History of Shrimp Farming and the Main Viral and Bacterial Diseases in Mexico
Abstract
1. Importance of Aquaculture
2. Global Farmed Shrimp Production
3. Shrimp Farming in Latin America
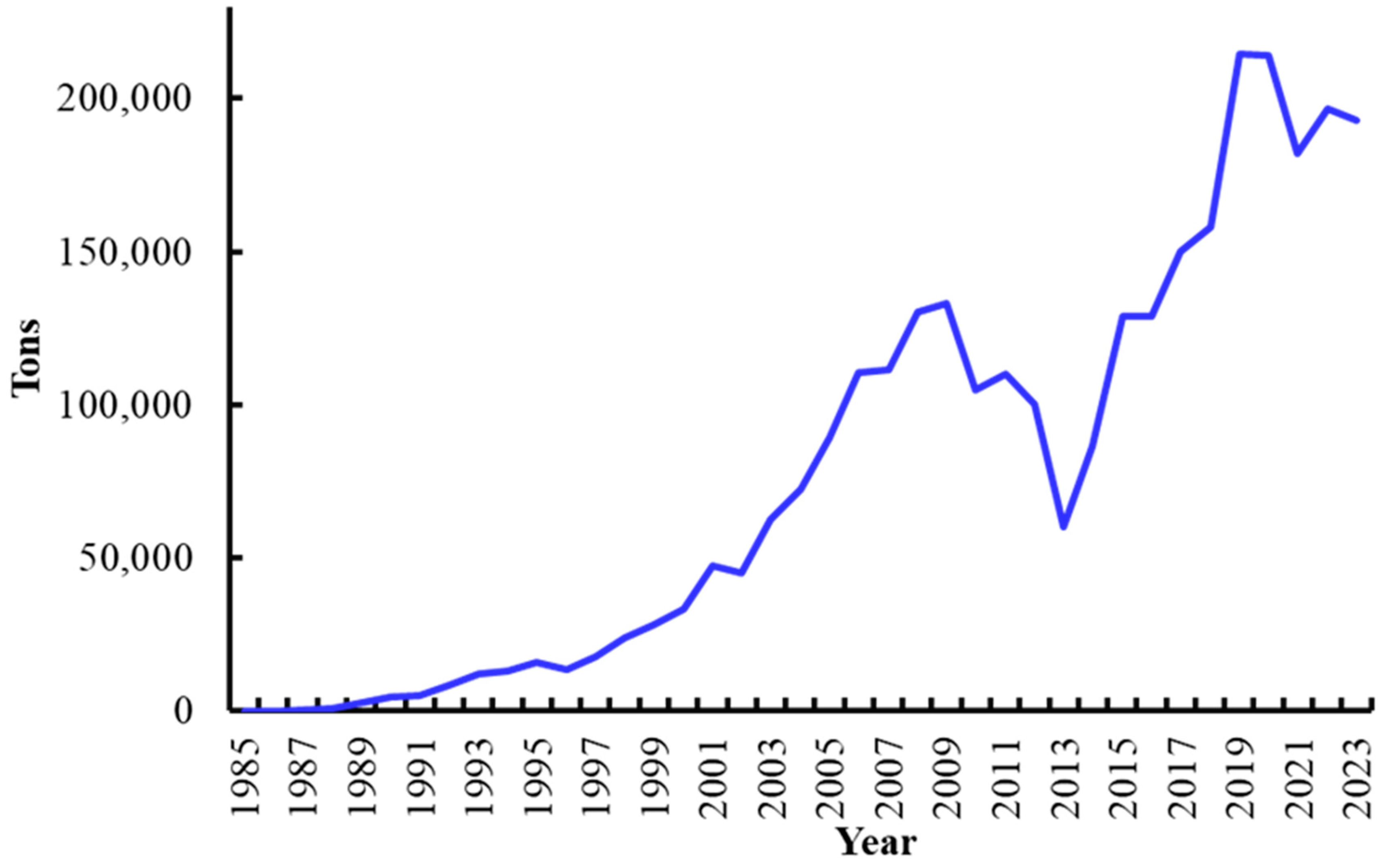
4. Shrimp Farming in Mexico
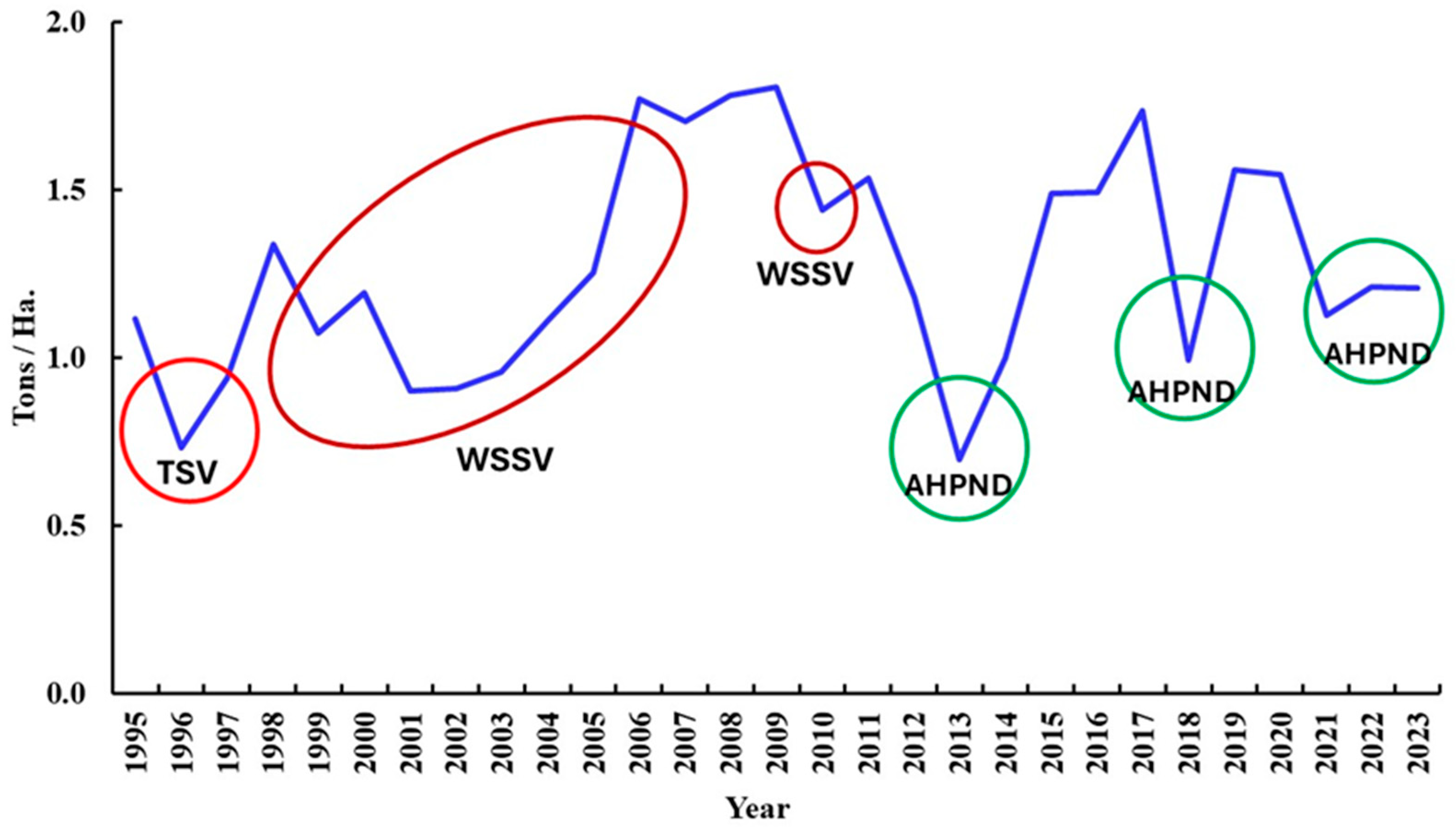
5. Major Shrimp Diseases in Mexico
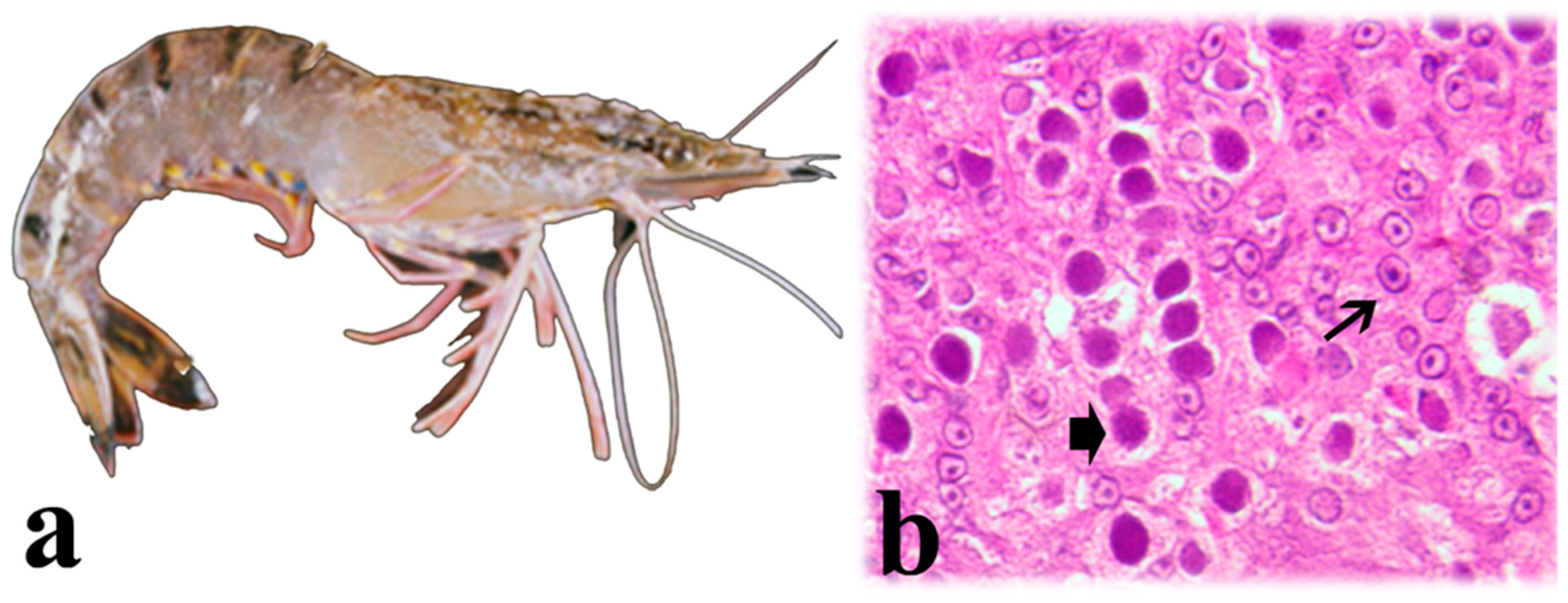
5.1. Baculovirus penaei (Penaeus vannamei Singly Enveloped Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus)
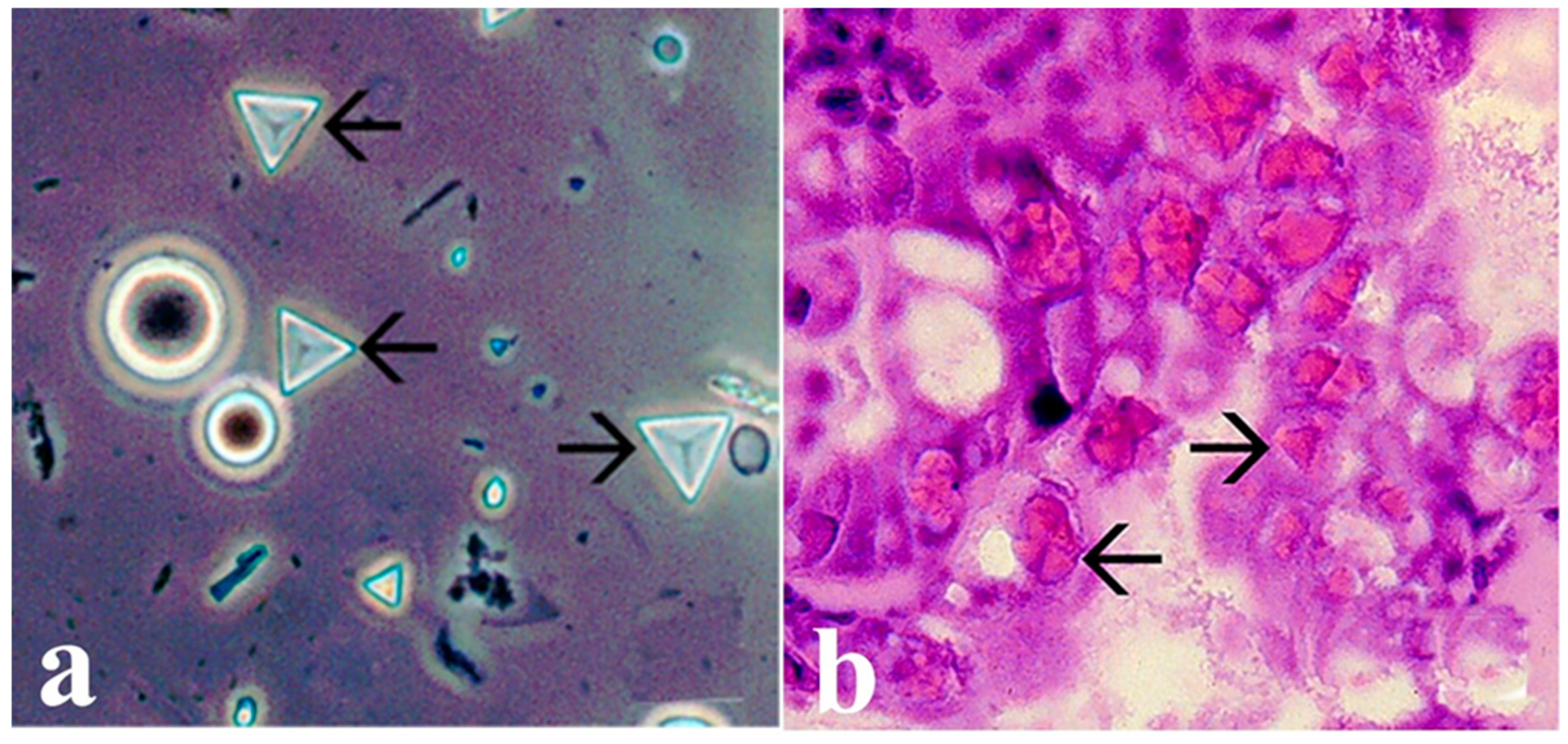
5.2. Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV) (Penstylhamaparvovirus 1)
5.3. Taura Syndrome Virus (TSV) (Aparavirus Dicistroviridae)

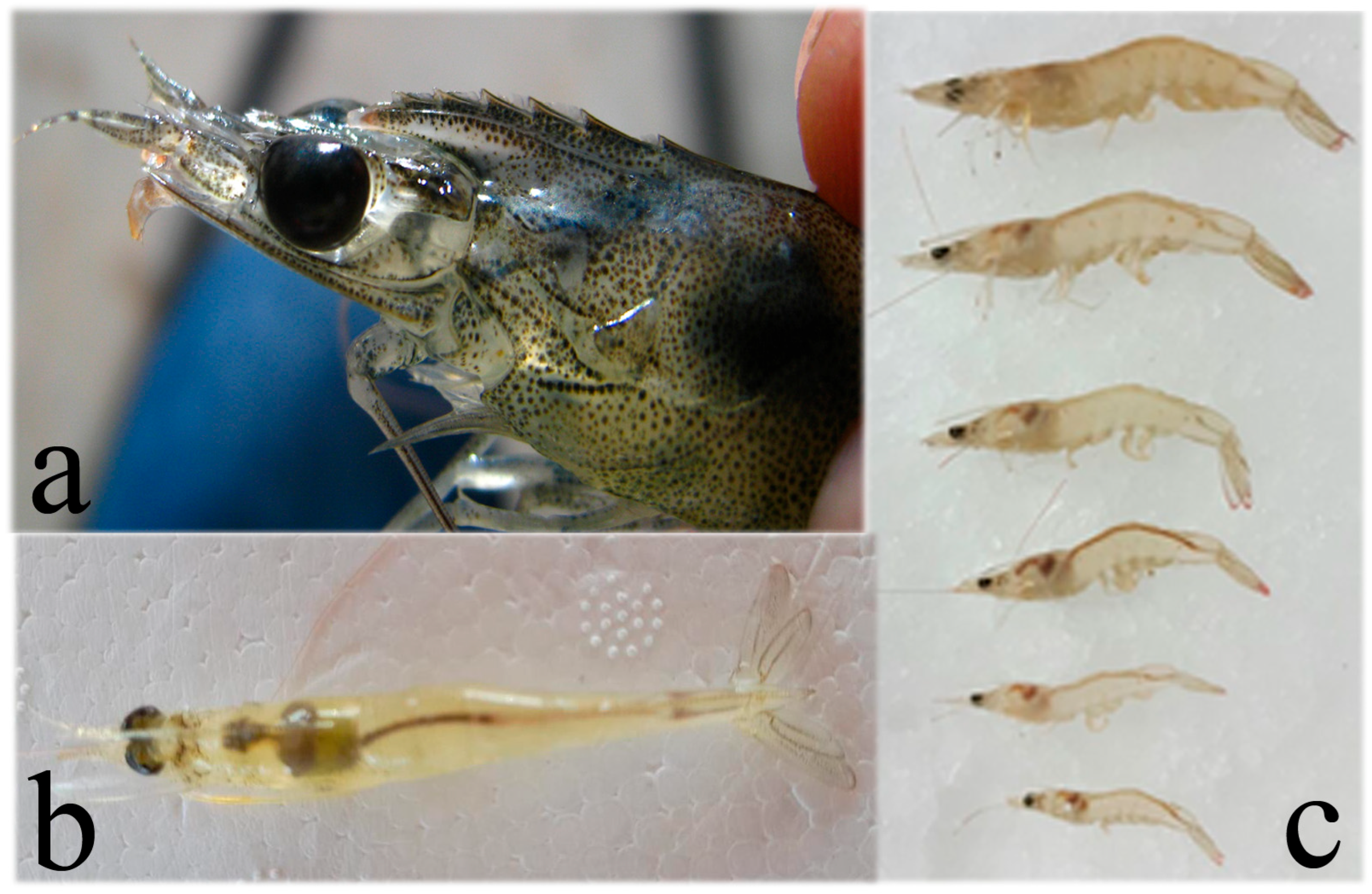
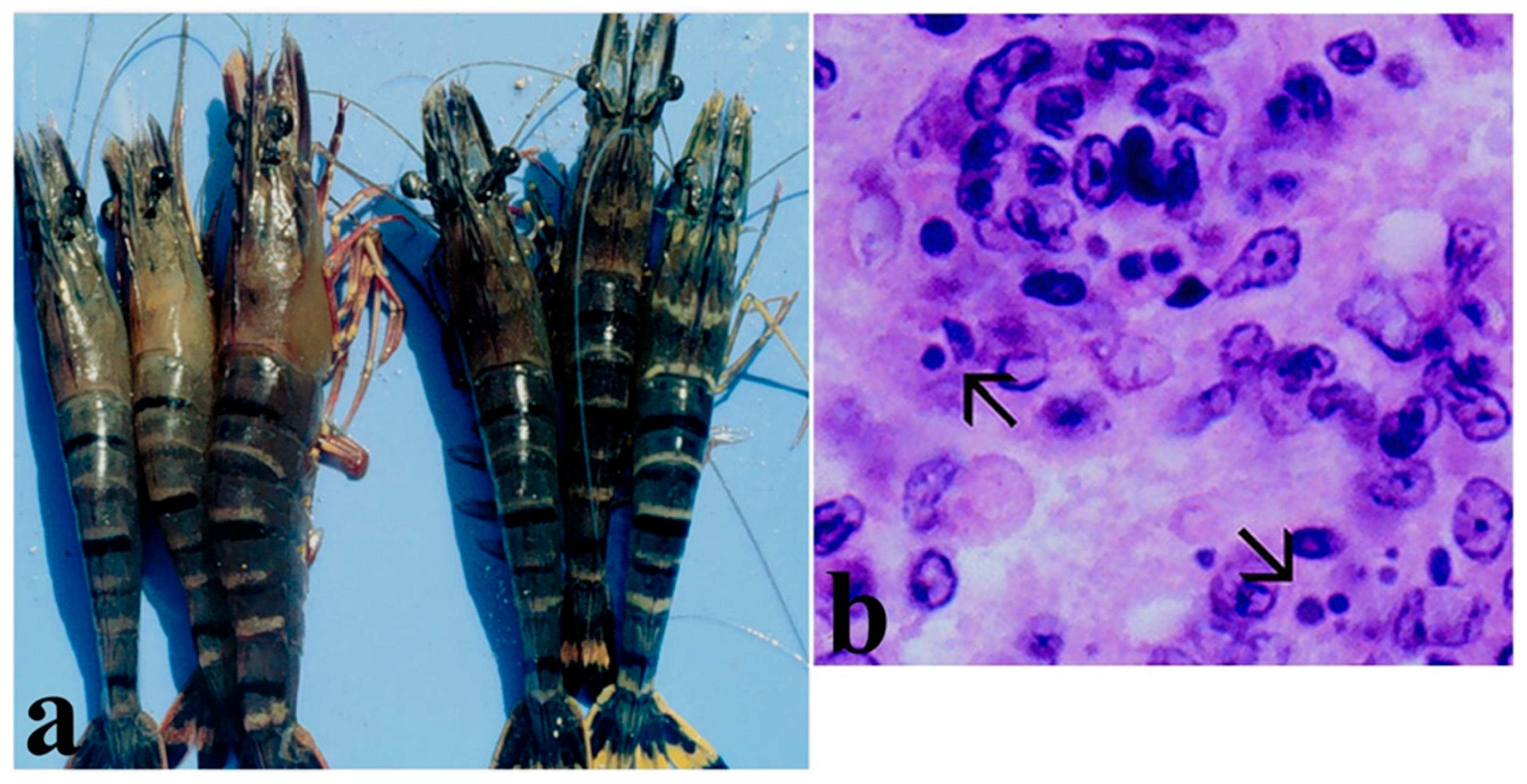
5.4. White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) (Whispovirus Nimaviridae)
5.5. Yellow-Head Virus–Gill Associated-Virus (YHV-GAV Complex: Roniviridae)
5.6. Necrotizing Hepatopancreatitis (NHP) (Hepatobacter penaei)
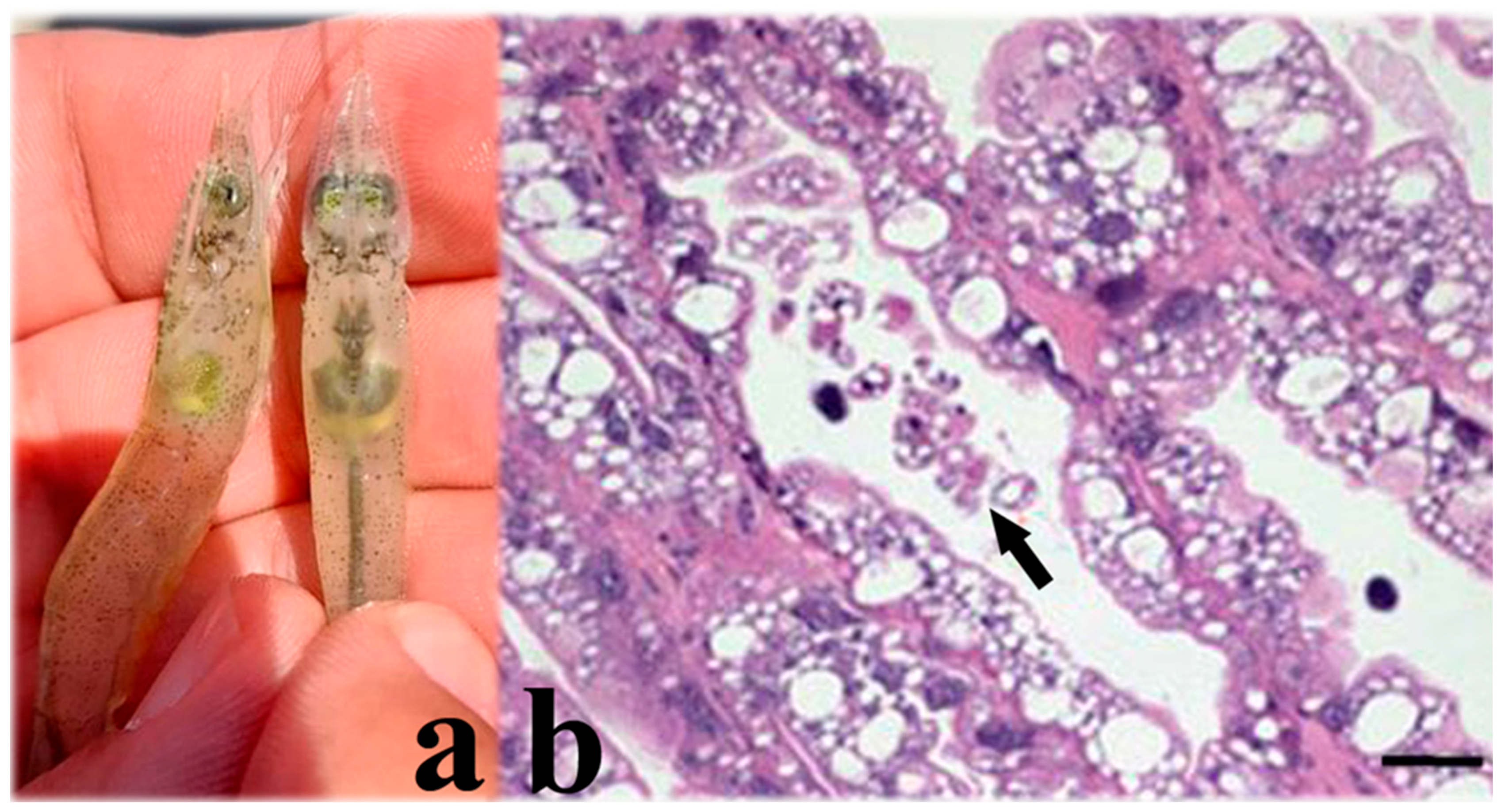
5.7. AHPND (Acute Hepatopancreas Necrosis Disease) (Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Other Species)
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024; Blue Transformation in action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- CONAPESCA. Anuario Estadístico de Acuacultura y Pesca, 2021th ed.; Comisión Nacional de Acuacultura y Pesca, SAGARPA: Mazatlán, Mexico, 2021; 289p, Available online: https://www.gob.mx/conapesca/documentos/anuario-estadistico-de-acuacultura-y-pesca (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Jory, D. Annual Farmed Shrimp Production Survey: A Slight Decrease in Production Reduction in 2023 with Hopes for Renewed Growth in 2024; Global Seafood Alliance: Portsmouth, NH, USA, 2023; 8p. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Fishstat, a Tool for Fishery Statistic Analysis Release: 4.04.11; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- USDA. Crustaceans, Shrimp, Cooked; Fooddata Central USDA; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- CONAPESCA. Anuario Estadístico de Acuacultura y Pesca, 2023th ed.; Comisión Nacional de Acuacultura y Pesca, SAGARPA: Mazatlán, Mexico, 2023; 278p, Available online: https://www.gob.mx/conapesca/documentos/anuario-estadistico-de-acuacultura-y-pesca (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2018; Meeting the Sustainable Development Goals; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo-Bonilla, C.M. Biology, morphology and antiviral defense of penaeid shrimp (Crustacea:Decapoda). In Shrimp: Evolutionary History, Ecological Significance and Effects on Dietary Consumption; Delaney, C.A., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2014; 56p. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Córdoba, L.R.; Peña-Messina, E. Biotic communities and feeding habits of Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone 1931) and Litopenaeus stylirostris (Stimpson 1974) in monoculture and polyculture semi-intensive ponds. Aquac. Res. 2005, 36, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, S.M.; Pruder, G.D. Characterization of organic particles associated with rapid growth in juvenile white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei Boone, reared under intensive culture conditions. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1995, 187, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, M.; Funge-Smith, S.; Subasinghe, R.P.; Phillips, M. Introductions and Movement of Penaeus Vannamei and Penaeus Stylirostris in Asia and the Pacific; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Bangkok, Thailand, 2004; 79p. [Google Scholar]
- Chim, L.; Lucien Brun, H.; Le Moullac, G. Chapter 2. Marine shrimp farming. In Fisheries and Aquaculture; Safran, P., Ed.; EOLSS Publishers-UNESCO: Oxford, UK, 2009; Volume IV, pp. 28–54. [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain, G.W. History of shrimp farming. In The Shrimp Book; Alday-Sanz, V., Ed.; Book I; 5M Books: Oxfordshire, UK, 2010; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Stickney, R.R.; Treece, G.D. Chapter 2. History of Aquaculture. In Aquaculture Production Systems; Tidwell, J.H., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2012; pp. 15–50. [Google Scholar]
- Jory, D.; Cabrera, T. Chapter 21. Marine shrimp. In Aquaculture Farming Aquatic Animals and Plants; Lucas, J.S., Southgate, P.C., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2012; pp. 476–513. [Google Scholar]
- Monsalve, E.R.; Quiroga, E. Farmed shrimp aquaculture in coastal wetlands of Latin America—A review of environmental issues. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 183, 113956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CRIP. Manual de cria de Camarones Peneidos en Estanques de Agua Salobre; Dirección general de comunicación social, Secretaría de Pesca: Mazatlán, Mexico, 1987; 42p. [Google Scholar]
- Aragón-Noriega, E.A.; Cordova-Murueta, J.H.; Trias-Hernández, H.L.; García-Juarez, A.R. Efecto de la densidad de siembra y la estacionalidad en la producción de camarón azul Litopenaeus stylirostris. Cienc. Pesq. INP SAGARPA 2000, 14, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- DeWalt, B.R.; Ramirez-Zavala, J.R.; Noriega, L.; González, R.E. Shrimp Aquaculture, the People and the Environment in Coastal Mexico; Report prepared under the World Bank, NACA, WWF and FAO Consortium Program on Shrimp Farming and the Environment. Work in Progress for Public Discussion; Consortium Book Sales & Distribution: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2002; 73p. [Google Scholar]
- Arredondo-Figueroa, J.L. El cultivo de camarón en México, actualidades y perspectivas. ContactoS 2002, 43, 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez de la Cruz, M.C.; Olvera Limas, R.M.; Fuentes Castellanos, D.; Palacios Fest, M.; Rosales Juarez, F.; Garcia Sandoval, S.; Ortiz Quintanilla, M.; Lorán Nuñez, R.M.; Morales Diaz, A.; Diaz López, M.d.l.L. Instituto Nacional de Pesca. 50 Años de Existencia; Memoria edicion especial; Centro de Estudios para el Desarrollo Rural Sustentable y la Soberanía Alimentaria: Mexico City, Mexico, 2014; 66p. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Vera, L.; Garza de Yta, A.; Pozas-Franco, A.L.; Torres-Origel, J.F.; Walther-Mendoza, M.; Montelongo-Alfaro, I. Situación de la acuacultura en México. In Diagnóstico de la Acuacultura en México; Vázquez-Vera, L., Chávez-Carreño, P., Eds.; Fondo Mexicano para la Conservación de la Naturaleza, A.C.: Mexico City, Mexico, 2022; pp. 14–59. [Google Scholar]
- Serralde, M.; Almada, E. Produccion de camarón azul Penaeus stylirostris (Stimpson 1871) en laboratorio, a partir de organismos silvestres y cultivados. Inf. Técnicos Del Inst. De Investig. Pesq. 1985, 125, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Cordova, L.R. Cultivo de Camarón Azul Penaeus Stylirostris en Corrales Flotantes en Diferentes Epocas del Año en Sonora, Mexico. Master’s Thesis, UNAM, Mexico City, Mexico, 1987; 81p. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Cordova, L.R. Culture of blue shrimp (Penaeus stylirostris) in floating cages. Progress. Fish-Cult. 1988, 50, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Direccion General de Acuacultura. Camaronicultura sustentable. In Proceedings of the Bangkok FAO Technical Consultation on Policies for Sustainable Shrimp Culture, Bangkok, Thailand, 8–11 December 1997; pp. 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez-Zavala, J.R. Estudio de la Camaronicultura en el Estado de Sinaloa; Universidad Autonoma de Sinaloa: Mazatlan, Sinaloa, 2000; 43p. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez Torres, P.; Ramirez Martinez, C.; Oribe Mendoza, A. Desarrollo de la acuacultura en Mexico y perspectivas de la acuacultura rural. In Proceedings of the Red de Acuicultura Rural en Pequeña Escala (ARPE), Taller ARPE, FAO-UCT, Temuco, Chile, 9–12 November 1999; 38p. [Google Scholar]
