Downregulation of oar-miR-125b Drives Blood–Brain Barrier Breakdown Through the TNFSF4–NF-κB Inflammatory Axis in Enterococcus Faecalis Meningitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Enterococcus Faecalis-Infected OBMECs
2.3. Cell Transfection
2.4. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Immunofluorescence
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
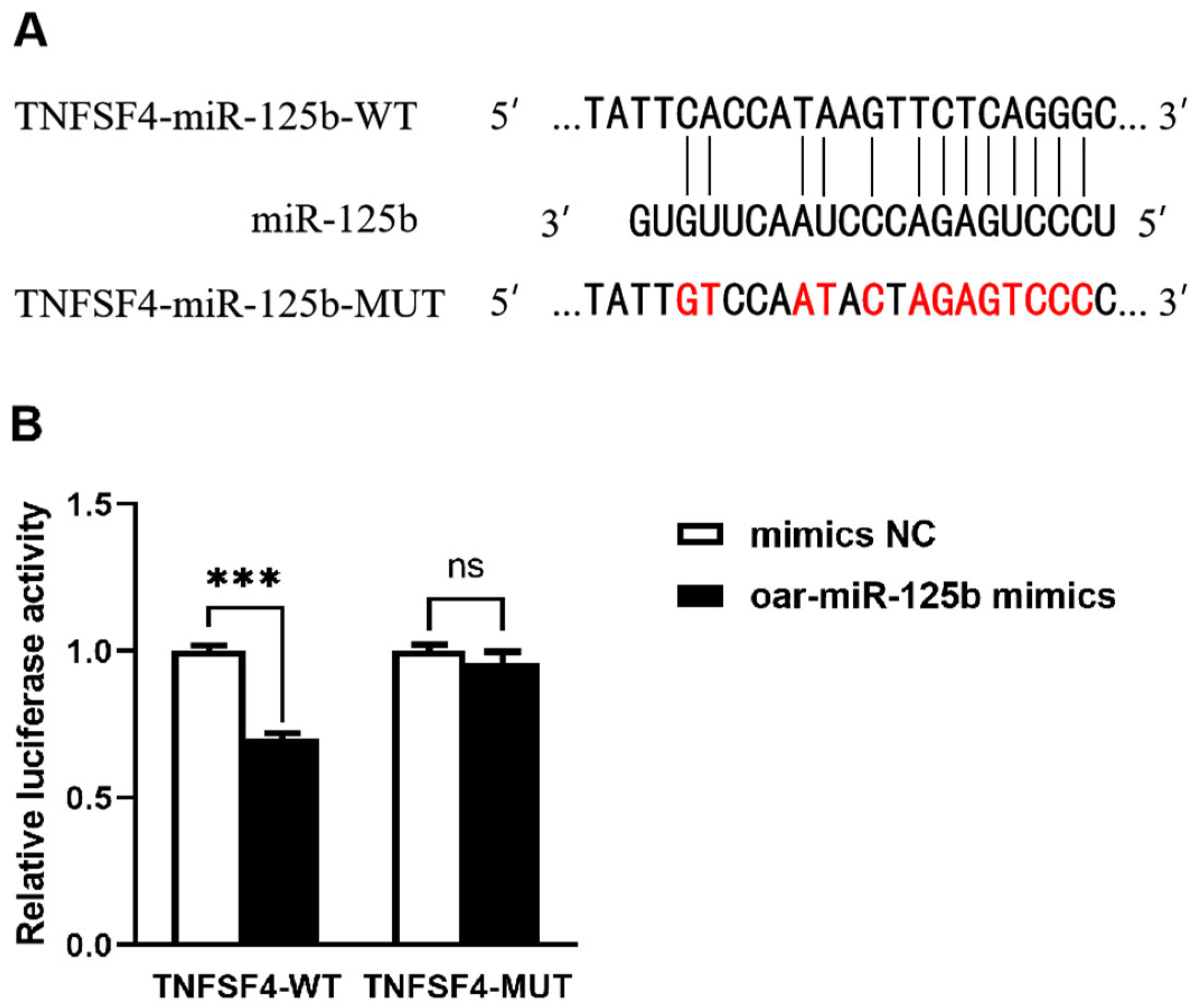
3.1. Potential Negative Regulation of the Proinflammatory Factor TNFSF4 by oar-miR-125b
3.2. TNFSF4 Has Been Identified as a Direct Target of oar-miR-125b
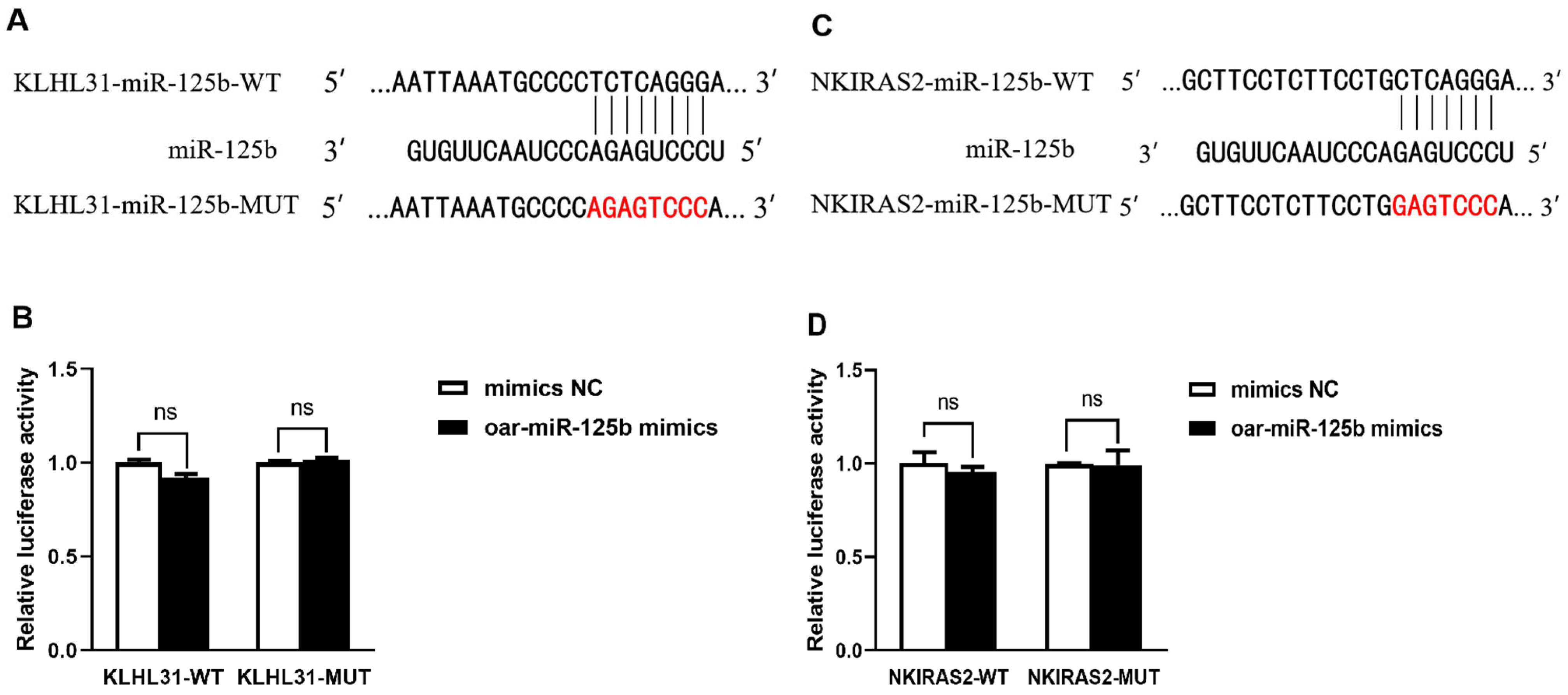
3.3. KLHL31 and NKIRAS2 Were Confirmed Not to Be Direct Targets of Sheep oar-miR-125b
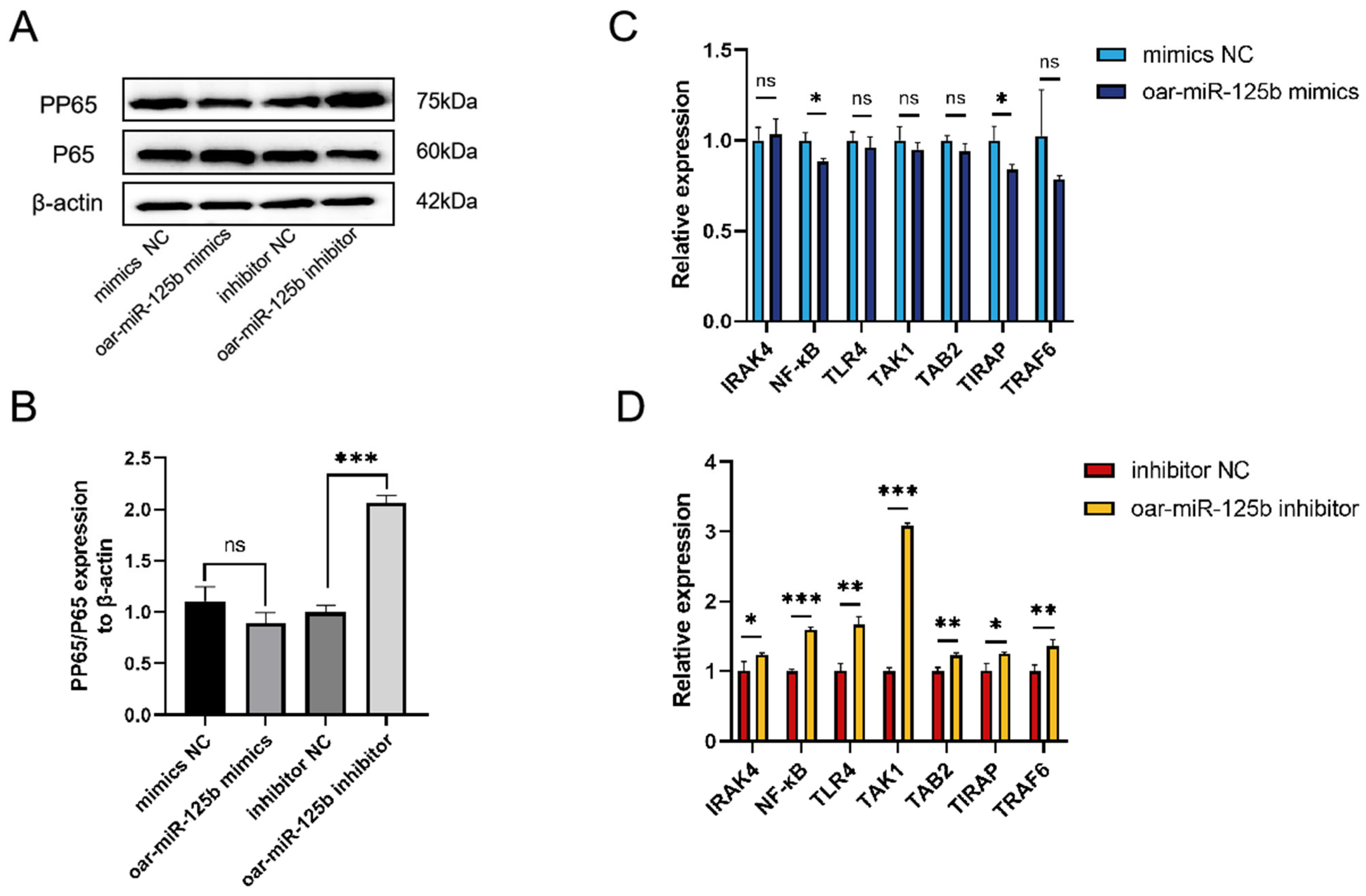
3.4. oar-miR-125b Negatively Regulates the NF-κB Pathway and Its Mediated Inflammatory Response by Targeting and Inhibiting TNFSF4
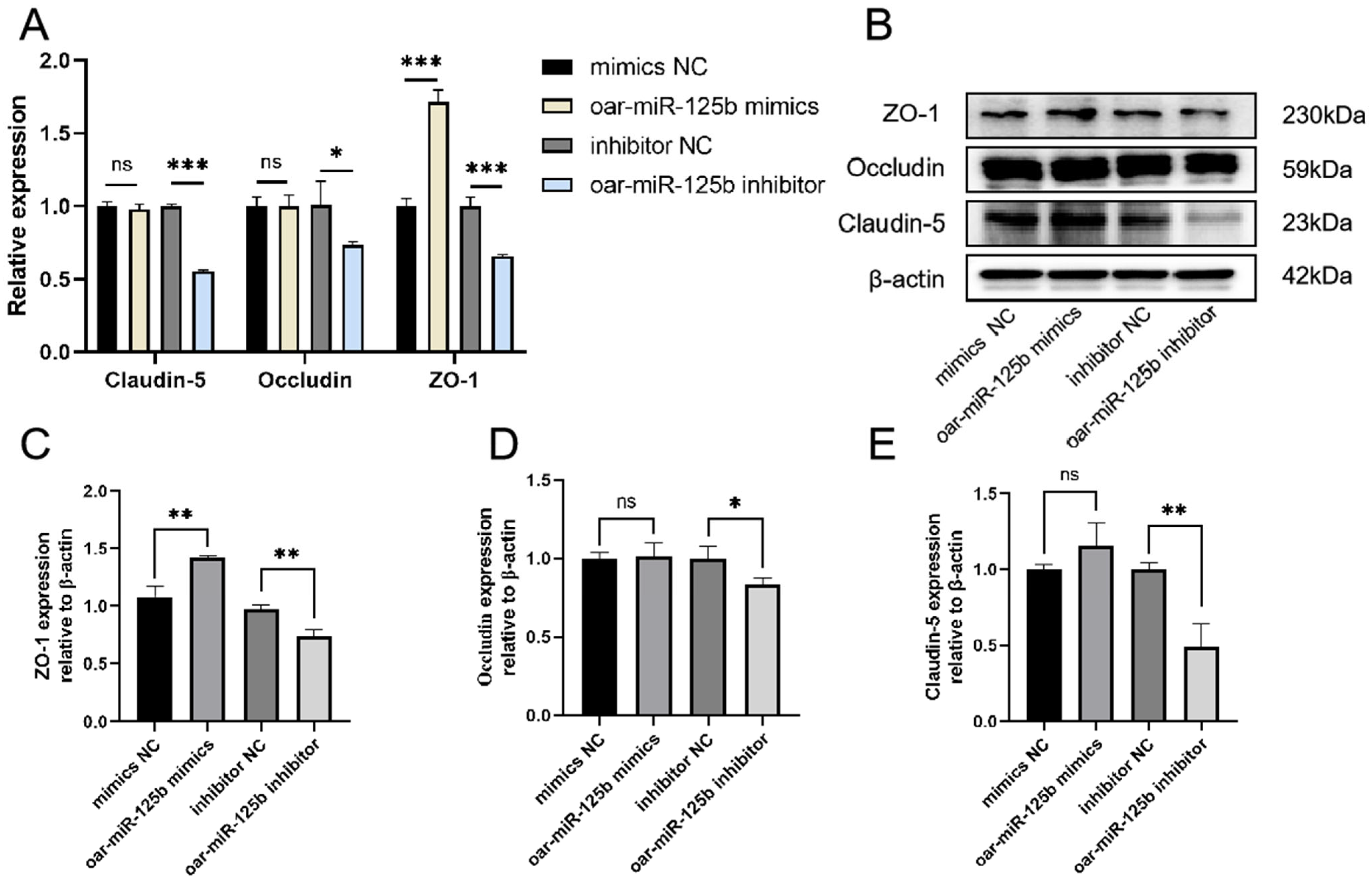
3.5. oar-miR-125b Is a Positive Regulator of Blood–Brain Barrier Integrity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodgers, E.; Bentley, S.D.; Borrow, R.; Bratcher, H.B.; Brisse, S.; Brueggemann, A.B.; Caugant, D.A.; Findlow, J.; Fox, L.; Glennie, L.; et al. The global meningitis genome partnership. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasbun, R. Progress and Challenges in Bacterial Meningitis. JAMA 2022, 328, 2147–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoikon, S.T.L.; Diallo, K.; Tuo, J.K.; Nasir, N.; Feteh, V.F.; Mzumara, G.; Aderoba, A.; Jacques, R.; Mandal, H.; Jolley, K.A.; et al. In silico and in vitro analyses for the improved diagnosis of bacterial meningitis. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1655490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempinen, L.; Saat, R.; Niemelä, S.; Laulajainen-Hongisto, A.; Aarnisalo, A.A.; Nieminen, T.; Jero, J. Neurological sequelae after childhood bacterial meningitis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2024, 183, 5203–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, C.; Zhou, C. Diagnosis of Enterococcus faecalis meningitis associated with long-term cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhoea using metagenomics next-generation sequencing: A case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Cao, G.