Non-Dominant Genotypes (GII, GIV and GV) of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Exhibit an Elevated Evolutionary Rate in Nature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Construction
2.2. Time-Scaled Phylogenetic Analysis of JEV Based on Complete Genomes
2.3. Structural Similarity Comparison of Genomic Regions Across Five Genotypes of JEV Representative Strains
2.4. Codon Usage Patterns in the Complete Genomes of Different JEV Genotypes
2.5. Analysis of Amino Acid Mutation Sites in the E Protein of Recent Human JEV Strains Compared to the Vaccine P3 Strain
2.6. Structural and Surface Charge Analysis of the E Protein of Recent Human JEV Strains and the Vaccine P3 Strain
3. Results
3.1. Dataset Construction
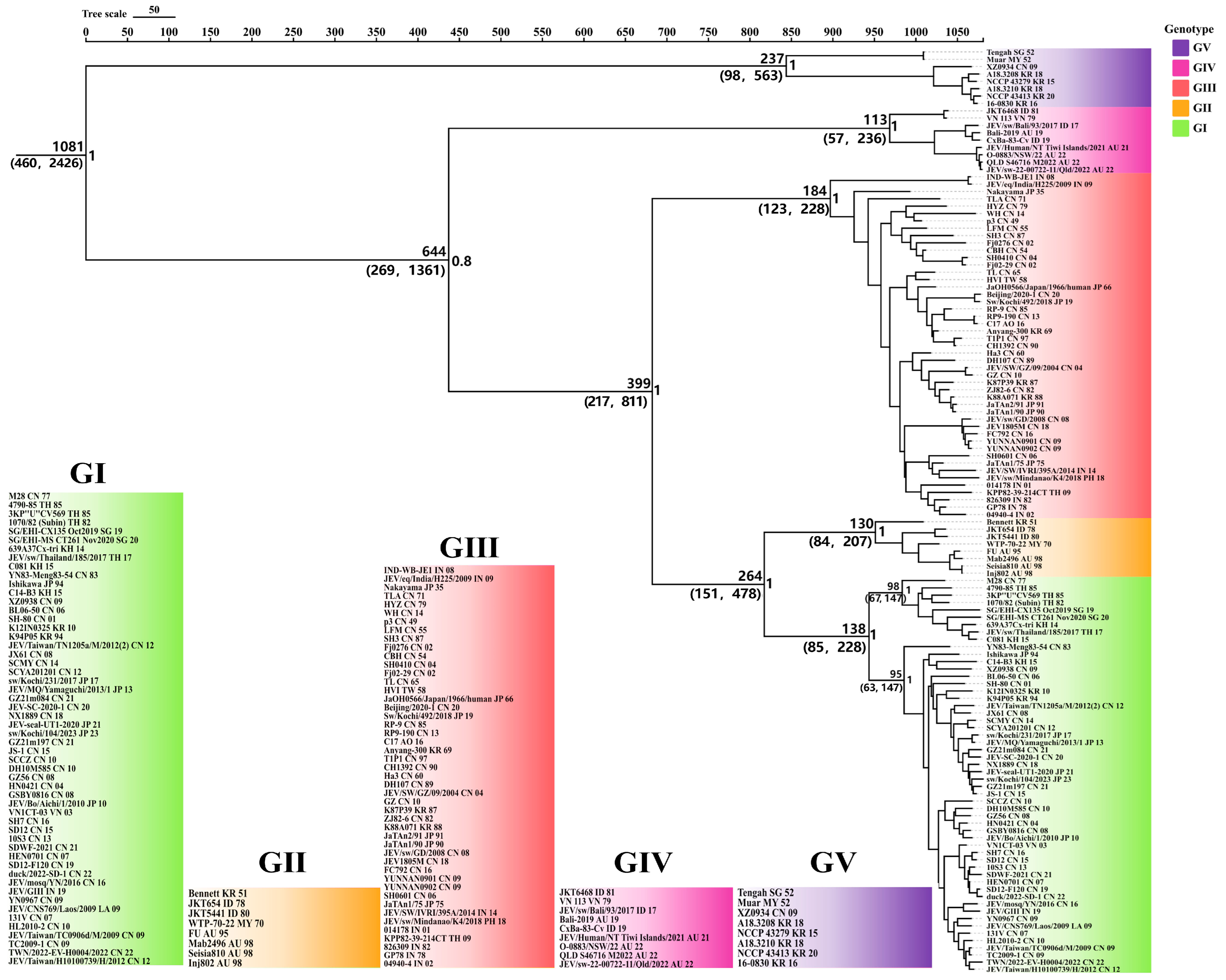
3.2. Time-Scaled Phylogenetic Analysis of JEV Based on Complete Genomes
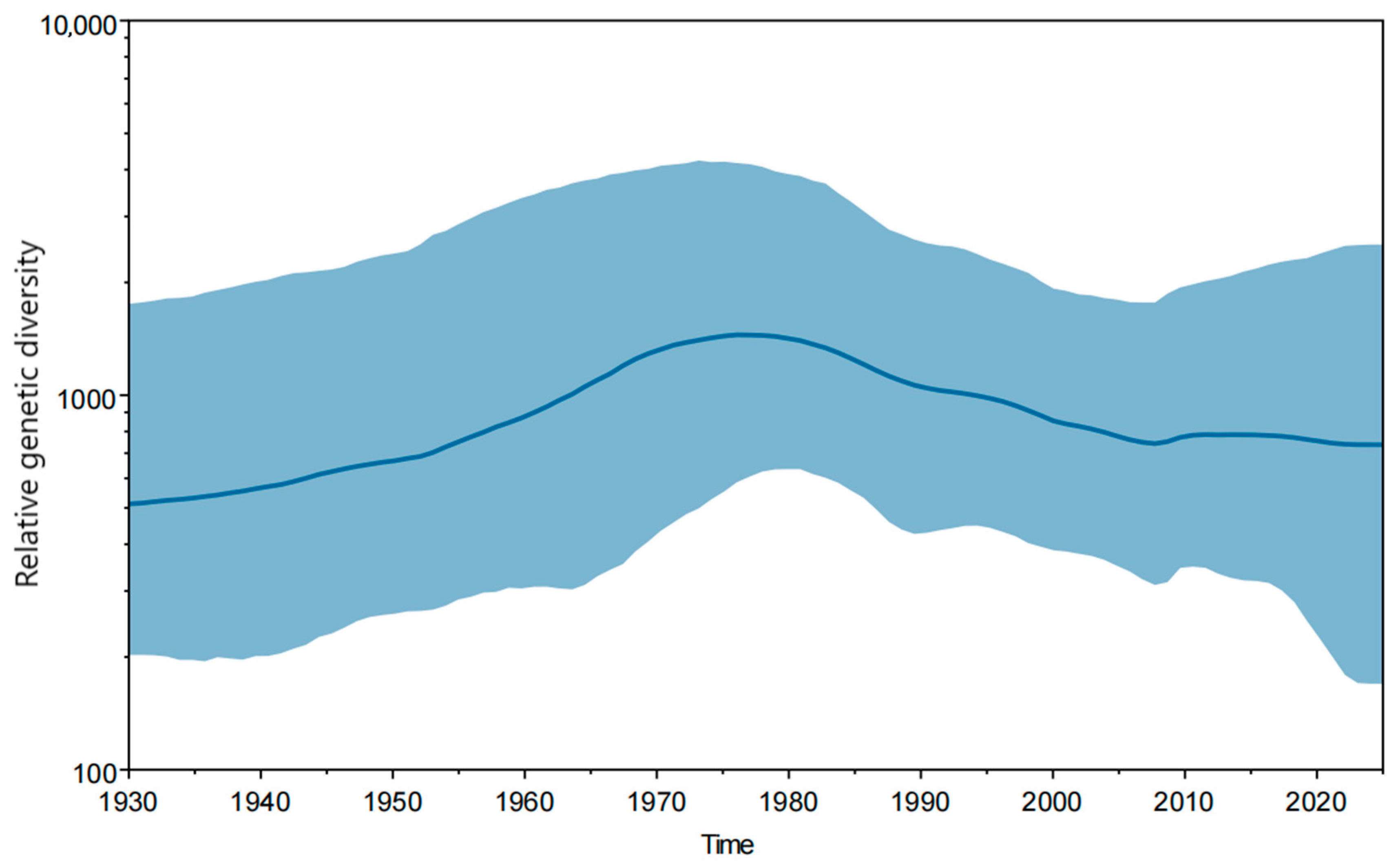
3.3. Evolutionary Rate and Population Dynamics Analysis of JEV
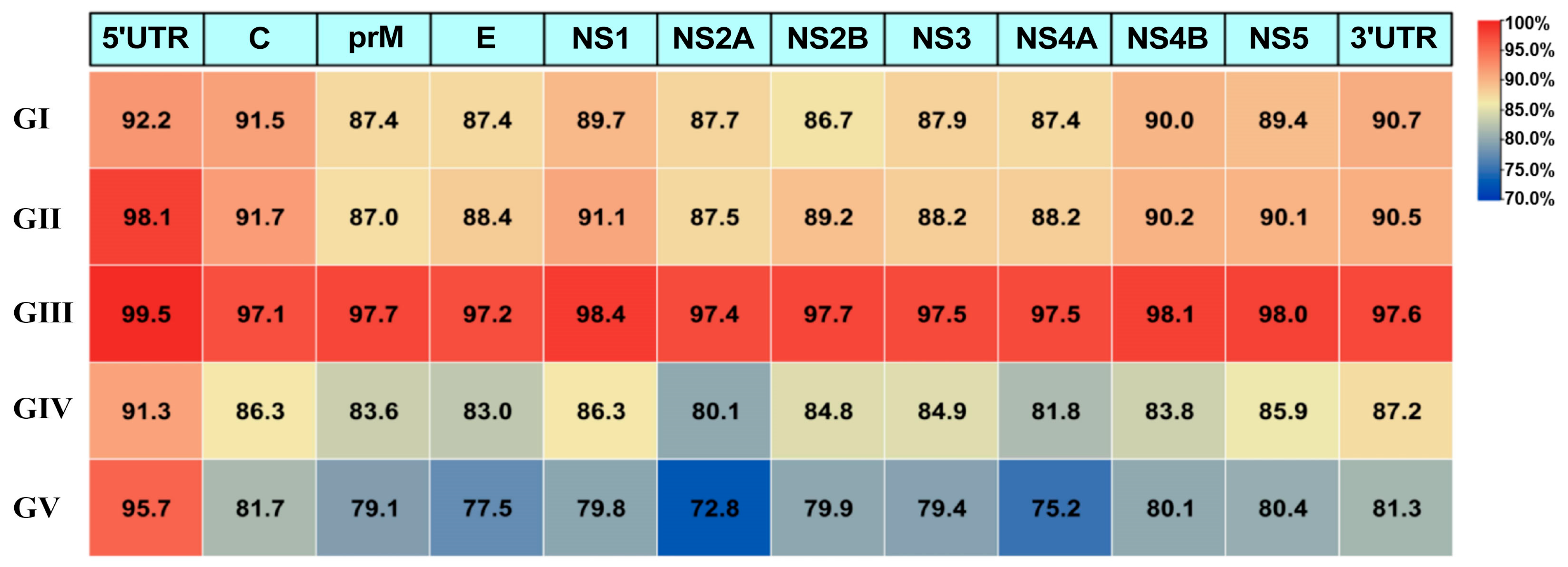
3.4. Structural Similarity Comparison of Genomic Regions Across Five Genotypes of JEV Representative Strains
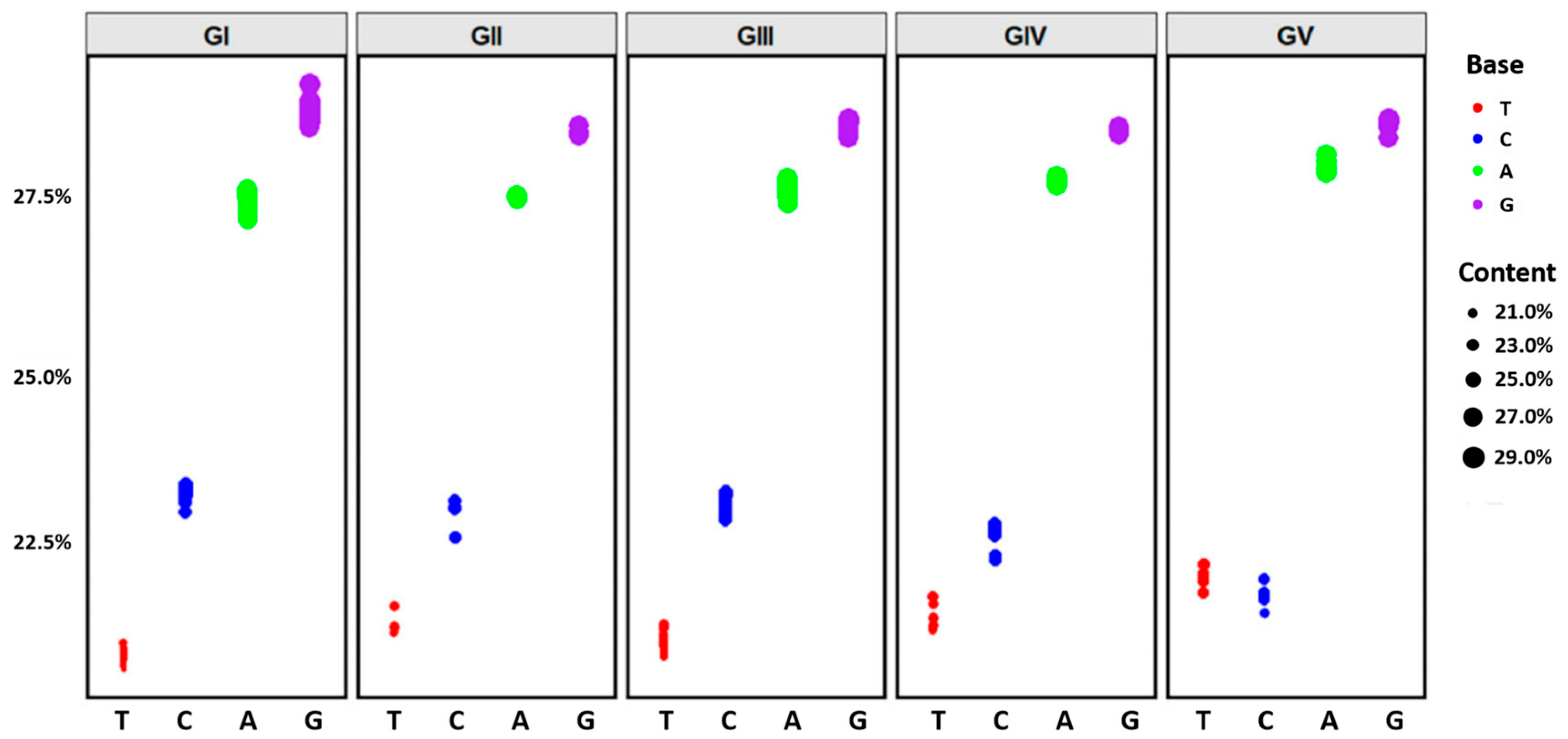
3.5. Codon Usage Patterns in the Complete Genomes of Different JEV Genotypes
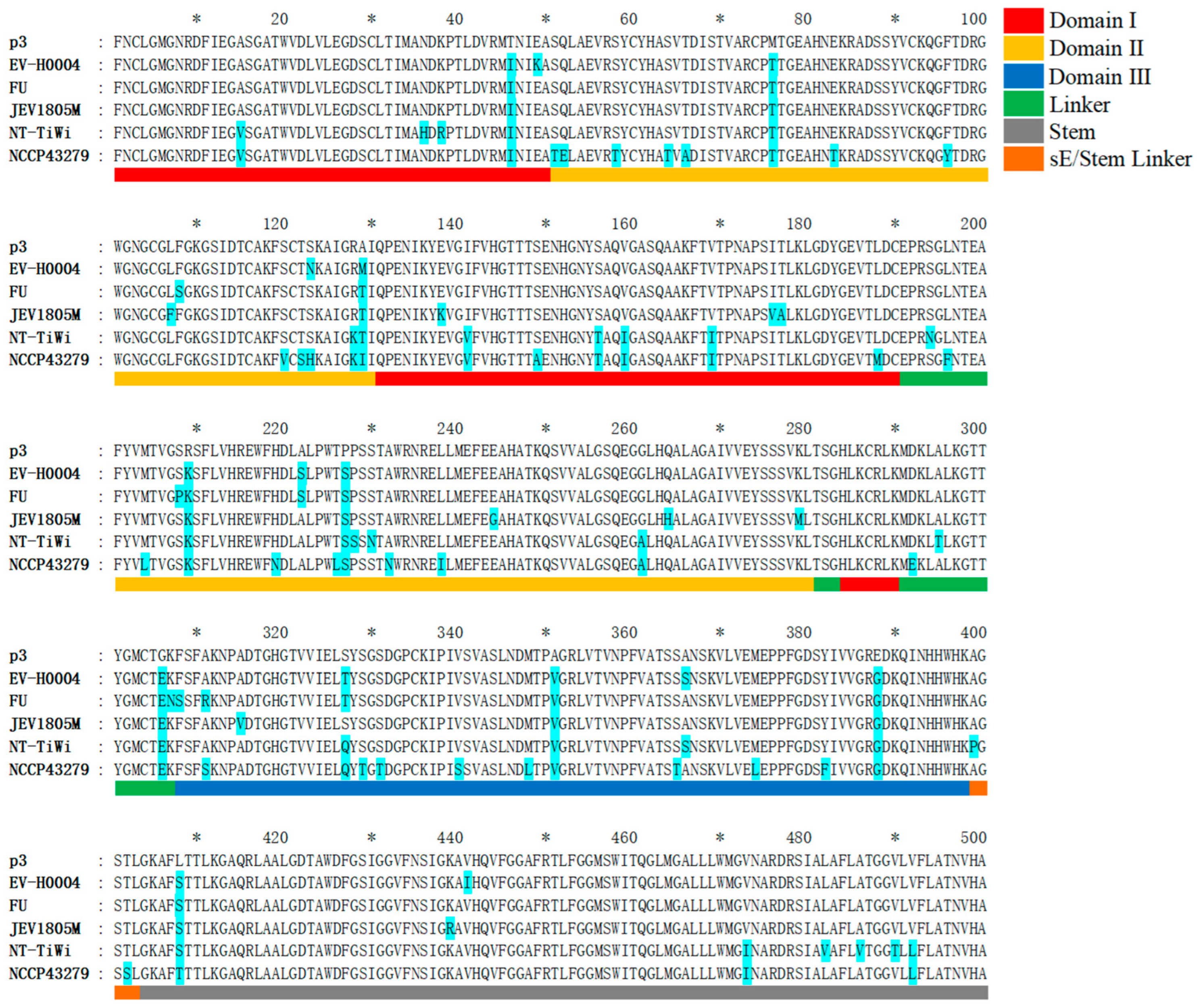
3.6. Analysis of Amino Acid Mutation Sites in the E Protein of Recent Human JEV Strains Compared to the Vaccine P3 Strain
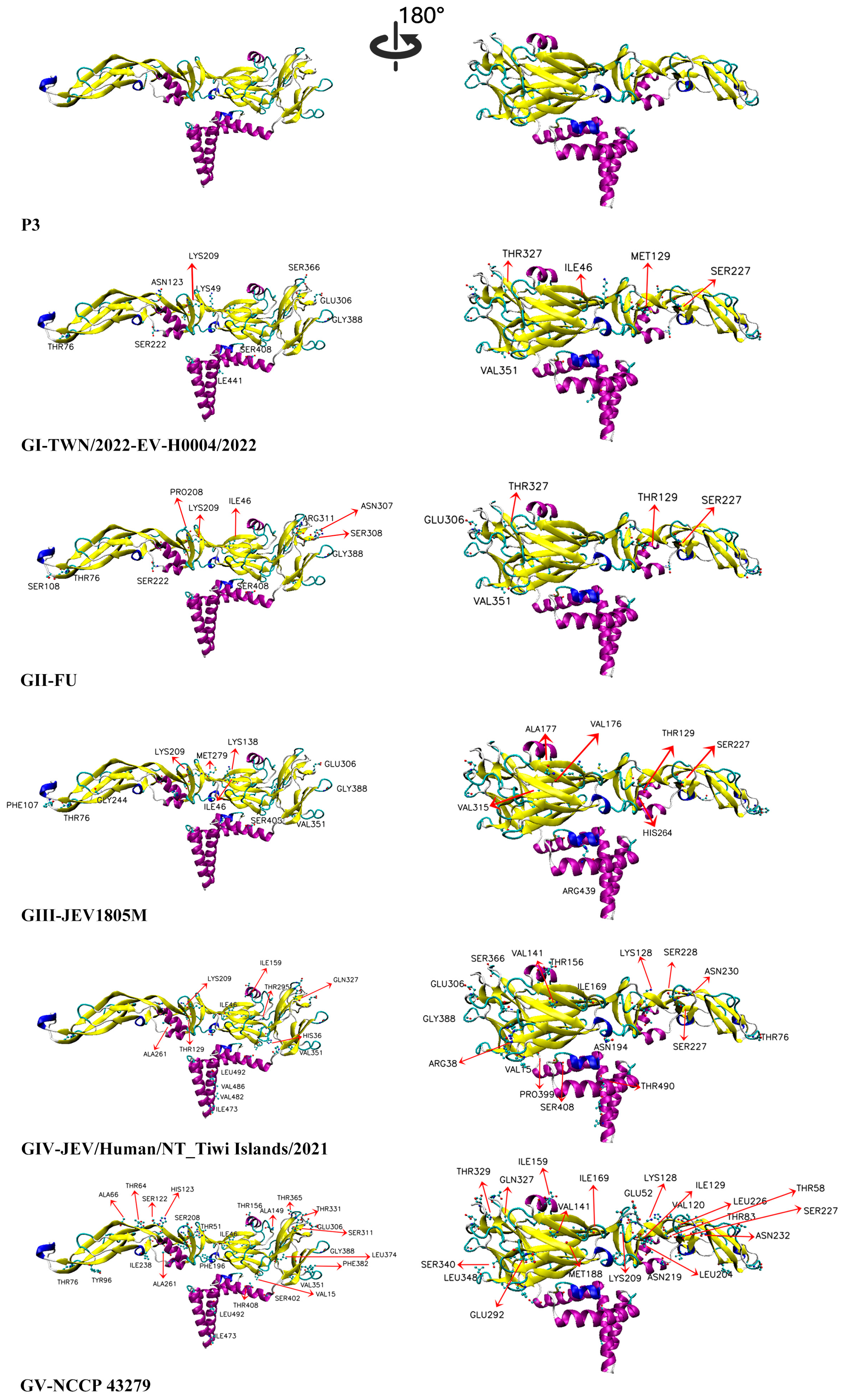
3.7. Structural and Surface Charge Analysis of the E Protein of Recent Human JEV Strains and the Vaccine P3 Strain
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopalco, P.L.; Biasio, L.R. Japanese Encephalitis can be devastating. Ann. Ig. 2024, 36, 370–375. [Google Scholar]
- Erlanger, T.E.; Weiss, S.; Keiser, J.; Utzinger, J.; Wiedenmayer, K. Past, present, and future of Japanese encephalitis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Japanese Encephalitis. World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/japanese-encephalitis (accessed on 6 August 2024).