- Berlanga-Robles, C.A.; Ruiz-Luna, A.; Hernández-Guzmán, R. Impact of shrimp farming on mangrove forest and other coastal wetlands: The case of Mexico. In Aquaculture and the Environment—A Shared Destiny; Sladonja, B., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- CONAPESCA. Anuario Estadístico de Pesca 1986; Secretaria de Pesca, Mexico, D.F.: Mexico City, Mexico, 1988; 357p. [Google Scholar]
- CONAPESCA. Anuario Estadístico de Acuacultura y Pesca, 2003th ed.; Secretaria de Pesca, Mexico, D.F.: Mexico City, Mexico, 2003; 400p. [Google Scholar]
- Gámez Frías, E. La camaronicultura en Sinaloa y Nayarit. Carta Económica Reg. 1999, 66, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Castellanos-Jimenez, A. Estudios Experimentales Sobre el Cultivo de Camarón Azul (Penaeus stylirostris) en sus Etapas de Maternidad y Pre-Engorda. Oceanólogo B.Sc. Thesis, Universidad de Sonora, Hermosillo, Sonora, 1982; 76p. [Google Scholar]
- DeWalt, B. Shrimp Aquaculture, People and the Environment on the Gulf of California; A report to the world wildlife fund; University of Pittsburgh: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2000; 87p. [Google Scholar]
- Ponce-Palafox, J.T.; Ruiz-Luna, A.; Castillo-Vargasmachuca, S.; García-Ulloa, M.; Arredondo-Figueroa, J.L. Technical, economics and environmental analysis of semi-intensive shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) farming in Sonora, Sinaloa and Nayarit states, at the east coast of the Gulf of California, México. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2011, 54, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, J.A.; Main, K.L. A Guide to the Common Problems and Diseases of Cultured Penaeus vannamei; World Aquaculture Society: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1994; 242p. [Google Scholar]
- Alabi, A.O.; Latchford, J.W.; Jones, D.A. Demonstration of residual antibacterial activity in plasma of vaccinated Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2000, 187, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegel, T.W. Historic emergence, impact and current status of shrimp pathogens in Asia. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 110, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, D.V.; Redman, R.M. Shrimp diseases and current diagnostic methods. Aquaculture 1998, 164, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.L.; Wang, K.H.; Yang, Y.H.; Tung, M.C.; Hu, C.H.; Lo, C.F.; Wang, C.H.; Hsu, T. Diagnosis of Penaeus monodon-type baculovirus by PCR and by ELISA of occlusion bodies. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2000, 40, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusoff, F.M.; Shariff, M.; Lee, Y.K.; Banerjee, S. Preliminary study on the use of Bacillus sp., Vibrio sp. and egg white to enhance growth, survival rate and resistance of Penaeus monodon Fabricius to white spot syndrome virus. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 14, 1477–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, J.A.; Lightner, D.V.; Bell, T.A. A review of four virus (BP, MBV, BMN, and IHHNV) diseases of penaeid shrimp with particular reference to clinical significance, diagnosis and control in shrimp aquaculture. In Proceedings of the 71st International Council for the Exploration of the Sea, Gothenburg, Sweden, 10–19 October 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Lightner, D.V. Virus diseases of farmed shrimp in the Western Hemisphere (the Americas): A review. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2011, 106, 110–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; Subasinghe, R.P.; Arthur, R.J.; Ogawa, K.; Chinabut, S.; Adlard, R.; Tan, Z.; Shariff, M. Disease and health management in Asian aquaculture. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 132, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo-Bonilla, C.M. Emerging Infectious Diseases Affecting Farmed Shrimp in Mexico. Austin J. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 3, 1062–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Thitamadee, S.; Prachumwat, A.; Srisala, J.; Jaroenlak, P.; Salachan, P.V.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Flegel, T.W.; Itsathitphaisarn, O. Review of current disease threats for cultivated penaeid shrimp in Asia. Aquaculture 2016, 452, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vago, C. A virus disease in Crustacea. Nature 1966, 209, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francki, R.I.B.; Fauquet, C.M.; Knudson, D.L.; Brown, F. (Eds.) Classification and Nomenclature of Viruses. Fifth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Virology Division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1991; 451p. [Google Scholar]
- Bonami, J.R.; Bruce, L.D.; Poulos, B.T.; Marie, J.; Lightner, D.V. Partial characterization and cloning of the genome of PvSNPV (= BP-type virus) pathogenic for Penaeus vannamei. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1995, 23, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuck, K.C.; Wang, S.Y. Establishment and persistence of Baculovirus penaei Infections in cultured Pacific white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1996, 68, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couch, J.A. An enzootic nuclear polyhedrosis virus of pink shrimp: Ultrastructure, prevalence, and enhancement. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1974, 24, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overstreet, R.M.; Stuck, K.C.; Krol, R.A.; Hawkins, W.E. Experimental infections with Baculovirus penaei in the white shrimp Penaeus vannamei (Crustacea: Decapoda) as a bioassay. J. World Aquac. Soc. 1988, 19, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, J.A.; Lightner, D.V. Diseases caused by microorganisms. In Diseases of Marine Animals 3 Introduction: Cephalopoda, Annelida, Crustacea, Chaetognatha, Echinodermata, Urochordata; Kinne, O., Ed.; Book 3; John Wiley: Hamburg, Germany, 1990; pp. 245–349. [Google Scholar]
- Lightner, D.V. Shrimp virus diseases: Diagnosis, distribution and management. In Proceedings of the Special Session on Shrimp Farming, Orlando, FL, USA, 22–25 May 1992; Wyban, J., Ed.; World Aquaculture Society: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1992; pp. 238–253. [Google Scholar]
- Lightner, D.V.; Redman, R.M.; Almada-Ruiz, E.A. Baculovirus penaei in Penaeus stylirostris (Crustacea: Decapoda) cultured in Mexico: Unique cytopathology and a new geographic record. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1989, 53, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-H.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-Y.; Chang, H.-W. Identification and genomic characterization of Baculovirus penaei in Litopenaeus vannamei in Taiwan. J. Fish Dis. 2023, 46, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira-Bueno, S.L.d; Meyer-Nascimento, R.; Nascimento, I. Baculovirus penaei infection in Penaeus subtilis: A new host and a new geographical range of the disease. J. World Aquac. Soc. 1990, 21, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, H.N.; Dhar, A.K. The complete genome sequence of Penaeus vannamei nudivirus (previously Baculovirus penaei or P. vannamei singly enveloped nuclear polyhedrosis virus). Microb. Genom. 2025, 11, 001360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; McGladdery, S.E.; East, I.; Subasinghe, R.P. Asia Diagnostic Guide to Aquatic Animal Diseases. In FAO Fisheries Technical Paper 402/2; Book Supplement 2; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2001; 240p. [Google Scholar]