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Yang, C. Effects of Clostridium butyricum and Enterococcus faecalison growth performance, immune function, intestinal morphology, volatile fatty acids, and intestinal flora in a piglet model. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 7844–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Hidalgo, L.; Fernández-Rubio, B.; Luque-Márquez, R.; López-Cortés, L.E.; Gil-Navarro, M.V.; de Alarcón, A. Treatment of Enterococcus faecalis Infective Endocarditis: A Continuing Challenge. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Du, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y. Enterococci independently increase the risk for initial antibiotic treatment failure and prolonged hospitalization in adult patients with complicated urinary tract infection: A retrospective cohort study. Infection 2024, 53, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Gong, X.; Ma, Y.; Shi, G.; Li, G.; Wu, G. Enterococci-related healthcare-associated ventriculitis and meningitis: A multicenter retrospective case series from clinical practice. BMC Neurol. 2025, 25, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Profaci, C.P.; Munji, R.N.; Pulido, R.S.; Daneman, R. The blood–brain barrier in health and disease: Important unanswered questions. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzookian, K.; Aliakbari, F.; Hourfar, H.; Sabouni, F.; Otzen, D.E.; Morshedi, D. The neuroprotective effect of human umbilical cord MSCs-derived secretome against α-synuclein aggregates on the blood-brain barrier. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 304, 140387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Han, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. The blood–brain barrier: Structure, regulation and drug delivery. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierfuss, B.; Larochelle, C.; Prat, A. Blood–brain barrier dysfunction in multiple sclerosis: Causes, consequences, and potential effects of therapies. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, K.I.; Bakhtawar, K.H.; Ge, Y.X.; Muhammad, M.; Mubin, M.K.; Hamid, K.; Shahid, B. The Impact of the Blood–Brain Barrier and Its Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease: Contributions to Pathogenesis and Progression. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 45663–45672. [Google Scholar]
- Fanini, F.; Fabbri, M. MicroRNAs and cancer resistance: A new molecular plot. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 99, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B. MiR-125b targeted regulation of MKNK2 inhibits multiple myeloma proliferation and invasion. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2024, 16, 3366–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Dang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Y.; Wei, Z. The miRNA, miR-125b, Inhibited Invasion and Metastasis of Gastric-Cancer Cells by Triggering the STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 8569–8580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Han, Y.-N.; Ge, M.; Wang, P.; Sun, L.; Liu, H.; Cao, T.; Nie, Y.; Fan, D.; et al. miR-125b Promotes Colorectal Cancer Migration and Invasion by Dual-Targeting CFTR and CGN. Cancers 2021, 13, 5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Cheng, K.; Wang, H.; Ji, Y.; Su, X.; Hao, M. Down-regulation of miR-125b by HPV16 E6 might promote cervical cancer progression through TAZ/TEAD. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1444874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-W.; Ramasamy, K.; Bouamar, H.; Lin, A.-P.; Jiang, D.; Aguiar, R.C.T. MicroRNAs miR-125a and miR-125b constitutively activate the NF-κB pathway by targeting the tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3, A20). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7865–7870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoreng, Z.-M.; Wei, D.-W.; Wang, X.-P. MiR-125b regulates inflammation in bovine mammary epithelial cells by targeting the NKIRAS2 gene. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 122. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, P.; Ren, M.; Han, Y. MiR-125b-5p ameliorates ox-LDL-induced vascular endothelial cell dysfunction by negatively regulating TNFSF4/TLR4/NF-κB signaling. BMC Biotechnol. 2025, 25, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Croft, M.; So, T.; Duan, W.; Soroosh, P. The significance of OX40 and OX40L to T-cell biology and immune disease. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 229, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takaori-Kondo, A.; Hori, T.; Fukunaga, K.; Morita, R.; Kawamata, S.; Uchiyama, T. Both Amino- and Carboxyl-Terminal Domains of TRAF3 Negatively Regulate NF-κB Activation Induced by OX40 Signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 272, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yue, L.-Y.; Xu, Y.; Tao, B.; He, C.-S. Association of TNFSF4 Gene Polymorphisms and Plasma TNFSF4 Level with Risk of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in a Chinese Population. Immunol. Investig. 2020, 51, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Bello, J.; Jiménez-Morales, S.; Barbosa-Cobos, R.E.; Sánchez-Zauco, N.; Hernández-Molina, G.; Luria-Pérez, R.; Fragoso, J.M.; Cabello-Gutiérrez, C.; Montúfar-Robles, I. TNFSF4 is a risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis but not for primary Sjögren’s syndrome in the Mexican population. Immunobiology 2022, 227, 152244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foks, A.C.; Van Puijvelde, G.H.M.; Bot, I.; ter Borg, M.N.D.; Habets, K.L.L.; Johnson, J.L.; Yagita, H.; van Berkel, T.J.C.; Kuiper, J. Interruption of the OX40–OX40 Ligand Pathway in LDL Receptor–Deficient Mice Causes Regression of Atherosclerosis. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4573–4580. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Park, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, H.M.; Rayhan, B.R.; Jeong, J.; Bothwell, A.L.; Shin, J.H. Trogocytosis-mediated immune evasion in the tumor microenvironment. Exp. Mol. Med. 2025, 57, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Sun, Z.; Hu, W.; Xue, D.; Yang, Z.; Duan, P.; Peng, H.; Fu, Y.