Abstract
During four outbreaks in 2023 and 2024, samples from pond-reared Nile tilapia were taken from different farms located in Kafr Elsheikh governorate, Egypt. Samples were submitted for laboratory examinations. Diseased fish exhibited bacterial septicemia and some cases died without showing any clinical signs. A total of 30 bacterial isolates were isolated and identified. Of these isolates, 57% were identified as Gram-positive bacteria, whereas the remaining 43% were identified as Gram-negative bacteria. PCR targeting the 16S rRNA gene and genome sequencing confirmed five bacterial isolates as Aeromonas veronii (30%), Vibrio alginolyticus (13.3%), Enterococcus faecalis (23.3%), Aerococcus viridans (16.7%), and Staphylococcus epidermidis (16.7%). The NCBI GenBank accession numbers of these strains were (PV018985) for A. veronii, (PV016854) for V. alginolyticus, (PV013413) for E. faecalis, (PV032005) for A. viridans, and (PV012491) for Staph. epidermidis. The antibiogram revealed that the bacterial strains showed resistance to most of the antibiotics tested. A. viridans exhibited resistance to nearly all the antibiotics except for intermediate sensitivity to ciprofloxacin and amoxycillin/clavulanic acid. However, A. veronii showed high sensitivity to amoxycillin/clavulanic acid, oxytetracycline, kanamycin, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and intermediate susceptibility to ciprofloxacin. Similarly, E. faecalis showed high susceptibility to amoxycillin/clavulanic acid, ciprofloxacin, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole in addition to intermediate sensitivity to ampicillin and kanamycin. Furthermore, Staph. epidermidis strain was highly susceptible to ampicillin, amoxycillin/clavulanic acid, oxytetracycline, novobiocin, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and was partially sensitive to kanamycin and ciprofloxacin. To conclude, summer mortalities recorded in farmed tilapia were closely related to a multifactorial bacterial origin with different sensitivity to antibiotic discs.
1. Introduction
Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) is one of the most farmed fish worldwide [1]. In Egypt, it is the cornerstone of fish farming and one of cheapest fish species [2,3]. Globally, Egypt is one of the top tilapia producers in Africa and ranks as the third largest producer of farmed tilapia after China and Indonesia, accounting for 17.4% of the world total production [4,5]. Kafr El-Sheikh province is a leading contributor to Egypt’s aquaculture industry, providing 324,479 tons, which accounts for 55% of overall production. It contributes with 259,583 tons in relation to the total production [6]. However, the expansion of the tilapia industry faces significant constraints due to the scarcity of freshwater resources and the frequent occurrence of disease outbreaks [7]. In Egypt, agricultural drainage water is permitted for use in aquaculture. This practice has serious consequences on the water quality, as it transfers various contaminants directly into the production systems [8]. The excessive use of agricultural fertilizers and pesticides is a dangerous problematic issue, which, in turn, pollutes surface and groundwater sources involving nitrates from fertilizers and bacteria from livestock waste [9,10]. It also increases the risk to fish health and plankton populations [11]. Regarding this issue, Ali et al. [12] declared a strong linkage between the poor water quality and the occurrence of tilapia mortalities in Egypt.
The increase in water temperatures during summer also has a great impact on flourishing bacterial fish pathogens directly by changing their biological properties or indirectly by changing the diversity of fish that are influenced. This may facilitate those bacteria to localize, proliferate, and enter fish tissues, which could lead to increasing the disease morbidity and mortality [13].
Egyptian fish farms have experienced multiple records of mass mortality outbreaks, mainly during the summer season, with substantial losses in farmed tilapia [14]. In this regard, Abdel-Moneam et al. [15] reported that the reason for the fish kills seemed to be attributed to multifactorial etiologies, which were triggered by various environmental factors. These authors declared that inferior water quality such as extreme levels of unionized ammonia and high water temperature have contributed to tilapia mortalities due to several bacterial pathogens such as Aeromonas hydrophila, Vibrio alginolyticus, and Vibrio cholerae in Kafr El-Sheikh. Several other researchers explained that “Summer Mortality” in tilapia is linked to a viral pathogen, as Fathi et al. [16] found that tilapia lake virus (TiLV) has been detected in tilapia affected by summer mortality in Egypt. On the other hand, Abbas et al. [17] described a case report of summer mortality syndrome in tilapia that was not linked to TiLV but caused mainly by pathogenic bacteria identified as Streptococcus agalactiae, A. hydrophila, and V. cholera. Similarly, Elsheshtawy et al. [18] proved that A. hydrophila was the causative agent of summer mortalities in semi-intensive tilapia farms in Kafr El-Sheikh. Nonetheless, disease eruptions in fish farms are not restricted to the summer months, but they could occur throughout the year. For instance, co-infections of V. alginolyticus, Aeromonas spp., and Enterococcus faecalis were recorded in early autumn during heavy mortalities of poly-cultured Nile tilapia and African catfish [19]. According to these authors, bad water quality represented by high concentrations of ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate together with high bacterial counts in water make cultured fish more vulnerable to bacterial infections. A. hydrophila, Pseudomonas fluorescens, and Streptococcus iniae were also isolated during spring, summer, and autumn seasons from 12 tilapia and carp farms experiencing severe mortalities in Kafr El-Sheikh [20]. Moreover, Enany et al. [21] identified A. hydrophila, Ps. fluorescens, and V. cholera strains in moribund tilapia during summer and winter mortalities.
Antibiotics were frequently prescribed for combating bacterial infections and even as prophylactics to reduce the occurrence of bacterial diseases of fish [22,23]. However, the inappropriate and extensive use of antibiotics directly contributes to the development of resistant bacteria in the aquatic environment [24]. This can also increase antibiotic resistance in fish pathogens and transfer this resistance also to bacterial pathogens affecting humans and land animals [25]. Antibiotic residues in aquatic products (fish fillets and their processed products) also pose high health risks to human beings [26]. Herein, the present study was carried out to investigate and characterize the pathogens, of bacterial origin, that are associated with tilapia mortality outbreaks in some Egyptian fish farms located in Kafr El-Sheikh province. Antibiotic sensitivity testing has also been carried out to effectively find the best chemotherapeutic for controlling the diagnosed bacterial infections, combating the problem of antibiotic resistance, and guiding effective fish health strategies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Outbreak Reporting and Case Detection
Sudden outbreaks associated with high mortalities have been recorded in farmed Nile tilapia at different localities in Kafr El-Sheikh province, Egypt. A total of 3 outbreaks occurred during summer seasons (2023 and 2024) in different private farms with a history of recorded mortalities during the last few years. A single outbreak has been reported in late spring of 2024. The sampled fish were reared in earthen ponds supplied with agricultural drainage from the Kafr El-Sheikh, Egypt. Diseased fish were off food, lethargic, and exhibited signs of bacterial septicemia. Of these, moribund specimens of average body weight (80.0 ± 20 g) from each region were sampled and transported on ice immediately to the Microbiology Unit at Alexandria Provincial Lab, Animal Health Research Institute, Agriculture Research Center, Alexandria, Egypt, for further examinations. Clinical and postmortem examinations were performed according to guidelines outlined by Noga [27].
