Epithelial–Macrophage Crosstalk in Host Responses to Campylobacter jejuni Infection in Humans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Campylobacter Culture
2.2. Stimulation of HT-29 Cells with Campylobacter
2.3. Evaluation of the Cytotoxic Effects of Campylobacter on HT-29 Cells
- -
- Compound-treated LDH: LDH activity in the HT-29 supernatant-treated wells;
- -
- Spontaneous LDH: LDH activity in the distilled water-treated wells (baseline release);
- -
- Maximum LDH: LDH activity after complete lysis of cells (total release).
2.4. Evaluation of IFN-γ Production in Campylobacter-Infected HT-29 Cells
2.5. Evaluation of NO Production in Macrophages Following Treatment with Supernatant from Campylobacter-Infected HT-29 Cells
2.6. Evaluation of Macrophage Migration Following Treatment with Supernatant from Campylobacter-Infected HT-29 Cells
2.7. Evaluation of Macrophage Phagocytic Activity Following Treatment with Supernatant from Campylobacter-Infected HT-29 Cells
2.8. Evaluation of Macrophage Bactericidal Activity Against Campylobacter Following Treatment with Supernatant from Campylobacter-Infected HT-29 Cells
2.9. Evaluation of Gene Expressions of Cytokine and Chemokine in Macrophages Following Treatment with Supernatant from Campylobacter-Infected HT-29 Cells
2.9.1. RNA Isolation and cDNA Preparation from Macrophages
2.9.2. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Campylobacter-IECs Interactions
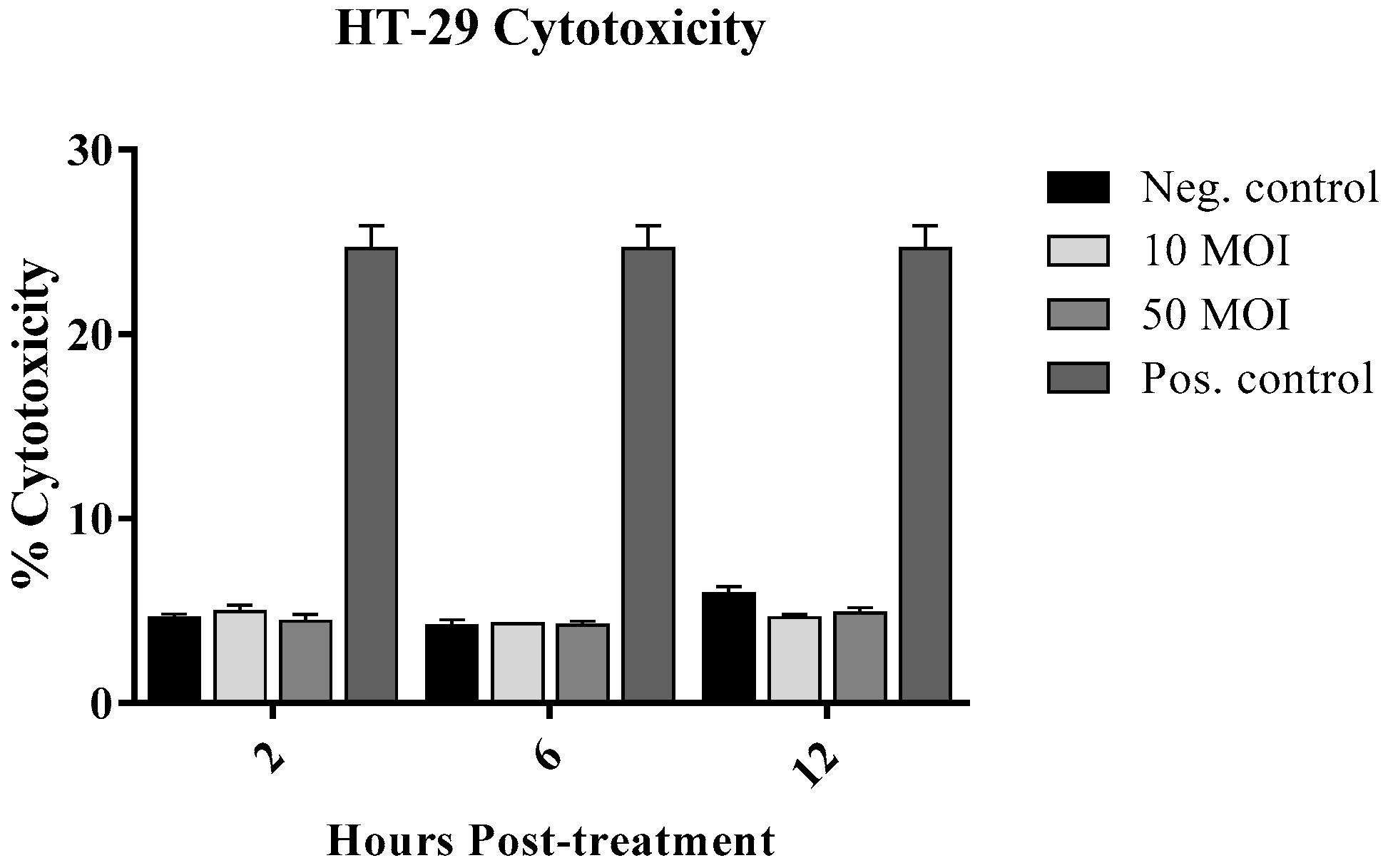
3.1.1. Cytotoxic Effect of Campylobacter on IECs
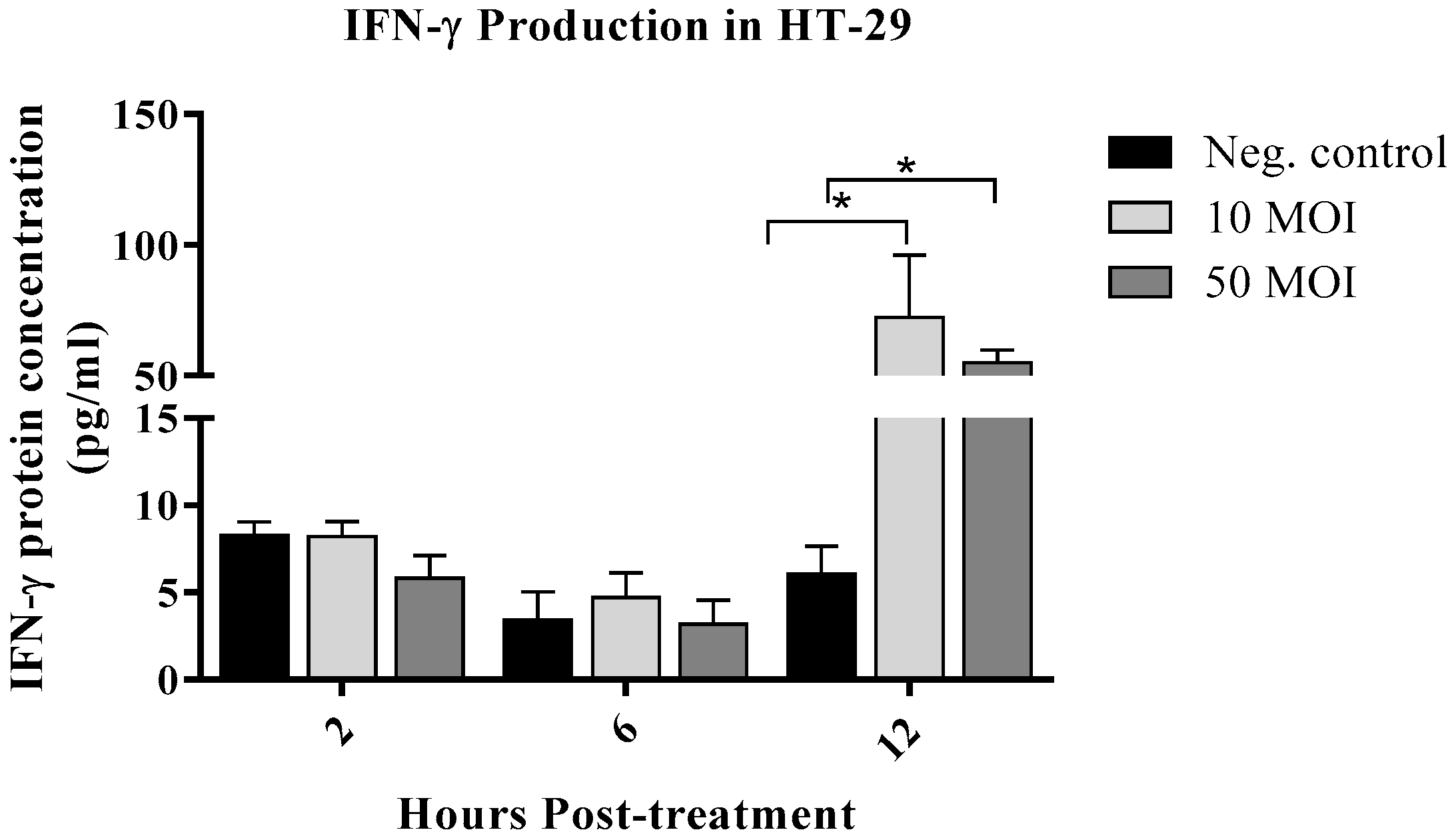
3.1.2. Campylobacter Enhanced IFN-γ Production by IECs
3.2. Campylobacter-Macrophage Interactions
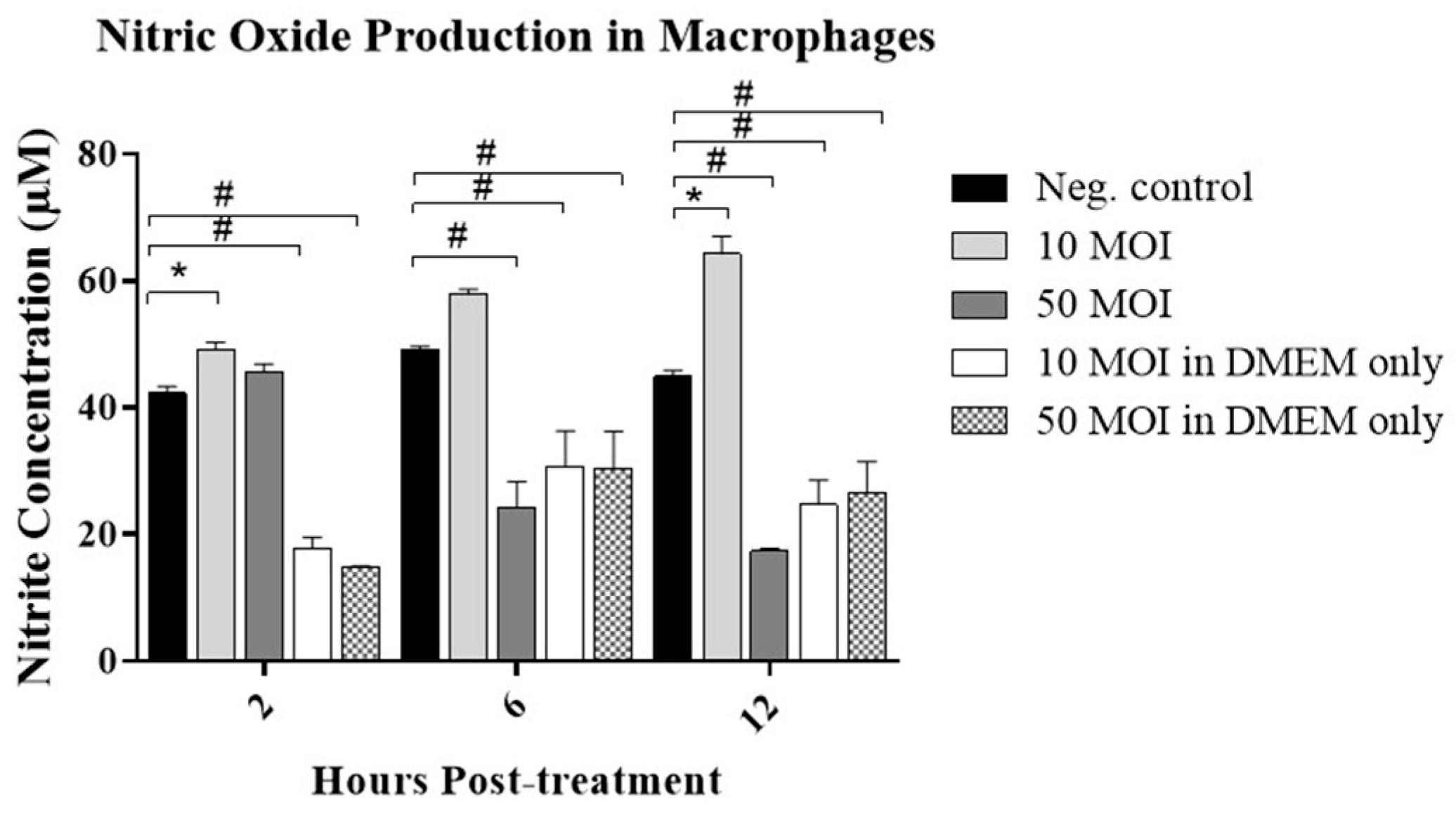
3.2.1. Soluble Factors Secreted by Campylobacter-Infected IECs Stimulate NO Production in Macrophages
