The Exploitation of Single-Chambered Microbial Fuel Cells for PET Removal in Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Procedure
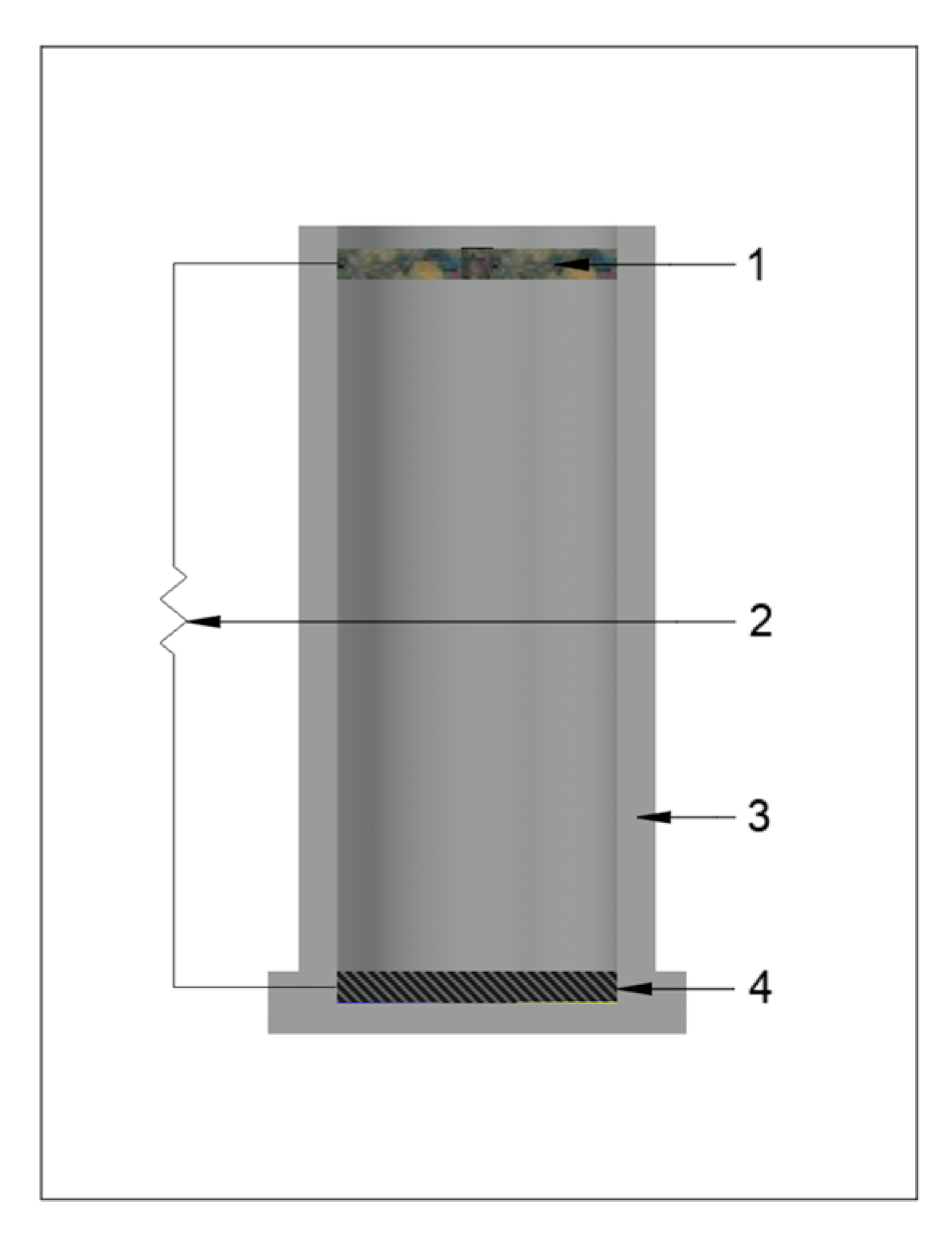
2.2. Design of Single-Chamber MFC
2.3. Polarization Test (P-Test)
2.4. Bacterial Activation and Inoculation
2.4.1. Inoculation of I. sakaiensis
2.4.2. Inoculation of G. sulfurreducens
2.4.3. Inoculation of Activated Sludge
2.5. Measurement Methods