2.2. Bacteriological Examination
Liver, kidney, and spleen from each specimen were aseptically cultured onto Tryptic Soy Broth (TSB; DifcoTM, Detroit, MI, USA) for pre-enrichment, incubated overnight at 30 °C. Sterile loopfuls were streaked onto Tryptic Soya Agar (TSA; DifcoTM) supplemented with 5% sheep blood to examine the hemolytic activity of the retrieved bacterial isolates. Loopfuls were also cultured on Thiosulphate Citrate Bile Salts Sucrose agar (TCBS; HiMediaTM) (the selective media for Vibrio species), Nutrient Agar (NA; DifcoTM), and Brain Heart Infusion Agar (BHIA; DifcoTM). Cultured plates were incubated for 24–48 h at 28 °C. Pure colonies were phenotypically characterized by culture morphology, Gram stain, and cell motility in semisolid media [28]. Consequently, biochemical identification of the retrieved isolates was carried out using cytochrome oxidase test, catalase test, triple sugar iron (TSI) test, salt tolerance test (NaCl 4%, 6%, 8%, and 10%), and VITEK® 2 Compact microbial identification system (BioMérieux, Marcy l’Etoile, France) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The purified isolates were cultured in TSB supplemented with 20% (v/v) glycerol and preserved at −80 °C for further molecular identification.
2.3. Molecular Screening of Bacterial Isolates
2.3.1. Genomic DNA Extraction
A total of 5 different pure-cultured bacteria were randomly selected. Molecular examination of these isolates was performed at the Central Laboratory for Evaluation of Veterinary Biologics, Agriculture Research Center, Cairo, Egypt. Briefly, the bacterial isolates were streaked onto TSB and incubated at 28 °C for 48 h. The bacterial DNA was extracted with QIAamp DNA mini kit, Catalogue No. 51304, USA, according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
2.3.2. PCR Using the Universal Bacterial Primer
According to the Supplementary Material (Table S1), PCR was performed using the universal 16S bacterial primers according to Lagacé et al. [29]. After amplification, 20 μL of PCR products were electrophoresed in 1.5% agarose gel, stained with ethidium bromide, photographed by gel documentation system, and the data was analyzed through computer software. Subsequently, amplicons were purified using QIA quick PCR Purification kit (QIAGEN, Germantown, MD, USA). Aeromonas spp. 16S rRNA gene (953 bp) was amplified using the DNA extracted from one bacterial isolate as reported by Gordon et al. [30]. The PCR products were electrophoresed, analyzed, and purified as mentioned earlier. Finally, a fraction of the purified PCR product was used for sequencing.
PCR amplification with Vibrio-specific primer (Vibrio-specific 16S rRNA) was used to amplify 663 bp from the general bacterial 16S rRNA as specified by Tarr et al. [31]. After PCR product analysis, the amplified region of the target gene was purified and prepared for sequencing.
2.4. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
The purified 16S rRNA gene fragments were sequenced using Applied Biosystems 3130 automated DNA Sequencer and a BigDye Terminator V3.1 cycle sequencing kit (Perkin-Elmer/Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA, Cat. No. 4336817). The sequencing procedures were performed at the National Laboratory for Veterinary Quality Control of Poultry Production in Giza, Egypt. The obtained sequential data were assembled, identified, and aligned against other available sequences published in the GenBank database using the BLAST search. The 16S rRNA gene (663, 953, and 1458 bp) sequences of the five selected bacterial isolates were deposited in GenBank. The phylogenetic analysis of consensus sequences was constructed by MEGA 12.0 software using the maximum-likelihood method and the confidence level was verified by bootstrap test for each branch at 1000 replicates [32].
2.5. Antibiotic Susceptibility Test
The antibiogram of the identified bacterial strains were examined using the disc diffusion methodology. The tested antimicrobial discs were penicillin (P, 10 µg), ampicillin (AMP, 10 µg), amoxycillin/clavulanic acid (AMC, 20/10 µg), trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (COT, 25 µg), ciprofloxacin (CIP, 5 µg), oxytetracycline (O, 30 µg), erythromycin (E, 15 µg), novobiocin (NV, 30 µg), and kanamycin (K, 30 µg). The antibiotic discs were placed on Mueller–Hinton agar (OxoidTM, Detroit, MI, USA) plates and incubated for 24 h at 25 °C. Inhibition zone diameters were measured, and the results were categorized as either susceptible (S), intermediate (I), or resistant (R), following the criteria established by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute [33].
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Signs and Necropsy Findings
The surviving fish had a history of anorexia, surface swimming, loss of equilibrium with no reflexes, and sudden onset of high mortalities. As shown in Figure 1, moribund and recently dead fish showed hemorrhagic patches over the skin, darkened skin color, unilateral exophthalmia, corneal opacity, eroded fins, and dropsy, and certain cases died without any signs. Internally, signs included congested kidney, enlarged friable liver, and enteritis with yellowish ascitic fluid that flowed out after dissection.
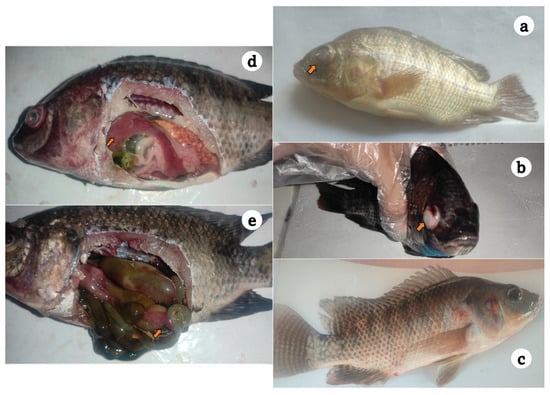
Figure 1.
Diseased Nile tilapia sampled from private farms at Kafr Elsheikh governorate showing unilateral exophthalmia (a), darkened skin color and corneal opacity (b), surface hemorrhages over the fish skin and hemorrhagic vent (c), friable and congested liver (d), and enteritis, inflamed intestinal tract, and yellow abdominal dropsy (e).
3.2. Distribution and Diversity of Bacterial Isolates
According to Table 1, a total of 30 (n) bacterial isolates were recovered from the examined tilapia specimens, which were phenotypically identified following the standard protocol described for bacterial isolation and identification. Out of the retrieved bacteria, 17 isolates were identified as Gram-positive bacteria, while the other 13 isolates were Gram-negative bacteria. The bacterial isolates were grouped into five different genera: Aeromonas spp., Vibrio spp., Aerococcus spp., Enterococcus spp., and Staphylococcus spp. The first outbreak was documented during the summer of 2023, in which the isolated bacteria was identified as Aeromonas veronii (n = 9). The second case occurred in spring of 2024, which was linked to Aerococcus viridans (n = 5). On the other hand, co-infecting pathogens have been reported in several fish samples of the third case, including Enterococcus faecalis (n = 7) and Staphylococcus epidermidis (n = 5) during the summer of 2024. In the last outbreak, Vibrio alginolyticus (n = 4) were retrieved from diseased fish during summer season of the same year. The distribution of these bacteria in various tissues of infected fish was (n = 13) in the liver, followed by spleen (n = 9) and kidney (n = 8).

