Four-Year Longitudinal Epidemiological Study on the Association Between a Multi-Item Saliva Testing System and Oral and Gut Microbiota
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Clinical Parameters
2.3. Salivary Multi Test (SMT)
2.4. Measurements of Oral and Gut Microbiota
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethics Statement
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
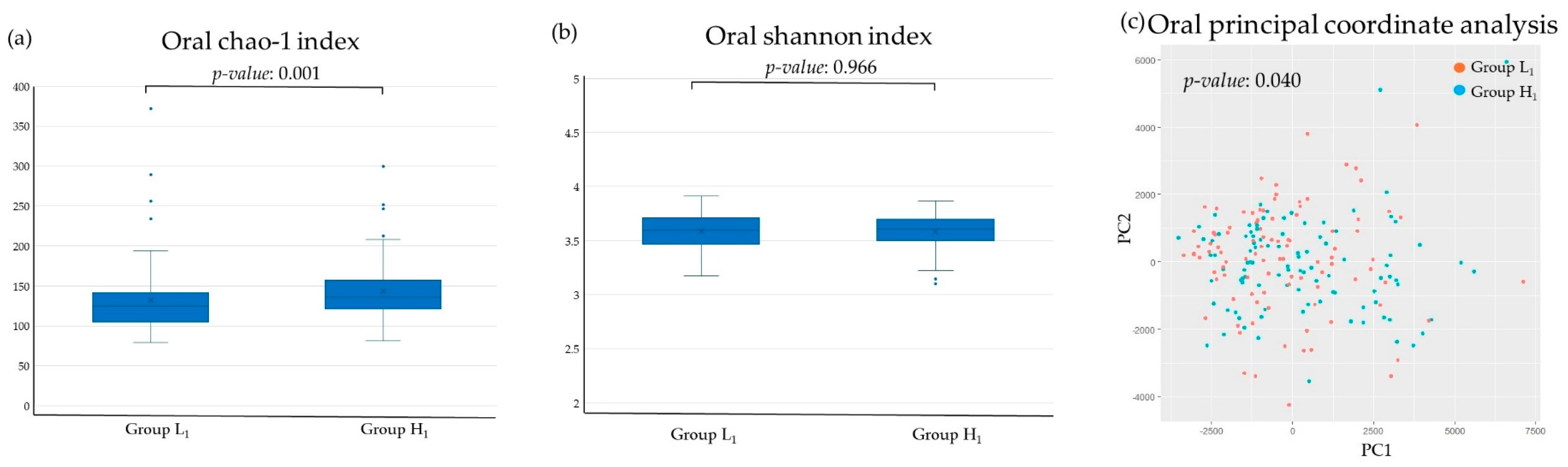
3.2. Diversity Analysis
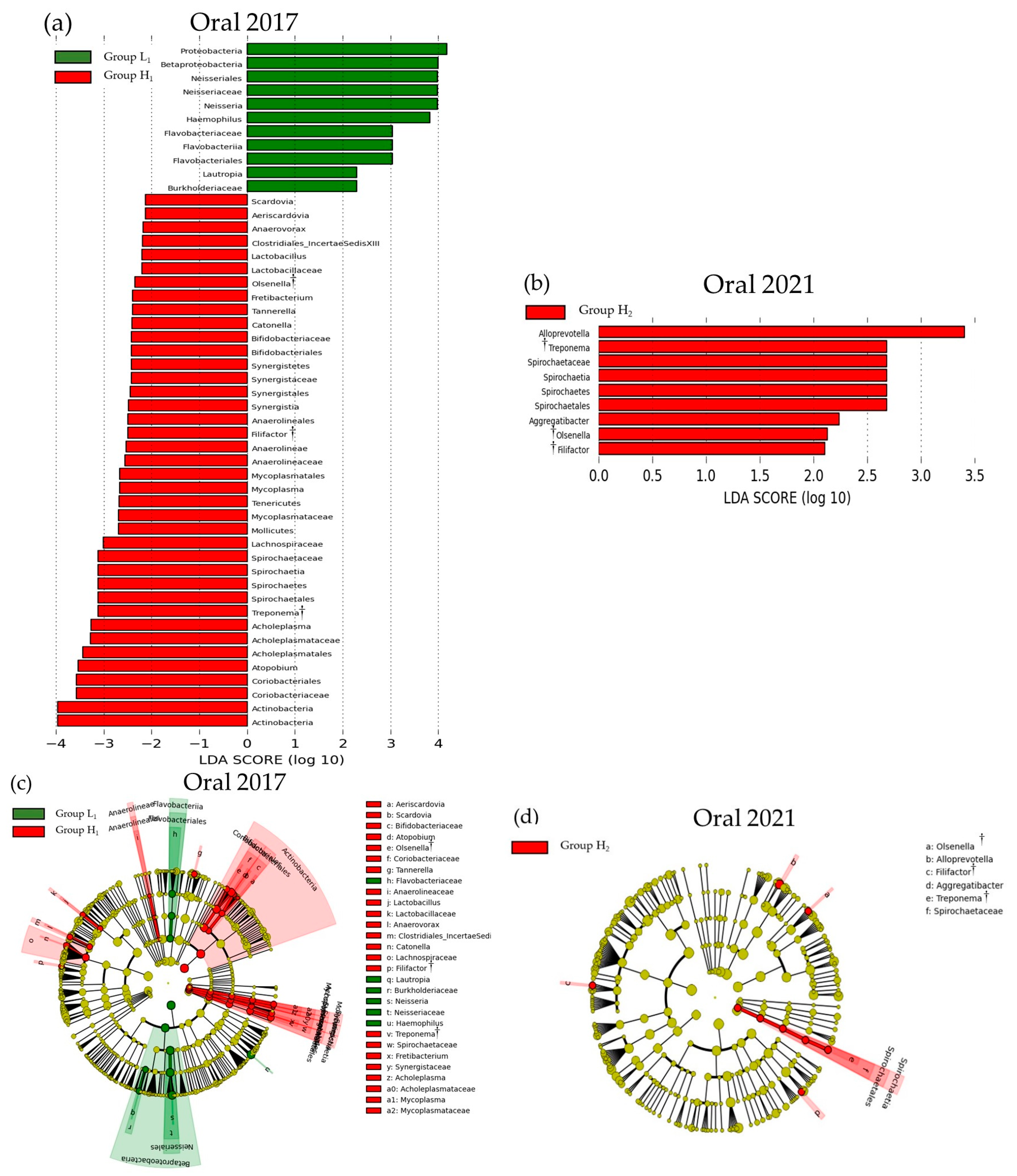
3.3. Comparison of the SMT Score and the Oral or Gut Bacterial Species in 2017 and 2021
3.4. Correlation Between SMT and Bacterial Species
3.5. Changes in SMT over 4 Years
3.6. Longitudinal Analysis
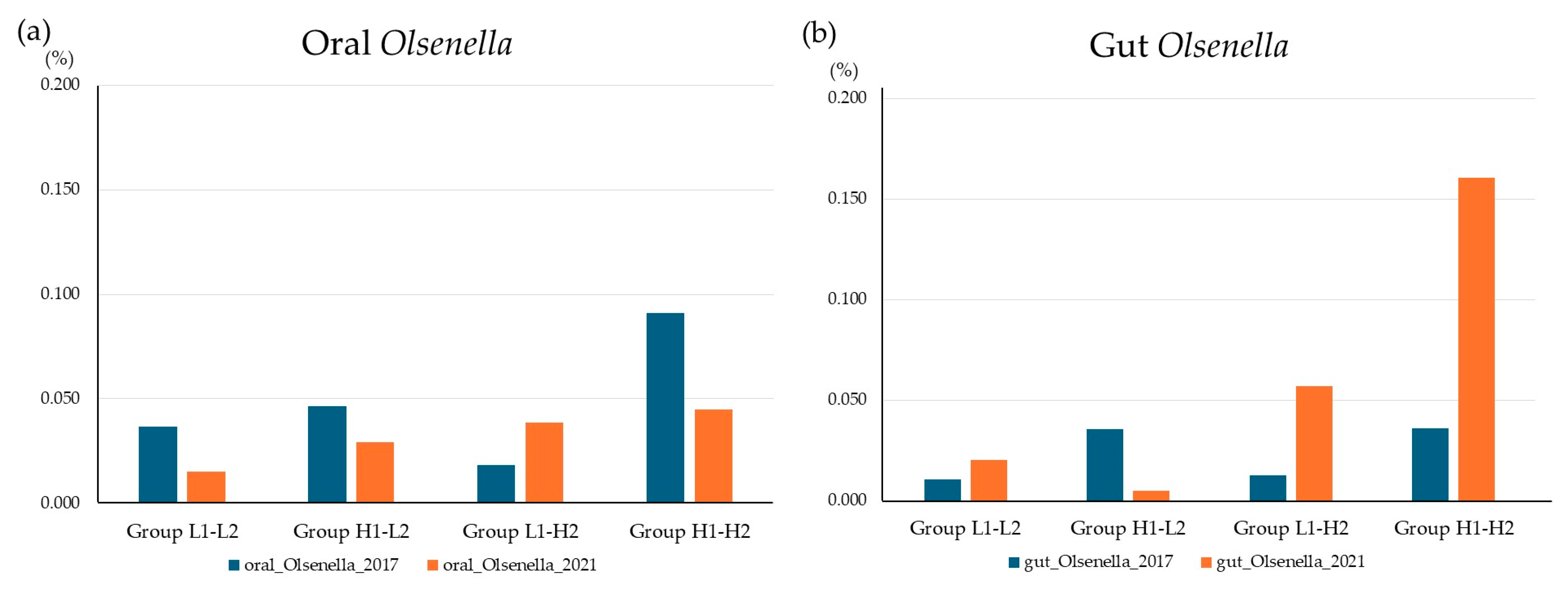
3.7. Olsenella Correlations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, C.; Correia-de-Sá, T.; Araujo, R.; Barbosa, F.; Burnet, P.W.J.; Ferreira-Gomes, J.; Sampaio-Maia, B. The oral-gut microbiota relationship in healthy humans: Identifying shared bacteria between environments and age groups. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1475159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.L.; Mark Welch, J.L.; Kauffman, K.M.; McLean, J.S.; He, X. The oral microbiome: Diversity, biogeography and human health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Jiang, W.; Deng, M.; Wang, W.; Xie, X.; Feng, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Song, D.; Yuan, Z.; et al. Alterations of oral microbiota in patients with panic disorder. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 9103–9112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Cui, J.; Zhu, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. The oral-gut microbiota axis: A link in cardiometabolic diseases. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2025, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atarashi, K.; Suda, W.; Luo, C.; Kawaguchi, T.; Motoo, I.; Narushima, S.; Kiguchi, Y.; Yasuma, K.; Watanabe, E.; Tanoue, T.; et al. Ectopic colonization of oral bacteria in the intestine drives TH1 cell induction and inflammation. Science 2017, 358, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwauchi, M.; Horigome, A.; Ishikawa, K.; Mikuni, A.; Nakano, M.; Xiao, J.Z.; Odamaki, T.; Hironaka, S. Relationship between oral and gut microbiota in elderly people. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2019, 7, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Wang, Y.; Gong, T. The interplay between oral microbiota, gut microbiota and systematic diseases. J. Oral Microbiol. 