Preharvest Control of Campylobacter Colonization in Chickens, with a Special Emphasis on Vaccination Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Campylobacter in Broilers—Biology and Public Health Impact
3. Overview of Preharvest Control Strategies
3.1. Biosecurity Measures
3.1.1. Managing Human Entry and Hygiene to Prevent Contamination
3.1.2. Equipment and Vehicle Sanitation
3.1.3. Pest and Wildlife Control
3.2. Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Postbiotics
3.3. Bacteriophage Application in Campylobacter Control
3.4. Feed Additives
3.5. Vaccination—A Targeted Approach
3.5.1. Types of Poultry Campylobacter Vaccines
Subunit Vaccines
Live-Attenuated Vaccines
Inactivated/Killed Vaccines
DNA and mRNA Vaccines
3.5.2. Challenges in Campylobacter Vaccine Development
Campylobacter Properties
Host Factors Influencing Vaccinal Immunity
Administration and Management of Vaccines
3.5.3. Positive Outcomes and Promising Campylobacter Vaccine Candidates
Autogenous Vaccines
Subunit Vaccines
Live Attenuated Vaccines
DNA Vaccine
| Vaccine | Chicken Breed (Chicken Type) | Age at Vaccination | Vaccination Regimen | Challenge | Reduction in Levels (Mean log10 CFU/Gram) of Campylobacter | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Strain (Dose) | ||||||
| Live attenuated Salmonella vaccine expressing CfrA or CmeC proteins | Cornish × Rock (broiler) | Day 7 | Oral administration of 200 μL of Salmonella (1 × 109 CFU/mL) expressing CfrA or CmeC | Day 28 | C. jejuni NCTC 11,168 (2 × 103 CFU/bird) | No significant reduction | [155] |
| Nanoparticle-encapsulated OMPs of C. jejuni 81–176 | Not specified | Day 7 and Day 21 | Oral administration of 25 or 125 µg of nanoparticle-encapsulated OMPs or OMPs alone | Day 35 | C. jejuni 81–176 (2 × 107 CFU/bird) | No significant reduction | [236] |
| Subcutaneous administration of 25 or 125 µg of nanoparticle-encapsulated OMPs or OMPs alone | |||||||
| Live Salmonella Typhimurium ΔaroA strain expressing CjaA of C. jejuni | Light Sussex (broiler) | Day 1 and Day 14 | Oral gavage of 0.3 mL of stationary phase culture (1 × 108 CFU/mL) | Day 28 | C. jejuni M1 (1 × 107 CFU/bird) | Significant 1.4 log10 CFU/g reduction | [160] |
| Purified recombinant CjaA | Light Sussex chickens (broiler) | Day 1 and Day 15, or Day 15 and Day 29 | Subcutaneous administration of 14 μg of rCjaA with TiterMax adjuvant | Day 29/Day 44 | No significant reduction | ||
| Autogenous poultry vaccine | Ross (broiler) | 14 and 18 weeks of age | Intramuscular administration of 0.5 mL of oil-based autogenous vaccine | Not a challenge study | Measured natural colonization | No significant reduction | [226] |
| FliD and FspA | White Leghorn (layer) | Day 1 and Day 14 | Subcutaneous administration of 4.3 × 1010 moles of each recombinant protein, FliD and FspA, with TiterMax Gold adjuvant | Day 28 | C. jejuni M1 (1 × 107 CFU/bird) | 2 log10 CFU/g in reduction with FliD (statistically significant) | [158] |
| Eimeria tenella-expressing CjaA | White Leghorn (layer) | Group 1: Day 1 Group 2: 1/3/7/20 | Oral administration of 100, 500, 3000, and 5000 fourth-generation CjaA-transfected parasites | Day 28 | C. jejuni 02M6380 (1 × 105 CFU/bird) | One-order reduction (statistically significant) | [225] |
| FlpA with ten N-heptasaccharide glycan moieties | White Leghorn (layer) | Day 0 and Day 14 | Subcutaneous administration of 100 μg of FlpA with TiterMax Gold or the molar equivalent of FlpA-10 × GT in 100 µL | Day 28 | C. jejuni NCTC11168H (1 × 105 CFU/bird) | No significant reduction | [239] |
| Ent–KLH conjugate vaccine | White Leghorn (layer) | Day 7, Day 21, and Day 35 | Intramuscular administration of 100 μg of Ent–KLH conjugate vaccine with Montanide adjuvant | Day 49 | C. jejuni (1 × 104 CFU/bird) | 3–4 log10 unit reduction in the cecum (statistically significant) | [227] |
| White Leghorn (layer) | Day 7 and Day 21 | Intramuscular administration of 100 μg of Ent–KLH conjugate vaccine with Montanide adjuvant | Day 35 | C. jejuni (1 × 104 CFU/bird) | 3–4 log10 unit reduction in the cecum (statistically significant) | ||
| Recombinant YP437 protein | Ross 308 (broiler) | Day 5 and Day 12 | Intramuscular administration of 100 µg of recombinant YP437 protein (YP437 I2, P I2, YP437 I4, and P I4) emulsified with adjuvant MONTANIDETM ISA 78 VG | Day 19 | C. jejuni (1 × 104 CFU/bird) | No significant reduction | [240] |
| Plasmid DNA prime/recombinant protein boost vaccination (YP437 and YP9817) | Ross 308 (broiler) | Day 12 | Intramuscular administration of 100 µg of recombinant protein emulsified in MONTANIDE™ ISA 78 VG | Day 19 | C. jejuni C97Anses640 (1 × 104 CFU/bird) | No significant reduction | [179] |
| Ross 308 (broiler) | Day 5 | Intramuscular administration of 50 μg of plasmid DNA | |||||
| Lactococcus lactis expressing JlpA | Vencobb (broiler) | Day 7 | Oral gavage of 1 × 109 CFU/100 µL of Lactococcus lactis expressing recombinant JlpA | Day 28 | C. jejuni isolate BCH71 (1 × 108 CFU/bird) | No significant reduction | [241] |
| Subcutaneous administration of 50 µg of recombinant JlpA emulsified in incomplete Freund’s adjuvant | |||||||
| Bacterin vaccine (mix of 13 Campylobacter suspensions) | Ross 308 (broiler) | 28, 30, 32, and 34 weeks | Intramuscular administration of 8.1 log10 CFU inactivated Campylobacter (7 log10 CFU/Campylobacter strain) | Day 7 Day 14 Day 21 | C. jejuni strain KC40 (102.5 and 103.5 CFU/bird) | No significant reduction | [203] |
| Subunit vaccine (6 immunodominant Campylobacter antigens) | Ross 308 (broiler) | Intramuscular administration of 75 µg of protein with Freund’s complete and incomplete adjuvant | |||||
| Diphtheria toxoid C. jejuni capsular polysaccharide- vaccine (CPSconj) | Ross 308 (broiler) | Day 7 and Day 21 | Subcutaneous administration of 25 μg of CPSconj with 10 μg CpG or 100 μL Addavax adjuvant | Day 29 | C. jejuni 81–176 (2 × 107 CFU/bird) | 0.64 log10 reduction (statistically significant) | [234] |
| Chitosan/pCAGGS-flaA nanoparticles | White Leghorn (layer) | Day 1, Day 15, and Day 29 | Intranasal administration of 150 μg chitosan/pCAGGS-flaA nanoparticles | Day 42 | C. jejuni ALM-80 (5 × 107 CFU/bird) | 2 log10 in the cecum (statistically significant) | [230] |
| LT-B/FlaA hybrid protein | Breed not specified (broiler) | Day 7 and Day 21 | Oral administration of 250 μg, 500 μg, 750 μg, and 1 mg of LT-B/flaA hybrid protein; intramuscular administration of 250 µg, and 1 mg of LT-B/Fla hybrid protein | Day 28 | C. jejuni A74 (2 × 108 CFU/bird) | Statistically significant reduction in the number of Campylobacter positive birds | [228] |
| CjaA, CjaD, and hybrid protein rCjaAD of C. jejuni | Hy-line (layer) | Day 1, Day 9, and Day 19 | Oral or subcutaneous administration of 2.5 × 109 CFU of L. salivarius GEM particles with CjaALysM and CjaDLysM | Day 30 | C. jejuni 12/2 (1 × 104 CFU/bird) | No significant reduction | [229] |
| Rosa 1 (broiler) | 18-day-old embryo | In ovo administration of 0.1 mL of inoculum rCjaAD with GEM particles or liposomes into the amniotic fluid | Day 14 | C. jejuni 12/2 (1 × 106 CFU/bird) | Statistically significant reduction in cecal loads of Campylobacter | ||
| Live attenuated Salmonella Typhimurium strain expressing C. jejuni CjaA | Cobb 500 (broiler) | Day 1 and Day 14 | Oral administration of ~108 CFU of S. Typhimurium strain χ9718 harboring pUWM1161 (Asd+ vector carrying the cjaA gene) | Day 28 | C. jejuni Wr1 (1 × 105 CFU/bird) | No significant reduction | [242] |
| Live attenuated Salmonella expressing linear peptides of C. jejuni (Cj0113, Cj0982c, and Cj0420) | Cobb-500 (broiler) | Day 1 | Oral gavage of 108 CFU/mL Salmonella | Day 21 | C. jejuni PHLCJ1-J3 (2.5 × 106 CFU/bird) | 4.8 log reduction in the ileum with Cj0113 (statistically significant) | [161] |
| 4 log reduction—undetectable level in the ileum with Cj0113 (statistically significant) | |||||||
| Live attenuated Salmonella expressing linear peptides of C. jejuni (Cj0113) | Oral gavage of 108 CFU/mL Salmonella 108 CFU/mL | ||||||
| CmeC and CfrA | Cobb 500 (broiler) | 18-day-old embryo | In ovo administration of 50 µg pCmeC-K or 50 µg pCfrA into the amniotic fluid | Day 14 | C. jejuni NCTC 11,168 (5 × 107 CFU/bird) | No significant reduction | [178] |
| In ovo administration of DNA vaccines emulsified with incomplete Freund’s adjuvant | Day 21 | No significant reduction | |||||
| pcDNA3-YP DNA vaccines YP_001000437.1, YP_001000562.1, YP_999817.1, and YP_999838.1 | Ross PM3 (broiler) | Day 5 and Day 12 | Intramuscular administration of with 300 μg of pcDNA3-YP, supplemented with 50 μg of unmethylated CpG ODN2007 followed by intramuscular administration of 100 μg of recombinant proteins emulsified in MONTANIDE™ ISA70 VG | Day 19 | C. jejuni C97Anses640 (1 × 105 CFU/bird) | 2.03, 3.61, 4.27, and 2.08 log 10 reductions of P562, YP437, YP9817, and P9838 groups, respectively (statistically significant) | [231] |
| Intramuscular administration of with 300 μg of pcDNA3-_999817.1, supplemented with 50 μg of unmethylated CpG ODN2007 followed by intramuscular administration of 100 μg of recombinant proteins emulsified in MONTANIDE™ ISA70 VG | No significant reduction | ||||||
| CmeC | Breed not specified (broiler) | Day 7 and Day 21 | Oral gavage with 50 or 200 μg of CmeC vaccine with or without with 10 μg of mLT | Day 35 | C. jejuni NCTC 11,168 (1 × 106 CFU/bird) | No significant reduction | [243] |
| White Leghorn chickens (layer) | Day 21 and Day 35 | Oral and subcutaneous administration of 50 or 200 μg of CmeC vaccine with or without 70 μg of mLT | Day 49 | C. jejuni NCTC 11,168 (1 × 105 CFU/bird) | No significant reduction | ||
| Lactococcus lactis NZ3900/pNZ8149 expressing cjaA | White leghorn (layer) | Day 5–11 and Day 19–25 | Oral administration of 2 × 1010 CFU of L. lactis NZ3900-sCjaA-Ltb, NZ3900-sCjaA, NZ3900-pNZ8149s, and NZ3900-pNZ8149 | Day 33 | C. jejuni NCTC 11,168 (1.5 × 106 CFU/bird) | 2.35 log10 and 2.05 log10 reduction with NZ3900-sCjaA vaccine group at post 5 DPI (statistically significant) | [163] |
| Glycoproteins of FlpA and SodB | White Leghorn (layer) | Day 6 and Day 16 | Intramuscular administration of 240 µg of FlpA and G-FlpA or 138 µg of SodB and G-SodB. | Day 20 | C. jejuni M1 (1 × 107 CFU/bird) | No significant reduction | [244] |
| C. jejuni M1 (102 CFU/bird) | No significant reduction | ||||||
| C. jejuni N-glycans + Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A (G-ExoA) | White Leghorn (layer) | Day 6 and Day 16 | Intramuscular administration of 95 µg protein of ExoA or G-ExoA with MontanideTM ISA 70 VG adjuvant | Day 20 | C. jejuni M1 (1 × 102 CFU/bird) | Reduction on Day 37 with ExoA-vaccinated group (statistically significant) | [235] |