Table 1.
Outbreaks and the sources of bacterial isolates retrieved from diseased Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus).
A. veronii, A. viridans, and E. faecalis showed α-hemolytic colonies on blood agar, while Staph. epidermidis revealed β-hemolytic activity and V. alginolyticus showed no hemolysis. Characteristic swarming and large yellow colonies of V. alginolyticus were also detected on TCBS selective media. Subsequently, light microscopy examination of recovered isolates revealed Gram-negative, short bacilli (A. veronii) or comma-shaped rods (V. alginolyticus) as well as Gram-positive spherical to ovoid cocci arranged in pairs (E. faecalis), long chains (A. viridans), or forming grape-like clusters (Staph. epidermidis).
3.3. Biochemical Characteristics of Bacterial Isolates
As summarized in Table 2, A. veronii were identified as oxidase- and catalase-positive, and the TSI test showed K/A reaction (alkaline slant and acidic butt) with no gas production. Similarly, V. alginolyticus were oxidase- and catalase-positive, while the TSI test showed A/A reaction (acidic slant and acidic butt) without gas production. These findings confirm the identity of both A. veronii and V. alginolyticus, which are in accordance with the expected phenotypic characteristics. Moreover, both E. faecalis and A. viridans were recorded as oxidase- and catalase-negative, whereas Staph. epidermidis were oxidase-negative and catalase-positive. Of interest, all bacterial strains showed salt tolerance up to 8% NaCl.

Table 2.
Phenotypic and biochemical characteristics of the recovered bacterial isolates.
Based on VITEK 2 biochemical identification, two isolates were confirmed and identified as E. faecalis with a probability estimated by 97% and Staph. epidermidis with a probability of 99% as reported in Supplementary Material (Table S2). The biochemical profile of E. faecalis showed typical positive reactions to production of Arginine dihydrolase2 (ADH2s), Pyrrolidonyl-arylamidase (PyrA), fermentation of ribose, sorbitol, trehalose, maltose, mannitol, mannose, and growth in media containing 6.5% NaCl. However, it tested negative for raffinose and lactose utilization, urea hydrolysis, and phosphatase production. The examined Staph. epidermidis was classified based upon positive reactions to urea hydrolysis, phosphatase production, utilization of lactose, mannose, and maltose, as well as growth in media containing 6.5% NaCl. Furthermore, this bacterial strain was typically negative to novobiocin resistance. It was also negative for ribose, sorbitol, trehalose, mannitol, and raffinose utilization tests. Based on the morphological and biochemical characters, five different bacterial strains were selected for additional molecular analysis.
3.4. 16S rRNA PCR, Sequencing, and Phylogenetic Analysis
PCR positively amplified the 1485 bp band of the 16S universal gene of A. viridans, E. faecalis, and Staph. epidermidis. Moreover, amplification bands of 953 bp and 663 bp of the 16S rRNA gene were detected specific to A. veronii and V. alginolyticus, respectively (Supplementary Material—Figures S1 and S2). The obtained sequences of these five isolates were deposited and published on GenBank database. The accession number of submitted nucleotide sequences were PV018985 for A. veronii, PV016854 for V. alginolyticus, PV013413 for E. faecalis, PV032005 for A. viridans, and PV012491 for S. epidermidis. BLAST analysis displayed high similarity and query coverage between our bacterial isolates and similar 16S rRNA sequences available on GenBank. To investigate evolutionary relationships, three maximum-likelihood phylogenetic trees were constructed based on 16S rRNA sequences using MEGA version 12.
A. veronii showed 100% similarity with (OQ625319) from Egypt, (PP727196–OQ255610–PV450195) from India, (PQ849052–PV653443) from Bangladesh, and (PV865519) from China. The derived maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree showed clear clustering of the sequenced 16S rRNA gene of A. veronii with their related sequences and separated from other Aeromonas spp., as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree showing clear clustering of the partial 16S rRNA gene sequence of A. veronii with other related partial 16S rRNA gene sequences of Aeromonas species with out-group Bacillus subtilis uploaded from the GenBank database. Phylogenetic analyses were conducted with MEGA12.0 software, using the maximum-likelihood method with Hasegawa–Kishino–Yano model with Gamma distribution (G). Percentage bootstrap values (1000 replicates) are shown at each branch point. The scale bar 0.050 represents substitutions per nucleotide position. The isolate recovered in the present study is marked with a solid blue circle.
V. alginolyticus shared 100% identity with (PV639165–PV639165) from Italy, (PV981846–PV833932) from India, and (PV984361–PV931893) from China. A maximum-likelihood-based phylogenetic tree revealed the evolutionary relatedness of the sequenced V. alginolyticus and their related sequences combined with another Vibrio spp., as represented in Figure 3.
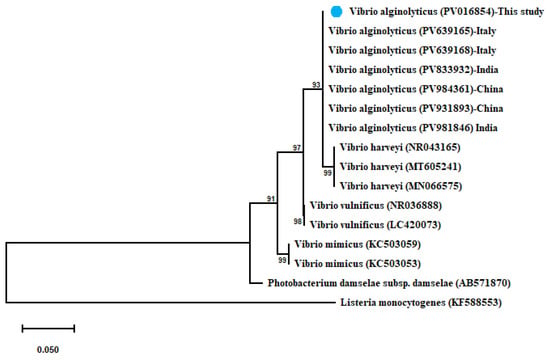
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree showing the relationship of the partial 16S rRNA gene sequence of V. alginolyticus with other related partial 16S rRNA gene sequences of Vibrio species with Listeria monocytogenes as out-group uploaded from the GenBank. Phylogenetic analyses used the maximum-likelihood method with the Kimura 2-parameter model with Gamma distribution (G). Percentage bootstrap values (1000 replicates) are shown at each branch point. The scale bar 0.050 represents substitutions per nucleotide position. The isolate recovered in the present study is marked with a solid blue circle.
In the same way, A. viridans showed 100% similarity with (HQ425688) from China, (AB680271) from Japan, (MN513224) from Republic of Korea, and (KY435764) from Malaysia, and this strain was 99.85% similar to (LC258156) from Japan. Moreover, E. faecalis shared 100% identity with (PQ497692) from Brazil and was 99.86% similar to (PV902291) from China and (PV682625) from South Korea. The sequenced S. epidermidis exhibited 100% similarity with (PV524033) from Turkey, (PV761041–PV571681) from India, (PQ849138–PQ849142) from Bangladesh, and (PV361796) from Iraq. The obtained maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of the identified three sequences was clustered with each and with their relevant sequences, as illustrated in Figure 4.
