A Multi-Approach for In Silico Detection of Chromosome Inversions in Mosquito Vectors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequencing Data Acquisition
2.2. Genome Reference
2.3. Genotyping by Sequencing and Variant Calling
2.4. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
2.5. Chromosome Inversion Identification
2.6. Chromosome Correlation Tests and Association Tests
2.7. Pipeline Validation with Known Variants for Anopheles gambiae
2.8. Comparative Genomics Analysis
3. Results
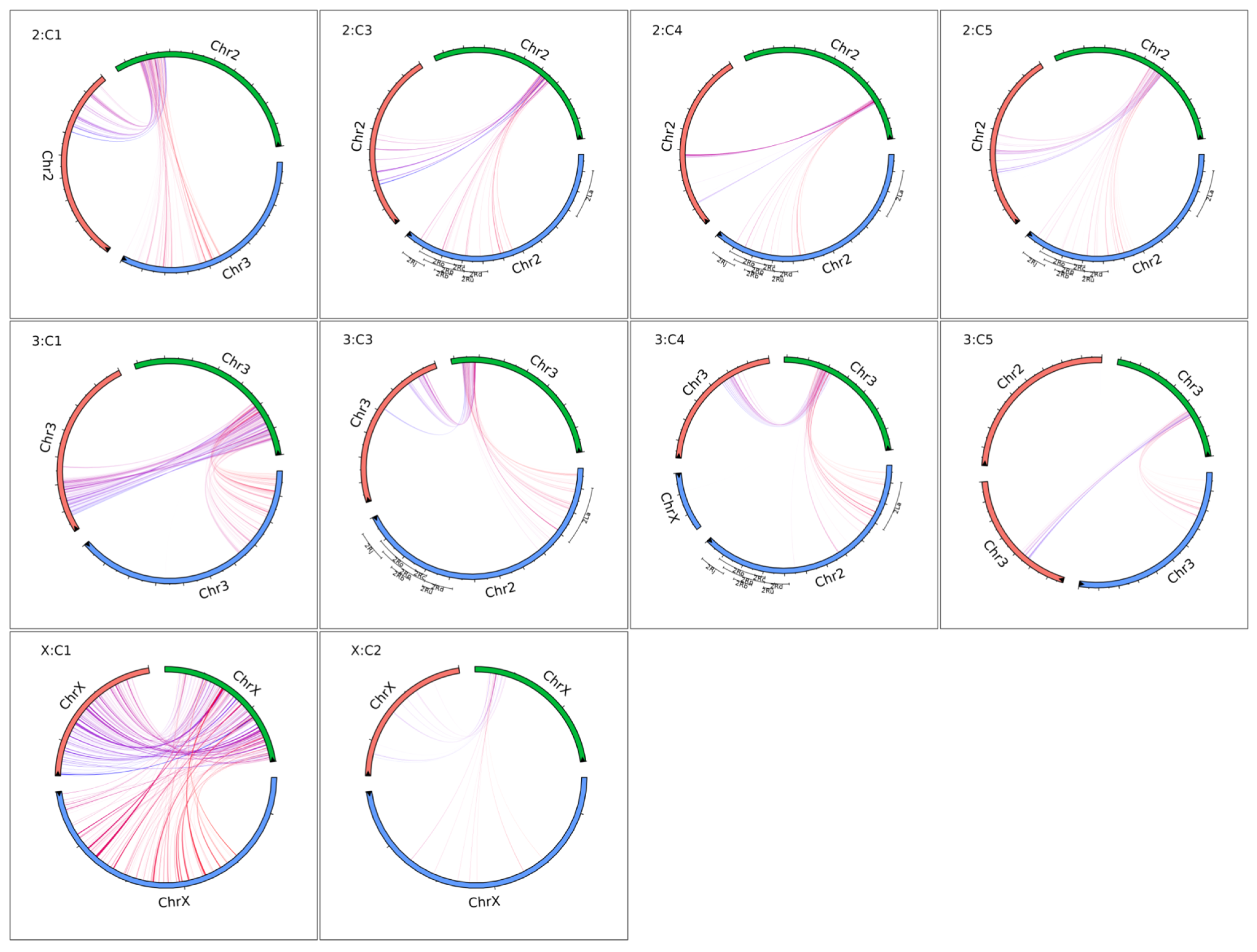
3.1. Ny. Darlingi Chromosome Inversions Detection
3.2. In Silico Validation of the Pipeline
3.3. Genome Synteny Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. World Malaria Report 2018; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 9789241565653.
