Bioavailability, Ecological Risk, and Microbial Response of Rare Earth Elements in Sediments of the Remediated Yitong River: An Integrated DGT and Multi-Parameter Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Sediment Property Analysis
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.2.1. DGT-Extraction Procedure
2.2.2. REE Concentration Calculation
2.3. Toxicity Data Compilation
2.4. Ecotoxicological Risk Models
2.4.1. Single-Element Risk (RQ)
2.4.2. Mixture Risk (SPI Model)
2.5. Microbial Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sediment Characteristics
3.2. Concentrations of Nutrient Elements, Metal Elements, and Rare Earth Elements
3.3. Correlation Between Sediments, Nutrient Elements, Metal Elements and Rare Earth Elements
3.4. Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment
3.4.1. Risk Assessment of Individual Rare Earth Elements
3.4.2. Probabilistic Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment
3.5. Analysis of Microbial Diversity and Its Correlation with Environmental Factors
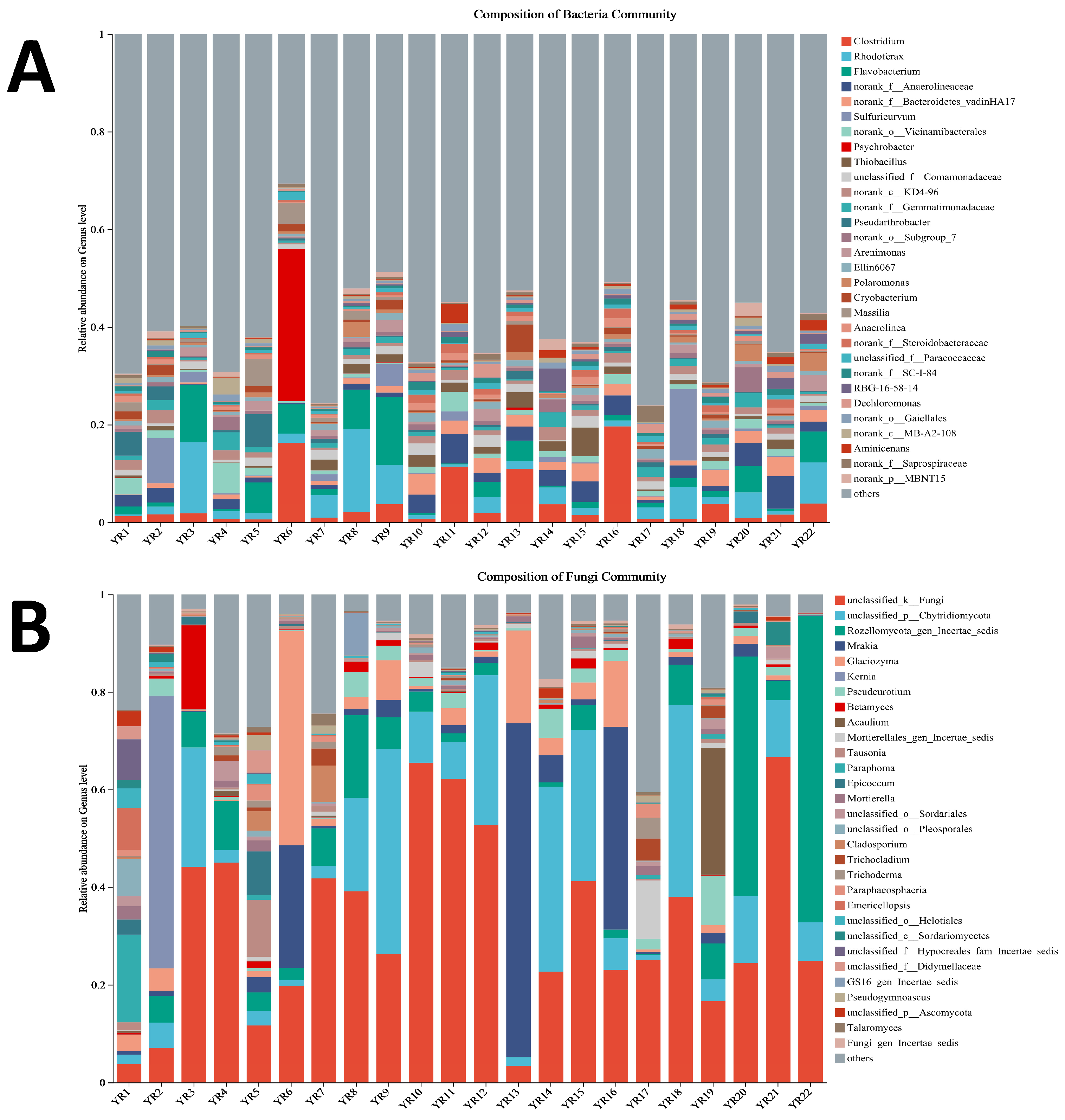
3.5.1. Analysis of Microbial Diversity
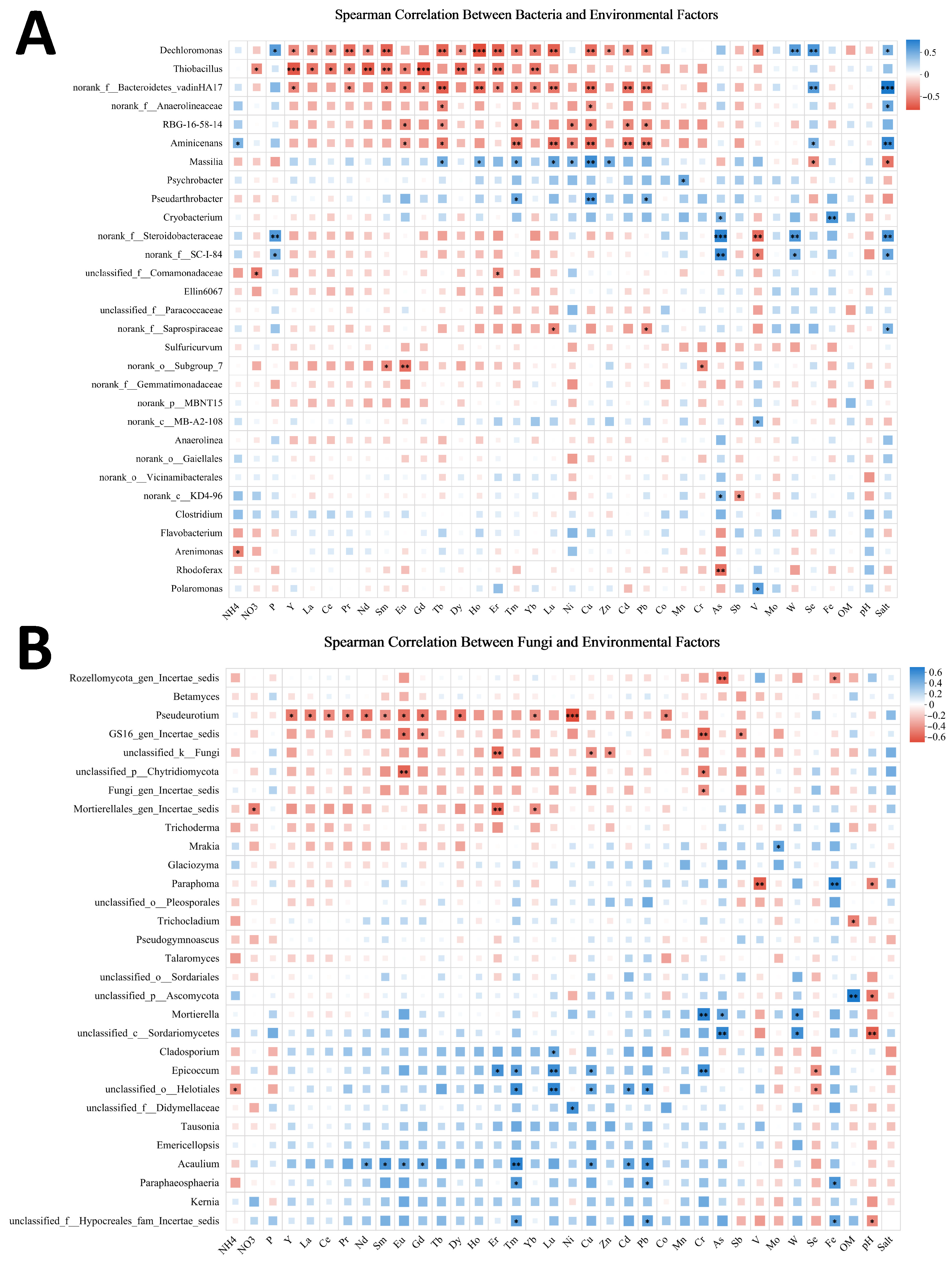
3.5.2. Correlation Analysis Between Microbial Diversity and Environmental Factors
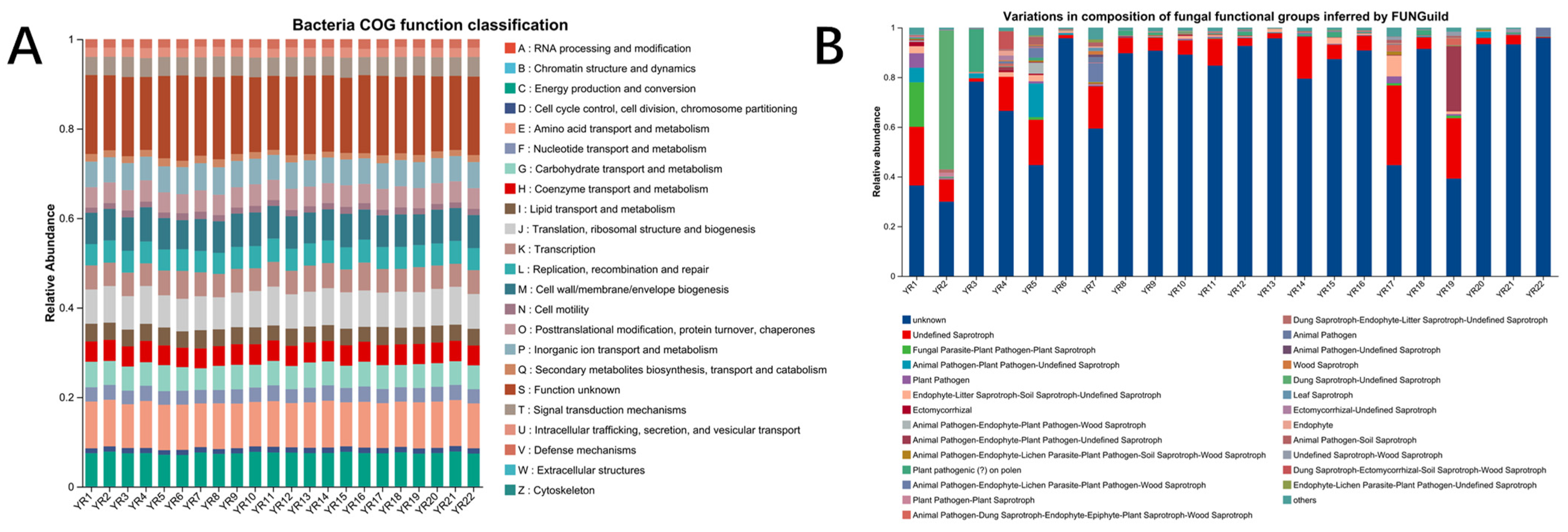
3.5.3. Microbial Function Prediction on Bacterial and Fungus Community
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheisson, T.; Schelter, E.J. Rare earth elements: Mendeleev’s bane, modern marvels. Science 2019, 363, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opare, E.O.; Struhs, E.; Mirkouei, A. A comparative state-of-technology review and future directions for rare earth element separation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 143, 110917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.N.; Gu, Y.G.; Wang, Z.H. Rare earth elements in different trophic level marine wild fish species. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. 3.01—Composition of the continental crust. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier : Pergamon, Turkey; Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- MacMillan, G.A.; Chételat, J.; Heath, J.P.; Mickpegak, R.; Amyot, M. Rare earth elements in freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems in the eastern Canadian Arctic. Environ. Sci. J. Integr. Environ. Res. Process. Impacts 2017, 19, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V. Rare earth elements: A review of applications, occurrence, exploration, analysis, recycling, and environmental impact. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 1285–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.G.; Gao, Y.P.; Huang, H.H.; Wu, F.X. First attempt to assess ecotoxicological risk of fifteen rare earth elements and their mixtures in sediments with diffusive gradients in thin films. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwenzi, W.; Mangori, L.; Danha, C.; Chaukura, N.; Dunjana, N.; Sanganyado, E. Sources, behaviour, and environmental and human health risks of high-technology rare earth elements as emerging contaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.B.; Martineau, C.; Demers, I.; Basiliko, N.; Fenton, N.J. The potential environmental risks associated with the development of rare earth element production in Canada. Environ. Rev. 2021, 29, 354–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, W.; Zhang, H. In situ speciation measurements of trace components in natural waters using thin-film gels. Nature. 1994, 367, 546–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppel, D.J.; King, C.K.; Brown, K.E.; Price, G.A.V.; Adams, M.S.; Jolley, D.F. Assessing the risk of metals and their mixtures in the Antarctic nearshore marine environment with diffusive gradients in thin-films. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.G. Risk assessment of eight metals and their mixtures to aquatic biota in sediments with diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT): A case study in Pearl River intertidal zone. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, E.D.; Chamani, P.M.; Taylor, A.M.; Maher, W.A.; Simpson, S.L.; Jolley, D.F. Field and laboratory evaluation of DGT for predicting metal bioaccumulation and toxicity in the freshwater bivalve Hyridella australis exposed to contaminated sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppel, D.J.; Adams, M.S.; King, C.K.; Jolley, D.F. Diffusive gradients in thin films can predict the toxicity of metal mixtures to two microalgae: Validation for environmental monitoring in Antarctic marine conditions. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Bai, M.X.; Dong, A.; Shen, M.N. Ecological health assessment of urban rivers in the middle temperate zone based on the improved TOPSIS model—A case study of the Yitong River in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, X.B.; Jiang, X.; Huang, J.G. Comprehensive evaluation of water quality of Changchun range in Yitong River. Glob. Geol. 2012, 31, 589–593. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund: Volume III—Part A, Process for Conducting Probabilistic Risk Assessment. 2001. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-09/documents/rags3adt_complete.pdf (accessed on 4 April 2025).
