In Vitro Assessment of Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized by Gamma Irradiation for Antimicrobial and Anticancer Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals Used
2.2. Mammalian Cell Lines
2.3. Preparation of PAM/Au and Chitosan/Au Nanoparticles
2.4. Irradiation Process
2.5. Antibacterial Activity of Au-NPs
2.6. Antifungal Activity of Au-NPs
2.7. Anticancer Activity of Au-NPs (MTT Assay)
2.8. Antiviral Activity of Au-NPs
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
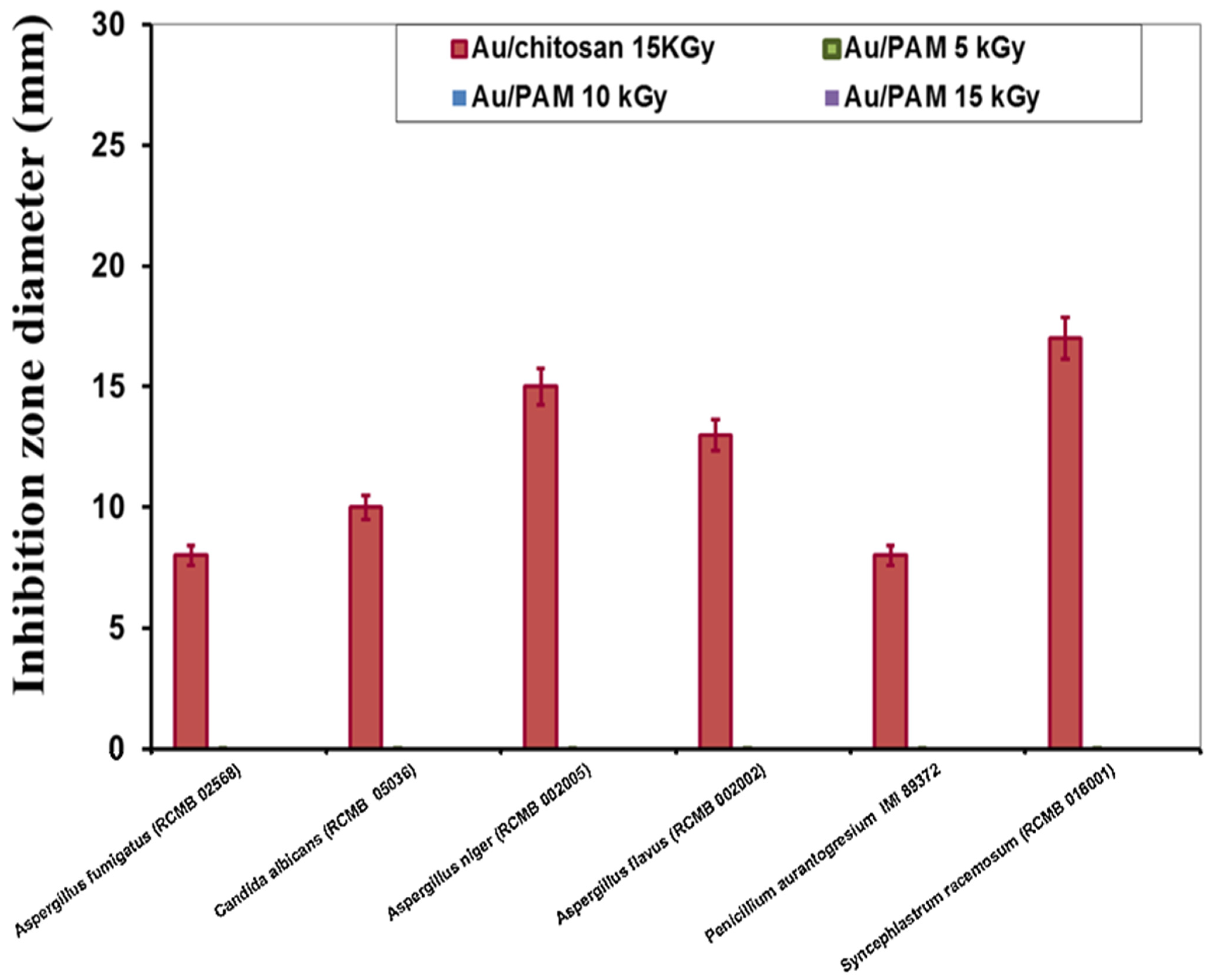
3.1. Antifungal Activity
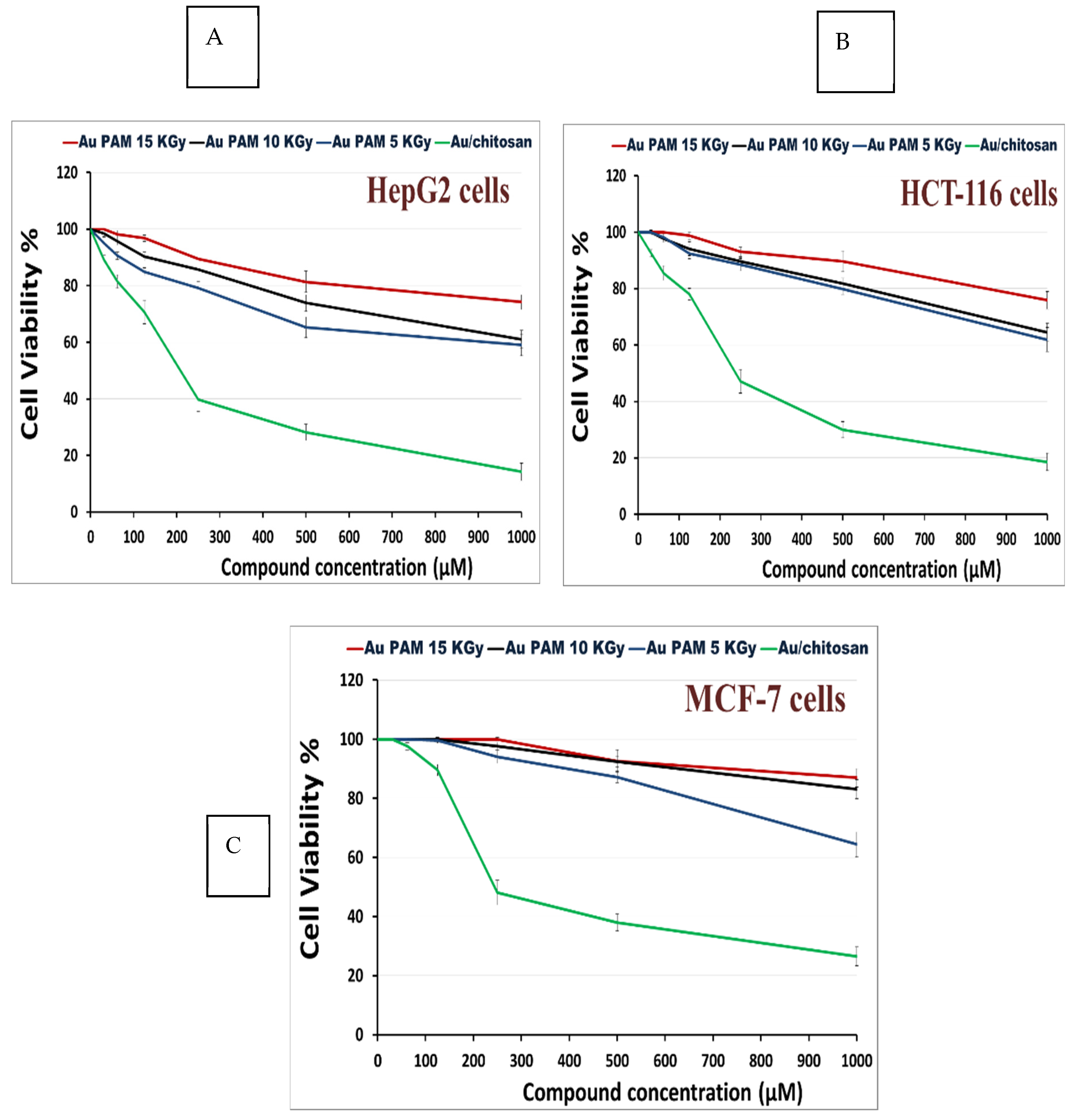
3.2. Anti-Cancer Activity
3.3. Antiviral Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boufi, S.; Vilar, M.R.; Ferraria, A.M.; do Rego, A.M.B. In situ photochemical generation of silver and gold nanoparticles on chitosan. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 439, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Lee, C.-S. Green biological synthesis of nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. In Applications of Nanotechnology for Green Synthesis; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 247–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Yeum, J.H.; Choi, J.H. Effects of Polymeric Stabilizers on the Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almajidi, Y.Q.; Gupta, J.; Sheri, F.S.; Zabibah, R.S.; Faisal, A.; Ruzibayev, A.; Adil, M.; Saadh, M.J.; Jawad, M.J.; Alsaikhan, F.; et al. Advances in chitosan-based hydrogels for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 253, 127278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Pan, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, H. Gold nanoparticles for cancer theranostics—A brief update. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2016, 9, 1630004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, C.M.; McCusker, C.D.; Yilmaz, T.; Rotello, V.M. Toxicity of gold nanoparticles functionalized with cationic and anionic side chains. Bioconjugate Chem. 2004, 15, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, S.C.; Zhao, G.; Saha, K.; Phillips, R.L.; Li, X.; Miranda, O.R.; Rotello, V.M.; El-Sayed, M.A.; Schmidt-Krey, I.; Bunz, U.H.F. Aggregation and interaction of cationic nanoparticles on bacterial surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6920–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.V.; Gunsolus, I.L.; Qiu, T.A.; Hurley, K.R.; Nyberg, L.H.; Frew, H.; Johnson, K.P.; Vartanian, A.M.; Jacob, L.M.; Lohse, S.E.; et al. Impacts of gold nanoparticle charge and ligand type on surface binding and toxicity to Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 5186–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzar, S.; Sohail, A.; Sherin, L.; Kim, P.S. Computer Methods for the Antimicrobial Efficacy of Metal Nanoparticles Against MDR Microbes. J. Nanotechnol. 2025, 2025, 8832103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, M.C.; Astruc, D. Gold nanoparticles: Assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 293–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.I.; Eisa, W.H.; Saleh, H.H.; Meligi, G.A.; El-Sokary, R. Radiation-Induced In Situ Synthesis of Gold Nanostructured Materials. Macromol. Symp. 2016, 364, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.S.; Eldehna, W.M.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; Elaasser, M.M.; Abdel-Aziz, M.M. Improvement of antibacterial activity of some sulfa drugs through linkage to certain phthalazin-1(2H)-one scaffolds. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 85, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, A.A.; Júnior Menezes, E.A.; Cunha, F.A.; Cunha, M.C.S.O.; Braz, B.H.L.; Capelo, L.G.; Silva, C.L.F. Comparação entre microdiluição e disco difusão para o teste de susceptibilidade aos antifúngicos contra Candida spp. Semin. Ciências Biológicas E Da Saúde 2012, 33, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Gomha, S.M.; Riyadh, S.M.; Mahmmoud, E.A.; Elaasser, M.M. Synthesis and Anticancer Activities of Thiazoles, 1, 3-Thiazines, and Thiazolidine Using Chitosan-Grafted-Poly (vinylpyridine) as Basic Catalyst. Heterocycles 2015, 91, 1227–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayan, P.; Raghu, C.; Ashok, G.; Dhanaraj, S.A.; Suresh, B. Antiviral activity of medicinal plants of Nilgiris. Indian J. Med. Res. 2004, 120, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Castilla-Serna, L.; Cravioto, J. Summarized Statistic for Investigation in Health Science, 1st ed.; México, D.F., Ed.; Editorial Trillas: Mexico City, Mexico, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rabea, E.I.; Badawy, M.E.-T.; Stevens, C.V.; Smagghe, G.; Steurbaut, W. Chitosan as antimicrobial agent: Applications and mode of action. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, L.R.; Mihu, M.R.; Tar, M.; Cordero, R.J.B.; Han, G.; Friedman, A.J.; Friedman, J.M.; Nosanchuk, J.D. Demonstration of antibiofilm and antifungal efficacy of chitosan against candidal biofilms, using an in vivo central venous catheter model. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 1436–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.S.; Abdelkader, A.; Mohamed, M.; Ashok, K. In Vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of a new series of benzo[g][1,2,4] triazolo [1,5-α]quinazolines. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2015, 34, 1926–1930. [Google Scholar]