-X.; Liang, Y. Dual targeting OX40 and IL-2 receptor enhances antitumor activity through tumor-infiltrating Treg depletion and CD8+ T-cell proliferation. J. Immunother. Cancer 2025, 13, e011638. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, P.F.; Jiao, L.L.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, R.Z.; Li, Y.J.; Qi, Y.Y.; Ren, J.J. Construction of a meningitis infection model in lambs induced by Enterococcus faecalis. Chin. J. Prev. Vet. Med. 2025, 47, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.-W.; Tsai, K.-N.; Chen, Y.-S.; Chang, R.-Y. Differential miRNA Expression Profiling Reveals Correlation of miR125b-5p with Persistent Infection of Japanese Encephalitis Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Chen, F.; Wang, L.; Lin, C.; Ying, M.; Li, B.; Huang, T.; Wang, S. iMSC exosome delivers hsa-mir-125b-5p and strengthens acidosis resilience through suppression of ASIC1 protein in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 107568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.-C.; Liang, J.; Hu, N.; Yao, B.; Zhang, Q.-J.; Zeng, X.-L.; Zhang, L.-J.; Zhang, X.; Chang, Z.-H.; Chen, C.; et al. Hypoxia preconditioned MSC exosomes attenuate high-altitude cerebral edema via the miR-125a-5p/RTEF-1 axis to protect vascular endothelial cells. Bioact. Mater. 2025, 52, 541–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhang, H. Mechanism of miR-125b-5p in the recovery of brain function after traumatic brain injury. Traffic Med. 2022, 36, 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Wang, X.; Ha, T.; Gao, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, R.; Yu, K.; Kalbfleisch, J.H.; Kao, R.L.; Williams, D.L.; et al. MicroRNA-125b Prevents Cardiac Dysfunction in Polymicrobial Sepsis by Targeting TRAF6-Mediated Nuclear Factor κB Activation and p53-Mediated Apoptotic Signaling. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, 1773–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Zhou, W.; Fan, J.; Jia, C.; Xiong, W.; Wei, H.; Tao, S. Diarrheal microbiota-derived extracellular vesicles drive intestinal homeostasis dysfunction via miR-125b/NF-κB-mediated macrophage polarization. Gut Microbes 2025, 17, 2541036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesch-Saadatmandi, C.; Wagner, A.E.; Wolffram, S.; Rimbach, G. Effect of quercetin on inflammatory gene expression in mice liver in vivo—Role of redox factor 1, miRNA-122 and miRNA-125b. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 65, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Yuan, S.; Song, S.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y. Breaking the fortress: A mechanistic review of meningitis-causing bacteria breaching tactics in blood brain barrier. Cell Commun. Signal. 2025, 23, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matur, E.; Özcan, M.; Ergül Ekiz, E.; Ergen, E.; Erek, M.; Or, E.; Dokuzeylül, B.; Erhan, S.; Bilgiç, B. Use of serum procalcitonin (PCT) level and PCT mRNA expression as a potential clinical biomarker in cats with bacterial and viral infections. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2022, 24, e595–e602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodero, G.; Gentili, C.; Mariani, F.; Pulcinelli, V.; Valentini, P.; Buonsenso, D. Procalcitonin and Presepsin as Markers of Infectious Respiratory Diseases in Children: A Scoping Review of the Literature. Children 2024, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Target Gene | Primer Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| oar-miR-125b | RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACCACAAG |
| TNFSF4 | F: CGCGTCCCTGAGACCCTAA |
| R: AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| F: CACGTTCCCCTTTTCCATATCT | |
| R: CCTCCTTTTGGGAAGTGAGGA | |
| TLR4 | F: TGTGAAGGACATGCCAGTGCTTG |
| R: TGACAACCGACACGCTGATGATC | |
| NFκB | F: ACAAGCCTGTCACAGCCAACATG |
| R: TGATGGTGAAGGCTCAGGAGGTG | |
| TAB2 | F: GGAAGCAGGACTCTAACGCACAG |
| R: GCCTTGAGGAACTTGAGCTGGTG | |
| TIRAP | F: CCTCAGCAGAGCCGCCTACC |