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, S.; Lurong, Q.; Qi, Z. Recent Advances in Antivirals for Japanese Encephalitis Virus. Viruses 2023, 15, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumiyoshi, H.; Mori, C.; Fuke, I.; Morita, K.; Kuhara, S.; Kondou, J.; Kikuchi, Y.; Nagamatu, H.; Igarashi, A. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Japanese encephalitis virus genome RNA. Virology 1987, 161, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Niu, Y.; Liang, G. The 5’ and 3’ Untranslated Regions of the Japanese Encephalitis Virus (JEV): Molecular Genetics and Higher Order Structures. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 730045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.R.; Tesh, R.B.; Rico-Hesse, R. Genetic variation of Japanese encephalitis virus in nature. J. Gen. Virol. 1990, 71 Pt 12, 2915–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, T.; Ni, H.; Beasley, D.W.; Ekkelenkamp, M.; Cardosa, M.J.; Barrett, A.D. Origin and evolution of Japanese encephalitis virus in southeast Asia. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 3091–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Takasaki, T.; Fu, S.H.; Sun, X.H.; Zhang, H.L.; Wang, Z.X.; Hao, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.K.; Tang, Q.; Kotaki, A.; et al. Molecular epidemiological analysis of Japanese encephalitis virus in China. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88 Pt 3, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Gao, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Cui, B.; Shen, X.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; et al. Re-Emerged Genotype IV of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Is the Youngest Virus in Evolution. Viruses 2023, 15, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Fu, S.; Liang, G. Insights into the evolutionary history of Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) based on whole-genome sequences comprising the five genotypes. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Fu, S.; Guo, Z.; Liang, G. Southernmost Asia is the source of Japanese encephalitis virus (genotype 1) diversity from which the viruses disperse and evolve throughout Asia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Ma, X.