| C. jejuni 11168H. C. jejuni M1 (1 × 104 CFU/bird) | Reduction on Day 37 with ExoA and G-ExoA-vaccinated groups (statistically significant) | ||||||
| Bacterin and subunit vaccine | Ross 308 (broiler) | 18-day-old embryo | In ovo administration of 7.4 log10 CFU inactivated Campylobacter/bacterin dose of bacterin vaccine injected into the amniotic cavity | Day 19 | C. jejuni KC4 (1 × 107 CFU/bird) | No significant reduction | [245] |
| In ovo administration of 28.5 μg of 6 immunodominant Campylobacter antigens with ESSAI IMS 1505101OVO1 adjuvant | |||||||
| C. jejuni Dps | Cornish × Rock (broiler) | Day 10 and Day 24 | Subcutaneous administration of 0.2 mg recombinant Dps protein with Freund’s complete adjuvant | Day 34 | C. jejuni NCTC11168 (1 × 105 CFU/bird) | No reduction | [224] |
| Day 3, Day 10, and Day 16 | Oral gavage of Salmonella Typhimurium strain χ9088 expressing C. jejuni Dps in 0.5 mL | Day 26 | 2.92 log10 reduction (statistically significant) | ||||
| PLGA-encapsulated CpG (E-CpG) ODN and C. jejuni lysate | Breed is not specified (layer) | Day 14 | Oral administration of 5 µg or 50 µg of soluble CpG | Day 15 | C. jejuni (107 CFU/bird) | 1.23 and 1.32 log reduction at 8 days post-infection with low and high doses, respectively (statistically significant) | [232] |
| Breed is not specified (layer) | Oral administration of 5 µg E-CpG | 0.9, 1.9, and 1.89 log reduction at 8, 15, and 22 days of post-infection (statistically significant) | |||||
| Breed is not specified (layer) | Oral administration with a high dose of E-CpG (25 µg) | 1.46 log10 reduction at day 22 post-infection (statistically significant) | |||||
| Breed is not specified (broiler) | Oral administration of a low dose of C. jejuni lysate (4.3 µg protein) | 2.14 and 2.14 log10 at day 8 and day 22 post-infection, respectively (statistically significant) | |||||
| Breed is not specified (broiler) | Oral administration of E-CpG ODN (25 µg) and C. jejuni lysate (4.3 µg protein) | 2.42 log10 at day 22 post-infection (statistically significant) | |||||
| C. jejuni Type VI secretion system (T6SS) protein Hcp encapsulated nanoparticles | Vencobb (broiler) | Day 7, Day 14, and Day 21 | Oral gavage of 50 μg rHcp loaded CS-TPP NPs (CS-TPP-Hcp) | Day 28 | C. jejuni isolate BCH71 (1 × 108 CFU/bird) | 1 log reduction (statistically significant) | [233] |
| Subcutaneous administration of 50 μg of rHcp emulsified with incomplete Freund’s adjuvant | 0.5 log reduction (statistically significant) | ||||||
| Recombinant NHC flagellin | Ross 308 (broiler) | 18.5-day-old embryo | In ovo administration of 40 or 20 μg NHC flagellar protein with 10 mM Tris (pH 9.0), 20% glycerol, 5 mM sucrose | day 18 | C. jejuni (1 × 105 CFU/bird) | No significant reduction | [246] |
| Recombinant C. jejuni peptides of CadF, FlaA, FlpA, CmeC, and CadF-FlaA-FlpA fusion protein | Cornish cross (broiler) | Day 6 and Day 16 | Intramuscular administration of 240 µg of GST-tagged 90-mer peptide or equal mixture of CadF-His, FlaA-His, and FlpA-His (trifecta group) emulsified in Montanide ISA 70 VG | Day 20 | C. jejuni (2 × 108 CFU/bird) | 3.1, 3.3, 3.1, and 1.7 log reductions observed with Trifecta, FlpA, FlaA and CadF, respectively (statistically significant) | [157] |
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives of Campylobacter Control
4.1. Future Prospects
4.1.1. Biosecurity Enhancing Innovations
4.1.2. Studies Targeting Campylobacter and Host Interactions
4.1.3. Genetic Selection of Campylobacter-Resistant Breeds
4.1.4. Developing Effective Vaccination Strategies
4.1.5. Microbiota Targeting Interventions
4.1.6. Cross-Sectoral Collaboratory Efforts (One Health)
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| CFU | Colony forming units |
| EOs | Essential oils |
| FMT | Fecal microbiota transplantation |
| FOS | Fructooligosaccharides |
| GBS | Guillain-Barré Syndrome |
| GIT | Gastrointestinal tract |
| GLAT | Gut-associated lymphoid tissue |
| GOS | Galactooligosaccharides |
| IBS | Irritable bowel syndrome |
| IMO | Isomalto-oligosaccharides |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| PPE | Personal protective equipment |
| QTL | Quantitative Trait Loci |
| VBNC | Viable but non-culturable state |
References
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne Illness Acquired in the United States-Major Pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, S.M.; Devleesschauwer, B. Estimates of Global Disease Burden Associated with Foodborne Pathogens. In Foodborne Infections and Intoxications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States 2019; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019.
- Hermans, D.; Pasmans, F.; Heyndrickx, M.; Van Immerseel, F.; Martel, A.; Van Deun, K.; Haesebrouck, F. A Tolerogenic Mucosal Immune Response Leads to Persistent Campylobacter Jejuni Colonization in the Chicken Gut. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 38, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, L.D.; Levy, K.; Menezes, N.P.; Freeman, M.C. Human Diarrhea Infections Associated with Domestic Animal Husbandry: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 108, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, G.V.; Ramires, T.; Kleinubing, N.R.; Scheik, L.K.; Fiorentini, Â.M.; Padilha da Silva, W. Virulence Factors of Foodborne Pathogen Campylobacter Jejuni. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 161, 105265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaakoush, N.O.; Castaño-Rodríguez, N.; Mitchell, H.M.; Man, S.M. Global Epidemiology of Campylobacter Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 687–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsterer, J. Triggers of Guillain–Barré Syndrome: Campylobacter Jejuni Predominates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyati, K.K.; Prasad, K.N.; Rizwan, A.; Verma, A.; Paliwal, V.K. TH1 and TH2 Response to Campylobacter Jejuni Antigen in Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Prasad, K.N.; Jain, D.; Nyati, K.K.; Pradhan, S.; Agrawal, S. Immunoglobulin IgG Fc-Receptor Polymorphisms and HLA Class II Molecules in Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2010, 122, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, J.; Spadaro, A.; Koyfman, A.; Long, B. High Risk and Low Prevalence Diseases: Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2024, 75, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, J.A.; Willison, H.J. Guillain-Barré Syndrome: A Century of Progress. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gölz, G.; Rosner, B.; Hofreuter, D.; Josenhans, C.; Kreienbrock, L.; Löwenstein, A.; Schielke, A.; Stark, K.; Suerbaum, S.; Wieler, L.H.; et al. Relevance of Campylobacter to Public Health–the Need for a One Health Approach. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, O.; Morishita, T.Y.; Zhang, Q. Campylobacter Colonization in Poultry: Sources of Infection and Modes of Transmission. Anim. Heal. Res. Rev. 2002, 3, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shane, S.M. The Significance of Campylobacter Jejuni Infection in Poultry: A Review. Avian Pathol. 1992, 21, 189–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, N.J.; Clavero, M.R.; Bailey, J.S.; Cox, N.A.; Robach, M.C. Campylobacter Spp. in Broilers on the Farm and after Transport. Poult. Sci. 1995, 74, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corry, J.E.; Atabay, H.I. Poultry as a Source of Campylobacter and Related Organisms. Symp. Ser. Soc. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 90, 96S–114S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.D.; Newell, D.G. Campylobacter in Poultry: Filling an Ecological Niche. Avian Dis. 2006, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenaar, J.A.; Van Bergen, M.A.P.; Mueller, M.A.; Wassenaar, T.M.; Carlton, R.M. Phage Therapy Reduces Campylobacter Jejuni Colonization in Broilers. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 109, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, S.; Chaloner, G.; Kemmett, K.; Davidson, N.; Williams, N.; Kipar, A.; Humphrey, T.; Wigley, P. Campylobacter Jejuni Is Not Merely a Commensal in Commercial Broiler Chickens and Affects Bird Welfare. mBio 2014, 5, e01364-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.K.; AbuOun, M.; Cawthraw, S.A.; Humphrey, T.J.; Rothwell, L.; Kaiser, P.; Barrow, P.A.; Jones, M.A. Campylobacter Colonization of the Chicken Induces a Proinflammatory Response in Mucosal Tissues. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, K.G.; Narciandi, F.; Cahalane, S.; Reiman, C.; Allan, B.; O’Farrelly, C. Comparative in Vivo Infection Models Yield Insights on Early Host Immune Response to Campylobacter in Chickens. Immunogenetics 2009, 61, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zoete, M.R.; Keestra, A.M.; Roszczenko, P.; Van Putten, J.P.M. Activation of Human and Chicken Toll-like Receptors by Campylobacter Spp. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, W.A.; Molnár, A.; Aschenbach, J.R.; Ghareeb, K.; Khayal, B.; Hess, C.; Liebhart, D.; Dublecz, K.; Hess, M. Campylobacter Infection in Chickens Modulates the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function. Innate Immun. 2015, 21, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, W.D.K.; Close, A.J.; Humphrey, S.; Chaloner, G.; Lacharme-Lora, L.; Rothwell, L.; Kaiser, P.; Williams, N.J.; Humphrey, T.J.; Wigley, P.; et al. Cytokine Responses in Birds Challenged with the Human Food-Borne Pathogen Campylobacter Jejuni Implies a Th17 Response. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2016, 3, 150541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawshaw, T.R.; Chanter, J.I.; Young, S.C.L.; Cawthraw, S.; Whatmore, A.M.; Koylass, M.S.; Vidal, A.B.; Salguero, F.J.; Irvine, R.M. Isolation of a Novel Thermophilic Campylobacter from Cases of Spotty Liver Disease in Laying Hens and Experimental Reproduction of Infection and Microscopic Pathology. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 179, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van, T.T.H.; Elshagmani, E.; Gor, M.C.; Scott, P.C.; Moore, R.J. Campylobacter hepaticus Sp. Nov., Isolated from Chickens with Spotty Liver Disease. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 4518–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottapu, C.; Sahin, O.; KEdison, L.; Srednik, M.E.; Kariyawasam, S. Complete genome sequences of Campylobacter hepaticus strains USA1 and USA5 isolated from a commercial layer flock in the United States. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2025, 14, e00919-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbi, M.; Béjaoui, A.; Hamrouni, S.; Arfaoui, A.; Maaroufi, A. Persistence of Campylobacter Spp. in Poultry Flocks after Disinfection, Virulence, and Antimicrobial Resistance Traits of Recovered Isolates. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibreel, A.; Taylor, D.E. Macrolide Resistance in Campylobacter Jejuni and Campylobacter Coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfredson, D.A.; Korolik, V. Antibiotic Resistance and Resistance Mechanisms in Campylobacter Jejuni and Campylobacter Coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 277, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.; Jeon, B. Contribution of Surface Polysaccharides to the Resistance of Campylobacter Jejuni to Antimicrobial Phenolic Compounds. J. Antibiot. 2015, 68, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.T.; Fliss, I.; Biron, E. Insights in the Development and Uses of Alternatives to Antibiotic Growth Promoters in Poultry and Swine Production. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasuriya, S.S.; Ault, J.; Ritchie, S.; Gay, C.G.; Lillehoj, H.S. Alternatives to Antibiotic Growth Promoters for Poultry: A Bibliometric Analysis of the Research Journals. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Clavero, A.B.; Vigre, H.; Læsø Madsen, A.; Christensen, L.S.; Johannessen, G. Campylobacter Vaccination of Poultry: Clinical Trials, Quantitative Microbiological Methods and Decision Support Tools for the Control of Campylobacter in Poultry. Ph.D. Thesis, National Food Institute, Technical University of Denmark, Søborg, Denmark, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Poudel, S.; Li, T.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, W.-H.; Sukumaran, A.T.; Kiess, A.S.; Zhang, L. Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Molecular Characterization of Campylobacter Isolated from Broilers and Broiler Meat Raised without Antibiotics. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0025122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Salem, H.M.; El-Tahan, A.M.; Soliman, M.M.; Youssef, G.B.A.; Taha, A.E.; Soliman, S.M.; Ahmed, A.E.; El-kott, A.F.; et al. Alternatives to Antibiotics for Organic Poultry Production: Types, Modes of Action and Impacts on Bird’s Health and Production. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slader, J.; Domingue, G.; Jørgensen, F.; McAlpine, K.; Owen, R.J.; Bolton, F.J.; Humphrey, T.J. Impact of Transport Crate Reuse and of Catching and Processing on Campylobacter and Salmonella Contamination of Broiler Chickens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, S.A.; Allen, V.M.; Domingue, G.; Jørgensen, F.; Frost, J.A.; Ure, R.; Whyte, R.; Tinker, D.; Corry, J.E.L.; Gillard-King, J.; et al. Sources of Campylobacter Spp. Colonizing Housed Broiler Flocks during Rearing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenaar, J.A.; French, N.P.; Havelaar, A.H. Preventing Campylobacter at the Source: Why Is It so Difficult? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakeem, M.J.; Lu, X. Survival and Control of Campylobacter in Poultry Production Environment. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 615049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauta, M.; Johannessen, G.; Laureano Adame, L.; Williams, N.; Rosenquist, H. The Effect of Reducing Numbers of Campylobacter in Broiler Intestines on Human Health Risk. Microb. Risk Anal. 2016, 2–3, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenquist, H.; Nielsen, N.L.; Sommer, H.M.; Nørrung, B.; Christensen, B.B. Quantitative Risk Assessment of Human Campylobacteriosis Associated with Thermophilic Campylobacter Species in Chickens. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 83, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA. Scientific Opinion on Campylobacter in Broiler Meat Production: Control Options and Performance Objectives and/or Targets at Different Stages of the Food Chain. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soro, A.B.; Whyte, P.; Bolton, D.J.; Tiwari, B.K. Strategies and Novel Technologies to Control Campylobacter in the Poultry Chain: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1353–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, R.Z.; Alsayeqh, A.F.; Aqib, A.I. Role of Bacteriophages for Optimized Health and Production of Poultry. Animals 2022, 12, 3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, D.G.; Elvers, K.T.; Dopfer, D.; Hansson, I.; Jones, P.; James, S.; Gittins, J.; Stern, N.J.; Davies, R.; Connerton, I.; et al. Biosecurity-Based Interventions and Strategies to Reduce Campylobacter Spp. on Poultry Farms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 8605–8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J. Novel Approaches for Campylobacter Control in Poultry. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2009, 6, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solow, B.T.; Cloak, O.M.; Fratamico, P.M. Effect of Temperature on Viability of Campylobacter Jejuni and Campylobacter Coli on Raw Chicken or Pork Skin. J. Food Prot. 2003, 66, 2023–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soro, A.B.; Whyte, P.; Bolton, D.J.; Tiwari, B.K. Modelling the Effect of UV Light at Different Wavelengths and Treatment Combinations on the Inactivation of Campylobacter Jejuni. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 69, 102626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, B.R.; Donoghue, A.M.; Jesudhasan, P.R. Select Phytochemicals Reduce Campylobacter Jejuni in Postharvest Poultry and Modulate the Virulence Attributes of C. Jejuni. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 725087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wideman, N.; Bailey, M.; Bilgili, S.F.; Thippareddi, H.; Wang, L.; Bratcher, C.; Sanchez-Plata, M.; Singh, M. Evaluating Best Practices for Campylobacter and Salmonella Reduction in Poultry Processing Plants. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakarienė, G.; Novoslavskij, A.; Meškinis, Š.; Vasiliauskas, A.; Tamulevičienė, A.; Tamulevičius, S.; Alter, T.; Malakauskas, M. Diamond like Carbon Ag Nanocomposites as a Control Measure against Campylobacter Jejuni and Listeria Monocytogenes on Food Preparation Surfaces. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2018, 81, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Ezeike, G.O.I.; Doyle, M.P.; Hung, Y.C.; Howell, R.S. Reduction of Campylobacter Jejuni on Poultry by Low-Temperature Treatment. J. Food Prot. 2003, 66, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Kim, T.-Y.; Lim, M.-C.; Khan, M.S.I. Campylobacter Control Strategies at Postharvest Level. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 33, 2919–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciolà, A.; Riso, R.; Avventuroso, E.; Visalli, G.; Delia, S.A.; Laganà, P. Campylobacter: From Microbiology to Prevention. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2017, 58, E79–E92. [Google Scholar]
- Hermans, D.; Van Deun, K.; Martel, A.; Van Immerseel, F.; Messens, W.; Heyndrickx, M.; Haesebrouck, F.; Pasmans, F. Colonization Factors of Campylobacter Jejuni in the Chicken Gut. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batz, M.B.; Hoffmann, S.; Morris, J.G. Ranking the Disease Burden of 14 Pathogens in Food Sources in the United States Using Attribution Data from Outbreak Investigations and Expert Elicitation. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, P.; Dodi, I. Campylobacter Jejuni/Coli Infection: Is It Still a Concern? Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessouky, Y.E.; Elsayed, S.W.; Abdelsalam, N.A.; Saif, N.A.; Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Elhadidy, M. Genomic Insights into Zoonotic Transmission and Antimicrobial Resistance in Campylobacter Jejuni from Farm to Fork: A One Health Perspective. Gut Pathog. 2022, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsak, D.; Maćkiw, E.; Rozynek, E.; Zyłowska, M. Prevalence of Campylobacter Spp. in Retail Chicken, Turkey, Pork, and Beef Meat in Poland between 2009 and 2013. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasschaert, G.; De Zutter, L.; Herman, L.; Heyndrickx, M. Campylobacter Contamination of Broilers: The Role of Transport and Slaughterhouse. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 322, 108564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, D.A. Infective Dose of Campylobacter Jejuni in Milk. Br. Med. J. 1981, 282, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.E.; Levine, M.M.; Clements, M.L.; Hughes, T.P.; Blaser, M.J.; Black, R.E. Experimental Campylobacter Jejuni Infection in Humans. J. Infect. Dis. 1988, 157, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawthraw, S.A.; Wassenaar, T.M.; Ayling, R.; Newell, D.G. Increased Colonization Potential of Campylobacter Jejuni Strain 81116 after Passage through Chickens and Its Implication on the Rate of Transmission within Flocks. Epidemiol. Infect. 1996, 117, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassenaar, T.M.; Van der Zeijst, B.A.M.; Ayling, R.; Newell, D.G. Colonization of Chicks by Motility Mutants of Campylobacter Jejuni Demonstrates the Importance of Flagellin A Expression. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1993, 139, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, D.G.; Fearnley, C. Sources of Campylobacter Colonization in Broiler Chickens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4343–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha-Abdelaziz, K.; Singh, M.; Sharif, S.; Sharma, S.; Kulkarni, R.R.; Alizadeh, M.; Yitbarek, A.; Helmy, Y.A. Intervention Strategies to Control Campylobacter at Different Stages of the Food Chain. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadek, S.A.S.; Shaapan, R.M.; Barakat, A.M.A. Campylobacteriosis in Poultry: A Review. J. Worlds Poult. Res. 2023, 13, 68–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, M.I.; Malkawi, I.; Walker, M.; Alaboudi, A.; Abu-Basha, E.; Blake, D.P.; Guitian, J.; Crotta, M. The Transmission Dynamics of Campylobacter Jejuni among Broilers in Semi-Commercial Farms in Jordan. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147, e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawson, T.; Dawkins, M.S.; Bonsall, M.B. A Mathematical Model of Campylobacter Dynamics within a Broiler Flock. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, T.; Du, X.; Yang, W.; Huang, J.; Jiao, X. Occurrence and Genotypes of Campylobacter Species in Broilers during the Rearing Period. Avian Pathol. 2017, 46, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO/WHO. Risk Assessment of Campylobacter Spp. in Broiler Chickens: Technical Report; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009; Volume 180.
