Differential Effects of Biogas Slurry Topdressing on Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Soil Enzyme–Microbe Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
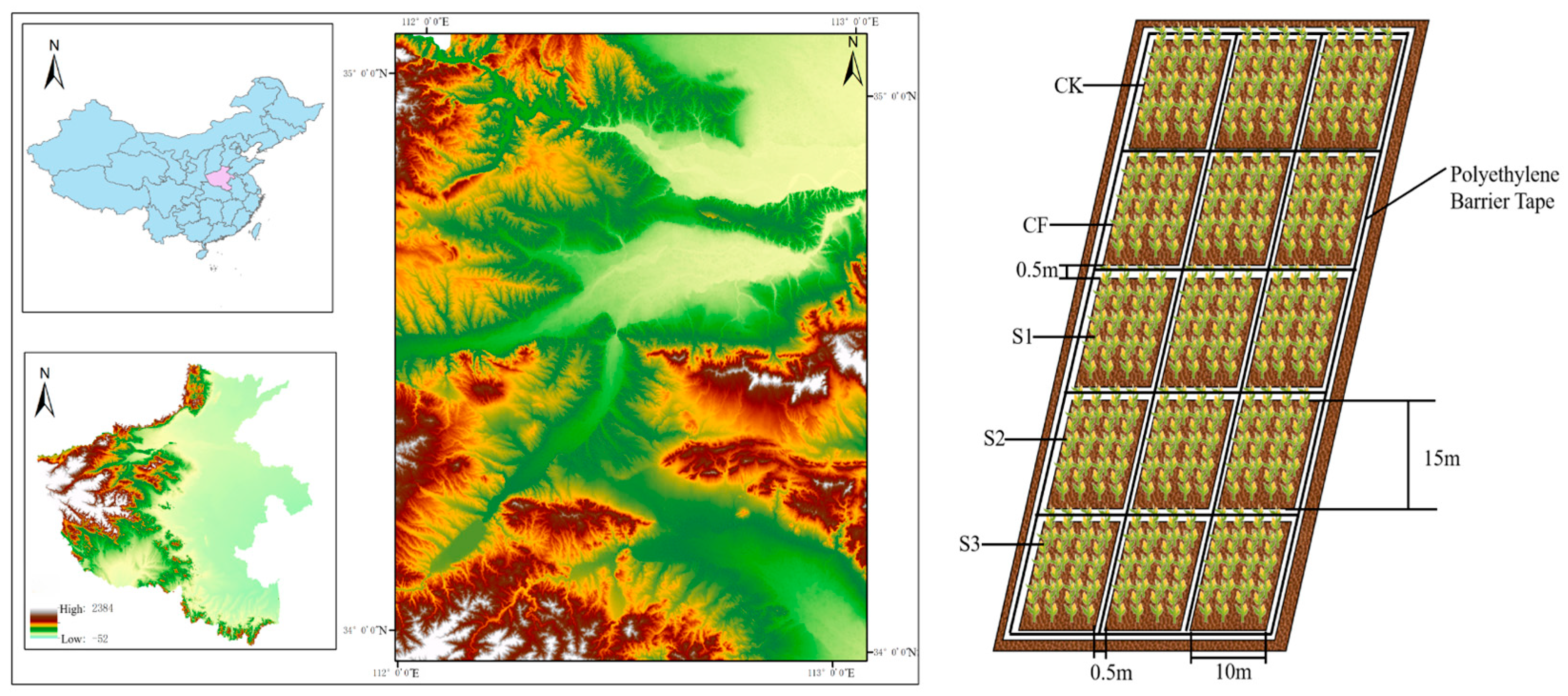
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Soil Sample Collection
2.3. Soil Physicochemical Property Analysis
2.4. Determination of Microbial Community Relative Abundance
2.5. Determination of Soil Enzyme Activities
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
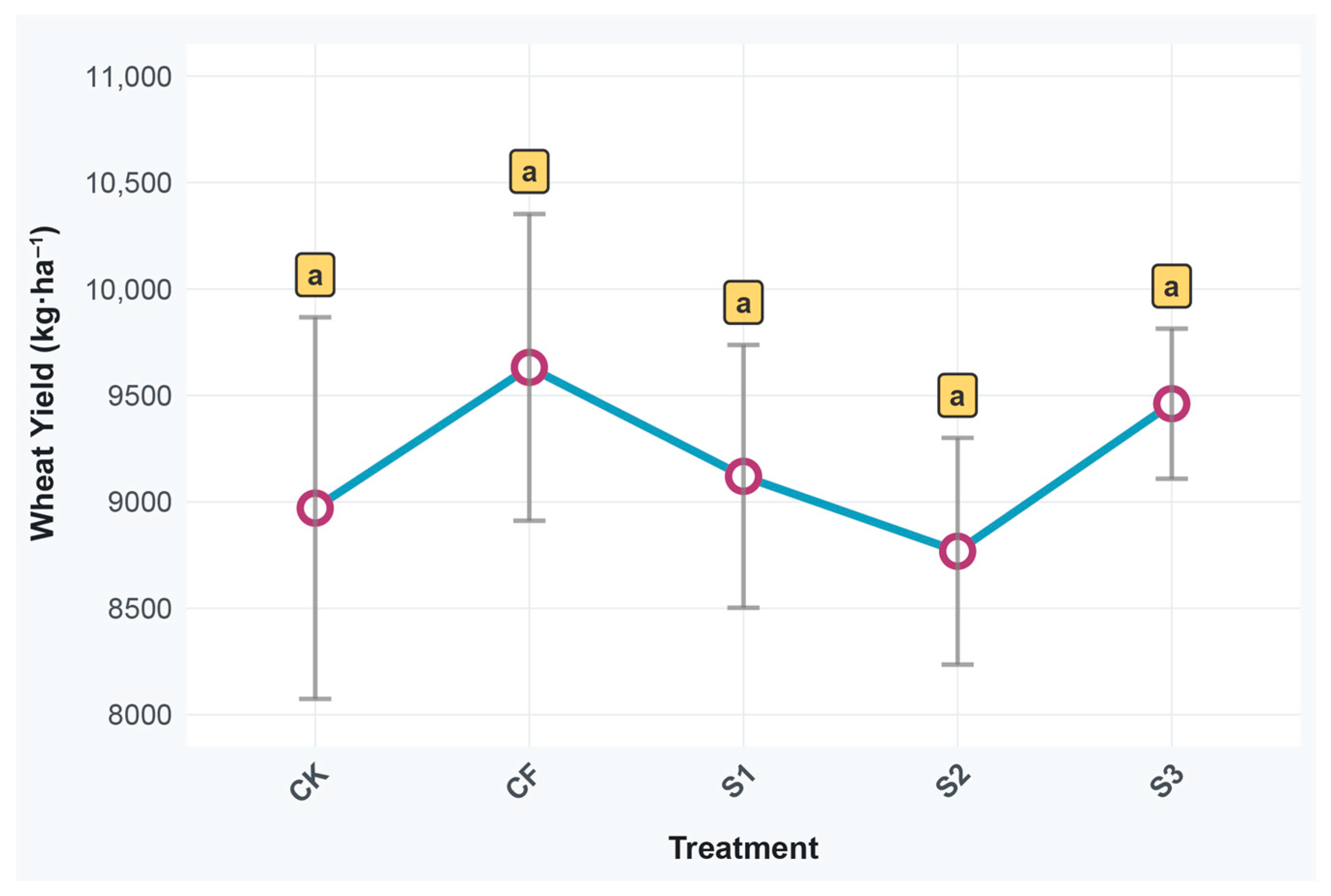
3.1. Wheat Yield Response to Different Treatments
3.2. Dynamics of Microbial Relative Abundance
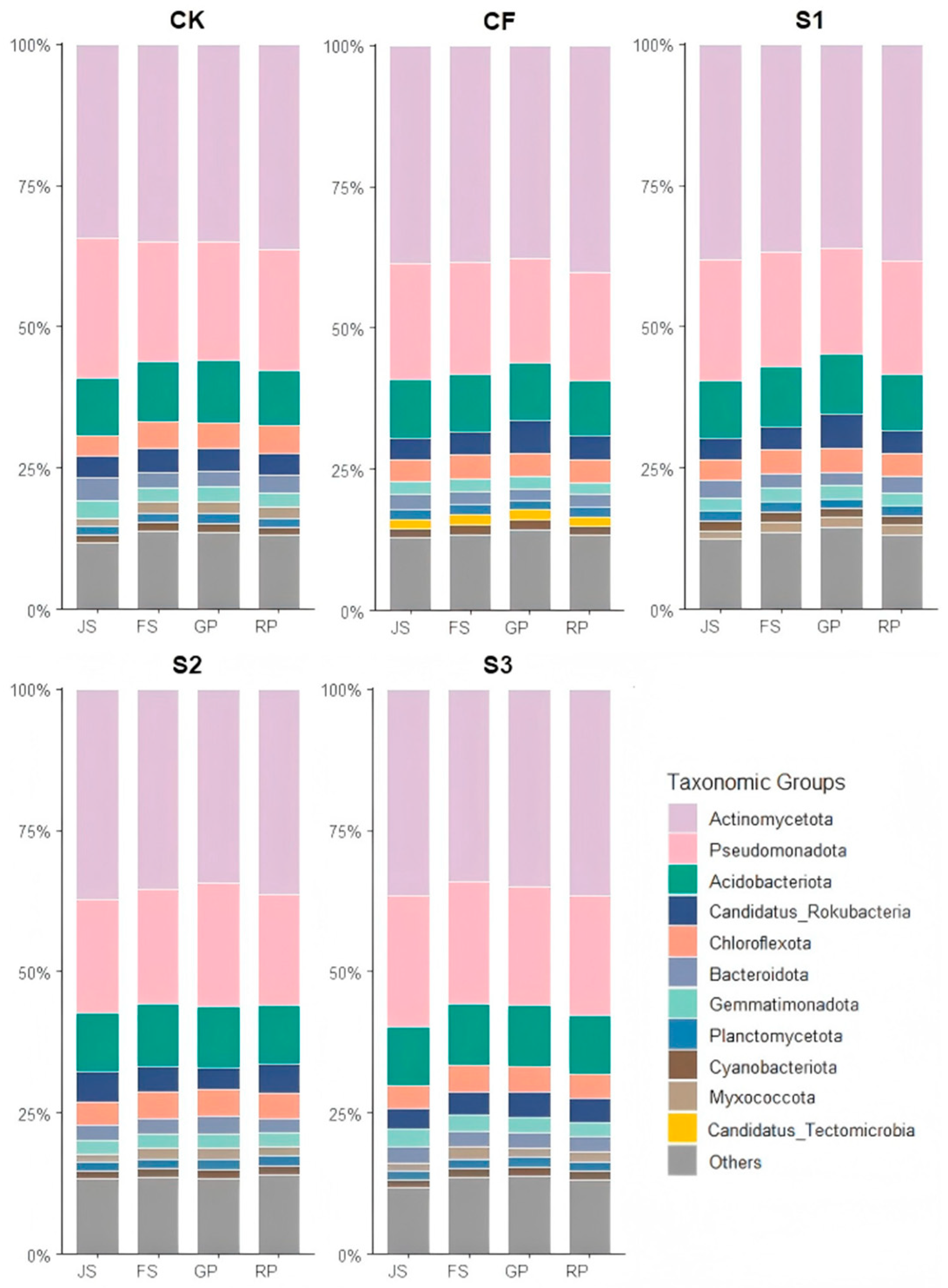
3.2.1. Dynamics of Soil Bacterial Community Composition at Phylum Level
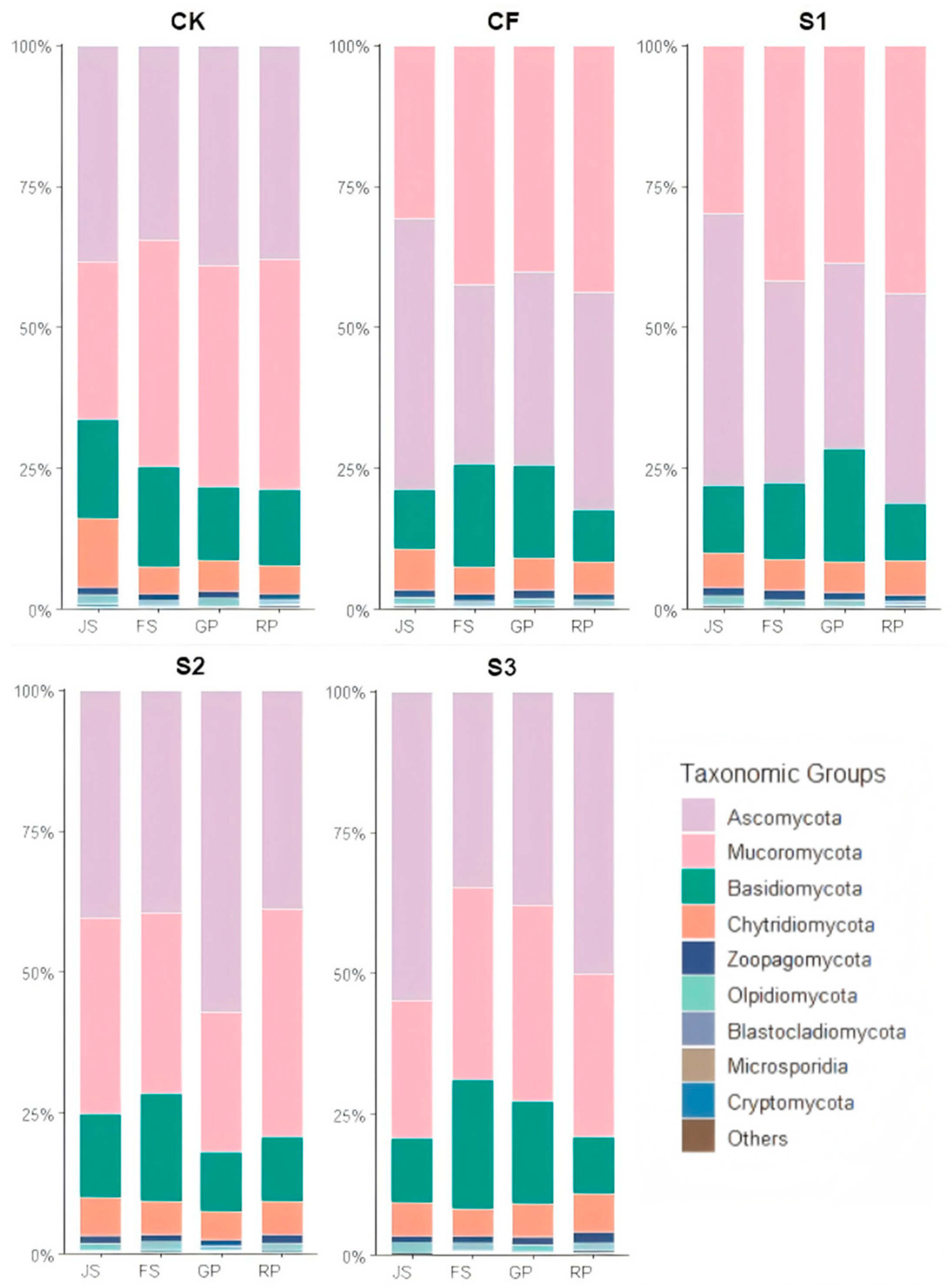
3.2.2. Dynamics of Soil Fungal Community Composition at Phylum Level
3.3. Dynamics of Soil Enzyme Activities
3.3.1. Dynamics of Soil UE Activity
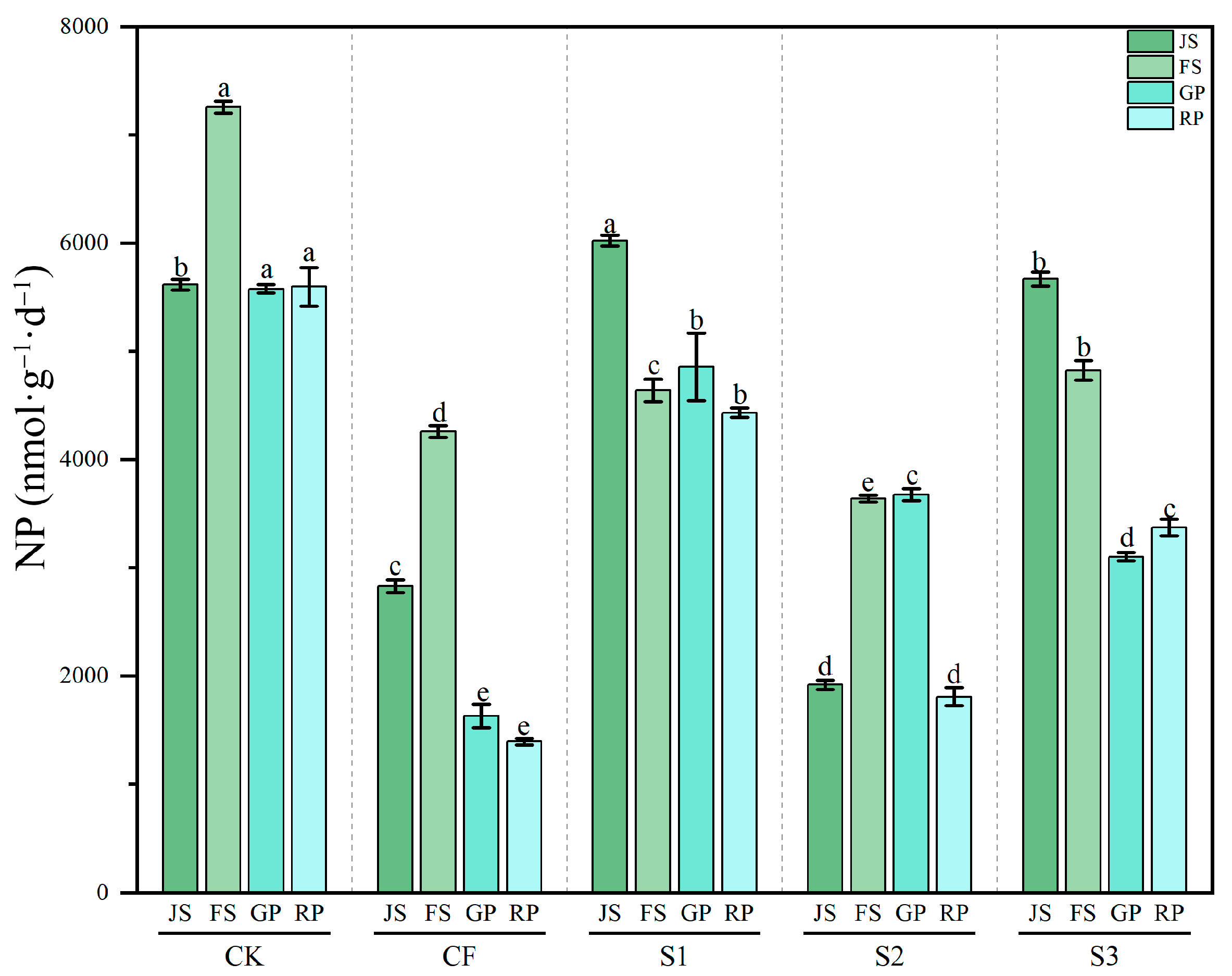
3.3.2. Dynamics of Soil NP Activity
3.3.3. Dynamics of Soil CAT Activity
3.3.4. Dynamics of Soil SC Activity
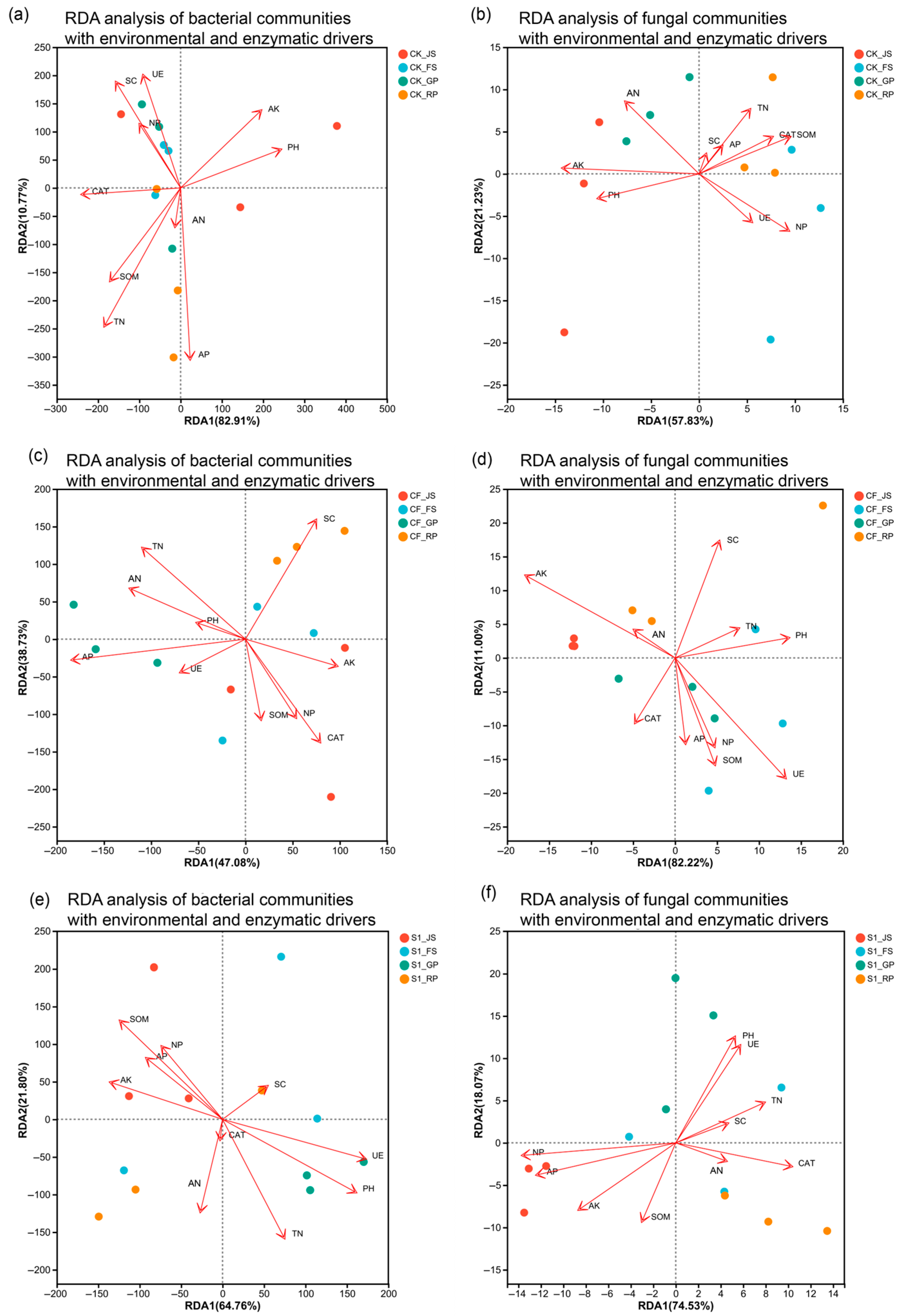
3.4. Response of Microbial Communities to Environmental and Enzymatic Drivers
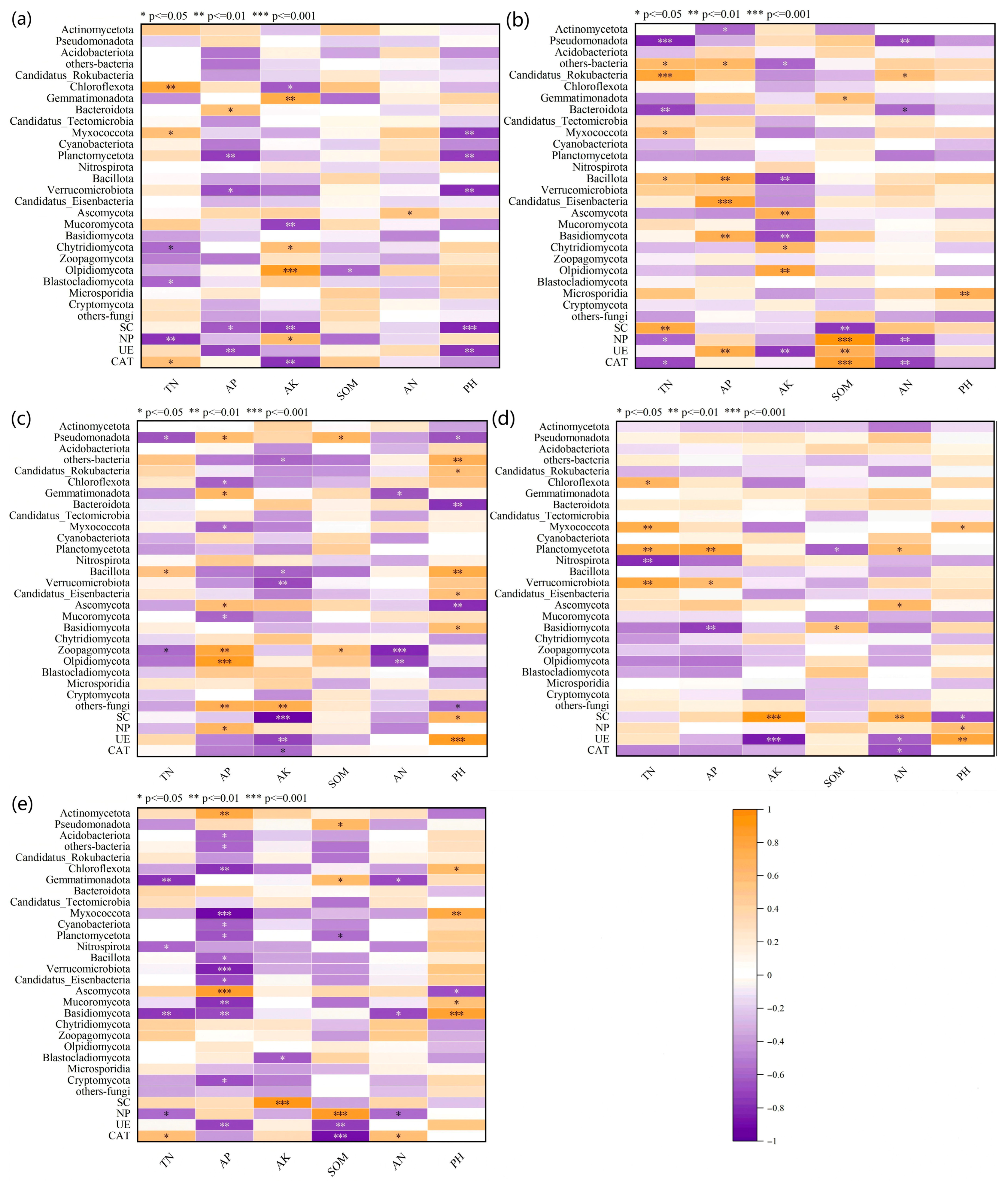
3.5. Correlation Analysis Between Environmental Factors, Microbial Relative Abundance, and Soil Enzyme Activities
3.6. Relationships Between Microbial Relative Abundance and Enzyme Activities
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of Soil Microorganisms to Biogas Slurry Application
4.2. Response of Soil Enzymes to Biogas Slurry Application
4.3. Synergistic Relationship Between Microorganisms and Enzymes Under Biogas Slurry Application
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ndabankulu, K.; Egbewale, S.O.; Tsvuura, Z.; Magadlela, A. Soil Microbes and Associated Extracellular Enzymes Largely Impact Nutrient Bioavailability in Acidic and Nutrient Poor Grassland Ecosystem Soils. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyar, S.; Appavoo, S.; Basker, M.; Pandiyarajan, P.; Kavimani, R. Effect of Zinc and Microbial Inoculation on Soil Enzyme Activities for Maize (Zea mays L.) in Black Soil. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2019, 8, 1804–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Dash, M.; Singh, S.K.; Jagadesh, M.; Mathpal, B.; Mishra, P.K.; Pandey, S.K.; Verma, K.K. Soil Microbes: A Natural Solution for Mitigating the Impact of Climate Change. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Walder, F.; Büchi, L.; Meyer, M.; Held, A.Y.; Gattinger, A.; Keller, T.; Charles, R.; van der Heijden, M.G. Agricultural Intensification Reduces Microbial Network Complexity and the Abundance of Keystone Taxa in Roots. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1722–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Spor, A.; Hénault, C.; Bru, D.; Bizouard, F.; Jones, C.M.; Sarr, A.; Maron, P.-A. Loss in Microbial Diversity Affects Nitrogen Cycling in Soil. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1609–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Eldridge, D.J.; Ochoa, V.; Gozalo, B.; Singh, B.K.; Maestre, F.T. Soil Microbial Communities Drive the Resistance of Ecosystem Multifunctionality to Global Change in Drylands across the Globe. Ecol. Lett. 2017, 20, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Ma, Y.; Song, Z.; Gao, P.; Ba, Y.; Wei, W. Soil Moisture Regulates Soil-Microbe-Enzyme Stoichiometries during Recovery Succession in Patchily Degraded Alpine Meadows on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 204, 107287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacava, P.T.; Machado, P.C.; De Andrade, P.H.M. Phosphate Solubilization by Endophytes from the Tropical Plants. In Endophytes: Mineral Nutrient Management, Volume 3; Maheshwari, D.K., Dheeman, S., Eds.; Sustainable Development and Biodiversity; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 26, pp. 207–226. ISBN 978-3-030-65446-7. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, D.L.N.; Aparna, K.; Mohanty, S.R. Microbiology and Biochemistry of Soil Organic Matter, Carbon Sequestration and Soil Health. Indian J. Fertil. 2019, 15, 124–138. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, O.Y.A.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Kuramae, E.E. Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances: Ecological Function and Impact on Soil Aggregation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Gao, Y. The Effects of Localized Plant–Soil–Microbe Interactions on Soil Nitrogen Cycle in Maize Rhizosphere Soil under Long-Term Fertilizers. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Akhdar, I.; Shabana, M.M.A.; El-Khateeb, N.M.M.; Elhawat, N.; Alshaal, T. Sustainable Wheat Cultivation in Sandy Soils: Impact of Organic and Biofertilizer Use on Soil Health and Crop Yield. Plants 2024, 13, 3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mgxaji, Y.; Mutengwa, C.S.; Mukumba, P.; Dzvene, A.R. Biogas Slurry as a Sustainable Organic Fertilizer for Sorghum Production in Sandy Soils: A Review of Feedstock Sources, Application Methods, and Agronomic Impacts. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De França, A.A.; Von Tucher, S.; Schmidhalter, U. Effects of Combined Application of Acidified Biogas Slurry and Chemical Fertilizer on Crop Production and N Soil Fertility. Eur. J. Agron. 