3.2.2. Soluble Factors Secreted by Campylobacter-Infected IECs Promote Macrophage Migration Activity
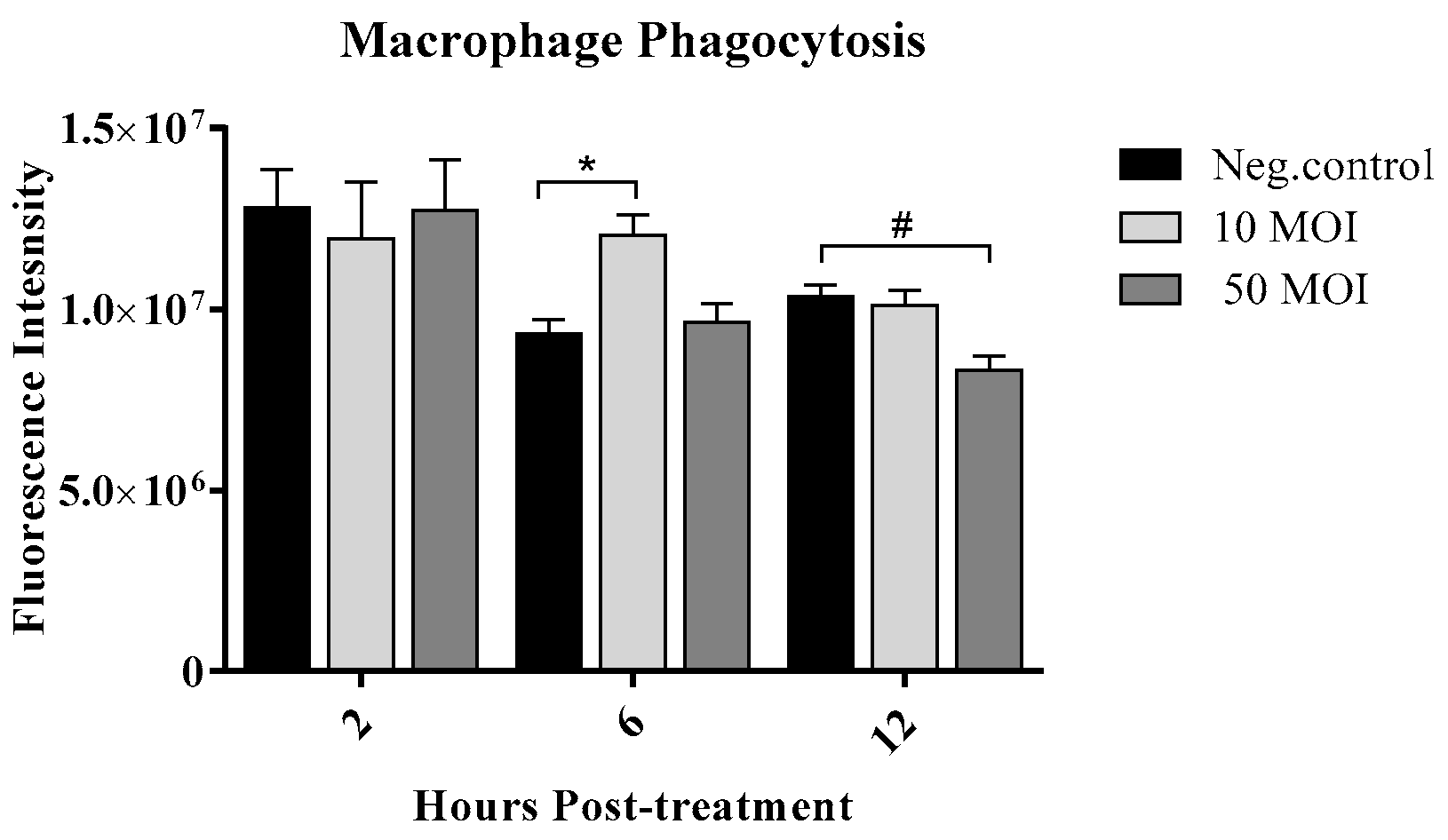
3.2.3. Soluble Factors Secreted by Campylobacter-Infected IECs Enhance Macrophage Phagocytic Activity
3.2.4. Soluble Factors Secreted by Campylobacter-Infected IECs Did Not Influence the Macrophage Killing Activity
3.2.5. Soluble Factors Secreted by Campylobacter-Infected IECs Alter Cytokine and Chemokine Gene Expression in Macrophages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taha-Abdelaziz, K.; Singh, M.; Sharif, S.; Sharma, S.; Kulkarni, R.R.; Alizadeh, M.; Yitbarek, A.; Helmy, Y.A. Intervention Strategies to Control Campylobacter at Different Stages of the Food Chain. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Sharma, S.; Schneider, A.; Wehmueller, S.; Abdelaziz, K. Comparative Effectiveness of Various Multi-Antigen Vaccines in Controlling Campylobacter jejuni in Broiler Chickens. Vaccines 2024, 12, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Sharma, S.; Schneider, A.; Bragg, A.J.; Abdelaziz, K. A multi-antigen Campylobacter vaccine enhances antibody responses in layer breeders and sustains elevated maternal antibody levels in their offspring. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 104898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda-Madej, A.; Gagat, P.; Wiśniewski, J.; Viscardi, S.; Krzyżek, P. Impact of Isoquinoline Alkaloids on the Intestinal Barrier in a Colonic Model of Campylobacter jejuni Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kaur, S.; Naguib, M.; Bragg, A.; Schneider, A.; Kulkarni, R.R.; Nazmi, A.; Abdelaziz, K. Major Foodborne Bacterial Pathogens in Poultry: Implications for Human Health and the Poultry Industry and Probiotic Mitigation Strategies. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha-Abdelaziz, K.; Astill, J.; Kulkarni, R.R.; Read, L.R.; Najarian, A.; Farber, J.M.; Sharif, S. In vitro assessment of immunomodulatory and anti-Campylobacter activities of probiotic lactobacilli. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, A. Human Immunity Against Campylobacter Infection. Immune Netw. 2019, 19, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmi, A.; Watson, E.; Sandu, P.; Gundogdu, O.; Mills, D.C.; Inglis, N.F.; Manson, E.; Imrie, L.; Bajaj-Elliott, M.; Wren, B.W.; et al. Campylobacter jejuni outer membrane vesicles play an important role in bacterial interactions with human intestinal epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 4089–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iovine, N.M.; Pursnani, S.; Voldman, A.; Wasserman, G.; Blaser, M.J.; Weinrauch, Y. Reactive nitrogen species contribute to innate host defense against Campylobacter jejuni. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketley, J.M. Pathogenesis of enteric infection by Campylobacter. Microbiology 1997, 143 Pt 1, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickey, T.E.; McVeigh, A.L.; Scott, D.A.; Michielutti, R.E.; Bixby, A.; Carroll, S.A.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Guerry, P. Campylobacter jejuni cytolethal distending toxin mediates release of interleukin-8 from intestinal epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 6535–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wine, E.; Chan, V.L.; Sherman, P.M. Campylobacter jejuni mediated disruption of polarized epithelial monolayers is cell-type specific, time dependent, and correlates with bacterial invasion. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 64, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Meng, J.; Zhao, S.; Singh, R.; Song, W. Campylobacter-induced interleukin-8 secretion in polarized human intestinal epithelial cells requires Campylobacter-secreted cytolethal distending toxin- and Toll-like receptor-mediated activation of NF-kappaB. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 4498–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikema, A.P.; Koning, R.I.; Rico, S.D.D.S.; Rempel, H.; Jacobs, B.C.; Endtz, H.P.; van Wamel, W.J.B.; Samsom, J.N. Enhanced, sialoadhesin-dependent uptake of Guillain-Barre syndrome-associated Campylobacter jejuni strains by human macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 2095–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassenaar, T.M.; Engelskirchen, M.; Park, S.; Lastovica, A. Differential uptake and killing potential of Campylobacter jejuni by human peripheral monocytes/macrophages. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 1997, 186, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banfi, E.; Cinco, M.; Zabucchi, G. Phagocytosis of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli by peritoneal macrophages. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1986, 132, 2409–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, W.A.; Sajecki, J.L.; Pitts, T.M.; Joens, L.A. Role of catalase in Campylobacter jejuni intracellular survival. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 6337–6345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha-Abdelaziz, K.; Yitbarek, A.; Alkie, T.N.; Hodgins, D.C.; Read, L.R.; Weese, J.S.; Sharif, S. PLGA-encapsulated CpG ODN and Campylobacter jejuni lysate modulate cecal microbiota composition in broiler chickens experimentally challenged with C. jejuni. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justus, C.R.; Leffler, N.; Ruiz-Echevarria, M.; Yang, L.V. In vitro cell migration and invasion assays. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 88, 51046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Puhar, A. Gentamicin Protection Assay to Determine the Number of Intracellular Bacteria during Infection of Human TC7 Intestinal Epithelial Cells by Shigella flexneri. Bio. Protoc. 2019, 9, e3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, K.; Nixon, T.; Joye, A.; Hassan, H.; Alizadeh, M.; Sharif, S.; Kulkarni, R.R. Modulation of functional activity of heat-stressed chicken macrophages by poultry-derived probiotic lactobacilli. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 104, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha-Abdelaziz, K.; Alkie, T.N.; Hodgins, D.C.; Yitbarek, A.; Shojadoost, B.; Sharif, S. Gene expression profiling of chicken cecal tonsils and ileum following oral exposure to soluble and PLGA-encapsulated CpG ODN, and lysate of Campylobacter jejuni. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 212, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Jo, H.; Echesabal-Chen, J.; Stamatikos, A. Combined LXR and RXR Agonist Therapy Increases ABCA1 Protein Expression and Enhances ApoAI-Mediated Cholesterol Efflux in Cultured Endothelial Cells. Metabolites 2021, 11, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, L.; Echesabal-Chen, J.; Miller, M.; Powell, R.R.; Bruce, T.; Paul, A.; Poudyal, N.; Saliutama, J.; Parman, K.; Paul, K.S.; et al. Cholesterol Efflux Decreases TLR4-Target Gene Expression in Cultured Macrophages Exposed to T. brucei Ghosts. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, C.; Jiménez-Marín, Á.; Martins, R.P.; Garrido, J.J. Interaction between Campylobacter and intestinal epithelial cells leads to a different proinflammatory response in human and porcine host. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2014, 162, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, S.M.; Dolislager, C.G.; Johnson, J.G. The Host Cellular Immune Response to Infection by Campylobacter spp. and Its Role in Disease. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e00116-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Vela, A.; Clohisey, S.M.; Athanasiadou, S.; Kaiser, P.; Stevens, M.P.; Vervelde, L. Host-specific differences in the response of cultured macrophages to Campylobacter jejuni capsule and O-methyl phosphoramidate mutants. Vet. Res. 2018, 49, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintoan-Uta, C. The host-pathogen interaction in Campylobacter jejuni infection of chickens: An understudied aspect that is crucial for effective control. Virulence 2017, 8, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Cui, Y.; Guo, F.; Guo, J.; Cao, X.; Lin, J.; Ding, B.; Xu, F. Campylobacter jejuni infection induces dynamic expression of avian host defense peptides in vitro and in vivo. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 277, 109631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.G.; Park, B.J.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.G. Infection of human intestinal epithelial cells by invasive bacteria activates NF-κB and increases ICAM-1 expression through NOD1. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2018, 33, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Liu, C.; Wu, B.; Lin, Y.; Ma, T.; Xiong, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Ma, C.; Tu, Z. Effects of IRF1 and IFN-β interaction on the M1 polarization of macrophages and its antitumor function. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Lim, G.; Yoon, S.-J.; Yi, H.-S.; Choi, D.W. The role of immunomodulatory metabolites in shaping the inflammatory response of macrophages. BMB Rep. 2022, 55, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, R.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Cawthraw, S.A.; van Pelt, W.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Owen, R.J. Host-Pathogen Interactions in Campylobacter Infections: The Host Perspective. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribble, D.R.; Baqar, S.; Scott, D.A.; Oplinger, M.L.; Trespalacios, F.; Rollins, D.; Walker, R.I.; Clements, J.D.; Walz, S.; Gibbs, P.; et al. Assessment of the Duration of Protection in Campylobacter jejuni Experimental Infection in Humans. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.A.; To, S.; Maskell, D.J.; Bryant, C.E.; Barrow, P.A. Induction of Proinflammatory Responses in the Human Monocytic Cell Line THP-1 by Campylobacter jejuni. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 2626–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, H.; Cogan, T.; Humphrey, T. Direction of neutrophil movements by Campylobacter-infected intestinal epithelium. Microbes Infect. 2011, 13, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bär, W. Role of murine macrophages and complement in experimental campylobacter infection. J. Med. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickey, T.E.; Majam, G.; Guerry, P. Intracellular Survival of Campylobacter jejuni in Human Monocytic Cells and Induction of Apoptotic Death by Cytholethal Distending Toxin. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 5194–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