- Lu, X.X.; Gu, Y.G.; Wang, Z.H.; Liang, R.Z.; Han, Y.J.; Li, H.S. Risk on assessment of 15 REEs and mixtures by DGT in Songhua River system sediments of China’s largest old industrial base. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.G.; Gao, Y.P.; Jordan, R.W.; Jiang, S.J. Dynamics of metal immobilization in coastal mariculture sediments: Insights from DGT and DIFS modeling. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 383, 126798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.B.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, J.D.; Zhang, H.D.; Zeng, Z.H.; Yang, Y.D. Characterization of antibiotic resistance genes and virulence factors in organic managed tea plantation soils in southwestern China by metagenomics. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, R.A.; Leonards, G.; Brinkman, T.; Barceló, D.; Tronczynski, J. Ecological risk assessment of agrochemicals in European estuaries. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; He, J.; Li, B.; He, B.; Huang, J.; Guo, M.; Luo, D. Hydrochemical evolution characteristics and genesis of groundwater under long-term infiltration (2007–2018) of reclaimed water in Chaobai River, Beijing. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonin, M.; Rocca, J.D.; Gerson, J.R.; Moore, E.; Brooks, A.C.; Czaplicki, L.; Ross, M.R.V.; Fierer, N.; Craine, J.M.; Bernhardt, E.S. Consistent declines in aquatic biodiversity across diverse domains of life in rivers impacted by surface coal mining. Ecol. Appl. 2021, 31, e02389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Xu, Z.; Tian, P. Habitat quality evaluation and pattern simulation of coastal salt marsh wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 174003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, D.C.; Crossley, D., Jr.; Hendrix, P.F. Fundamentals of Soil Ecology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Yuan, H.; Zhao, J.; Qi, Y.; Cao, W.W.; Liu, J.M.; Guo, W.; Bao, Z.H. Multiple factors influence bacterial community diversity and composition in soils with rare earth element and heavy metal co-contamination. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 225, 112749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, B.S.; Philippot, L. Insights into the resistance and resilience of the soil microbial community. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 112–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.Q.; Liu, W.S.; Chen, Y.M.; Chen, W.H.; Zhao, L.H.; Ding, Q.B.; Wang, S.Z.; Tang, Y.T.; Zhang, T.; Qiu, R.L. Structure, variation, and co-occurrence of soil microbial communities in abandoned sites of a rare earth elements mine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11481–11490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffner, C.; Holzapfel, S.; Wunderlich, A.; Einsiedl, F.; Schloter, M.; Schulz, S. Dechloromonas and close relatives prevail during hydrogenotrophic denitrification in stimulated microcosms with oxic aquifer material. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiab004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.R.; Yang, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, X.Y. Advances of using Dehalogenimonas in anaerobic degradation of chlorinated compounds and biore-mediation of contaminated sites. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 3565–3577. [Google Scholar]
- Borgmann, U.; Couillard, Y.; Doyle, P.; Dixon, D.G. Toxicity of sixty-three metals and metalloids to Hyalella azteca at two levels of water hardness. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.A. Effects of REEs on Development of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Master’s Thesis, Qingdao University of Science & Technology, Qingdao, China, 2011; p. 61. [Google Scholar]
- Dubé, M.; Auclair, J.; Hanana, H.; Turcotte, P.; Gagnon, C.; Gagné, F. Gene expression changes and toxicity of selected rare earth elements in rainbow trout juveniles. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 223, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, V.; Vignati, D.A.L.; Leyval, C.; Giamberini, L. Environmental fate and ecotoxicity of lanthanides: Are they a uniform group beyond chemistry? Environ. Int. 2014, 71, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucki, M.; Kejlova, K.; Vlkova, K.; Jirova, D.; Dvorakova, M.; Svobodova, L.; Kandarova, H.; Letasiova, S.; Kolarova, H.; Mannerstrom, M.; et al. Evaluation of toxicity profiles of rare earth elements salts (lanthanides). Rare Earths 2020, 39, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Tai, P.D.; Li, P.J.; Ke, X. Toxic effects of lanthanides on Chlorella autotrophica. Chin. J. Ecol. 2005, 24, 382–384, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tai, P.D.; Zhao, Q.; Su, D.; Li, P.J.; Stagnitti, F. Biological toxicity of lanthanide elements on algae. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
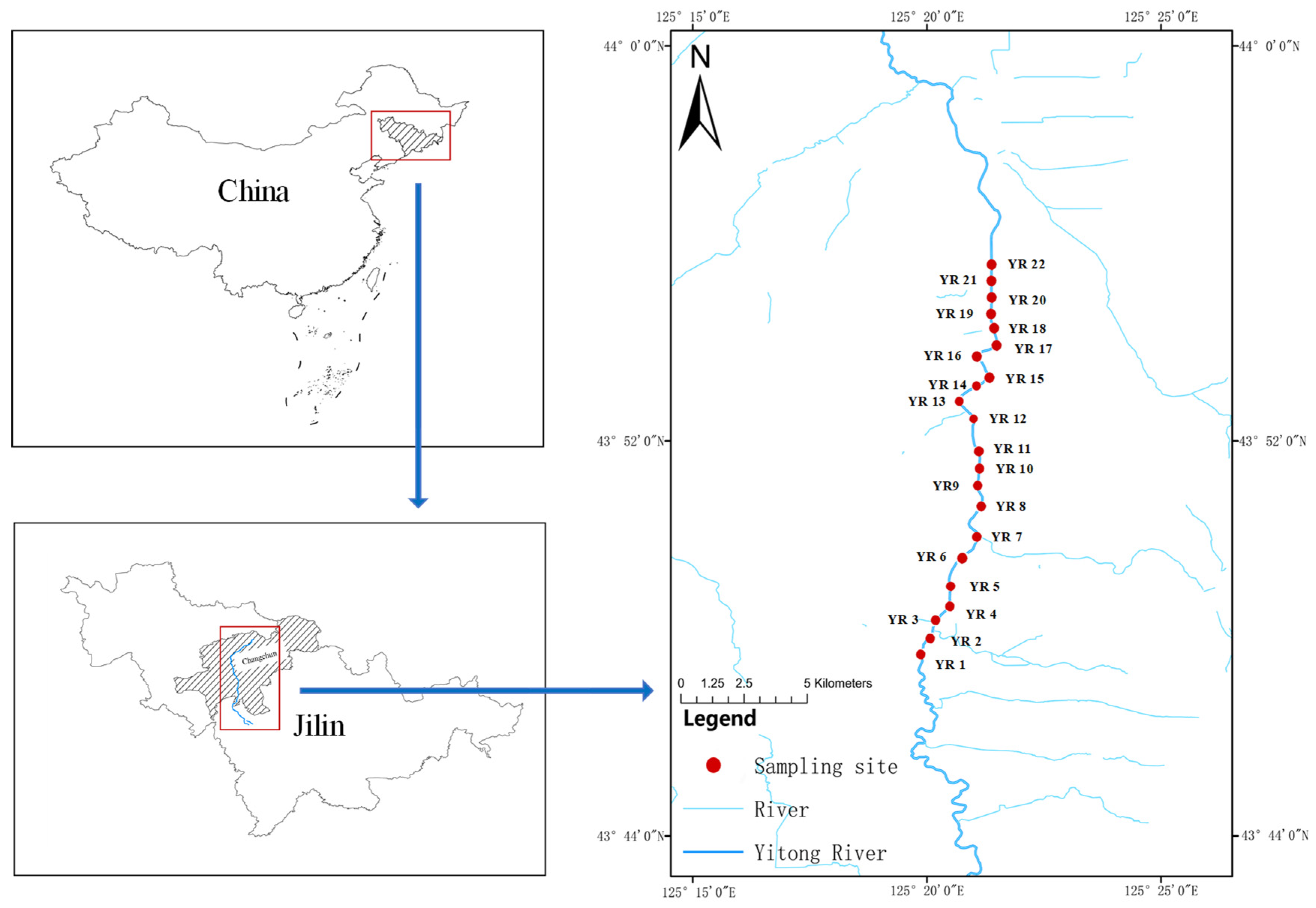
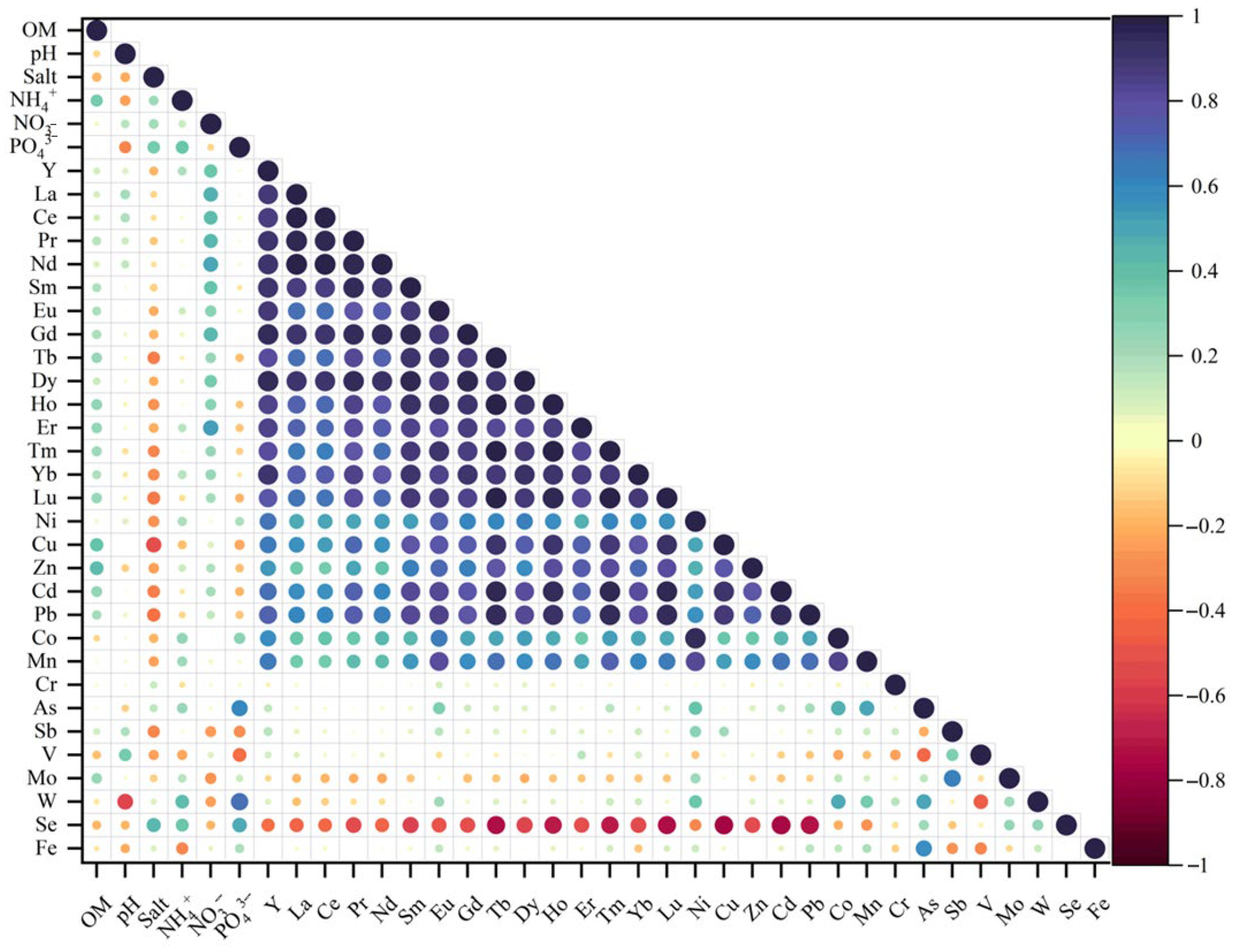

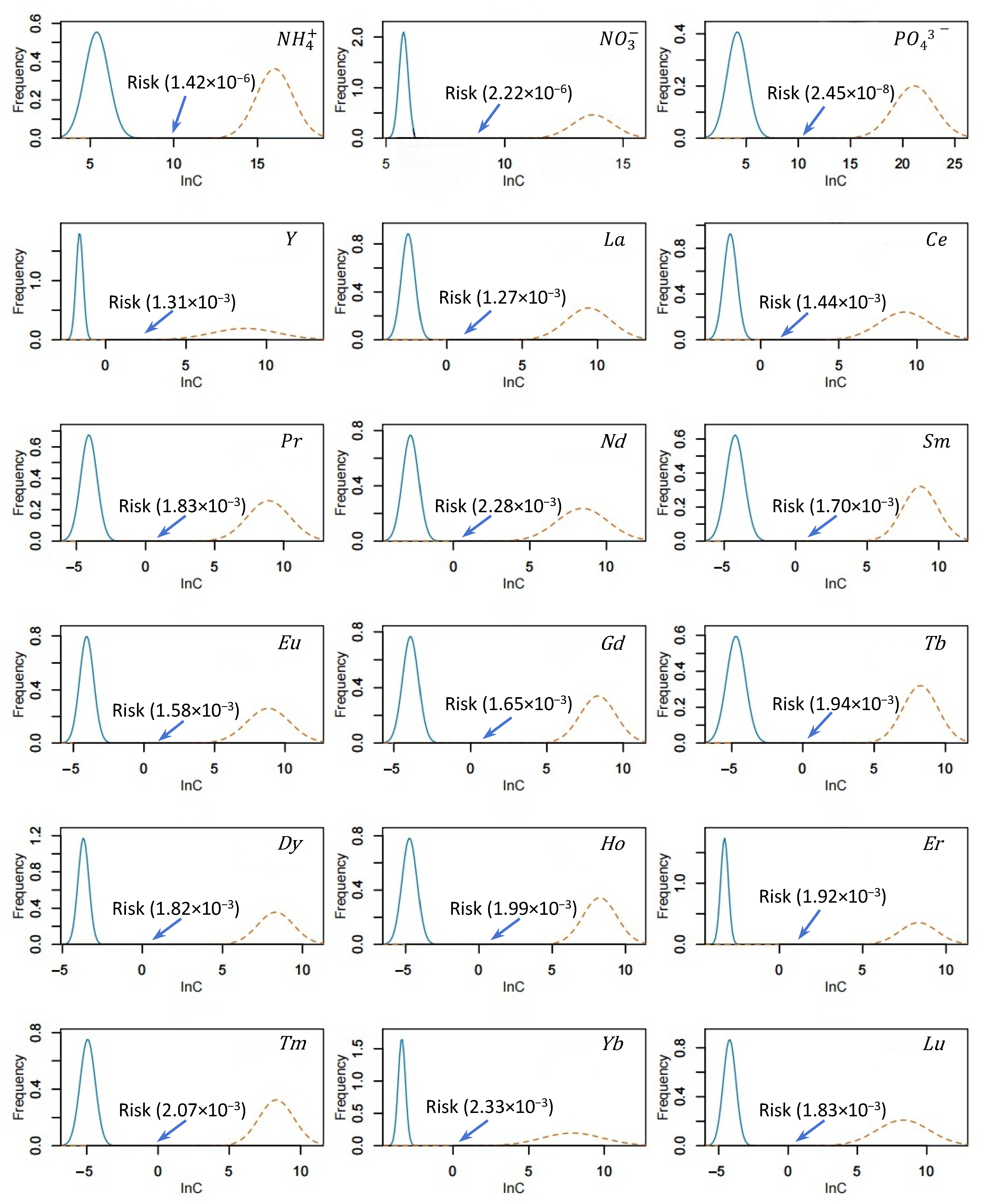
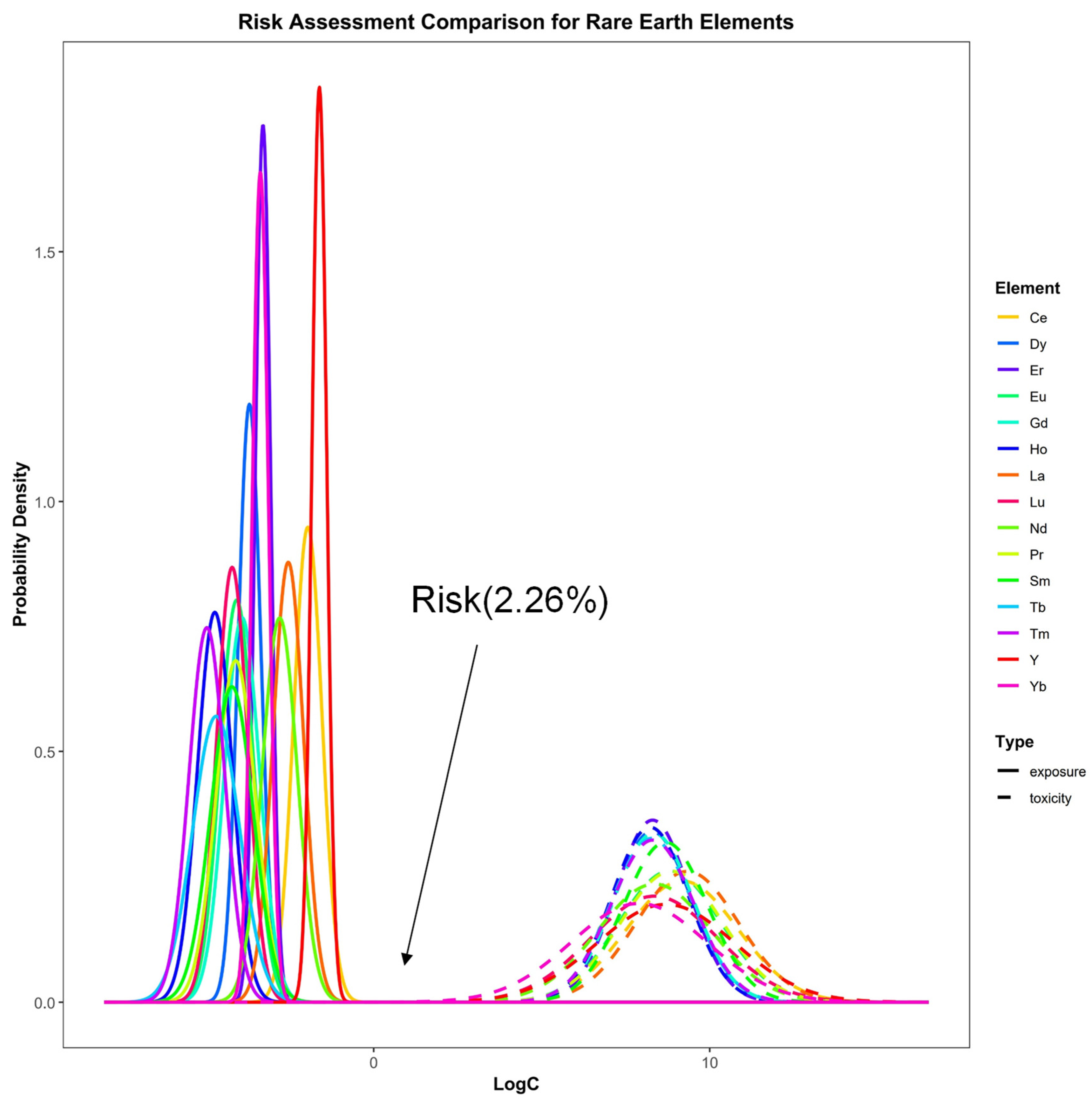
| Site | ∑REEs | LREEs | HREE | LREEs/HREEs | OM (g·kg−1) | pH | Salt (ppt) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | S.D. | Mean | S.D. | Mean | S.D. | Mean | S.D. | Mean | S.D. | Mean | S.D. | Mean | S.D. | |
| YR 1 | 1.69 | 0.01 | 0.88 | 0.01 | 0.44 | 0.00 | 2.00 | 0.01 | 45.33 | 0.93 | 7.59 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.00 |
| YR 2 | 0.88 | 0.01 | 0.41 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.00 | 1.54 | 0.03 | 49.94 | 0.71 | 7.32 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.00 |
| YR 3 | 1.47 | 0.03 | 0.91 | 0.03 | 0.29 | 0.00 | 3.18 | 0.08 | 30.38 | 0.41 | 8.40 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| YR 4 | 1.04 | 0.00 | 0.55 | 0.00 | 0.24 | 0.00 | 2.33 | 0.02 | 32.41 | 2.04 | 7.98 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.01 |