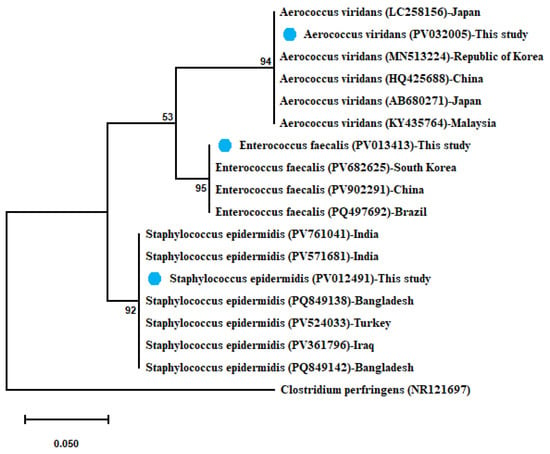
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic tree showing clear clustering of 16S rRNA partial sequences of E. faecalis, A. viridans, and Staph. epidermidis with out-group Clostridium perfringens retrieved from GenBank database. The maximum-likelihood method used the Jukes–Cantor model with uniform rates. The support level in percentage, after 1000 repetitions, is indicated next to each branch. The scale bar 0.050 represents substitutions per nucleotide position. The isolates recovered in the present study are marked with solid blue circles.
3.5. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profile
The antibiogram findings are outlined in Table 3. V. alginolyticus strain showed marked resistance to all antimicrobials used. Furthermore, A. viridans strain displayed high resistance to most antibiotics except intermediate sensitivity to amoxycillin/clavulanic acid and ciprofloxacin. However, some isolates were recorded susceptible to antibiotics; for instance, A. veronii strain was highly sensitive to amoxycillin/clavulanic acid, oxytetracycline, kanamycin, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and was intermediately susceptible to ciprofloxacin. In addition, E. faecalis strain was also found sensitive to amoxycillin/clavulanic acid, ciprofloxacin, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and was moderately susceptible to ampicillin and kanamycin. High antibiotic sensitivity was expressed by Staph. epidermidis strain to ampicillin, amoxycillin/clavulanic acid, oxytetracycline, novobiocin, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and it showed intermediate susceptibility to kanamycin and ciprofloxacin.

Table 3.
Results of the antibiotic sensitivity test using the disc diffusion method.
4. Discussion
Tilapia mass mortalities, particularly during summer seasons, represent a puzzling dilemma in Egyptian aquaculture. In this study, deteriorating water quality associated with high water temperatures was observed during the eruption of clinical infections. In addition, fish were cultivated in earthen ponds that were supplied with agriculture drainage water. A total of 30 bacterial isolates were retrieved from cultured O. niloticus encountered in heavy mortalities between August 2023 and 2024 in Kafr El-Sheikh province. The bacterial species were recognized as A. veronii (30%), V. alginolyticus (13.3%), E. faecalis (23.3%), A. viridans (16.7%), and Staph. epidermidis (16.7%). Accordingly, the Gram-positive bacteria were the prevalent group with approximately 57% of the isolates, while the remaining 43% represented the Gram-negative. Prior to 2009, Gram-negative bacteria were the predominant etiological agents of bacterial infections in Egyptian aquaculture. From 2009 to date, Gram-positive bacteria have been frequently isolated in many disease outbreaks [34]. Str. agalactiae, E. faecalis, and Lactococcus garvieae have been reported as the most significant bacterial species causing disease outbreak in Kafr El-Sheikh’s tilapia farms [35]. E. faecalis and A. viridans were serious causative agents that cause disease problems in tilapia farms in El Fayoum and El Sharkia governorates [36]. This might be attributed to various challenges such as sewage pollution, high organic loads in earthen ponds, and use of untreated poultry manure as pond fertilizers, which could add new pathogens to tilapia production systems [37,38,39].
In the current study, we report four different cases of sudden outbreaks among farmed Nile tilapia along these lines. In the first case, A. veronii was recorded in mortality episodes of farmed tilapia in August of 2023. Elgendy et al. [40] reported that A. veronii was a critical pathogen causing hemorrhagic septicemia and tilapia mortalities during the summer season in Kafr El-Sheikh. Raised water temperatures, high unionized ammonia levels, and high water pH were considered the most prominent contributing factors that could increase the risk of A. veronii infection [41,42]. The interaction between this pathogenic bacteria, impaired fish immunity, and poor water quality on initiating summer mortality has been investigated [43].
In the second case, A. viridans was recovered from moribund tilapia during mass kills in late spring of 2024. This bacterial infection was firstly reported by Ke et al. [44] in a commercial fishery of tilapia during spring and summer seasons in China. It has emerged as a serious fish pathogen and is considered a new candidate for tilapia aquaculture in Egypt [45]. Elgohary et al. [36] revealed the highest rate of A. viridans infection among O. niloticus in spring at El Fayoum; however, it had a high prevalence in the summer at El Sharkia governorate.
The mixed infection of Staph. epidermidis and E. faecalis was detected in several specimens gathered from tilapia mortality in June of 2024. Saleh et al. [34] clarified that Staph. epidermidis has been reported as a prevalent pathogen, causing mass mortality in farmed tilapia in Kafr Elsheikh. Those authors hypothesized that the practice of irrigating farms with the same canal water used for wastewater drainage facilitated the spread of Staph. epidermidis and reinfection in the affected farms. Another study pointed to their involvement in summer mortalities of tilapia fries within the same geographical area [46]. Furthermore, E. faecalis is among the most severe and frequent infections targeting tilapia fish farms, particularly during summer months in Egypt [47,48]. Abdelsalam et al. [19] also documented a case report of mortalities in cultured tilapia and African catfish due to co-infection of E. faecalis with Aeromonas spp., and V. alginolyticus. It was noted that E. faecalis could induce severe economic losses in tilapia farms, especially when accompanied by other co-infecting agents. This could be linked to synergetic interactions between two or more bacterial pathogens, which lead to worsening the fish’s health status and accelerating the progression and increasing the intensity of disease [49].
V. alginolyticus has been isolated from the mortality outbreak affecting tilapia fish in August of 2024. Coinciding with these results, Ali et al. [50] identified V. alginolyticus among bacterial isolates causing summer mortality syndrome of Nile tilapia at different localities, including Kafr El-Sheikh. Previous studies investigated V. alginolyticus in cultured O. niloticus and Tilapia zillii as well as V. alginolyticus and V. vulnificus infection in farmed tilapia [51,52]. The epidemiology, geographical spread, and frequency of vibriosis is obviously increased by climate change combined with environmental pollution. This explains why Vibrio spp. could thrive and cause disease even in low-salinity environments [53].
