Metagenomic Analysis of Gut Microbiota Structure and Function in Adults with Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Cross-Sectional Study in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Thyroid Function Test
2.4. Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
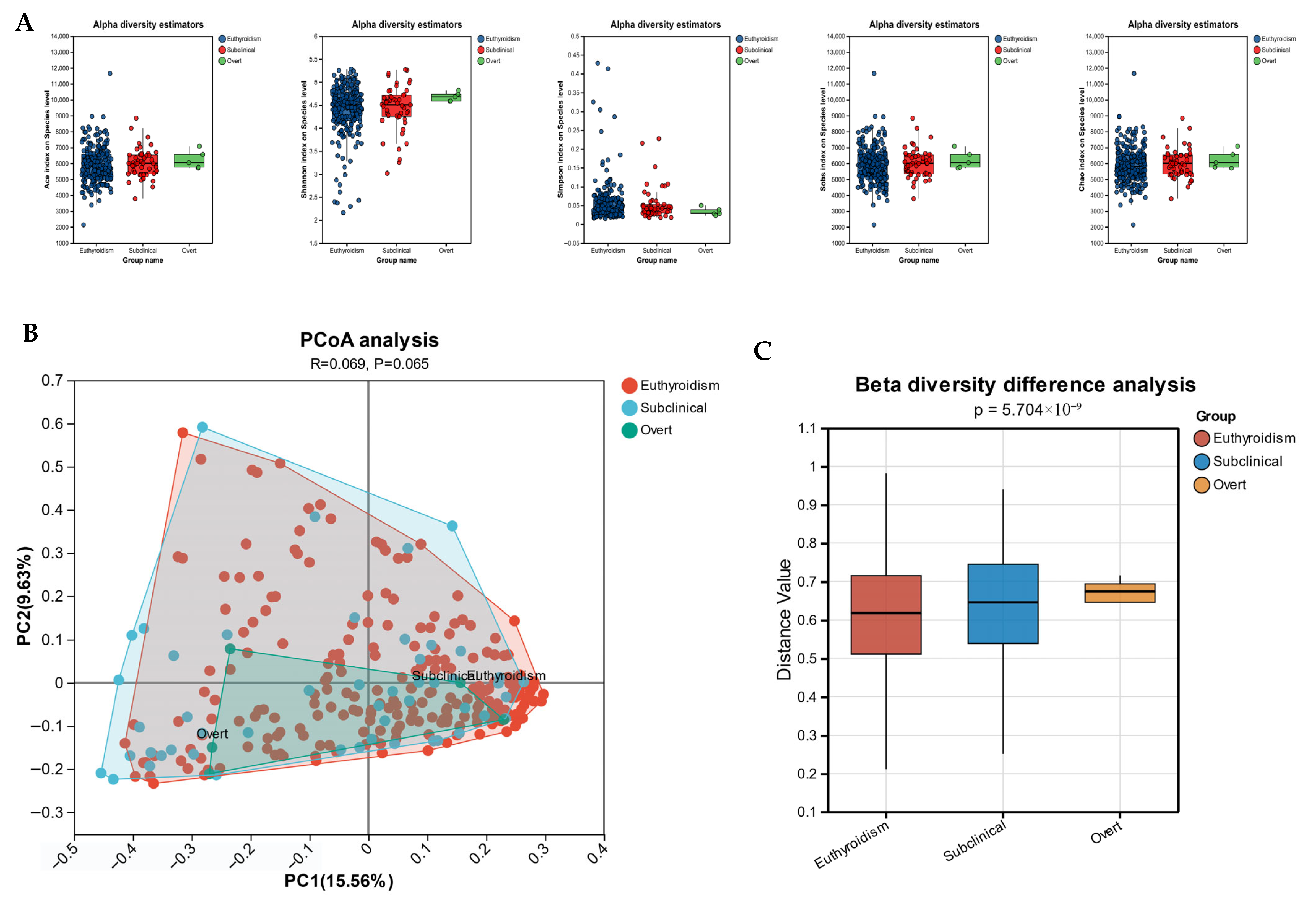
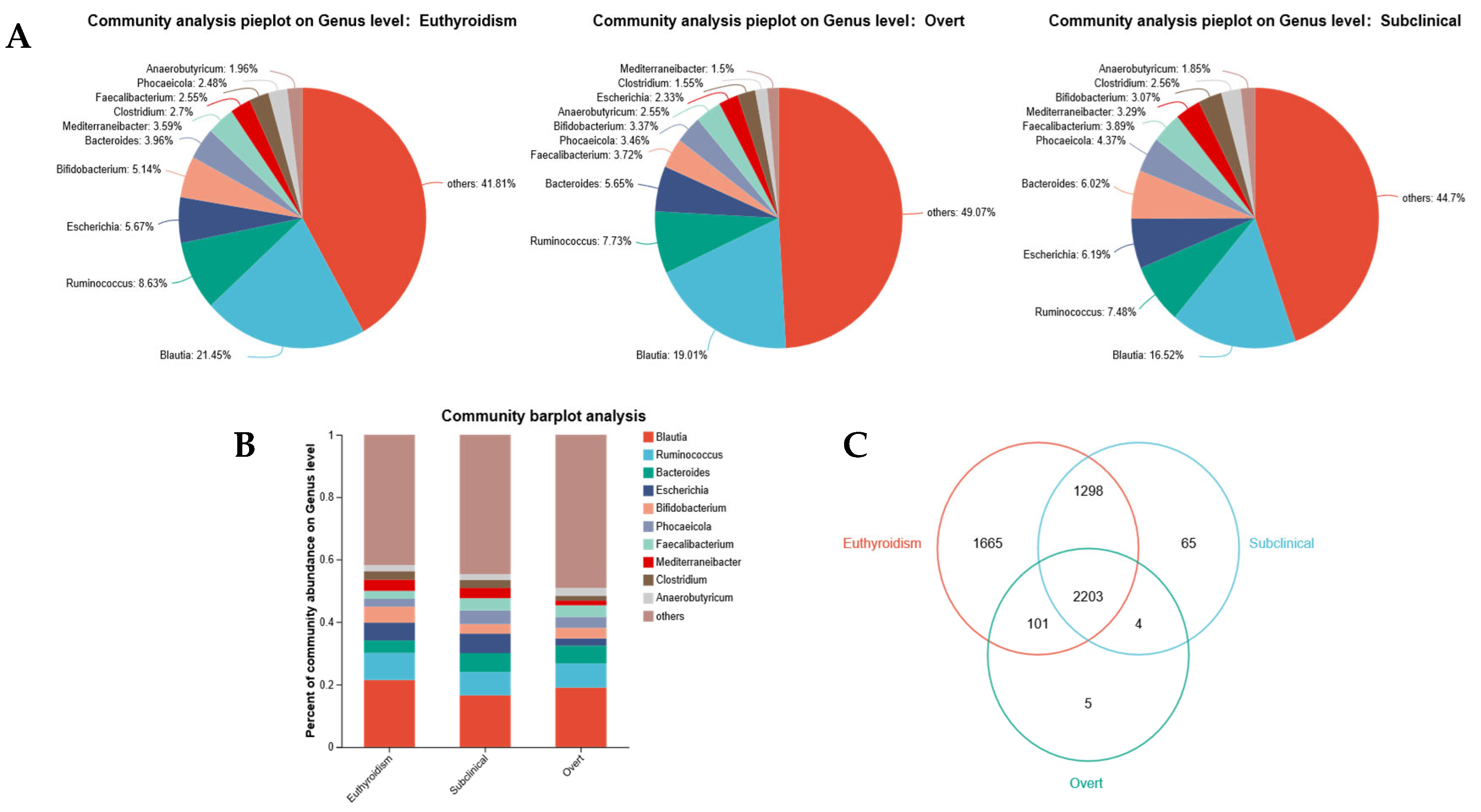
3.2. Gut Microbiota Diversity Analysis
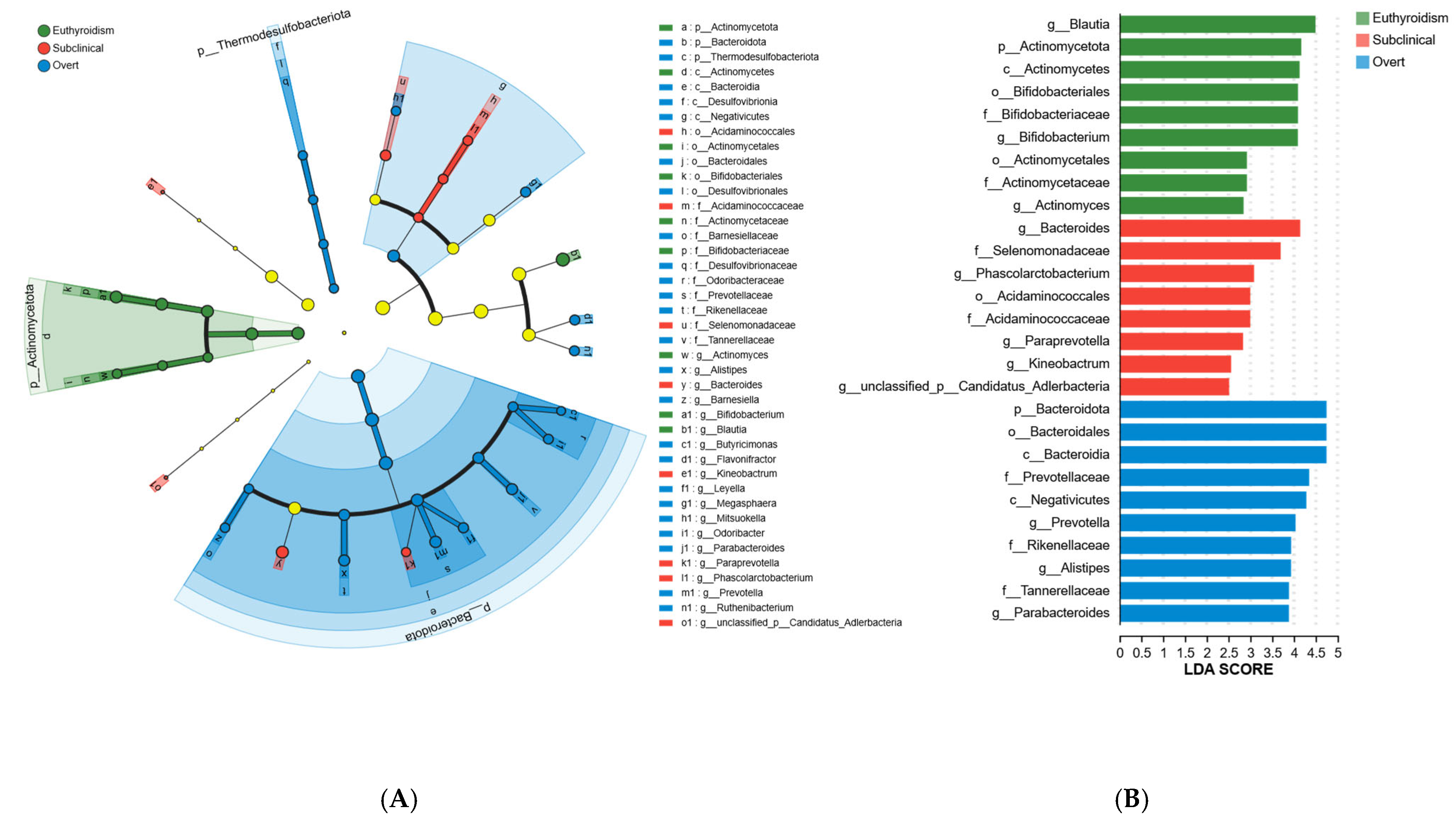
3.3. Characteristic Gut Microbiota Alterations
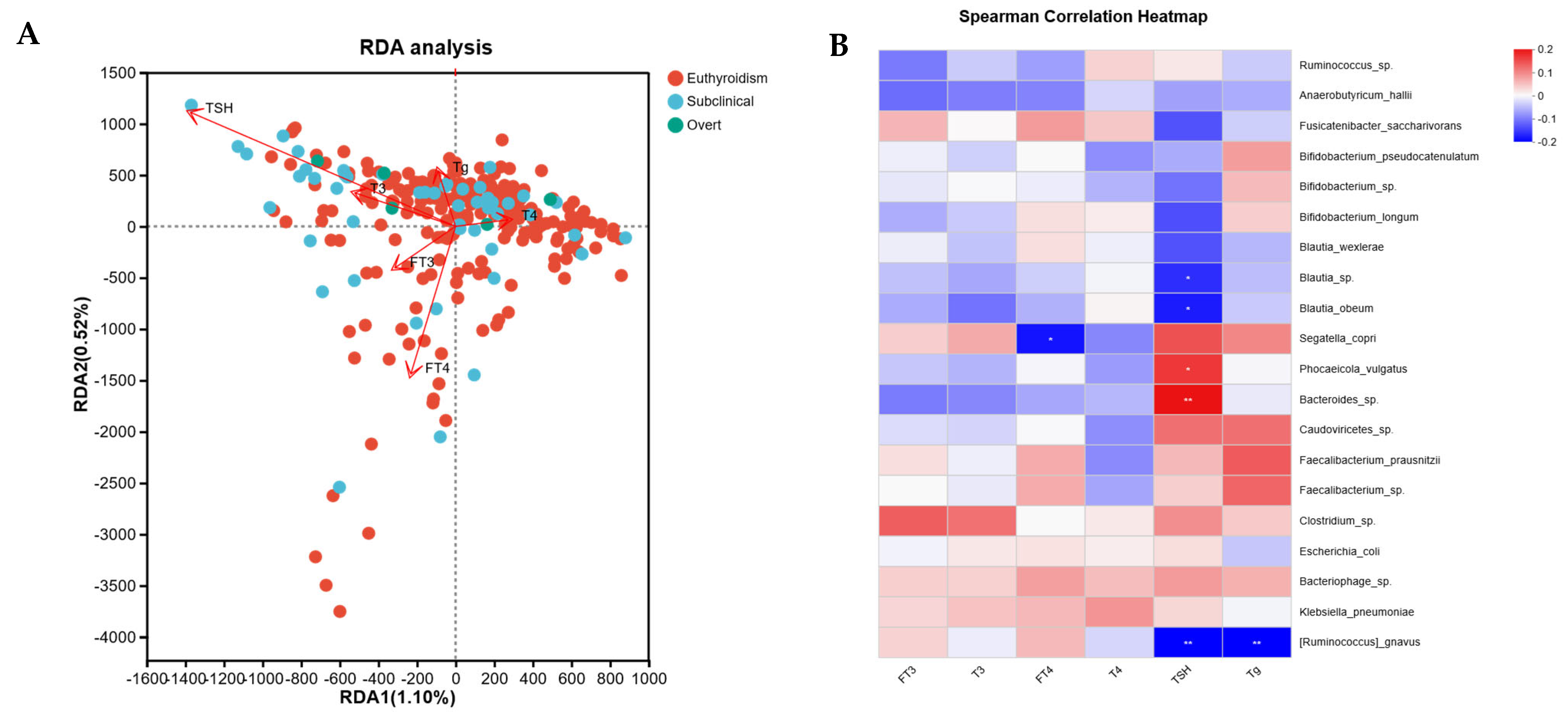
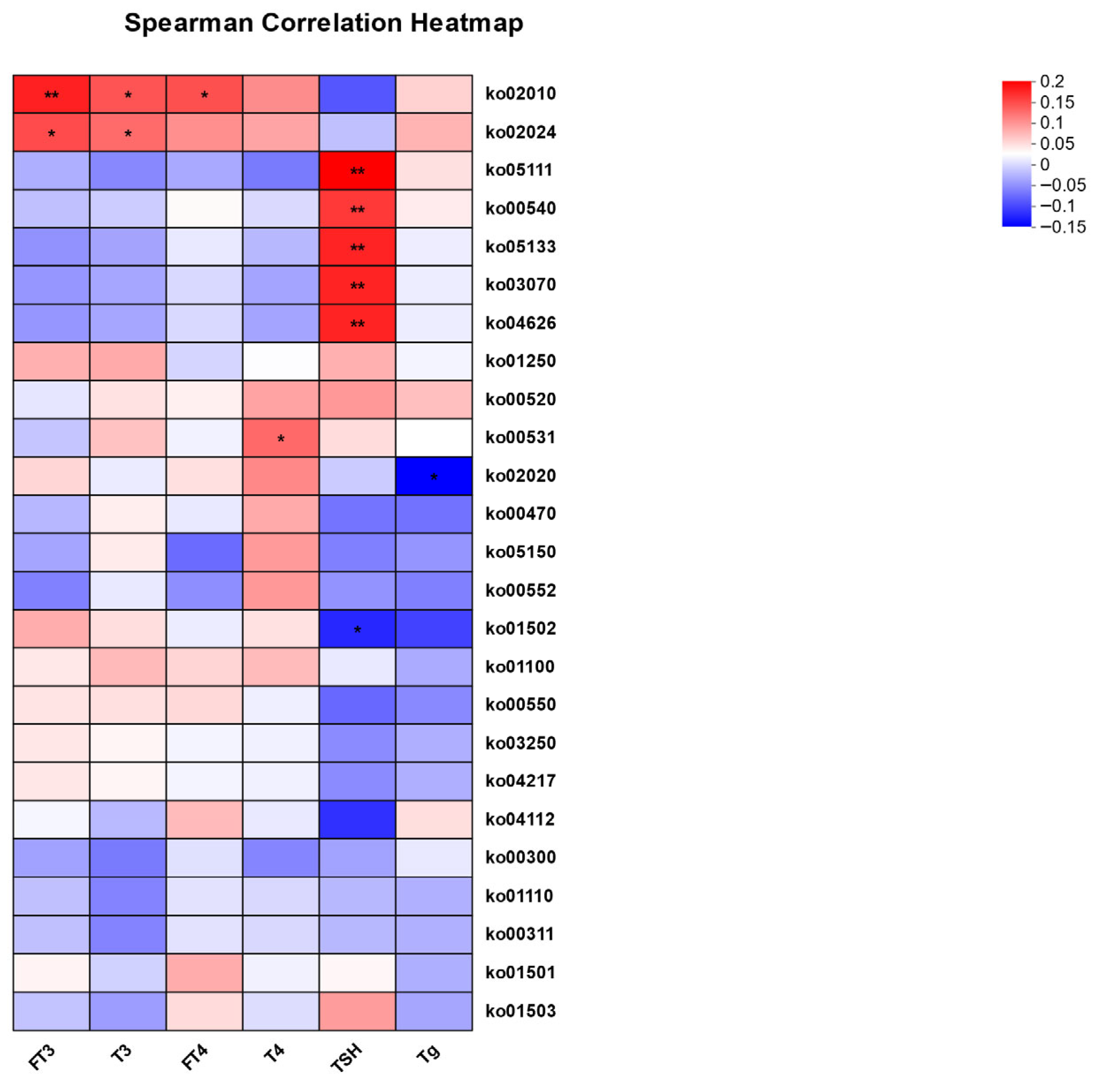
3.4. Correlation Analysis Between Thyroid Function Indicators and Gut Microbiota
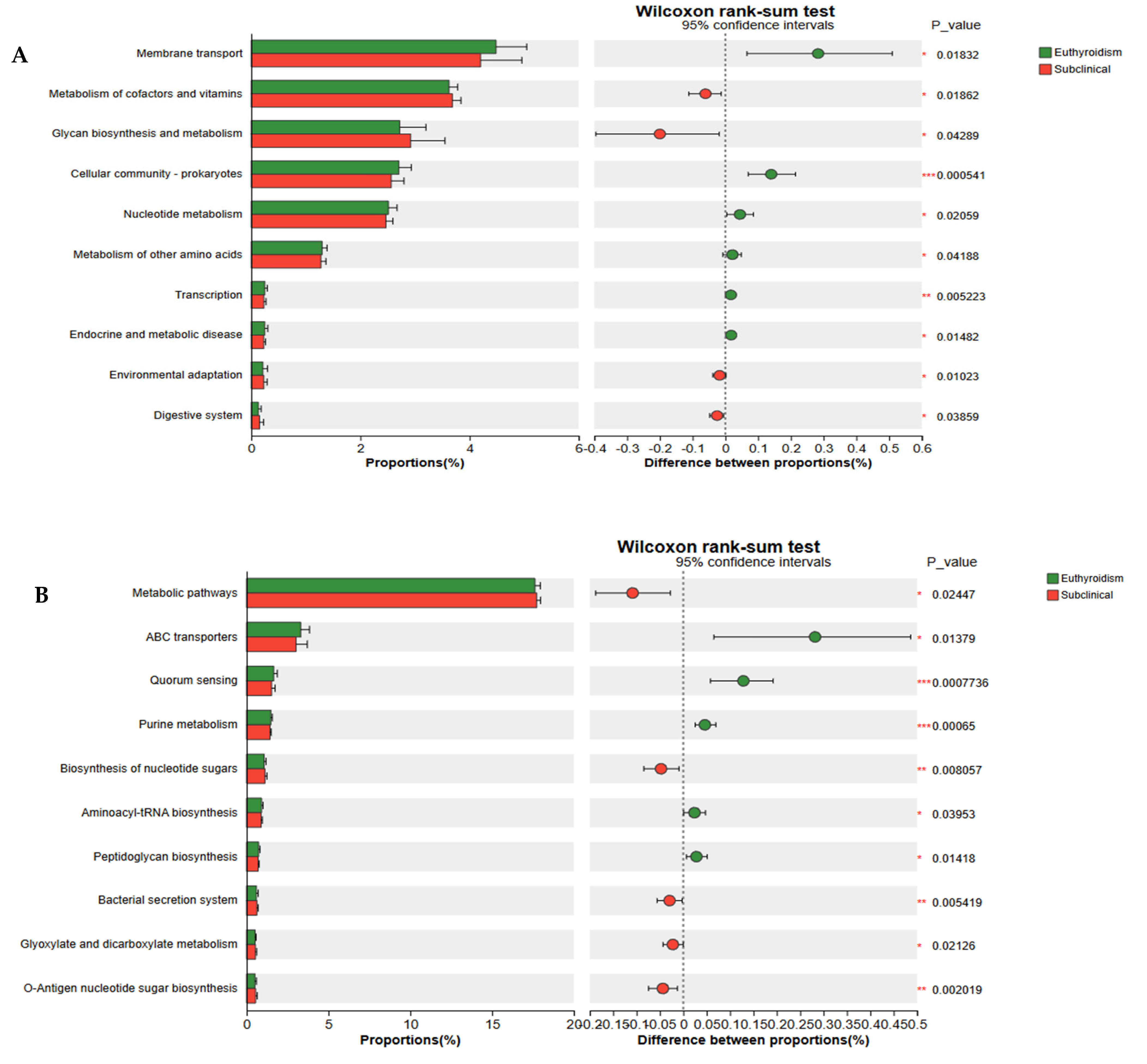
3.5. Functional Gene Analysis of the Gut Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burekovic, A.; Halilovic, D.; Sahbaz, A. Hypothyroidism and Subclinical Hypothyroidism as a Consequence of COVID-19 Infection. Med. Arch. 2022, 76, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, M.T. Hypothyroidism. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, itc1–itc16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, F.; Fallahi, P.; Elia, G.; Gonnella, D.; Paparo, S.R.; Giusti, C.; Churilov, L.P.; Ferrari, S.M.; Antonelli, A. Hashimotos’ thyroiditis: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinic and therapy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 33, 