| YR 5 | 0.67 | 0.01 | 0.30 | 0.00 | 0.18 | 0.00 | 1.70 | 0.01 | 60.79 | 1.21 | 7.41 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| YR 6 | 0.87 | 0.00 | 0.42 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 2.13 | 0.06 | 21.57 | 1.12 | 8.89 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| YR 7 | 0.67 | 0.06 | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 2.20 | 0.07 | 12.93 | 0.63 | 9.26 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| YR 8 | 0.47 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 1.75 | 0.02 | 33.04 | 0.22 | 9.37 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| YR 9 | 0.55 | 0.00 | 0.27 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 2.27 | 0.08 | 32.95 | 0.44 | 8.67 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.01 |
| YR 10 | 0.45 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 1.63 | 0.16 | 23.75 | 2.77 | 9.15 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.00 |
| YR 11 | 0.56 | 0.00 | 0.28 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 2.22 | 0.02 | 29.80 | 0.63 | 7.61 | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.02 |
| YR 12 | 0.74 | 0.00 | 0.40 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 2.88 | 0.11 | 45.60 | 1.25 | 8.14 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.00 |
| YR 13 | 0.52 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 1.63 | 0.04 | 60.87 | 0.41 | 7.54 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| YR 14 | 0.69 | 0.00 | 0.34 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.00 | 2.24 | 0.08 | 77.63 | 0.08 | 8.47 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| YR 15 | 0.48 | 0.01 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 1.80 | 0.01 | 31.51 | 1.20 | 8.45 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.01 |
| YR 16 | 0.74 | 0.01 | 0.36 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.00 | 2.38 | 0.11 | 12.89 | 1.23 | 9.30 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.01 |
| YR 17 | 0.48 | 0.00 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 1.87 | 0.04 | 16.23 | 0.51 | 6.64 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| YR 18 | 0.49 | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 1.68 | 0.04 | 15.82 | 1.65 | 6.72 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.00 |