- Anjum, S.; Akhtar, A.; Aldaqal, S.M.; Abduh, M.S.; Ahmad, H.; Mustafa, R.; Naseer, F.; Sadia, M.; Ahmad, T. Enhanced targeted treatment of cervical cancer using nanoparticle-based doxycycline delivery system. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prüss, A.; Kay, D.; Fewtrell, L.; Bartram, J. Estimating the burden of disease from water, sanitation, and hygiene at a global level. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 110, 537–542. [Google Scholar]
- Costerton, J.W.; Cheng, K.J.; Geesey, G.G.; ILadd, T.; Nickel, J.C.; Dasgupta, M.; Marrie, T.J. Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1987, 41, 435–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Yu, C.; Wang, Y. Promising therapeutic strategies against microbial biofilm challenges. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafer, M.M.; Mohamed, G.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Ghosh, S.; Bornman, C.; Elfaky, M.A. Biofilm-mediated infections by multidrug-resistant microbes: A comprehensive exploration and forward perspectives. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, M.; Ghosh, P.S.; Rotello, V.M. Applications of Nanoparticles in Biology. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 4225–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.E.; Chen, Z.G.; Shin, D.M. Nanoparticle therapeutics: An emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Le, N.D.B.; Gupta, A.; Rotello, V.M. Cell surface-based sensing with metallic nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4264–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Kasiakou, S.K.; Saravolatz, L.D. Colistin The revival of polymyxins for the management of multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacterial infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Iwamoto, A.; Lian, J.Q.; Neoh, H.-M.; Maruyama, T.; Horikawa, Y.; Hiramatsu, K. Novel mechanism of antibiotic resistance originating in vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Nikaido, H. Efflux-mediated drug resistance in bacteria. Drugs 2004, 64, 159–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courvalin, P. Vancomycin resistance in gram-positive cocci. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42 (Suppl. S1), S25–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, A.J.; Kwon, Y.J. “Nanoantibiotics”: A new paradigm for treating infectious diseases using nanomaterials in the antibiotics resistant era. J. Control Release 2011, 156, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.P.; Wang, L.; Benicewicz, B.C.; Decho, A.W. Inorganic nanoparticles engineered to attack bacteria. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 7787–7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, I. The increasing use of silver-based products as antimicrobial agents: A useful development or a cause for concern. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 59, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.R.; Mihu, M.R.; Han, G.; Frases, S.; Cordero, R.J.B.; Casadevall, A.J.; Friedman, A.J.; Friedman, J.M.; Nosanchuk, J.D. The use of chitosan to damage Cryptococcus neoformans biofilms. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, S.; Ingle, A.; Gade, A.; Rai, M.; Falanga, A.; Incoronato, N.; Russo, L.; Galdiero, S.; Galdiero, M. Antiviral activity of mycosynthesized silver nanoparticles against herpes simplex virus and human parainfluenza virus type. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4303–4314. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, J.; Sindac, J.A.; Barraza, S.J.; Dobry, C.J.; Blakely, P.K.; Irani, D.N.; Keep, R.F.; Miller, D.J.; Larsen, S.D. Optimization of novel indole-2-carboxamide inhibitors of neurotropic alphavirus replication. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9222–9241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Trefry, J.C.; Wooley, D.P. Silver nanoparticles inhibit vaccinia virus infection by preventing viral entry through a macropinocytosis-dependent mechanism. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 1624–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.-Y.; Chen, D.-Y.; Wen, H.-W.; Ou, J.-L.; Chiou, S.-S.; Chen, J.-M.; Wong, M.-L.; Hsu, W.-L. Inhibition of Enveloped Viruses Infectivity by Curcumin. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradowska, E.; Studzińska, M.; Jabłońska, A.; Lozovski, V.; Rusinchuk, N.; Mukha, I.; Vitiuk, N.; Leśnikkowski, Z.J. Antiviral effect of nonfunctionalized gold nanoparticles against Herpes Simplex Virus Type-1 (HSV-1) and possible contribution of near-field interaction mechanism. Molecules 2021, 26, 5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Baram-Pinto, D.; Shukla, S.; Perkas, N.; Gedanken, A.; Sarid, R. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1 infection by silver nanoparticles capped with mercaptoethane sulfonate. Bioconjugate Chem. 2009, 20, 1497–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baram-Pinto, D.; Shukla, S.; Gedanken, A.; Sarid, R. Inhibition of