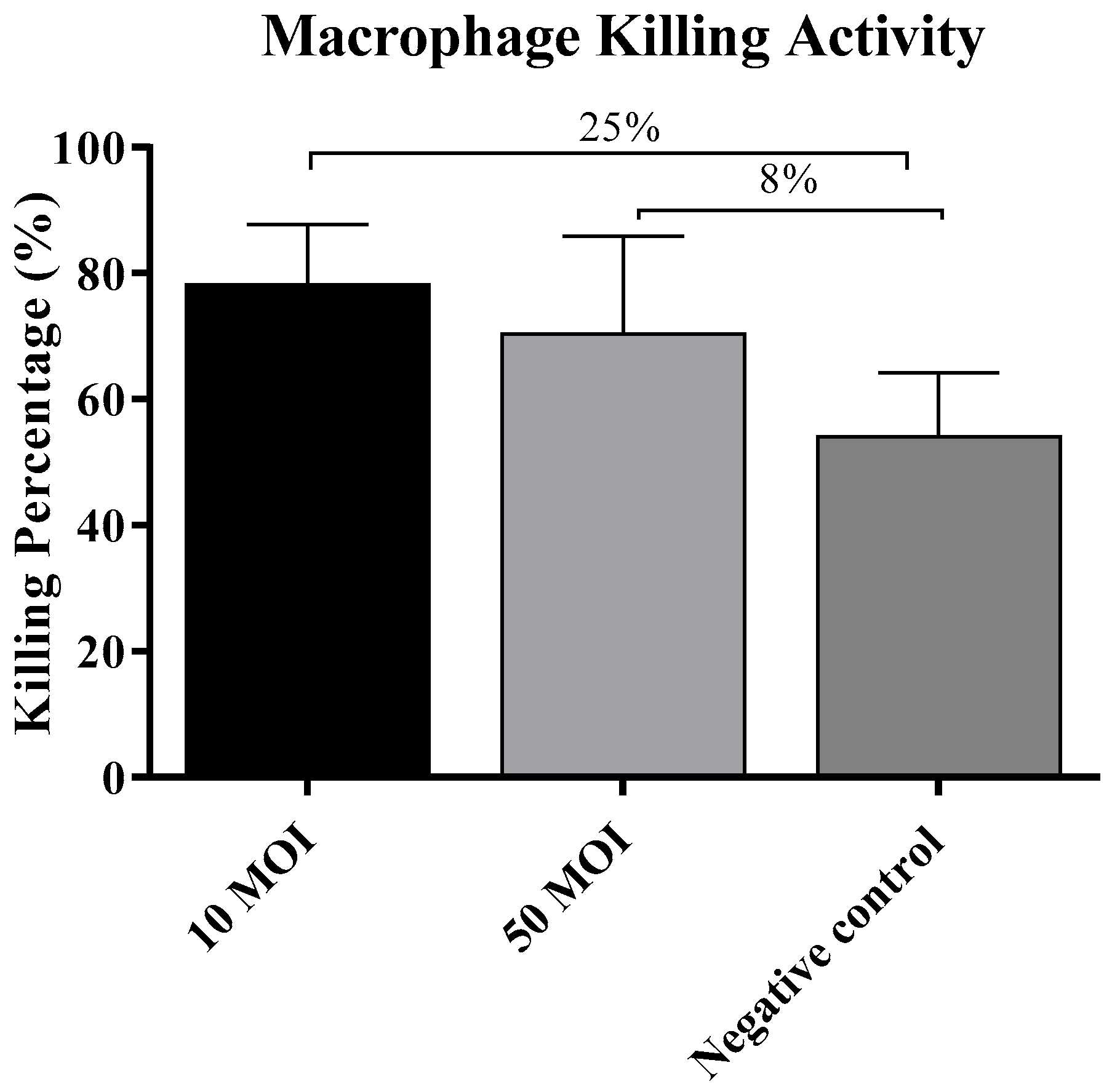

| Gene | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | TGACCTCAACTACATGGTCTACA | CTTCCCATTCTCGGCCTTG | [23] |
| CCL2 | GTCCCTGTCATGCTTCTG | CTGCTGGTGATCCTCTTG | [23] |
| IL-6 | TCTATACCACTTCACAAGTCGGA | GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT | [24] |
| IL-1β | GAAATGCCACCTTTTGACAGTG | TGGATGCTCTCATCAGGACAG | [24] |
| TNF-α | CAGGCGGTGCCTATGTCTC | CGATCACCCCGAAGTTCAGTAG | [24] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelaziz, K.; Sharma, S.; Naguib, M.; Stamatikos, A. Epithelial–Macrophage Crosstalk in Host Responses to Campylobacter jejuni Infection in Humans. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2808. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122808
Abdelaziz K, Sharma S, Naguib M, Stamatikos A. Epithelial–Macrophage Crosstalk in Host Responses to Campylobacter jejuni Infection in Humans. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(12):2808. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122808
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelaziz, Khaled, Shreeya Sharma, Mostafa Naguib, and Alexis Stamatikos. 2025. "Epithelial–Macrophage Crosstalk in Host Responses to Campylobacter jejuni Infection in Humans" Microorganisms 13, no. 12: 2808. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122808
APA StyleAbdelaziz, K., Sharma, S., Naguib, M., & Stamatikos, A. (2025). Epithelial–Macrophage Crosstalk in Host Responses to Campylobacter jejuni Infection in Humans. Microorganisms, 13(12), 2808. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122808