- Venkatesan, P. The 2023 WHO World Malaria Report. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimenta, P.F.P.; Orfano, A.S.; Bahia, A.C.; Duarte, A.P.M.; Ríos-Velásquez, C.M.; Melo, F.F.; Pessoa, F.A.C.; Oliveira, G.A.; Campos, K.M.M.; Villegas, L.M.; et al. An Overview of Malaria Transmission from the Perspective of Amazon Anopheles Vectors. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2015, 110, 23–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Aguiar, G.M.S.C.; da Silva Picoli, M.E.F.; Ananias, F. Comportamento Epidemiológico Da Malária No Período Entre 2010 E 2020, No Brasil. Braz. J. Dev. 2022, 8, 73299–73315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaki, S.S.; Chaves, L.S.M.; López, R.V.M.; Bergo, E.S.; Laporta, G.Z.; Conn, J.E.; Sallum, M.A.M. Host Feeding Patterns of Nyssorhynchus darlingi (Diptera: Culicidae) in the Brazilian Amazon. Acta Trop. 2021, 213, 105751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, L.M.C.; Souto, R.N.P.; Dos Anjos Ferreira, R.M.; Scarpassa, V.M. Behavioral Patterns, Parity Rate and Natural Infection Analysis in Anopheline Species Involved in the Transmission of Malaria in the Northeastern Brazilian Amazon Region. Acta Trop. 2016, 164, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafael, M.S.; Tadei, W.P. Metaphase Karyotypes of Anopheles (Nyssorhynchus) darlingi Root and A. (N.) nuneztovari Gabaldón (Diptera; Culicidae). Genet. Mol. Biol. 1998, 21, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadei, W.P.; dos Santos, J.M.M.; Rabbani, M.G. Biologia de Anofelinos Amazônicos. V. Polimorfismo Cromossômico de Anopheles Darlingi Root (Diptera, Culicidae). Acta Amazon. 