Characteristics and Differences in the Antler Velvet Microbiota During Regeneration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Statistics Analysis
3. Results
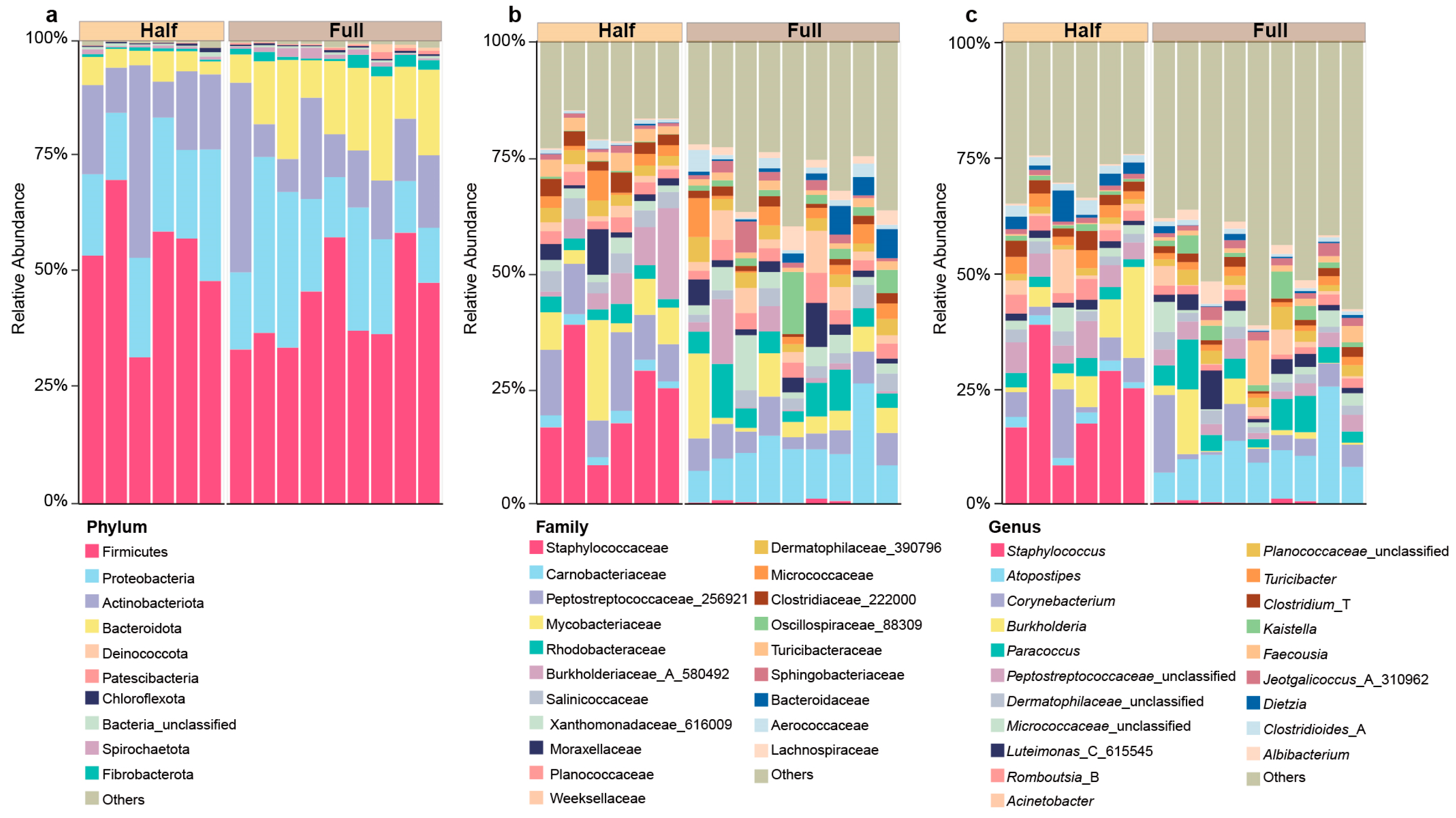
3.1. Characterization of the Microbial Composition of Antler Velvet
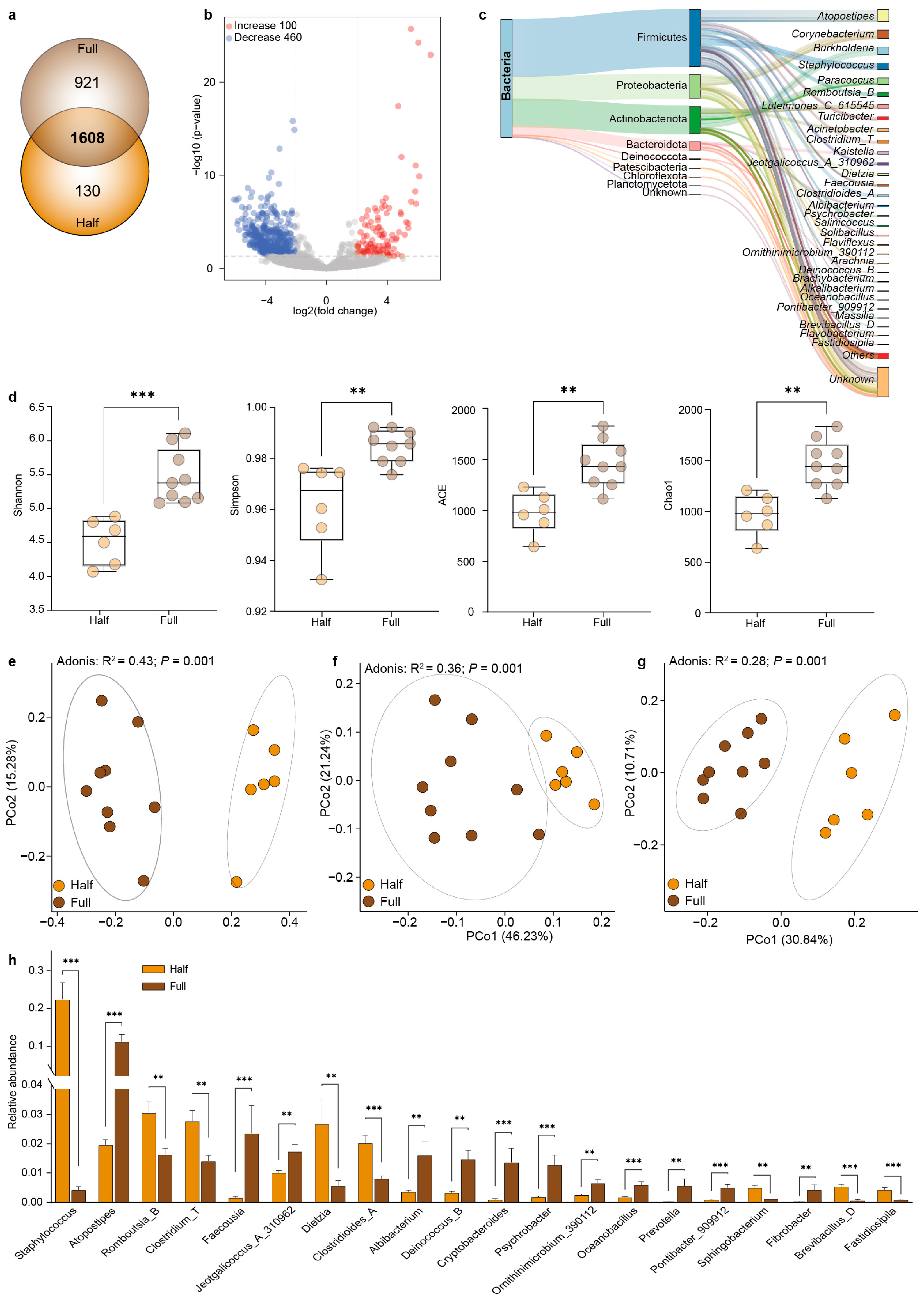
3.2. Comparison of the Microbial Composition Between the Half and Full Groups
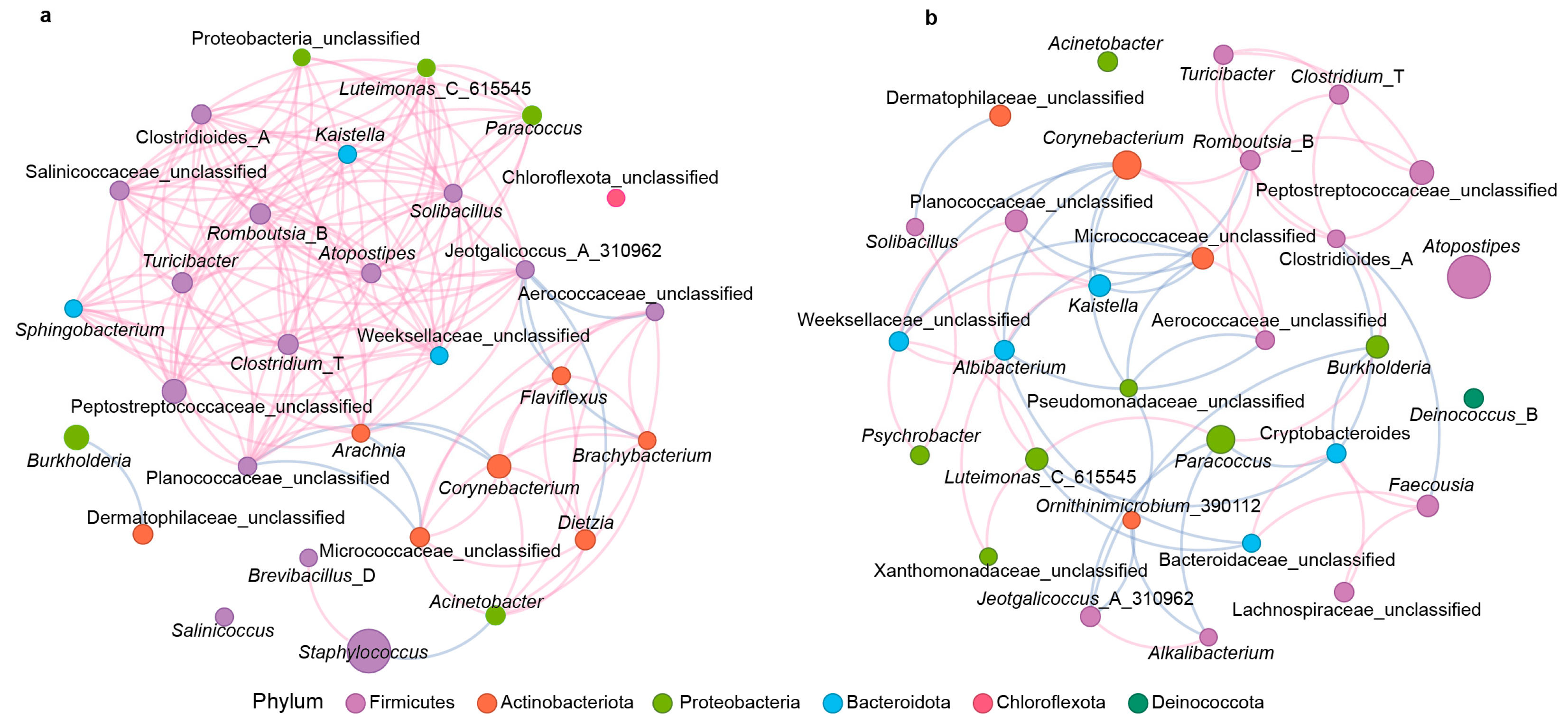
3.3. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis of the Microbial Interactions
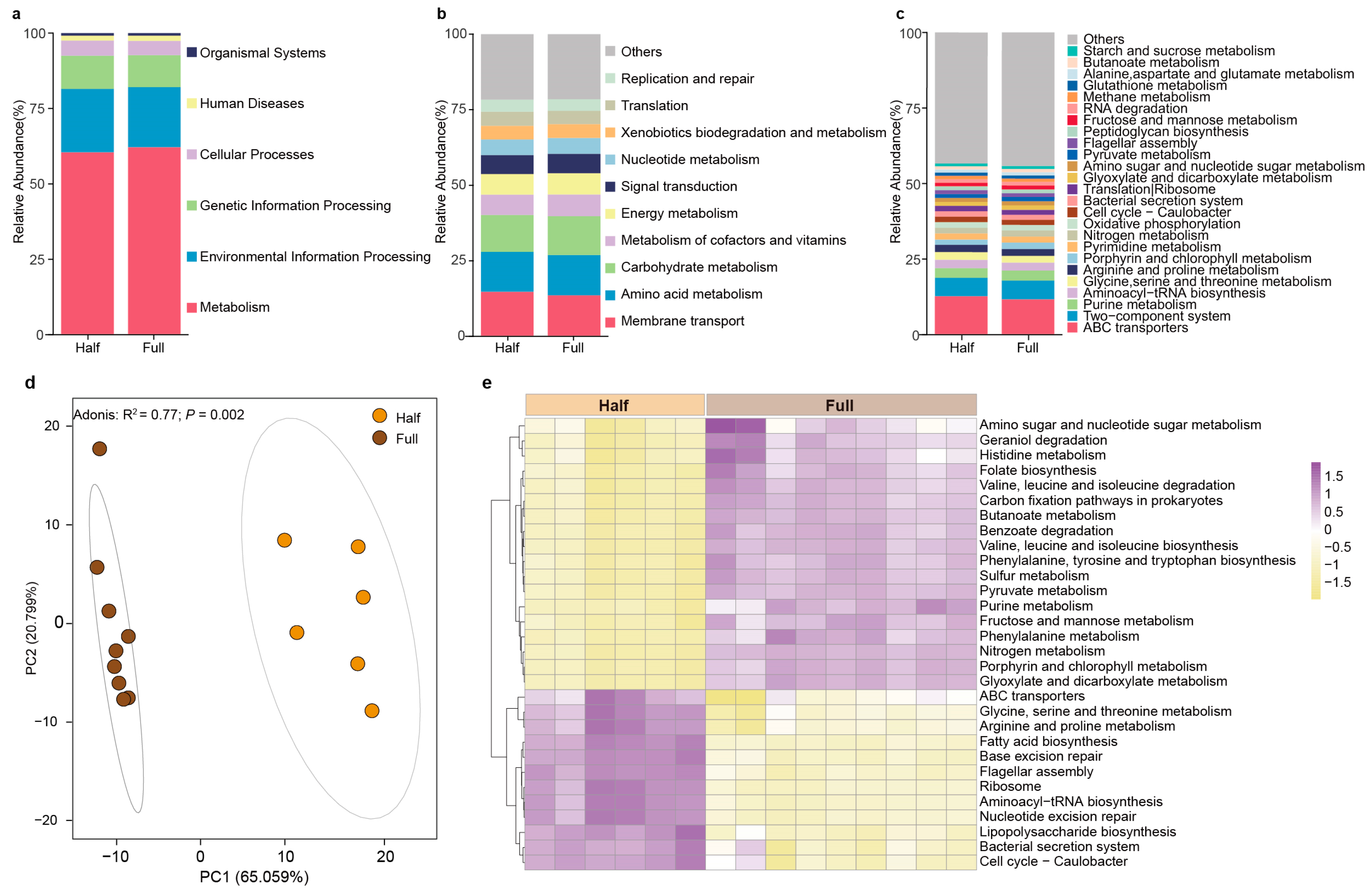
3.4. Changes in the Function of Antler Velvet Microbes Between the Two Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Proksch, E.; Brandner, J.M.; Jensen, J.M. The skin: An indispensable barrier. Exp. Dermatol. 2008, 17, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoica, A.E.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Hermenean, A.O.; Andronescu, E.; Vasile, B.S. Scar-free healing: Current concepts and future perspectives. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monavarian, M.; Kader, S.; Moeinzadeh, S.; Jabbari, E. Regenerative scar-free skin wound healing. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2019, 25, 294–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, C.K.; Gordillo, G.M.; Roy, S.; Kirsner, R.; Lambert, L.; Hunt, T.K.; Gottrup, F.; Gurtner, G.C.; Longaker, M.T. Human skin wounds: A major and snowballing threat to public health and the economy. Wound Repair Regen. 2009, 17, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascharak, S.; desJardins-Park, H.E.; Davitt, M.F.; Griffin, M.; Borrelli, M.R.; Moore, A.L.; Chen, K.; Duoto, B.; Chinta, M.; Foster, D.S.; et al. Preventing Engrailed-1 activation in fibroblasts yields wound regeneration without scarring. Science 2021, 372, eaba2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenstein, E.S.; Falone, W.; Patterson, T.; Cesario, K.; Mitchell, L.; Martel, T.; Rivera, J.; Vooijs, M.; Norton, S. Treating chronic wounds in an acute care setting: The forgotten diagnosis. Wound Manag. Prev. 2024, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billingham, R.E.; Mangold, R.; Silvers, W.K. The neogenesis of skin in the antlers of deer. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1959, 83, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Sparks, H.D.; Labit, E.; Robbins, H.N.; Gowing, K.; Jaffer, A.; Kutluberk, E.; Arora, R.; Raredon, M.S.B.; Cao, L.; et al. Fibroblast inflammatory priming determines regenerative versus fibrotic skin repair in reindeer. Cell 2022, 185, 4717–4736.e4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Zhang, G.; Yang, Y.; Gao, C.; Chu, W.