| YR 19 | 0.62 | 0.01 | 0.29 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 2.14 | 0.09 | 23.36 | 0.36 | 6.51 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.01 |
| YR 20 | 0.56 | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 1.68 | 0.07 | 10.52 | 0.50 | 8.02 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.01 |
| YR 21 | 0.60 | 0.00 | 0.30 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 2.37 | 0.11 | 31.32 | 0.39 | 6.69 | 0.06 | 0.20 | 0.00 |
| YR 22 | 1.19 | 0.01 | 0.72 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.01 | 3.69 | 0.21 | 30.54 | 1.09 | 9.49 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, Y.; Wu, C.; E, J.; Gu, Y.; Chi, H.; Du, X. Bioavailability, Ecological Risk, and Microbial Response of Rare Earth Elements in Sediments of the Remediated Yitong River: An Integrated DGT and Multi-Parameter Assessment. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112443
Zhong Y, Wu C, E J, Gu Y, Chi H, Du X. Bioavailability, Ecological Risk, and Microbial Response of Rare Earth Elements in Sediments of the Remediated Yitong River: An Integrated DGT and Multi-Parameter Assessment. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(11):2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112443
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Yu, Chanchan Wu, Jiayi E, Yangguang Gu, Hai Chi, and Xinglin Du. 2025. "Bioavailability, Ecological Risk, and Microbial Response of Rare Earth Elements in Sediments of the Remediated Yitong River: An Integrated DGT and Multi-Parameter Assessment" Microorganisms 13, no. 11: 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112443
APA StyleZhong, Y., Wu, C., E, J., Gu, Y., Chi, H., & Du, X. (2025). Bioavailability, Ecological Risk, and Microbial Response of Rare Earth Elements in Sediments of the Remediated Yitong River: An Integrated DGT and Multi-Parameter Assessment. Microorganisms, 13(11), 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112443






