Analysis of Gut Microbial Communities and Functions in Passer ammodendri Under Two Extreme Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
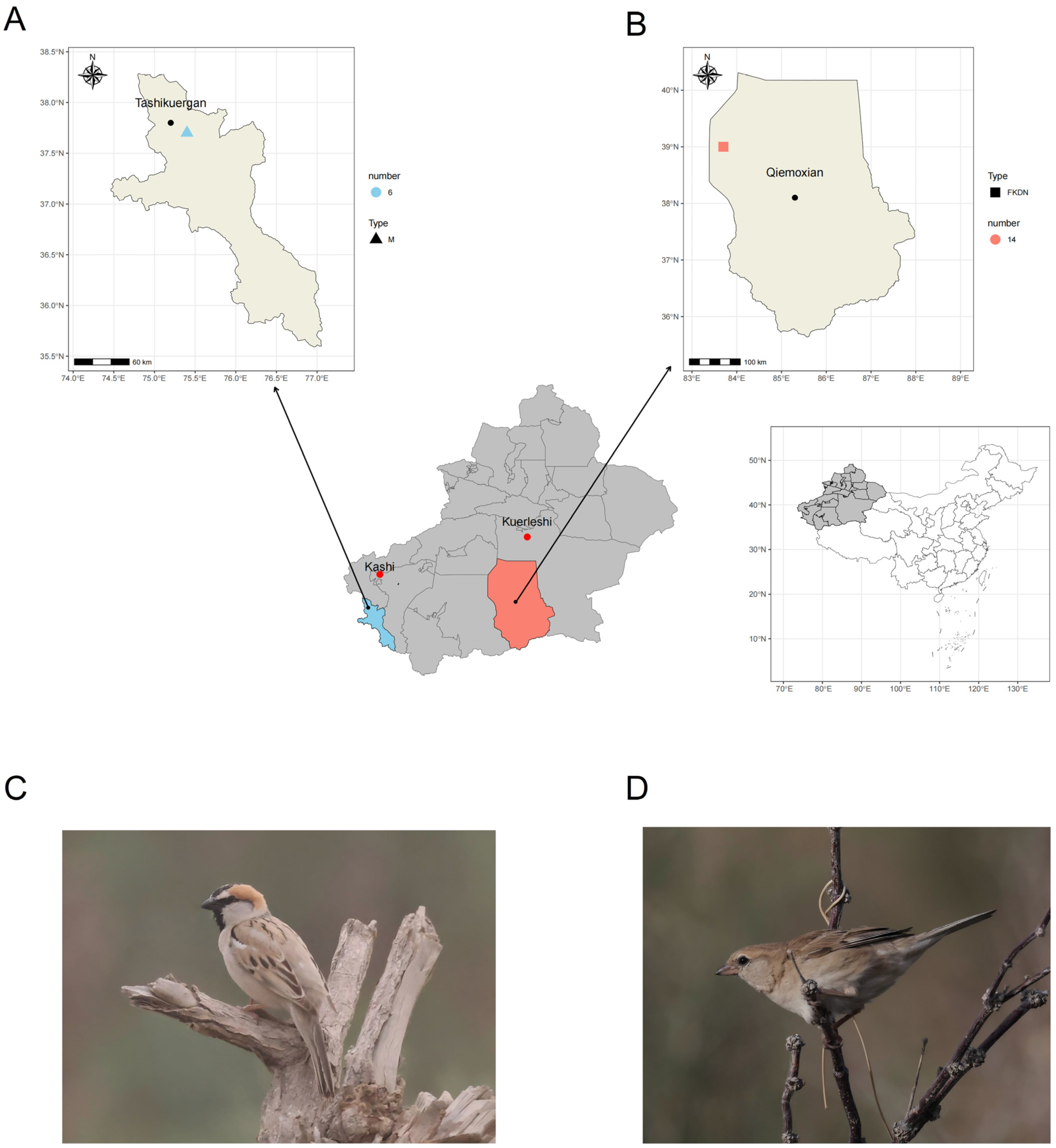
2.1. Fecal Sample Collection
2.2. Fecal DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.3. Quality Assessment of Sequencing Data
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. OTU Clustering, Taxonomic Annotation, and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4.2. Alpha Diversity Analysis
2.4.3. Beta Diversity Analysis
2.4.4. Intergroup Significance Analysis
2.4.5. Functional Gene Prediction Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Sequencing Data Quality Evaluation Results
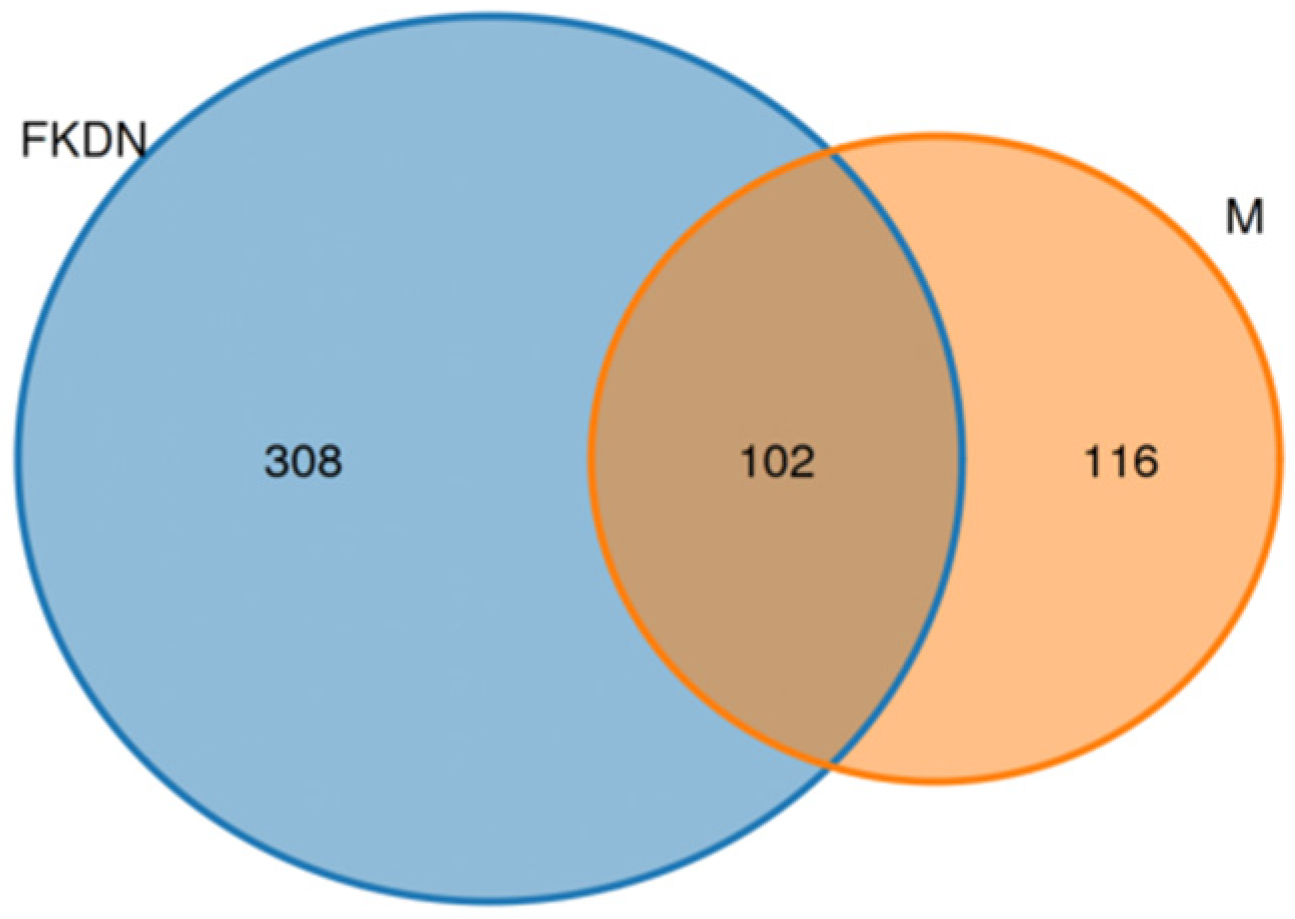
3.2. Composition and Relative Abundance of Gut Microbiota
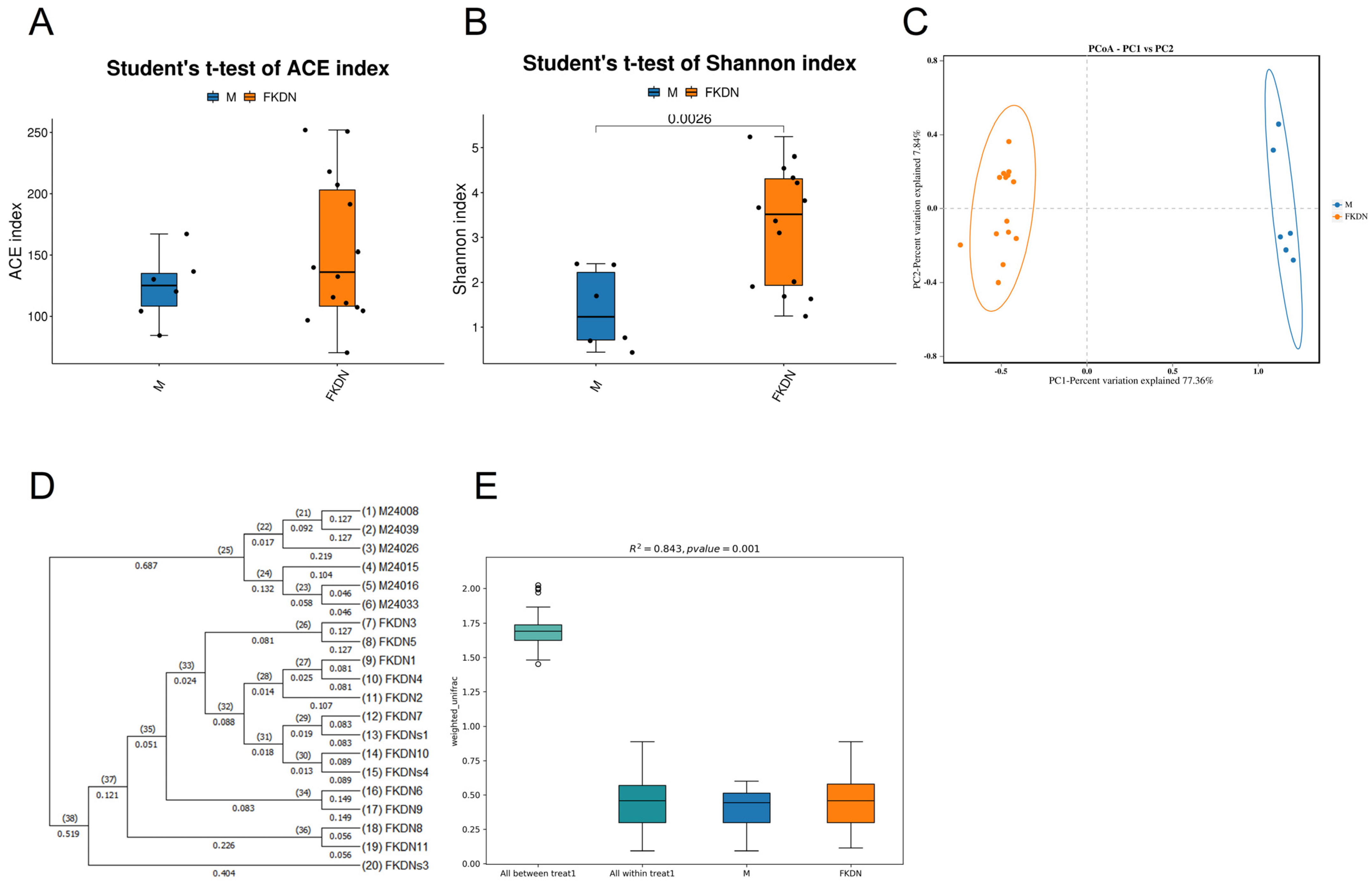
3.3. Differences in Richness, Diversity, and Composition Structure of Gut Microbiota
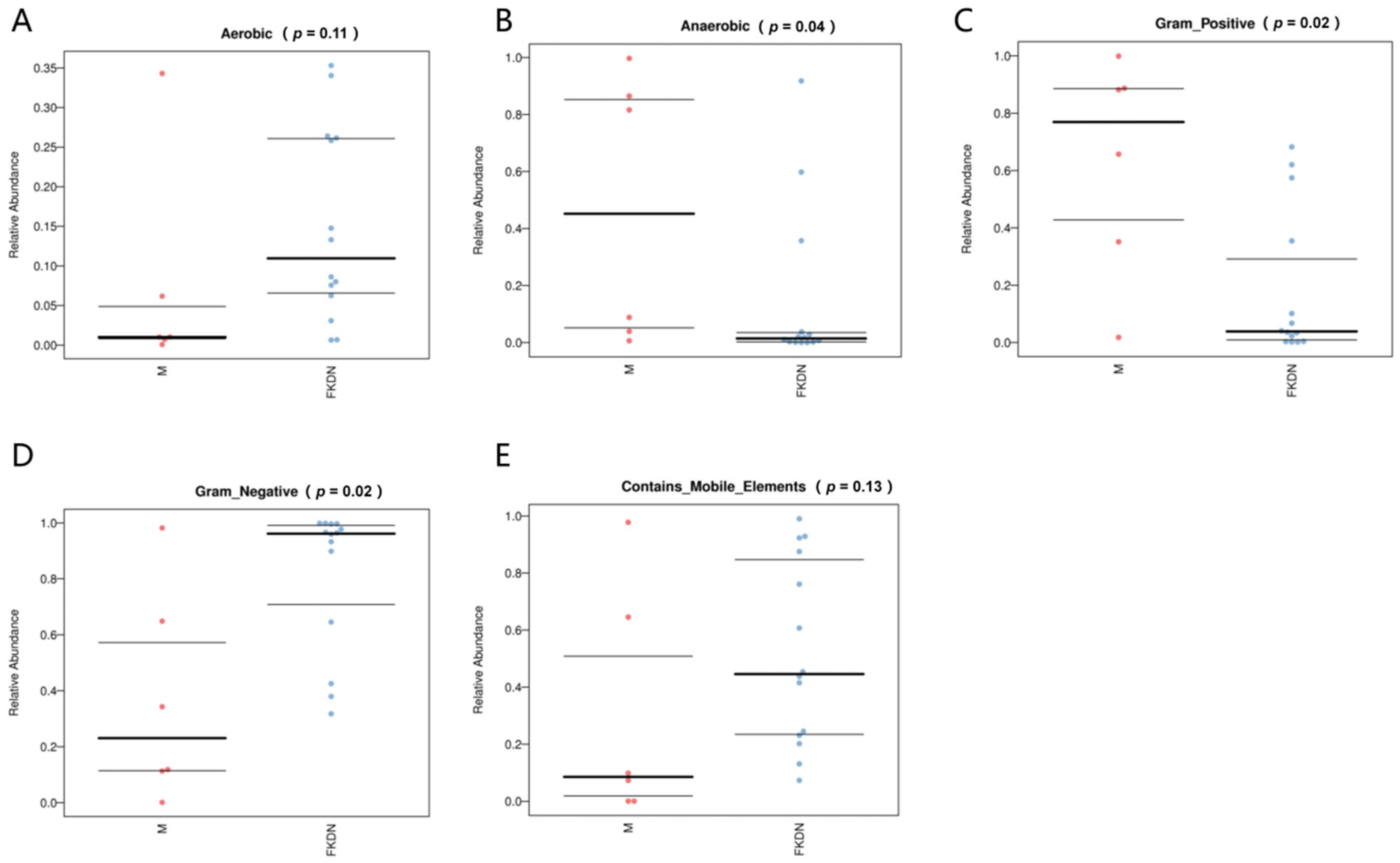
3.4. Functional Prediction of Gut Microbiota in Two Groups of Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.E.; Tun, H.M.; Bennett, D.C.; Leung, F.C.; Cheng, K.M. Microbial diversity and metabolic function in duodenum, jejunum and ileum of emu (Dromaius novaehollandiae). Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhou, H.; Pan, X.; Xu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zi, X.; Jiang, Y. Cassava foliage affects the microbial diversity of Chinese indigenous geese caecum using 16S rRNA sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45697. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, K.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, A.; Wang, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, P.; et al. Metagenomics research on the gut microbiota of the Marmota himalayana of the Sanjiangyuan National Nature Reserve in Qinghai Province, China. Biosaf. Health 2025, 7, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, T.; Song, G.; Zhang, M.; Xu, X.; Duan, J.; She, H.; Fang, Y.; Li, W.; Wen, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Gut microbiota contribute to high-altitude adaptation in tree sparrows. mSystems 2025, 10, e00630-25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liang, C.; Xu, B.; Song, P.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; Gu, H.; Jiang, F.; Gao, H.; Cai, Z.; et al. Extreme winter environment dominates gut microbiota and metabolome of white-lipped deer. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 297, 128182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Guo, T.; Zheng, C.; Wang, F.; Liu, T.; Yuan, C.; Lu, Z. Multi-omics insights into key microorganisms and metabolites in Tibetan sheep’s high-altitude adaptation. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1616555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chu, D.; Yan, H.; Sun, S.; Wu, X.; Fu, H.; Yuan, S. The role of gut microbes in drought adaptation in the five-toed jerboa (Orientallactaga sibirica). BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cao, L.; Yin, H.; Xu, M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Deng, Y. Habitat environments impacted the gut microbiome of long-distance migratory swan geese but central species conserved. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Li, D. Coping with extremes: Alternations in diet, gut microbiota, and hepatic metabolic functions in a highland passerine. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesare, D.A.; Valle, Ì.F.D.; Sala, C.; Sirri, F.; Astolfi, A.; Castellani, G.; Manfreda, G. Effect of a low protein diet on chicken ceca microbiome and productive performances. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 3963–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, D.W.; Taylor, M.W. Exploring the avian gut microbiota: Current trends and future directions. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, G.L.; Wiley, N.; Cooke, A.C.; Johnson, C.N.; Fouhy, F.; Reichert, M.S.; Hera, I.; Crane, J.M.S.; Kulahci, I.G.R.; Ross, P.; et al. Diet induces parallel changes to the gut microbiota and problem solving performance in a wild bird. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Halimubieke, N.; Sun, M.; Halimubieke, N.; Fang, B.; Valdebenito, J.O.; Xu, X.; Sheppard, S.K.; Székely, T.; Zhang, T.; et al. Gut microbiome in two high-altitude bird populations showed heterogeneity in sex and life stage. FEMS Microbes 2024, 5, xtae020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Cai, H.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. Extreme drought shapes the gut microbiota composition and function of common cranes (Grus grus) wintering in Poyang Lake. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1489906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G. A Checklist on the Classification and Distribution of the Birds of China, 2nd ed.; China Science Publishing & Media Ltd. (CSPM): Beijing, China, 2011; p. 352. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z. Chinese Ornithology; Jilin Science & Technology Publishing House: Changchun, China, 2001; pp. 776–777. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, S. Comparative Study of Gut Microbiome in Urban and Rural Eurasian Tree Sparrows. Animals 2024, 14, 3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Shen, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, Z.; Su, R.; Jin, F.; Zhang, Y. Responses of the gut microbiota to environmental heavy metal pollution in tree sparrow (Passer montanus) nestlings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 264, 115480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.R.; Vinson, A.E.; King, G.M.; Lattin, C.R. No Guts About It: Captivity, But Not Neophobia Phenotype, Influences the Cloacal Microbiome of House Sparrows (Passer domesticus). Integr. Org. Biol. 2022, 4, obac010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florkowski, M.R.; Yorzinski, J.L. Gut microbiome diversity and composition is associated with exploratory behavior in a wild-caught songbird. Anim. Microbiome 2023, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, K.D.; Brun, A.; Bordenstein, S.R.; Caviedes-Vidal, E.; Karasov, W.H. Gut microbes limit growth in house sparrow nestlings (Passer domesticus) but not through limitations in digestive capacity. Integr. Zool. 2018, 13, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X. The Behaviours of Saxaul Sparrow (Passer ammodendri) Around the Nest in Breeding Season. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M. Genetic Diversity and Spatial Genetic Structure Among Breeding Populations of the Saxaul Sparrow. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q. Life History Traits of Saxaul Sparrow (Passer ammodendri) in Anxi, Gansu. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X. Developmental and Succession of Gut Microbes in Saxaul Sparrow Chicks. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Passeridae (Old World Sparrows). Available online: https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Passeridae/ (accessed on 7 August 2025).