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, K.; Li, B.; et al. Shift in dominant genotypes of Japanese encephalitis virus and its impact on current vaccination strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1302101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.L.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.Y.; Fu, S.H.; Liu, H.Z.; Zhang, H.L.; Li, M.H.; Gao, X.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Sun, X.H.; et al. Emergence of genotype I of Japanese encephalitis virus as the dominant genotype in Asia. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9847–9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, J.N.; Ritchie, S.A.; Phillips, D.A.; Shield, J.; Bailey, M.C.; Mackenzie, J.S.; Poidinger, M.; McCall, B.J.; Mills, P.J. An outbreak of Japanese encephalitis in the Torres Strait, Australia, 1995. Med. J. Aust. 1996, 165, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.T.; Wang, L.F.; Daniels, P.W.; Mackenzie, J.S. Molecular characterization of the first Australian isolate of Japanese encephalitis virus, the FU strain. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81 Pt 10, 2471–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyke, A.T.; Burtonclay, P.; Poudel, N.; Ingall, W.; Nair, N.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Craig, S.B.; Smith, C.; Wang, W.; Darbro, J.M.; et al. First Isolation of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Genotype IV from Mosquitoes in Australia. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2024, 24, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yin, Q.; Wang, H.; Liang, G. The reemerging and outbreak of genotypes 4 and 5 of Japanese encephalitis virus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1292693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Cha, G.W.; Jeong, Y.E.; Lee, W.G.; Chang, K.S.; Roh, J.Y.; Yang, S.C.; Park, M.Y.; Park, C.; Shin, E.H. Detection of Japanese encephalitis virus genotype V in Culex orientalis and Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae) in Korea. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.H.; Jeong, Y.E.; Jo, J.E.; Shim, S.M.; Ryou, J.; Kim, K.C.