1982, 12, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cornel, A.J.; Brisco, K.K.; Tadei, W.P.; Secundino, N.F.; Rafael, M.S.; Galardo, A.K.; Medeiros, J.F.; Pessoa, F.A.; Ríos-Velásquez, C.M.; Lee, Y.; et al. Anopheles darlingi Polytene Chromosomes: Revised Maps Including Newly Described Inversions and Evidence for Population Structure in Manaus. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2016, 111, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Tan, J.C.; Hahn, M.W.; Besansky, N.J. Systems Genetic Analysis of Inversion Polymorphisms in the Malaria Mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E7005–E7014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouet, C.; Gray, E.; Besansky, N.J.; Costantini, C. Adaptation to Aridity in the Malaria Mosquito Anopheles gambiae: Chromosomal Inversion Polymorphism and Body Size Influence Resistance to Desiccation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, E.M.; Rocca, K.A.C.; Costantini, C.; Besansky, N.J. Inversion 2La Is Associated with Enhanced Desiccation Resistance in Anopheles gambiae. Malar. J. 2009, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, D.; Fontaine, M.C.; Cohuet, A.; Fontenille, D.; Vitalis, R.; Simard, F. Chromosomal Inversions, Natural Selection and Adaptation in the Malaria Vector Anopheles funestus. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorjanc, G.; Dumasy, J.