- The Pamir Plateau. Available online: https://baike.baidu.hk/item/%E5%B8%95%E7%B1%B3%E5%B0%94%E9%AB%98%E5%8E%9F/651091 (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Tazhong Town—Baidu Encyclopedia. Available online: https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%A1%94%E4%B8%AD%E9%95%87/18253888 (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Wang, W.; Cao, J.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.; Zheng, S.; Sharshov, K.; Li, L. High-throughput sequencing reveals the core gut microbiome of Bar-headed goose (Anser indicus) in different wintering areas in Tibet. MicrobiologyOpen 2016, 5, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qu, M.; Bi, Y.; Liu, W.J.; Ma, S.; Wan, B.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, G.; Gao, G.F. The multi-kingdom microbiome catalog of the chicken gastrointestinal tract. Biosaf. Health 2024, 6, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavande, P.V.; Basak, A.; Sen, S.; Lepcha, K.; Murmu, N.; Rai, V.; Mazumdar, D.; Saha, S.P.; Das, V.; Ghosh, S. Functional characterization of thermotolerant microbial consortium for lignocellulolytic enzymes with central role of Firmicutes in rice straw depolymerization. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoliński, J.; Czyż, K.; Kleszcz, A.; Trusz, A.; Wyrostek, A.; Zajfert, K. A preliminary study on farmed and free-ranging mouflons core microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 19555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D. Human gut microbiome: Hopes, threats and promises. Gut 2018, 67, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yang, J.; Yuan, H. Recent progress in research on the gut microbiota and highland adaptation on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Evol. Biol. 2021, 34, 1514–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.L.; Zhang, H.T.; Li, M.; Li, W.J.; Hua, Z.S. Recovery of nearly 3000 archaeal genomes from 152 terrestrial geothermal spring metagenomes. Sci. Data 2025, 12, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.L.; Chen, Y.T.; Xie, Y.G.; Li, Y.X.; Rao, Y.Z.; Li, M.M.; Xie, Q.J.; Cao, X.R.; Chen, L.; Qu, Y.N.; et al. Analysis of nearly 3000 archaeal genomes from terrestrial geothermal springs sheds light on interconnected biogeochemical processes. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setlow, P. Spore Resistance Properties. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isom, C.M.; Fort, B.; Anderson, G.G. Evaluating Metabolic Pathways and Biofilm Formation in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J. Bacteriol. 2022, 204, e00398-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heczko, U.; Abe, A.; Finlay, B.B. Segmented filamentous bacteria prevent colonization of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O103 in rabbits. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelblum, K.L.; Sharon, G.; Singh, G.; Odenwald, M.A.; Sailer, A.; Cao, S.; Ravens, S.; Thomsen, I.; Bissati, K.E.; McLeod, R.; et al. The Microbiome Activates CD4 T-cell-mediated Immunity to Compensate for Increased Intestinal Permeability. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 4, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ye, Y.; Wan, B.; Shao, R.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, H. Revealing the spatial heterogeneity of the gut microbiota of red-feather ducks and their interaction with environmental microorganisms. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 105593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlow, M.; Wada, H.; Derryberry, E.P. Experimental Exposure to Noise Alters Gut Microbiota in a Captive Songbird. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 84, 1264–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aikedai, S.; He, Q.; Ailimul, A.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xianmixinuer, K. Diurnal Variation Characteristics of Precipitation from April to September in the Eastern Parts of the Pamir Plateau. Desert Oasis Meteorol. 2022, 16, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, W.; Yao, J.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Shen, Y. Change Characteristics of Extreme Temperature-rising Process in the East Pamirs during 1961–2017. Arid Zone Res. 2019, 36, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Cao, G.; Ma, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, L.; Sanders, N.J.; et al. Alpine grassland plants grow earlier and faster but biomass remains unchanged over 35 years of climate change. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.; Huang, Z.; Tan, X.; Zang, J. Insect Diversity on the Tibetan Plateau. Xizang Sci. Technol. 2024, 46, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Z.; Yang, D.; Kong, D.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, Y. Distribution Patterns of Insect Diversity Along Elevation Gradients in Southeastern Margin of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Res. Environ. Sci. 2024, 37, 2138–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Sparrows: A Study of the Genus Passer 9781472597397, 9781408138243, 9781408138236. 2023. Available online: https://ebin.pub/the-sparrows-a-study-of-the-genus-passer-9781472597397-9781408138243-9781408138236.html (accessed on 6 August 2025).