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, J.Y. Genetic Characterization of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Genotype 5 Isolated from Patient, South Korea, 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.H.; Fu, S.H.; Chen, W.X.; Wang, H.Y.; Guo, Y.H.; Liu, Q.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Luo, H.M.; Da, W.; Duo Ji, D.Z.; et al. Genotype v Japanese encephalitis virus is emerging. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huson, D.H.; Bryant, D. The SplitsTree App: Interactive analysis and visualization using phylogenetic trees and networks. Nat. Methods 2024, 21, 1773–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ravenzwaaij, D.; Cassey, P.; Brown, S.D. A simple introduction to Markov Chain Monte-Carlo sampling. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2018, 25, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.Y.; Duchêne, S. Molecular-clock methods for estimating evolutionary rates and timescales. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 5947–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippmann, H.F. Analysis for free: Comparing programs for sequence analysis. Brief. Bioinform. 2004, 5, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burland, T.G. DNASTAR’s Lasergene sequence analysis software. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 132, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clewley, J.P.; Arnold, C. MEGALIGN. The multiple alignment module of LASERGENE. Methods Mol. Biol. 1997, 70, 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecher, G.; Tamura, K.; Kumar, S. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) for macOS. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1237–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavsson, E.K.; Zhang, D.; Reynolds, R.H.; Garcia-Ruiz, S.; Ryten, M. ggtranscript: An R package for the visualization and interpretation of transcript isoforms using ggplot2. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 3844–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, H.; Humble, M.S. YASARA: A Tool to Obtain Structural Guidance in Biocatalytic Investigations. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1685, 43–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grell, L.; Parkin, C.; Slatest, L.; Craig, P.A. EZ-Viz, a tool for simplifying molecular viewing in PyMOL. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2006, 34, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zheng, H.; Tong, W.; Li, G.; Wang, T.; Li, L.; Gao, F.; Shan, T.; Yu, H.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Acidity/Alkalinity of Japanese Encephalitis Virus E Protein Residue 138 Alters Neurovirulence in Mice. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00108–e00118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faizah, A.N.; Kobayashi, D.; Maekawa, Y.; Amoa-Bosompem, M.; Fauziyah, S.; Mulyatno, K.C.; Subekti, S.; Rohmah, E.A.; Lusida, M.I.; Mori, Y.; et al. Identification and Isolation of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Genotype IV from Culex vishnui Collected in Bali, Indonesia in 2019. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 105, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, C.; Tiemensma, M.; Currie, B.J.; Williams, D.T.; Baird, R.W.; Krause, V.L. Japanese Encephalitis in Australia—A Sentinel Case. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 661–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.R.; Kim, S.H.; Hong, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Oh, J.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Ishikawa, T.; Shim, S.M.; Lee, H.I.; et al. Characterization of genotype V Japanese encephalitis virus isolates from Republic of Korea. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2362392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanborn, M.A.; Wuertz, K.M.; Kim, H.C.; Yang, Y.; Li, T.; Pollett, S.D.; Jarman, R.G.; Berry, I.M.; Klein, T.A.; Hang, J. Metagenomic analysis reveals Culex mosquito virome diversity and Japanese encephalitis genotype V in the Republic of Korea. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 5470–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, A.J.; Tesh, R.B.; Barrett, A.D. Genetic characterization of Japanese encephalitis virus genotype II strains isolated from 1951 to 1978. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92 Pt 3, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniraju, M.; Munir, M.; Parthiban, A.R.; Banyard, A.C.; Bao, J.; Wang, Z.; Ayebazibwe, C.; Ayelet, G.; El Harrak, M.; Mahapatra, M.; et al. Molecular evolution of peste des petits ruminants virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 2023–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Shen, L.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, X.L.; Liang, G.D.; Ji, H.F. From discovery to outbreak: The genetic evolution of the emerging Zika virus. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2016, 5, e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Williams, D.T.; van den Hurk, A.F.; Smith, D.W.; Currie, B.J. Japanese Encephalitis Virus: The Emergence of Genotype IV in Australia and Its Potential Endemicity. Viruses 2022, 14, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Fu, S.; Gao, X.; Li, M.; Cui, S.; Li, X.; Cao, Y.; Lei, W.; Lu, Z.; He, Y.; et al. Low Protective Efficacy of the Current Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine against the Emerging Genotype 5 Japanese Encephalitis Virus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, R.; Nie, K.; Fu, S.; Xu, S.; Li, F.; Cui, Q.; Liu, D.; Wang, H.; et al. Spatiotemporal Distribution and Host-Vector Dynamics of Japanese Encephalitis Virus. Viruses 2025, 17, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tang, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shi, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, M.; Li, Y. E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCH5 positively regulates Japanese encephalitis virus infection by catalyzing the K27-linked polyubiquitination of viral E protein and inhibiting MAVS-mediated type I interferon production. mBio 2025, 16, e0020825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.M.; Cho, J.E.; Ju, Y.R.; Kim, S.Y.; Ryou, J.; Han, M.G.; Choi, W.Y.; Jeong, Y.E. Molecular epidemiology of Japanese encephalitis virus circulating in South Korea, 1983–2005. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, B.; Wang, Z.; Farid, A.; Wang, Z.; Wei, K.; Ren, N.; Yang, F.; Liu, H. The Application and Challenges of Brain Organoids in Exploring the Mechanism of Arbovirus Infection. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.K.; Wang, H.Y.; Liang, G.D. Progress in research on Japanese encephalitis virus in China. Virol. Sin. 2024, 40, 580–587. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