2021, 123, 126224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Malav, L.C.; Malav, M.K.; Khan, S.A. Biogas Slurry: Source of Nutrients for Eco-Friendly Agriculture. Int. J. Extensive Res. 2015, 2, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Niyungeko, C.; Liang, X.; Liu, C.; Zhou, J.; Chen, L.; Lu, Y.; Tiimub, B.M.; Li, F. Effect of Biogas Slurry Application on Soil Nutrients, Phosphomonoesterase Activities, and Phosphorus Species Distribution. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 900–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeskops, B.; Sukristiyonubowo; Buchan, D.; Sleutel, S.; Herawaty, L.; Husen, E.; Saraswati, R.; Setyorini, D.; De Neve, S. Soil Microbial Communities and Activities under Intensive Organic and Conventional Vegetable Farming in West Java, Indonesia. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 45, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, S.J.; Basavarajappa, R.; Shimalli, G.; Babalad, H.B. Soil Microbial Dynamics and Enzyme Activities as Influenced by Organic and Inorganic Nutrient Management in Vertisols under Aerobic Rice Cultivation. J. Environ. Biol. 2017, 38, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, C.; Hernández, D.; García-Gil, J.C.; Polo, A. Microbial Activity in Pig Slurry-Amended Soils under Semiarid Conditions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Guan, T.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, T. Effects of Combined Application of Biogas Slurry and Chemical Fertilizer on Winter Wheat Rhizosphere Soil Microorganisms and Enzyme Activities. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 22, 1007–1012. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, R.; Sudhishri, S.; Khanna, M.; Lal, K.; Dass, A.; Kushwaha, H.L.; Bandyopadhyay, K.; Suman, A.; Singh, A.; Singh, R.K.; et al. A Greener Approach to Spinach Farming: Drip Nutrigation with Biogas Slurry Digestate. Agronomy 2024, 14, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Naveed, M.; Azeem, M.; Yaseen, M.; Ullah, R.; Alamri, S.; Ain Farooq, Q.U.; Siddiqui, M.H. Efficiency of Wheat Straw Biochar in Combination with Compost and Biogas Slurry for Enhancing Nutritional Status and Productivity of Soil and Plant. Plants 2020, 9, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, J.; Hida, A.; Ogawa, K.; Nonoyama, T.; Yoshikawa, N.; Imai, K. Impact of Long-Term Fertilizer Treatment on the Microeukaryotic Community Structure of a Rice Field Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 80, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapp, M.; Harrison, M.; Hany, U.; Charlton, A.; Thwaites, R. Comparing the Effect of Digestate and Chemical Fertiliser on Soil Bacteria. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 86, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, M.S.; Shahzadi, F.; Ali, F.; Shakeela, Q.; Niaz, Z.; Ahmed, S. Comparative Effect of Fertilization Practices on Soil Microbial Diversity and Activity: An Overview. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 3644–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubaker, J.; Cederlund, H.; Arthurson, V.; Pell, M. Bacterial Community Structure and Microbial Activity in Different Soils Amended with Biogas Residues and Cattle Slurry. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2013, 72, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.-Y.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Jin, L.; Wang, B.-T.; Xu, X.; Zou, X.; Ruan, H.-H.; Jin, F.-J. Contrasting Responses of Fungal and Bacterial Communities to Biogas Slurry Addition in Rhizospheric Soil of Poplar Plantations. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 175, 104427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atav, V.; Yüksel, O.; Namlı, A.; Gürbüz, M.A. Biogas Liquid Digestate Application: Influence on Soil Microbial Biomass and CO2 Respiration. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2024, 26, 3525–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryń, G.; Gryń, G.; Paluszak, Z.; Olszewska, H.; Keutgen, A.J. Chemical and Microbiological Properties of Luvisol after Addition of Post-Fermentation Residue. J. Elem. 2020, 25, 701–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.H.; Håkan Borg, L.A. A Spectrophotometric Method for Determination of Catalase Activity in Small Tissue Samples. Anal. Biochem. 1988, 174, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yao, J.; Cai, M.; Qian, Y.; Guo, Y.; Richnow, H.H.; Blake, R.E.; Doni, S.; Ceccanti, B. Effects of Petroleum Contamination on Soil Microbial Numbers, Metabolic Activity and Urease Activity. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Qiao, Z.; Yao, C.; Sun, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, J. Effects of the Novel HPPD-Inhibitor Herbicide QYM201 on Enzyme Activity and Microorganisms, and Its Degradation in Soil. Ecotoxicology 2021, 30, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Z.; Shi, L.; Chen, Y. The Great Potential for Phytoremediation of Abandoned Tailings Pond Using Ectomycorrhizal Pinus Sylvestris. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, T.H.; Kumar, U.; Mo, J.; Shakoor, A.; Wang, J.