2.5.1. Electroactivity Measurements
2.5.2. Physiological Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mass Reduction
3.2. Size Reduction
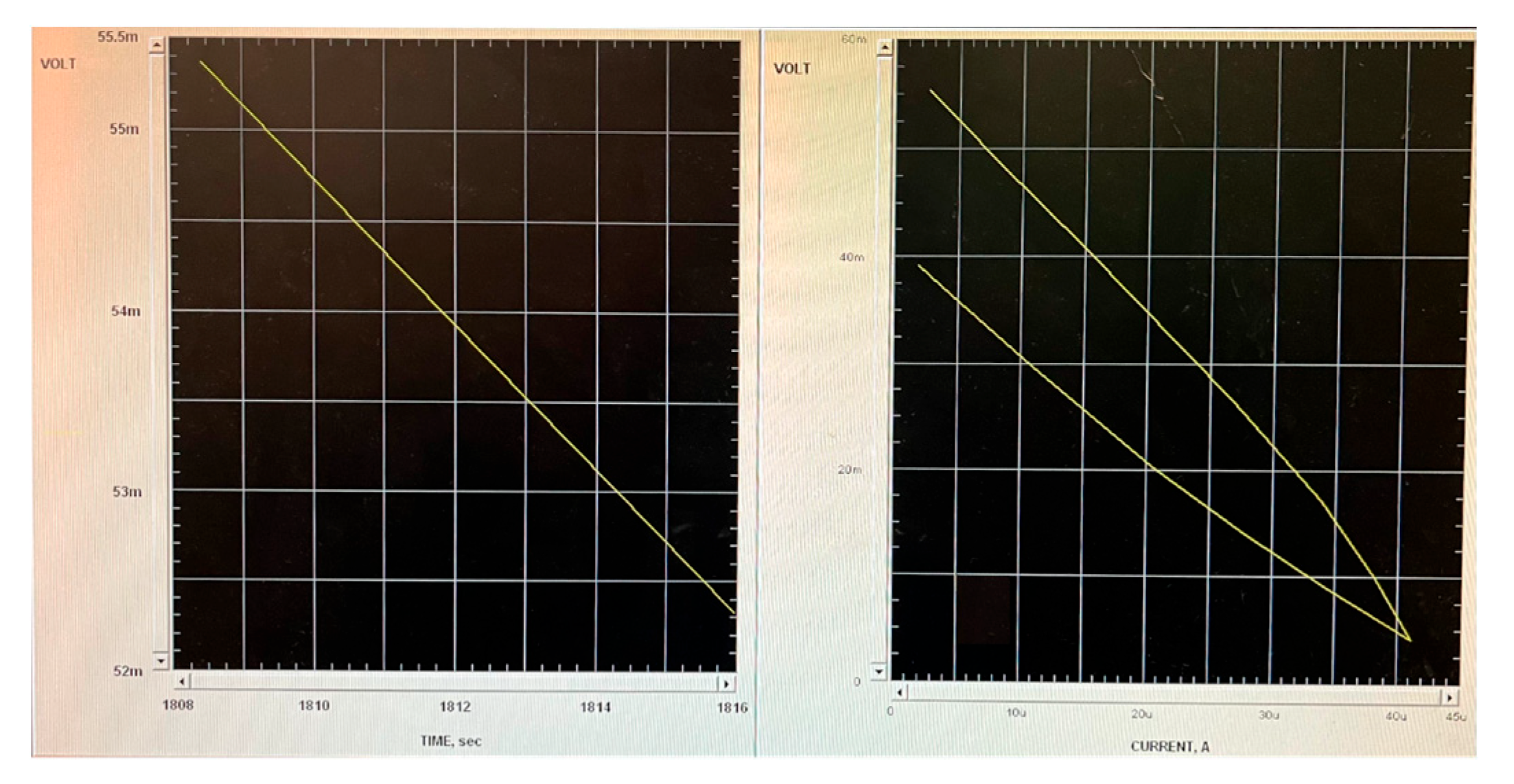
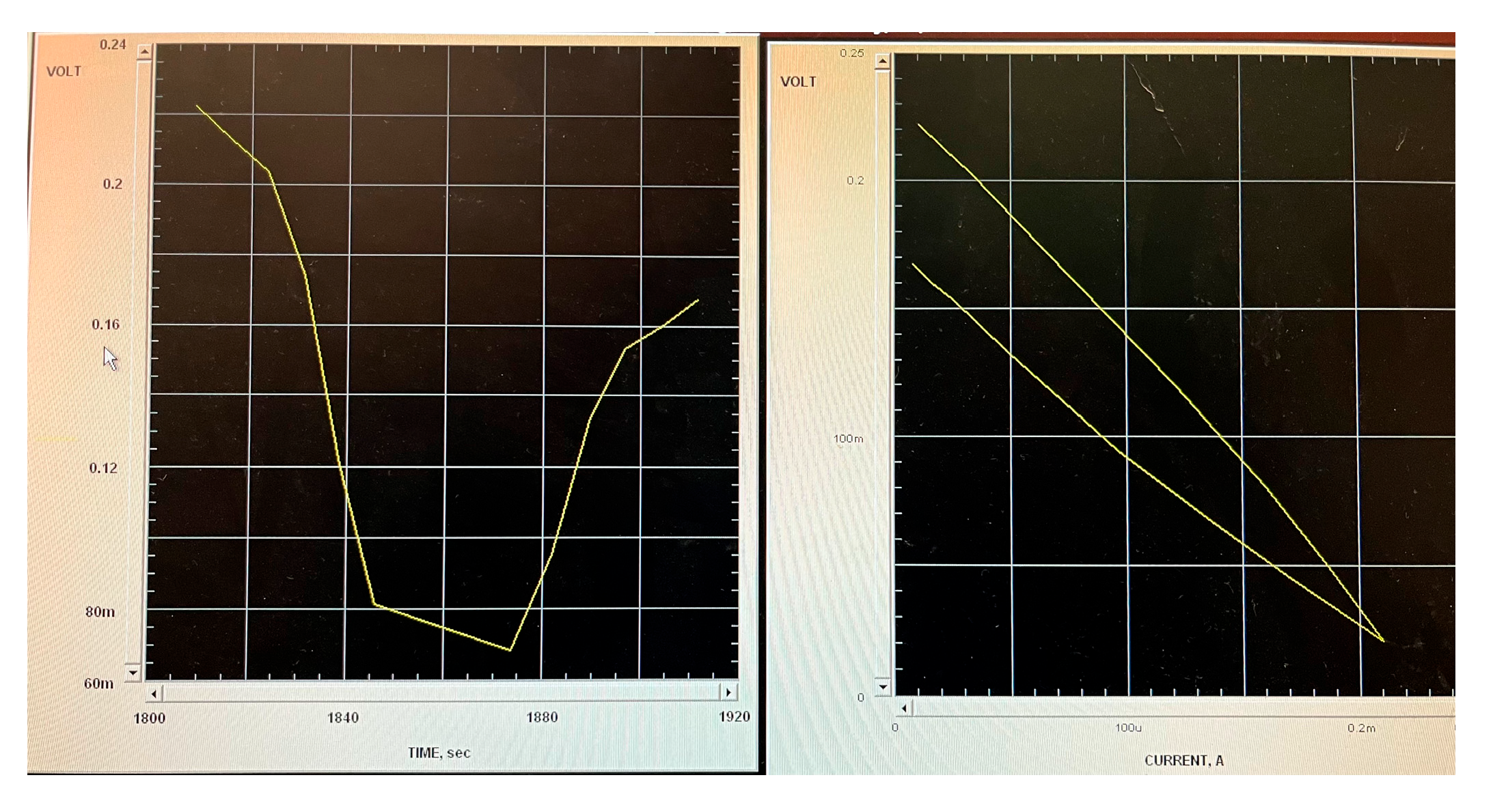
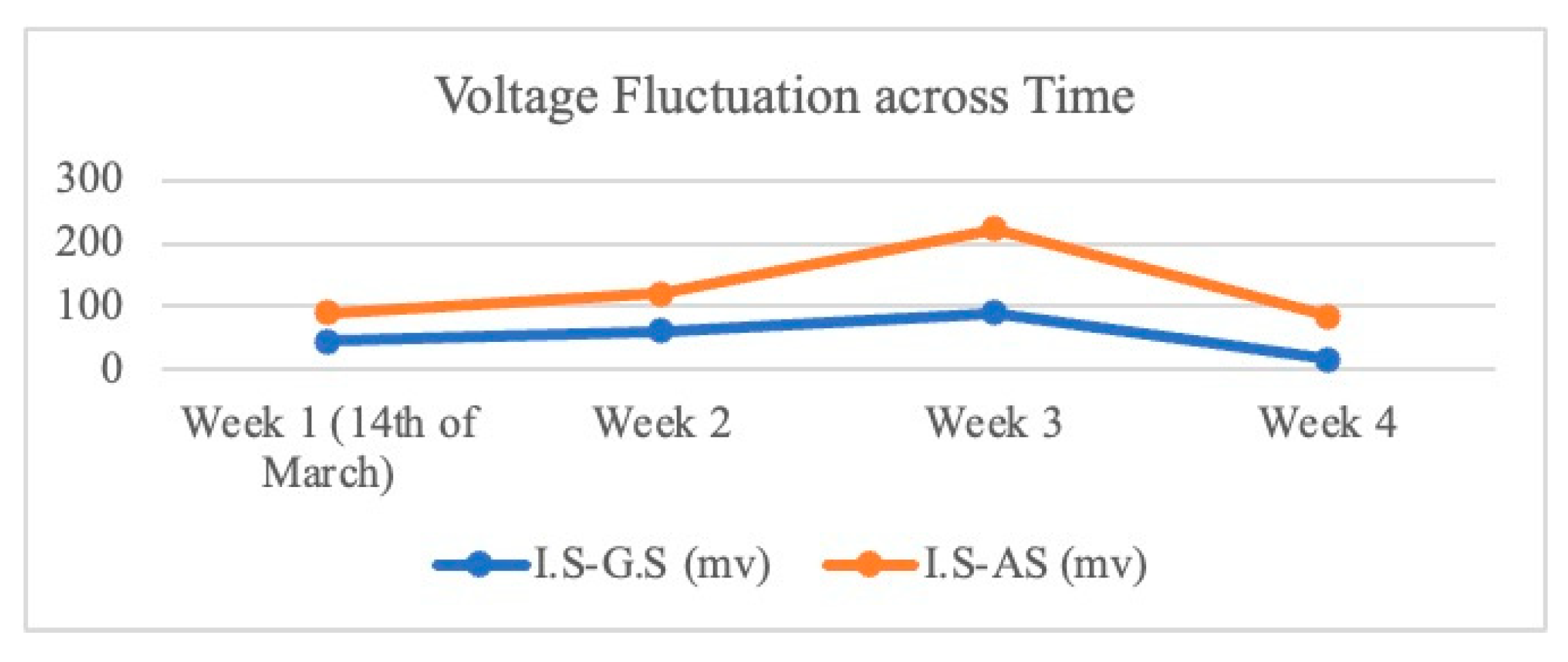
3.3. Electroactivity
3.4. Discussion
3.4.1. Result Analysis
3.4.2. Limitation and Future Perspective
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MFC | Microbial fuel cell |
| PET | Polyethylene terephthalate |
| MP | Microplastic |
| UNEP | United Nations Environment Program |
| BES | Bio-electrochemical systems |
| I. Sakaiensis | Ideonella Sakaiensis |
| G. sulfurreducens | Geobacter sulfurreducens |
| SC-MFCs | Single-chamber microbial fuel cells |
| I.S-G.S | Co-culture of I. sakaiensis and G. sulfurreducens |
| I.S-AS | Co-culture of I. sakaiensis and activated sludge |
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| P-test | Polarization test |
| Rext | External resistance |
| OCV | Open circuit voltage |
| Rint | Internal resistance |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
References
- Our Planet is Choking on Plastic. Available online: https://www.unep.org/interactives/beat-plastic-pollution/#:~:text=While%20plastic%20has%20many%20valuable,are%20used%20worldwide%20every%20year (accessed on 23 May 2024).