-F.; Gonen, S.; Gaynor, R.C.; Antolin, R.; Hickey, J.M. Potential of Low-Coverage Genotyping-by-Sequencing and Imputation for Cost-Effective Genomic Selection in Biparental Segregating Populations. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 1404–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, D.; Sudbery, I.; Ilott, N.E.; Heger, A.; Ponting, C.P. Sequencing Depth and Coverage: Key Considerations in Genomic Analyses. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Boer, M.P.; van Eeuwijk, F.A. Accurate Genotype Imputation in Multiparental Populations from Low-Coverage Sequence. Genetics 2018, 210, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasaniuc, B.; Rohland, N.; McLaren, P.J.; Garimella, K.; Zaitlen, N.; Li, H.; Gupta, N.; Neale, B.M.; Daly, M.J.; Sklar, P.; et al. Extremely Low-Coverage Sequencing and Imputation Increases Power for Genome-Wide Association Studies. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustagi, N.; Zhou, A.; Watkins, W.S.; Gedvilaite, E.; Wang, S.; Ramesh, N.; Muzny, D.; Gibbs, R.A.; Jorde, L.B.; Yu, F.; et al. Extremely Low-Coverage Whole Genome Sequencing in South Asians Captures Population Genomics Information. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sidore, C.; Kang, H.M.; Boehnke, M.; Abecasis, G.R. Low-Coverage Sequencing: Implications for Design of Complex Trait Association Studies. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, M.V.N.; Alonso, D.P.; Kadri, S.M.; Rufalco-Moutinho, P.; Bernardes, I.A.F.; de Mello, A.C.F.; Souto, A.C.; Carrasco-Escobar, G.; Moreno, M.; Gamboa, D.; et al. Nyssorhynchus darlingi Genome-Wide Studies Related to Microgeographic Dispersion and Blood-Seeking Behavior. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and Accurate Short Read Alignment with Burrows–Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, B.L.; Browning, S.R. Genotype Imputation with Millions of Reference Samples. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 98, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: A Flexible Suite of Utilities for Comparing Genomic Features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weeks, J.P. Plink: AnRPackage for Linking Mixed-Format Tests Using IRT-Based Methods. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 35, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araz, Ö.M.; Olson, D.L. R Programming Language and RStudio. In Risk and Predictive Analytics in Business with R; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2025; pp. 9–14. ISBN 9781003562399. [Google Scholar]
- Irizarry, R.A. The Tidyverse. In Introduction to Data Science; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 52–71. ISBN 9781003220923. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Minimap2: Pairwise Alignment for Nucleotide Sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Li, L.; Myers, J.R.; Marth, G.T. ART: A next-Generation Sequencing Read Simulator. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 593–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and Applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emms, D.M.; Kelly, S. OrthoFinder: Phylogenetic Orthology Inference for Comparative Genomics. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.-H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A Toolkit for Detection and Evolutionary Analysis of Gene Synteny and Collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowling, R.J.; Manke, K.R.; Emrich, S.J. Detecting Inversions with PCA in the Presence of Population Structure. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowling, R.J.; Fallas-Moya, F.; Sadovnik, A.; Emrich, S.; Aleck, M.; Leskiewicz, D.; Peters, J.G. Fast, Low-Memory Detection and Localization of Large, Polymorphic Inversions from SNPs. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, A.; González, J.R. Following the Footprints of Polymorphic Inversions on SNP Data: From Detection to Association Tests. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seich Al Basatena, N.-K.; Hoggart, C.J.; Coin, L.J.; O’Reilly, P.F. The Effect of Genomic Inversions on Estimation of Population Genetic Parameters from SNP Data. Genetics 2013, 193, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Cheng, B.; Zhu, G.; Shen, D.; Liang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Tang, J.; Cao, J.; Sharakhov, I.V.; et al. Comparative Physical Genome Mapping of Malaria Vectors Anopheles sinensis and Anopheles gambiae. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Peery, A.; Hall, A.B.; Sharma, A.; Chen, X.-G.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Komissarov, A.; Riehle, M.M.; Shouche, Y.; Sharakhova, M.V.; et al. Genome Analysis of a Major Urban Malaria Vector Mosquito, Anopheles stephensi. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soboleva, E.S.; Kirilenko, K.M.; Fedorova, V.S.; Kokhanenko, A.A.; Artemov, G.N.; Sharakhov, I.V. Two Nested Inversions in the X Chromosome Differentiate the Dominant Malaria Vectors in Europe, Anopheles atroparvus and Anopheles messeae. Insects 2024, 15, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
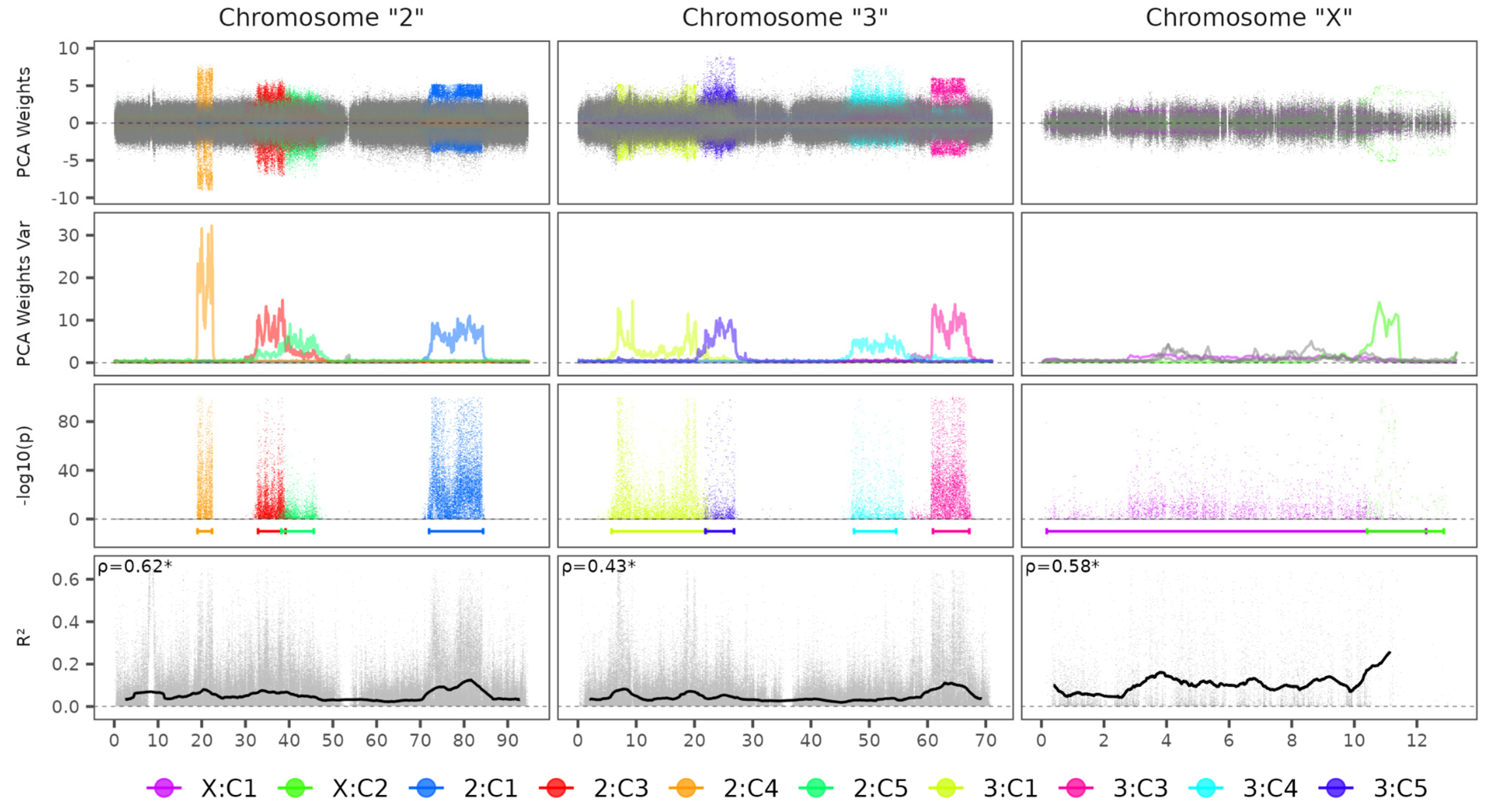
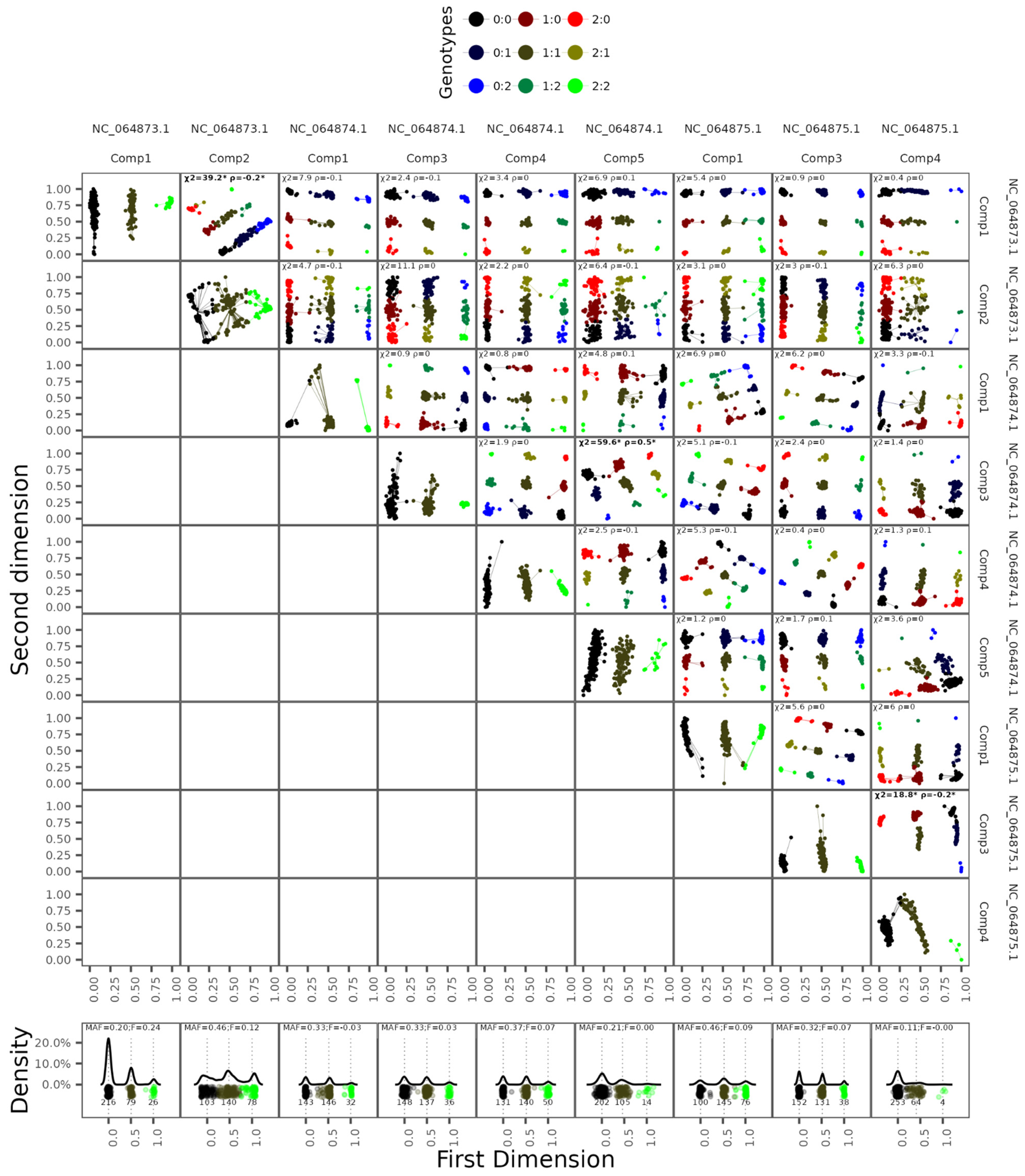
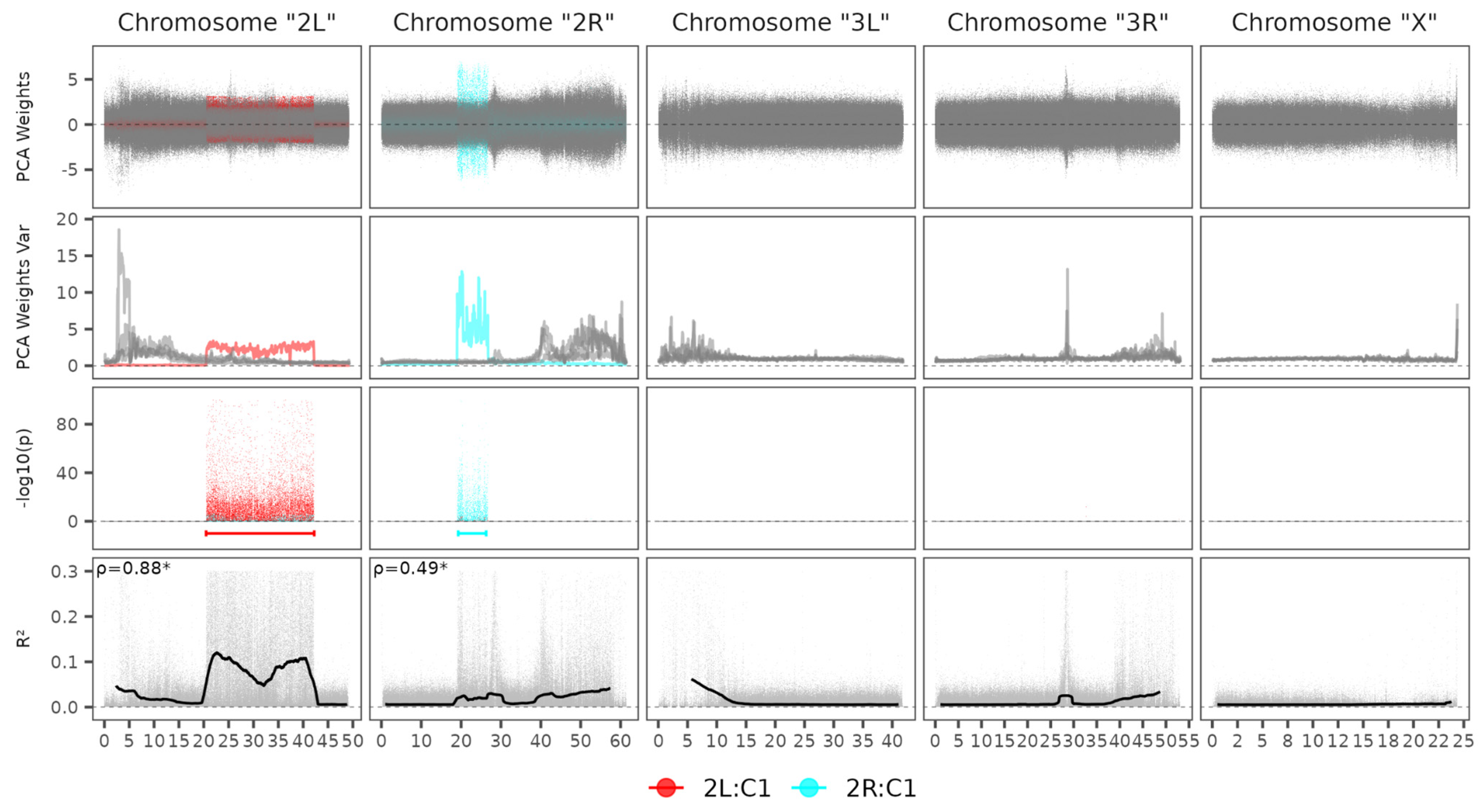
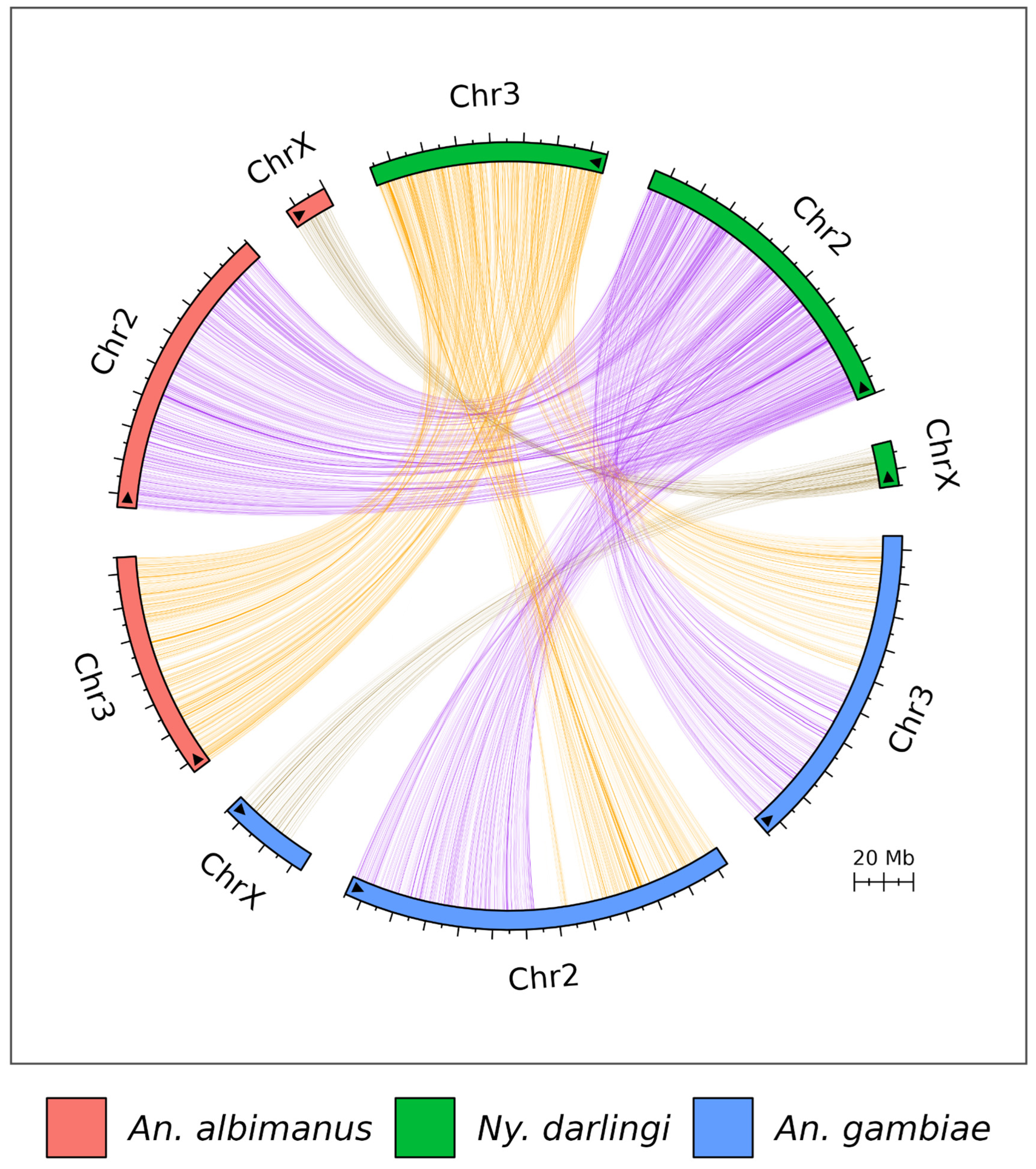
| Specie | Reference Accession | Number of Chromosomes | Genome Size | Scaffold N50 (L50) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nyssorhynchus darlingi | GCF_943734745.1 | 3 | 181.6 Mb | 95 Mb (1) |
| Anopheles gambiae | GCF_943734735.2 | 3 | 264.5 Mb | 99 Mb (2) |
| Anopheles albimanus | GCF_013758885.1 | 3 | 172.6 Mb | 89 Mb (1) |
| Chromosome | Accession Code | Component | Start | End | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | NC_064874.1 | C1 | 71,998,919 | 84,371,386 | 12,372,467 |
| 2 | NC_064874.1 | C3 | 32,875,093 | 39,167,094 | 6,292,001 |
| 2 | NC_064874.1 | C4 | 19,048,046 | 22,354,438 | 3,306,392 |
| 2 | NC_064874.1 | C5 | 38,207,551 | 45,614,642 | 7,407,091 |
| 3 | NC_064875.1 | C1 | 5,786,821 | 22,248,013 | 16,461,192 |
| 3 | NC_064875.1 | C3 | 60,944,934 | 67,169,663 | 6,224,729 |
| 3 | NC_064875.1 | C4 | 47,375,561 | 54,594,956 | 7,219,395 |
| 3 | NC_064875.1 | C5 | 21,879,305 | 26,791,351 | 4,912,046 |
| X | NC_064873.1 | C1 | 169,219 | 12,292,796 | 12,123,577 |
| X | NC_064873.1 | C2 | 10,405,329 | 12,856,594 | 2,451,265 |