In this study, we suppose that higher water temperatures during summer play a key role in these outbreaks. The deleterious effects of elevated water temperature could induce a stressful condition, which successively decreases the fish immunity and increases their susceptibility for infection [54,55]. On top of that, it also allows bacterial pathogens to locate, multiply, and attack stressed fish through different mechanisms [56]. The virulence factors such as adhesions, motility, endotoxins, iron acquisition, proteolytic enzymes, and hemolysins were responsible for the infection scenario of Gram-negative bacteria [57]. On the other hand, the biofilm formation of Staph. epidermidis and lipoteichoic acid of E. faecalis facilitate their pathogenesis in the affected host [58,59]. Therefore, the virulence factors could enable these pathogens to initiate clinical disease. The affected fish showed similar signs of septicemia, including anorexia, detached scales, skin pigmentation, ulcers, exophthalmia, corneal opacity, fin rot, ascites, and hemorrhages on external body surfaces [60]. The macroscopic findings were similar to those that were listed by Ghetas et al. [61], such as congestion of liver, spleen, and kidney and the abdominal cavity being filled with watery and bloody fluids. Moreover, we tested the hemolytic activity of the isolated bacteria on sheep blood agar and found that A. veronii produced α-hemolytic colonies as described by Sadique et al. [62], while this result differs from Sun et al. [63], who found that this strain was β-hemolytic. V. alginolyticus showed no hemolysis, as reported in similar previous studies [64,65]. Both A. viridans and E. faecalis demonstrated α-hemolytic activity [35,36]. In this study, Staph. epidermidis showed β-hemolysis [66]; however, it also produced either α-hemolytic colonies [67] or showed no hemolysis [34].
The 16S rRNA sequencing has become a reliable molecular tool for accurate identification and fast diagnosis of bacterial infections [68]. Bacterial isolates were genotypically categorized using sequencing and BLAST analysis of 16S rRNA gene. Sequencing verified that retrieved isolates belonged to the genus Aeromonas, Vibrio, Aerococcus, Enterococcus, and Staphylococcus spp. By comparing obtained nucleotide sequences, isolates were similar to their related bacteria (>99.5%) and identified as A. veronii (PV018985), V. alginolyticus (PV016854), E. faecalis (PV013413), A. viridans (PV032005), and Staph. epidermidis (PV012491).
The economic losses associated with summer mortality syndrome are very costly in O. niloticus farming in Egypt. Therefore, investigating the etiologies and triggers behind such mortalities is highly required to recommend the best corrective action. Thermal stress accompanied by heatwaves was the major trigger resulting in consequent stress responses, involving decreased D.O. level, elevated toxic ammonia concentrations, oxidative stress, and increasing plasma cortisol. Fish turned immune-compromised and subsequently highly vulnerable to infectious diseases [69]. Tilapia farms relied mainly on agriculture drainage water and treated wastewater that contain various bacterial pathogens, specifically aeromonads, Vibrios, and enterococci, causing health hazards to fish and aquatic animals [38,70]. As a result, these bacteria are recognized as opportunists that can invade stressed fish and initiate the disease [71]. Ali et al. [12] declared that there was a significant correlation between water sources (surface and irrigation canals) and both the incidence and level of unusual tilapia mortalities. Intensification also contributed to tilapia disease outbreaks worldwide, with bacterial infections resulting in morbidities, mortalities, and influencing sustainable production [72]. So, bad farming practices and biosecurity measures have a crucial role in disease occurrence [73].
Antibiotics are used violently in agricultural activities, including in aquaculture, humans, and livestock, making them ubiquitous in aquatic ecosystems, posing serious health risks to the exposed aquatic animals and humans [74,75]. The antibiotic sensitivity (antibiogram) test is usually carried out to evaluate the susceptibility of bacteria to field-used antibiotics. The bacterial isolates retrieved from diseased Nile tilapia farmed in Kafr El-Sheikh province, Egypt, showed variability to the antibiogram tests. For instance, A. hydrophila, Ps. fluorescens, and Str. iniae isolated from diseased Nile tilapia showed high sensitivity to ciprofloxacin [20]. According to El-Gohary et al. [76], most of the isolated aeromonad species displayed the highest resistance to chloramphenicol, azithromycin, and kanamycin, while showing lower resistance against streptomycin, amoxicillin, and cefotaxime. These differences may be attributed to the presence of different antibiotic resistance genes in the bacterial isolates.
Our study emphasized that most bacterial strains revealed a notable resistance to tested antibiotics. V. alginolyticus strain showed high resistance against all antibacterials: penicillin, ampicillin, ciprofloxacin, oxytetracycline, erythromycin, novobiocin, amoxycillin/clavulanic acid, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, and kanamycin. Moreover, A. viridans strain was resistant to all antibiotics except for intermediate sensitivity to amoxycillin/clavulanic acid and ciprofloxacin. According to previous review, multiple registered antibiotics were available to combat bacterial infections in Mediterranean finfish farming, including fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines, penicillin, potentiated sulfa, and chloramphenicol. The same authors explained that oxytetracycline and quinolone drugs are the most used antibiotics in aquaculture [77]. Sulfonamides (sulfamethoxazole or the combined form sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim) represent the third most prevalent antimicrobial after tetracyclines and quinolones used in fish farming [78]. Recently, Elsherbiny et al. [79] confirmed that tetracyclines, quinolones, and sulfonamides are major antimicrobial classes used in aquaculture. The inappropriate use of drugs or inaccurate doses derived from rushed diagnosis without any veterinarian supervision will lead to the presence of bacterial resistance to these antimicrobials [80]. Conversely, A. veronii strain showed high sensitivity to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, amoxycillin/clavulanic acid, oxytetracycline, and kanamycin and moderate sensitivity to ciprofloxacin. These findings align with El Latif et al. [81], who presented that A. veronii was only sensitive to sulfamethoxazole–trimethoprim and ofloxacin and resistant to ampicillin, gentamycin, lincomycin, tetracycline, and oxytetracycline. Another study established that this strain was sensitive to florfenicol, sulfamethoxazole–trimethoprim, ciprofloxacin, chloramphenicol, enrofloxacin, and nitrofurantoin and resistant to penicillin, ampicillin, and amoxicillin [42]. Our study demonstrated that E. faecalis strain was sensitive to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, amoxycillin/clavulanic acid, and ciprofloxacin and was partially susceptible to ampicillin and kanamycin. These results agree with Abu-Elala et al. [35], in which E. faecalis was susceptible to sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim and penicillin, intermediately resistant to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid and ciprofloxacin but resistant to ampicillin, erythromycin, neomycin, streptomycin, and gentamycin. Abdel-moneam et al. [82] declared that this isolate was sensitive to ciprofloxacin, trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole, levofloxacin, chloramphenicol, and penicillin. In addition, Staph. epidermidis strain exhibited a high degree of sensitivity to ampicillin, amoxycillin/clavulanic acid, oxytetracycline, novobiocin, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and intermediate susceptibility to kanamycin and ciprofloxacin. These results seem to be consistent with Kubilay and Uluköy [66], who found that this strain was sensitive to ciprofloxacin, trimethoprim, sulfamethoxazole, norfloxacin, and chloramphenicol and resistant to erythromycin, penicillin, ampicillin–sulbactam, ampicillin, gentamycin, oxytetracycline, and streptomycin. Finally, these antibiotics that showed sensitivity could be recommended for control during the peak of disease only. However, vaccination programs, probiotics, and enhanced production systems are three examples that are considered valid alternative practices to reduce the use of antibiotics in aquaculture [78].