- Guo, J.-J.; Huang, X.-P.; Xiang, L.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Li, Y.-W.; Li, H.; Cai, Q.-Y.; Mo, C.-H.; Wong, M.-H. Source, migration and toxicology of microplastics in soil. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microplastics. 2013. Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/12079/brochure-microplastics.pdf?sequence=1&%3BisAllowed= (accessed on 23 May 2024).
- Viulu, S.; Nakamura, K.; Kojima, A.; Yoshiyasu, Y.; Saitou, S.; Takamizawa, K. Geobacter sulfurreducens subsp. ethanolicus, subsp. nov., an ethanol-utilizing dissimilatory Fe(III)-reducing bacterium from a lotus field. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 59, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Luo, Y.; Li, R.; Zhou, Q.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Yin, N.; Yang, J.; Tu, C.; Zhang, Y. Effective uptake of submicrometre plastics by crop plants via a crack-entry mode. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Deng, T.; Duan, J.; Xie, J.; Yuan, J.; Chen, M. Exposure to polystyrene microplastics causes reproductive toxicity through oxidative stress and activation of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besseling, E.; Foekema, E.M.; Van Franeker, J.A.; Leopold, M.F.; Kühn, S.; Bravo Rebolledo, E.L.; Heße, E.; Mielke, L.; Ijzer, J.; Kamminga, P.; et al. Microplastic in a macro filter feeder: Humpback whale Megaptera novaeangliae. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüst, M.; Meijer, J.; Westerink, R.H.S. The plastic brain: Neurotoxicity of micro- and nanoplastics. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, V.; Patel, M.R.; Patel, J.V. Pet Waste Management by Chemical Recycling: A Review. J. Polym. Environ. 2010, 18, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreillard, M.; Barros, C.D.F.; Rouchon, V.; Emonnot, C.; Lefebvre, V.; Moreaud, M.; Guillaume, D.; Rimbault, F.; Pagerey, F. Quantification and morphological characterization of microfibers emitted from textile washing. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 154973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, J.; Cai, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; He, M. Dynamic flows of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic in China. Waste Manag. 2021, 124, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccardo, M.; Provenza, F.; Grazioli, E.; Cavallo, A.; Terlizzi, A.; Renzi, M. PET microplastics toxicity on marine key species is influenced by pH, particle size and food variations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.; Sugahara, A.; Shinzawa, H.; Yamane, S.; Nakamura, S.; Sato, H.; Hagihara, H.; Oishi, A.; Mizukado, J.; Ueda, Y.; et al. Photodegradation behavior of polyethylene terephthalate analyzed by MALDI-TOFMS and ATR-FTIR microscopic analysis in combination with two-trace two-dimensional (2T2D) correlation mapping. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 208, 110246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brems, A.; Baeyens, J.; Beerlandt, J.; Dewil, R. Thermogravimetric pyrolysis of waste polyethylene-terephthalate and polystyrene: A critical assessment of kinetics modelling. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewert, B.; Plassmann, M.M.; MacLeod, M. Pathways for degradation of plastic polymers floating in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arhant, M.; Le Gall, M.; Le Gac, P.-Y.; Davies, P. Impact of hydrolytic degradation on mechanical properties of PET—Towards an understanding of microplastics formation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 161, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, A.B.; Hassan, A.B.; Noor, Z.Z.; Samsudin, S.B.; Abd Hamid, M.; Bello, A.; Oladokun, O.; Sabeen, A.H.; Shamiri, A. Process simulation of bis (2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate and its recovery using two–stage evaporation systems. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2018, 63, 655–660. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, C.; Fang, C.; Yu, R.; Li, Y.; Lei, W. Structure and thermal properties of various alcoholysis products from waste poly (ethylene terephthalate). Waste Manag. 2019, 85, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaka, V.; Singh, S.; Anil, A.G.; Sunil Kumar Naik, T.S.; Garg, S.; Samuel, J.; Kumar, M.; Ramamurthy, P.C.; Singh, J. Occurrence, toxicity and remediation of polyethylene terephthalate plastics. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1777–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishwanathan, A.S. Microbial fuel cells: A comprehensive review for beginners. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, M.C.; Harms, H.; Schlosser, D. Prospects for microbiological solutions to environmental pollution with plastics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 8857–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalathil, S.; Miller, M.; Reisner, E. Microbial Fermentation of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Plastic Waste for the Production of Chemicals or Electricity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202211057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gariepy, Y.; Adekunle, A.; Raghavan, V. Effective and Economical 3D Carbon Sponge with Carbon Nanoparticles as Floating Air Cathode for Sustainable Electricity Production in Microbial Fuel Cells. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 196, 1820–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, P.; Hussain, A.; Tartakovsky, B.; Neburchilov, V.; Raghavan, V.; Wang, H.; Guiot, S. Electricity generation from carbon monoxide in a single chamber microbial fuel cell. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2010, 46, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasupawat, S.; Takehana, T.; Yoshida, S.; Hiraga, K.; Oda, K. Ideonella sakaiensis sp. nov., isolated from a microbial consortium that degrades poly(ethylene terephthalate). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 2813–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zellkulturen, D.S.v.M.u. DSMZ Medium 826. Available online: https://www.dsmz.de/microorganisms/medium/pdf/DSMZ_Medium826.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Caccavo, F., Jr.; Lonergan, D.J.; Lovley, D.R.; Davis, M.; Stolz, J.F.; McInerney, M.J. Geobacter sulfurreducens sp. nov., a hydrogen- and acetate-oxidizing dissimilatory metal-reducing microorganism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 3752–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.P.; Malvankar, N.S. A Simple and Low-Cost Procedure for Growing Geobacter sulfurreducens Cell Cultures and Biofilms in Bioelectrochemical Systems. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2016, 43, A.4k.1–A.4k.27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaey, K.; Boon, N.; Höfte, M.; Verstraete, W. Microbial phenazine production enhances electron transfer in biofuel cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3401–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, X.A.; Greenman, J.; Ieropoulos, I.A. Microbial fuel cells directly powering a microcomputer. J. Power Sources 2020, 446, 227328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, S.; Hiraga, K.; Taniguchi, I.; Oda, K. Ideonella sakaiensis, PETase, and MHETase: From identification of microbial PET degradation to enzyme characterization. Methods Enzymol. 2021, 648, 187–205. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquier, G.; Doyen, P.; Kazour, M.; Dehaut, A.; Diop, M.; Duflos, G.; Amara, R. Manta Net: The Golden Method for Sampling Surface Water Microplastics in Aquatic Environments. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 811112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics Measured | Activated Sludge | G. sulfurreducenns | Pretreated |
|---|---|---|---|
| MP dry weight (mg) | 700 | 800 | 1000 |
| MP total weight loss (mg) | 300 | 200 | / |
| Total weight loss (%) | 30 | 20 | / |
| Experimental Results | I.S-AS | I.S-G.S | Untreated |
|---|---|---|---|
| MP Particle Size (mm2) | 1.48 | 3.49 | 7.5 |
| MP Particle Size Loss (%) | 80 | 54 | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hadji-Thomas, A.; Wang, S.; Gariepy, Y.; Raghavan, V. The Exploitation of Single-Chambered Microbial Fuel Cells for PET Removal in Water. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112500
Hadji-Thomas A, Wang S, Gariepy Y, Raghavan V. The Exploitation of Single-Chambered Microbial Fuel Cells for PET Removal in Water. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(11):2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112500
Chicago/Turabian StyleHadji-Thomas, Andre, Shuyao Wang, Yvan Gariepy, and Vijaya Raghavan. 2025. "The Exploitation of Single-Chambered Microbial Fuel Cells for PET Removal in Water" Microorganisms 13, no. 11: 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112500
APA StyleHadji-Thomas, A., Wang, S., Gariepy, Y., & Raghavan, V. (2025). The Exploitation of Single-Chambered Microbial Fuel Cells for PET Removal in Water. Microorganisms, 13(11), 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112500







