Microbial Community Restructuring and Functional Response in Giant Duckweed (Spirodela polyrhiza) Fronds Driven by Cadmium Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Processing Conditions
2.2. Phenotypic Observation and Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
2.4. Library Preparation, Sequencing, and Data Processing
2.5. ASV Clustering and Taxonomic Annotation
2.6. Diversity Analysis
2.7. Functional Prediction
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Status of S. polyrhiza Fronds Under Different Cadmium Concentrations
3.2. Microbiome Profiling of S. polyrhiza Fronds Under Cadmium Stress
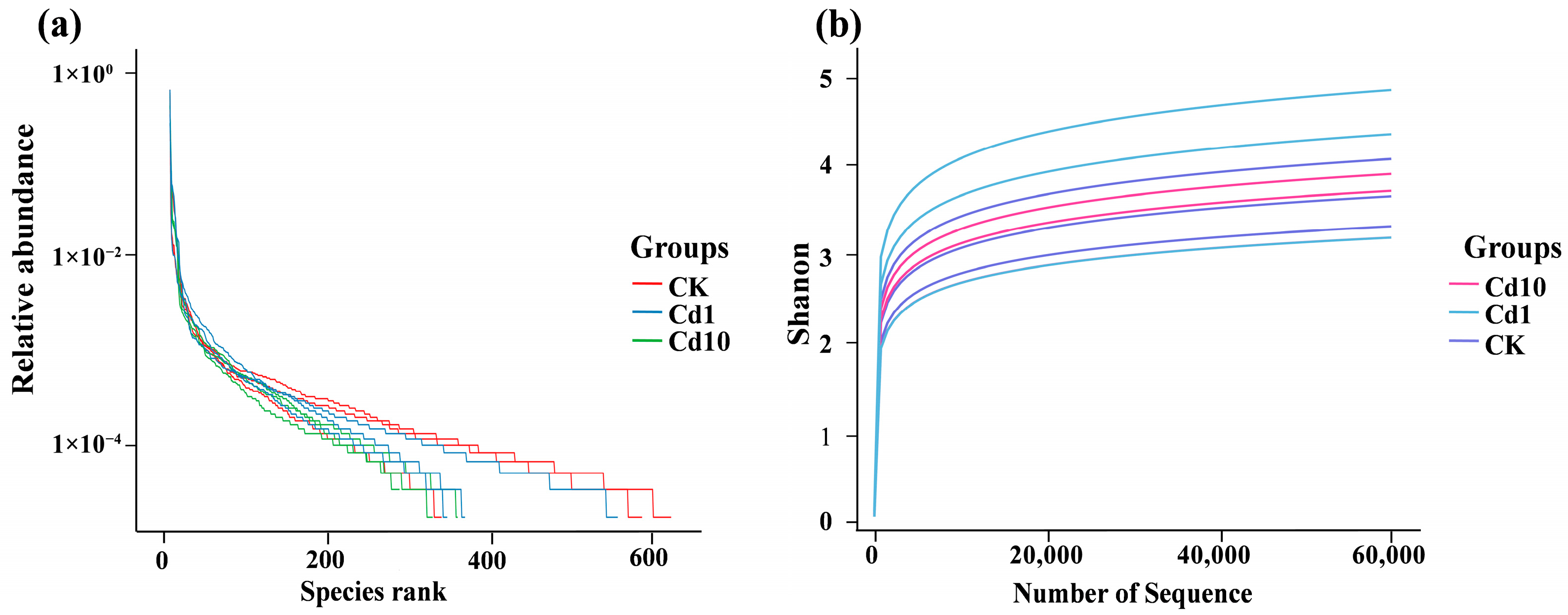
3.3. Alpha Diversity of the Epiphytic Bacterial Community on S. polyrhiza Fronds
3.4. Beta Diversity Analysis of Bacterial Communities in S. polyrhiza Fronds
3.5. Microbial Community Structure and Composition Under Cd Treatment
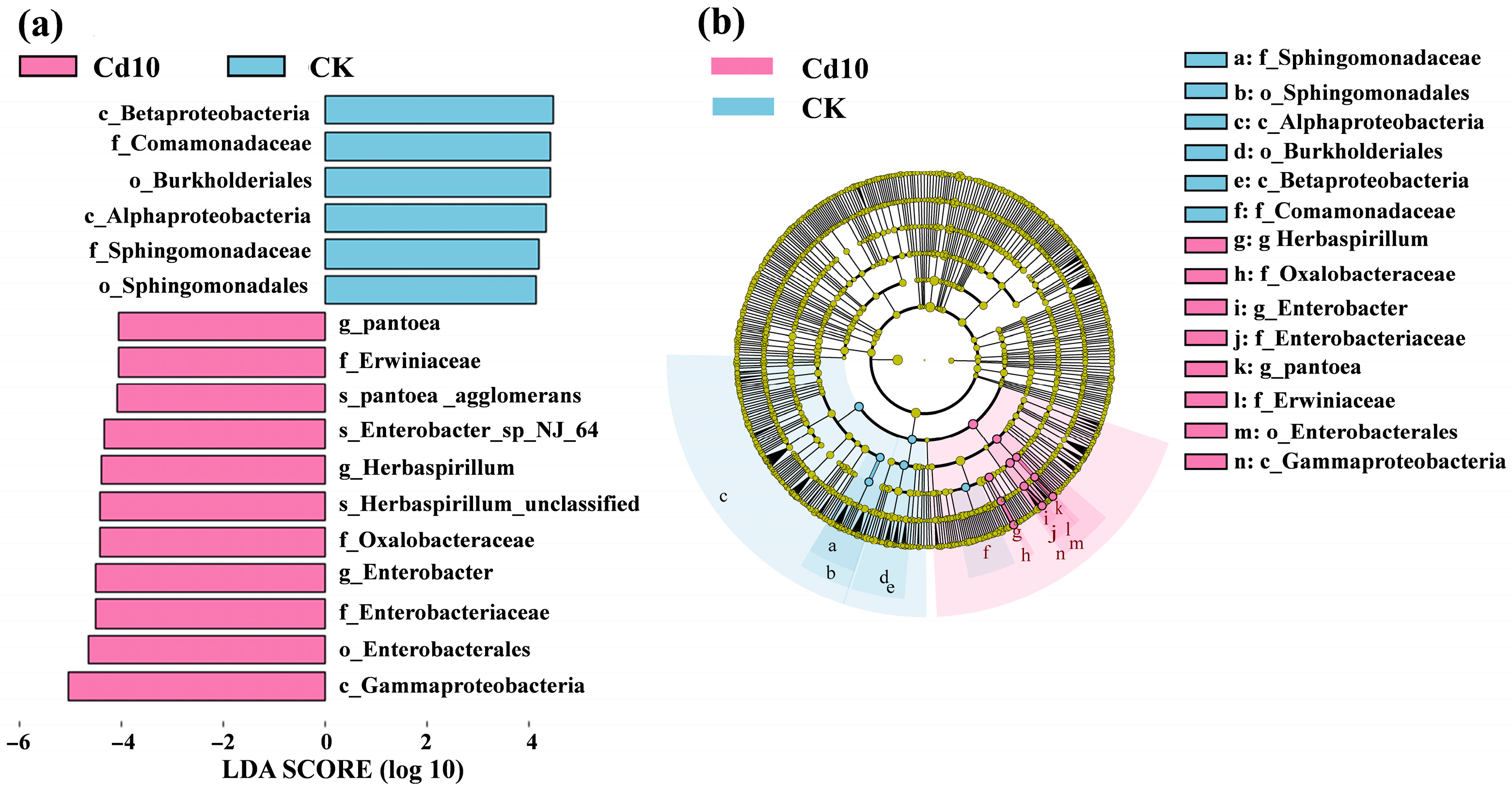
3.6. Linear Discriminant Analysis Effect Size (LEfSe) for Identification of Differential Bacterial Community in S. polyrhiza Fronds
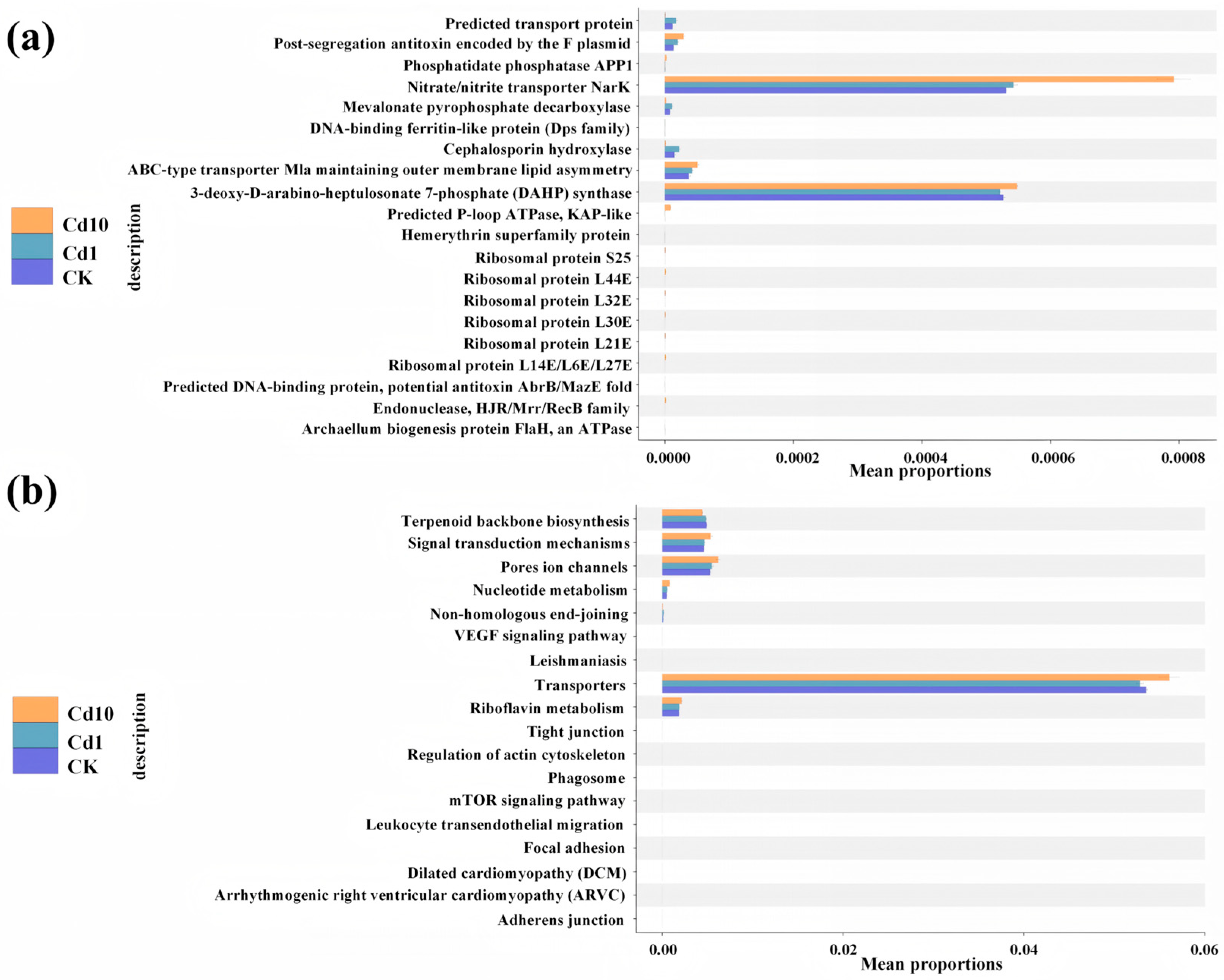
3.7. Functional Prediction of the Epiphytic Bacteria Community on S. polyrhiza Fronds
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Cadmium Stress on S. polyrhiza Leaf Physiology
4.2. Effects of Cadmium Stress on the Epiphytic Bacterial Composition of S. polyrhiza Fronds
4.3. Functional Differentiation of S. polyrhiza Frond Bacterial Communities Under Cadmium Stress
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, M.A.; Wani, G.A.; Majid, H.; Farooq, F.U.; Reshi, Z.A.; Husaini, A.M.; Shah, M.A. Differential Bioaccumulation of Select Heavy Metals from Wastewater by Lemna minor. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 105, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yu, C.; Xia, X.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, G. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Duckweed (Landoltia punctata) in Response to Cadmium Provides Insights into Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Hyperaccumulation. Chemosphere 2018, 190, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, K.; Ming, R.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, P. Exploring the Effects of Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Buprofezin and Cadmium on Tadpoles: A Phenotypic and Molecular Analysis. Environ. Res. 2025, 278, 121735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattar, S.; Yahya, M.; Aslam, S.; Hussain, R.; Shah, S.M.M.; Rauf, Z.; Zamir, A.; Ullah, R.; Shahzad, A. Environmental Occurrence, Hazards, and Remediation Strategies for the Removal of Cadmium from the Polluted Environment. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 104322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwazono, Y.; Kido, T.; Nakagawa, H.; Nishijo, M.; Honda, R.; Kobayashi, E.; Dochi, M.; Nogawa, K. Biological Half-Life of Cadmium in the Urine of Inhabitants after Cessation of Cadmium Exposure. Biomarkers 2009, 14, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Huang, X.; Sha, A.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Xiao, W.; Peng, L.; Zou, L.; Liu, B.; Li, Q. Analysis of Growth Physiological Changes and Metabolome of Highland Barley Seedlings under Cadmium (II) Stress. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 367, 125664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, F.U.; Liqun, C.; Coulter, J.A.; Cheema, S.A.; Wu, J.; Zhang, R.; Wenjun, M.; Farooq, M. Cadmium Toxicity in Plants: Impacts and Remediation Strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 211, 111887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; Li, L.; Duan, Q.; Liu, X.; Chen, M. Progress in Our Understanding of Plant Responses to the Stress of Heavy Metal Cadmium. Plant Signal. Behav. 2021, 16, 1836884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushtaq, G.; Agrawal, S.; Kushwah, A.; Kumar, A.; Lone, R. Cadmium Toxicity in Plants and Its Remediation Management: A Review. Plant Stress 2025, 16, 100894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, C.; Chen, J.; Coppens, F.; Inzé, D.; Verbruggen, N. Low Magnesium Status in Plants Enhances Tolerance to Cadmium Exposure. New Phytol. 2011, 192, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkai, D.; Chiofalo, M.T.; Torre, D.; Mileto, S.; Genovese, G.; Cimino, F.; Toscano, G.; Iannazzo, D.; Trifilò, P. Chronic Mild Cadmium Exposure Increases the Vulnerability of Tomato Plants to Dehydration. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 217, 109200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, P.; Kaushal, J. Role of Phytoremediation in Reducing Cadmium Toxicity in Soil and Water. J. Toxicol. 2018, 2018, 4864365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, C.R.; García-Martínez, B.; Zamudio-Cuevas, Y.; Fernández-Torres, J.; Martínez-Flores, K. Cadmium Exposure and Its Role in Joint Disease: A Brief Review of Experimental and Population-Based Evidence. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2025, 89, 127651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehzomi, Z.S.; Shirani, K. The Gut Microbiota: A Key Player in Cadmium Toxicity—Implications for Disease, Interventions, and Combined Toxicant Exposures. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2025, 88, 127570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Shi, H.; Liu, C.; Kang, X.; Chen, L.; Liang, X.; Jin, L. Duckweed Diversity Decreases Heavy Metal Toxicity by Altering the Metabolic Function of Associated Microbial Communities. Chemosphere 2018, 203, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, D.; Sun, D.