101367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.J.; Hegedüs, L. Graves’ Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1552–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeFevre, M.L. Screening for thyroid dysfunction: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondi, B.; Cappola, A.R.; Cooper, D.S. Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Review. JAMA 2019, 322, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandelwal, D.; Tandon, N. Overt and subclinical hypothyroidism: Who to treat and how. Drugs 2012, 72, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Moneim AGaber, A.M.; Gouda, S.; Osama, A.; Othman, S.I.; Allam, G. Relationship of thyroid dysfunction with cardiovascular diseases: Updated review on heart failure progression. Hormones 2020, 19, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaker, L.; Bianco, A.C.; Jonklaas, J.; Peeters, R.P. Hypothyroidism. Lancet 2017, 390, 1550–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.S.; Daya, N.; Lutsey, P.L.; Matsushita, K.; Fretz, A.; McEvoy, J.W.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Coresh, J.; Greenland, P.; Kottgen, A.; et al. Thyroid Function, Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and Incident Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 3306–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, D.C.d.S.; Chiamolera, M.I.; Silva, R.E.; de Souza, M.D.C.B.; Antunes, R.A.; Souza, M.M.; Mancebo, A.C.A.; Arêas, P.C.F.; Reis, F.M.; Turco, E.G.L.; et al. Metabolomic analysis of follicular fluid from women with Hashimoto thyroiditis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boelen, A.; Zwaveling-Soonawala, N.; Heijboer, A.C.; van Trotsenburg, A.S.P. Neonatal screening for primary and central congenital hypothyroidism: Is it time to go Dutch? Eur. Thyroid J. 2023, 12, e230041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.B. Sedentary lifestyle and risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Lipids 2003, 38, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, J.G.; Milani, C.; de Giori, G.S.; Sesma, F.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. Bacteria as vitamin suppliers to their host: A gut microbiota perspective. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natividad, J.M.; Verdu, E.F. Modulation of intestinal barrier by intestinal microbiota: Pathological and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekirov, I.; Russell, S.L.; Antunes, L.C.; Finlay, B.B. Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 859–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenneman, A.C.; Bruinstroop, E.; Nieuwdorp, M.; van der Spek, A.H.; Boelen, A. A Comprehensive Review of Thyroid Hormone Metabolism in the Gut and Its Clinical Implications. Thyroid 2023, 33, 32–44, Erratum in Thyroid 2023, 33, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezevic, J.; Starchl, C.; Tmava Berisha, A.; Amrein, K. Thyroid-Gut-Axis: How Does the Microbiota Influence Thyroid Function? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Teng, D.; Ba, J.; Chen, B.; Du, J.; He, L.; Lai, X.; Teng, X.; Shi, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Long-Term Universal Salt Iodization on Thyroid Disorders: Epidemiological Evidence from 31 Provinces of Mainland China. Thyroid 2020, 30, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome. Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Lu, G.; Qiao, T.; Yu, X.; Luo, Q.; Tong, J.; Fan, S.; Chai, L.; Gao, D.; Wang, R.; et al. Integrated microbiome and metabolome analysis reveals a distinct microbial and metabolic signature in Graves’ disease and hypothyroidism. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, V.E.; Makhovskiĭ, V.Z. Cicatricial stenosis of the stomach and small intestine after a chemical burn. Khirurgiia 1984, 11, 138. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Gurav, A.; Sivaprakasam, S.; Brady, E.; Padia, R.; Shi, H.; Thangaraju, M.; Prasad, P.D.; Manicassamy, S.; Munn, D.H.; et al. Activation of Gpr109a, receptor for niacin and the commensal metabolite butyrate, suppresses colonic inflammation and carcinogenesis. Immunity 2014, 40, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, K. Preparation of selenium/zinc-enriched probiotics and their effect on blood selenium and zinc concentrations, antioxidant capacities, and intestinal microflora in canine. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 141, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, E.; Wahl, R. Microbiota and Thyroid Interaction in Health and Disease. Trends. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 30, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Zhao, H.; Chen, W. Relationship between gut microbiota and thyroid function: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1240752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, H.M.; Mohammad, I.S.; Guo, H.; Shahzad, M.; Hou, Y.J.; Ma, C.; Naseem, Z.; Wu, X.; Shi, P.; Xu, J. Molecular estimation of alteration in intestinal microbial composition in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis patients. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yu, X.; Kosik, R.O.; Song, Y.; Qiao, T.; Tong, J.; Liu, S.; Fan, S.; Luo, Q.; Chai, L.; et al. Gut Microbiota May Play a Significant Role in the Pathogenesis of Graves’ Disease. Thyroid 2021, 31, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-León, M.J.; Mangalam, A.K.; Regaldiz, A.; González-Madrid, E.; Rangel-Ramírez, M.A.; Álvarez-Mardonez, O.; Vallejos, O.P.; Méndez, C.; Bueno, S.M.; Melo-González, F.; et al. Gut microbiota short-chain fatty acids and their impact on the host thyroid function and diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1192216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vought, R.L.; Brown, F.A.; Sibinovic, K.H.; McDaniel, E.G. Effect of changing intestinal bacterial flora on thyroid function in the rat. Horm. Metab. Res. 1972, 4, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, J.P.; Nazar, M.; Mascanfroni, I.D.; Pellizas, C.G.; Masini-Repiso, A.M. NF-kappaB p65 subunit mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced Na(+)/I(-) symporter gene expression by involving functional interaction with the paired domain transcription factor Pax8. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 1846–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VélEz, M.L.; Costamagna, E.; Kimura, E.T.; Fozzatti, L.; Pellizas, C.G.; Montesinos, M.M.; Lucero, A.M.; Coleoni, A.H.; Santisteban, P.; Masini-Repiso, A.M. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide stimulates the thyrotropin-dependent thyroglobulin gene expression at the transcriptional level by involving the transcription factors thyroid transcription factor-1 and paired box domain transcription factor 8. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 3260–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicola, J.P.; Vélez, M.L.; Lucero, A.M.; Fozzatti, L.; Pellizas, C.G.; Masini-Repiso, A.M. Functional toll-like receptor 4 conferring lipopolysaccharide responsiveness is expressed in thyroid cells. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Total (n = 277) | Euthyroidism (n = 222) | SCH (n = 50) | OH (n = 5) | p a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, Mean ± SD | 49.66 ± 12.30 | 49.08 ± 12.26 | 51.82 ± 12.29 | 53.80 ± 13.37 | 0.272 |
| BMI, kg/m2, Mean ± SD | 24.48 ± 3.88 | 24.31 ± 3.94 | 25.31 ± 3.69 | 23.60 ± 2.09 | 0.230 |
| Sex, n (%) | 0.059 | ||||
| Male | 98 (35.38) | 85 (38.29) | 13 (26.00) | 0 (0.00) | |
| Female | 179 (64.62) | 137 (61.71) | 37 (74.00) | 5 (100.00) | |
| FT3, pmol/L, M (Q1, Q3) | 4.98 (4.54, 5.42) | 5.04 (4.55, 5.42) | 4.75 (4.54, 5.43) | 4.35 (3.78, 4.92) | 0.078 |
| T3, nmol/L, M (Q1, Q3) | 1.91 (1.72, 2.16) | 1.92 (1.72, 2.16) | 1.92 (1.70, 2.21) | 1.78 (1.71, 1.91) | 0.732 |
| FT4, pmol/L, M (Q1, Q3) | 16.11 (14.90, 17.71) | 16.47 (15.20, 17.98) | 15.04 (13.75, 16.45) # | 11.24 (10.58, 11.71) # | <0.001 |
| T4, nmol/L, M (Q1, Q3) | 116.10 (100.70, 130.20) | 117.20 (102.50, 130.65) | 110.00 (97.85, 127.93) | 83.01 (82.90, 91.25) # | 0.009 |
| TSH, µIU/mL, M (Q1, Q3) | 2.41 (1.69, 3.65) | 2.00 (1.50, 2.89) | 5.13 (4.57, 5.96) # | 7.57 (5.27, 8.76) # | <0.001 |
| Tg, ng/mL, M (Q1, Q3) | 11.38 (6.52, 19.05) | 10.10 (5.99, 17.41) | 16.32 (11.88, 21.97) # | 7.43 (0.15, 16.16) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Ma, X.; Wu, L.; Mo, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, R.; Xing, M. Metagenomic Analysis of Gut Microbiota Structure and Function in Adults with Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Cross-Sectional Study in China. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2643. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112643
Li X, Ma X, Wu L, Mo Z, Chen Z, Zhang R, Xing M. Metagenomic Analysis of Gut Microbiota Structure and Function in Adults with Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Cross-Sectional Study in China. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(11):2643. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112643
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xueqing, Xue Ma, Lizhi Wu, Zhe Mo, Zhijian Chen, Ronghua Zhang, and Mingluan Xing. 2025. "Metagenomic Analysis of Gut Microbiota Structure and Function in Adults with Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Cross-Sectional Study in China" Microorganisms 13, no. 11: 2643. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112643
APA StyleLi, X., Ma, X., Wu, L., Mo, Z., Chen, Z., Zhang, R., & Xing, M. (2025). Metagenomic Analysis of Gut Microbiota Structure and Function in Adults with Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Cross-Sectional Study in China. Microorganisms, 13(11), 2643. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112643