5. Conclusions
The present study reported five bacterial strains, A. veronii, V. alginolyticus, E. faecalis, and Staph. Epidermidis, that have been isolated and characterized from different mass tilapia mortalities during summer months of 2023 and 2024 in Kafr El-Sheikh province, Egypt. High water temperatures during summer may contribute to increasing the risk of these infections. E. faecalis and Staph. epidermidis have been occurring as bacterial co-infections and appear to result in high mortality rates and significant economic losses in farmed fish. Moreover, A. viridans has been identified as an emerging bacterial pathogen for tilapia aquaculture. The most worrying aspect is the high antibiotic resistance in the isolated strains against most of the tested antibiotics. Thus, it is crucial to perform antibiogram testing prior to administering antibiotics in aquaculture to guarantee effective treatment and to minimize the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms13112448/s1, Figure S1. PCR amplification of the 16S rRNA gene of Gram-negative bacterial strains isolated from diseased Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Lane (P): the control positive sample; lane (N): the negative control sample; 100 bp DNA ladder; and lane (V1): the Vibrio sample. The PCR products shown correspond to the predicted molecular mass of 663 bp (16S rRNA gene). In addition, lane (A) represents the Aeromonas sample. The PCR products shown correspond to the predicted molecular mass of 953 bp (16S rRNA gene). Figure S2. PCR amplification of the universal 16S rRNA gene of Gram-positive bacterial strains isolated from diseased Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Lane (P): the control positive sample; lane (N): the negative control sample, 100 bp DNA ladder; lane (1): the Enterococcus faecalis sample; lane (2): the Staphylococcus epidermidis sample; and lane (8): the Aerococcus viridans sample. The PCR products shown correspond to the predicted molecular mass of 1485 bp (16S rRNA gene). Table S1: Primers used in this study. Table S2. Biochemical profile of bacterial isolates using VITEK 2 with 97% probability of E. faecalis and 99% probability of Staph. epidermidis.
Author Contributions
M.M.A.H.: Fish sampling; Laboratory examination; Methodology; Writing—original draft; R.H.K.: Methodology; Funding acquisition; Validation; M.M.A.: Investigation, Methodology, Validation; M.T.A.: Investigation, Validation, Methodology; H.M.R.A.-L.: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing—review and editing. All authors share the same contribution to the works conducted in the present study. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The protocols including fish sampling and handling were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use committee, Alexandria University, under Approval Number AU013091020230360, Approval Date: 9 October 2023.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Soliman, N.F.; Yacout, D.M.M. Aquaculture in Egypt: Status, constraints and potentials. Aquac. Int. 2016, 24, 1201–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.-F.M. Tilapia Co-culture in Egypt. In Tilapia in Intensive Co-Culture; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 211–236. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, T. Diseases of Nile tilapia with special emphasis on water pollution. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 13, 29–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.-F.M.; Fitzsimmons, K. From Africa to the world—The journey of Nile tilapia. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; Wang, W. Trends of aquaculture production and trade: Carp, tilapia, and shrimp. Asian Fish. Sci. FAO 2020, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, M.M.; Elsbaay, A.M.; AbouZaher, S.E.; Abdelmotaleb, I.A. Energetic performance assessment of a thermo-solar greenhouse fish (Nile tilapia) hatchery. Misr J. Agric. Eng. 2016, 33, 1649–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, A.E.; Attia, M.M.; Elgendy, M.Y.; Ismail, G.A.; Sabry, N.M.; Prince, A.; Mahmoud, M.A.; El-Demerdash, G.O.; Abdelsalam, M.; Derwa, H.I.M. Streptococcus, Centrocestus formosanus and Myxobolus tilapiae concurrent infections in farmed Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Microb. Pathog. 2021, 158, 105084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaalan, M.; El-Mahdy, M.; Saleh, M.; El-Matbouli, M. Aquaculture in Egypt: Insights on the Current Trends and Future Perspectives for Sustainable Development. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2018, 26, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdy, S.; Mohamed, H.; Fayza, A.; Abdel-Rahman, K. Agricultural Drainage Water as a Source of Water for Fish Farming in Egypt. Ecol. Evol. Biol. 2016, 1, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; El Safty, A.; Siha, M. Current situation of water pollution and its effect on aquatic life in Egypt. Egypt. J. Occup. Med. 2013, 37, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.E.-H.; Abd El-Gawad, A.; Ali, N.; Bassuny, N. The impact of agricultural drains on water quality and Phyto-zooplankton communities in fish farms, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2013, 17, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ali, S.E.; Jansen, M.D.; Mohan, C.V.; Delamare-Deboutteville, J.; Charo-Karisa, H. Key risk factors, farming practices and economic losses associated with tilapia mortality in Egypt. Aquaculture 2020, 527, 735438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaramonte, L.; Munson, D.; Trushenski, J. Climate Change and Considerations for Fish Health and Fish Health Professionals. Fisheries 2016, 41, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Asely, A.M.; Youssuf, H.; Abdel Gawad, E.; Elabd, H.; Matter, A.; Shaheen, A.; Abbass, A. Insight into summer mortality syndrome in farmed Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) associated with bacterial infection. Benha Vet. Med. J. 2020, 39, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Moneam, D.; Ibrahim, R.; Nashaat, M.; Shaalan, M.J.B.E.A.F.P. Multifactorial causes of mass mortality in Oreochromis niloticus in Kafr El-Sheikh, Egypt. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2021, 41, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, M.; Dickson, C.; Dickson, M.; Leschen, W.; Baily, J.; Muir, F.; Ulrich, K.; Weidmann, M. Identification of Tilapia Lake Virus in Egypt in Nile tilapia affected by ‘summer mortality’ syndrome. Aquaculture 2017, 473, 430–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.; Soliman, W.; Elgendy, M.Y.; Youins, N.A.; Abu-Elala, N.M.; Marzouk, M. Insight on the potential microbial causes of summer mortality syndrome in the cultured Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2022, 26, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheshtawy, A.; Yehia, N.; Elkemary, M.; Soliman, H. Investigation of Nile tilapia Summer Mortality in Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate, Egypt. Genet. Aquat. Org. 2019, 3, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, M.; Ewiss, M.A.Z.; Khalefa, H.S.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Elgendy, M.Y.; Abdel-Moneam, D.A. Coinfections of Aeromonas spp., Enterococcus faecalis, and Vibrio alginolyticus isolated from farmed Nile tilapia and African catfish in Egypt, with an emphasis on poor water quality. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 160, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbaz, N.F.; Abd Al Fatah, M.E. Bacterial diseases outbreaks in some freshwater fish farms in Kafr El-Sheikh, Egypt. J. Appl. Aquac. 2024, 36, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enany, M.; Eidaroos, N.; Eltamimy, N. Microbial Causes of Summer Mortality in Farmed Fish in Egypt. Suez Canal Vet. Med. J. 2019, 24, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoba, E.; Adu, F.; Agyare, C.; Boamah, V. Antibiotic use and practices in selected fish farms in the Ashanti region of Ghana. J. Infect. Dis. Treat. 2017, 3, 21617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo-Bolaños, K.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, J.A.; Sancho-Blanco, C.; Barquero-Chanto, J.E.; Peña-Navarro, N.; Escobedo-Bonilla, C.M.; Umaña-Castro, R. Molecular identification of Streptococcus sp. and antibiotic resistance genes present in Tilapia farms (Oreochromis niloticus) from the Northern Pacific region, Costa Rica. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 2337–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.; Feijoó, C.G.; Navarrete, P. Antibiotics in aquaculture–use, abuse and alternatives. Health Environ. Aquac. 2012, 159, 159–198. [Google Scholar]
- Cabello, F.C. Heavy use of prophylactic antibiotics in aquaculture: A growing problem for human and animal health and for the environment. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Steele, J.C.; Meng, X.-Z. Usage, residue, and human health risk of antibiotics in Chinese aquaculture: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noga, E.J. Fish Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Buller, N.B. Bacteria and Fungi from Fish and Other Aquatic Animals: A Practical Identification Manual; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lagacé, L.; Pitre, M.; Jacques, M.; Roy, D. Identification of the Bacterial Community of Maple Sap by Using Amplified Ribosomal DNA (rDNA) Restriction Analysis and rDNA Sequencing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 2052–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, L.; Giraud, E.; Ganière, J.P.; Armand, F.; Bouju-Albert, A.; De La Cotte, N.; Mangion, C.; Le Bris, H. Antimicrobial resistance survey in a river receiving effluents from freshwater fish farms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarr Cheryl, L.; Patel Jayna, S.; Puhr Nancy, D.; Sowers Evangeline, G.; Bopp Cheryl, A.; Strockbine Nancy, A. Identification of Vibrio Isolates by a Multiplex PCR Assay and rpoB Sequence Determination. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Suleski, M.; Sanderford, M.; Sharma, S.; Tamura, K. MEGA12: Molecular Evolutionary Genetic Analysis version 12 for adaptive and green computing. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2024, 41, msae263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI M100; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twenty-Fourth Informational Supplement. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Malvern, PA, USA, 2014.