HSV-1 attachment, entry, and cell-to-cell spread by functionalized multivalent gold nanoparticles. Small 2010, 6, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saed, M.; Ayivi, R.D.; Wei, J.; Obare, S.O. Gold nanoparticles antibacterial activity: Does the surface matter? Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2024, 62, 100804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, M.; Ziamajidi, N.; Khodadadi, I.; Dehghan, A.; Kalantarian, G.; Abbasalipourkabir, R. The effect of insulin-loaded trimethylchitosan nanoparticles on rats with diabetes type I. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, B.; Du, J.; Chen, J.; Jiang, J.; Tugarova, A.V.; Kamnev, A.A.; et al. Selenite reduction by Proteus sp. YS02: New insights revealed by comparative transcriptomics and antibacterial effectiveness of the biogenic Se⁰ nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 845321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

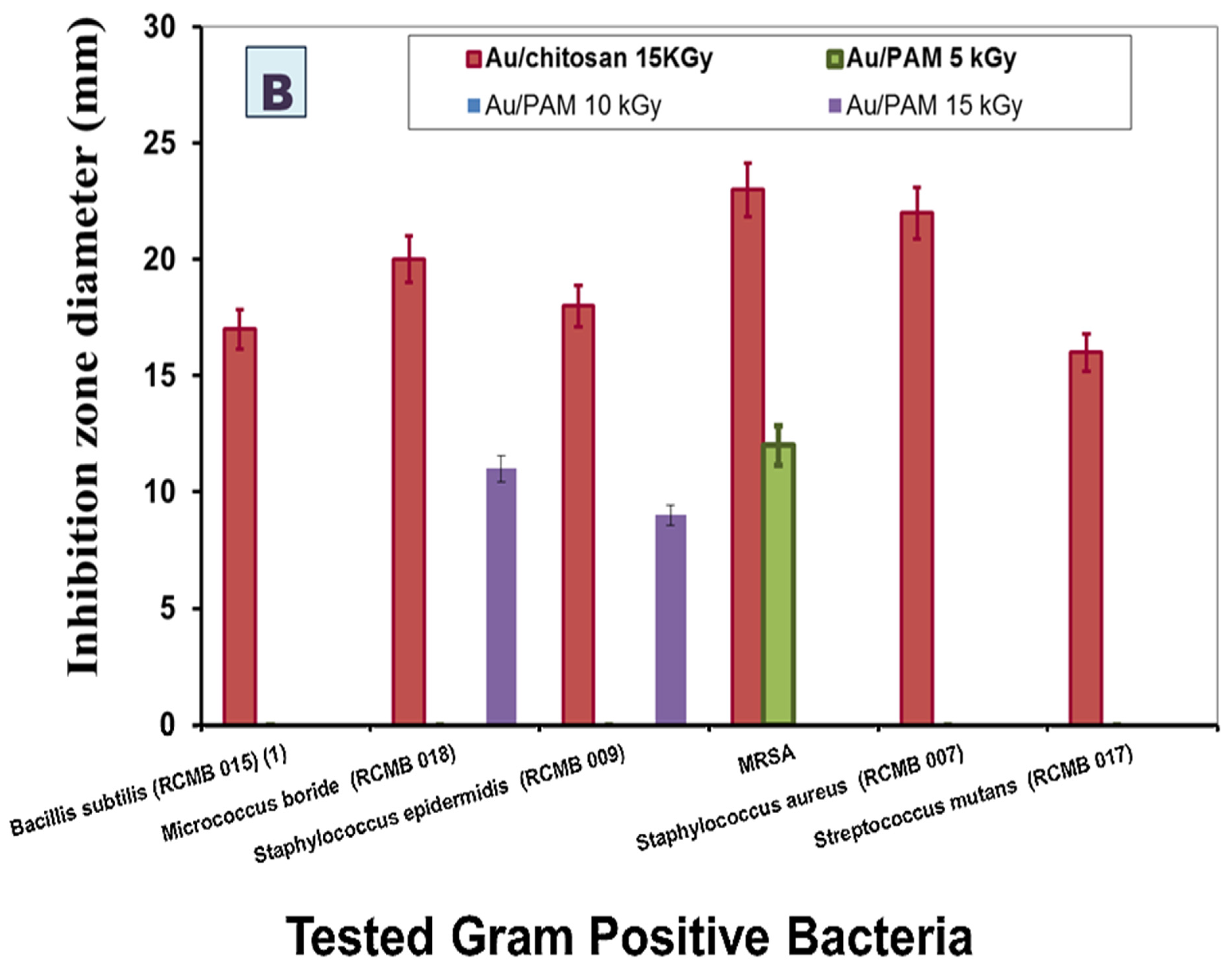
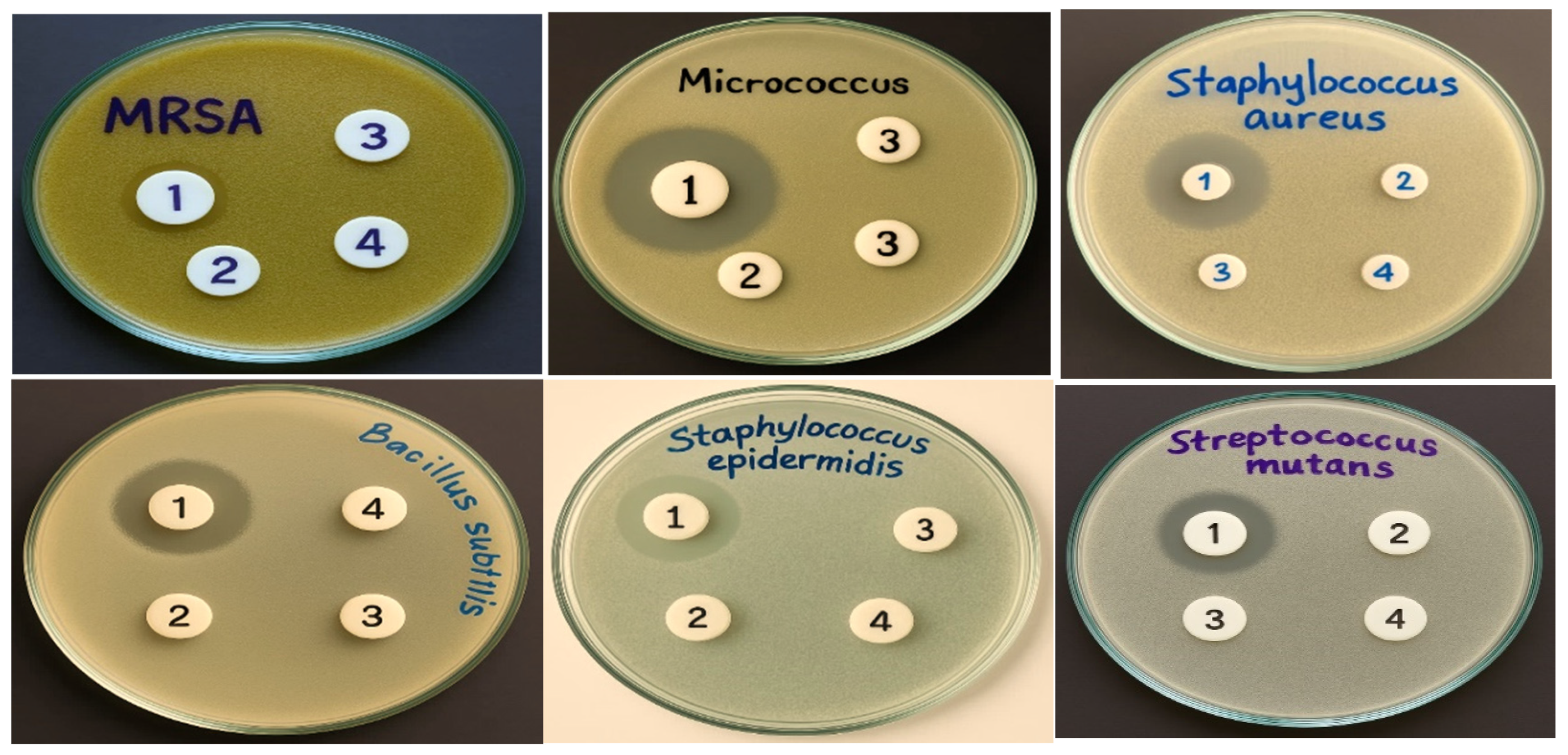
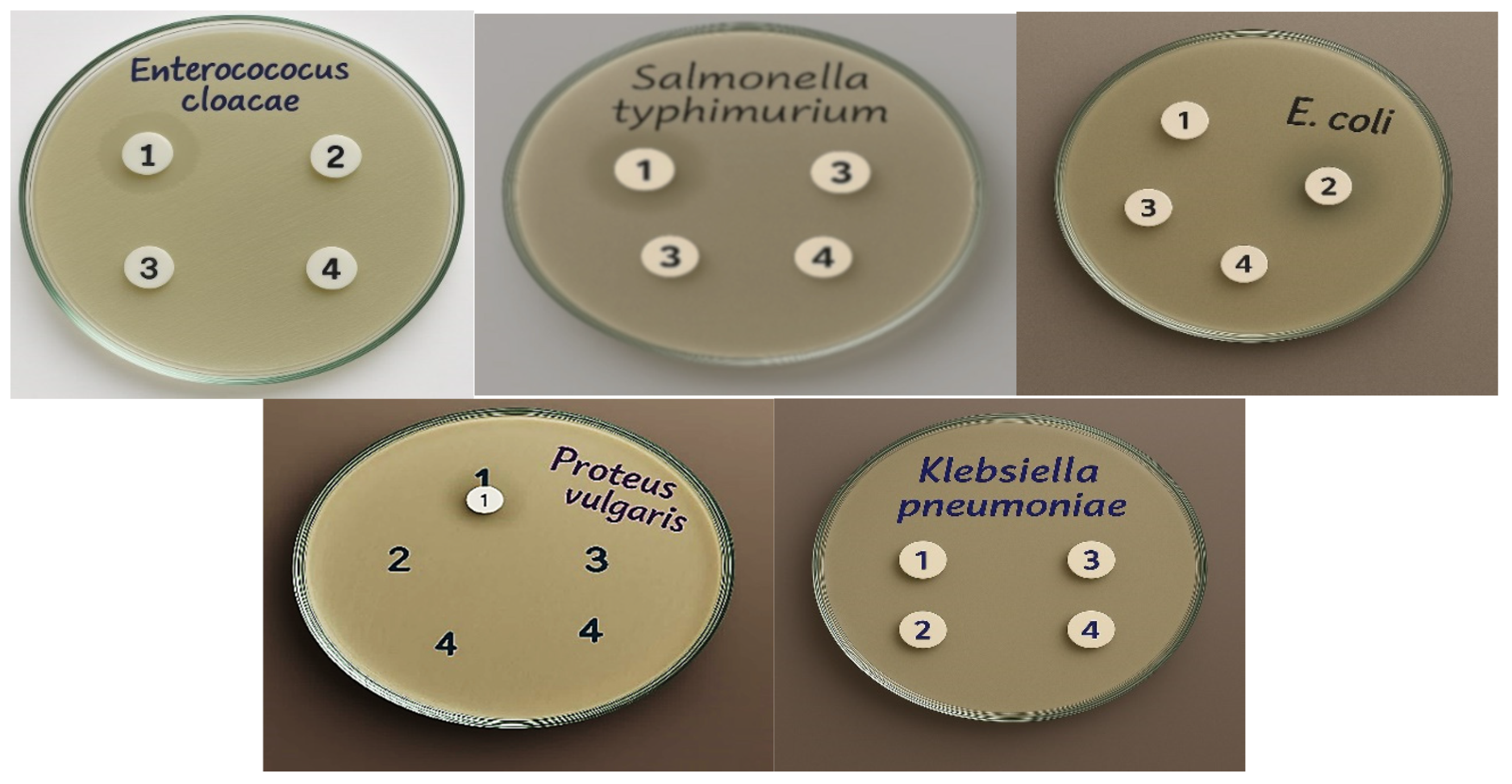
| Tested Gram-Positive Bacteria | MIC (µM) | Tested Gram-Negative Bacteria | MIC (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillis subtilis (RCMB 015) (1) | 250 | Salmonella sp. (RCMB 010043) | 125 |
| Micrococcus boride (RCMB 018) | 125 | Escherichia coli (RCMB 010052) | 63 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis (RCMB 009) | 63 | Enterococcus cloaca ATCC 23355 | 125 |
| MRSA | 250 | Klebsiella pneumonia ATCC 13883 | undetermined |
| Staphylococcus aureus (RCMB 007) | 125 | Proteus vulgaris ATCC 13315 | 250 |
| Streptococcus mutans (RCMB 017) | 125 | Salmonella typhimorium ATCC 4028 | 125 |
| Tested Fungi | Au/Chitosan (MIC; µM) |