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, C. Transplanted antler stem cells stimulated regenerative healing of radiation-induced cutaneous wounds in rats. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29, 963689720951549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, D.; Ren, J.; Li, J.; Guo, Q.; Shi, L.; Li, C. Antler stem cell-derived exosomes promote regenerative wound healing via fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition inhibition. J. Biol. Eng. 2023, 17, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Fan, C.; Huang, J. VAP-PLGA microspheres (VAP-PLGA) promote adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs)-induced wound healing in chronic skin ulcers in mice via PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α pathway. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 10264–10284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, H.H.; Segre, J.A. Skin microbiome: Looking back to move forward. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.E.; Fischbach, M.A.; Belkaid, Y. Skin microbiota-host interactions. Nature 2018, 553, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grice, E.A.; Kong, H.H.; Renaud, G.; Young, A.C.; Bouffard, G.G.; Blakesley, R.W.; Wolfsberg, T.G.; Turner, M.L.; Segre, J.A. A diversity profile of the human skin microbiota. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Di Nardo, A.; Nakatsuji, T.; Leichtle, A.; Yang, Y.; Cogen, A.L.; Wu, Z.R.; Hooper, L.V.; Schmidt, R.R.; von Aulock, S.; et al. Commensal bacteria regulate Toll-like receptor 3-dependent inflammation after skin injury. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuscó, A.; Sánchez, A.; Altet, L.; Ferrer, L.; Francino, O. Individual signatures define canine skin microbiota composition and variability. Front. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Zhao, J.; Guo, W.; Zhang, S.; Hua, Y.; Tang, J.; Kong, F.; Yang, X.; Fu, L.; Liao, K.; et al. High-altitude living shapes the skin microbiome in humans and pigs. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manus, M.B.; Yu, J.J.; Park, L.P.; Mueller, O.; Windsor, S.C.; Horvath, J.E.; Nunn, C.L. Environmental influences on the skin microbiome of humans and cattle in rural Madagascar. Evol. Med. Public Health 2017, 2017, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, S.M.; Cardona, L.; Rohrbach, E.; Mathis, A.; Holliger, C.; Verhulst, N.O. Environment rather than breed or body site shapes the skin bacterial community of healthy sheep as revealed by metabarcoding. Vet. Dermatol. 