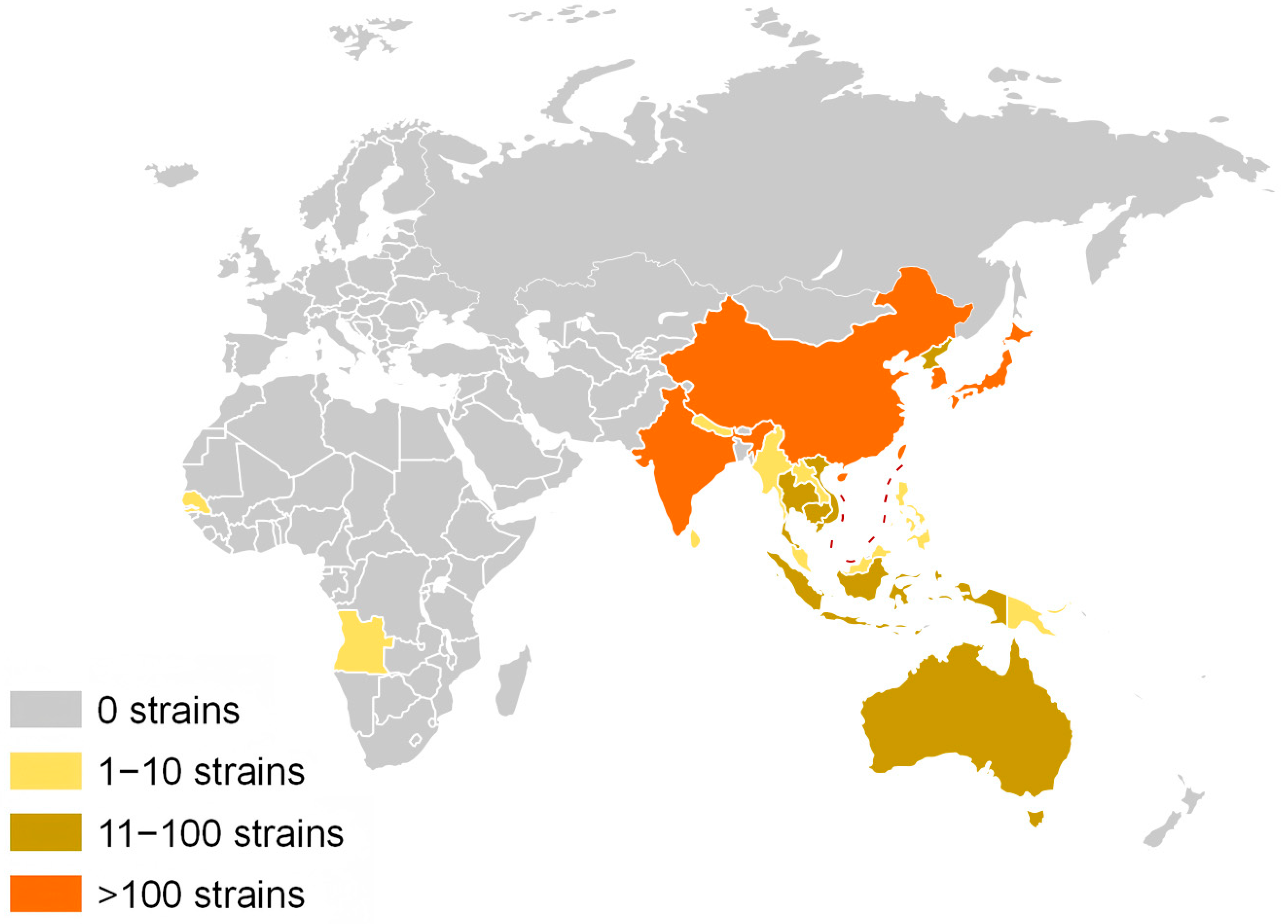
| Continent | Country | Genotype | Vector/Host | Year | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | V | Mosquito | Midges | Human | Pig | Horse | Duck | Cattle | Seal | 1930s | 1940s | 1950s | 1960s | 1970s | 1980s | 1990s | 2000s | 2010s | 2020s | ||
| Asia | China | 34 | / | 28 | / | 1 | 33 | 1 | 15 | 14 | / | 1 | / | / | / | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 21 | 19 | 7 |
| Cambodia | 3 | / | / | / | / | 1 | / | 1 | 1 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 3 | / | |
| India | 1 | / | 7 | / | / | 2 | / | 4 | 1 | 1 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1 | 1 | / | 4 | 2 | / | |
| Indonesia | / | 2 | / | 3 | / | 4 | / | / | 1 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1 | 2 | / | / | 2 | / | |
| Japan | 6 | / | 6 | / | / | 2 | / | 2 | 6 | / | / | 1 | 1 | 1 | / | / | 1 | 1 | / | 3 | 4 | / | 2 | |
| Korea | 1 | / | / | / | / | 1 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1 | / | / | / | |
| Laos | 1 | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1 | / | / | |
| Malaysia | / | 1 | / | / | 1 | 1 | / | 1 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1 | / | 1 | / | / | / | / | / | |
| Philippines | / | / | 1 | / | / | / | / | / | 1 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1 | / | |
| Singapore | 2 | / | / | / | 1 | 2 | / | 1 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1 | / | / | / | / | / | 1 | 1 | |
| South Korea | 1 | 1 | 3 | / | 5 | 2 | / | 6 | 2 | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1 | 1 | / | 2 | / | / | 5 | 1 | |
| Thailand | 4 | / | 1 | / | / | 2 | / | 2 | 1 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 3 | / | 1 | 1 | / | |
| Viet Nam | 1 | / | / | 1 | / | 1 | / | 1 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1 | / | / | 1 | / | / | |
| Africa | Angola | / | / | 1 | / | / | / | / | 1 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 1 | / |
| Oceania | Australia | / | 4 | / | 5 | / | 1 | / | 3 | 5 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 4 | / | 1 | 4 |