- AGDAFF-NACA. Aquatic Animal Diseases Significant to Asia–Pacific: Identification Field Guide, Australian Government Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry, Canberra; AGDAFF-NACA: Canberra, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lightner, D.V.; Redman, R.M.; Bell, T.A. Infectious Hypodermal and hematopoietic Necrosis, a newly recognized virus disease of penaeid shrimp. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1983, 42, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.K.; Kaizer, K.N.; Lakshman, D.K. Transcriptional analysis of Penaeus stylirostris densovirus genes. Virology 2010, 402, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pénzes, J.J.; Söderlund-Venermo, M.; Canuti, M.; Eis-Hübinger, A.M.; Hughes, J.; Cotmore, S.F.; Harrach, B. Reorganizing the family Parvoviridae: A revised taxonomy independent of the canonical approach based on host association. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 2133–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, D.V. The penaeid shrimp viruses TSV, IHHNV, WSSV and YHV: Current status in the Americas, available diagnostic methods and management strategies. J. Appl. Aquac. 1999, 9, 27–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.F.J.; Poulos, B.T.; Wang, J.; Redman, R.M.; Shih, H.H.; Lightner, D.V. Geographic variations among infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) isolates and characteristics of their infection. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2003, 53, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightner, D.V.; Williams, R.R.; Bell, T.A.; Redman, R.M.; Perez, A. A collection of case histories documenting the introduction and spread of the virus disease IHHN in penaeid shrimp culture facilities in Northwestern Mexico. ICES Mar. Sci. Symp. 1992, 194, 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Nunan, L.M.; Poulos, B.T.; Lightner, D.V. Use of polymerase chain reaction for the detection of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus in penaeid shrimp. Mar. Biotechnol. 2000, 2, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightner, D.V. The Penaeid Shrimp Viral Pandemics due to IHHNV, WSSV, TSV and YHV: History in the Americas and Current Status. In Proceedings of the Thirty-second US Japan Symposium on Aquaculture US–Japan Cooperative Program in Natural Resources (UJNR), Tokyo, Japan, 18–19 October 1971; Sakai, Y., McVey, J.P., Jang, D., McVey, E., Caesar, M., Eds.; US Department of Commerce, N.O.A.A.: Silver Spring, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lightner, D.V. A Handbook of Pathology and Diagnostic Procedures for Diseases of Penaeid Shrimp; World Aquaculture Society: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-Covarrubias, M.S.; Nunan, L.M.; Lightner, D.V.; Mota-Urbina, J.C.; Garza-Aguirre, M.C.; Chávez-Sanchez, M.C. Prevalence of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) in wild adult blue shrimp Penaeus stylirostris from the northern gulf of California, Mexico. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1999, 11, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunan, L.M.; Arce, S.M.; Staha, R.J.; Lightner, D.V. Prevalence of Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV) and White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) in Litopenaeus vannarnei in the Pacific Ocean off the Coast of Panama. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2001, 32, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorelli, S.; Overstreet, R.M.; Jovonovich, J.A. First report of viral pathogens WSSB and IHHNV in Argentine crustaceans. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2010, 86, 117–131. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Song, X.L.; Huang, J.; Shi, C.Y.; Liu, L. Evidence of existence of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus in penaeid shrimp cultured in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 120, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonami, J.R.; Trumper, B.; Mari, J.; Brehelin, M.; Lightner, D.V. Purification and characterization of the infectious hypodermal and haematopoietic necrosis virus of penaeid shrimps. J. Gen. Virol. 1990, 71, 2657–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, J.; Bonami, J.R.; Lightner, D.V. Partial cloning of the genome of infectious hypodermal and haematopoietic necrosis virus, an unusual parvovirus pathogenic for penaeid shrimps; diagnosis of the disease using a specific probe. J. Gen. Virol. 1993, 74, 2637–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shike, H.; Dhar, A.K.; Burns, J.C.; Shimizu, C.; Jousset, F.X.; Klimpel, K.R.; Bergoin, M. Infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus of shrimp is related to mosquito Brevidensoviruses. Virology 2000, 277, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo-Bonilla, C.M.; Rangel-Ibarra, J.L. Susceptibility to an inoculum of infectious hypodermal and haematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) in three batches of whiteleg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931). Zookeys 2014, 457, 355–365, Erratum in Zookeys 2016, 609, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Subcommittee on Aquaculture (JSA). An Evaluation of Potential Shrimp Virus Impacts on Cultured Shrimp and Wild Shrimp Populations in the Gulf of Mexico and Southeastern U.S. Atlantic Coastal Waters; National Marine Fisheries Service, U.S. Department of Commerce: Silver Spring, MD, USA; Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture: Riverdale, MD, USA; National Center for Environmental Assessment, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA; Fish and Wildlife Service, U.S. Department of Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; 65p. [Google Scholar]
- Lightner, D.V. Epizootiology, distribution and the impact on international trade of two penaeid shrimp viruses in the Americas. Rev. Sci. Et Tech. 1996, 15, 579–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightner, D.V.; Redman, R.M.; Poulos, B.T.; Nunan, L.M.; Mari, J.L.; Hasson, K.W. Risk of spread of penaeid shrimp viruses in the Americas by the international movement of live and frozen shrimp. Rev. Sci. Et Tech. 1997, 16, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalagayan, H.; Godin, D.; Kanna, R.; Hagino, G.; Sweeney, J.; Wyban, J. IHHN virus as an etiological factor in runt-deformity syndrome (RDS) of juvenile Penaeus vannamei cultured in Hawaii. J. World Aquac. Soc. 1991, 22, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chayaburakul, K.; Lightner, D.V.; Sriurairattana, S.; Tang-Nelson, K.; Withyachumnarnkul, B. Different responses to infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) in Penaeus monodon and P. vannamei. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2005, 67, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withyachumnarnkul, B.; Chayaburakul, K.; Lao-Aroon, S.; Plodpai, P.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Nash, G.L. Low impact of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) on growth and reproductive performance of Penaeus monodon. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2006, 69, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.K.; Robles-Sikisaka, R.; Saksmerprome, V.; Lakshman, D.K. Chapter Three—Biology, genome organization, and evolution of Parvoviruses in marine shrimp. In Advances in Virus Research; Maramorosch, K., Murphy, F.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; Volume 89, pp. 85–139. [Google Scholar]
- Lotz, J.M. Special topic review: Viruses, biosecurity and specific pathogen-free stocks in shrimp aquaculture. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 13, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoja, C.R.; Lightner, D.V.; Holtschmit, K.-H. Prevalence and geographic distribution of Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV) in wild blue shrimp Penaeus stylirostris from the Gulf of California, Mexico. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1999, 11, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasson, K.; Lightner, D.V.; Poulos, B.; Redman, R.; White, B.; Brock, J.A.; Bonami, J.R. Taura syndrome in Penaeus vannamei: Demonstration of a viral etiology. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1995, 23, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, D.V.; Redman, R.M.; Hasson, K.W.; Pantoja, C.R. Taura Syndrome in Penaeus vannamei (Crustacea: Decapoda): Gross signs, histopathology and ultrastructure. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1995, 21, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Huang, H.T.; Chuang, S.H.; Hsu, J.P.; Kuo, S.T.; Li, N.J.; Hsu, T.L.; Li, M.C.; Lin, S.Y. Taura syndrome in Pacific white shrimp Penaeus vannamei cultured in Taiwan. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1999, 38, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.S.; Peng, S.E.; Yu, H.T.; Liu, F.C.; Wang, C.H.; Lo, C.F.; Kou, G.H. Genetic and phenotypic variations of isolates of shrimp Taura syndrome virus found in Penaeus monodon and Metapenaeus ensis in Taiwan. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2963–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.; Sang-oum, W.; Cheevadhanarak, S.; Flegel, T.W. Taura syndrome virus (TSV) in Thailand and its relationship to TSV in China and the Americas. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2005, 63, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, J.W.; Cha, S.J.; Lee, N.S.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, J.D.; Park, J.W. Taura syndrome virus from Penaeus vannamei cultured in Korea. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2006, 70, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, D.V. Taura syndrome: An economically important viral disease impacting the shrimp farming industries of the Americas including the United States. In Proceedings of the 99th Annual Meeting USAHA, Reno, NV, USA, 28 October–3 November 1995; Pat Campbell & Associates: Richmond, Viginia, 1995; pp. 36–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zarain-Herzberg, M.; Ascencio-Valle, F. Taura syndrome in Mexico: Follow-up study in shrimp farms of Sinaloa. Aquaculture 2001, 193, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CANAINPES (Cámara Nacional de la Industria Pesquera Sección Acuacultura). El cultivo de Camarón en México. Reporte del Estado de Producción de Camarón por Acuacultura en el ciclo 1996–1997 en Mazatlán, Sinaloa; CANAINPES (Cámara Nacional de la Industria Pesquera Sección Acuacultura): Guaymas, Mexico, 1997; 6p. [Google Scholar]
- Hasson, K.W.; Lightner, D.V.; Mohney, L.L.; Redman, R.M.; Poulos, B.T.; White, B.M. Taura syndrome virus (TSV) lesion development and the disease cycle in the Pacific white shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1999, 36, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Tellez, N.A.; Corbalá-Cornejo, J.A.; Bustamante-Unzueta, M.L.; Silva-Ledezma, L.P.; Vidal-Martínez, V.M.; Rodriguez-Canul, R. History, impact, and status of infectious diseases of the Pacific white shrimp Penaeus vannamei (Bonne, 1831) cultivated in Mexico. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2020, 51, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, J.A. Special topic review: Taura syndrome, a disease important to shrimp farms in the Americas. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 13, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argue, B.J.; Arce, S.M.; Lotz, J.M.; Moss, S.M. Selective breeding of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) for growth and resistance to Taura syndrome virus. Aquaculture 2002, 204, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH). Aquatic Animal Health Code, 25th ed.; World Organization for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2023; 395p. [Google Scholar]
- Bonami, J.R.; Hasson, K.W.; Mari, J.; Poulos, B.T.; Lightner, D.V. Taura syndrome of marine penaeid shrimp: Characterization of the viral agent. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 3131–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mari, J.; Poulos, B.T.; Lightner, D.V.; Bonami, J.R. Shrimp Taura syndrome virus: Genomic characterization and similarity with members of the genus Cricket paralysis-like viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Sikisaka, R.; García, D.K.; Klimpel, K.R.; Dhar, A.K. Nucleotide sequence of 3′-end of the genome of Taura syndrome virus of shrimp suggests that it is related to insect picornaviruses. Arch. Virol. 2001, 146, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevallos, R.C.; Sarnow, P. Factor-independent assembly of elongation-competent ribosomes by an internal ribosome entry site located in an RNA virus that infects penaeid shrimp. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valles, S.M.; Chen, Y.; Firth, A.E.; Guérin, D.M.A.; Hashimoto, Y.; Herrero, S.; de Miranda, J.R.; Ryabov, E.; Consortium, I.R. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Dicistroviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 355–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, J.A.; Gose, R.; Lightner, D.V.; Hasson, K. An overview on Taura syndrome, an important disease of farmed Penaeus vannamei. In Swimming Through Troubled Water, Proceedings of the Special Session on Shrimp Farming, Aquculture’95, San Diego, CA, USA, 1–4 February 1995; Hopkins, J.S., Ed.; World Aquaculture Society, Browdy, C.L.: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Lotz, J.M. Effect of host size on virulence of Taura syndrome to the marine shrimp Penaeus vannamei (Crustacea: Penaeidae). Dis. Aquat. Org. 1997, 30, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisuvan, T.; Tang, K.F.J.; Lightner, D.V. Experimental infection of Penaeus monodon with Taura syndrome virus (TSV). Dis. Aquat. Org. 2005, 67, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overstreet, R.M.; Lightner, D.V.; Hasson, K.W.; McIlwan, S.; Lotz, J.M. Susceptibility to TSV of some penaeid shrimp native to the Gulf of Mexico and southeast Atlantic Ocean. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1997, 69, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Chiang, H.C.; Lo, C.F. Pathogenicity of a baculovirus infection causing white spot syndrome in cultured penaeid shrimp in Taiwan. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1995, 23, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaviz-Silva, L.; Molina-Garza, Z.J.; Alcocer-Gonzalez, J.M.; Rosales-Encinas, J.L.; Ibarra-Gamez, C. White spot syndrome virus genetic variants detected in Mexico by a new multiplex PCR method. Aquaculture 2004, 242, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo-Bonilla, C.M.; Alday-Sanz, V.; Wille, M.; Sorgeloos, P.; Pensaert, M.B.; Nauwynck, H.J. A review on the morphology, molecular characterization, morphogenesis and pathogenesis of white spot syndrome virus. J. Fish Dis. 2008, 31, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightner, D.V.; Redman, R.M.; Pantoja, C.; Tang, K.F.J.; Noble, B.L.; Schofield, P.; Mohney, L.L.; Nunan, L.M.; Navarro, S.A. Historic emergence, impact and current status of shrimp pathogens in the Americas. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 110, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; White, B.L.; Redman, R.M.; Lightner, D.V. Per os challenge of Litopenaeus vannamei postlarvae and Farfantepenaeus duorarum juveniles with six geographic isolates of white spot syndrome virus. Aquaculture 1999, 170, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasson, K.; Fan, Y.; Reisinger, T.; Venuti, J.; Varner, P.W. White-spot syndrome virus (WSSV) introduction into the Gulf of Mexico and Texas freshwater systems through imported, frozen bait-shrimp. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2006, 71, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, W.A.; Hawke, J.P.; Bowles, K.; Varner, P.W.; Hasson, K.W. Primary diagnosis and surveillance of white spot syndrome virus in wild and farmed crawfish (Procambarus clarkii, P. zonangulus) in Louisiana, USA. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2009, 85, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, S.V.; Tang, K.F.J.; Lightner, D.V. Frozen commodity shrimp: Potential avenue for introduction of white spot syndrome virus and yellow head virus. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2000, 12, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Chakraborty, A.; Joseph, B.; Otta, S.K.; Karunasagar, I.; Karunasagar, I. Detection of new hosts for white spot syndrome virus of shrimp using nested polymerase chain reaction. Aquaculture 2001, 198, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.L.; Namikoshi, A.; Nishizawa, T.; Mushiake, K.; Teruya, K.; Muroga, K. Effects of shrimp density on transmission of penaeid acute viremia in Penaeus japonicus by cannibalism and the waterborne route. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2001, 47, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijangos-Alquisires, Z.; Quintero-Arredondo, N.; Castro-Longoria, R.; Grijalva-Chon, J.M.; Ramos-Paredes, J. White spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in Litopenaeus vannamei captured from the Gulf of California near an area of extensive aquaculture activity. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2006, 71, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONAPESCA. Anuario Estadístico de Acuacultura y Pesca, 1995th ed.; Comisión Nacional de Acuacultura y Pesca, SAGARPA: Mazatlán, Mexico, 1996; 218p, Available online: https://www.gob.mx/conapesca/documentos/anuario-estadistico-de-acuacultura-y-pesca (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- Wongteerasupaya, C.; Vickers, J.E.; Sriurairatana, S.; Nash, G.L.; Akarajamorn, A.; Boonsaeng, V.; Panyim, S.; Tassanakajon, A.; Withyachumnarnkul, B.; Flegel, T.W. A non-occluded, systemic baculovirus that occurs in cells of ectodermal and mesodermal origin and causes high mortality in the black tiger prawn Penaeus monodon. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1995, 21, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, S.; Lightner, D.V.; Nunan, L.M.; Redman, R.M.; Mari, J.; Bonami, J.R. Application of gene probes as diagnostic tools for white spot baculovirus (WSBV) of penaeid shrimp. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1996, 27, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Lo, C.F.; Leu, J.H.; Chou, C.M.; Yeh, P.Y.; Chou, H.Y.; Tung, M.C.; Chang, C.F.; Su, M.S.; Kou, G.H. Purification and genomic analysis of baculovirus associated with white spot syndrome (WSBV) of Penaeus monodon. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1995, 23, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.S.; Lo, C.F.; Wang, Y.C.; Kou, G.H. Identification of white spot syndrome virus associated baculovirus (WSBV) target organs in the shrimp Penaeus monodon by in situ hybridization. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1996, 27, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hulten, M.C.W.; Witteveldt, J.; Peters, S.; Kloosterboer, N.; Tarchini, R.; Fiers, M.; Sandbrink, H.; Klein-Langhorst, R.; Vlak, J.M. The white spot syndrome virus DNA genome sequence. Virology 2001, 286, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; He, J.; Lin, X.; Li, Q.; Pan, D.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X. Complete genome sequence of the shrimp white spot bacilliform virus. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 11811–11820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.L.; Wang, H.C.; Huang, C.J.; Peng, S.E.; Chen, Y.G.; Lin, S.J.; Chen, W.Y.; Dai, C.F.; Yu, H.T.; Wang, C.H. Transcriptional analysis of the DNA polymerase gene of shrimp white spot syndrome virus. Virology 2002, 301, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Q.; Xu, X.; Hew, C.L. Characterization of a novel envelope protein (VP281) of shrimp white spot syndrome virus by mass spectrometry. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 2385–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadala, E.C.B.; Tapay, L.M.; Loh, P.C. Characterization of a non-occluded baculovirus-like agent pathogenic to penaeid shrimp. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1998, 33, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlak, J.M.; Bonami, J.R.; Flegel, T.W.; Kou, G.H.; Lightner, D.V.; Lo, C.F.; Loh, P.C.; Walker, P.W. Nimaviridae. In Virus Taxonomy: VIIIth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; Fauquet, C.M., Mayo, M.A., Maniloff, J., Desselberger, U., Ball, L.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Hong Kong, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kawato, S.; Shitara, A.; Wang, Y.; Nozaki, R.; Kondo, H.; Hirono, I. Genome sequence of Chionoecetes opilio bacilliform virus, a nimavirus infecting the snow crab Chionoecetes opilio. Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliseikina, M.G.; Boyko, A.V.; Shamshurina, E.V.; Ryazanova, T.V. Complete genome of the new bacilliform virus that causes Milky Hemolymph Syndrome in Chionoecetes bairdi (Rathbun, 1924). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2024, 206, 108179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawato, S.; Shitara, A.; Wang, Y.; Nozaki, R.; Kondo, H.; Hirono, I. Crustacean Genome Exploration Reveals the Evolutionary Origin of White Spot Syndrome Virus. J. Virol. 2019, 93, 10–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.F.; Ho, C.H.; Peng, S.E.; Chen, C.H.; Hsu, H.C.; Chiu, Y.L.; Chang, C.F.; Liu, K.F.; Su, M.S.; Wang, C.H.; et al. White spot syndrome baculovirus (WSBV) detected in cultured and captured shrimp, crabs and other arthropods. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1996, 27, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasornchandra, J.; Boonyaratpalin, S.; Itami, T. Detection of white spot syndrome in cultured penaeid shrimp in Asia: Microscopic observation and polymerase chain reaction. Aquaculture 1998, 164, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Hassan, M.D.; Shariff, M.; Zamri, S.M.; Chen, X. Histopatholy and cytopathology of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in cultured Penaeus monodon from peninsular Malaysia with emphasis on pathogenesis and the mechanism of white spot formation. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1999, 39, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, D.V.; Hasson, K.W.; White, B.L.; Redman, R.M. Experimental infection of western hemisphere penaeid shrimp with asian white spot syndrome virus and asian yellow head virus. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1998, 10, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, S.; Lightner, D.V.; Redman, R.M.; Bonami, J.R. Ultrastructure and morphogenesis of white spot syndrome baculovirus. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1997, 29, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegel, T.W. Special topic review: Major viral diseases of the black tiger prawn (Penaeus monodon) in Thailand. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 13, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahul-Hameed, A.S.; Anilkumar, M.; Raj, M.L.S.; Jayaraman, K. Studies on the pathogenicity of systemic ectodermal and mesodermal baculovirus and its detection in shrimp by immunological methods. Aquaculture 1998, 160, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, G.H.; Peng, S.E.; Chiu, Y.L.; Lo, C.F. Tissue distribution of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in shrimp and crabs. In Advances in Shrimp Biotechnology; Flegel, T.W., Ed.; National Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology: Bangkok, Thailand, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Karunasagar, I.; Otta, S.K.; Karunasagar, I. Histopathological and bacteriological study of white spot syndrome of Penaeus monodon along the west coast of India. Aquaculture 1997, 153, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotz, J.M.; Soto, A.M. Model of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) epidemics in Litopenaeus vannamei. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2002, 50, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Nunan, L.M.; Lightner, D.V. Identification of genomic variations among geographic isolates of white spot syndrome virus using restriction analysis and southern blot hybridization. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2000, 43, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Lo, C.F.; Chang, P.S.; Kou, G.H. Experimental infection of white spot baculovirus in some cultured and wild decapods in Taiwan. Aquaculture 1998, 164, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, F.; Volkaert, F.A.M.; Calderón, J. Pathogenicity of white spot syndrome virus on postlarvae and juveniles of Penaeus (Litopenaeus) vannamei. Aquaculture 2005, 250, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.F.; Ho, C.H.; Chen, C.H.; Liu, K.F.; Chiu, Y.L.; Yeh, P.Y.; Peng, S.E.; Hsu, H.C.; Liu, H.C.; Chang, C.F.; et al. Detection and tissue tropism of white spot syndrome baculovirus (WSBV) in captured brooders of Penaeus monodon with a special emphasis on reproductive organs. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1997, 30, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma, A.; Koteeswaran, A.; Karunasagar, I.; Karunasagar, I. Prevalence of white spot syndrome virus and monodon baculovirus in Penaeus monodon broodstock and postlarvae from hatcheries in southeast coast of India. Curr. Sci. 2005, 89, 1619–1622. [Google Scholar]