- Li, C.; Lei, J.; Xu, X.; Tang, Q.; Gao, P.; Wang, Y. The stoichiometric characteristics of C, N, P for artificial plants and soil in the hinterland of Taklimakan Desert. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 5760–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xu, X. Experiment on Planting the Introduced Plants in the Hinterland of the Taklimakan Desert. Arid Zone Res. 2004, 4, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joakim, R.L.; Irham, M.; Haryoko, R.T.; Rowe, K.M.C.; Dalimunthe, Y.; Anita, S.; Achmadi, A.S.; McGuire, J.A.; Perkins, S.; Bowie, R.C.K. Geography and elevation as drivers of cloacal microbiome assemblages of a passerine bird distributed across Sulawesi, Indonesia. Anim. Microbiome 2023, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Nabi, G.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, C.; Cao, P.; Wu, Y.; Li, D. The effect of air pollution on immunological, antioxidative and hematological parameters, and body condition of Eurasian tree sparrows. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gou, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Genome Resequencing Identifies Unique Adaptations of Tibetan Chickens to Hypoxia and High-Dose Ultraviolet Radiation in High-Altitude Environments. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheinfeldt, L.B.; Soi, S.; Thompson, S.; Ranciaro, A.; Woldemeskel, D.; Beggs, W.; Lambert, C.; Jarvis, J.P.; Abate, D.; Belay, G.; et al. Genetic adaptation to high altitude in the Ethiopian highlands. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Lozupone, C.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ramey, R.R.; Bircher, J.S.; Schlegel, M.L.; Tucker, T.A.; Schrenzel, M.D.; Knight, R.; et al. Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science 2008, 320, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Pathogenic Microorganism Resource Repository. Available online: https://www.nprc.org.cn/#/DiseaseSearch?selectall=%E8%82%Ba%E7%82%8E%E5%85%8B%E9%9B%B7%E4%BC%AF%E6%B0%8F%E8%8F%8C (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Bhagat, N.R.; Bharti, V.K.; Shukla, G.; Rishi, P.; Chaurasia, O.P. Gut bacteriome dynamics in high altitude-adapted chicken lines: A key to future poultry therapeutics. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.M.; Trigo, S.; Cardoso, G.C.; Xavier, R. Cloaca- and feather-associated bacteria communities in common waxbills Estrilda astrild. J. Avian Biol. 2022, 2022, e02910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobniak, S.M.; Cichoń, M.; Janas, K.; Barczyk, J.; Gustafsson, L.; Zagalska-Neubauer, M. Habitat shapes diversity of gut microbiomes in a wild population of blue tits Cyanistes caeruleus. J. Avian Biol. 2022, 2022, e02829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolores Barón, M.; Stanback, M.; Martínez-Renau, E.; Soler, J.J.; Martín-Vivaldi, M. Characterizing bacterial communities of wild birds: Insights from three southern African hornbill species. J. Avian Biol. 2025, 2025, e03347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrer, S.D.; Jiménez-Uzcátegui, G.; Parker, P.G.; Chubiz, L.M. Composition and function of the Galapagos penguin gut microbiome vary with age, location, and a putative bacterial pathogen. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.C.; Skeen, H.R.; Cuellar, C.; Hird, S.M. Canada goose fecal microbiota correlate with geography more than host-associated factors. J. Avian Biol. 2025, 2025, e03360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drovetski, S.V.; O’mahoney, M.; Ransome, E.J.; Matterson, K.O.; Lim, H.C.; Chesser, R.T.; Graves, G.R. Spatial Organization of the Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Urban Canada Geese. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Tao, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Fu, C.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, Y. Temporal Variations in the Gut Microbiota of the Globally Endangered Sichuan Partridge (Arborophila rufipectus): Implications for Adaptation to Seasonal Dietary Change and Conservation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e00747-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