2023, 15, 2213112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechir, F.; Pacurar, M.; Tohati, A.; Bataga, S.M. Comparative Study of Salivary pH, Buffer Capacity, and Flow in Patients with and without Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.B.; Patil, B.R. Saliva: A diagnostic biomarker of periodontal diseases. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2011, 15, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segawa, K.; Shigeishi, H.; Fujii, M.; Noumi, K.; Yamanaka, F.; Kamikawa, K.; Arakawa, S.; Sugiyama, M. Relationship of Salivary Occult Blood With General and Oral Health Status in Employees of a Japanese Department Store. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2019, 11, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bhogadia, M.; Edgar, M.; Hunwin, K.; Page, G.; Grootveld, M. Detection and Quantification of Ammonia as the Ammonium Cation in Human Saliva by 1H NMR: A Promising Probe for Health Status Monitoring, with Special Reference to Cancer. Metabolites 2023, 13, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belstrøm, D. The salivary microbiota in health and disease. J. Oral Microbiol. 2020, 12, 1723975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belstrøm, D.; Sembler-Møller, M.; Grande, M.; Kirkby, N.; Cotton, S.; Paster, B.; Twetman, S.; Holmstrup, P. Impact of oral hygiene discontinuation on supragingival and salivary microbiomes. JDR Clin. Transl. Res. 2018, 3, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattarai, K.R.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.J. Compliance with Saliva Collection Protocol in Healthy Volunteers: Strategies for Managing Risk and Errors. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, A.S.; Habte, H.; Mthembu, Y.; Peacocke, J.; de Beer, C. Mucus and Mucins: Do they have a role in the inhibition of the human immunodeficiency virus? Virol. J. 2017, 14, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, F.; Ge, S.; Chen, B.; Yan, F. Periodontitis may induce gut microbiota dysbiosis via salivary microbiota. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2022, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Lu, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, B.; Bao, J.; Wang, L.; Cui, D.; Luo, B.; Yan, F. Periodontitis Salivary Microbiota Worsens Colitis. J. Dent. Res. 2022, 101, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishinaga, E.; Uchiyama, C.; Maki, R.; Saito, K.; Fukasawa, T.; Suzuki, N.; Yamamoto, T.; Murakoshi, M.; Odera, M.; Fukuta, I.; et al. Development