- Munro, J.; Owens, L. Yellow head-like viruses affecting the penaeid aquaculture industry: A review. Aquac. Res. 2007, 38, 893–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijegoonawardane, P.K.M.; Cowley, J.A.; Phan, T.; Hodgson, R.A.J.; Nielsen, L.; Kiatpathomchai, W.; Walker, P.J. Genetic diversity in yellow head virus nidovirus complex. Virology 2008, 380, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.J.; Cowley, J.A.; Dong, X.; Huang, J.; Moody, N.; Ziebuhr, J.; Consortium, I.R. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Roniviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 001514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantanachookin, C.; Boonyaratpalin, S.; Kasornchandra, J.; Direkbusarakom, S.; Ekpanithanpong, U.; Supamattaya, K.; Sriurairatana, S.; Flegel, T.W. Histology and ultrastructure reveal a new granulosis-like virus in Penaeus monodon affected by yellow-head disease. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1993, 17, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athula, J.A.; Walpita, C.N.; Ruwandeepika, H.A.D.; Thilakasin, T.N.S.; Dayananda, E.G.R.; Chandraratne, P.N. Stock health of penaeid shrimps in Sri Lanka: A comprehensive molecular-based study on seven diseases found in the Asian region. J. Agric. Sci. —Sri Lanka 2024, 19, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, P.J.; Sittidilokratna, N. Yellow Head Virus. In Encyclopedia of Virology; Mahy, B.W.J., van Regenmortel, M.H.V., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.J.; Mohan, C.V. Viral disease emergence in shrimp aquaculture: Origins, impact and the effectiveness of health management strategies. Rev. Aquac. 2009, 1, 125–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, J.A.; Dimmock, C.M.; Wongteerasupaya, C.; Boonsaeng, V.; Panyim, S.; Walker, P.J. Yellow head virus from Thailand and gill-associated virus from Australia are closely related but distinct prawn viruses. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1999, 36, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Rosa-Vélez, J.; Cedano-Thomas, Y.; Cid-Becerra, J.; Méndez-Payán, J.C.; Vega-Pérez, C.; Zambrano-García, J.; Bonami, J.R. Presumptive detection of yellow head virus by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and dot-blot hybridization in Litopenaeus vannamei and L. stylirostris cultured on the Northwest coast of Mexico. J. Fish Dis. 2006, 29, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Longoria, R.; Quintero-Arredondo, N.; Grijalva-Chon, J.M.; Ramos-Paredes, J. Detection of the yellow-head virus (YHV) in wild blue shrimp, Penaeus stylirostris, from the Gulf of California and its experimental transmission to the Pacific white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei. J. Fish Dis. 2008, 31, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Barajas, M.; Liñan-Cabello, M.A.; Mena-Herrera, A. Detection of yellow-head disease in intensive freshwater production systems of Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Int. 2009, 17, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyaratpalin, S.; Supamattaya, K.; Kasornchandra, J.; Direcbusaracom, S.; Aekpanithanpong, U.; Chantanachooklin, C. Non-occluded baculo-like virus, the causative agent of yellow-head disease in the black tiger prawn (Penaeus monodon). Gyobyo Kenkyu 1993, 28, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadala, E.C.B.; Tapay, L.M.; Loh, P.C. Yellow-Head virus: A rhabdovirus-like pathogen of penaeid shrimp. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1997, 31, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongteerasupaya, C.; Sriurairatana, S.; Vickers, J.E.; Akrajamorn, A.; Boonsaeng, V.; Panyim, S.; Tassanakajon, A.; Withyachumnarnkul, B.; Flegel, T.W. Yellow-head virus of Penaeus monodon is an RNA virus. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1995, 22, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, J.A.; Walker, P.J. The complete genome sequence of gill-associated virus of Penaeus monodon prawns indicates a gene organisation unique among nidoviruses. Arch. Virololgy 2002, 147, 1977–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.F.J.; Lightner, D.V. A yellow head virus gene probe: Nucleotide sequence and application for in situ hybridization. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1999, 35, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowley, J.A.; Dimmock, C.M.; Spann, K.M.; Walker, P.J. Gill-associated virus of Penaeus monodon prawns: An invertebrate virus with ORF1a and ORF1b genes related to arteri- and coronaviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Tapay, L.M.; Loh, P.C.; Brock, J.A.; Gose, R.B. Distribution of yellow-head virus in selected tissues and organs of penaeid shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1995, 23, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Overstreet, R.M.; Jovonovich, J.A. Daggerblade grass shrimp (Palaemonetes pugio): A reservoir host for yellow-head virus (YHV). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2009, 101, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.T. 1-Diseases Caused by Viruses, Rickettsiae, Bacteria, and Fungi. In The Biology of Crustacea; Provenzano, A.J., Ed.; Book 6 Pathobiology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 1–78. [Google Scholar]
- Krol, R.M.; Hawkins, W.E.; Overstreet, R.M. Rickettsial and Mollicute infections in hepatopancreatic cells of cultured Pacific white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1991, 57, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.K. Handbook of Shrimp Diseases; Sea Grant College Program; Texas A&M: Galveston, TX, USA, 1990; 25p. [Google Scholar]
- Frelier, P.F.; Sis, R.F.; Bell, T.A.; Lewis, D.H. Microscopic and ultrastructural studies of necrotizing hepatopancreatitis in Pacific white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) cultured in Texas. Vet. Pathol. 1992, 29, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frelier, P.F.; Loy, J.K.; Kruppenbach, B. Transmission of nectrotizing hepatopancreatitis in Penaeus vannamei. Journa Invertebr. Pathol. 1993, 61, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Lightner, D.V.; Redman, R.M. An epizootic of necrotizing hepatopancreatitis in cultured penaeid shrimp (Crustacea: Decapoda) in northwestern Peru. Aquaculture 1994, 122, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, D.V.; Redman, R.M.; Bonami, J.R. Morphological evidence for a single bacterial etiology in Texas necrotizing hepatopancreatitis in Penaeus vannamei (Crustacea: Decapoda). Dis. Aquat. Org. 1992, 13, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, J.K.; Frelier, P.F.; Varner, P.; Templeton, J.W. Detection of the etiologic agent of necrotizing hepatopancreatitis in cultured Penaeus vannamei from Texas and Peru by polymerase chain reaction. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1996, 25, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, A.G.; Lotz, J.M. Advances in research of necrotizing hepatopancreatitis bacterium (NHPB) affecting penaeid shrimp aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2007, 15, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuellar-Anjel, J.; Corteel, M.; Galli, L.; Alday-Sanz, V.; Hasson, K.W. Principal shrimp infectious diseases, diagnosis and management. In The Shrimp Book; Alday-Sanz, V., Ed.; Book I.; 5M Books: Oxfordshire, UK, 2010; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- del Rio-Rodriguez, R.E.; Soto-Rodriguez, S.; Lara-Flores, M.; Cu-Escamilla, A.D.; Gomez-Solano, M.I. A necrotizing hepatopancreatitis (NHP) outbreak in a shrimp farm in Campeche, Mexico: A first case report. Aquaculture 2006, 255, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, J.K.; Dewhirst, F.E.; Weber, W.; Frelier, P.F.; Garbar, T.L.; Tasca, S.I.; Templeton, J.W. Molecular phylogeny and in situ detection of the etiologic agent of necrotizing hepatopancreatitis in shrimp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 3439–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, A.G.; Lotz, J.M. Effect of salinity on transmission of necrotizing hepatopancreatitis bacterium (NHPB) to Kona stock Litopenaeus vannamei. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2007, 75, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunan, L.M.; Pantoja, C.R.; Gómez-Jimenez, S.; Lightner, D.V. “Candidatus Hepatobacter penaei,” an intracellular pathogenic enteric bacterium in the hepatopancreas of the marine shrimp Penaeus vannamei (Crustacea: Decapoda). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1407–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsing, F.; Barnes, A.C. The rise of the opportunists: What are the drivers of the increase in infectious diseases caused by environmental and commensal bacteria? Rev. Aquac. 2024, 16, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyton, Y.; Riquelme, C. Vibrios en los sistemas marinos costeros. Rev. De Biol. Mar. Y Oceanogr. 2008, 43, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabina, D.; Swaminathan, R.T.; Mohandas, S.P.; Anjana, J.C.; Manjusha, K.; Preena, P.G. Investigation of antibiotic-resistant vibrios associated with shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) farms. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchanayake, T.; Salleh, A.; Amal, M.N.A.; Yasin, I.S.M.; Zamri-Saad, M. Pathology and pathogenesis of Vibrio infection in fish: A review. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 28, 101459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-T.; Chen, I.-T.; Yang, Y.-T.; Ko, T.-P.; Huang, Y.-T.; Huang, J.-Y.; Huang, M.-F.; Lin, S.-J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lin, S.-S.; et al. The opportunistic marine pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus becomes virulent by acquiring a plasmid that expresses a deadly toxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10798–10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Ng, T.H.; Wang, H.-C. Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease in penaeid shrimp. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1867–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirikharin, R.; Taengchaiyaphum, S.; Sanguanrut, P.; Chi, T.D.; Mavichak, R.; Proespraiwong, P.; Nuangsaeng, B.; Thitamadee, S.; Flegel, T.W.; Sritunyalucksana, K. Characterization and PCR detection of binary, Pir-like toxins from Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates that cause acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in shrimp. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.; Nunan, L.; Redman, R.M.; Mohney, L.L.; Pantoja, C.R.; Fitzsimmons, K.; Lightner, D.V. Determination of the infectious nature of the agent of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis syndrome affecting penaeid shrimp. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2013, 105, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Peña, L.D.; Cabillon, N.A.R.; Catedral, D.D.; Amar, E.C.; Usero, R.C.; Monotilla, W.D.; Calpe, A.T.; Fernandez, D.D.G.; Saloma, C.P. Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) outbreaks in Penaeus vannamei and P. monodon cultured in the Philippines. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 116, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, L.; Bayot, B.; Arciniega, S.; Bajaña, L.; Betancourt, I.; Panchana, F.; Reyes-Muñoz, A. PirVP genes causing AHPND identified in a new Vibrio species (Vibrio punensis) within the commensal Orientalis clade. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Uddin, M.; Islam, H.; Fardoush, J.; Rupom, M.; Hossain, M.; Farjana, N.; Afroz, R.; Hasan-Uj-Jaman Roy, H.; Shehab, M.; et al. Diagnosis, genetic variations, virulence, and toxicity of AHPND-positive Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Penaeus monodon. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 2531–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangman, P.; Chaivisuthangkura, P.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Taengchaiyaphum, S.; Senapin, S.; Pengsuk, C.; Sithigorngul, P.; Longyant, S. Development of monoclonal antibodies specific to ToxA and ToxB of Vibrio parahaemolyticus that cause acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND). Aquaculture 2017, 474, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Roy, S.; Behera, B.K.; Bossier, P.; Das, B.K. Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease (AHPND): Virulence, Pathogenesis and Mitigation Strategies in Shrimp Aquaculture. Toxins 2021, 13, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunan, L.; Lightner, D.V.; Pantoja, C.; Gomez-Jimenez, S. Detection of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in Mexico. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2014, 111, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Rodriguez, S.A.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Lozano-Olvera, R.; Betancourt-Lozano, M.; Morales-Covarrubias, M.S. Field and Experimental Evidence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus as the Causative Agent of Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease of Cultured Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in Northwestern Mexico. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovando-Solís, M.; Velázquez-Velázquez, E.; Penagos-García, F.E.; Velázquez, L.A. Acute hepatopancreatitis necrosis affecting penaeid shrimp culture in Mexico. Espac. I+D Innov. Más Desarro. 2022, 10, 137–148. [Google Scholar]
- CONAPESCA. Anuario Estadístico de Acuacultura y Pesca, 2013th ed.; Comisión Nacional de Acuacultura y Pesca, SAGARPA: Mazatlán, Mexico, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; Arthur, R.J. FAO technical Assistance efforts to deal with Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease of cultured shrimp. In AHPND Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease; FAO: Rome, Italy; Asian Fisheries Society: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2018; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Muthukrishnan, S.; Defoirdt, T.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Yusoff, F.M.; Shariff, M.; Ismail, S.I.; Natrah, I. Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio harveyi causing Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease (AHPND) in Penaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) isolated from Malaysian shrimp ponds. Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Navarro, N.; Castro-Vásquez, R.; Vargas-Leitón, B.; Dolz, G. Molecular detection of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in Penaeus vannamei shrimps in Costa Rica. Aquaculture 2020, 523, 735190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.E.; Tang, K.F.J.; Tran, L.H.; Lightner, D.V. Photorhabdus insect-related (Pir) toxin-like genes in a plasmid of Vibrio parahaemolyticus, the causative agent of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) of shrimp. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 113, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorriehzahra, M.J.; Banaederakhshan, R. Early Mortality Syndrome (EMS) as new emerging threat in shrimp industry. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2015, 3, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. FAO 2nd International Technical Seminar/Workshop on Acute hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease (AHPND): There Is a Way Forward; FAO: Bangkok, Thailand, 2017; 96p. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Li, S.