G.; Chhabra, S.; Prasad, R. Role of soil microbes in biogeochemical cycle for enhancing soil fertility. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Harman, G.; Khadka, R.; Doni, F.; Uphoff, N. Benefits to plant health and productivity from enhancing plant microbial symbionts. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 610065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, A.K.; Akhtar, N.; Sher, F.; Navarrete, A.A.; Américo-Pinheiro, J.H.P. Microbial adaptation to different environmental conditions: Molecular perspective of evolved genetic and cellular systems. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Y.; Bier, R.; Li, X.; Daniels, M.; Smith, A.; Yu, L.; Kan, J. Agricultural practices influence soil microbiome assembly and interactions at different depths identified by machine learning. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Dou, X.; Liao, D.; Li, K.; An, C.; Li, G.; Dong, Z. Microbial fertilizers improve soil quality and crop yield in coastal saline soils by regulating soil bacterial and fungal community structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 175127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Wu, Y.; He, G.; Wen, S.; Yang, L.; Ji, L. Fertilization regime changes rhizosphere microbial community assembly and interaction in Phoebe bournei plantations. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, M.S.; Shahzadi, F.; Ali, F.; Shakeela, Q.; Niaz, Z.; Ahmed, S. Comparative effect of fertilization practices on soil microbial diversity and activity: An overview. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 3644–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; O’hara, R.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 1.17-4. 2010. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 6 June 2025).
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Luo, F.; Zhou, J. Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In Proceedings of the Third International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media (ICWSM-09), San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M.M.; Guo, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, N.; Ning, D.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; et al. Climate warming enhances microbial network complexity and stability. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Deng, Y.; Tiedje, J.M.; Zhou, J. A general framework for quantitatively assessing ecological stochasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 16892–16898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, W.T.; Lunn, M.; Woodcock, S.; Head, I.M.; Nee, S.; Curtis, T.P. Quantifying the roles of immigration and chance in shaping prokaryote community structure. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, S.; Liu, X.; Yao, P.; Ge, T.; Zhang, X.-H. Spatiotemporal dynamics of the archaeal community in coastal sediments: Assembly process and co-occurrence relationship. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1463–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, D.; Yuan, M.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Y.; Arkin, A.P.; Firestone, M.K.; Zhou, J. A quantitative framework reveals ecological drivers of grassland microbial community assembly in response to warming. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dincă, L.C.; Grenni, P.; Onet, C.; Onet, A. Fertilization and Soil Microbial Community: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coller, E.; Cestaro, A.; Zanzotti, R.; Bertoldi, D.; Pindo, M.; Larger, S.; Albanese, D.; Mescalchin, E.; Donati, C. Microbiome of vineyard soils is shaped by geography and management. Microbiome 2019, 7, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti Taguali, S.; Pöter, R.; Aloi, F.; Fernández-Trujillo, C.; Acedo, A.; La Spada, F.; Li Destri Nicosia, M.G.; Pane, A.; Schena, L.; Cacciola, S.O. Influence of environmental and agronomic variables on soil microbiome in citrus orchards: A comparative analysis of organic and conventional farming system. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 299, 128260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangid, K.; Williams, M.A.; Franzluebbers, A.J.; Sanderlin, J.S.; Reeves, J.H.; Jenkins, M.B.; Endale, D.M.; Coleman, D.C.; Whitman, W.B. Relative impacts of land-use, management intensity and fertilization upon soil microbial community structure in agricultural systems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2843–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, A.A.; Haq, S.; Bhat, R.A. Actinomycetes benefaction role in soil and plant health. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 111, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhao, P.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, N. Effects of a Nanonetwork-Structured Soil Conditioner on Microbial Community Structure. Biology 2023, 12, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.D.; Jiménez-Ocampo, R.; Rosales-Serna, R.; Rodríguez-González, J.A.; Santos-De la Cruz, J.L.; Cruz-Bravo, R.K.; Alvarado-Aguilar, P.; Gamboa-Gómez, C.I.; Guerrero-Romero, F. A simple thermal-detoxified method for castor bean (Ricinus communis L.) cake, and its potential nutraceutical properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 174, 114151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mould, D.L.; Hogan, D.A. Intraspecies heterogeneity in microbial interactions. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2021, 62, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulier, S.; Gillis, A.; Colau, G.; Licciardi, F.; Liépin, M.; Desoignies, N.; Modrie, P.; Legrève, A.; Mahillon, J.; Bragard, C. Versatile Antagonistic Activities of Soil-Borne Bacillus spp. and Pseudomonas spp. against Phytophthora infestans and Other Potato Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingjing, L.; Xuemei, H.; Rui, L.; Chunhua, Z.; Ruimei, H.; Guibin, X.; Guorui, L.; Jianjun, D.; Cheng, W.; Xiaohui, G.; et al. By promoting growth and development, castor bean meal biofertilizer improves the yield and quality of Tartary buckwheat and indirectly improves the growth and development of Tartary buckwheat sprouts. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1584608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Han, X.; Yan, J.; Yan, L.; Zou, W. Impact of combined organic amendments and chemical fertilizers on soil microbial limitations, soil quality, and soybean yield. Plant Soil 2025, 507, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, M.; Feng, R.; Xiao, H.; Xue, C. Impact of Organic Amendments on Black Wheat Yield, Grain Quality, and Soil Biochemical Properties. Agronomy 2025, 15, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Yang, B.; Zhang, M.; Song, D.; Xu, X.; Ai, C.; Liang, G.; Zhou, W. Investigating the effects of organic amendments on soil microbial composition and its linkage to soil organic carbon: A global meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 164899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lori, M.; Symnaczik, S.; Mäder, P.; De Deyn, G.; Gattinger, A. Organic farming enhances soil microbial abundance and activity—A meta-analysis and meta-regression. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazcano, C.; Zhu-Barker, X.; Decock, C. Effects of organic fertilizers on the soil microorganisms responsible for N2O emissions: A review. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amadou, A.; Song, A.; Tang, Z.-X.; Li, Y.; Wang, E.-Z.; Lu, Y.-Q.; Liu, X.-D.; Yi, K.; Zhang, B.; Fan, F. The effects of organic and mineral fertilization on soil enzyme activities and bacterial community in the below- and above-ground parts of wheat. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; Luo, F.; He, Z.; Tu, Q.; Zhi, X. Functional molecular ecological networks. mBio 2010, 1, e00169-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; He, P.; Li, S.; Liang, G.; Zhou, W.; et al. The stronger impact of inorganic nitrogen fertilization on soil bacterial community than organic fertilization in short-term condition. Geoderma 2021, 382, 114752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.-Y.; He, H.-Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, L.; Mao, W.-J.; Zhai, M.-Z. Positive effects of organic fertilizers and biofertilizers on soil microbial community composition and walnut yield. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 175, 104457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, X.; Tan, W.; Di, H.; Xu, J.; Li, Y. High manure load reduces bacterial diversity and network complexity in a paddy soil under crop rotations. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2020, 2, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, N. Seasonal dynamics of the pink root fungus (Setophoma terrestris) in rhizosphere soil: Effect of crop species and rotation. Plant Pathol. 2022, 71, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.M.; Bascompte, J.; Dupont, Y.L.; Jordano, P. The modularity of pollination networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19891–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, S.; Mitter, B.; Oswald, A.; Schloter-Hai, B.; Schloter, M.; Declerck, S.; Sessitsch, A. Rhizosphere microbiomes of potato cultivated in the High Andes show stable and dynamic core microbiomes with different responses to plant development. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegwart, L.; Piton, G.; Jourdan, C.; Piel, C.; Sauze, J.; Sugihara, S.; Bertrand, I. Carbon and nutrient colimitations control the microbial response to fresh organic carbon inputs in soil at different depths. Geoderma 2023, 440, 116729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatayud, J.; Andivia, E.; Escudero, A.; Melián, C.J.; Bernardo-Madrid, R.; Stoffel, M.; Aponte, C.; Medina, N.G.; Molina-Venegas, R.; Arnan, X.; et al. Positive associations among rare species and their persistence in ecological assemblages. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyte, K.Z.; Schluter, J.; Foster, K.R. The ecology of the microbiome: Networks, competition, and stability. Science 2015, 350, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dini-Andreote, F.; Stegen, J.C.; Van Elsas, J.D.; Salles, J.F. Disentangling mechanisms that mediate the balance between stochastic and deterministic processes in microbial succession. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1326–E1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Luan, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Zou, W.; Han, X.; Duan, Y.; Zhu, B.; Li, Y.; et al. Community assembly of organisms regulates soil microbial functional potential through dual mechanisms. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hu, H.; Yan, H.; Hou, D.; Wang, Y.; Dong, P.; Zhang, D. Archaeal biogeography and interactions with microbial community across complex subtropical coastal waters. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 3101–3118, Erratum in Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 2124–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Lu, H.P.; Sastri, A.; Yeh, Y.C.; Gong, G.C.; Chou, W.C.; Hsieh, C.H. Contrasting the relative importance of species sorting and dispersal limitation in shaping marine bacterial versus protist communities. ISME J. 2018, 12, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Liu, X.-Y.; Di, H.-H.; He, X.-S.; Sun, Y.; Xiang, S.; Huang, Z.-B. The mechanism of microbial community succession and microbial co-occurrence network in soil with compost application. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnee, L.; Koehler, H.; Ngakou, A.; Eickhorst, T. Long-term impact of single biochar and compost application on soil aggregation. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Bogor, Indonesia, 16–18 September 2020; p. 012160. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Shi, Y.; Kong, L.; Tong, L.; Cao, H.; Zhou, H.; Lv, Y. Long-Term Application of Bio-Compost Increased Soil Microbial Community Diversity and Altered Its Composition and Network. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Deng, G.; Hu, C.; Hou, X.; Wang, Z. Bioremediation Potential of Rhodococcus qingshengii PM1 in Sodium Selenite-Contaminated Soil and Its Impact on Microbial Community Assembly. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, S.F.; Deppe, N.A.; Berhow, M.A.; Evangelista, R.L. Lesquerella press cake as an organic fertilizer for greenhouse tomatoes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2010, 32, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-C.; Qi, J.-F.; Xiao, D.-R.; Wang, Y.; Shi, W.-Y.; Wang, H. Bacterial community diversity and underlying assembly patterns along vertical soil profiles in wetland and meadow habitats on the Zoige Plateau, China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 184, 109076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Bello, M.; Lee, H.; Goyal, A.; Gore, J. Resource-diversity relationships in bacterial communities reflect the network structure of microbial metabolism. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 1424–1434, Erratum in Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibocha-Bonilla, J.D.; Kumar, M.; Richelle, A.; Godoy-Silva, R.D.; Zengler, K.; Zuñiga, C. Dynamic resource allocation drives growth under nitrogen starvation in eukaryotes. NPJ Syst. Biol. Appl. 2020, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Ling, N.; Quaiser, A.; Guo, J.; Ruan, J.; Guo, S.; Shen, Q.; Vandenkoornhuyse, P. Rare Bacteria Assembly in Soils Is Mainly Driven by Deterministic Processes. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 83, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logares, R.; Tesson, S.V.M.; Canbäck, B.; Pontarp, M.; Hedlund, K.; Rengefors, K. Contrasting prevalence of selection and drift in the community structuring of bacteria and microbial eukaryotes. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 2231–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaton, E.D.; Stevenson, B.S.; King-Sharp, K.J.; Stamps, B.W.; Nunn, H.S.; Stuart, M. Local and Regional Diversity Reveals Dispersal Limitation and Drift as Drivers for Groundwater Bacterial Communities from a Fractured Granite Formation. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albright, M.B.N.; Martiny, J.B.H. Dispersal alters bacterial diversity and composition in a natural community. ISME J. 2018, 12, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, R.L.S.; Severino, L.S.; Sampaio, L.R.; Sofiatti, V.; Gomes, J.A.; Beltrão, N.E.M. Blends of castor meal and castor husks for optimized use as organic fertilizer. Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 33, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.-H.; Zheng, K.-X.; Wong, S.C.; Tzou, Y.-M.; Wang, S.; Lin, S.-R.; Yang, H.-Y.; Fu, C.-Y.; Wu, J.J.; Liu, C.-H. Fate, transport, and plant uptake of ricinine in soils amended with castor cake organic fertilizer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 494, 138454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Adonis | ANOSIM | MRPP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | R | p | δ | p | |
| Samples | 9.1505 | 0.001 | 0.6081 | 0.001 | 0.3936 | 0.001 |
| Network Name | Topological Properties | CK0 | CK1 | CBC1 | CBC2 | CBC3 | CF1 | CF2 | CF3 | OF1 | OF2 | OF3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Empirical | Similarity threshold | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.98 |
| Total nodes | 699 | 683 | 529 | 638 | 664 | 705 | 679 | 749 | 629 | 610 | 497 | |
| Total links | 2836 | 3157 | 2232 | 2929 | 3561 | 3546 | 3239 | 3523 | 1472 | 1769 | 828 | |
| Average degree (avgk) | 8.114 | 9.245 | 8.439 | 9.182 | 10.726 | 10.060 | 9.541 | 9.407 | 4.680 | 5.800 | 3.332 | |
| Centralization of degree (CD) | 0.049 | 0.054 | 0.134 | 0.052 | 0.081 | 0.048 | 0.049 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.076 | 0.056 | |
| Average path distance (GD) | 6.696 | 5.932 | 4.170 | 5.747 | 5.598 | 6.297 | 6.109 | 5.752 | 7.060 | 5.620 | 5.496 | |
| Average clustering coefficient (avgCC) | 0.443 | 0.352 | 0.330 | 0.312 | 0.351 | 0.394 | 0.326 | 0.285 | 0.370 | 0.404 | 0.377 | |
| Centralization of betweenness (CB) | 0.218 | 0.106 | 0.233 | 0.087 | 0.140 | 0.106 | 0.101 | 0.105 | 0.212 | 0.201 | 0.100 | |
| Modularity | 0.829 | 0.799 | 0.692 | 0.795 | 0.730 | 0.810 | 0.772 | 0.763 | 0.865 | 0.822 | 0.897 | |
| Random networks | Modularity | 0.308 ± 0.004 | 0.286 ± 0.004 | 0.298 ± 0.004 | 0.288 ± 0.004 | 0.258 ± 0.004 | 0.271 ± 0.003 | 0.281 ± 0.004 | 0.285 ± 0.004 | 0.456 ± 0.005 | 0.386 ± 0.004 | 0.583 ± 0.006 |
| Average path distance (GD) | 3.294 ± 0.019 | 3.142 ± 0.012 | 3.090 ± 0.020 | 3.140 ± 0.013 | 2.970 ± 0.011 | 3.065 ± 0.013 | 3.121 ± 0.012 | 3.157 ± 0.011 | 3.919 ± 0.029 | 3.572 ± 0.024 | 4.607 ± 0.058 | |
| Average clustering coefficient (avgCC) | 0.032 ± 0.003 | 0.029 ± 0.003 | 0.049 ± 0.004 | 0.025 ± 0.002 | 0.043 ± 0.003 | 0.033 ± 0.002 | 0.029 ± 0.003 | 0.027 ± 0.002 | 0.020 ± 0.003 | 0.030 ± 0.004 | 0.013 ± 0.004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Huang, F.; Fan, Z.; Peng, M. Ecological Modulation of Soil Microbial Communities by Fertilization Regimes: Insights from Castor Bean Cake, Chemical Fertilizers, and Organic Fertilizer. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2841. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122841
Hu C, Wu Y, Li Z, Wang Z, Huang F, Fan Z, Peng M. Ecological Modulation of Soil Microbial Communities by Fertilization Regimes: Insights from Castor Bean Cake, Chemical Fertilizers, and Organic Fertilizer. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(12):2841. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122841
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Chongyang, Yalijuan Wu, Zecheng Li, Zhiyong Wang, Fenglan Huang, Zhiquan Fan, and Mu Peng. 2025. "Ecological Modulation of Soil Microbial Communities by Fertilization Regimes: Insights from Castor Bean Cake, Chemical Fertilizers, and Organic Fertilizer" Microorganisms 13, no. 12: 2841. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122841
APA StyleHu, C., Wu, Y., Li, Z., Wang, Z., Huang, F., Fan, Z., & Peng, M. (2025). Ecological Modulation of Soil Microbial Communities by Fertilization Regimes: Insights from Castor Bean Cake, Chemical Fertilizers, and Organic Fertilizer. Microorganisms, 13(12), 2841. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122841