| R: GCATGACAGCGTCCTTGACTTGG | |
| IRAK4 | F: CTCAAGTGATGGCGATGACCTCTG |
| R: CCATCCAAGCAAGCCAGTCTGTC | |
| TAK1 | F: TCCGCCGCTTCTTCCTCCTC |
| R: GCTCCTCTTCCAACAACCTCTTCC | |
| TRAF6 | F: ACTGAGGCATCTTGAGGAGCATC |
| R: TTCTGGAAGAGACGCTGGCATTG | |
| β-actin | F: ACTGGGACGACATGGAGAAGA |
| R: GCGTACAGGGACAGCACAG | |
| IL-6 | F: AGACTACTTCTGACCACTCCA |
| R: TCACACTCGTCATTCTTCTCAC | |
| TNF-α | F: GACGGGCTTTACCTCATCTAC |
| R: CTTGATGGCAGAGAGGATGTT | |
| IL1β | F: AGGAAATGAGCCGAGAAGTG |
| R: ATTCTTGTCCCTGATACCCAAG | |
| IL-10 | F: TGCTGGATGACTTTAAGGG |
| R: AGGGCAGAAAACGATGACA | |
| U6 | F: GCTTCGGCAGCACATATACT |
| R: TTCACGAATTTGCGTGTCAT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, L.; Wu, Y.; Qi, B.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Ren, J.; Cao, S.; Qi, Y. Downregulation of oar-miR-125b Drives Blood–Brain Barrier Breakdown Through the TNFSF4–NF-κB Inflammatory Axis in Enterococcus Faecalis Meningitis. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122644
Jiao L, Wu Y, Qi B, Zhao P, Zhou M, Zhang R, Li Y, Ren J, Cao S, Qi Y. Downregulation of oar-miR-125b Drives Blood–Brain Barrier Breakdown Through the TNFSF4–NF-κB Inflammatory Axis in Enterococcus Faecalis Meningitis. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(12):2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122644
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Longling, You Wu, Borui Qi, Pengfei Zhao, Ming Zhou, Runze Zhang, Yongjian Li, Jingjing Ren, Shuzhu Cao, and Yayin Qi. 2025. "Downregulation of oar-miR-125b Drives Blood–Brain Barrier Breakdown Through the TNFSF4–NF-κB Inflammatory Axis in Enterococcus Faecalis Meningitis" Microorganisms 13, no. 12: 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122644
APA StyleJiao, L., Wu, Y., Qi, B., Zhao, P., Zhou, M., Zhang, R., Li, Y., Ren, J., Cao, S., & Qi, Y. (2025). Downregulation of oar-miR-125b Drives Blood–Brain Barrier Breakdown Through the TNFSF4–NF-κB Inflammatory Axis in Enterococcus Faecalis Meningitis. Microorganisms, 13(12), 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122644