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Yu, K.; Li, F. Pathogenicity of a Vibrio owensii strain isolated from Fenneropenaeus chinensis carrying pirAB genes and causing AHPND. Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Van, P.T.; Dang, L.T.; Hirono, I. Draft genome sequence of non-Vibrio parahaemolyticus acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease strain KC13.17.5, isolated from diseased shrimp in Vietnam. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00978-00915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.S.; Piamsomboon, P.; Tang, K.F.J.; Han, J.E.; Kim, J.H. Complete genome sequence of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease-causing Vibrio campbellii LA16-V1, isolated from Penaeus vannamei cultured in a Latin American country. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, 10–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, H.; Zou, P.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, J. Complete genome sequence of Vibrio campbellii strain 20130629003S01 isolated from shrimp with acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xiao, J.; Xia, X.; Pan, Y.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y. Draft Genome Sequence of Vibrio owensii Strain SH-14, which causes shrimp acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e01395-01315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, H.T.; Thi, P.T.D.; Lan, T.T.; Huy, N.D.; Tram, N.D.Q.; Lien, N.T.T. Development of a diagnostic scar marker for Vibrio shilonii caused acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease in whiteleg shrimp. Adv. Life Sci. 2020, 7, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- González-Castillo, A.; Enciso-Ibarra, J.; Gómez-Gil, B. Genomic taxonomy of the Mediterranei clade of the genus Vibrio (Gammaproteobacteria). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Portillo, E.; Martin-Cuadrado, A.B.; Carballo-Rodriguez, A.M.; Rohwer, F.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Antón, J. Virulence as a side effect of interspecies interaction in Vibrio coral pathogens. mBio 2020, 11, e00201-00220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-H.; Kuo, W.-C.; Wang, H.-C.; Chen, Y.-M. Biocontrol of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in shrimp using a microalgal-bacterial consortium. Aquaculture 2020, 521, 734990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.F.J.; Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; Arthur, R.J.; MacKinnon, B.; Hao, B.; Alday-Sanz, V.; Liang, Y.; Dong, X. Shrimp Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease Strategy Manual; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Circular No. 1190; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020; 65p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sritunyalucksana, K.; Sanguanrut, P.; Salachan, P.V.; Thitamadee, S.; Flegel, T.W. Urgent Appeal to Control Spread of the Shrimp Microsporidian Parasite Enterocytozoon Hepatopenaei (EHP); Network of Aquaculture Centres in Asia-Pacific (NACA): Bangkok, Thailand, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tourtip, S.; Wongtripop, S.; Stentiford, G.D.; Bateman, K.S.; Sriurairatana, S.; Chavadej, J.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Withyachumnarnkul, B. Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei sp. nov. (Microsporida: Enterocytozoonidae), a parasite of the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon (Decapoda: Penaeidae): Fine structure and phylogenetic relationships. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2009, 102, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriurairatana, S.; Boonyawiwat, V.; Gangnonngiw, W.; Laosutthipong, C.; Hiranchan, J.; Flegel, T.W. White feces syndrome of shrimp arises from transformation, sloughing and aggregation of hepatopancreatic microvilli into vermiform bodies superficially resembling gregarines. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Chen, M.-M.; Wan, X.-Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Q.-L.; Wang, R.-Y.; Cheng, D.-Y.; Dong, X.; Yang, B.; Wang, X.-H.; et al. Characterization of a new member of Iridoviridae, shrimp hemocyte iridescent virus (SHIV), found in white leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Yang, H.; Liu, S.; Zhu, L.; Yang, B.; Jin, J.; Ding, L.; Wang, X.; et al. A new nodavirus is associated with covert mortality disease of shrimp. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2700–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAGARPA. Amplia SAGARPA la restricción de importación de crustáceos a cuatro países de Asia. Announcement 2013, 7, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cala-Moreno, N.; Campos-Montes, G.; Caballero-Zamora, A.; Berruecos-Villalobos, J.; Castillo-Juárez, H. Genotype-by-environment interaction in white shrimp associated with White Spot Disease. Abanico Vet. 2021, 11, e111. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Juárez, H.; Montaldo, H.H.; Campos-Montes, G.R.; Quintana-Casares, J.C.; Soto-Rodríguez, S.A.; Betancourt-Lozano, M.; Martínez-Ortega, A.; Lozano-Olvera, R.; Gómez-Gil, B.; Caballero-Zamora, A.; et al. Heritability, genetic line and inbreeding effects on resistance of whiteleg shrimp Penaeus vannamei Boone 1931 to Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease (AHPND) in Mexico. Asian Fish. Sci. 2018, 31, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, F. Efficient gene transfer techniques in shrimp and their cellular applications. Genom. Appl. Biol. 2024, 15, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, J.X.H.; Tan, L.T.-H.; Law, J.W.-F.; Ser, H.-L.; Khaw, K.-Y.; Letchumanan, V.; Lee, L.-H.; Goh, B.-H. Harnessing the potentialities of probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, paraprobiotics, and postbiotics for shrimp farming. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 1478–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ranking | Country | Volume (Tons) | Species | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 2,575,789 | P. vannamei P. monodon P. japonicus | 31.6 |
| 2 | India | 1,240,646 | P. vannamei P. monodon | 15.3 |
| 3 | Ecuador | 1,220,200 | P. vannamei | 15.0 |
| 4 | Vietnam | 1,167,383 | P. vannamei P. monodon | 14.4 |
| 5 | Indonesia | 934,825 | P. vannamei P. monodon P. merguiensis | 11.5 |
| 6 | Thailand | 392,470 | P. vannamei P. monodon P. merguiensis | 4.8 |
| 7 | Mexico | 194,066 | P. vannamei P. stylirostris | 2.4 |
| 8 | Brazil | 127,466 | P. vannamei | 1.6 |
| 9 | Bangladesh | 86,079 | P. monodon | 1.0 |
| 10 | Philippines | 64,273 | P. vannamei P. monodon P. merguiensis | 0.8 |
| 11 | Malaysia | 54,379 | P. vannamei P. monodon | 0.7 |
| 12 | Peru | 42,927 | P. vannamei | 0.5 |
| 13 | Nicaragua | 32,000 | P. vannamei | 0.4 |
| Total | 8,132,503 | 100.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Escobedo-Bonilla, C.M.; Colula-Ocampo, J.I.; Hernández-Herrera, R.I.; Gracia-Valenzuela, M.H.; San Martín del Ángel, P. History of Shrimp Farming and the Main Viral and Bacterial Diseases in Mexico. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112631
Escobedo-Bonilla CM, Colula-Ocampo JI, Hernández-Herrera RI, Gracia-Valenzuela MH, San Martín del Ángel P. History of Shrimp Farming and the Main Viral and Bacterial Diseases in Mexico. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(11):2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112631
Chicago/Turabian StyleEscobedo-Bonilla, Cesar Marcial, Jareli Itzel Colula-Ocampo, Rosa Idalia Hernández-Herrera, Martina Hilda Gracia-Valenzuela, and Pablo San Martín del Ángel. 2025. "History of Shrimp Farming and the Main Viral and Bacterial Diseases in Mexico" Microorganisms 13, no. 11: 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112631
APA StyleEscobedo-Bonilla, C. M., Colula-Ocampo, J. I., Hernández-Herrera, R. I., Gracia-Valenzuela, M. H., & San Martín del Ángel, P. (2025). History of Shrimp Farming and the Main Viral and Bacterial Diseases in Mexico. Microorganisms, 13(11), 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112631