- Rosenquist, H.; Boysen, L.; Galliano, C.; Nordentoft, S.; Ethelberg, S.; Borck, B. Danish Strategies to Control Campylobacter in Broilers and Broiler Meat: Facts and Effects. Epidemiol. Infect. 2009, 137, 1742–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, N.J.; Hiett, K.L.; Alfredsson, G.A.; Kristinsson, K.G.; Reiersen, J.; Hardardottir, H.; Briem, H.; Gunnarsson, E.; Georgsson, F.; Lowman, R.; et al. Campylobacter Spp. in Icelandic Poultry Operations and Human Disease. Epidemiol. Infect. 2003, 130, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in Zoonotic and Indicator Bacteria from Humans, Animals and Food in 2022–2023. EFSA J. 2025, 23, e9237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera-Ramírez, A.M.; McEwan, N.R.; Stanley, K.; Nava-Diaz, R.; Aguilar-Tipacamú, G. A Systematic Review on the Role of Wildlife as Carriers and Spreaders of Campylobacter Spp. Animals 2023, 13, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Vaddu, S.; Bhumanapalli, S.; Mishra, A.; Applegate, T.; Singh, M.; Thippareddi, H. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Sources of Campylobacter in Poultry Production (Preharvest) and Their Relative Contributions to the Microbial Risk of Poultry Meat. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, E.; Barnhart, H.; Dreesen, D.W.; Stern, N.J.; Corn, J.L. Epidemiological Study of Campylobacter Spp. in Broilers: Source, Time of Colonization, and Prevalence. Avian Dis. 1997, 41, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hald, B.; Skovgård, H.; Bang, D.D.; Pedersen, K.; Dybdahl, J.; Jespersen, J.B.; Madsen, M. Flies and Campylobacter Infection of Broiler Flocks. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1490–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, D.G. The Ecology of Campylobacter Jejuni in Avian and Human Hosts and in the Environment. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 6, S16–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FSIS. Compliance Guideline for Controlling Salmonella and Campylobacter in Poultry, 3rd ed.; FSIS: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Royden, A.; Christley, R.; Prendiville, A.; Williams, N.J. The Role of Biosecurity in the Control of Campylobacter: A Qualitative Study of the Attitudes and Perceptions of UK Broiler Farm Workers. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 751699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, M.; Beauvais, W.; Guitian, J. Effect of Enhanced Biosecurity and Selected On-Farm Factors on Campylobacter Colonization of Chicken Broilers. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in Zoonotic and Indicator Bacteria from Humans, Animals and Food in 2021–2022. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e8583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.S.; Rossi, D.A.; Braz, R.F.; Fonseca, B.B.; Guidotti–Takeuchi, M.; Alves, R.N.; Beletti, M.E.; Almeida-Souza, H.O.; Maia, L.P.; de Souza Santos, P.; et al. Roles of Viable but Non-Culturable State in the Survival of Campylobacter Jejuni. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1122450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisowwong, W.; Kusumoto, A.; Hashimoto, M.; Harada, T.; Maklon, K.; Kawamoto, K. Physiological Characterization of Campylobacter Jejuni under Cold Stresses Conditions: Its Potential for Public Threat. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2012, 74, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemelka, K.W.; Brown, A.W.; Wallace, S.M.; Jones, E.; Asher, L.V.; Pattarini, D.; Applebee, L.; Gilliland, T.C.; Guerry, P.; Baqar, S. Immune Response to and Histopathology of Campylobacter Jejuni Infection in Ferrets (Mustela Putorius Furo). Comp. Med. 2009, 59, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marks, S.L.; Rankin, S.C.; Byrne, B.A.; Weese, J.S. Enteropathogenic Bacteria in Dogs and Cats: Diagnosis, Epidemiology, Treatment, and Control. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macartney, L.; Al-Mashat, R.R.; Taylor, D.J.; McCandlish, I.A. Experimental Infection of Dogs with Campylobacter Jejuni. Vet. Rec. 1988, 122, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemmons, E.A.; Jean, S.M.; Machiah, D.K.; Breding, E.; Sharma, P. Extraintestinal Campylobacteriosis in Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta). Comp. Med. 2014, 64, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.K.; Oh, J.Y.; Jeong, O.M.; Moon, O.K.; Kang, M.S.; Jung, B.Y.; An, B.K.; Youn, S.Y.; Kim, H.R.; Jang, I.; et al. Prevalence of Campylobacter Species in Wild Birds of South Korea. Avian Pathol. 2017, 46, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysok, B.; Sołtysiuk, M.; Stenzel, T. Wildlife Waterfowl as a Source of Pathogenic Campylobacter Strains. Pathogens 2022, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, C.; Bahrndorff, S.; Lowenberger, C. Campylobacter Jejuni in Musca Domestica: An Examination of Survival and Transmission Potential in Light of the Innate Immune Responses of the House Flies. Insect Sci. 2017, 24, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hald, B.; Skovgård, H.; Pedersen, K.; Bunkenborg, H. Influxed Insects as Vectors for Campylobacter Jejuni and Campylobacter Coli in Danish Broiler Houses. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 1428–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Guk, J.H.; Mun, S.H.; An, J.U.; Kim, W.; Lee, S.; Song, H.; Seong, J.K.; Suh, J.G.; Cho, S. The Wild Mouse (Micromys Minutus): Reservoir of a Novel Campylobacter Jejuni Strain. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkkola, S.; Rossi, M.; Jaakkonen, A.; Simola, M.; Tikkanen, J.; Hakkinen, M.; Tuominen, P.; Huitu, O.; Niemimaa, J.; Henttonen, H.; et al. Host-Dependent Clustering of Campylobacter Strains From Small Mammals in Finland. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 621490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerburg, B.G.; Jacobs-Reitsma, W.F.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Kijlstra, A. Presence of Salmonella and Campylobacter Spp. in Wild Small Mammals on Organic Farms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 960–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindels, L.B.; Delzenne, N.M.; Cani, P.D.; Walter, J. Opinion: Towards a More Comprehensive Concept for Prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO/WHO. Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food Including Powder Milk with Liver Lactic Acid Bacteria. Food and Agriculture Organization and World Health Organization Joint Report. Prevention 2001, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Verschuere, L.; Rombaut, G.; Sorgeloos, P.; Verstraete, W. Probiotic Bacteria as Biological Control Agents in Aquaculture. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000, 64, 655–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwehand, A.C.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E. Probiotics: An Overview of Beneficial Effects. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 82, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Roberfroid, M.B. Dietary Modulation of the Human Colonic Microbiota: Introducing the Concept of Prebiotics. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermudez-Brito, M.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Muñoz-Quezada, S.; Gómez-Llorente, C.; Gil, A. Probiotic Mechanisms of Action. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 61, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, A.A.; Lee, Y.; Lillehoj, H.S. Beneficial Effects of Dietary Supplementation of Bacillus Strains on Growth Performance and Gut Health in Chickens with Mixed Coccidiosis Infection. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 277, 109009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, F.; Muccee, F.; Shahab, A.; Safi, S.Z.; Alomar, S.Y.; Qadeer, A. Isolation and in Vitro Assessment of Chicken Gut Microbes for Probiotic Potential. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 10, 1278439–12784395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Long, S.; Mahfuz, S.; Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Piao, X. Effects of Probiotics as Antibiotics Substitutes on Growth Performance, Serum Biochemical Parameters, Intestinal Morphology, and Barrier Function of Broilers. Animals 2019, 9, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Junaid, N.; Kumawat, M.; Qureshi, S.; Mandal, A.B. Influence of Dietary Supplementation of Probiotics on Intestinal Histo-Morphometry, Blood Chemistry and Gut Health Status of Broiler Chickens. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 48, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruwa, C.E.; Pillay, C.; Nyaga, M.M.; Sabiu, S. Poultry Gut Health—Microbiome Functions, Environmental Impacts, Microbiome Engineering and Advancements in Characterization Technologies. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedford, M.R.; Apajalahti, J.H. The Role of Feed Enzymes in Maintaining Poultry Intestinal Health. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 5848–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabetafika, H.N.; Razafindralambo, A.; Ebenso, B.; Razafindralambo, H.L. Probiotics as Antibiotic Alternatives for Human and Animal Applications. Encyclopedia 2023, 3, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varastegani, A.; Dahlan, I. Influence of Dietary Fiber Levels on Feed Utilization and Growth Performance in Poultry. J. Anim. Pro. Adv. 2014, 4, 557–565. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Y.; Kumar, S.; Oakley, B.; Kim, W.K. Chicken Gut Microbiota: Importance and Detection Technology. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavijo, V.; Flórez, M.J.V. The Gastrointestinal Microbiome and Its Association with the Control of Pathogens in Broiler Chicken Production: A Review. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, J.M.D.; Casanova, N.A.; Miyakawa, M.E.F. Microbiota, Gut Health and Chicken Productivity: What Is the Connection? Microorganisms 2019, 7, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torok, V.A.; Hughes, R.J.; Mikkelsen, L.L.; Perez-Maldonado, R.; Balding, K.; MacAlpine, R.; Percy, N.J.; Ophel-Keller, K. Identification and Characterization of Potential Performance-Related Gut Microbiotas in Broiler Chickens across Various Feeding Trials. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 5868–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idowu, P.A.; Mpofu, T.J.; Magoro, A.M.; Modiba, M.C.; Nephawe, K.A.; Mtileni, B. Impact of Probiotics on Chicken Gut Microbiota, Immunity, Behavior, and Productive Performance—A Systematic Review. Front. Anim. Sci. 2025, 6, 1562527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourabedin, M.; Zhao, X. Prebiotics and Gut Microbiota in Chickens. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnv122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.; Lu, Y.; Ding, W.; Xu, B.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Jian, F.; Huang, S. The Role of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Postbiotics in Livestock and Poultry Gut Health: A Review. Metabolites 2025, 15, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeem, M.; Bourassa, D. Probiotics in Poultry: Unlocking Productivity Through Microbiome Modulation and Gut Health. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.; Das, R.; Oak, S.; Mishra, P. Probiotics (Direct-fed Microbials) in Poultry Nutrition and Their Effects on Nutrient Utilization, Growth and Laying Performance, and Gut Health: A Systematic Review. Animals 2020, 10, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggìa, F.; Mattarelli, P.; Biavati, B. Probiotics and Prebiotics in Animal Feeding for Safe Food Production. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, S15–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilingiri, K.; Rescigno, M. Postbiotics: What Else? Benef. Microbes 2013, 4, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcial-Coba, M.S.; Pjaca, A.S.; Andersen, C.J.; Knøchel, S.; Nielsen, D.S. Dried Date Paste as Carrier of the Proposed Probiotic Bacillus Coagulans BC4 and Viability Assessment during Storage and Simulated Gastric Passage. LWT 2019, 99, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.; Vinderola, G. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 649–667, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 671; Erratum in Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burcelin, R.; Serino, M.; Chabo, C.; Blasco-Baque, V.; Amar, J. Gut Microbiota and Diabetes: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Perspective. Acta Diabetol. 2011, 48, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, T.V.; Loh, T.C.; Foo, H.L.; Yaakub, H.; Bejo, M.H. Effects of Liquid Metabolite Combinations Produced by Lactobacillus Plantarum on Growth Performance, Faeces Characteristics, Intestinal Morphology and Diarrhoea Incidence in Postweaning Piglets. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2011, 43, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, Q.; Wang, J.; Tan, H.; Jin, X.; Fan, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, J.; Peng, N. Postbiotics from Pichia Kudriavzevii Promote Intestinal Health Performance through Regulation of Limosilactobacillus Reuteri in Weaned Piglets. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 3463–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachi, S.; Kanmani, P.; Tomosada, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Yuri, T.; Egusa, S.; Shimazu, T.; Suda, Y.; Aso, H.; Sugawara, M.; et al. Lactobacillus Delbrueckii TUA4408L and Its Extracellular Polysaccharides Attenuate Enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli-Induced Inflammatory Response in Porcine Intestinal Epitheliocytes via Toll-like Receptor-2 and 4. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 2080–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.; Sawant, S.; Hauff, K.; Hampp, G. Validated Postbiotic Screening Confirms Presence of Physiologically-Active Metabolites, Such as Short-Chain Fatty Acids, Amino Acids and Vitamins in Hylak® Forte. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodridge, L.D.; Bisha, B. Phage-Based Biocontrol Strategies to Reduce Foodborne Pathogens in Foods. Bacteriophage 2011, 1, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenquist, H.; Boysen, L.; Krogh, A.L.; Jensen, A.N.; Nauta, M. Campylobacter Contamination and the Relative Risk of Illness from Organic Broiler Meat in Comparison with Conventional Broiler Meat. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 162, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinivasagam, H.N.; Estella, W.; Maddock, L.; Mayer, D.G.; Weyand, C.; Connerton, P.L.; Connerton, I.F. Bacteriophages to Control Campylobacter in Commercially Farmed Broiler Chickens, in Australia. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, P.J.; Connerton, P.L.; Connerton, I.F. Phage Biocontrol of Campylobacter Jejuni in Chickens Does Not Produce Collateral Effects on the Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghmare, S.; Gupta, M.; Bahiram, K.B.; Korde, J.P.; Bhat, R.; Datar, Y.; Rajora, P.; Kadam, M.M.; Kaore, M.; Kurkure, N.V. Effects of Organic Acid Blends on the Growth Performance, Intestinal Morphology, Microbiota, and Serum Lipid Parameters of Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 104546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Xin, H.; Yang, C.; Yang, X. Impact of Essential Oils and Organic Acids on the Growth Performance, Digestive Functions and Immunity of Broiler Chickens. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.U.; Naz, S.; Raziq, F.; Qudratullah, Q.; Khan, N.A.; Laudadio, V.; Tufarelli, V.; Ragni, M. Prospects of Organic Acids as Safe Alternative to Antibiotics in Broiler Chickens Diet. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 32594–32604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani-López, E.; García, H.S.; López-Malo, A. Organic Acids as Antimicrobials to Control Salmonella in Meat and Poultry Products. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibner, J.J.; Buttin, P. Use of Organic Acids as a Model to Study the Impact of Gut Microflora on Nutrition and Metabolism. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2002, 11, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, F.; Nirmal, N.; Wang, P.; Jin, H.; Grøndahl, L.; Li, L. Recent Advances in Essential Oils and Their Nanoformulations for Poultry Feed. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusdi, R.; Hasanuddin, A.; Arief, R. Evaluation of Eleutherine (Eleutherine Americana) Potential as Feed Additive for Poultry. J. Agrisains 2016, 17, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kamatou, G.P.P.; Viljoen, A.M. A Review of the Application and Pharmacological Properties of α-Bisabolol and α-Bisabolol-Rich Oils. JAOCS J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2010, 87, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, M.G. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Essential Oils: A Short Review. Molecules 2010, 15, 9252–9287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, M.; Stanley, R.; Cusack, A.; Yasmina, S. Combinations of Plant-Derived Compounds Against Campylobacter in Vitro. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2015, 24, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sar, T.; Akbas, M.Y. Antimicrobial Activities of Olive Oil Mill Wastewater Extracts against Selected Microorganisms. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.R.; Davoodi, H. Herbal Plants and Their Derivatives as Growth and Health Promoters in Animal Nutrition. Vet. Res. Commun. 2011, 35, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannenas, I.; Bonos, E.; Filliousis, G.; Stylianaki, I.; Kumar, P.; Lazari, D.; Christaki, E.; Florou-Paneri, P. Effect of a Polyherbal or an Arsenic-Containing Feed Additive on Growth Performance of Broiler Chickens, Intestinal Microbiota, Intestinal Morphology, and Lipid Oxidation of Breast and Thigh Meat. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2019, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, S. Essential Oils: Their Antibacterial Properties and Potential Applications in Foods—A Review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windisch, W.; Schedle, K.; Plitzner, C.; Kroismayr, A. Use of Phytogenic Products as Feed Additives for Swine and Poultry. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 86, E140–E148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, T.; Watanabe-Yanai, A.; Tamamura-Andoh, Y.; Arai, N.; Akiba, M.; Kusumoto, M. Tryptanthrin Reduces Campylobacter Jejuni Colonization in the Chicken Gut by a Bactericidal Mechanism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e01701-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, B.; Saisom, T.; Sasipreeyajan, J.; Luangtongkum, T. Live-Attenuated Oral Vaccines to Reduce Campylobacter Colonization in Poultry. Vaccines 2022, 10, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, D.; Van Deun, K.; Messens, W.; Martel, A.; Van Immerseel, F.; Haesebrouck, F.; Rasschaert, G.; Heyndrickx, M.; Pasmans, F. Campylobacter Control in Poultry by Current Intervention Measures Ineffective: Urgent Need for Intensified Fundamental Research. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 152, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwaran, A.; Okoh, A.I. Molecular Determination of Genetic Diversity among Campylobacter Jejuni and Campylobacter Coli Isolated from Milk, Water, and Meat Samples Using Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus PCR (ERIC-PCR). Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2020, 10, 1830701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelo Taboada, A.C.; Pavic, A. Vaccinating Meat Chickens against Campylobacter and Salmonella: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, L.J.; Zeng, X.; Lin, J. Development and Evaluation of Two Live Salmonella-Vectored Vaccines for Campylobacter Control in Broiler Chickens. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, M.; Guyard-Nicodème, M.; Dory, D.; Chemaly, M. Control Strategies against Campylobacter at the Poultry Production Level: Biosecurity Measures, Feed Additives and Vaccination. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 1139–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal-McKinney, J.M.; Samuelson, D.R.; Eucker, T.P.; Nissen, M.S.; Crespo, R.; Konkel, M.E. Reducing Campylobacter Jejuni Colonization of Poultry via Vaccination. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintoan-Uta, C.; Cassady-Cain, R.L.; Stevens, M.P. Evaluation of Flagellum-Related Proteins FliD and FspA as Subunit Vaccines against Campylobacter Jejuni Colonisation in Chickens. Vaccine 2016, 34, 1739–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszyńska, A.; Raczko, A.; Lis, M.; Jagusztyn-Krynicka, E.K. Oral Immunization of Chickens with Avirulent Salmonella Vaccine Strain Carrying C. Jejuni 72Dz/92 CjaA Gene Elicits Specific Humoral Immune Response Associated with Protection against Challenge with Wild-Type Campylobacter. Vaccine 2004, 22, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, A.M.; Wang, J.; Hudson, D.L.; Grant, A.J.; Jones, M.A.; Maskell, D.J.; Stevens, M.P. Evaluation of Live-Attenuated Salmonella Vaccines Expressing Campylobacter Antigens for Control of C. Jejuni in Poultry. Vaccine 2010, 28, 1094–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layton, S.L.; Morgan, M.J.; Cole, K.; Kwon, Y.M.; Donoghue, D.J.; Hargis, B.M.; Pumford, N.R. Evaluation of Salmonella-Vectored Campylobacter Peptide Epitopes for Reduction of Campylobacter Jejuni in Broiler Chickens. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yuan, F. A Comprehensive Comparison of DNA and RNA Vaccines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2024, 210, 115340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, H.; Guo, F.; Yang, B.; Su, X.; Lin, J.; Xu, F. Oral Immunization of Chickens with Lactococcus Lactis Expressing CjaA Temporarily Reduces Campylobacter Jejuni Colonization. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2020, 17, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, F.A.; dos Reis Cortines, J.; Essus, V.A.; da Silva, I.B.N. Vaccine Engineering & Structural Vaccinology. In System Vaccinology: The History, the Translational Challenges and the Future; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Nothaft, H.; Perez-Muñoz, M.E.; Gouveia, G.J.; Duar, R.M.; Wanford, J.J.; Lango-Scholey, L.; Panagos, C.G.; Srithayakumar, V.; Plastow, G.S.; Coros, C.; et al. Coadministration of the Campylobacter Jejuni N-Glycan-Based Vaccine with Probiotics Improves Vaccine Performance in Broiler Chickens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01523-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumtang-On, P.; Mahony, T.J.; Hill, R.A.; Vanniasinkam, T. A Systematic Review of Campylobacter Jejuni Vaccine Candidates for Chickens. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, J.R.; Vos, A.; Blanton, J.; Müller, T.; Chipman, R.; Pieracci, E.G.; Cleaton, J.; Wallace, R. Environmental Distribution of Certain Modified Live-Virus Vaccines with a High Safety Profile Presents a Low-Risk, High-Reward to Control Zoonotic Diseases. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, J.P. Principles of Immunization. In Travel Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Naguib, M.; Sharma, S.; Schneider, A.; Wehmueller, S.; Abdelaziz, K. Comparative Effectiveness of Various Multi-Antigen Vaccines in Controlling Campylobacter Jejuni in Broiler Chickens. Vaccines 2024, 12, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, M.; Tominaga, A.; Ueda, M.; Ohshima, R.; Kobayashi, M.; Tsukada, M.; Yokoyama, E.; Takehara, K.; Deguchi, K.; Honda, T.; et al. Irrelevance between the Induction of Anti-Campylobacter Humoral Response by a Bacterin and the Lack of Protection against Homologous Challenge in Japanese Jidori Chickens. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2012, 74, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konkel, M.E.; Joens, L.A. Adhesion to and Invasion of HEp-2 Cells by Campylobacter Spp. Infect. Immun. 1989, 57, 2984–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burakova, Y.; Madera, R.; McVey, S.; Schlup, J.R.; Shi, J. Adjuvants for Animal Vaccines. Viral Immunol. 2018, 31, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravikumar, R.; Chan, J.; Prabakaran, M. Vaccines against Major Poultry Viral Diseases: Strategies to Improve the Breadth and Protective Efficacy. Viruses 2022, 14, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodman-Harris, O.; Rollier, C.S.; Iqbal, M. Approaches to Enhance the Potency of Vaccines in Chickens. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whalen, R.G. DNA Vaccines, Cyberspace and Self-Help Programs. Intervirology 1996, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, G. Plasmid DNA: A New Era in Vaccinology. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitner, W.W.; Ying, H.; Restifo, N.P. DNA and RNA-Based Vaccines: Principles, Progress and Prospects. Vaccine 1999, 18, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Adams, L.J.; Zeng, X.; Lin, J. Evaluation of in Ovo Vaccination of DNA Vaccines for Campylobacter Control in Broiler Chickens. Vaccine 2019, 37, 3785–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloanec, N.; Guyard-Nicodème, M.; Brunetti, R.; Quesne, S.; Keita, A.; Chemaly, M.; Dory, D. Plasmid DNA Prime/Protein Boost Vaccination against Campylobacter Jejuni in Broilers: Impact of Vaccine Candidates on Immune Responses and Gut Microbiota. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meunier, M.; Guyard-Nicodème, M.; Vigouroux, E.; Poezevara, T.; Béven, V.; Quesne, S.; Amelot, M.; Parra, A.; Chemaly, M.; Dory, D. A DNA Prime/Protein Boost Vaccine Protocol Developed against Campylobacter Jejuni for Poultry. Vaccine 2018, 36, 2119–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gote, V.; Bolla, P.K.; Kommineni, N.; Butreddy, A.; Nukala, P.K.; Palakurthi, S.S.; Khan, W. A Comprehensive Review of MRNA Vaccines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capozzo, A.V.E.; Ramírez, K.; Polo, J.M.; Ulmer, J.; Barry, E.M.; Levine, M.M.; Pasetti, M.F. Neonatal Immunization with a Sindbis Virus-DNA Measles Vaccine Induces Adult-Like Neutralizing Antibodies and Cell-Mediated Immunity in the Presence of Maternal Antibodies. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 5671–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickan, E.; Yu, Z.; Rouse, B.T. DNA Immunization of Neonates Induces Immunity despite the Presence of Maternal Antibody. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 2371–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannotta, G.; Murrone, A.; Giannotta, N. COVID-19 MRNA Vaccines: The Molecular Basis of Some Adverse Events. Vaccines 2023, 11, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, M.R.; Poland, G.A. Critical Aspects of Packaging, Storage, Preparation, and Administration of MRNA and Adenovirus-Vectored COVID-19 Vaccines for Optimal Efficacy. Vaccine 2021, 39, 457–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefébure, T.; Bitar, P.D.P.; Suzuki, H.; Stanhope, M.J. Evolutionary Dynamics of Complete Campylobacter Pan-Genomes and the Bacterial Species Concept. Genome Biol. Evol. 2010, 2, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.; Lévesque, S.; Kumar, N.; Fresia, P.; Ferrés, I.; Lawley, T.D.; Iraola, G. Pangenome Analysis Reveals Genetic Isolation in Campylobacter Hyointestinalis Subspecies Adapted to Different Mammalian Hosts. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemmell, M.R.; Berry, S.; Mukhopadhya, I.; Hansen, R.; Nielsen, H.L.; Bajaj-Elliott, M.; Nielsen, H.; Hold, G.L. Comparative Genomics of Campylobacter Concisus: Analysis of Clinical Strains Reveals Genome Diversity and Pathogenic Potential. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Qu, B.; Hu, G.; Ning, K. Pan-Genome Analysis of Campylobacter: Insights on the Genomic Diversity and Virulence Profile. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01029-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayrou, C.; Barratt, N.A.; Ketley, J.M.; Bayliss, C.D. Phase Variation During Host Colonization and Invasion by Campylobacter Jejuni and Other Campylobacter Species. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 705139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, K.L.; Atack, J.M.; Srikhanta, Y.N.; Eckert, A.; Novotny, L.A.; Bakaletz, L.O.; Jennings, M.P. Selection for Phase Variation of Los Biosynthetic Genes Frequently Occurs in Progression of Non-Typeable Haemophilus Influenzae Infection from the Nasopharynx to the Middle Ear of Human Patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Woude, M.W.; Bäumler, A.J. Phase and Antigenic Variation in Bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 581–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Woude, M.W. Re-Examining the Role and Random Nature of Phase Variation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 254, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Woude, M.W. Phase Variation: How to Create and Coordinate Population Diversity. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnham, P.M.; Hendrixson, D.R. Campylobacter Jejuni: Collective Components Promoting a Successful Enteric Lifestyle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Marmion, M.; Ferone, M.; Wall, P.; Scannell, A.G.M. On Farm Interventions to Minimise Campylobacter Spp. Contamination in Chicken. Br. Poult. Sci. 2021, 62, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, W.A.; Hess, C.; Hess, M. Re-Thinking the Chicken–Campylobacter Jejuni Interaction: A Review. Avian Pathol. 2018, 47, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Hakeem, W.G.; Fathima, S.; Shanmugasundaram, R.; Selvaraj, R.K. Campylobacter Jejuni in Poultry: Pathogenesis and Control Strategies. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, O.; Luo, N.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Q. Effect of Campylobacter-Specific Maternal Antibodies on Campylobacter Jejuni Colonization in Young Chickens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5372–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreeve, J.E.; Toszeghy, M.; Pattison, M.; Newell, D.G. Sequential Spread of Campylobacter Infection in a Multipen Broiler House. Avian Dis. 2000, 44, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs-Reitsma, W.F.; Van de Giessen, A.W.; Bolder, N.M.; Mulder, R.W.A.W. Epidemiology of Campylobacter Spp. at Two Dutch Broiler Farms. Epidemiol. Infect. 1995, 114, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.J.; Sayers, A.R. A Longitudinal Study of Campylobacter Infection of Broiler Flocks in Great Britain. Prev. Vet. Med. 2000, 46, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haems, K.; Van Rysselberghe, N.; Goossens, E.; Strubbe, D.; Rasschaert, G.; Martel, A.; Pasmans, F.; Garmyn, A. Reducing Campylobacter Colonization in Broilers by Active Immunization of Naive Broiler Breeders Using a Bacterin and Subunit Vaccine. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 103075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haems, K.; Strubbe, D.; Van Rysselberghe, N.; Rasschaert, G.; Martel, A.; Pasmans, F.; Garmyn, A. Role of Maternal Antibodies in the Protection of Broiler Chicks against Campylobacter Colonization in the First Weeks of Life. Animals 2024, 14, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, E.; Sun, L.; Cervin, G.; Pavia, H.; Tällberg, G.; Ellström, P.; Ivarsson, E. No Colonization Resistance to Campylobacter Jejuni in Broilers Fed Brown Algal Extract-Supplemented Diets. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 104898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, M.; Sharma, S.; Schneider, A.; Bragg, A.J.; Abdelaziz, K. A Multi-Antigen Campylobacter Vaccine Enhances Antibody Responses in Layer Breeders and Sustains Elevated Maternal Antibody Levels in Their Offspring. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 104898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacharme-Lora, L.; Chaloner, G.; Gilroy, R.; Humphrey, S.; Gibbs, K.; Jopson, S.; Wright, E.; Reid, W.; Ketley, J.; Humphrey, T.; et al. B Lymphocytes Play a Limited Role in Clearance of Campylobacter Jejuni from the Chicken Intestinal Tract. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintoan-Uta, C.; Cassady-Cain, R.L.; Al-Haideri, H.; Watson, E.; Kelly, D.J.; Smith, D.G.E.; Sparks, N.H.C.; Kaiser, P.; Stevens, M.P. Superoxide Dismutase SodB Is a Protective Antigen against Campylobacter Jejuni Colonisation in Chickens. Vaccine 2015, 33, 4545–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, P.A.; Huggins, M.B.; Lovell, M.A.; Simpson, J.M. Observations on the Pathogenesis of Experimental Salmonella Typhimurium Infection in Chickens. Res. Vet. Sci. 1987, 42, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilroy, R.; Wedley, A.; Jopson, S.; Hall, J.; Wigley, P. The Immunobiology of Persistent Intestinal Infection by Campylobacter Jejuni in the Chicken. bioRixv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Matos, R.; Morrisey, J.K. Marek’s Disease. In Comparative Veterinary Anatomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 1355–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Ceccopieri, C.; Madej, J.P. Chicken Secondary Lymphoid Tissues—Structure and Relevance in Immunological Research. Animals 2024, 14, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Kaiser, P. Antigen Presenting Cells in a Non-Mammalian Model System, the Chicken. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Shira, E.; Friedman, A. Development and Adaptations of Innate Immunity in the Gastrointestinal Tract of the Newly Hatched Chick. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervelde, L.; Jeurissen, S.H.M. Postnatal Development of Intra-Epithelial Leukocytes in the Chicken Digestive Tract: Phenotypical Characterization in Situ. Cell Tissue Res. 1993, 274, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillehoj, H.S.; Trout, J.M. Avian Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissues and Intestinal Immune Responses to Eimeria Parasites. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 9, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeurissen, S.H.M.; Janse, E.M.; Koch, G.; De Boer, G.F. Postnatal Development of Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissues in Chickens. Cell Tissue Res. 1989, 258, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, W.I.; Bryden, W.L.; Husband, A.J. Immunity, Vaccination and the Avian Intestinal Tract. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2000, 24, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nochi, T.; Jansen, C.A.; Toyomizu, M.; van Eden, W. The Well-Developed Mucosal Immune Systems of Birds and Mammals Allow for Similar Approaches of Mucosal Vaccination in Both Types of Animals. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, X.; Cui, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. How to Break through the Bottlenecks of in Ovo Vaccination in Poultry Farming. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, S.K.; Sharma, J.M.; Ahmad, J.; Reddy, D.N.; McMillen, J.K.; Cook, S.M.; Wild, M.A.; Schwartz, R.D. Protective Efficacy of a Recombinant Herpesvirus of Turkeys as an in Ovo Vaccine against Newcastle and Marek’s Diseases in Specific-Pathogen-Free Chickens. Vaccine 1996, 14, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Ghany, W.A. In Ovo Vaccination Technology: An Alternative Approach to Post-Hatch Vaccination in Modern Poultry Operations. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérin, J.L.; Balloy, D.; Pinson, M.; Jbenyeni, A.; Delpont, M. Vaccination Technology in Poultry: Principles of Vaccine Administration. Avian Dis. 2023, 67, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoret, J.R.; Cooper, K.K.; Zekarias, B.; Roland, K.L.; Law, B.F.; Curtiss, R.; Joens, L.A. The Campylobacter Jejuni Dps Homologue Is Important for in Vitro Biofilm Formation and Cecal Colonization of Poultry and May Serve as a Protective Antigen for Vaccination. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 1426–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.D.; Oakes, R.D.; Redhead, K.; Crouch, C.F.; Francis, M.J.; Tomley, F.M.; Blake, D.P. Eimeria Species Parasites as Novel Vaccine Delivery Vectors: Anti-Campylobacter Jejuni Protective Immunity Induced by Eimeria Tenella-Delivered CjaA. Vaccine 2012, 30, 2683–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calland, J.K.; Pesonen, M.E.; Mehat, J.; Pascoe, B.; Haydon, D.J.; Lourenco, J.; Lukasiewicz, B.; Mourkas, E.; Hitchings, M.D.; La Ragione, R.M.; et al. Genomic Tailoring of Autogenous Poultry Vaccines to Reduce Campylobacter from Farm to Fork. NPJ Vaccines 2024, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Guo, F.; Guo, J.; Cao, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, B.; Zhou, H.; Su, X.; Zeng, X.; Lin, J.; et al. Immunization of Chickens with the Enterobactin Conjugate Vaccine Reduced Campylobacter Jejuni Colonization in the Intestine. Vaccines 2020, 8, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, C.A.; Meinersmann, R.J. A Genetic Hybrid of the Campylobacter Jejuni FlaA Gene with LT-B of Escherichia Coli and Assessment of the Efficacy of the Hybrid Protein as an Oral Chicken Vaccine. Avian Dis. 1995, 39, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobierecka, P.A.; Wyszynska, A.K.; Gubernator, J.; Kuczkowski, M.; Wisniewski, O.; Maruszewska, M.; Wojtania, A.; Derlatka, K.E.; Adamska, I.; Godlewska, R.; et al. Chicken Anti-Campylobacter Vaccine—Comparison of Various Carriers and Routes of Immunization. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.A.; Huang, J.L.; Yin, Y.X.; Pan, Z.M.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, A.P.; Liu, X.F. Intranasal Immunization with Chitosan/PCAGGS-Fla A Nanoparticles Inhibits Campylobacter Jejuni in a White Leghorn Model. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 589476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, M.; Guyard-Nicodème, M.; Vigouroux, E.; Poezevara, T.; Beven, V.; Quesne, S.; Bigault, L.; Amelot, M.; Dory, D.; Chemaly, M. Promising New Vaccine Candidates against Campylobacter in Broilers. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha-Abdelaziz, K.; Hodgins, D.C.; Alkie, T.N.; Quinteiro-Filho, W.; Yitbarek, A.; Astill, J.; Sharif, S. Oral Administration of PLGA-Encapsulated CpG ODN and Campylobacter Jejuni Lysate Reduces Cecal Colonization by Campylobacter Jejuni in Chickens. Vaccine 2018, 36, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Nisaa, K.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Mallick, A.I. Immunogenicity and Protective Efficacy of Mucosal Delivery of Recombinant Hcp of Campylobacter Jejuni Type VI Secretion System (T6SS) in Chickens. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 111, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgins, D.C.; Barjesteh, N.; St. Paul, M.; Ma, Z.; Monteiro, M.A.; Sharif, S. Evaluation of a Polysaccharide Conjugate Vaccine to Reduce Colonization by Campylobacter Jejuni in Broiler Chickens. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohra, P.; Chintoan-Uta, C.; Bremner, A.; Mauri, M.; Terra, V.S.; Cuccui, J.; Wren, B.W.; Vervelde, L.; Stevens, M.P. Evaluation of a Campylobacter Jejuni N-Glycan-ExoA Glycoconjugate Vaccine to Reduce C. Jejuni Colonisation in Chickens. Vaccine 2021, 39, 7413–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, T.; Pina-Mimbela, R.; Kumar, A.; Binjawadagi, B.; Liu, Z.; Renukaradhya, G.J.; Rajashekara, G. Evaluation of Nanoparticle-Encapsulated Outer Membrane Proteins for the Control of Campylobacter Jejuni Colonization in Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psifidi, A.; Kranis, A.; Rothwell, L.M.; Bremner, A.; Russell, K.; Robledo, D.; Bush, S.J.; Fife, M.; Hocking, P.M.; Banos, G.; et al. Quantitative Trait Loci and Transcriptome Signatures Associated with Avian Heritable Resistance to Campylobacter. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psifidi, A.; Fife, M.; Howell, J.; Matika, O.; van Diemen, P.M.; Kuo, R.; Smith, J.; Hocking, P.M.; Salmon, N.; Jones, M.A.; et al. The Genomic Architecture of Resistance to Campylobacter Jejuni Intestinal Colonisation in Chickens. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona-Torres, R.; Vohra, P.; Chintoan-Uta, C.; Bremner, A.; Terra, V.S.; Mauri, M.; Cuccui, J.; Vervelde, L.; Wren, B.W.; Stevens, M.P. Evaluation of a FlpA Glycoconjugate Vaccine with Ten N-Heptasaccharide Glycan Moieties to Reduce Campylobacter Jejuni Colonisation in Chickens. Vaccines 2024, 12, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloanec, N.; Guyard-Nicodème, M.; Brunetti, R.; Quesne, S.; Keita, A.; Chemaly, M.; Dory, D. Evaluation of Two Recombinant Protein-Based Vaccine Regimens against Campylobacter Jejuni: Impact on Protection, Humoral Immune Responses and Gut Microbiota in Broilers. Animals 2023, 13, 3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorain, C.; Singh, A.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Kundu, A.; Lahiri, A.; Gupta, S.; Mallick, A.I. Mucosal Delivery of Live Lactococcus Lactis Expressing Functionally Active JlpA Antigen Induces Potent Local Immune Response and Prevent Enteric Colonization of Campylobacter Jejuni in Chickens. Vaccine 2020, 38, 1630–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łaniewski, P.; Kuczkowski, M.; Chrzastek, K.; Woźniak, A.; Wyszyńska, A.; Wieliczko, A.; Jagusztyn-Krynicka, E.K. Evaluation of the Immunogenicity of Campylobacter Jejuni CjaA Protein Delivered by Salmonella Enterica Sv. Typhimurium Strain with Regulated Delayed Attenuation in Chickens. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Xu, F.; Lin, J. Development and Evaluation of CmeC Subunit Vaccine against Campylobacter Jejuni. J. Vaccines Vaccin. 2010, 1, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vohra, P.; Chintoan-uta, C.; Terra, V.S.; Bremner, A.; Cuccui, J.; Wren, B.W.; Vervelde, L.; Stevens, M.P. Evaluation of Glycosylated FLPA and SODB as Subunit Vaccines against Campylobacter Jejuni Colonisation in Chickens. Vaccines 2020, 8, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandeputte, J.; Martel, A.; Van Rysselberghe, N.; Antonissen, G.; Verlinden, M.; De Zutter, L.; Heyndrickx, M.; Haesebrouck, F.; Pasmans, F.; Garmyn, A. In Ovo Vaccination of Broilers against Campylobacter Jejuni Using a Bacterin and Subunit Vaccine. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5999–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radomska, K.A.; Vaezirad, M.M.; Verstappen, K.M.; Wösten, M.M.S.M.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Van Putten, J.P.M. Chicken Immune Response after in Ovo Immunization with Chimeric TLR5 Activating Flagellin of Campylobacter Jejuni. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibanda, N.; McKenna, A.; Richmond, A.; Ricke, S.C.; Callaway, T.; Stratakos, A.C.; Gundogdu, O.; Corcionivoschi, N. A Review of the Effect of Management Practices on Campylobacter Prevalence in Poultry Farms. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boodhoo, N.; Shoja Doost, J.; Sharif, S. Biosensors for Monitoring, Detecting, and Tracking Dissemination of Poultry-Borne Bacterial Pathogens Along the Poultry Value Chain: A Review. Animals 2024, 14, 3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilli, G.; Laconi, A.; Galuppo, F.; Mughini-Gras, L.; Piccirillo, A. Assessing Biosecurity Compliance in Poultry Farms: A Survey in a Densely Populated Poultry Area in North East Italy. Animals 2022, 12, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelaude, P.; Schlepers, M.; Verlinden, M.; Laanen, M.; Dewulf, J. Biocheck.UGent: A Quantitative Tool to Measure Biosecurity at Broiler Farms and the Relationship with Technical Performances and Antimicrobial Use. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 2740–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafutdinov, I.; Linz, B.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Backert, S. Therapeutic and Protective Approaches to Combat Campylobacter Jejuni Infections. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 191–198+1572616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connell, S.; Meade, K.G.; Allan, B.; Lloyd, A.T.; Kenny, E.; Cormican, P.; Morris, D.W.; Bradley, D.G.; O’Farrelly, C. Avian Resistance to Campylobacter Jejuni Colonization Is Associated with an Intestinal Immunogene Expression Signature Identified by MRNA Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.K.; Kaiser, P.; Rothwell, L.; Humphrey, T.; Barrow, P.A.; Jones, M.A. Campylobacter Jejuni-Induced Cytokine Responses in Avian Cells. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 2094–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaughnessy, R.G.; Meade, K.G.; Cahalane, S.; Allan, B.; Reiman, C.; Callanan, J.J.; O’Farrelly, C. Innate Immune Gene Expression Differentiates the Early Avian Intestinal Response between Salmonella and Campylobacter. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 132, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, D.; Yang, X.; Wei, F.; Wen, Q.; Feng, Y.; Jin, X.; Liu, D.; Guo, Y.; Hu, Y. Integrated Multi-Omics Reveals the Roles of Cecal Microbiota and Its Derived Bacterial Consortium in Promoting Chicken Growth. mSystems 2023, 8, e00844-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, L.; Soh, P.X.Y.; McEnearney, T.E.; Cain, J.A.; Dale, A.L.; Cordwell, S.J. Multi-Omics of Campylobacter Jejuni Growth in Chicken Exudate Reveals Molecular Remodelling Associated with Altered Virulence and Survival Phenotypes. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagle, B.R.; Quach, A.; Yeo, S.; Assumpcao, A.L.F.V.; Arsi, K.; Donoghue, A.M.; Jesudhasan, P.R.R. A Multiomic Analysis of Chicken Serum Revealed the Modulation of Host Factors Due to Campylobacter Jejuni Colonization and In-Water Supplementation of Eugenol Nanoemulsion. Animals 2023, 13, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Xu, H.; Ning, C.; Xiang, L.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, R. Multi-Omics Approach Reveals the Potential Core Vaccine Targets for the Emerging Foodborne Pathogen Campylobacter Jejuni. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 665858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Barrios, P.; Hempen, M.; Messens, W.; Stella, P.; Hugas, M. Quantitative Microbiological Risk Assessment (QMRA) of Food-Borne Zoonoses at the European Level. Food Control 2013, 29, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, M.; Guyard-Nicodème, M.; Hirchaud, E.; Parra, A.; Chemaly, M.; Dory, D. Identification of Novel Vaccine Candidates against Campylobacter through Reverse Vaccinology. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 5715790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintel, B.K.; Prongay, K.; Lewis, A.D.; Raué, H.-P.; Hendrickson, S.; Rhoades, N.S.; Messaoudi, I.; Gao, L.; Slifka, M.K.; Amanna, I.J. Vaccine-Mediated Protection against Campylobacter-Associated Enteric Disease. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Kumar, A. Designing an Efficient Multi-Epitope Vaccine against Campylobacter Jejuni Using Immunoinformatics and Reverse Vaccinology Approach. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saggese, A.; Baccigalupi, L.; Donadio, G.; Ricca, E.; Isticato, R. The Bacterial Spore as a Mucosal Vaccine Delivery System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śmiałek, M.; Kowalczyk, J.; Koncicki, A. The Use of Probiotics in the Reduction of Campylobacter Spp. Prevalence in Poultry. Animals 2021, 11, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Looft, T.; Zhang, Q.; Sahin, O. Deciphering the Association between Campylobacter Colonization and Microbiota Composition in the Intestine of Commercial Broilers. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.; Beyi, A.F.; Looft, T.; Zhang, Q.; Sahin, O. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Reduces Campylobacter Jejuni Colonization in Young Broiler Chickens Challenged by Oral Gavage but Not by Seeder Birds. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babo Martins, S.; Rushton, J.; Stärk, K.D.C. Economics of Zoonoses Surveillance in a “One Health” Context: An Assessment of Campylobacter Surveillance in Switzerland. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
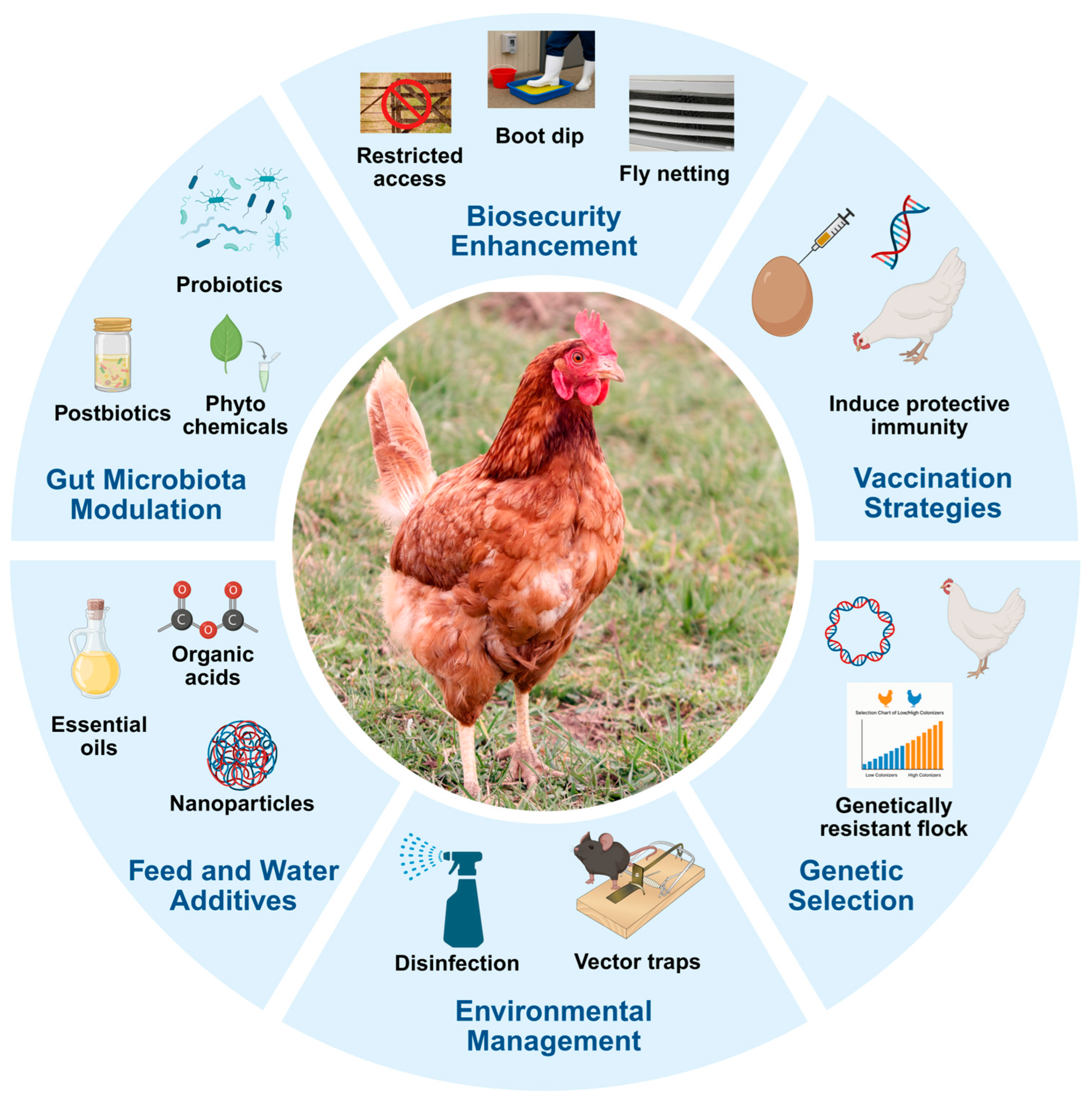
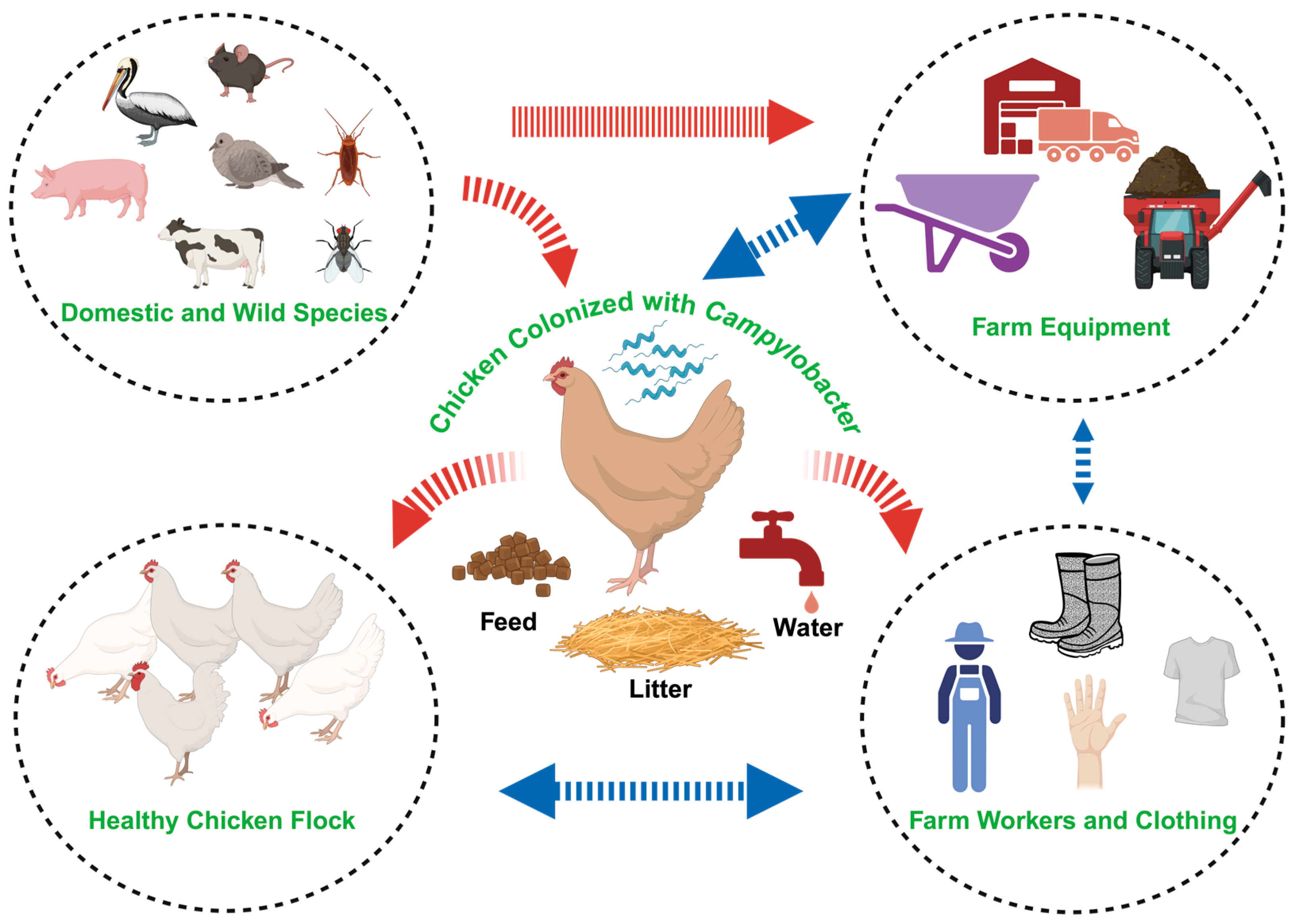
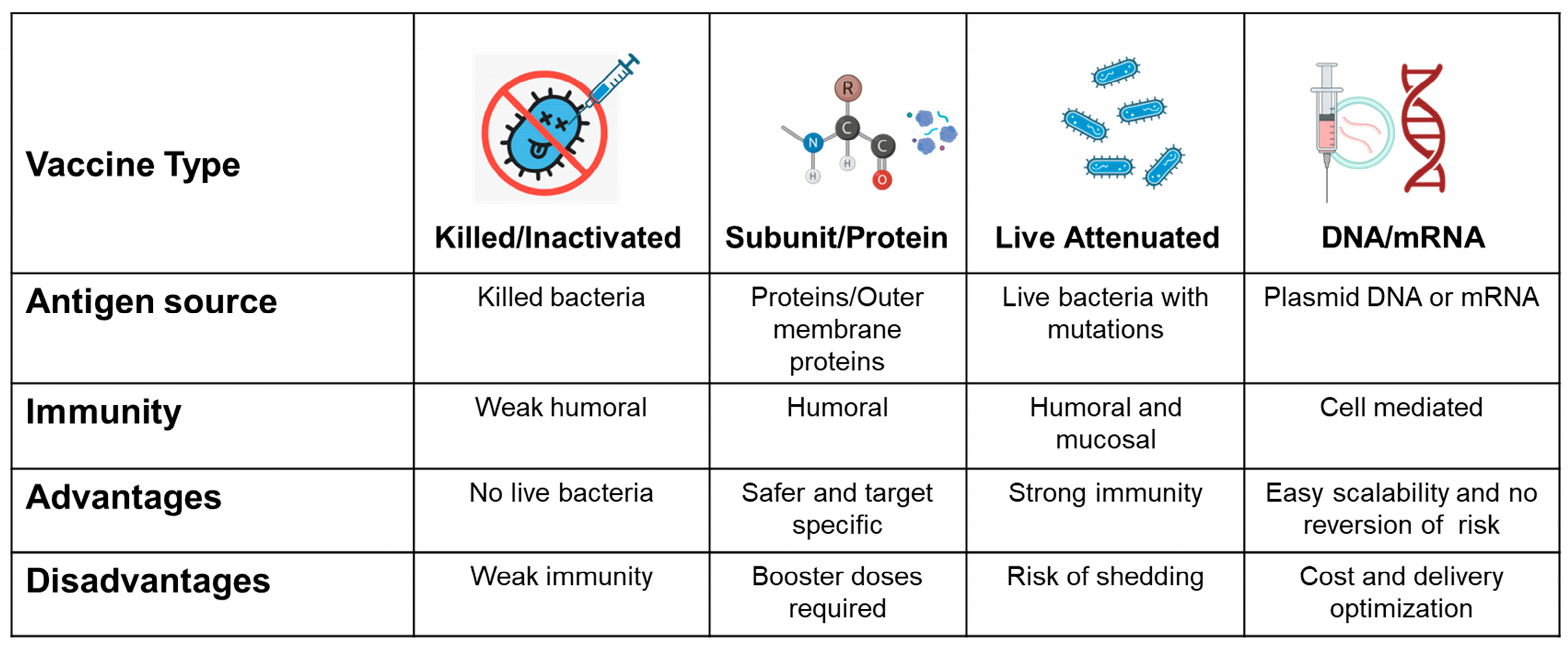
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gottapu, C.; Edison, L.K.; Butcher, G.D.; Kariyawasam, S. Preharvest Control of Campylobacter Colonization in Chickens, with a Special Emphasis on Vaccination Strategies. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2378. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102378
Gottapu C, Edison LK, Butcher GD, Kariyawasam S. Preharvest Control of Campylobacter Colonization in Chickens, with a Special Emphasis on Vaccination Strategies. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(10):2378. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102378
Chicago/Turabian StyleGottapu, Chaitanya, Lekshmi K. Edison, Gary D. Butcher, and Subhashinie Kariyawasam. 2025. "Preharvest Control of Campylobacter Colonization in Chickens, with a Special Emphasis on Vaccination Strategies" Microorganisms 13, no. 10: 2378. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102378
APA StyleGottapu, C., Edison, L. K., Butcher, G. D., & Kariyawasam, S. (2025). Preharvest Control of Campylobacter Colonization in Chickens, with a Special Emphasis on Vaccination Strategies. Microorganisms, 13(10), 2378. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102378