- Saleh, A.; Eissa, A.E.; Ghazy, M.A.; Makled, S.O.; Abdel-Mawgood, A. Insights into Staphylococcus epidermidis in Farmed Nile Tilapia in Egypt: Molecular Characterization and Antibiotic Resistance. Egypt. J. Vet. Sci. 2025, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Elala, N.M.; Abd-Elsalam, R.M.; Younis, N.A. Streptococcosis, Lactococcosis and Enterococcosis are potential threats facing cultured Nile tilapia (Oreochomis niloticus) production. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 4183–4195, Corrigendum in Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 5273–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgohary, I.; Eissa, A.E.; Fadel, N.G.; Ibrahim Abd Elatief, J.; Mahmoud, M.A. Bacteriological, molecular, and pathological studies on the Gram-positive bacteria Aerococcus viridans and Enterococcus faecalis and their effects on Oreochromis niloticus in Egyptian fish farms. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 2220–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Elala, N.M.; Abd-Elsalam, R.M.; Marouf, S.; Abdelaziz, M.; Moustafa, M. Eutrophication, ammonia intoxication, and infectious diseases: Interdisciplinary factors of mass mortalities in cultured Nile tilapia. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2016, 28, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.A.; Abdelsalam, M.; Mahdy, O.A.; El Miniawy, H.M.F.; Ahmed, Z.A.M.; Osman, A.H.; Mohamed, H.M.H.; Khattab, A.M.; Zaki Ewiss, M.A. Infectious bacterial pathogens, parasites and pathological correlations of sewage pollution as an important threat to farmed fishes in Egypt. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minich, J.J.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, Z.Z.; Amir, A.; Ngochera, M.; Simwaka, M.; Allen, E.E.; Zidana, H.; Knight, R. Microbial effects of livestock manure fertilization on freshwater aquaculture ponds rearing tilapia (Oreochromis shiranus) and North African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). MicrobiologyOpen 2018, 7, e00716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgendy, M.Y.; Shaalan, M.; Abdelsalam, M.; Eissa, A.E.; El-Adawy, M.M.; Seida, A.A. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles against antibiotic-resistant Aeromonas veronii infections in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.), in vitro and in vivo assay. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 901–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, A.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Abdelsalam, M.; Eissa, E.-S.H.; Sherif, A.H. Aeromonas veronii infection in cultured Oreochromis niloticus: Prevalence, molecular and histopathological characterization correlated to water physicochemical characteristics, with the protective autochthonous probiotic. Aquac. Int. 2025, 33, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, R.M.; El-Murr, A.; Abd Elhakim, Y.; El-Shahat, W. Aeromonas veronii detection in Egyptian fish farms with summer tilapia mortality outbreaks and the role of formic acid in limiting its spread. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 940–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakry, K.A.; Emeish, W.F. Aeromonas veronii causes hemorrhagic septicemia in cultured nile tilapia in qena governorate. SVU-Int. J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 5, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Lu, M.; Ye, X.; Gao, F.; Zhu, H.; Huang, Z. Recovery and pathogenicity analysis of Aerococcus viridans isolated from tilapia (Orecohromis niloticus) cultured in southwest of China. Aquaculture 2012, 342–343, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, K.M.; Al-Maary, K.S.; Mubarak, A.S.; Dawoud, T.M.; Moussa, I.M.I.; Ibrahim, M.D.S.; Hessain, A.M.; Orabi, A.; Fawzy, N.M. Characterization and susceptibility of streptococci and enterococci isolated from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) showing septicaemia in aquaculture and wild sites in Egypt. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, A.; Younis, N.A.; Moustafa, M.; Abdelaziz, M.A. Survey on the most common bacterial pathogens of the Nile tilapia fries in Kafr El sheikh governorate, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2021, 25, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.A.; Abdel-Naeim, N.S.; Mabrok, M.; Dessouki, A.A.; Hassan, A.M. Isolation and identification of Enterococcus faecalis from cultured Oreochromis niloticus and Mugil cephalus with a special emphasis on a possible integrated control strategy. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 5521–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, E.; Mahgoub, H.A.; Abdelhamid, F.; Sadeyen, J.-R.; Risha, E. Experimental pathogenesis and host immune responses of Enterococcus faecalis infection in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; El-Matbouli, M. The nature and consequences of co-infections in tilapia: A review. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.E.; Mahana, O.; Mohan, C.V.; Delamare-Deboutteville, J.; Elgendy, M.Y. Genetic characterization and antimicrobial profiling of bacterial isolates collected from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) affected by summer mortality syndrome. J. Fish Dis. 2022, 45, 1857–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.; Algammal, A.; Abouel-Atta, M.; Mabrok, M.; Emam, A. Pathogenicity, genetic typing, and antibiotic sensitivity of Vibrio alginolyticus isolated from Oreochromis niloticus and Tilapia zillii. Rev. Méd. Vét. 2019, 4–6, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Younes, A.; Fares, M.; Gaafar, A.; Mohamed, L. Isolation of Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus Strains from Cultured Oreochromis niloticus Around Qarun Lake, Egypt. Glob. Vet. 2016, 16, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, A.; Silva, V.; Poeta, P.; Aonofriesei, F. Vibrio spp.: Life Strategies, Ecology, and Risks in a Changing Environment. Diversity 2022, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.M.M.; Sultana, R.; Imran, M.; Jannat, M.F.T.; Ashaf-Ud-Doulah, M.; Rohani, M.F.; Brown, C.; Shahjahan, M. Elevated temperature affects growth and hemato-biochemical parameters, inducing morphological abnormalities of erythrocytes in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 4361–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magouz, F.I.; Moustafa, E.M.; Abo-Remela, E.M.; Halawa, M.R.; Barakaat, P.M.; Omar, A.A. Summer mortality syndrome bacterial pathogens in farmed Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Open Vet. J. 2024, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsing, F.; Barnes, A.C. The rise of the opportunists: What are the drivers of the increase in infectious diseases caused by environmental and commensal bacteria? Rev. Aquac. 2024, 16, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, J.; Reimundo, P.; Pérez-Pascual, D.; Navais, R.; Gómez, E.; Cascales, D.; Guijarro, J.A. An overview of virulence-associated factors of gram-negative fish pathogenic bacteria. Health Environ. Aquac. 2012, 5, 133–156. [Google Scholar]