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, G.; Jho, E.H.; Joo, J.C.; Zhao, X.; et al. Decoupling Soil pH and Geography: Universal Drivers of Cadmium Bioavailability in Rice across Terrains. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 381, 125297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kumar, T.; Das, D.K.; Mittal, A.; Verma, N. Vinod Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals in Soil—Concepts, Advancements, and Future Directions. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2025, 25, 1253–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhuo, R. Recent Advances in Phyto-Combined Remediation of Heavy Metal Pollution in Soil. Biotechnol. Adv. 2024, 72, 108337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hu, L.; Wu, D.; Huang, T.; Zhang, B.; Cai, G.; Gao, G.; Liu, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhong, Z. Large-Scale Screening and Characterization of Cd Accumulation and Ultrastructural Deformation in Duckweed. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 154948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Zhou, J.; Xu, X.; Na, M.; Xu, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zheng, X. Inoculation of Cadmium-Tolerant Bacteria to Regulate Microbial Activity and Key Bacterial Population in Cadmium-Contaminated Soils during Bioremediation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 271, 115957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozma, P.; Roșca, M.; Minuț, M.; Gavrilescu, M. Phytoremediation: A Sustainable and Promising Bio-Based Approach to Heavy Metal Pollution Management. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 1001, 180458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, G.; Saeed, M.; Choi, H.-K. Duckweeds: Their Utilization, Metabolites and Cultivation. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2021, 64, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Xu, J.; Peng, L.; Cheng, Z.; Kuang, X.; Li, D.; Peng, C.; Song, H. Cadmium Accumulation in Rice Grains Is Mitigated by Duckweed-like Hydrophyte through Adsorption and Increased Ammonia Nitrogen. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 890, 164510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Lenaghan, S.C. Duckweed: A Potential Phytosensor for Heavy Metals. Plant Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 2231–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pei, J.; Xu, H. Cadmium Induced Changes in Rhizosphere Microecology to Enhance Cd Intake by Ligusticum sinense cv. Chuanxiong. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 468, 133851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yu, L.; Wang, J.; Qin, L.; Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Chen, S. Chemotaxis of Rhizosphere Pseudomonas sp. Induced by Foliar Spraying of Lanthanum Reduces Cadmium Uptake by Pakchoi. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 482, 136625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Xia, M.; Ba, S.; Lim, B.L.; Hou, H. Biomonitoring of Heavy Metals and Their Phytoremediation by Duckweeds: Advances and Prospects. Environ. Res. 2024, 245, 118015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Li, T.; Liu, L.; Bao, X.; Yang, X.; Song, H.; Li, Y.; Bai, J.; He, L.; Wang, Q.; et al. Mechanistic Study on the Mitigation of Cadmium Accumulation in Ligusticum sinense cv. Chuanxiong Through Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria Arthrobacter sp. CX-2. Plant Stress. 2025, 15, 100748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Ma, X.; Chu, S.; You, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, T.; et al. Nitrogen Cycle Induced by Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria Drives “Microbial Partners” to Enhance Cadmium Phytoremediation. Microbiome 2025, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tan, A.-J.; Zheng, M.-M.; Feng, D.; Mao, K.; Yang, G.-L. Physiological Response, Microbial Diversity Characterization, and Endophytic Bacteria Isolation of Duckweed under Cadmium Stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parihar, A.; Malaviya, P. Textile Wastewater Phytoremediation Using Spirodela polyrhiza (L.) Schleid. Assisted by Novel Bacterial Consortium in a Two-Step Remediation System. Environ. Res. 2023, 221, 115307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, M.; Guan, D.-X.; Ma, L.Q. Plant-Microbiome Interactions for Enhanced Crop Production under Cadmium Stress: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 965, 178538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, W.; Blust, R.; Dwyer, R.; Mount, D.; Nordheim, E.; Rodriguez, P.H.; Spry, D. Bioavailability Assessment of Metals in Freshwater Environments: A Historical Review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 39, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logue, J.B.; Stedmon, C.A.; Kellerman, A.M.; Nielsen, N.J.; Andersson, A.F.; Laudon, H.; Lindström, E.S.; Kritzberg, E.S. Experimental Insights into the Importance of Aquatic Bacterial Community Composition to the Degradation of Dissolved Organic Matter. ISME J. 2016, 10, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857, Erratum in Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for Prediction of Metagenome Functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drost, W.; Matzke, M.; Backhaus, T. Heavy Metal Toxicity to Lemna Minor: Studies on the Time Dependence of Growth Inhibition and the Recovery after Exposure. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Ma, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, P.; Wei, R.; Chen, Q.; Weng, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y. Foliar Cadmium Uptake, Transfer, and Redistribution in Chili: A Comparison of Foliar and Root Uptake, Metabolomic, and Contribution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 453, 131421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Peng, J.; Yu, P.; Fei, J.; Huang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Yang, X.; Luo, J.; Li, T.; Huang, Y. Foliar Uptake, Translocation and Its Contribution to Cadmium Accumulation in Rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 177945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, T.; Toh, S.; Torii, K.U. Chemical Control of Stomatal Function and Development. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2021, 60, 102010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Torii, K.U. Hormonal and Environmental Signals Guiding Stomatal Development. BMC Biol. 2018, 16, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Yu, P.; Zuo, M.; Tong, Z.; Huang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Chang, R.; Peng, J.; Deng, Y.; Huang, Y. Screening of Rice Varieties with Low Accumulation of Heavy Metals Based on Leaf Morphology. J. Plant Physiol. 2025, 311, 154540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, X.-G. Stomata Conductance as a Goalkeeper for Increased Photosynthetic Efficiency. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2022, 70, 102310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almuwayhi, M.A. Effect of Cadmium on the Molecular and Morpho-Physiological Traits of Pisum sativum L. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2021, 35, 1374–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Liao, Q.; Huang, B.-F.; Xin, J.-L.; Wang, L.; Fu, H.-L. Characterization of Cadmium Accumulation Mechanism between Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) Cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1097998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijanzadeh, E.; Boostani, H.R.; Hardie, A.G.; Najafi-Ghiri, M. Co-Application of Silicon and Biochar Affected Anatomical and Biochemical Properties of Corn Leaf (Zea mays L.) Under Soil Nickel Toxicity. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cai, D.; Ji, M.; Chen, Z.; Yao, L.; Han, H. Isolation of Heavy Metal-Immobilizing and Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria and Their Potential in Reducing Cd and Pb Uptake in Water Spinach. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 153242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Bhatnagar, A.K. Spatial Distribution of Arsenic in Different Leaf Tissues and Its Effect on Structure and Development of Stomata and Trichomes in Mung Bean, Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2015, 109, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Ma, M.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, K.; Sun, R.; Zhan, X.; Cui, D. Leaf Development and Its Interaction with Phyllospheric Microorganisms: Impacts on Plant Stress Responses. Plant Stress 2025, 16, 100843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorente, B.E.; Alasia, M.A.; Larraburu, E.E. Biofertilization with Azospirillum brasilense Improves In Vitro Culture of Handroanthus ochraceus, a Forestry, Ornamental and Medicinal Plant. New Biotechnol. 2016, 33, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, K.; Kohli, S.K.; Ohri, P.; Bhardwaj, R.; Ahmad, P. Agroecotoxicological Aspect of Cd in Soil–Plant System: Uptake, Translocation and Amelioration Strategies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 30908–30934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyno, G. Biological Defence against Cadmium Stress in Wheat with Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Trichoderma: Synergistic Effects on Plant and Soil Health. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 229, 110470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Y.; Qu, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Cai, Z.; Dai, C.; Huang, X. Effects of Soil Management Strategies Based on Different Principles on Soil Microbial Communities and the Outcomes for Plant Health. Biol. Control 2025, 201, 105708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Leach, J.E.; Tringe, S.G.; Sa, T.; Singh, B.K. Plant–Microbiome Interactions: From Community Assembly to Plant Health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; He, Z.; Xin, X.; Shi, X.; Chen, L.; He, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y. Evidence That Beneficial Microbial Inoculation Enhances Heavy Metal-Contaminated Soil Remediation: Variations in Plant Endophyte Communities. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzewiecka, D. Significance and Roles of Proteus spp. Bacteria in Natural Environments. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 72, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosławiecka, A.K.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. The Effect of Heavy Metals on Microbial Communities in Industrial Soil in the Area of Piekary Śląskie and Bukowno (Poland). Microbiol. Res. 2022, 13, 626–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Hu, T.; Peng, O.; Chen, A.; Tie, B.; Shao, J. Impact of Heavy Metal Passivators on the Nitrogenase Activity and Diazotrophic Community in a Cadmium-Contaminated Paddy Field. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2022, 175, 105506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachalam, J.; Mohan, H.; Seralathan, K.-K. Significance of Herbaspirillum sp. in Biodegradation and Biodetoxification of Herbicides, Pesticides, Hydrocarbons and Heavy Metals—A Review. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velichko, N.S.; Grinev, V.S.; Fedonenko, Y.P. Characterization of Biopolymers Produced by Planktonic and Biofilm Cells of Herbaspirillum lusitanum P6-12. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1349–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ju, W.; Beiyuan, J.; Chao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Cui, Q.; Qiu, T.; Zhang, W.; Huang, M.; et al. Bacterial Consortium Amendment Effectively Reduces Pb/Cd Bioavailability in Soil and Their Accumulation in Wheat. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Pramanik, K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Mondal, S.; Ghosh, S.K.; Maiti, T.K. A Potent Cadmium Bioaccumulating Enterobacter Cloacae Strain Displays Phytobeneficial Property in Cd-Exposed Rice Seedlings. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2022, 3, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, X.; Chen, Y.; Luo, S.; Qin, Z.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Yu, F. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of the Mechanism of Cd Toxicity in Enterobacter sp. FM-1: Comparison of Different Growth Stages. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 336, 122513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Guo, Z.; He, X.; Yang, J.; Jiang, L.; Yang, A.; Xiao, X.; Xu, R. Stress Mitigation Mechanism of Rice Leaf Microbiota amid Atmospheric Deposition of Heavy Metals. Chemosphere 2024, 362, 142680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, K.L.; Kour, D.; Kaur, T.; Devi, R.; Yadav, A.N.; Yadav, N.; Dhaliwal, H.S.; Saxena, A.K. Endophytic Microbes: Biodiversity, Plant Growth-Promoting Mechanisms and Potential Applications for Agricultural Sustainability. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1075–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Lin, X.; Li, S.; Liang, Z.; Wang, H.; Tang, T. Endophytic Bacillus sp. AP10 Harboured in Arabis Paniculata Mediates Plant Growth Promotion and Manganese Detoxification. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Xie, T.; Wang, X.; Bai, J.; Tang, L.; Zhao, H.; Wei, W.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Y. Metagenomic Analysis of Microbial Community and Function Involved in Cd-Contaminated Soil. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskulak, M.; Grobelak, A.; Vandenbulcke, F. Effects of Sewage Sludge Supplementation on Heavy Metal Accumulation and the Expression of ABC Transporters in Sinapis alba L. During Assisted Phytoremediation of Contaminated Sites. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, A.; Seth, C.S. Transgenic Brassicaceae. In Transgenic Plant Technology for Remediation of Toxic Metals and Metalloids; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 239–255. ISBN 978-0-12-814389-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, H.; Ghouri, F.; Sun, L.; Xia, W.; Ashraf, S.; Ashraf, M.Z.; Fu, X.; Ali, S.; Shahid, M.Q. Energy Metabolism, Antioxidant Defense System, Metal Transport, and Ion Homeostasis Are Key Contributors to Cd Tolerance in SSSL Derived from Wild Rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 488, 137009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shen, L.; Chen, M.; Sun, H.; Fu, L.; Zhang, G.; Shen, Q. Rhizosphere Microbial Communities of Bacteria and Fungi Responding to Cadmium Stress in Wheat. Crop Des. 2025, 4, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
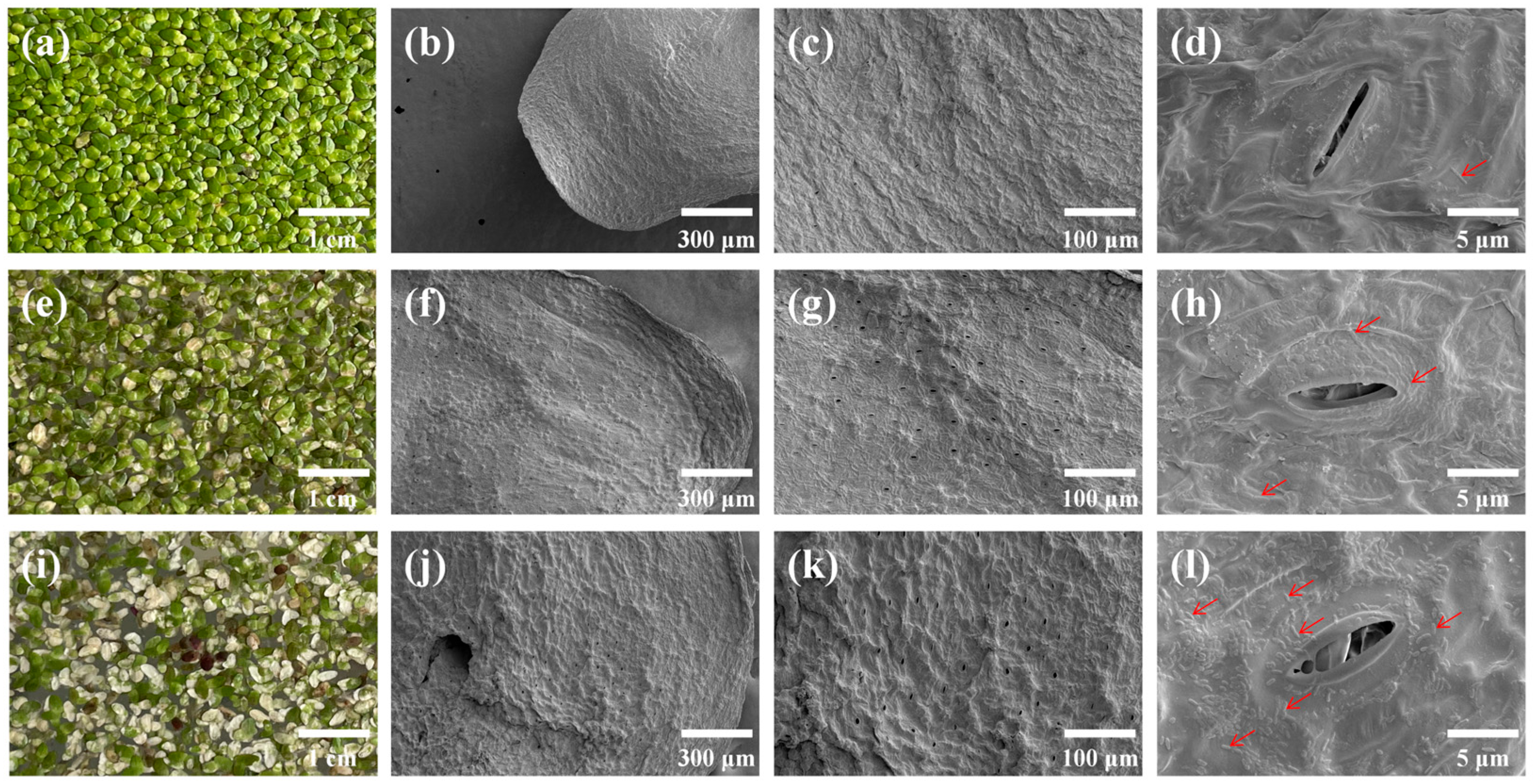



| Treatments | Stomatal Length (μm) | Stomatal Width (μm) | Stomatal Area (μm2) | Stomatal Density (No./mm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 12.25 ± 1.29 | 1.25 ± 0.39 b | 12.12 ± 3.96 b | 36.28 ± 12.32 b |
| Cd1 | 12.43 ± 1.41 | 3.38 ± 1.48 a | 29.81 ± 13.04 a | 156 ± 21.62 a |
| Cd10 | 12.39 ± 0.7 | 2.53 ± 0.61 a | 24.74 ± 4.16 a | 189.11 ± 27.94 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Yang, C.; Wan, X.; Chen, S.; Tao, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X. Microbial Community Restructuring and Functional Response in Giant Duckweed (Spirodela polyrhiza) Fronds Driven by Cadmium Stress. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112423
Liu B, Yang C, Wan X, Chen S, Tao Y, Li Q, Zhao H, Wang X. Microbial Community Restructuring and Functional Response in Giant Duckweed (Spirodela polyrhiza) Fronds Driven by Cadmium Stress. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(11):2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112423
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Bingliang, Chen Yang, Xin Wan, Suming Chen, Yang Tao, Qiang Li, Hai Zhao, and Xinhui Wang. 2025. "Microbial Community Restructuring and Functional Response in Giant Duckweed (Spirodela polyrhiza) Fronds Driven by Cadmium Stress" Microorganisms 13, no. 11: 2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112423
APA StyleLiu, B., Yang, C., Wan, X., Chen, S., Tao, Y., Li, Q., Zhao, H., & Wang, X. (2025). Microbial Community Restructuring and Functional Response in Giant Duckweed (Spirodela polyrhiza) Fronds Driven by Cadmium Stress. Microorganisms, 13(11), 2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112423