|---|---|
| Aspergillus fumigatus (RCMB 02568) | 1000 |
| Candida albicans (RCMB 05036) | 500 |
| Aspergillus niger (RCMB 002005) | 250 |
| Aspergillus flavus (RCMB 002002) | 500 |
| Penicillium aurantogresium IMI 89372 | 1000 |
| Syncephlastrum racemosum (RCMB 016001) | 125 |
| Gold Nanoparticles | Antiviral Effect On | |
|---|---|---|
| HSV-1 | HAV-10 | |
| Au/PAM (15 KGy) | -ve | -ve |
| Au/PAM (10 KGy) | -ve | -ve |
| Au/PAM (5 KGy) | -ve | -ve |
| Au/chitosan | + | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Hadedy, D.E.; Safwat, N.A.; Saleh, H.H.; Ali, Z.I. In Vitro Assessment of Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized by Gamma Irradiation for Antimicrobial and Anticancer Effects. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112424
El-Hadedy DE, Safwat NA, Saleh HH, Ali ZI. In Vitro Assessment of Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized by Gamma Irradiation for Antimicrobial and Anticancer Effects. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(11):2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112424
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Hadedy, Doaa E., Nesreen A. Safwat, Hoda H. Saleh, and Zakaria I. Ali. 2025. "In Vitro Assessment of Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized by Gamma Irradiation for Antimicrobial and Anticancer Effects" Microorganisms 13, no. 11: 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112424
APA StyleEl-Hadedy, D. E., Safwat, N. A., Saleh, H. H., & Ali, Z. I. (2025). In Vitro Assessment of Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized by Gamma Irradiation for Antimicrobial and Anticancer Effects. Microorganisms, 13(11), 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112424