of Comprehensive Salivary Test System—Validity and Reliability of a Newly-developed Salivary Multi-test System (AL-55) Compared with Standard Methods. Jpn. J. Conserv. Dent. 2015, 58, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishinaga, E.; Maki, R.; Saito, K.; Fukasawa, T.; Suzuki, N.; Uchiyama, C.; Yamamoto, T.; Murakoshi, M.; Odera, M.; Fukuta, I.; et al. Development of Comprehensive Salivary Test System—Efficiency of a Newly-developed Salivary Multi-test System (AL-55). Jpn. J. Conserv. Dent. 2015, 58, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, X.; Yang, Z.; Li, M.D. Effect of cigarette smoke on gut microbiota: State of knowledge. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 673341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaji, S.; Ihara, K.; Sawada, K.; Parodi, S.; Umeda, T.; Takahashi, I.; Murashita, K.; Kurauchi, S.; Tokuda, I. Social innovation for life expectancy extension utilizing a platform-centered system used in the Iwaki health promotion project: A protocol paper. SAGE Open Med. 2021, 9, 20503121211002606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Tomita, J.; Nishioka, K.; Hisada, T.; Nishijima, M. Development of a prokaryotic universal primer for simultaneous analysis of Bacteria and Archaea using next-generation sequencing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhang, C.; Hu, Z.; Leng, W.; Xia, L. Association between periodontitis and dental caries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2024, 28, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyvad, B.; Takahashi, N. Integrated hypothesis of dental caries and periodontal diseases. J. Oral Microbiol. 2020, 12, 1710953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomlöf, J.; Jansson, L.; Blomlöf, L.; Lindskog, S. Root surface etching at neutral pH promotes periodontal healing. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1996, 23, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliga, S.; Muglikar, S.; Kale, R. Salivary pH: A diagnostic biomarker. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2013, 17, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uitto, V.J.; Nieminen, A.; Coil, J.; Hurttia, H.; Larjava, H. Oral fluid elastase as an indicator of periodontal health. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1996, 23, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, G.A.; Miozza, V.; Delgado, A.; Busch, L. Determination of salivary levels of mucin and amylase in chronic periodontitis patients. J. Periodontal Res. 2011, 46, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederman, R.; Brunkhorst, B.; Smith, S.; Weinreb, R.N.; Ryder, M.I. Ammonia as a potential mediator of adult human periodontal infection: Inhibition of neutrophil function. Arch. Oral Biol. 1990, 35, S205–S209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.; Kotronia, E.; Ramsay, S.E. Frailty, aging, and periodontal disease: Basic biologic considerations. Periodontol 2000 2021, 87, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Pang, E.K. Relationship between periodontitis and systemic health conditions: A narrative review. Ewha Med. J. 2025, 48, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papapanou, P.N. Periodontal diseases: Epidemiology. Ann. Periodontol. 1996, 1, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.N.; Kalburgi, N.B.; Koregol, A.C.; Warad, S.B.; Patil, S.; Ugale, M.S. Female sex hormones and periodontal health-awareness among gynecologists—A questionnaire survey. Saudi Dent. J. 2012, 24, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabine Elisabeth, G.; Yuxi, Z.; Jiawen, Y.; Lei, W.; Sabine, R.; Joerg, M. Systemic, Lifestyle and Environmental Modifying Factors in the Pathogenesis of Periodontitis. J. Periodontal Res. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xie, G.; Chen, M.; He, Y.; Yu, W.; Chen, X.; Mao, W.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, Q.; et al. Oral microbial dysbiosis in patients with periodontitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1121399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Park, H.J.; Jeong, S.J.; Auh, Q.S.; Jung, J.; Lee, G.J.; Shin, S.; Hong, J.Y. Oral microbiome profiles of gingivitis and periodontitis by next-generation sequencing among a group of hospital patients in Korea: A cross-sectional study. J. Oral Biosci. 2025, 67, 100591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Liu, S.; Jia, N.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Han, C. Olsenella uli-induced pneumonia: A case report. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2022, 21, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewhirst, F.E.; Paster, B.J.; Tzellas, N.; Coleman, B.; Downes, J.; Spratt, D.A.; Wade, W.G. Characterization of novel human oral isolates and cloned 16S rDNA sequences that fall in the family Coriobacteriaceae: Description of olsenella gen. nov., reclassification of Lactobacillus uli as Olsenella uli comb. nov. and description of Olsenella profusa sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraatz, M.; Wallace, R.J.; Svensson, L. Olsenella umbonata sp. nov., a microaerotolerant anaerobic lactic acid bacterium from the sheep rumen and pig jejunum, and emended descriptions of Olsenella, Olsenella uli and Olsenella profusa. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Silva, W.O.; Romeiro, K.; Gominho, L.F.; Alves, F.R.F.; Rôças, I.N. Apical root canal microbiome associated with primary and posttreatment apical periodontitis: A systematic review. Int. Endod. J. 2024, 57, 1043–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, E.J.; Park, O.J.; Lee, J.S.; Yoo, Y.J.; Perinpanayagam, H.; Jeong, Y.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Bae, J.W.; Kum, K.Y.; Han, S.H. Microbiota associated with caries and apical periodontitis: A next-generation sequencing study. Int. Endod. J. 2025, 58, 890–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, P.M.; Jacinto, R.C.; Dal Pizzol, T.S.; Ferreira, M.B.; Montagner, F. Resistance profiles to antimicrobial agents in bacteria isolated from acute endodontic infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 48, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogtmann, E.; Yano, Y.; Zouiouich, S.; Hua, X.; Wan, Y.; Purandare, V.; Li, S.; Dagnall, C.L.; Jones, K.; Hicks, B.D.; et al. The human oral microbiome and risk of colorectal cancer within three prospective cohort studies in the United States. Cancer 2025, 131, e35802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Geng, Y.; Wang, P.; Cai, M.; Neng, J.; Hu, J.; Xia, D.; Cao, W.; Yang, K.; Sun, P. Ferulic acid improves intestinal barrier function through altering gut microbiota composition in high-fat diet-induced mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 3767–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, C.; Liang, Y.T.; Lv, J.; Yang, L.F.; Zhao, B.N. Study on the Antipyretic and Anti-inflammatory Mechanism of Shuanghuanglian Oral Liquid Based on Gut Microbiota-Host Metabolism. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 843877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Q.; Du, H.; Cheng, X.; Cheng, X.; Tang, Y.; Pan, L.; Wang, Q.; Lin, J. Characteristics of fecal gut microbiota in patients with colorectal cancer at different stages and different sites. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 4834–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Zhou, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Lu, B.; Zhang, A.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; et al. The alternations of gut microbiota in diabetic kidney disease: Insights from a triple comparative cohort. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1606700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Y.; Wan, L. Causal effect of gut microbiota on juvenile idiopathic arthritis: A two-sample Mendelian a randomization study. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e70183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, I.; Yamazaki, K. Can oral bacteria affect the microbiome of the gut? J. Oral Microbiol. 2019, 11, 1586422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenςo, T.G.B.; Spencer, S.J.; Alm, E.J.; Colombo, A.P.V. Defining the gut microbiota in individuals with periodontal diseases: An exploratory study. J. Oral Microbiol. 2018, 10, 1487741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, N.; Yang, F.; Li, A.; Prifti, E.; Chen, Y.; Shao, L.; Guo, J.; Le Chatelier, E.; Yao, J.; Wu, L.; et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis. Nature 2014, 513, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manenzhe, S.C.; Koutras, S.; Zwane, N.B.; Masilana, A.I.; Shangase, S.L. The impact of Filifactor alocis on the severity of periodontitis among diabetic and non-diabetic patients: A narrative review. Front. Dent. Med. 2024, 5, 1408839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sela, M.N. Role of Treponema denticola in periodontal diseases. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2001, 12, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, L.; Fu, J.; Du, J.; Luo, Z.; Guo, L.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y. Porphyromonas gingivalis aggravates colitis via a gut microbiota-linoleic acid metabolism-Th17/Treg cell balance axis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimomura, Y.; Sugi, Y.; Kume, A.; Tanaka, W.; Yoshihara, T.; Matsuura, T.; Komiya, Y.; Ogata, Y.; Suda, W.; Hattori, M.; et al. Strain-level detection of Fusobacterium nucleatum in colorectal cancer specimens by targeting the CRISPR-Cas region. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0512322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, N.; Také, A.; Uojima, H.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Gotoh, K.; Satoh, T.; Hidaka, H.; Horio, K.; Mizokami, M.; Hayashi, S.; et al. Complete Match of Streptococcus salivarius from Oral Saliva and Stool in a Patient with Hepatic Encephalopathy. Intern. Med. 2025, 64, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Ozato, N.; Tsuda, H.; Mori, K.; Kinoshita, K.; Katashima, M.; Katsuragi, Y.; Nakaji, S.; Maeda, H. Mouse Model of Anti-Obesity Effects of Blautia hansenii on Diet-Induced Obesity. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 7147–7160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozato, N.; Saito, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Katashima, M.; Tokuda, I.; Sawada, K.; Katsuragi, Y.; Kakuta, M.; Imoto, S.; Ihara, K. Blautia genus associated with visceral fat accumulation in adults 20–76 years of age. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2019, 5, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Hrncir, T.; Hrncirova, L.; Kverka, M.; Hromadka, R.; Machova, V.; Trckova, E.; Kostovcikova, K.; Kralickova, P.; Krejsek, J.; Tlaskalova-Hogenova, H. Gut microbiota and NAFLD: Pathogenetic mechanisms, microbiota signatures, and therapeutic interventions. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosomi, K.; Saito, M.; Park, J.; Murakami, H.; Shibata, N.; Ando, M.; Nagatake, T.; Konishi, K.; Ohno, H.; Tanisawa, K. Oral administration of Blautia wexlerae ameliorates obesity and type 2 diabetes via metabolic remodeling of the gut microbiota. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
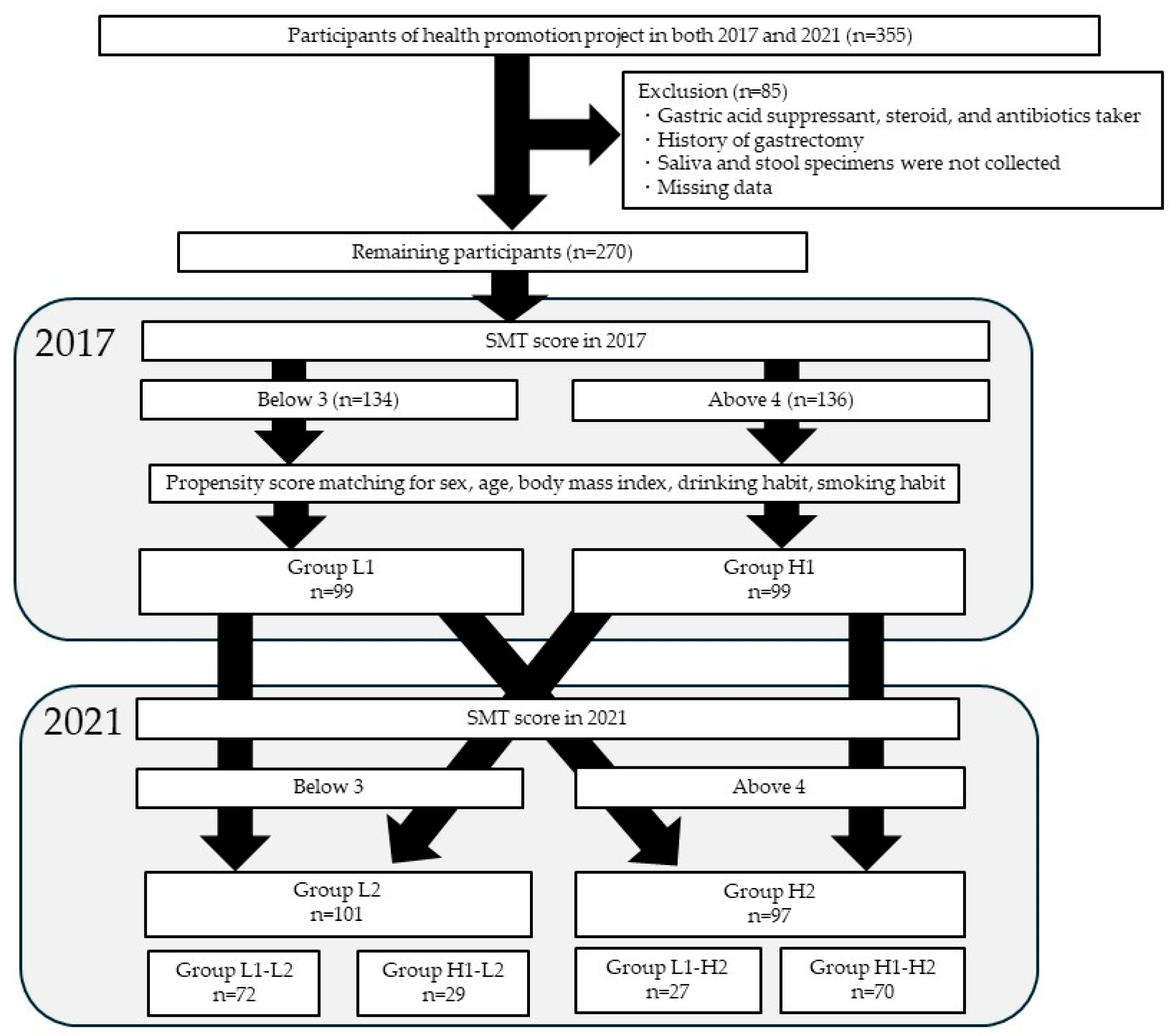


| Group L1 (n = 134) | Group H1 (n = 136) | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, male | 44 (32.8%) | 64 (47.1%) | 0.019 | ||
| Age (years) | 50.0 | (39.0–59.3) | 57.0 | (44.3–63.0) | <0.001 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 22.1 | (19.9–24.0) | 23.0 | (20.5–25.3) | 0.049 |
| SMT score | 2.0 | (1.0–3.0) | 5.0 | (4.0–6.0) | <0.001 |
| Caries bacteria | 2.9 | (2.5–3.5) | 4.8 | (4.0–6.6) | <0.001 |
| Acidity | 63.3 | (54.6–72.9) | 67.9 | (61.4–73.4) | 0.004 |
| Buffering capacity | 82.7 | (75.4–88.3) | 75.8 | (69.5–81.2) | <0.001 |
| Occult blood | 53.7 | (44.2–63.6) | 29.4 | (19.3–38.1) | <0.001 |
| White blood cells | 50.3 | (39.5–63.2) | 32.6 | (29.9–37.5) | <0.001 |
| Protein | 72.5 | (69.3–75.8) | 61.4 | (55.8–66.3) | <0.001 |
| Ammonia | 15.9 | (12.5–20.1) | 10.7 | (9.2–12.9) | <0.001 |
| Drinking habit | 30 (22.4%) | 25 (18.4%) | 0.452 | ||
| Smoking habit | 19 (14.2%) | 19 (14.0%) | 0.999 | ||
| Group L1 (n = 99) | Group H1 (n = 99) | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, male | 38 (38.4%) | 34 (34.3%) | 0.658 | ||
| Age (years) | 54.0 | (43.0–62.0) | 54.0 | (39.0–61.0) | 0.695 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 22.5 | (20.1–24.4) | 22.1 | (19.9–24.5) | 0.631 |
| SMT score | 2.0 | (1.0–3.0) | 5.0 | (4.0–5.0) | <0.001 |
| Caries bacteria | 2.9 | (2.5–3.5) | 4.7 | (3.8–6.6) | <0.001 |
| Acidity | 62.3 | (54.5–70.5) | 68.0 | (62.1–73.8) | <0.001 |