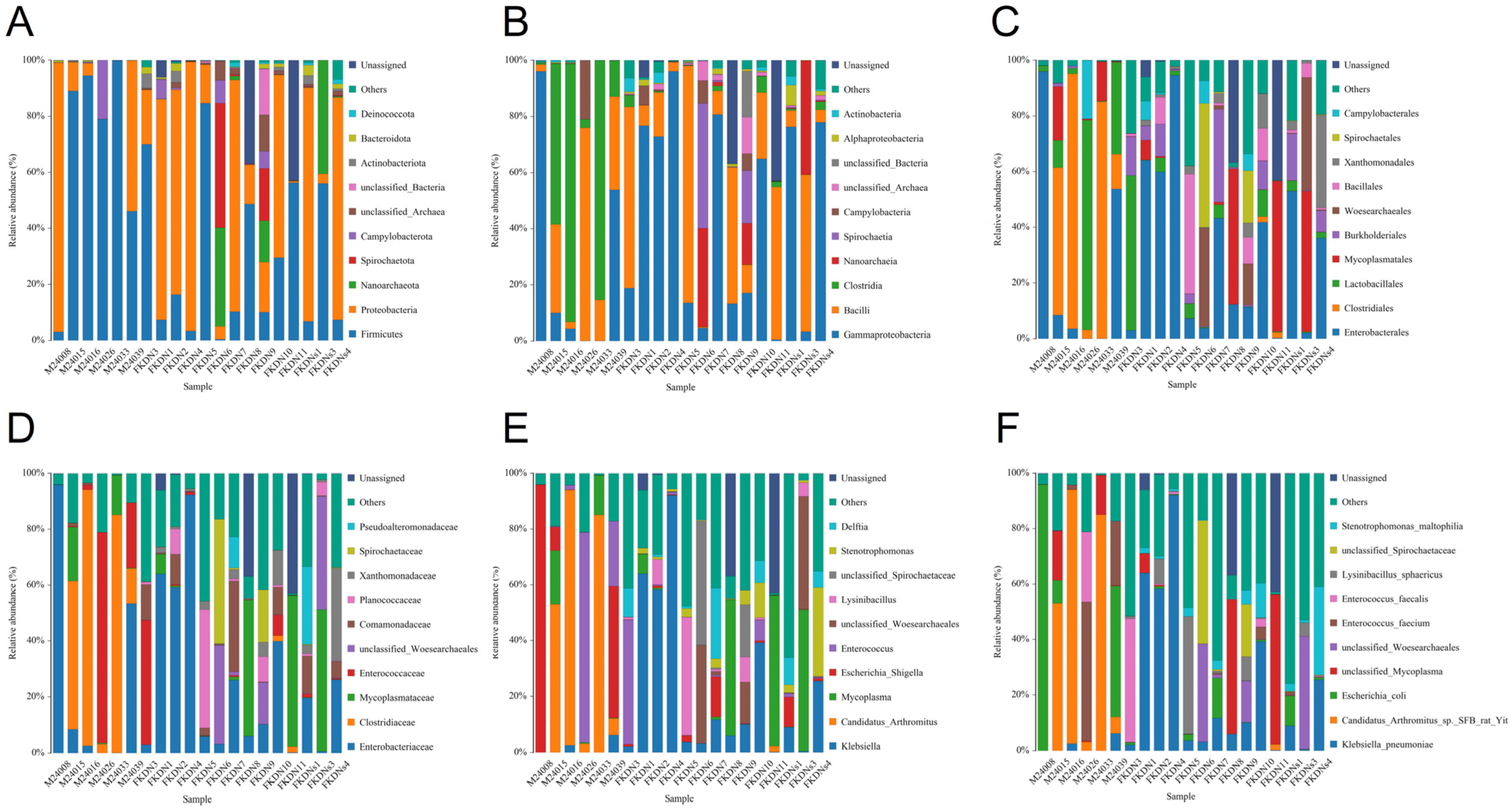
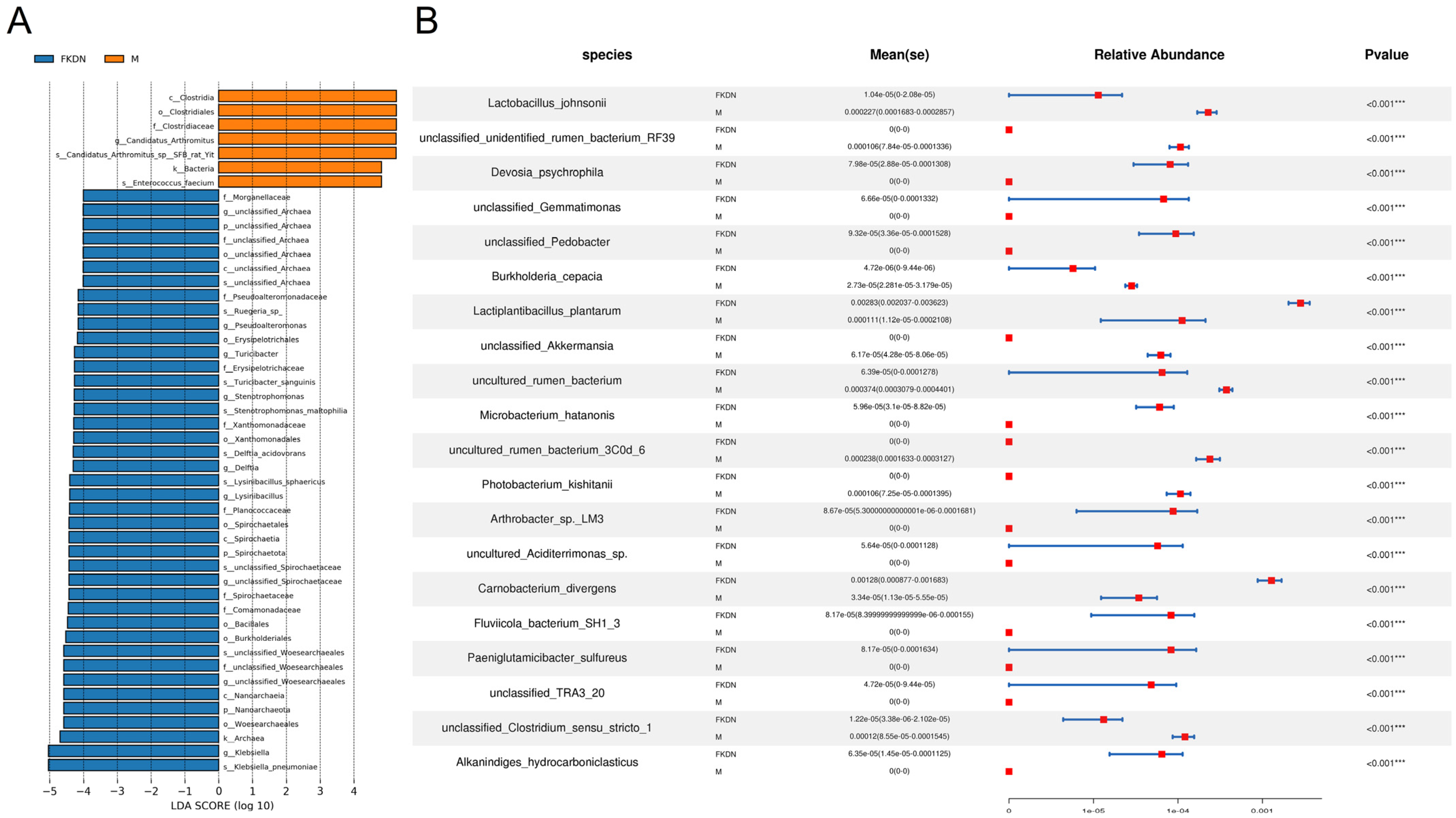
| Relative Abundance (%) | Pamir Plateau Group (M) | Tazhong Town Group (FKDN) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dominant Bacteria | |||
| Candidatus Arthromitus sp. SFB rat Yit | 39.76 | 0.14 | |
| Escherichia coli | 25.26 | 2.19 | |
| Enterococcus faecium | 12.49 | 0.45 | |
| Enterococcus faecalis | 4.27 | 3.52 | |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 1.45 | 23.25 | |
| Lysinibacillus sphaericus | 0 | 4.80 | |
| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | 1.58 × 10−3 | 4.57 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; He, P.; Liu, D.; Song, Y.; Jia, C.; Wang, D.; Jin, Q.; Song, G.; Wei, Q. Analysis of Gut Microbial Communities and Functions in Passer ammodendri Under Two Extreme Environments. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2642. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112642
Liu Y, He P, Liu D, Song Y, Jia C, Wang D, Jin Q, Song G, Wei Q. Analysis of Gut Microbial Communities and Functions in Passer ammodendri Under Two Extreme Environments. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(11):2642. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112642
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yaqi, Peng He, Dongxin Liu, Yang Song, Chenxi Jia, Duochun Wang, Qinghua Jin, Gang Song, and Qiang Wei. 2025. "Analysis of Gut Microbial Communities and Functions in Passer ammodendri Under Two Extreme Environments" Microorganisms 13, no. 11: 2642. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112642
APA StyleLiu, Y., He, P., Liu, D., Song, Y., Jia, C., Wang, D., Jin, Q., Song, G., & Wei, Q. (2025). Analysis of Gut Microbial Communities and Functions in Passer ammodendri Under Two Extreme Environments. Microorganisms, 13(11), 2642. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112642