2024, 35, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloos, W.E.; Zimmerman, R.J.; Smith, R.F. Preliminary studies on the characterization and distribution of Staphylococcus and Micrococcus species on animal skin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1976, 31, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Sweren, E.; Liu, H.; Wier, E.; Alphonse, M.P.; Chen, R.; Islam, N.; Li, A.; Xue, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Bacteria induce skin regeneration via IL-1β signaling. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 777–791.e776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saheb Kashaf, S.; Proctor, D.M.; Deming, C.; Saary, P.; Hölzer, M.; Taylor, M.E.; Kong, H.H.; Segre, J.A.; Almeida, A.; Finn, R.D. Integrating cultivation and metagenomics for a multi-kingdom view of skin microbiome diversity and functions. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjerre, R.D.; Hugerth, L.W.; Boulund, F.; Seifert, M.; Johansen, J.D.; Engstrand, L. Effects of sampling strategy and DNA extraction on human skin microbiome investigations. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Bai, X.; Peng, T.; Yi, X.; Luo, L.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; He, T.; Wang, X.; et al. New insights into the skin microbial communities and skin aging. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 565549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekadim, C.; Skalnikova, H.K.; Cizkova, J.; Cizkova, V.; Palanova, A.; Horak, V.; Mrazek, J. Dysbiosis of skin microbiome and gut microbiome in melanoma progression. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Tomita, J.; Nishioka, K.; Hisada, T.; Nishijima, M. Development of a prokaryotic universal primer for simultaneous analysis of bacteria and archaea using next-generation sequencing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, K.; Hall, M.W.; Lynch, M.D.; Moreno-Hagelsieb, G.; Neufeld, J.D. Evaluating bias of illumina-based bacterial 16S rRNA gene profiles. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5717–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.A.; Müller, K.M.; Weese, J.S.; Neufeld, J.D. Comprehensive skin microbiome analysis reveals the uniqueness of human skin and evidence for phylosymbiosis within the class Mammalia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5786–E5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, G.; Yilmaz, P.; Kumar, S.; Forster, R.J.; Kelly, W.J.; Leahy, S.C.; Guan, L.L.; Janssen, P.H. Improved taxonomic assignment of rumen bacterial 16S rRNA sequences using a revised SILVA taxonomic framework. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cui, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, M. microeco: An R package for data mining in microbial community ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiaa255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aßhauer, K.P.; Wemheuer, B.; Daniel, R.; Meinicke, P. Tax4Fun: Predicting functional profiles from metagenomic 16S rRNA data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2882–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009; pp. 361–362. [Google Scholar]
- Grice, E.A.; Kong, H.H.; Conlan, S.; Deming, C.B.; Davis, J.; Young, A.C.; Bouffard, G.G.; Blakesley, R.W.; Murray, P.R.; Green, E.D.; et al. Topographical and temporal diversity of the human skin microbiome. Science 2009, 324, 1190–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, E.A.; Snitkin, E.S.; Yockey, L.J.; Bermudez, D.M.; Liechty, K.W.; Segre, J.A. Longitudinal shift in diabetic wound microbiota correlates with prolonged skin defense response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14799–14804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, M.K.; Peacock, T.J.; Akers, K.S.; Burmeister, D.M. Initial characterization of the pig skin bacteriome and its effect on In vitro models of wound healing. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ahmad, A.A.; Jia, Y.; Dingkao, R.; Du, M.; Liang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Bature, I.; Yan, P.; Salekdeh, G.H.; et al. Comparison of dynamics of udder skin microbiota from grazing yak and cattle during the perinatal period on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 864057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekman, L.; Bagge, E.; Nyman, A.; Persson Waller, K.; Pringle, M.; Segerman, B. A shotgun metagenomic investigation of the microbiota of udder cleft dermatitis in comparison to healthy skin in dairy cows. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Yue, Y.; Kou, X.; Hou, W.; Wang, M.; Yang, X.; Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, C. Dynamic distribution of skin microorganisms in donkeys at different ages and various sites of the body. Animals 2023, 13, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.E.; Tsao, H. The skin microbiome: Current perspectives and future challenges. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 69, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxberger, M.; Cenizo, V.; Cassir, N.; La Scola, B. Challenges in exploring and manipulating the human skin microbiome. Microbiome 2021, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, M.; Vicaretti, M.; Sparks, J.; Bansal, S.; Bush, S.; Liu, M.; Darling, A.; Harry, E.; Burke, C.M. A longitudinal study of the diabetic skin and wound microbiome. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, K.M.; Davis, R.R.; Liu, S.Y.; Greenhalgh, D.G.; Tran, N.K. Longitudinal profiling of the burn patient cutaneous and gastrointestinal microbiota: A pilot study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjar, F.; Weaver, A.J.; Peacock, T.J.; Nguyen, J.Q.; Brandenburg, K.S.; Leung, K.P. Identification of metagenomics structure and function associated with temporal changes in rat (Rattus norvegicus) skin microbiome during health and cutaneous burn. J. Burn Care Res. 2020, 41, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamus, L.J.; Theoret, C.; Costa, M.C. Use of next generation sequencing to investigate the microbiota of experimentally induced wounds and the effect of bandaging in horses. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseyenko, A.V.; Perez-Perez, G.I.; De Souza, A.; Strober, B.; Gao, Z.; Bihan, M.; Li, K.; Methé, B.A.; Blaser, M.J. Community differentiation of the cutaneous microbiota in psoriasis. Microbiome 2013, 1, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; Gallo, R.L. The role of the skin microbiome in atopic dermatitis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015, 15, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganju, P.; Nagpal, S.; Mohammed, M.H.; Nishal Kumar, P.; Pandey, R.; Natarajan, V.T.; Mande, S.S.; Gokhale, R.S. Microbial community profiling shows dysbiosis in the lesional skin of Vitiligo subjects. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Haque, A.; Mukhopadhyay, G.; Narayan, R.P.; Prasad, R. Interactions between bacteria and Candida in the burn wound. Burns 2005, 31, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannigan, G.D.; Hodkinson, B.P.; McGinnis, K.; Tyldsley, A.S.; Anari, J.B.; Horan, A.D.; Grice, E.A.; Mehta, S. Culture-independent pilot study of microbiota colonizing open fractures and association with severity, mechanism, location, and complication from presentation to early outpatient follow-up. J. Orthop. Res. 2014, 32, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerritsen, J.; Hornung, B.; Ritari, J.; Paulin, L.; Rijkers, G.T.; Schaap, P.J.; de Vos, W.M.; Smidt, H. A comparative and functional genomics analysis of the genus Romboutsia provides insight into adaptation to an intestinal lifestyle. BioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangifesta, M.; Mancabelli, L.; Milani, C.; Gaiani, F.; de’Angelis, N.; de’Angelis, G.L.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M.; Turroni, F. Mucosal microbiota of intestinal polyps reveals putative biomarkers of colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekio, I.; Sakamoto, M.; Hayashi, H.; Amagai, M.; Suematsu, M.; Benno, Y. Characterization of skin microbiota in patients with atopic dermatitis and in normal subjects using 16S rRNA gene-based comprehensive analysis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 1675–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Xu, J.B.; Nie, Y.; Wu, X.L. Pan-genomic analysis reveals that the evolution of Dietzia species depends on their living habitats. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 861–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paharik, A.E.; Horswill, A.R. The Staphylococcal biofilm: Adhesins, regulation, and host response. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, S.E.; Hillis, S.L.; Heilmann, K.; Segre, J.A.; Grice, E.A. The neuropathic diabetic foot ulcer microbiome is associated with clinical factors. Diabetes 2013, 62, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plichta, J.K.; Gao, X.; Lin, H.; Dong, Q.; Toh, E.; Nelson, D.E.; Gamelli, R.L.; Grice, E.A.; Radek, K.A. Cutaneous burn injury promotes shifts in the bacterial microbiome in autologous donor skin: Implications for skin grafting outcomes. Shock 2017, 48, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linehan, J.L.; Harrison, O.J.; Han, S.J.; Byrd, A.L.; Vujkovic-Cvijin, I.; Villarino, A.V.; Sen, S.K.; Shaik, J.; Smelkinson, M.; Tamoutounour, S.; et al. Non-classical immunity controls microbiota impact on skin immunity and tissue repair. Cell 2018, 172, 784–796.e718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, S.; Bouladoux, N.; Linehan, J.L.; Han, S.J.; Harrison, O.J.; Wilhelm, C.; Conlan, S.; Himmelfarb, S.; Byrd, A.L.; Deming, C.; et