| Buffering capacity | 81.9 | (73.5–87.4) | 77.3 | (71.4–81.6) | <0.001 |
| Occult blood | 52.1 | (44.2–62.9) | 29.5 | (17.0–38.8) | <0.001 |
| White blood cells | 49.8 | (39.2–61.4) | 32.7 | (29.9–37.5) | <0.001 |
| Protein | 71.8 | (68.8–75.4) | 62.5 | (56.9–67.2) | <0.001 |
| Ammonia | 14.9 | (11.8–19.0) | 10.9 | (9.6–13.3) | <0.001 |
| Drinking habit | 27 (27.3%) | 18 (18.2%) | 0.174 | ||
| Smoking habit | 13 (13.1%) | 14 (14.1%) | 0.999 | ||
| Oral_Olsenella Change | Gut_Olsenella Change | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Change in SMT Parameters | ρ | p-Value | ρ | p-Value |
| Caries bacteria | 0.112 | 0.118 | −0.049 | 0.495 |
| Acidity | 0.103 | 0.149 | −0.076 | 0.289 |
| Buffering | −0.032 | 0.650 | −0.119 | 0.094 |
| Occult blood | −0.238 | 0.001 | −0.207 | 0.003 |
| White blood cells | −0.071 | 0.318 | −0.087 | 0.224 |
| Protein | −0.120 | 0.091 | −0.190 | 0.007 |
| Ammonia | −0.003 | 0.968 | −0.047 | 0.509 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sato, S.; Chinda, D.; Mikami, K.; Tobinai, M.; Ishidoya, N.; Furusawa, K.; Miyashiro, K.; Yoshida, K.; Iino, C.; Sawada, K.; et al. Four-Year Longitudinal Epidemiological Study on the Association Between a Multi-Item Saliva Testing System and Oral and Gut Microbiota. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2483. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112483
Sato S, Chinda D, Mikami K, Tobinai M, Ishidoya N, Furusawa K, Miyashiro K, Yoshida K, Iino C, Sawada K, et al. Four-Year Longitudinal Epidemiological Study on the Association Between a Multi-Item Saliva Testing System and Oral and Gut Microbiota. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(11):2483. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112483
Chicago/Turabian StyleSato, Satoshi, Daisuke Chinda, Keita Mikami, Masakazu Tobinai, Nao Ishidoya, Keisuke Furusawa, Kaede Miyashiro, Kenta Yoshida, Chikara Iino, Kaori Sawada, and et al. 2025. "Four-Year Longitudinal Epidemiological Study on the Association Between a Multi-Item Saliva Testing System and Oral and Gut Microbiota" Microorganisms 13, no. 11: 2483. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112483
APA StyleSato, S., Chinda, D., Mikami, K., Tobinai, M., Ishidoya, N., Furusawa, K., Miyashiro, K., Yoshida, K., Iino, C., Sawada, K., Mikami, T., Nakaji, S., Murashita, K., & Sakuraba, H. (2025). Four-Year Longitudinal Epidemiological Study on the Association Between a Multi-Item Saliva Testing System and Oral and Gut Microbiota. Microorganisms, 13(11), 2483. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112483