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Tufail, M.A.; Chen, X.; Yan, W. Intercropping of Peanut–Tea Enhances Soil Enzymatic Activity and Soil Nutrient Status at Different Soil Profiles in Subtropical Southern China. Plants 2021, 10, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkay, F.Ş.H.; Durmuş, M.; Yakupoğlu, T. Exploring Catalase Activity as A Biological Indicator in Degraded Soils. Anadolu Tarım Bilim. Derg. 2024, 39, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmakeerthi, R.S.; Thenabadu, M.W. Urease activity in soils: A review. J. Natl. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 1996, 24, 159–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocabruna, P.C.; Domene, X.; Preece, C.; Peñuelas, J. Relationship among Soil Biophysicochemical Properties, Agricultural Practices and Climate Factors Influencing Soil Phosphatase Activity in Agricultural Land. Agriculture 2024, 14, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalchuk, G.A.; Stephen, J.R.; Boer, W.D.; Prosser, J.I.; Embley, T.M.; Woldendorp, J.W. Analysis of Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria of the Beta Subdivision of the Class Proteobacteria in Coastal Sand Dunes by Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis and Sequencing of PCR-Amplified 16S Ribosomal DNA Fragments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauber, C.L.; Strickland, M.S.; Bradford, M.A.; Fierer, N. The Influence of Soil Properties on the Structure of Bacterial and Fungal Communities across Land-Use Types. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaig, A.E.; Glover, L.A.; Prosser, J.I. Molecular Analysis of Bacterial Community Structure and Diversity in Unimproved and Improved Upland Grass Pastures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, R.I.; Thomson, B.C.; James, P.; Bell, T.; Bailey, M.; Whiteley, A.S. The Bacterial Biogeography of British Soils. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1642–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Pyrosequencing-Based Assessment of Soil pH as a Predictor of Soil Bacterial Community Structure at the Continental Scale. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5111–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb, K.C.; Karaoz, U.; Hanson, C.A.; Santee, C.A.; Bradford, M.A.; Treseder, K.K.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Brodie Eoin, L. Differential Growth Responses of Soil Bacterial Taxa to Carbon Substrates of Varying Chemical Recalcitrance. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, K.S.; Craine, J.M.; Fierer, N. Nitrogen Fertilization Inhibits Soil Microbial Respiration Regardless of the Form of Nitrogen Applied. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 2336–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Ni, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, L.; Borrás-Hidalgo, O.; Cui, R. High Nitrogen Concentration Alter Microbial Community in Allium Fistulosum Rhizosphere. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241371, Erratum in PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Litter Quality Regulates Litter Decomposition Process in an Alpine Meadow: Based on Microbial Communities in Both Litter and Soil Layers and Their Enzymatic Stoichiometry. Ph.D. Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2024. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Manici, L.M.; Caputo, F.; De Sabata, D.; Fornasier, F. The Enzyme Patterns of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota Fungi Reveal Their Different Functions in Soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 196, 105323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X. Effects and Mechanisms of Green Waste Compost Impacts on Nursery Soil Fertility. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Mora-Salguero, D.; Ranjard, L.; Morvan, T.; Dequiedt, S.; Jean-Baptiste, V.; Sadet-Bourgeteau, S. Long-Term Effect of Repeated Application of Pig Slurry Digestate on Microbial Communities in Arable Soils. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, V.; Macci, C.; Peruzzi, E.; Masciandaro, G. Biochemical Activity and Chemical-Structural Properties of Soil Organic Matter after 17 Years of Amendments with Olive-Mill Pomace Co-Compost. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 147, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Holden, N.M. The Relationship between Soil Microbial Activity and Microbial Biomass, Soil Structure and Grassland Management. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 146, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, A.T.; Lewu, F.B.; Mulidzi, R.; Ncube, B. The Biological Activities of β-Glucosidase, Phosphatase and Urease as Soil Quality Indicators: A Review. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçak, B. Importance of Urease Activity in Soil. In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Vocational Studies Congress—Science and Health (BILMES SH 2020), Istanbul, Turkey, 12–15 December 2020; pp. 51–60, ISBN 978-605-74786-0-3. [Google Scholar]