al. Commensal-dendritic-cell interaction specifies a unique protective skin immune signature. Nature 2015, 520, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luqman, A.; Muttaqin, M.Z.; Yulaipi, S.; Ebner, P.; Matsuo, M.; Zabel, S.; Tribelli, P.M.; Nieselt, K.; Hidayati, D.; Götz, F. Trace amines produced by skin bacteria accelerate wound healing in mice. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.K.; Karau, M.J.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Tilahun, A.Y.; Krogman, A.; David, C.S.; Pritt, B.S.; Patel, R.; Rajagopalan, G. Superantigen-producing Staphylococcus aureus elicits systemic immune activation in a murine wound colonization model. Toxins 2015, 7, 5308–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojtov, N.; Ross, H.F.; Novick, R.P. Global repression of exotoxin synthesis by Staphylococcal superantigens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10102–10107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, H.; Huang, X.; He, C.; Ma, J.; Wang, Z. Metabolic reprogramming in skin wound healing. Burn. Trauma 2024, 12, tkad047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano, F. Metabolism and functions of amino acids in the skin. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1265, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guccione, E.; Richard, S. The regulation, functions and clinical relevance of arginine methylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 642–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kämpfer, H.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Frank, S. Expression and activity of arginase isoenzymes during normal and diabetes-impaired skin repair. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 121, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariggiò, M.A.; Cassano, A.; Vinella, A.; Vincenti, A.; Fumarulo, R.; Lo Muzio, L.; Maiorano, E.; Ribatti, D.; Favia, G. Enhancement of fibroblast proliferation, collagen biosynthesis and production of growth factors as a result of combining sodium hyaluronate and aminoacids. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2009, 22, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaides, N.J.S. Skin lipids: Their biochemical uniqueness: Unlike internal organs, the skin biosynthesizes and excretes unusual fat soluble substances. Science 1974, 186, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keseler, I.M.; Mackie, A.; Peralta-Gil, M.; Santos-Zavaleta, A.; Gama-Castro, S.; Bonavides-Martínez, C.; Fulcher, C.; Huerta, A.M.; Kothari, A.; Krummenacker, M.; et al. EcoCyc: Fusing model organism databases with systems biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Hwang, O.; Park, S. Effect of dietary protein levels on composition of odorous compounds and bacterial ecology in pig manure. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 28, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotta, M.A.; Whitehead, T.R.; Collins, M.D.; Lawson, P.A. Atopostipes suicloacale gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from an underground swine manure storage pit. Anaerobe 2004, 10, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apprill, A.; Robbins, J.; Eren, A.M.; Pack, A.A.; Reveillaud, J.; Mattila, D.; Moore, M.; Niemeyer, M.; Moore, K.M.; Mincer, T.J. Humpback whale populations share a core skin bacterial community: Towards a health index for marine mammals? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fan, Y.; Jin, R.; Peng, Y.; Chai, J.; Wei, X.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, F.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.J.F. Exploring the intestinal microbial community of lantang pigs through metagenome-assembled genomes and carbohydrate degradation Genes. Fermentation 2024, 10, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, B.; Yu, S.; Li, S.; Wright, A.-D.G.; Du, R.; Si, H.; Li, Z. Characteristics and Differences in the Antler Velvet Microbiota During Regeneration. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010036
Li Y, Zhu Y, Yang B, Yu S, Li S, Wright A-DG, Du R, Si H, Li Z. Characteristics and Differences in the Antler Velvet Microbiota During Regeneration. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(1):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010036
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yongxiang, Yuhang Zhu, Bo Yang, Shaochen Yu, Songze Li, André-Denis G. Wright, Rui Du, Huazhe Si, and Zhipeng Li. 2025. "Characteristics and Differences in the Antler Velvet Microbiota During Regeneration" Microorganisms 13, no. 1: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010036
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhu, Y., Yang, B., Yu, S., Li, S., Wright, A.-D. G., Du, R., Si, H., & Li, Z. (2025). Characteristics and Differences in the Antler Velvet Microbiota During Regeneration. Microorganisms, 13(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010036