- Baik, J.E.; Ryu, Y.H.; Han, J.Y.; Im, J.; Kum, K.-Y.; Yun, C.-H.; Lee, K.; Han, S.H. Lipoteichoic Acid Partially Contributes to the Inflammatory Responses to Enterococcus faecalis. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xie, T.-T.; Zeng, H. Formation, Antibiotic Resistance, and Control Strategies of Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm. In Bacterial Biofilms; Dincer, S., Sumengen Ozdenefe, M., Arkut, A., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.; Abdel-Rahman, M.; Mansour, E.S.; Monir, W. Prevalence and Antibiotic Susceptibility of Bacterial Pathogens Implicating the Mortality of Cultured Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Egypt. J. Aquac. 2020, 10, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghetas, H.; Neiana, A.; Khalil, R.; Hussein, A.M.; Khallaf, M. Streptococcus agalactiae Isolation and Characterization in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) with Histopathological Studies. J. Curr. Vet. Res. 2021, 3, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadique, A.; Neogi, S.B.; Bashar, T.; Sultana, M.; Johura, F.-T.; Islam, S.; Hasan, N.A.; Huq, A.; Colwell, R.R.; Alam, M. Dynamics, Diversity, and Virulence of Aeromonas spp. in Homestead Pond Water in Coastal Bangladesh. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 692166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X.; Jiang, Q.; Wen, Y.; Lin, L. Characterization of Virulence Properties of Aeromonas veronii Isolated from Diseased Gibel Carp (Carassius gibelio). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filik, N.; Kubilay, A. Detection of Quorum Sensing System (Cell to Cell Communication) Using Marker Strains in Vibrio alginolyticus Strains and Determine Virulence under Master of this System. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2023, 73, 4945–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Khalil, R.; Saad, T.; Abdel-latif, H. Co-infection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio alginolyticus isolated from diseased cultured European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Alex. J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 75, 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kubilay, A.; Uluköy, G. First isolation of Staphylococcus epidermidis from cultured gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) in Turkey. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2004, 24, 5368. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.-L.; Chen, W.-C.; Shei, M.-C.; Liao, I.-C.; Chen, S.-N. Studies on epizootiology and pathogenicity of Staphylococcus epidermidis in Tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) cultured in Taiwan. Zool. Stud. 1999, 38, 178–188. [Google Scholar]
- Patwardhan, A.; Ray, S.; Roy, A. Molecular markers in phylogenetic studies—A review. J. Phylogenetics Evol. Biol. 2014, 2, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; El-Nokrashy, A.; Gouda, M.; Aboyadak, I. Summer Mortality Syndrome Affecting Cultured European Seabass at Kafrelsheikh Province, Egypt. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 717360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnaggar, A.; El-Alfy, M. Physiochemical Properties of Water and Sediments in Manzala Lake, Egypt. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 45, 157–174. [Google Scholar]
- Dayana Senthamarai, M.; Rajan, M.R.; Bharathi, P.V. Current risks of microbial infections in fish and their prevention methods: A review. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 185, 106400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenen, O.L.M.; Dong, H.T.; Hoai, T.D.; Crumlish, M.; Karunasagar, I.; Barkham, T.; Chen, S.L.; Zadoks, R.; Kiermeier, A.; Wang, B.; et al. Bacterial diseases of tilapia, their zoonotic potential and risk of antimicrobial resistance. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 154–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subasinghe, R.; Alday-Sanz, V.; Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; Jie, H.; Shinn, A.P.; Sorgeloos, P. Biosecurity: Reducing the burden of disease. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2023, 54, 397–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbu, S.M. Antibiotics Use in African Aquaculture: Their Potential Risks on Fish and Human Health. In Current Microbiological Research in Africa: Selected Applications for Sustainable Environmental Management; Abia, A.L.K., Lanza, G.R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 203–221. [Google Scholar]
- Limbu, S.M.; Chen, L.-Q.; Zhang, M.-L.; Du, Z.-Y. A global analysis on the systemic effects of antibiotics in cultured fish and their potential human health risk: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 1015–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gohary, F.A.; Zahran, E.; Abd El-Gawad, E.A.; El-Gohary, A.H.; Abdelhamid, F.M.; El-Mleeh, A.; Elmahallawy, E.K.; Elsayed, M.M. Investigation of the Prevalence, Virulence Genes, and Antibiogram of Motile Aeromonads Isolated from Nile Tilapia Fish Farms in Egypt and Assessment of their Water Quality. Animals 2020, 10, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigos, G.; Troisi, G.M. Antibacterial Agents in Mediterranean Finfish Farming: A Synopsis of Drug Pharmacokinetics in Important Euryhaline Fish Species and Possible Environmental Implications. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2005, 15, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, G.; Lauteri, C.; Vergara, A. Antibiotic Resistance in the Finfish Aquaculture Industry: A Review. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsherbiny, F.; El Bayomi, R.M.; Mahmoud, A.F.A.; El-Shaieb, A.; Shosha, A.; Darwish, W.S. A review on antimicrobial residues in Aquaculture, Public Health Importance and Control Measures. Egypt. J. Vet. Sci. 2025, 56, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Nagano, I.; Masunaga, S.; Kitazawa, D.; Matsuda, H. Antibiotics, antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and resistance genes in aquaculture: Risks, current concern, and future thinking. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 11054–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Latif, A.M.A.; Elabd, H.; Amin, A.; Eldeen, A.I.N.; Shaheen, A.A. High mortalities caused by Aeromonas veronii: Identification, pathogenicity, and histopathologicalstudies in Oreochromis niloticus. Aquac. Int. 2019, 27, 1725–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-moneam, D.A.; Khalefa, H.S.; Rashad, M.M.; Ali, G.E.; Ahmed, Y.H.; Ragab, E.; Fouad, O.A.; Geioushy, R.A.; Mahmoud, S.B. Thyme-synthesized silver nanoparticles mitigate immunosuppression, oxidative damage, and histopathological alterations induced by multidrug-resistant Enterococcus faecalis in Oreochromis niloticus: In vitro and in vivo assays. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 51, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).