- Neemisha; Sharma, S. Soil Enzymes and Their Role in Nutrient Cycling. In Structure and Functions of Pedosphere; Giri, B., Kapoor, R., Wu, Q.-S., Varma, A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 173–188. ISBN 978-981-16-8770-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Jin, M. Effects of Phosphogypsum Addition on Soil Fertility and Enzyme Activity of the Cultivated Layer in Saline-Sodic Paddy Fields. Soils 2025, 57, 325–332. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeler, E.; Eder, G. Effect of Cattle Slurry in Grassland on Microbial Biomass and on Activities of Various Enzymes. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1993, 16, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubaker, J.; Risberg, K.; Pell, M. Biogas Residues as Fertilisers—Effects on Wheat Growth and Soil Microbial Activities. Appl. Energy 2012, 99, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.A.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, Y.; Zhan, X.; Li, G. Biogas Slurry Application Could Potentially Reduce N2O Emissions and Increase Crop Yield. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. Study on Green Production Technology of Rice in Coastal Areas Based on Application of Biogas Slurry and Soil Fertility Substrate. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2022. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Seafatullah, M.; Hoque, M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Islam, M.M.; Islam, M.N. Effect of Cow Dung, Biogas Slurry and Vermicompost on Phosphorus Adsorption Behavior of Soil. J. Sci. Res. 2015, 7, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepetiene, A.; Kochiieru, M.; Jurgutis, L.; Mankeviciene, A.; Skersiene, A.; Belova, O. The Effect of Anaerobic Digestate on the Soil Organic Carbon and Humified Carbon Fractions in Different Land-Use Systems in Lithuania. Land 2022, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, J.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, K.; Yan, D. Effects of Sorbitol-Chelated Potassium Through Foliar Spraying on Wheat Yield, Potassium Availability, and Rhizosphere Microbiome. Soils 2025, 57, 290–299. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y. Effects of Green Manure Incorporation on Soilnutrients, Bacterial Community Structure and Maize N and P Use Efficiency in Yellow Soil of Guizhou. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou Minzu University, Guiyang, China, 2022. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M. Effect of Magnetized Water Irrigarion on Cadmium Absorption by Sedum Alfredii. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia University of Science & Technology, Baotou, China, 2022. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Verma, S.; Pradhan, S.S.; Singh, A.; Kushuwaha, M. Effect of Organic Manure on Different Soil Properties: A Review. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2024, 36, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano, C.; Zhu-Barker, X.; Decock, C. Effects of Organic Fertilizers on the Soil Microorganisms Responsible for N2O Emissions: A Review. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Zeng, B.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Cui, R.; Ren, L. Food Waste Anaerobic Biogas Slurry as Fertilizer: Potential Salinization on Different Soil Layer and Effect on Rhizobacteria Community. Waste Manag. 2022, 144, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mdlambuzi, T.; Tsubo, M.; Muchaonyerwa, P. Maize (Zea mays L.) Production from Co-Application of Biogas Slurry with Chemical Fertilizer and Effects on Soil Quality in a Semi-Arid Region of South Africa. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2022, 53, 2574–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Name of Soil Enzyme | Functional Classification | Abbreviation | Enzyme Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sucrase | Hydrolysis | SC | It can catalyze the hydrolysis of sucrose into glucose and fructose [34] |
| Catalase | Oxidation | CAT | It can degrade the buildup of H2O2 caused by soil organisms’ metabolic activity [35] |
| Urease | Hydrolysis | UE | It can catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea [36] |
| Neutral phosphatase | Hydrolysis | NP | It can release P contained in organic matter for reuse by living organisms [37] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, D.; Wang, B.; Qin, J.; Liu, W.; Niu, X.; Chen, D.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F. Differential Effects of Biogas Slurry Topdressing on Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Soil Enzyme–Microbe Interactions. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112494
Yin D, Wang B, Qin J, Liu W, Niu X, Chen D, Zhu J, Zhang F. Differential Effects of Biogas Slurry Topdressing on Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Soil Enzyme–Microbe Interactions. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(11):2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112494
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Dongxue, Baozhong Wang, Jiajun Qin, Wei Liu, Xiaoli Niu, Dongdong Chen, Jie Zhu, and Fengshun Zhang. 2025. "Differential Effects of Biogas Slurry Topdressing on Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Soil Enzyme–Microbe Interactions" Microorganisms 13, no. 11: 2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112494
APA StyleYin, D., Wang, B., Qin, J., Liu, W., Niu, X., Chen, D., Zhu, J., & Zhang, F. (2025). Differential Effects of Biogas Slurry Topdressing on Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Soil Enzyme–Microbe Interactions. Microorganisms, 13(11), 2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112494