| MAF | Genotype Concordance | Allelic Concordance | Dosage R2 | N | N FP | FP Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0, 0.1] | 92.48% | 96.19% | 0.8482 | 14,082 | - | - |
| (0.1, 0.2] | 90.80% | 95.28% | 0.8227 | 1,097,632 | 8557 | 0.7736% |
| (0.2, 0.3] | 85.27% | 92.40% | 0.7537 | 1,161,704 | 141 | 0.0121% |
| (0.3, 0.4] | 80.67% | 90.02% | 0.6898 | 830,122 | 158 | 0.0190% |
| (0.4, 0.5] | 77.89% | 88.64% | 0.6379 | 712,671 | 342 | 0.0480% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alvarez, M.V.N.; Bozoni, F.T.; Alonso, D.P.; Ribolla, P.E.M. A Multi-Approach for In Silico Detection of Chromosome Inversions in Mosquito Vectors. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102231
Alvarez MVN, Bozoni FT, Alonso DP, Ribolla PEM. A Multi-Approach for In Silico Detection of Chromosome Inversions in Mosquito Vectors. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(10):2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102231
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlvarez, Marcus Vinicius Niz, Filipe Trindade Bozoni, Diego Peres Alonso, and Paulo Eduardo Martins Ribolla. 2025. "A Multi-Approach for In Silico Detection of Chromosome Inversions in Mosquito Vectors" Microorganisms 13, no. 10: 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102231
APA StyleAlvarez, M. V. N., Bozoni, F. T., Alonso, D. P., & Ribolla, P. E. M. (2025). A Multi-Approach for In Silico Detection of Chromosome Inversions in Mosquito Vectors. Microorganisms, 13(10), 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102231