| JEV Genotypes | tMRCA (95%HPD) | Substitution Rate S/S/Y (95%HPD) | Nucleotide Content Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| JEV all five genotypes | 1081 (460, 2426) | 3.3 × 10−4 (1.9 × 10−4, 4.7 × 10−4) | T: 21.0 C: 23.0 A: 27.5 G: 28.5 |
| GI | 138 (85, 228) | 7.3 × 10−4 (4.4 × 10−4, 1.1 × 10−3) | T: 20.8 C: 23.2 A: 27.3 G: 28.7 |
| GII | 130 (84, 207) | 8.2 × 10−4 (5.0 × 10−4, 1.0 × 10−3) | T: 21.3 C: 22.9 A: 27.4 G: 28.4 |
| GIII | 184 (123, 228) | 4.4 × 10−5 (2.3 × 10−7, 8.9 × 10−5) | T: 21.0 C: 23.0 A: 27.5 G: 28.5 |
| GIV | 113 (57, 236) | 1.7 × 10−3 (4.5 × 10−4, 3.9 × 10−3) | T: 21.4 C: 22.6 A: 27.6 G: 28.4 |
| GV | 237 (98, 563) | 2.2 × 10−3 (4.0 × 10−8, 8.9 × 10−3) | T: 21.9 C: 21.8 A: 27.9 G: 28.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Zhen, L.; Wei, K.; Cui, B.; Wang, Z.; Farid, A.; Xia, X.; Sun, X.; Liu, H.; Liang, G. Non-Dominant Genotypes (GII, GIV and GV) of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Exhibit an Elevated Evolutionary Rate in Nature. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122792
Wang Z, Zhen L, Wei K, Cui B, Wang Z, Farid A, Xia X, Sun X, Liu H, Liang G. Non-Dominant Genotypes (GII, GIV and GV) of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Exhibit an Elevated Evolutionary Rate in Nature. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(12):2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122792
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhijie, Limin Zhen, Kaiyue Wei, Baoqiu Cui, Zeyu Wang, Anum Farid, Xinyue Xia, Xiaofeng Sun, Hong Liu, and Guodong Liang. 2025. "Non-Dominant Genotypes (GII, GIV and GV) of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Exhibit an Elevated Evolutionary Rate in Nature" Microorganisms 13, no. 12: 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122792
APA StyleWang, Z., Zhen, L., Wei, K., Cui, B., Wang, Z., Farid, A., Xia, X., Sun, X., Liu, H., & Liang, G. (2025). Non-Dominant Genotypes (GII, GIV and GV) of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Exhibit an Elevated Evolutionary Rate in Nature. Microorganisms, 13(12), 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122792






